Abstract
In this case study, we investigated the responses of glyphosate-susceptible and glyphosate-resistant Amaranthus palmeri to an organic 10% acetic acid herbicide solution instead of the standard 20% acetic acid solution. We showed that, although both forms respond differently to glyphosate-based herbicides, both will respond in the same way to organic-based herbicides that contain acetic acid. After treatment with the 10% acetic acid solution, eighty-five percent (85%) of the glyphosate susceptible plants died within 24 h, while 100% of the glyphosate-resistant plants died within 24 h. Using a lower concentration may be better for the environment since there will be less buildup over time, and it is more cost-effective for the farmer.
1. Introduction
In fields, Amaranthus palmeri grow rapidly by up to 2–3 inches a day. The growing season typically occurs between March and September and temperatures may range between 5 °C and 35 °C. Amaranthus palmeri is a dioecious plant and has the innate ability to increase its genetic diversity to allow the species to overcome stresses. In recent years, two forms of Amaranthus palmeri, glyphosate-resistant (GR) and glyphosate-susceptible (GS), have evolved. Glyphosate-based herbicides are the most widely used agricultural herbicides around the world. It is used extensively in Roundup Ready corn, cotton, and soybean crops in the Midwestern United States [1]. It is also used in non-GMO crops as a desiccant to help speed up the drying process so that farmers can harvest more quickly [2,3]. It inhibits the enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (ESPS) in plants. This prevents the biosynthesis of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan, and results in plant death [4,5].
Plants become resistant to glyphosate through two main pathways; non-target-site and target-site mechanisms [1]. Non-target site resistance is due to altered translocation within the plant, and altered translocation is reported to be the most common mechanism of resistance [6,7]. Target site resistance is attributed to altered glyphosate herbicide interaction with the target ESPS enzyme. Both GR and GS A. palmeri contain the ESPS enzyme, but GR A. palmeri produce more ESPS enzymes than GS A. palmeri. Glyphosate inhibits the ESPS enzyme in both plants; however, because the GR A. palmeri contains a greater amount of the enzyme, it is resistant to the effects of glyphosate [8].
Species resistance in weeds evolves when a particular population of a species develops genetic resistance to a herbicide and then out-competes the genetically susceptible population of the species for resources. The susceptible populations of the species will die off leaving only genetically resistant populations of the weed.
Farmers unwittingly created an artificial selective pressure, increasing the odds that Amaranthus palmeri will become resistant [9,10]. The existence of GR A. palmeri was confirmed in the state of Georgia in 2005 [6]. Glyphosate resistance most likely evolved once [11]. Over the years, GR A. palmeri spread from North Carolina to California. Because the GR form of A. palmeri has become more prevalent, there is a greater need for alternative herbicides [12]. Organic herbicides, i.e., chemicals that occur naturally in nature, are a good alternative. One example is Weed Pharm™. It is an agricultural vinegar, and thus contains 20% acetic acid [13].
When organic herbicides, such as agricultural vinegar, are sprayed directly on young and small weeds, they suppress and kill them [14]. When sprayed early enough (before the desired crop emerges and when A. palmeri is young and less than 8cm tall), it is effective at the 10% level. Because the acetic acid solution is sprayed before the desired crop emerges, it causes no harm to it. When applied to the leaves, the acetic acid eats through the leaf surface, including the epicuticular wax and cuticle. Several studies have shown the effectiveness of strong agricultural vinegar as a weed control product. For instance, agricultural vinegar led to a 100% mortality of two-leaf redroot pigweed, Amaranthus retroflexus, nine days after treatment [12]. The more acidic the solution, the more effective it will be at controlling weeds. However, it can also be more dangerous to handle as the concentration increases [15]. As a herbicide, agricultural vinegar has proven to be effective, but it produces a build up over time in the soil that may prove harmful to the ecosystem. Therefore, in our study, we applied lower concentrations of acetic acid to the young leaves of developing A. palmeri. The overall goal was to compare the differences between both forms of A. palmeri in order to determine how best to control plant growth, prevent the loss of desired crops and use as little acetic acid as possible. We do not know the long-term impact of acetic acid deposition on the soil or on other plants or organisms in the environment. Considering this fact, it is better to lessen the amount of acetic acid used when possible and target it to specific plants. The herbicide will kill all contacted tissue so a good spray coverage is essential [16].
2. Materials and Methods
In a greenhouse, Amaranthus palmeri was grown in 24 pots using Carolina® Seed Starter mi. (12 replicates of GS Amaranthus palmeri and 12 replicates of GR Amaranthus palmeri). We measured cardboard pieces to create a four section divider for each pot. Each pot was approximately six inches in diameter. The seeds were purchased from Azlin Seed Company in Leland, MS and kept in a dry storage area. For planting, they were loosely placed in the soil about an inch from the top. There was no dormancy-breaking treatment before planting. The lighting was placed on a timer and set for 12 h of light and 12 h of dark. The young glyphosate-susceptible and glyphosate-resistant Amaranthus palmeri leaves were sprayed using a spray bottle with a 10% acetic acid solution. We then watched our plants and watered them when necessary, waiting until enough growth was present in both GS and GR Amaranthus palmeri. We noticed that our GS plants germinated before the GR plants. Once the plants germinated and their leaves were apparent, they were then treated at the 0 h and 2 h stages with 10% acetic solution. The experiment was designed to show that, after spraying with acetic acid, the leaves of both the glyphosate-resistant and glyphosate-susceptible forms of Amaranthus palmeri will respond in the same way and show signs of high stress and death via wilting and closed stomata.
After treatment, we viewed the upper surface of the leaves using scanning electron microscopy to see if stomata were open. These plants were C4 plants and thus had a stomata on their adaxial and abaxial leaf surfaces. Most leaves have stomata only on their abaxial surfaces. We also viewed plants and leaves for physical signs of wilting and death.
3. Results
The results showed that Amaranthus palmeri stopped growing and started wilting when sprayed with a 10% solution of acetic acid (see Figure 1). All seedlings died after being sprayed. They were all young and under 10 cm tall, and the decline was visible within 4 h of being sprayed, when they started to wilt. There was a slight difference in the death rate in that 100% of the glyphosate-resistant seedlings died within 24 h of treatment; 85% of the glyphosate susceptible seedlings died within 24 h of treatment; and 100% died within 72 h of treatment.
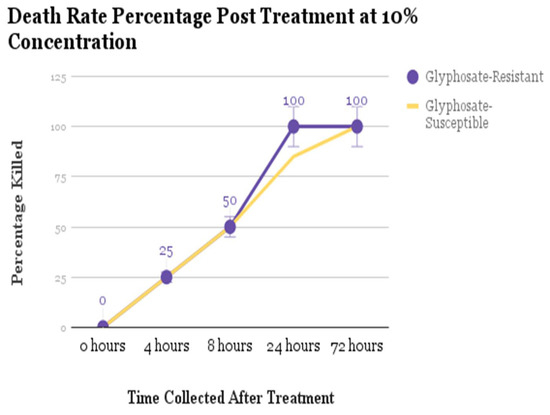
Figure 1.
The 10% acetic acid treatment kills 100% of the glyphosate-resistant (GR) Amaranthus palmeri seedlings and 85% of glyphosate-susceptible (GS) Amaranthus palmeri seedlings within 24 h. All other seedlings die within 72 h. t-test for significance: 0.4575. There is no statistical difference in death rate.
Figure 2 and Figure 3 show that the stomata star to close soon after treatment. These stomata are on the upper surface and are in direct contact with any herbicide that is sprayed. Figure 4 and Figure 5 represent stomata as they normally appear before treatment.
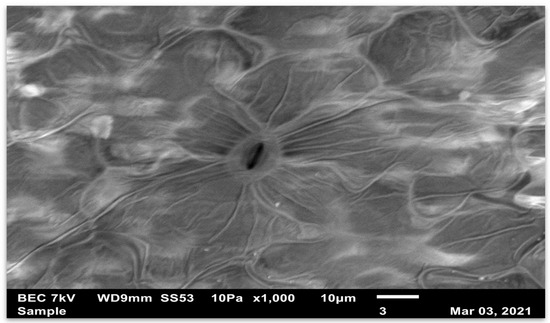
Figure 2.
This is the adaxial surface of a glyphosate-susceptible Amaranthus palmeri leaf. This micrograph was taken with the JEOL Scanning Electron Microscope immediately after the leaves of Amaranthus palmeri were sprayed and treated with a 10% acetic acid solution. The stomata show stress.
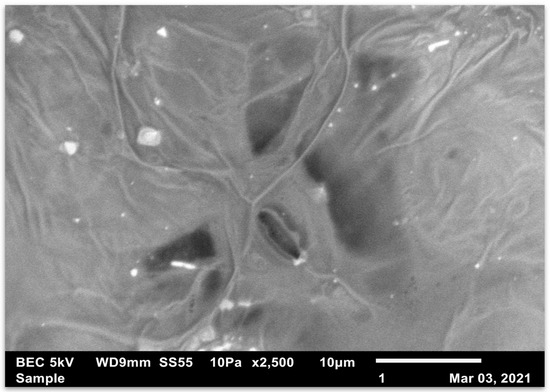
Figure 3.
This is the adaxial surface of a glyphosate-susceptible Amaranthus palmeri leaf. This micrograph was taken with the JEOL Scanning Electron Microscope immediately after the leaves of Amaranthus palmeri were sprayed and treated with a 10% acetic acid solution. The stomata show stress. They start to close soon after treatment.

Figure 4.
This is a micrograph of the adaxial leaf surface of glyphosate resistant Amaranthus palmeri taken with the JEOL Scanning Electron Microscope. It has not been treated with acetic acid and represents the control. The above stomata appear normal and open as they are not under stress.

Figure 5.
This is a micrograph of the adaxial leaf surface of glyphosate-susceptible Amaranthus palmeri taken with the JEOL Scanning Electron Microscope. It has not been treated with acetic acid. It represents the control. The above stomata appear normal and open as they are not under stress.
4. Conclusions
Under similar conditions in our greenhouse laboratory, the susceptible and resistant strains were able to grow up to 14 inches. Our results show that, within 72 h of treatment, all treated Amaranthus seedlings die. Using a 10% solution of acetic acid as a growth control agent is successful and impacts the environment less. Future studies will assess genomic data at different spraying times.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Y.; data collection, Y.Y., I.C. and A.M.; resources, Y.Y.; writing—original draft, Y.Y., I.C. and A.M.; writing—review and editing, Y.Y.; funding acquisition, Y.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation. Proposal #: 1800864.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prairie View A & M University’s biology and chemistry departments. Tony Grady provided assistance with the JEOL Scanning Electron Microscope.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chahal, P.S.; Aulakh, J.S.; Jugulam, M.; Jhala, A.J. Herbicide-Resistant Palmer amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri S. Wats.) in the United States—Mechanisms of Resistance, Impact, and Management. In Herbicides, Agronomic Crops, and Weed Biology; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benbrook, C. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, F.; Youngblood, Y. Agricultural Vinegar as a growth control agent for both Glyphosate susceptible (GS) Amaranthus palmeri and Glyphosate resistant (GR) Amaranthus palmeri. Pursue 2017, 1, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, A.M.; Gervais, J.A.; Luukinen, B.; Buhl, K.; Stone, D. Glyphosate General Fact Sheet; National Pesticide Information Center, Oregon State University Extension Services: Corvalis, OR, USA, 2010; Available online: http://npic.orst.edu/factsheets/glyphogen.html (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Maroli, A.S.; Nandula, V.K.; Dayan, F.E.; Duke, S.O.; Gerard, P.; Tharayil, N. Metabolic Profiling and Enzyme Analyses Indicate a Potential Role of Antioxidant Systems in Complementing Glyphosate Resistance in an Amaranthus palmeri Biotype. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9199–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnoskie, L.; Culpepper, A.; Grey, T.; Webster, T. Severed stems of Amaranthus palmeri are capable of regrowth and seed production in Gossypium hirsutum. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2014, 165, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, J.R.; Burton, J.D.; York, A.C.; Jordan, D.L.; Chandi, A. Physiology of Glyphosate-Resistant and Glyphosate-Susceptible Palmer Amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) Biotypes Collected from North Carolina. Int. J. Agron. 2013, 2013, 429294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, T.L.; Shilling, D.; Scientific Research Publishing Inc. Susceptible and Glyphosate-Resistant Palmer Amaranth (Amaranthus palmeri) Response to Glyphosate Using C14 As a Tracer: Retention, Uptake, and Translocation. 2018. Available online: https://file.scirp.org/Html/3-2603878_88371.htm (accessed on 30 July 2019).
- Smith, R. Herbicide Resistance Changing Sunbelt Production Options; Southeast Farm Press: Corvalis, OR, USA, 2013; Volume 40, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yancy, J. Weed Scientists Develop Plan to Combat Glyphosate Resistance; Southeast Farm Press: Corvalis, OR, USA, 2005; Volume 32, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Molin, W.T.; Wright, A.A.; Lawton-Rauh, A.; Saski, C.A. The Unique Genomic Landscape Surrounding the EPSPS Gene in Glyphosate Resistant Amaranthus palmeri: A Repetitive Path to Resistance. 2017. Available online: https://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12864-016-3336-4 (accessed on 17 June 2019).
- Quarles, W. Alternative Herbicides in Turfgrass and Organic Agriculture. 2010. Available online: http://www.birc.org/MayJune2010.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2017).
- Legleiter, T.; Johnson, B. Palmer Amaranth Biology, Identification, and Management. 2013. Available online: https://www.extension.purdue.edu/extmedia/ws/ws-51-w.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2017).
- Harper, L. Uses of Vinegar as a Weed Killer. 2017. Available online: http://www.gardenguides.com/110646-uses-vinegar-weed-killer.html (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Zelman, J. Organic Herbicides to Fight Weeds. 2011. Available online: http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2011/07/31/organic-herbicides-weeds_n_914313.html (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Lanini, W. Organic Herbicides—Do They Work? 2012. Available online: http://ucnfanews.ucanr.edu/Articles/Feature_Stories/Organic_Herbicdes_-_Do_They_Work/ (accessed on 28 March 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).