Abstract
Background/Objectives: Thyroid hormones are key regulators in hepatic metabolic pathways. Although they regulate various hepatic genes, only a few are known to be under direct transcriptional regulation through thyroid hormone receptors. To better understand the roles of thyroid hormones in the liver, it is critical to identify thyroid hormone-responsive genes at the cellular level. Methods: A cDNA microarray analysis was applied to primary cultures of rat hepatic cells treated with triiodothyronine (T3) at 10−9 M for 24 h to identify the differentially expressed genes. The identified gene expressions were further examined in vivo using F344 rats. The reporter gene assay was performed to investigate the transcriptional activity of the upstream region of the gene. Results: A limited number of genes were listed, and only three of them, pyridoxal kinase (Pdxk), phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (Pck1), and solute carrier family 17 member 2 (Slc17a2), were confirmed to be upregulated by quantitative RT-PCR. The mRNA expression of these genes increased in the livers of F344 rats after T3 injection, suggesting the physiological relevance in vivo. There are two partially conserved thyroid hormone-responsive elements (TREs) in the upstream region of the rat Pdxk gene. The reporter gene assay indicated that an imperfect TRE (5′-gGGTCAxxxxAGGaCt-3′) located at −2146 was sufficient for the thyroid hormone-induced transcription of the gene. Conclusions: The present study identified novel T3-responsive genes, pdxk and Slc17a2. Promoter analyses showed that a single TRE in the pdxk gene accounts for the transcriptional regulation by T3.
1. Introduction
Thyroid hormones—triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)—play crucial roles in normal development, growth, neural differentiation, and metabolic regulation in mammals [1,2]. Thyroid hormones bind to thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) to activate the transcription of target genes [3,4]. There are two TR genes, TRα and TRβ, which are transcribed into splice variants, including TRα1, TRα2, TRβ1, and TRβ2 [5]. TRs bind to thyroid hormone-responsive elements (TREs) in the promoter regions of target genes to activate transcription with the recruitment of coactivators such as SRC and NCoR [6].
The liver is a well-known thyroid hormone target organ [7]. Thyroid hormones regulate lipogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, and cholesterol and carbohydrate metabolism. Conversely, the liver regulates thyroid hormone levels through activation, inactivation, and metabolism [8]. In other words, the liver is essential to the thyroid hormone homeostasis-maintaining mechanism, in addition to the hypothalamus–pituitary–thyroid axis [9]. Thus, analyzing this complex relationship between thyroid hormones and the liver is essential for understanding thyroid hormones’ physiological functions and the related diseases in the liver. To address this complex relationship, we identified the hepatic genes directly regulated by thyroid hormones in the present study. Although early biochemical studies indicated that thyroid hormones controlled about 8% of hepatic genes in vivo, only a small number of genes are known as direct targets of the hormones, including malic enzyme, spot 14, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, cholesterol 7α hydroxylase, and iodothyronine deiodinase [10,11,12,13]. More recently, a cDNA microarray analysis was applied to find hepatic genes controlled by thyroid hormones in vivo, in which a diverse range of genes involved in gluconeogenesis, lipogenesis, and insulin signaling were identified [14,15,16]. However, in these studies, T3 was given in vivo to identify the hormone-responsive genes, which included both directly and indirectly or systemically regulated genes.
Thus, we performed a cDNA microarray analysis of cultured primary rat hepatic cells treated with T3 at a physiologically relevant concentration (10−9 M). We identified pyridoxal kinase (Pdxk) as a novel thyroid hormone-responsive gene. The 5′-flanking region of the gene was examined to understand the mechanisms underlying its hormone-induced transcription.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
Primary cultured male rat hepatocytes were purchased from Lonza Co. (Basel, Switzerland) and seeded in collagen-coated 6-well plates with Hepatocyte Basal Medium containing growth factors (Lonza Co.). Ac2F, a hepatic cell line derived from normal liver tissue of Donryu rats, was obtained from the Health Science Research Resources Bank (Osaka, Japan). The cell line was maintained in DME medium (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) containing penicillin and streptomycin with 10% fetal bovine serum (Biosolutions Japan Co., Osaka, Japan). For the T3 treatment, the cells were kept for 1 week in DME medium containing dextran-charcoal-treated serum.
2.2. Animal Study
The animal experiment was approved by the Animal Experiment Committee of Hiroshima University (Document #A21-111, 21 September 2021) and conducted following “A Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of Hiroshima University” and the Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines. Five-week-old male F344 rats were obtained from Charles River Japan Co. (Kanagawa, Japan). They were maintained in cages with free access to a basal diet and tap water. The animal facility conditions were as follows: temperature of 23.0 °C ± 2.0 °C, relative humidity of 50.0% ± 10.0%, and a 12-h light cycle. After 2 weeks of acclimatation, water containing 0.05% propylthiouracil (PTU) was given for 1 week. Then, T3 (Sigma Chemicals, St. Louis, MO, USA) was intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected at −10 µg/100 g body weight. The animals were euthanized under isoflurane anesthesia at 3, 6, and 24 h after the injection. Each group consisted of 3 rats, whereas 4 were used for the control group (the total number of rats was 13). Pieces of liver tissue were fixed in RNAlater solution (Ambion/Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and stored at −80 °C.
2.3. Microarray Analysis
Primary cultured hepatic cells were treated with T3 at 10−9 M for 24 h and harvested in RA1 lysis buffer. Total RNA was extracted using an RNA isolation kit (NucleoSpin RNA II; Machery-Nagel GmbH & Co. KG, Düren, Germany). Total RNA from control and T3-treated cells was subjected to cDNA microarray analysis using a GeneChip Array (Rat Genome 230 2.0) as described previously [15]. One GeneChip analysis was performed per sample.
2.4. Quantitative RT-PCR
Q-RT-PCR was performed as described previously [17]. The primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Table S1. The determined mRNA levels were normalized with reference to the levels of β-actin mRNA, which were confirmed to be stable among the cDNA samples derived from the same amount of total RNA.
2.5. Construction of Reporter Plasmids and Transient Transfection
The 5′-flanking region of the rat Pdxk gene was cloned by PCR using primers at positions −3150 and +87 from the transcription start site (5′-ATTAGTTTCCAAGTTGCCCCAC-3′ and 5′-TGCTTTAAGCACGCGCAG-3′, respectively). PCR was performed using PrimStar Taq (Takara Bio., Otsu, Japan) and genomic DNA from F344 rat liver following the manufacturer’s recommended conditions. After adding an adenosine residue, the PCR fragment was cloned into the pCR2.1-TOPO TA cloning vector (Invitrogen/Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and verified by sequencing.
Truncated fragments of the 5′-flanking region of the gene were also prepared by PCR using LA-Taq (Takara Bio.) between positions −2558, −2292, −2030, −506, and +87 from the cloned 5′-flanking fragment and were cloned into the PCR2.1-TOPO vector. KpnI/XhoI-digested fragments were then inserted into the corresponding restriction enzyme sites of the pGL4.10 luciferase reporter plasmid (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) and designated as pGL410-rpdxk-p−3150, −2558, −2292, −2030, and −506, respectively.
Deletions were introduced into the reporter plasmid using a QuikChange Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Agilent Technology, Santa Clara, CA, USA). TRE-like sequences between positions −2477/−2450 and −2146/−2120 were deleted from pGL410-rpdxk-p−2558. The rTRα expression plasmid pSG5-rTRα was constructed as described previously [18], and phRL-CMV (Promega) was used as an internal control.
Ac2F cells were plated at 4.0 × 104 cells/well in 48-well plates and transiently transfected with 300 ng reporter plasmid, 30 ng pSG5-rTRα, and 2 ng phRL-CMV using the Hilymax transfection reagent (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). The weight ratio of the reagent to DNA was 1:1. After 24 h of incubation, the cells were harvested in 25 µL cell lysis buffer (Promega). Firefly and Renilla luciferase activity was determined using a Dual Luciferase Assay Kit (Promega) by measuring luminescence with a luminometer/fluorometer (Fluoroskan Ascent, Thermo Fisher Scientific). Firefly luciferase reporter activity was normalized to Renilla luciferase activity from phRL-CMV.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All values are expressed as means ± standard error (S.E.). Multiple comparisons were made with Dunnett’s test using the R package “SimComp” (http://cran.r-project.org), accessed on 10 September 2024. Paired comparisons were performed with the t-test function of the Microsoft Excel 2021 program.
3. Results
3.1. T3-Responsive Genes in Primary Cultured Rat Hepatocytes
Differentially expressed genes found by the GeneChip analysis comparing the control versus T3-treated cells are listed in Table 1. The original data are registered in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database under accession #GSE282664. A minimal change of 2.8-fold was applied to select upregulated genes. Eight genes are listed, and only the top three genes, pyridoxal kinase (Pdxk), phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (Pck1), and solute carrier family 17 member 2 (Slc17a2), were confirmed to be upregulated according to the quantitative RT-PCR analysis.

Table 1.
Genes differentially expressed by T3 in the primary culture of rat hepatic cells.
3.2. T3-Responsive Induction of mRNA for the Identified Genes in Rat Liver
The changes in Pdxk, Pck1, and Slc17a2 mRNA levels after the administration of T3 at 10 µg/100 g body weight (i.p.) are summarized in Figure 1. The mRNA expressions of all three genes were significantly elevated after T3 injection in vivo, while the change in Slc17a2 expression was more gradual.
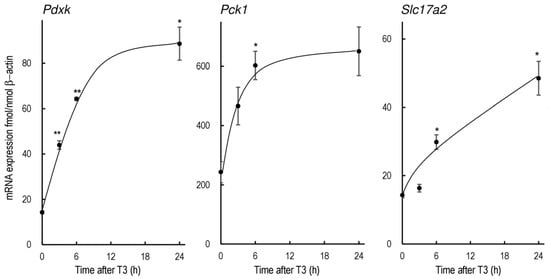
Figure 1.
Expression of rPdxk, rPck1, and rSlc17a2 mRNA in the livers of rats treated with T3. Male F344 rats were treated with PTU for 1 week to reduce the endogenous thyroid hormones. T3 was administered at 10 µg/100 g body weight (i.p.). The bars indicate mean ± SEM, n = 3 or 4, * p < 0.05, and ** p < 0.01 vs. control.
3.3. T3-Dependent Promoter Activity of the 5′-Flanking Region of Pdxk
The luciferase activity of the 5′-flanking region −3150/+87 and the successive truncated regions in Ac2F cells treated with T3 is summarized in Figure 2A. The numbers indicate the relative positions from the transcription start site (+1). The luciferase activity was significantly elevated with pGL410-rpdxk-p−3150, -p−2558, and -p−2292, but not -p−2030 or -p−506, while the induction of pGL410-rpdxk-p−2558 was higher than that of -p−2292. The activity of pGL410-rpdxk-p−2558 was T3-dose-dependent (Figure 2B) and also depended on the presence of the thyroid hormone expression vector pSG5-rTRα (Figure 2C). The activity reached the maximum level with 3 ng plasmid/well at either 10−9 or 10−7 M of T3.
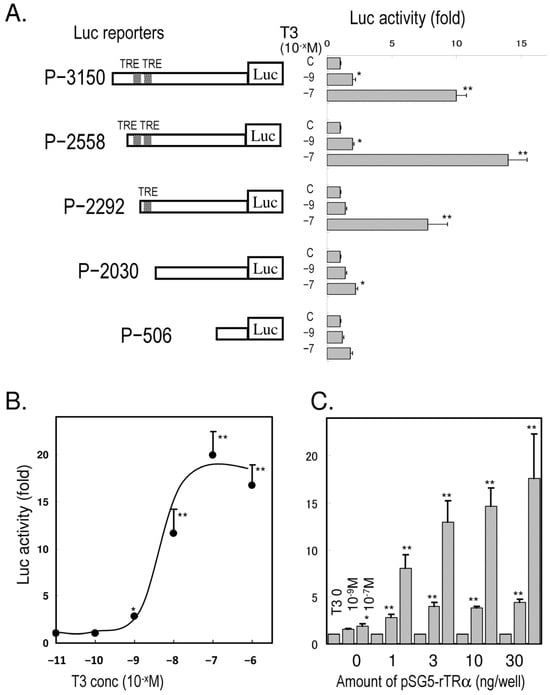
Figure 2.
T3-dependent transcriptional activity of the rPdxk gene in Ac2F cells. (A): Successively truncated fragments of the 5′-flanking region of the rPdxk gene were inserted into a luciferase (Luc) reporter, pGL410. The numbers indicate the relative positions from the transcription start site (+1). The reporter plasmids were transfected with pSG5-rTRα (30 ng). T3 was added at a concentration of 10−9 or 10−7 M. (B): T3-dose-responsive induction of luciferase activity from pGL410-rpdxk-p−2558. (C): TRα-dependent activity of pGL410-rpdxk-p−2558. The bars indicate mean ± SEM, n = 4, * p < 0.05, and ** p < 0.01 vs. control.
Since there are two partially conserved TREs at −2477 (5′-AaaTCAxxxxAGGTtc-3′) and −2146 (5′-gGGTCAxxxxAGGaCt-3′, reversed), the luciferase activities of the rpdxk-p−2558 reporters with deletions of these regions were tested (Figure 3). The constructs in which the distal TRE-like motif was removed displayed similar responses to T3 as the original rpdxk-p−2558 reporter. However, the deletion of the proximal TRE-like motif reduced T3-responsive transcription.
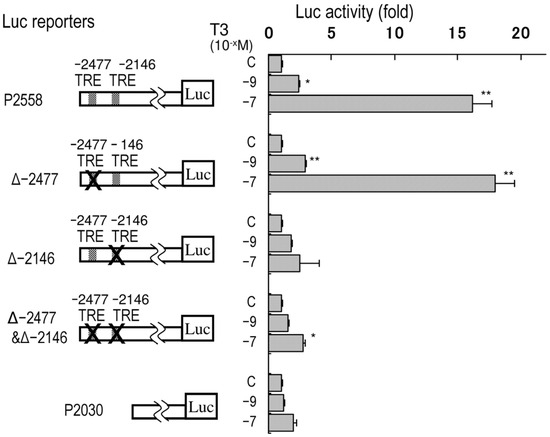
Figure 3.
Requirement of the imperfect TRE at −2146 for T3-responsive transcription of the rPdxk gene in Ac2F cells. Deletion mutants of pGL410-rpdxk-p−2558 were transfected with pSG5-rTRα. T3 was added at concentrations of 10−9 or 10−7 M. The bars indicate mean ± SEM, n = 4, * p < 0.05, and ** p < 0.01 vs. control.
4. Discussion
We applied cDNA microarray analysis to primary cultures of rat hepatocytes to identify thyroid hormone-responsive genes. Pdxk and Slc17a2 were identified as new thyroid hormone-responsive genes along with the previously known T3-responsive gene Pck1. Reporter gene analysis of the 5′-flanking region of the Pdxk gene revealed that an imperfect direct repeat of a TRE separated by four nucleotides located at −2146, far upstream in the promoter region, is responsible for the thyroid hormone-induced transcription of the gene. Our findings of these genes directly regulated by T3 could help to further understand the thyroid hormone regulation mechanisms in hepatic metabolic pathways as well as related hepatic diseases.
Thyroid hormones are essential for normal growth, development, and maintenance of metabolic balance [19,20]. The liver has been used for the investigation of thyroid hormone actions [9]. The cDNA microarray analysis was applied to find genes regulated by thyroid hormones in vivo, and carbohydrate/fatty acid metabolism and cell proliferation-related genes were found to be upregulated [14,15,16]. The genes identified in these in vivo studies may be indirectly regulated. For instance, since T3 rapidly increases growth hormone (GH) levels, many of these ‘identified’ upregulated genes in vivo may be downstream of GH [21]. Then, in the present study, primary cultured hepatocytes were subjected to GeneChip analysis to identify genes directly regulated by thyroid hormones at the cellular level. The number of identified genes was unexpectedly small: eight genes were induced by more than 2.8-fold in the GeneChip analysis, and only three of these were confirmed to be upregulated by T3 in the quantitative RT-PCR, which was probably due to the minimum set of samples—one-T3 treated vs. one control. It may also indicate the limitation of the use of primary culture cells [22]. Although our results demonstrated transcriptional regulations of these three genes by T3, the changes in protein levels after T3 stimulation need to be investigated in future studies.
Recently, investigations combining RNA-seq or cDNA microarray-based transcriptome analysis and ChIP-seq-based cistrome analysis have provided more comprehensive identification of genes mediated by thyroid hormone receptors [16]. An analysis in a human hepatoma cell line, HepG2, found a series of genes regulated by T3 [23]. A study in a neural progenitor cell line, C17.2, demonstrated that this method could identify a number of T3-regulated genes and classify the thyroid hormone binding sites of each gene [24]. The future application of these techniques on hepatic primary culture cells will provide a more complete view of differential expression by T3.
Vitamin B6 is a dietary precursor for pyridoxal-5′-phosphate, which is an essential cofactor for numerous enzymatic reactions of intermediary metabolism in transamination, decarboxylation, and deamination [25,26]. PDXK catalyzes the synthesis of pyridoxal-5′-phosphate from vitamin B6 in the liver. It may not be surprising that thyroid hormones regulate this key enzyme, as they generally increase the metabolism of proteins and carbohydrates. The Pdxk gene was recognized as a Parkinson’s disease gene in a study based on single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis [27,28]. Hormone-responsive regulation of the pdxk gene may also play a role in neurons and be related to Parkinson’s disease, which requires further investigation. A recent study of cuproptosis-related genes suggested that the increased expression of Pdxk could be involved in the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma [29]. Pdxk might play a role in the actions of thyroid hormones in liver cancer [30].
The actions of thyroid hormones are mediated through TRs (TRα and TRβ) that bind to specific binding sites or TREs in the promoter regions of target genes [4,31]. The core consensus sequence of these elements is a pair of hexanucleotide “half-sites” of AGGT(C/A)A that could be arranged as a direct repeat separated by four nucleotides (DR4) or a palindrome repeat [32,33]. TRs are able to bind to TREs in the absence of ligands as monomers, homodimers, or heterodimers with the retinoic X receptor but are only able to activate transcription when T3/T4 is also bound. TREs are generally found in the proximal region of promoters. The GH gene, a well-known T3-regulated gene in the pituitary, contains multiple TREs within −200 bp from the transcription start site [34]. The Pck1 gene has two TRE-like motifs at −332 and −250 bp [10].
Functional TREs have also been identified in the proximal region of promoters of the human uncoupling protein-3 and rat malic enzyme genes. However, TREs can also be found far upstream in the 5′-flanking region. In the case of the rat Cyp7a1 gene, another T3-responsive gene in the liver, two TREs are located in the 5′-flanking region at approximately −3000 bp [11]. The present study found that the TRE in the Pdxk gene was also located rather far upstream, at −2146, and this single TRE seems to be sufficient to control the T3-responsive transcription of the gene. Even though this TRE is located far upstream in the Pdxk promoter, the induction level was similar to that of a TRE reporter we reported previously that consisted only of synthesized TREs (DR4 × 2) [18]. It is worth noting that the Δ−2477&Δ−2146-rpdxk-p−2558 reporter still displayed a weak response to T3 in Figure 3, although the biological significance is unclear. The nucleotide sequences of the promoter of the Pdxk gene are partially conserved between rats and mice. The matching score was 69.8% when 3000 bp of the 5′-flanking regions of the Pdxk genes from these two species were aligned. Interestingly, the TRE-like motif at −2146 in the rat Pdxk gene is identical to that of the mouse, while the other putative TRE at −2477 is not conserved in the mouse gene, which also supports the hypothesis that the TRE-like motif at −2146 is physiologically significant and may function similarly in the mouse Pdxk gene. Although these data suggest an interaction between the TRE-like motif at −2146 and thyroid hormone receptors, future studies are required to examine the direct interaction using the chromatin precipitation method.
The promoter mechanism of Slc17a2 was not explored in the present study. SLC17A2, also known as sodium/phosphate cotransporter 3, is a membrane protein expressed in the liver, kidney, and intestine [35]. The time-dependent increase in the mRNA expression of Slc17a2 in vivo after T3 administration was slower than that of Pdxk and Pck1, which may suggest that a more complex pathway is involved in its regulation. Further studies are required to understand the T3-responsive transcriptional mechanisms of Slc17a2 expression.
5. Conclusions
We identified novel thyroid hormone-responsive genes, Pdxk and Slc1a2, using cDNA microarray analysis in hepatic primary culture cells. Their regulation was further confirmed in rat liver in vivo. The luciferase reporter gene assay of the 5′ flanking region of the Pdxk gene demonstrated that a single TRE located at −2146 in the upstream region is sufficient to control the T3-responsive transcription. The limitations of the study include the following: (1) there is no direct evidence showing interaction between a TRE-like sequence of the Pdxk gene and a TR, and (2) the protein expressions of the newly identified genes were not examined, which needs to be addressed in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/dna5020018/s1, Table S1: Primer sequences used for Q-PCR analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.F.; investigation, N.F. and S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, N.F.; writing—review and editing, N.F. and S.K.; funding acquisition, N.F. and S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS Kakenhi Grants (#24K11680 and 20K08886).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal experiment was approved by the Animal Experiment Committee of Hiroshima University (Document #A21-111, 21 September 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article. The sequence data referred to in the present study are publicly available in the GenBank nucleotide database. The microarray data have been deposited into the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database under accession number GSE282664.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ChIP | Chromatin immunoprecipitation |
| DR4 | A direct repeat separated by four nucleotides |
| GH | Growth hormone |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| Q-RT-PCR | Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| T3 | Triiodothyronine |
| T4 | Thyroxine |
| TR | Thyroid hormone receptor |
| TRE | Thyroid hormone-responsive element |
References
- Zhang, J.; Lazar, M.A. The mechanism of action of thyroid hormones. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2000, 62, 439–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiga-Carvalho, T.M.; Chiamolera, M.I.; Pazos-Moura, C.C.; Wondisford, F.E. Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 1387–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Brent, G.A. Mechanisms of thyroid hormone action. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3035–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brtko, J. Thyroid hormone and thyroid hormone nuclear receptors: History and present state of art. Endocr. Regul. 2021, 55, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyetei-Anum, C.S.; Roggero, V.R.; Allison, L.A. Thyroid hormone receptor localization in target tissues. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 237, R19–R34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astapova, I. Role of co-regulators in metabolic and transcriptional actions of thyroid hormone. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, 73–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, L.; Kim, A.; Ni, B.; Celi, F.S. Thyroid hormone action and liver disease, a complex interplay. Hepatology 2023, 81, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piantanida, E.; Ippolito, S.; Gallo, D.; Masiello, E.; Premoli, P.; Cusini, C.; Rosetti, S.; Sabatino, J.; Segato, S.; Trimarchi, F.; et al. The interplay between thyroid and liver: Implications for clinical practice. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 43, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, J.H.; Schwartz, H.L.; Mariash, C.N.; Kinlaw, W.B.; Wong, N.C.; Freake, H.C. Advances in our understanding of thyroid hormone action at the cellular level. Endocr. Rev. 1987, 8, 288–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.A.; Jerden, D.C.; Bahouth, S.W. Regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene transcription by thyroid hormone involves two distinct binding sites in the promoter. Biochem. J. 1995, 309, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.-J.; Plateroti, M.; Samarut, J.; Osborne, T.F. Two uniquely arranged thyroid hormone response elements in the far upstream 5′ flanking region confer direct thyroid hormone regulation to the murine cholesterol 7alpha hydroxylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 3853–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, Y.; Dridi, S.; Vinson, C.; Hillgartner, F.B. Role of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein, histone acetylation, and coactivator recruitment in the regulation of malic enzyme transcription by thyroid hormone. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2005, 245, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Kim, S.; Harney, J.W.; Larsen, P.R. Further characterization of thyroid hormone response elements in the human type 1 iodothyronine deiodinase gene. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Jiang, Y.; Meltzer, P.; Yen, P.M. Thyroid hormone regulation of hepatic genes in vivo detected by complementary DNA microarray. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Morales, A.; Gullberg, H.; Fernandez, L.; Ståhlberg, N.; Lee, N.H.; Vennström, B.; Norstedt, G. Patterns of liver gene expression governed by TRbeta. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Zekri, Y.; Guyot, R.; Flamant, F. An Atlas of Thyroid Hormone Receptors’ Target Genes in Mouse Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, N.; Igarashi, K.; Kanno, J.; Inoue, T. Identification of estrogen-responsive genes in the GH3 cell line by cDNA microarray analysis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 91, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Sanoh, S.; Ohta, S.; Kitamura, S.; Sugihara, K.; Fujimoto, N. An improved thyroid hormone reporter assay to determine the thyroid hormone-like activity of amiodarone, bithionol, closantel and rafoxanide. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 208, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.S. Thyroid hormone biosynthesis and its role in brain development and maintenance. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2024, 142, 329–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gobel, A.; Gottlich, M.; Reinwald, J.; Rogge, B.; Uter, J.C.; Heldmann, M.; Sartorius, A.; Brabant, G.; Munte, T.F. The Influence of Thyroid Hormones on Brain Structure and Function in Humans. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2020, 128, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seelig, S.; Liaw, C.; Towle, H.C.; Oppenheimer, J.H. Thyroid hormone attenuates and augments hepatic gene expression at a pretranslational level. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 4733–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Sekine, S.; Song, B.; Ito, K. Use of Primary Rat Hepatocytes for Prediction of Drug-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2017, 72, 14.16.1–14.16.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.H.; Liu, H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chi, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Yang, C.-C.; Yeh, C.-T.; Tan, B.C.-M.; Lin, K.-H. ChIP-on-chip analysis of thyroid hormone-regulated genes and their physiological significance. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22448–22459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatonnet, F.; Guyot, R.; Benoît, G.; Flamant, F. Genome-wide analysis of thyroid hormone receptors shared and specific functions in neural cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E766–E775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Salvo, M.L.; Safo, M.K.; Contestabile, R. Biomedical aspects of pyridoxal 5′-phosphate availability. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 897–913. [Google Scholar]
- Eliot, A.C.; Kirsch, J.F. Pyridoxal phosphate enzymes: Mechanistic, structural, and evolutionary considerations. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 383–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elstner, M.; Morris, C.M.; Heim, K.; Lichtner, P.; Bender, A.; Mehta, D.; Schulte, C.; Sharma, M.; Hudson, G.; Goldwurm, S.; et al. Single-cell expression profiling of dopaminergic neurons combined with association analysis identifies pyridoxal kinase as Parkinson’s disease gene. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wider, C.; Ross, O.A.; Wszolek, Z.K. Genetics of Parkinson disease and essential tremor. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2010, 23, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, L.; Huang, W.; Abisola, F.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yao, L. Identification of a prognostic cuproptosis-related signature in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biol. Direct 2023, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.M.; Cheng, W.L.; Lin, C.D.; Lin, K.H. Thyroid hormone actions in liver cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 1915–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, P.M.; Ando, S.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Maruvada, P.; Xia, X. Thyroid hormone action at the cellular, genomic and target gene levels. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 246, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, R.W.; Subauste, J.S.; Koenig, R.J. The interplay of half-site sequence and spacing on the activity of direct repeat thyroid hormone response elements. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 5238–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umesono, K.; Murakami, K.K.; Thompson, C.C.; Evans, R.M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell 1991, 65, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, M.F.; Lavin, T.N.; Baxter, J.D.; West, B.L. The rat growth hormone gene contains multiple thyroid response elements. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 12063–12073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, D.; Havelaar, A.C.; Verbeek, E.; Smit, G.P.A.; Benedetti, A.; Mancini, G.M.S.; Verheijen, F. NPT4, a new microsomal phosphate transporter: Mutation analysis in glycogen storage disease type Ic. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2004, 27, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).