Comprehensive Analysis of Ocean Current and Sea Surface Temperature Trend under Global Warming Hiatus of Kuroshio Extent Delineated Using a Combination of Spatial Domain Filters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Ocean Currents
2.2.2. SST
2.2.3. Ocean Vector Winds
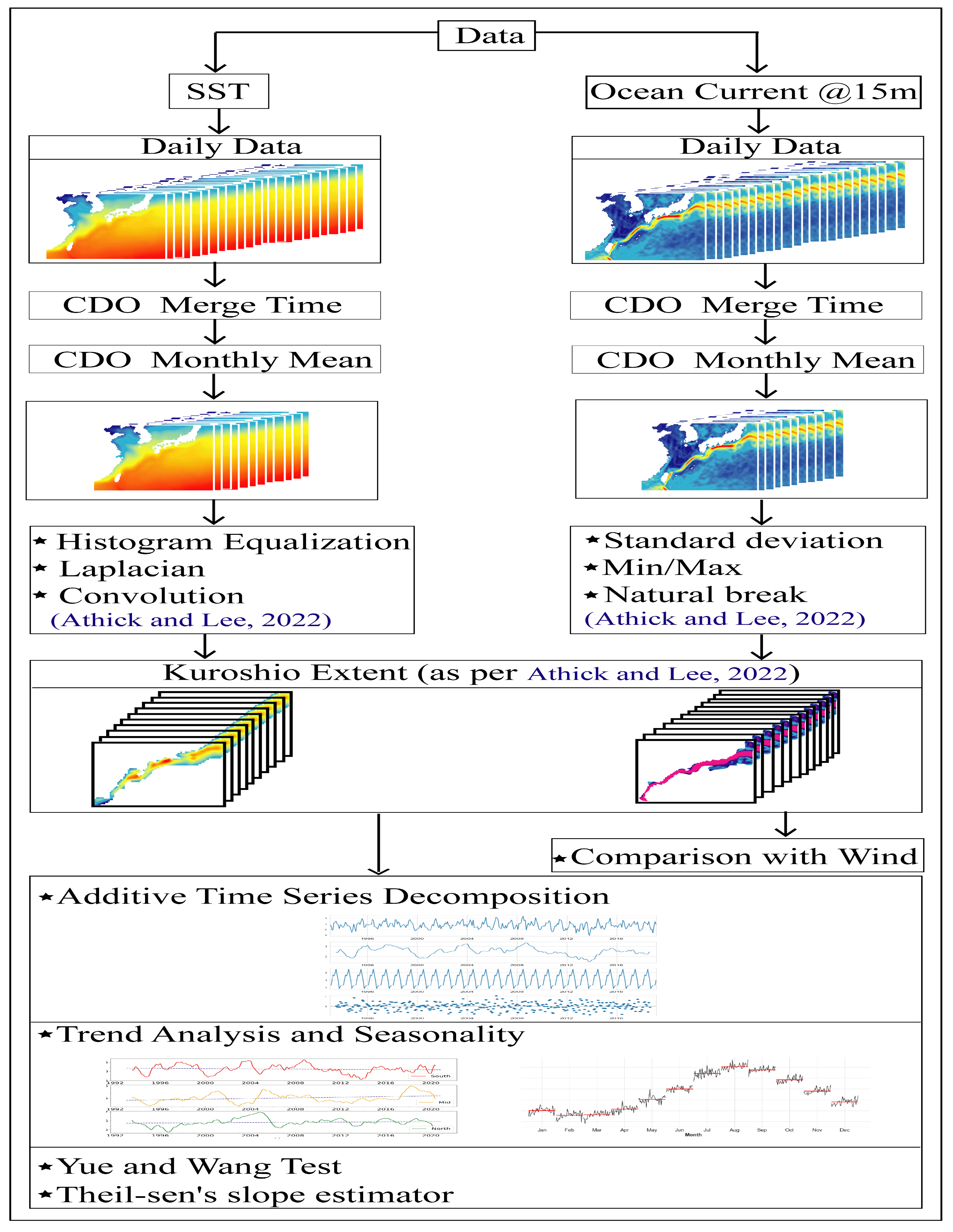
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Delineation of Kuroshio
2.3.2. Trend Analysis
2.3.3. Yue and Wang Modified MK Test
2.3.4. Theil–Sen’s Slope Estimator
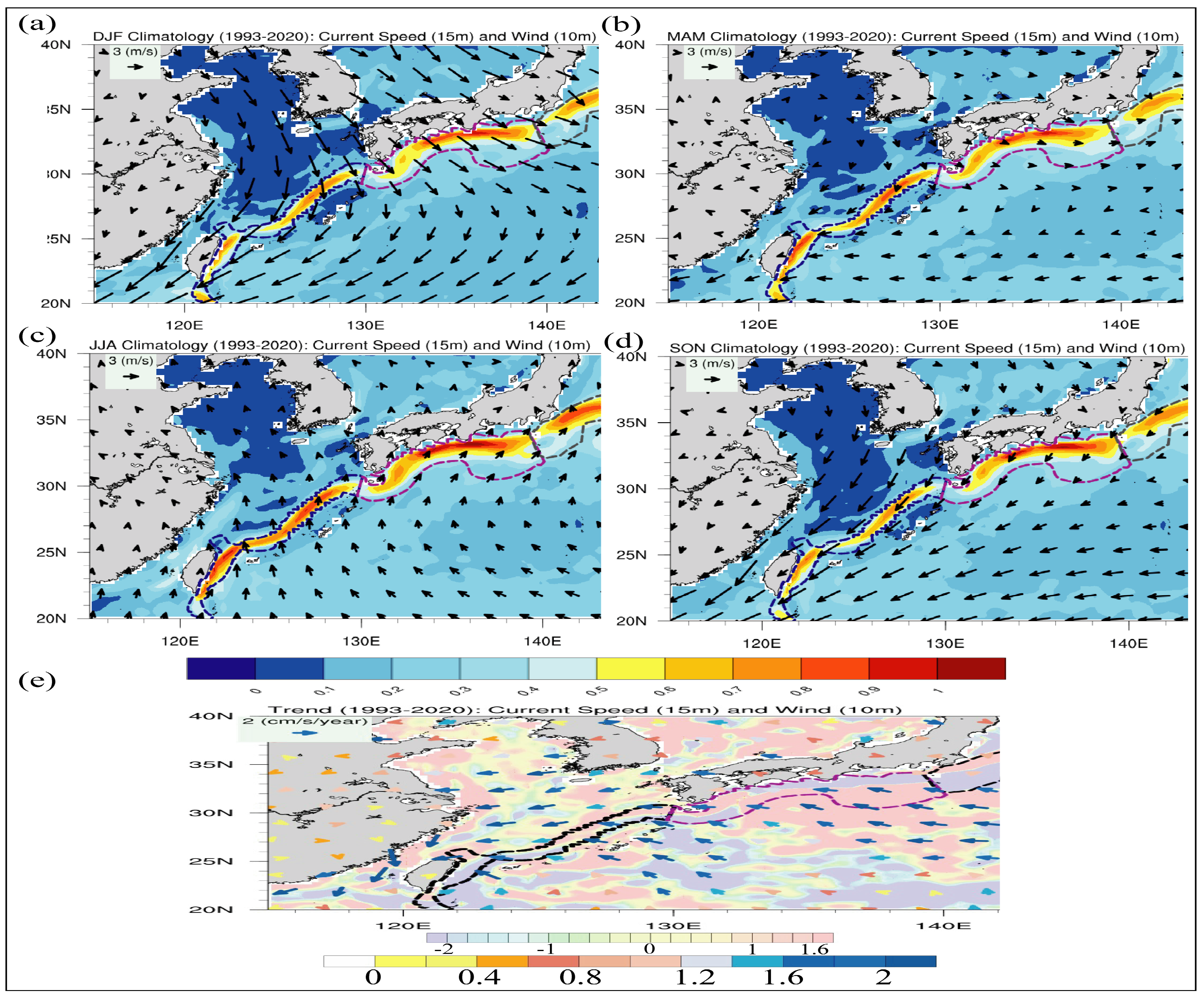
2.3.5. Wind Climatology
3. Results
3.1. Detection of KC Front
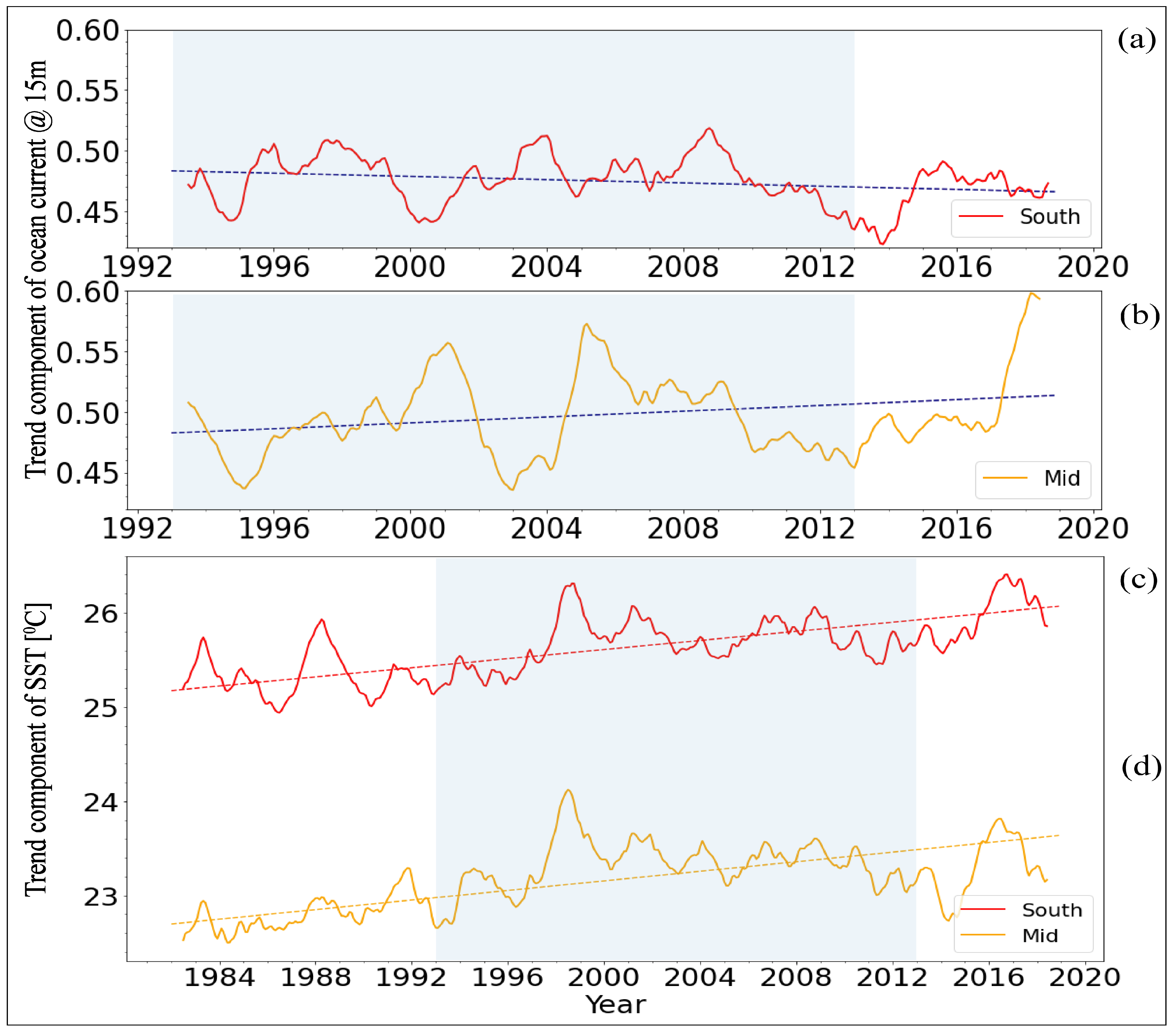
3.2. Time Series Decomposition
3.3. Trend Computation Using Yue and Wang Modified MK Test and Theil–Sen’s Slope Estimator
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdul Athick, A.M.; Shankar, K.; Naqvi, H.R. Data on time series analysis of land surface temperature variation in response to vegetation indices in twelve Wereda of Ethiopia using mono window, split window algorithm and spectral radiance model. Data Brief 2019, 27, 104773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, S. IPCC (2007): Climate change the physical science basis. Agu Fall Meet. Abstr. 2007, 2007, U43D-01. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Cai, W.; Zhang, L.; Nakamura, H.; Timmermann, A.; Joyce, T.; McPhaden, M.J.; Alexander, M.; Qiu, B.; Visbeck, M.; et al. Enhanced warming over the global subtropical western boundary currents. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Jones, P.D.; Ambenje, P.; Bojariu, R.; Easterling, D.; Tank, A.K.; Parker, D.; Rahimzadeh, F.; Renwick, J.A.; Rusticucci, M.; et al. Observations: Surface and atmospheric climate change. In Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group 1 to the 4th Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rhein, M.; Aoki, S.; Aoyama, M. Observations: Ocean 2. Notes 2011, 19, 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Levitus, S.; Antonov, J.I.; Boyer, T.P.; Locarnini, R.A.; Garcia, H.E.; Mishonov, A.V. Global ocean heat content 1955–2008 in light of recently revealed instrumentation problems. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L07608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lohmann, G.; Wei, W.; Dima, M.; Ionita, M.; Liu, J. Intensification and poleward shift of subtropical western boundary currents in a warming climate. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 4928–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, R.D.; deSzoeke, S.P.; Xie, S.; O’neill, L.; Seo, H.; Song, Q.; Cornillon, P.; Spall, M.; Minobe, S. Air–sea interaction over ocean fronts and eddies. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2008, 45, 274–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.A.; Small, R.J.; Samelson, R.; Qiu, B.; Joyce, T.M.; Kwon, Y.O.; Cronin, M.F. Western boundary currents and frontal air–sea interaction: Gulf Stream and Kuroshio Extension. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 5644–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.P.; Hafner, J.; Tanimoto, Y.; Liu, W.T.; Tokinaga, H.; Xu, H. Bathymetric effect on the winter sea surface temperature and climate of the Yellow and East China Seas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 81-1–81-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xu, M.; Xie, S.P.; Wang, Y. Deep atmospheric response to the spring Kuroshio over the East China Sea. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4959–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.N.; Schneider, N. Interannual to decadal Gulf Stream variability in an eddy-resolving ocean model. Ocean. Model. 2011, 39, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyama, T.; Nonaka, M.; Nakamura, H.; Kuwano-Yoshida, A. A striking early-summer event of a convective rainband persistent along the warm Kuroshio in the East China Sea. Tellus Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2012, 64, 18962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, I.M. Rapid warming of Large Marine Ecosystems. Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 81, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, M. Warming trend in northern East China Sea in recent four decades. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2009, 27, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Ren, G. Climatological characteristics and long-term change of SST over the marginal seas of China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 77, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Wu, L.; Cai, W.; Gupta, A.S.; Ganachaud, A.; Qiu, B.; Gordon, A.L.; Lin, X.; Chen, Z.; Hu, S.; et al. Pacific western boundary currents and their roles in climate. Nature 2015, 522, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Joyce, T.M. Interannual variability in the mid-and low-latitude western North Pacific. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1992, 22, 1062–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.J.; Cayan, D.R.; Barnett, T.P.; Graham, N.E.; Oberhuber, J.M. Interdecadal variability of the Pacific Ocean: Model response to observed heat flux and wind stress anomalies. Clim. Dyn. 1994, 9, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Sahu, N. Trend analysis of seasonal rainfall and temperature pattern in Kalahandi, Bolangir and Koraput districts of Odisha, India. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2019, 20, e932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R.; Wehner, M.F. Is the climate warming or cooling? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L08706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, M.H.; McGregor, S.; Spence, P.; Meehl, G.A.; Timmermann, A.; Cai, W.; Gupta, A.S.; McPhaden, M.J.; Purich, A.; Santoso, A. Recent intensification of wind-driven circulation in the Pacific and the ongoing warming hiatus. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R. The Pacific decadal oscillation. J. Oceanogr. 2002, 58, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Kharecha, P.; Von Schuckmann, K. Earth’s energy imbalance and implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 13421–13449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Portmann, R.W.; Daniel, J.S.; Davis, S.M.; Sanford, T.J.; Plattner, G.K. Contributions of stratospheric water vapor to decadal changes in the rate of global warming. Science 2010, 327, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, B.D.; Bonfils, C.; Painter, J.F.; Zelinka, M.D.; Mears, C.; Solomon, S.; Schmidt, G.A.; Fyfe, J.C.; Cole, J.N.; Nazarenko, L.; et al. Volcanic contribution to decadal changes in tropospheric temperature. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Daniel, J.S.; Neely, R.R., III; Vernier, J.P.; Dutton, E.G.; Thomason, L.W. The persistently variable “background” stratospheric aerosol layer and global climate change. Science 2011, 333, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tung, K.K. Varying planetary heat sink led to global-warming slowdown and acceleration. Science 2014, 345, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, Y.; Xie, S.P. Recent global-warming hiatus tied to equatorial Pacific surface cooling. Nature 2013, 501, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Fasullo, J.T.; Branstator, G.; Phillips, A.S. Seasonal aspects of the recent pause in surface warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitani, H. Beginning of the Kuroshio. In Kuroshio, Physical Aspect of the Japan Current; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.O.; Alexander, M.A.; Bond, N.A.; Frankignoul, C.; Nakamura, H.; Qiu, B.; Thompson, L.A. Role of the Gulf Stream and Kuroshio–Oyashio systems in large-scale atmosphere–ocean interaction: A review. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 3249–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.R.; Chang, Y.L.; Oey, L.Y.; Chang, C.W.J.; Hsin, Y.C. Air-sea interaction between tropical cyclone Nari and Kuroshio. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumi, T. Oceanic biology: Spawning of eels near a seamount. Nature 2006, 439, 929. [Google Scholar]
- Hsin, Y.C.; Qiu, B.; Chiang, T.L.; Wu, C.R. Seasonal to interannual variations in the intensity and central position of the surface Kuroshio east of Taiwan. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 4305–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.R. Interannual modulation of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) on the low-latitude western North Pacific. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 110, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, W.; Kawamura, H. Detection method of the Kuroshio front using the satellite-derived chlorophyll-a images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AS, M.A.A.; Lee, S.Y. A Combination of Spatial Domain Filters to Detect Surface Ocean Current from Multi-Sensor Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athick, A.M.A.; Naqvi, H.R. A method for compositing MODIS images to remove cloud cover over Himalayas for snow cover mapping. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 4901–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.N.; Hughes, D.; Smith, I.P. Oceans and marine resources in a changing climate. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2013, 51, 71–192. [Google Scholar]
- Dunstan, P.K.; Foster, S.D.; King, E.; Risbey, J.; O’Kane, T.J.; Monselesan, D.; Hobday, A.J.; Hartog, J.R.; Thompson, P.A. Global patterns of change and variation in sea surface temperature and chlorophyll a. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, R. Spatial and temporal variability of SST and ocean color in the Gulf of Maine based on cloud-free SST and chlorophyll reconstructions in 2003–2012. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.A.; Lee, E.Y.; Chang, E.; Hong, S. Spatial and temporal variability of sea surface temperature and warming trends in the Yellow Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 143, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramska, M.; Białogrodzka, J. Spatial and temporal variability of sea surface temperature in the Baltic Sea based on 32-years (1982–2013) of satellite data. Oceanologia 2015, 57, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, A.R. A modified Mann–Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, M.N.; Ouarda, T.B.; Gachon, P.; Sushama, L.; St-Hilaire, A. Identification of hydrological trends in the presence of serial and cross correlations: A review of selected methods and their application to annual flow regimes of Canadian rivers. J. Hydrol. 2009, 368, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonali, P.; Kumar, D.N. Review of trend detection methods and their application to detect temperature changes in India. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beurs, K.; Henebry, G. A statistical framework for the analysis of long image time series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1551–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Borak, J.S.; Devadiga, S.; Wolfe, R.E.; Zheng, M.; Descloitres, J. The MODIS land product quality assessment approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbesselt, J.; Hyndman, R.; Newnham, G.; Culvenor, D. Detecting trend and seasonal changes in satellite image time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlert, T. Non-parametric trend tests and change-point detection. CC BY-ND 2016, 14, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Machida, F.; Andrzejak, A.; Matias, R.; Vicente, E. On the effectiveness of Mann–Kendall test for detection of software aging. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops (ISSREW), Pasadena, CA, USA, 4–7 November 2013; pp. 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazar, S.M.; Ferdosi, F.B. An investigation on spatial and temporal trends in frost indices in Northern Iran. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 141, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandhi, A.; Perumal, S.; Gowda, P.H.; Knapp, M.; Hutchinson, S.; Harrington, J.; Murray, L.; Kirkham, M.B.; Rice, C.W. Long-term spatial and temporal trends in frost indices in Kansas, USA. Clim. Chang. 2013, 120, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztopal, A.; Şen, Z. Innovative trend methodology applications to precipitation records in Turkey. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, Z.; Şişman, E.; Dabanli, I. Innovative polygon trend analysis (IPTA) and applications. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O. An innovative method for trend analysis of monthly pan evaporations. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Kumar, A.; Guhathakurta, P.; Kisi, O. Spatial-temporal trend analysis of seasonal and annual rainfall (1966–2015) using innovative trend analysis method with significance test. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanikhani, H.; Kisi, O.; Mirabbasi, R.; Meshram, S.G. Trend analysis of rainfall pattern over the Central India during 1901–2010. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Jiang, T.; Jin, W. Recent trends in observed temperature and precipitation extremes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2006, 83, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Wang, C. The Mann–Kendall test modified by effective sample size to detect trend in serially correlated hydrological series. Water Resour. Manag. 2004, 18, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, A.; Simane, B.; Hassen, A.; Bantider, A. Variability and time series trend analysis of rainfall and temperature in northcentral Ethiopia: A case study in Woleka sub-basin. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2018, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhane, A.; Hadgu, G.; Worku, W.; Abrha, B. Trends in extreme temperature and rainfall indices in the semi-arid areas of Western Tigray, Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2020, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.S.; Edet, C.O.; Oche, C.O.; Agbo, E. Trend analysis of temperature in Gombe state using Mann Kendall trend test. J. Sci. Res. Rep. 2018, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Getachew, B. Trend analysis of temperature and rainfall in South Gonder zone, Anhara Ethiopia. J. Degrad. Min. Lands Manag. 2018, 5, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Ali, R.; Pham, Q.B.; Montenegro Gambini, J.; Gupta, V.; Malik, A.; Linh, N.T.T.; Joshi, Y.; Anh, D.T.; Nam, V.T.; et al. Seasonality shift and streamflow flow variability trends in central India. Acta Geophys. 2020, 68, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partal, T.; Kahya, E. Trend analysis in Turkish precipitation data. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2006, 20, 2011–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkeş, M.; Koç, T.; Sariş, F. Spatiotemporal variability of precipitation total series over Turkey. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 29, 1056–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, R.; Şenocak, S. Precipitation Trends for Western Turkey in associated with North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) Index. 2004. Available online: https://iahs.info/uploads/Conferences/2010%20Prague/265.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Ay, M.; Kisi, O. Investigation of trend analysis of monthly total precipitation by an innovative method. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 120, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, M.; Mulet, S.; Picot, N. New global Mean Dynamic Topography from a GOCE geoid model, altimeter measurements and oceanographic in-situ data. In Proceedings of the ESA Living Planet Symposium, Edinburgh, UK, 9–13 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rio, M. GLOBCURRENT Product Data Handbook: The Combined Geostrophy+ Ekman Currents. 2015. Available online: ftp://ifremer.fr/ifremer/cersat/documentation/gridded/GLOBCURRENT/GLOBCURRENTD-280-Product_Handbook_L4_combined_mhr.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Ubelmann, C.; Klein, P.; Fu, L.L. Dynamic interpolation of sea surface height and potential applications for future high-resolution altimetry mapping. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2015, 32, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Rayner, N.A.; Smith, T.M.; Stokes, D.C.; Wang, W. An improved in situ and satellite SST analysis for climate. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Smith, T.M.; Liu, C.; Chelton, D.B.; Casey, K.S.; Schlax, M.G. Daily high-resolution-blended analyses for sea surface temperature. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5473–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Banzon, V.F.; Freeman, E.; Lawrimore, J.; Liu, W.; Peterson, T.C.; Smith, T.M.; Thorne, P.W.; Woodruff, S.D.; Zhang, H.M. Extended reconstructed sea surface temperature version 4 (ERSST. v4). Part I: Upgrades and intercomparisons. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 911–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; L’Heureux, M.; Hu, Z.Z.; Zhang, H.M. Ranking the strongest ENSO events while incorporating SST uncertainty. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 9165–9172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.; Scott, J.; Hoffman, R.; Leidner, M.; Atlas, R.; Ardizzone, J. Remote Sensing Systems Cross-Calibrated Multi-Platform (CCMP) 6-hourly ocean vector wind analysis product on 0.25 deg grid, Version 2.0. Remote Sens. Syst. 2015. Available online: www.remss.com/measurements/ccmp (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Atlas, R.; Hoffman, R.N.; Ardizzone, J.; Leidner, S.M.; Jusem, J.C.; Smith, D.K.; Gombos, D. Supplement: A cross-calibrated, multiplatform ocean surface wind velocity product for meteorological and oceanographic applications. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, ES4–ES8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mears, C.A.; Scott, J.; Wentz, F.J.; Ricciardulli, L.; Leidner, S.M.; Hoffman, R.; Atlas, R. A near-real-time version of the cross-calibrated multiplatform (CCMP) ocean surface wind velocity data set. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 6997–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athick, A.; Shankar, K. Data on land use and land cover changes in Adama Wereda, Ethiopia, on ETM+, TM and OLI-TIRS landsat sensor using PCC and CDM techniques. Data In Brief 2019, 24, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AS Mohammed, A.A.; Naqvi, H.R.; Firdouse, Z. An assessment and identification of avalanche hazard sites in Uri sector and its surroundings on Himalayan mountain. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 12, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayula, J.F.; Cornillon, P. Edge detection algorithm for SST images. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1992, 9, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, I.; Mikhailichenko, Y.G. Thermohaline structure of the frontal zone of the northwest pacific-ocean at 160-degrees-e. Okeanologiya 1986, 26, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Belkin, I.; Shan, Z.; Cornillon, P. Global survey of oceanic fronts from Pathfinder SST and in-situ data. Eos Trans. AGU 1998, 79, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Paris, S.; Hasinoff, S.W.; Kautz, J. Local Laplacian filters: Edge-aware image processing with a Laplacian pyramid. Commun. ACM 2015, 58, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaragi, T. Classification Methods for Spatial Data Representation; Working Paper 40; The Centre for Advanced Spatial Analysis, University College London: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, H.V. Applications in business and economic statistics: Some personal views. Stat. Sci. 1990, 5, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, R.B.; Cleveland, W.S.; McRae, J.E.; Terpenning, I. STL: A seasonal-trend decomposition. J. Off. Stat. 1990, 6, 3–73. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S-PLUS; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.M. Assessment of irrigation system sustainability using the Theil–Sen estimator of slope of time series. Sustain. Sci. 2014, 9, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.T. How should trends in hydrological extremes be estimated? Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6756–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.W.; Pan, J.; Li, C.Y. Global oceanic wind speed trends. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2016, 129, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, A.; Yu, H. Sea Surface Temperature variations over Kuroshio in the East China Sea. E3S Web Conf. EDP Sci. 2019, 131, 01048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hou, Y. Kuroshio Front in the East China sea from satellite SST and remote sensing data. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2011, 9, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. Seasonality extraction by function fitting to time-series of satellite sensor data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.R.; Wang, Y.L.; Lin, Y.F.; Chiang, T.L.; Wu, C.C. Weakening of the Kuroshio Intrusion Into the South China Sea Under the Global Warming Hiatus. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2016, 9, 5064–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, G.; Xie, S.P.; Liu, W. Why does global warming weaken the Gulf Stream but intensify the Kuroshio? J. Clim. 2019, 32, 7437–7451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Candidates | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | 50% Percentile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed: ocean current (Taiwan to Tokara Strait) | 0.47 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.63 | 0.47 |
| Seasonal: ocean current (Taiwan to Tokara Strait) | −2.22 × 10−20 | 4.08 × 10−2 | −5.8 × 10 | 7.5 × 10−2 | −1.5 × 10−3 |
| Trend: ocean current (Taiwan to Tokara Strait) | 0.47 | 0.02 | 0.42 | 0.51 | 0.47 |
| Residual: ocean current (Taiwan to Tokara Strait) | 0.0008 | 0.03 | −0.08 | 0.10 | 0.002 |
| Observed: ocean current (Tokara Strait to Nagoya ) | 0.49 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.65 | 0.49 |
| Seasonal: ocean current (Tokara Strait to Nagoya ) | −2.7 × 10−20 | 2.3 × 10−2 | −2.9 × 10−2 | 4.9 × 10−2 | −9.42 × 10−4 |
| Trend: ocean current (Tokara Strait to Nagoya ) | 0.49 | 0.03 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 0.49 |
| Residual: ocean current (Tokara Strait to Nagoya ) | −0.00007 | 0.03 | −0.11 | 0.08 | 0.001 |
| Observed: SST (Taiwan to Tokara Strait ) | 25.63 | 2.29 | 21.44 | 30.02 | 25.66 |
| Seasonal: SST (Taiwan to Tokara Strait ) | 2.92 × 10−16 | 2.24 | −3.18 | 3.19 | 6.14 × 10−2 |
| Trend: SST (Taiwan to Tokara Strait ) | 25.63 | 0.32 | 24.94 | 26.40 | 25.64 |
| Residual: SST (Taiwan to Tokara Strait ) | 0.002 | 0.35 | −1.04 | 0.89 | 0.023 |
| Observed: SST (Tokara Strait to Nagoya ) | 23.17 | 3.16 | 17.6 | 29.37 | 3.16 |
| Seasonal: SST (Tokara Strait to Nagoya ) | 2.7 × 10−18 | 3.11 | −3.99 | 4.87 | −0.34 |
| Trend: SST (Tokara Strait to Nagoya ) | 23.18 | 0.34 | 22.5 | 24 | 23.23 |
| Residual: SST (Tokara Strait to Nagoya ) | −0.00028 | 0.38 | −1.37 | 1.11 | −0.017 |
| Candidates | Trend | Tau | S | Sen’s Slope | Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ocean current (Taiwan to Tokara Strait) | decreasing | −0.05 | −2430 | −5.2 × 10−5 | −2.61 |
| Ocean current (Tokara Strait to Nagoya) | increasing | 0.89 | 4344 | 8.4 × 10−5 | 2.56 |
| SST (Taiwan to Tokara Strait) | increasing | 0.088 | 9681 | 0.002 | 14.22 |
| SST (Tokara Strait to Nagoya) | increasing | 0.070 | 7740 | 0.002 | 7.89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AS, M.A.A.; Lee, S.-Y. Comprehensive Analysis of Ocean Current and Sea Surface Temperature Trend under Global Warming Hiatus of Kuroshio Extent Delineated Using a Combination of Spatial Domain Filters. Geomatics 2022, 2, 415-434. https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics2040023
AS MAA, Lee S-Y. Comprehensive Analysis of Ocean Current and Sea Surface Temperature Trend under Global Warming Hiatus of Kuroshio Extent Delineated Using a Combination of Spatial Domain Filters. Geomatics. 2022; 2(4):415-434. https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics2040023
Chicago/Turabian StyleAS, Mohammed Abdul Athick, and Shih-Yu Lee. 2022. "Comprehensive Analysis of Ocean Current and Sea Surface Temperature Trend under Global Warming Hiatus of Kuroshio Extent Delineated Using a Combination of Spatial Domain Filters" Geomatics 2, no. 4: 415-434. https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics2040023
APA StyleAS, M. A. A., & Lee, S.-Y. (2022). Comprehensive Analysis of Ocean Current and Sea Surface Temperature Trend under Global Warming Hiatus of Kuroshio Extent Delineated Using a Combination of Spatial Domain Filters. Geomatics, 2(4), 415-434. https://doi.org/10.3390/geomatics2040023






