Abstract
This study investigated the decolorization of Remazol Black (RBB) using a TiO2 photocatalyst modified by S and Co co-doped TiO2 (S-Co-TiO2) from a single precursor. X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and UV–Vis specular reflectance spectroscopy were used to characterize the photocatalysts. The results revealed that the band-gap energy of the doped and co-doped TiO2 decreased, with the S-Co-TiO2 8% showing the greatest one, and was found to be 2.78 eV while undoped TiO2 was 3.20 eV. The presence of S and Co was also identified through SEM-EDX. An activity study on RBB removal revealed that the S-Co-TiO2 photocatalyst showed the best result compared to undoped TiO2, S-TiO2, and Co-TiO2. The S-Co-TiO2 8% photocatalyst reduced RBB concentration (20 mg L−1) up to 96% after 90 min of visible light irradiation, whereas S-TiO2, Co-TiO2, and undoped TiO2 reduced it to 89%, 56%, and 39%, respectively. A pH optimization study showed that the optimum pH of RBB decolorization by S-Co-TiO2 was 3.0, the optimum mass was 0.6 g L−1, and reuse studies show that S-Co-TiO2 8% has the potential to be used repeatedly to remove colored pollutants. The results obtained indicate that the modification of S, Co co-doped titania synthesized using a single precursor has been successfully carried out and showed excellent characteristics and activity compared to undoped or doped TiO2.
1. Introduction
Dyestuff waste is a significant source of contamination in the aquatic environment. Among various synthetic dyes, Remazol Black (RBB) is the most widely used because of its low energy consumption during the dyeing process, water fastness, color brightness, and good fixation characteristics on fabric fibers [1,2]. However, due to its complex chemical structure, this dye is stable and difficult to biodegrade, so the concentration in the environment does not tend to decrease [3,4,5,6]. The release of this dye into the environment is extremely hazardous because it can produce toxic, mutagenic, and harmful by-products of oxidation, hydrolysis, and other chemical reactions that occur in the wastewater mixture, which are toxic, mutagenic, and harmful to microorganisms, aquatic life, and humans [5]. Therefore, an efficient method is needed to remove the dye concentration from wastewater before being discharged into the environment.
One of the effective methods for dealing with various organic pollutants such as dyestuff waste is advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) using heterogeneous photocatalysts [7,8]. Compared to other semiconductors, TiO2 is the most widely used due to its advantages such as high photocatalytic activity, stability, non-toxicity, and low cost, and it has been widely used for environmental pollution control, especially water pollution by dyestuff waste [9,10]. However, due to its large band gap (anatase 3.2 eV), TiO2 can only be activated by UV radiation, which is only 3–4% of the available total solar radiation. To improve the efficiency of photocatalyst activity in the visible light region, TiO2 should be further modified [11,12,13].
Modification with dopants has been shown to reduce the band-gap energy and increase the responsivity of TiO2 to the visible light region. The use of single dopants has been widely studied. However, there are several drawbacks to the effects of single doping, including that high doping levels are almost unattainable due to the mismatch of ionic charge and/or atomic radius of the dopants with TiO2, thermal instability, and the rate of electron recombination being increased compared to undoped conditions [14], which can inhibit the photocatalytic activity of TiO2. Co-doping can be an alternative to solve this problem. The co-doping technique is an effective method for lowering the band gap energy of TiO2, allowing TiO2 to be responsive in the visible light range [15,16,17,18]. Meanwhile, the combination of metallic and non-metallic dopants proved to be effective in reducing the band gap energy of TiO2 significantly, reducing electron and hole recombination that might result from a single doping effect, thereby increasing photocatalytic activity in the visible spectrum for efficient utilization of sunlight [19].
Compared to other non-metallic dopants such as N and C, sulfur is considered advantageous due to its ability to narrow the band gap, high thermal stability, and enhanced photocatalytic activity [10,20,21,22]. Meanwhile, incorporation of 3D transition metals into TiO2 is also an effective approach to reducing the band gap energy. The unfilled d-electron structure in transition metals can accommodate more electrons, allowing transition dopants to act as a photogenerated electron–hole pair trap, reducing the occurrence of electron–hole pair recombination on the photocatalyst surface [23]. Among other transition metals such as V, Cr, Mn, Fe, and Co, cobalt is considered a good candidate for TiO2 doping due to the similarity of the ionic radius of Co2+ to Ti4+, and it has been shown to increase the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 in the visible region [24,25,26]. Co-doping modification of TiO2 with S and Co has been reported. However, to the best of our knowledge, no studies have reported the use of a single precursor as a source of S and Co dopant, as well as activity assays for photocatalytic decontamination of Remazol Black under visible light exposure. Furthermore, we developed light-emitting diodes (LED) as a light source due to their long lifetime and high energy efficiency compared to typical light sources such as Xe lamps and Hg-Xe lamps [27].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Titanium(IV) isopropoxide (TTIP, 97%) was purchased from Hangzhou Jiu Peng Material Co., Ltd. (Zhejiang, China). Ethanol (C2H5OH, 99.5%), cobalt(II) sulfate (CoSO4), thiourea (CH4N2S), cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate (CoCl2·6H2O), hydrochloric acid (HCl, 36%), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and Remazol Black (RBB, C26H21O19N5S6Na4, MW = 991.82 g mol−1) were obtained from Merck, and deionized water was used in this work. The chemical structure of RBB is shown in Figure S1.
2.2. Synthesis of Photocatalysts
The sol-gel method was used to synthesize all of the photocatalysts. Under magnetic stirring, titanium(IV) isopropoxide (97%) was stoichiometrically dissolved in 20 mL ethanol. In separate bins, 0.24 g of thiourea was dissolved in a mixture of distilled water and ethanol (1:1 volume ratio) to obtain a dopant concentration of 10% S (w/w). The prepared TTIP solution was added dropwise to this solution under magnetic stirring, and the pH of the solution was adjusted to 3 with the addition of 1 M HCl. Stirring was continued for 2 h, and then the mixture was allowed to stand for 24 h for the gel ripening process. Then, the gel that formed was dried in an oven at 80 °C for 4 h, and the solid obtained was calcined at 450 °C for 3 h. The catalyst obtained was labeled S-TiO2.
To synthesize Co-doped TiO2, a similar method to the previous one was used. CoCl2·6H2O 4% (w/w) as a source of Co dopant was dissolved into a mixture of distilled water and ethanol to obtain a solution of Co. The prepared titanium solution was added dropwise into this dopant solution, followed by a similar procedure for the S-TiO2 synthesis, and then the catalyst was marked as Co-TiO2.
To synthesize S and Co co-doped TiO2, a stoichiometric amount of titanium(IV) isopropoxide was dissolved in ethanol absolute under magnetic stirring (solution A). At the same time, 47.91 mg of CoSO4 was dissolved in a mixture of distilled water and ethanol (volume ratio 1:1) to obtain the desired ratio of 4% (w/w) Ti: CoSO4 dopant concentration (solution B). Solution A was added dropwise to solution B under magnetic stirring, then the solution pH was adjusted to 3.0 with the addition of 1 M HCl, and stirring continued for 6 h, followed by aging for 24 h. Afterward, the gels were dried at 80 °C for 4 h to evaporate water and organic materials. Then, dry gels were calcined at 450 °C for 3 h to control the crystal phase of the catalyst. The final catalyst was thoroughly milled and labeled as S-Co-TiO2 2%. A similar procedure was followed to prepare S-Co-TiO2 with concentration ratios of 6%, 8%, and pure TiO2 without adding dopants.
2.3. Photocatalyst Characterization
The composition and crystalline phase of the photocatalyst was identified by X-ray diffractometer (XRD Shimadzu 6000, Cu Kα radiation λ = 0.15406 nm as the source of X-rays, operated at 40 kV, 30 mA, the angular range of 2θ = 5–90° and nickel as the filter). The crystallite size of the prepared photocatalyst was estimated by Scherrer equation (Equation (1)):
where k is a shape factor (0.94), λ is the wavelength of Cu Kα source used, β is the full width at half maximum (FWHM), and θ is the angle of diffraction.
A Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectrophotometer (Shimadzu Prestige 21) was used to verify the functional groups and chemical bonds in the photocatalyst in the wavenumber 400–4000 cm−1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) equipped with Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDX) was used to determine nanoparticle morphology and nanoparticle composition, and to identify the photocatalyst light absorption profiles, UV–Vis Specular Reflectance Spectroscopy (UV–Vis SRS) was used.
2.4. Photocatalytic Activity
The photocatalytic activity of the synthesized S-Co-TiO2 was studied for Remazol Black (RBB) decolorization using a batch system in a closed reactor equipped with 4 UV lamps (@20 W, intensity 200 lm/m2) and 4 visible lamps (TL-D, intensity @20 W, 2000 lm/m2), which can be adjusted for use (Figure S2). For comparison, photocatalytic activity tests were performed under the same conditions on other prepared photocatalysts TiO2, S-TiO2, and Co-TiO2. The variables studied included the type of photocatalyst, light source, initial pH, photocatalyst dose, dye concentration, and photocatalyst reuse test. In the study of light source parameters, visible light or UV light can be adjusted as needed, so the visible and UV tests were carried out under different conditions. At the beginning of the photocatalytic reaction, the prepared photocatalyst was dispersed in RBB solution and then magnetically stirred for 30 min in the dark without irradiation to achieve adsorption–desorption equilibrium conditions. The following process is a photocatalytic reaction initiated by contacting the solution with visible/UV light under continuous stirring. The photocatalyst was separated from the solution by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 10 min at certain time intervals. Furthermore, the residual concentration after the photocatalytic process was investigated using a UV–Vis spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 598 nm (λmax = 598 nm). The efficiency of RBB removal by photocatalyst was determined using Equation (3):
where Ci was the initial RBB concentration (mg L−1) and Cf was the final RBB concentration (mg L−1). Each experiment was repeated four times.
2.5. pH Point of Zero Charge (pHPZC) of TiO2-S-Co
pHPZC of S-Co-TiO2 was determined using the procedures from previous work [28] with a few modifications. A 0.1 g measure of catalyst was added to 25 mL 0.1 M NaNO3. The pH of the solution was adjusted by adding HCl or NaOH solution to obtain pH values in the range of 2–11. The final pH values of the solution were determined after constant shaking for 2 h at 293 K and left for 24 h.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Photocatalyst Characterization
3.1.1. XRD Analysis
The crystal phase of the photocatalyst was analyzed using XRD, and the XRD pattern is shown in Figure 1. The diffraction pattern of pure TiO2, S-TiO2, Co-TiO2, and co-doped S-Co-TiO2 showed the major peaks of the crystal planes for (101), (200), (105), (211), (204), and (215) corresponded to the anatase phase of TiO2 (JCPDS reference No. 21-1272), and no other phases such as rutile or brookite appeared in the samples.
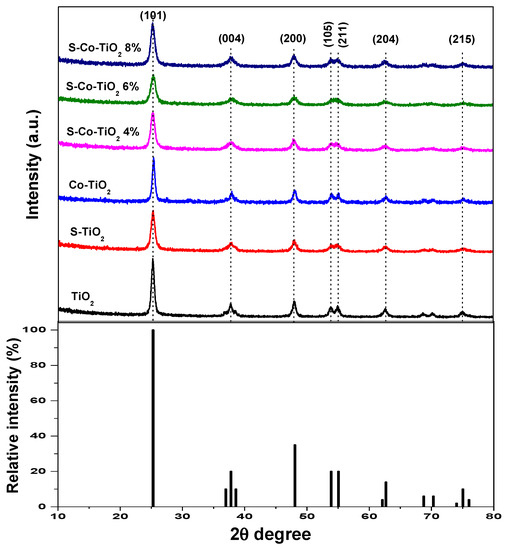
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of undoped, doped, and co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst.
There were no other crystallite peaks for S and Co ions in any samples, indicating that the S and Co dopants were evenly distributed on the titania surface [15]. Furthermore, the diffraction peaks of doped and co-doped samples shifted narrowly to a larger diffraction angle, followed by a decrease in peak intensity compared to undoped TiO2. The difference was also observed in the average crystallite size (D) (Table 1), which is estimated using Scherrer’s equation (Equation (1)). It was shown that the presence of dopant reduced the average crystallite size, with the most significant decrease attributed to the co-doping effect. As previously reported, the shift in diffraction peaks accompanied by a decrease in intensity and the average crystallite size after co-doping can be attributed to the presence of new bonds formed after the addition of sulfur and cobalt dopant to titania, in the form of Ti–O–S or Ti–O–Co bonds or both, which suppresses titania crystal growth and causes distortion of the crystal structure [25,29,30].

Table 1.
The average crystallite sizes and the band gap energy of undoped TiO2 and S-TiO2, Co-TiO2, and S-Co-TiO2.
3.1.2. FTIR Analysis
The functional groups formed on the photocatalyst before and after doped and co-doping were identified using the FTIR spectrum (Figure 2). Based on Figure 2, the spectrum of undoped TiO2 displayed a broad absorption band at 3400–3600 and 1635 cm−1, which were identified as stretching and bending vibrations of the hydroxyl groups on the TiO2 surface [20]. The adsorption band at 2924 cm−1 was defined as the Ti–OH2 group vibration, and the strong absorption band at 500–800 cm−1 was defined for Ti–O strain vibrations [31]. In the S-TiO2 and Co-TiO2 doped samples, the Ti–O absorption band widens and shifts slightly to a lower wavenumber due to the substitution of Ti4+ ions by Co2+ ions [32] and Ti4+ by S6+/S4+ ions [33,34]. A more significant shift occurred in the S-Co-TiO2 sample, which was associated with the substitution of the Ti4+ ion by the two dopants S6+ and Co2+ ions. This replacement caused more defects, particularly oxygen vacancies, due to the charge neutrality after the replacement of Ti4+ by Co2+ or/and S6+S4+ [32,35]. Then, in the S-TiO2 and S-Co-TiO2 samples, a new peak appeared at 1047–1080 cm−1, which corresponds to the bending vibration of Ti–O–S. This bond is formed from the substitution of Ti4+ by S6+/S4+, which also causes the Ti–O bond to weaken [36]. Furthermore, the peak at 1120–1125 cm−1 confirmed the S–O bending vibration in the form of SO42−, indicating that S was presented in cationic species (S6+/S4+) since the substitution of Ti4+ by S6+/S4+ is chemically more favorable than the substitution of O2− by S2− (anionic sulfur), because of the ionic radius of S2− (1.7 Å) is quite larger than O2− (1.22 Å), so this substitution is difficult to achieve compared to the substitution by the cationic sulfur [20,34]. Meanwhile, the shift in the Ti–O absorption peak was greater in the co-doped sample than the doped sample, indicating that more Ti ions were replaced by S and Co dopants [15,18].
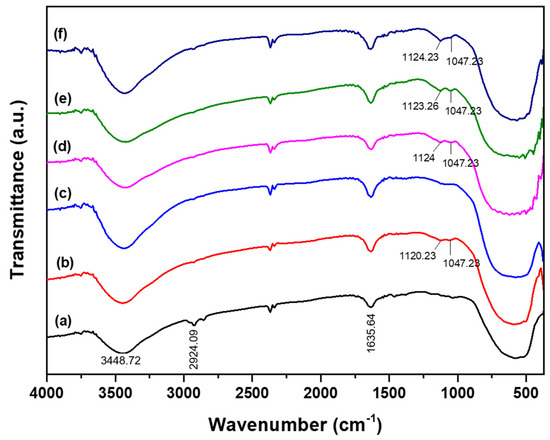
Figure 2.
FTIR spectra of (a) pure TiO2, (b) S-TiO2, (c) Co-TiO2, (d) S-Co-TiO2 4%, (e) S-Co-TiO2 6%, and (f) S-Co-TiO2 8%.
3.1.3. SEM Analysis
SEM analysis was used to identify the surface morphology of the photocatalysts, and the SEM micrographs of undoped, doped, and co-doped TiO2 are presented in Figure 3. The surface of pure TiO2 showed a uniform spherical morphology and size homogeneity. After being modified with Co dopant, the photocatalyst showed a surface with large and inhomogeneous agglomerates, while after co-doped with S and Co, the particles formed homogeneous spherical agglomerates with smaller sizes.
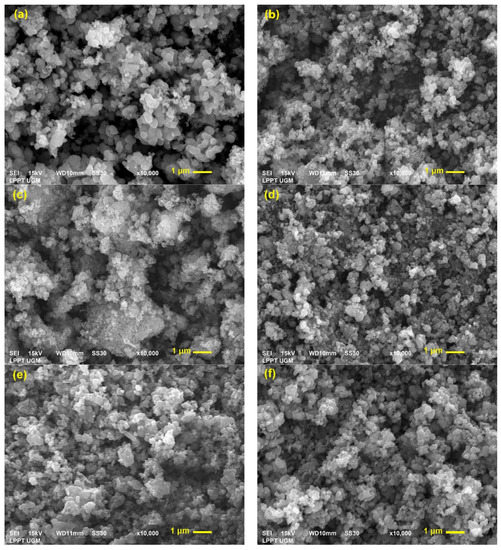
Figure 3.
SEM images of (a) pure TiO2, (b) S-TiO2, (c) Co-TiO2, (d) S-Co-TiO2 4%, (e) S-Co-TiO2 6%, and (f) S-Co-TiO2 8%.
EDX was employed to classify the elemental composition of the photocatalyst. The EDX pattern confirmed the presence of S, Co, or both dopants in the S-TiO2, Co-TiO2, or co-doped TiO2 samples in addition to the main elements Ti and O (Figure 3). A small amount of sulfur could not be identified in the S-Co-TiO2 4% sample, which may be due to the dopants’ content being too small. Other than that, the EDX pattern confirmed that all the targeted elements are in the TiO2 co-doped sample (Table 2).

Table 2.
The elemental composition of undoped TiO2, S-TiO2, Co-TiO2, and S-Co-TiO2.
3.1.4. UV–Vis SRS Analysis
The UV–Vis SRS spectrum revealed the optical properties and band gap energy of the photocatalyst. Figure 4 exhibits the UV–Vis SRS spectrum and Tauc’s plot of undoped, doped, and co-doped TiO2. As shown in Figure 4a, TiO2 shows an ultraviolet absorption semiconductor profile (200–400 nm) due to the large band gap energy of anatase TiO2 (3.2 eV). A small red-shift to the visible region was observed in the S-TiO2 sample due to the formation of a new sub-band gap in the valence band (VB) from the formation of the Ti–O–S bond after S doped to titania [37]. The new sub-band gap is formed by mixing the S3p orbital with the O2p orbital, which narrows the band gap of TiO2 [25]. The distinctive red-shift was also observed in the Co-TiO2 sample, indicating that Co-TiO2 has an absorption in the visible region. The optical absorption mechanism of undoped TiO2 is the transition energy from the valence band to the conduction band. The sp-d exchange interaction between the band electrons and the localized d-electrons of the Co2+ ion replacing the Ti4+ cation is responsible for the red-shift in the Co-TiO2 sample. This interaction between sp and pd causes a downward shift in the conduction band (CB) and an upward shift in VB, narrowing the band gap system [38].
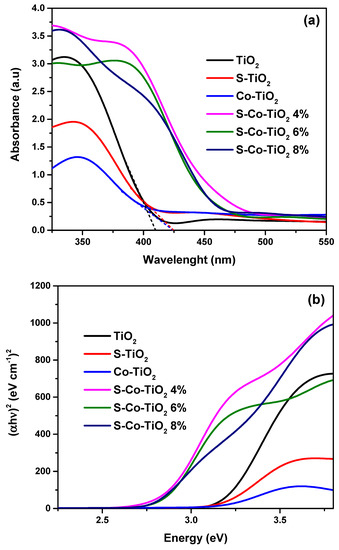
Figure 4.
(a) UV–Vis SRS spectrum and (b) Tauc’s plot of prepared photocatalysts.
Meanwhile, the red shift in the co-doping sample (S-Co-TiO2) was the most significant compared to the previous two doping samples (S-TiO2 or Co-TiO2). The S-Co-TiO2 sample displayed a high adsorption profile in the ultraviolet region, even higher than undoped and doped TiO2. Then, the absorption bands are significantly widened to the visible light region, implying that the photocatalyst activity in visible light has increased due to the impurity of S and Co co-dopants in TiO2. The SRUV–Vis absorption data were implemented into a Tauc’s plot between (αhʋ)2 versus hʋ to determine the band gap energy before and after modification, and the results are presented in Figure 4b. The band gap energy of undoped TiO2 was identified to be 3.2 eV. When impurity S is present in TiO2, the band gap is reduced to 3.16 eV, while doping by Co lowered the band gap to 3.15 eV. The decrease in band gap energy was more significant when TiO2 was co-doped by S and Co. The addition of 4% and 6% CoSO4 as a single precursor of co-dopants caused a decrease in the band gap to 2.82 and 2.83, respectively. The most significant decrease occurred at the S-Co-TiO2 8% sample, resulting in a band-gap width of 2.78 eV (Table 1). The more significant band-gap narrowing in the co-doped sample may be due to the formation of two impurity states close to the VB and CB. One is formed by mixing the S3p orbitals with the O2p orbitals of the S dopant, and the other is formed by exchange interactions between the sp on the electrons band and d-electrons of the Co2+ ion that replaces the Ti4+ ion [25,38,39].
3.2. Photocatalytic Performance on RBB Removal
3.2.1. Effect of Different Photocatalyst
The prepared photocatalysts TiO2, S-TiO2, Co-TiO2, and S-Co-TiO2, were used in the photocatalytic removal of RBB under visible or UV-light irradiation separately to evaluate the photocatalytic activity before and after modification. In this experiment, 20 mg L−1 of RBB solution was added with the prepared photocatalyst and then irradiated with visible/UV light for a certain time. The results of RBB removal using various photocatalysts are shown in Figure 5.
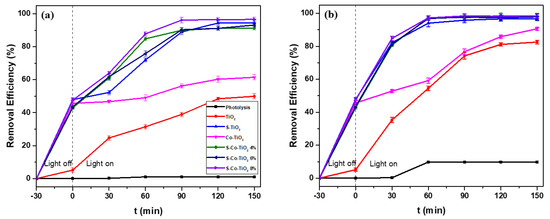
Figure 5.
The effect of various photocatalysts on the removal efficiency of RBB using (a) visible, and (b) UV–light irradiation, RBB concentration: 20 mg L−1, photocatalyst dosage: 1 g L−1, and pH: 5.5.
In order to determine the photolysis properties of RBB, the removal concentration without the addition of the photocatalyst was also investigated. The results showed that RBB did not undergo photolysis after 150 min of UV or visible light exposure.
Figure 5a shows the photocatalytic activity of various prepared photocatalysts under visible light. A reasonably good result is shown in the S-TiO2 sample. The undoped TiO2 was only able to degrade 49% of RBB after 150 min of visible light exposure. Meanwhile, after dopant addition, the removal efficiency of RBB increased to 94% and 61% for S-TiO2 and Co-TiO2 after 120 min of exposure, respectively. However, the most effective removal of RBB was obtained from the TiO2 co-doped by S and Co 8% (S-Co-TiO2 8%) photocatalyst. Although S-TiO2 reduced 94% of dye concentration, time efficiency can be achieved in co-doped samples (S-Co-TiO2 8%), which can remove 96% of RBB in 90 min of visible light irradiation. Thus, the S-Co-TiO2 8% demonstrated the best photocatalytic performance compared to other prepared photocatalysts.
Under UV irradiation, the S-Co-TiO2 8% sample also demonstrated the highest photocatalytic activity compared to other photocatalysts. During 90 min of UV irradiation, 98% of RBB could be removed, while S-TiO2, Co-TiO2, and pure TiO2 removed 95%, 76%, and 74% of RBB concentration, respectively. These findings confirm that S-and-Co-co-doped TiO2 (S-Co-TiO2) exhibits the most significant increase in photocatalytic activity in visible or UV light.
Pure TiO2 displayed significant photocatalytic activity in UV light but not in visible light since the energy from visible light is insufficient to activate TiO2. The UV light energy corresponds to the expansive band-gap energy of TiO2 (3.2 eV). However, the presence of S and Co as impurity dopants in the titania structure can enhance the photocatalytic activity in visible light due to the formation of new sub-levels energy in the titania structure, resulting in a narrowing of the TiO2 band gap energy [25]. The new energy level formed by the S atom was attributed to the substitution of Ti4+ by S6+ from mixing the S3p orbital with the O2p orbital close to the valence band (VB), which narrowed the band gap of TiO2 and increased the absorption of visible light [13,25,29]. On the other hand, Co dopant contributes to lowering the band gap energy from the substitution of Ti4+ by Co2+. Co dopant directs the sp-d exchange interaction between the band electrons and localized d-electrons of the Co2+ ion that replace the Ti4+ ion. This interaction causes a downward shift of the conduction band (CB), resulting in a narrowing of the band gap system [25,30,38]. The synergetic effect of S and Co dopants forming two new energy levels on the S-Co-TiO2 sample resulted in the most optima in decreasing the band gap energy and encouraging the visible-light absorption compared to S-TiO2 or Co-TiO2 samples.
Although both were doped, S-TiO2 had a much higher photocatalytic activity than Co-TiO2. According to the literature, the higher activity of S-TiO2 can be attributed to the presence of hydroxyl groups on the surface of the sulfur oxide photocatalyst, which can create an acidic environment on the surface. Then, the substitution of Ti4+ by S6+ ions in the TiO2 lattice causes a charge imbalance in the structure of TiO2. The extra positive charge formed will attract anions from the solution, such as hydroxide ions, to the surface of the photocatalyst, thereby neutralizing the charge imbalance [40]. Furthermore, this extra positive charge can adsorb the hvb+ formed by the photocatalyst induced by light to produce hydroxyl radicals, which have strong oxidizing power to decompose the organic compounds such as RBB dyes. The difference in electronegativity between the S and O atoms in the Ti-O-S bond causes electron transfer from the less electronegative S atom to the more electronegative O atom. This causes the sulfur atom to be deprived of electrons and will retain e− generated by the photocatalyst. As a result, the electron and hole recombination rate decreases, and hvb+ will be abundantly available to generate more hydroxyl radicals on the surface of the photocatalyst [13]. The abundant availability of hydroxyl radicals will increase the decontamination efficiency of organic compounds such as RBB dyes.
The co-doped samples demonstrated the most superior photocatalytic activity in visible or UV-light due to a variety of factors, including a better narrowing in band gap, a decrease in particle size, and an increase in surface-area-reduced electron and hole recombination [15,41]. This result is in accordance with the band gap energy (Eg) obtained from the UV–vis SRS data, such that S-Co-TiO2 8% produces the most significant decrease in Eg, which is 2.78 eV and corresponds to the energy of visible light irradiation.
The decolorization process by the photocatalyst starts with the surface adsorption process and continues with the photocatalytic reaction. In order to evaluate the surface adsorption properties of the S-Co-TiO2 8% photocatalyst as well as to evaluate whether the adsorption process continued along with the photocatalytic process, the adsorption of the S-Co-TiO2 8% catalyst was carried out in the dark for 150 min without irradiation as shown in Figure 6. The undoped TiO2 adsorption test was also used for comparison purposes. The results indicate that adsorption takes place in the first 15 min and the concentration of the dye tends not to decrease, which implies that the next process is photocatalytic decolorization after a contact period of 15 min.
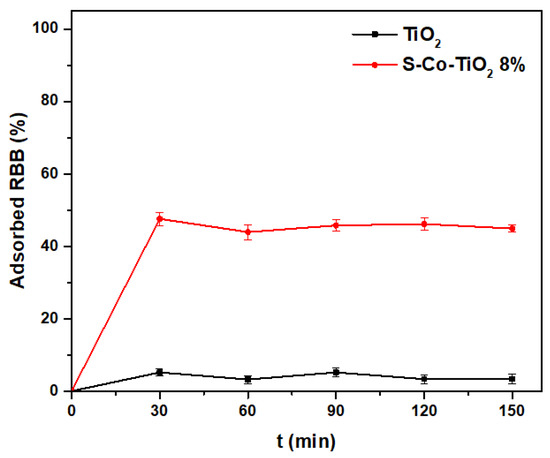
Figure 6.
Adsorption of RBB by TiO2 and S-Co-TiO2 8% in the dark condition at RBB concentration: 20 mg L−1, photocatalyst dosage: 1 g L−1, and initial pH: 5.5.
3.2.2. Effect of pH
The effect of pH is a critical parameter in the efficiency of the decolorization process because it can affect the photocatalyst surface, dye characteristics, and the rate of decolorization. As shown in Figure 7, the effect of the initial pH on RBB removal by the S-CoTiO2 8% catalyst under 60 min of visible light exposure was evaluated in the range of 2.0–10.0.
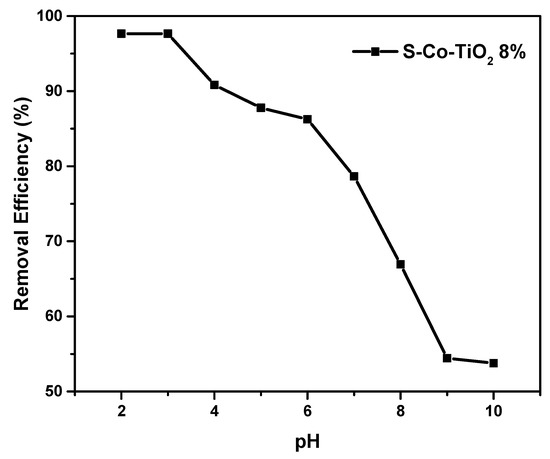
Figure 7.
Influence of pH on photocatalytic decolorization of RBB under 60 min of visible light irradiation by the S-Co-TiO2 8% photocatalyst, RBB concentration: 20 mg L−1, photocatalyst dosage: 1 g L−1.
As shown in Figure 7, when the initial pH was reduced from 5.0 to 3.0, the decolorization efficiency of RBB increased from 88% to 97% at 60 min of irradiation. However, there was no increase in decolorization when the pH was reduced to 2.0. However, increasing the solution pH to 8.0, 9.0, and 10.0 reduced the decolorization efficiency to 67%, 54%, and 53%, respectively. This result can be explained by the fact that TiO2 has a positive or negative charge depending on the pH of the solution:
pH < pHZPC: Ti-OH + H+ → TiOH2+
pH > pHZPC: Ti-OH + OH− → TiO− + H2O
The optimum pH for RBB decolorization was found to be 3.0, and the pHPZC of S-Co-TiO2 8% was found to be 6.41 (Figure 8). When the solution pH is below the pHPZC, the TiO2 surface will be positively charged. At acidic medium (pH = 3.0), RBB has sulfonate (SO3−) and sulfite (SO32−) groups, which can be adequately adsorbed by the positive charge on the surface of TiO2 through electrostatic force at the beginning of the decolorization process [3,42]. As a result, the optimal pH of RBB adsorption on the catalyst surface is 3.0. When the pH of the solution is lowered from 7.0 to 10.0, the removal efficiency decreases as well. It can be explained because at alkaline pH conditions, the surface of TiO2 is negatively charged, leading to charge repulsion with the RBB, which is also negative.
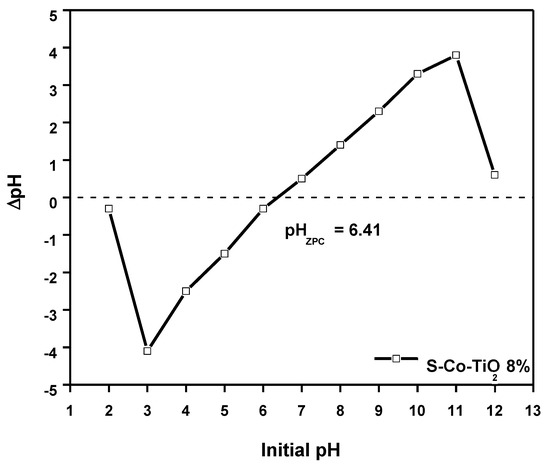
Figure 8.
pHPZC of the S-Co-TiO2 8% photocatalyst.
3.2.3. Effect of Catalyst Dosage
The effect of photocatalyst amount on the RBB removal under visible light irradiation was investigated by varying the mass of the S-Co-TiO2 8% from 0.2 to 1.0 g L−1 (C0 = 20 mg L−1, pH = 3.0). The obtained results are shown in Figure 9.
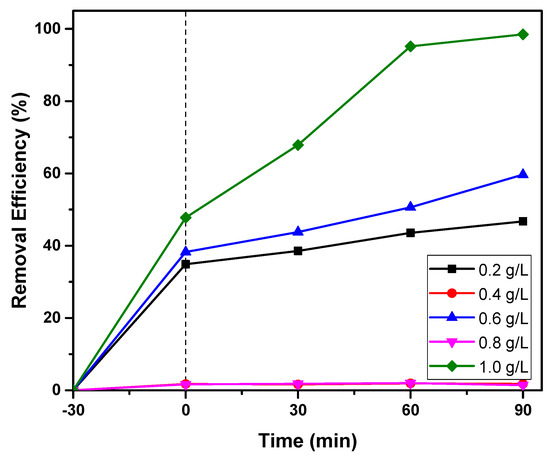
Figure 9.
The effect of the S-Co-TiO2 8% photocatalyst dosage on RBB removal at RBB concentration: 20 mg L−1 and initial pH: 3.0.
As shown in Figure 9, increasing the photocatalyst mass from 0.2 to 1.0 mg L−1 resulted in additional RBB removal, which was associated with an increased adsorption rate on the catalyst surface and increased hydroxyl radical formation. The photocatalyst mass of 1.0 g L−1 provided the highest decolorization efficiency. However, the amount of dye adsorbed on the surface of the photocatalyst was very high at the beginning of the reaction, whereas the photocatalytic reaction became insignificant. It can be seen that after 60 min of irradiation, the photocatalytic reaction did not continue since an excessive amount of photocatalyst had increased the number of active sites on the surface of the photocatalyst, allowing adsorption to dominate at the start of the process while the photocatalytic reaction becomes insignificant.
The photocatalyst mass of 0.6 mg L−1 was chosen for further investigation due to its high photocatalytic efficiency after 30 min of adsorption–desorption. When the photocatalyst dosage was increased from 0.6 to 1.0 mg L−1, decolorization was almost insignificantly different.
3.2.4. Effect of Dye Concentration
The color removal process is affected by the initial concentration of pollutants. Therefore, the effect of RBB concentration on the efficiency of decolorization by the S-Co-TiO2 8% photocatalyst was carried out by varying the RBB concentration from 20 to 50 mg L−1, and the results obtained are presented in Figure 10. The decolorization efficiency decreased from 98% to 57% as the RBB concentration increased from 20 mg L−1 to 50 mg L−1. This is due to the fact that as the dye concentration increases, the number of molecules adsorbed on the photocatalyst surface increases, obstructing direct contact with the holes and inhibiting the formation of hydroxyl radicals. Furthermore, at higher concentrations, the dye molecules adsorbed more photons, thereby reducing the light intensity and decolorization efficiency [28,43].
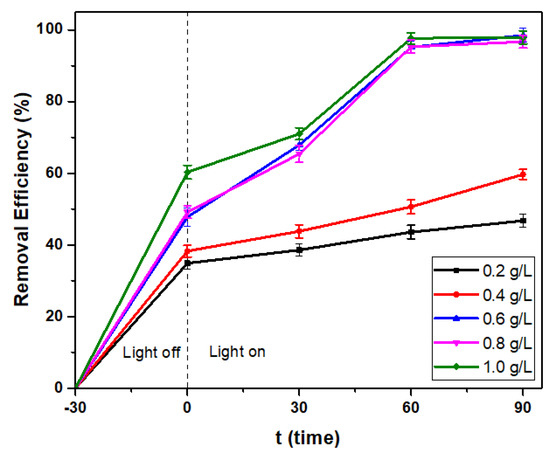
Figure 10.
The effect of RBB concentration on S-Co-TiO2 8% dose 0.6 g L−1, initial pH: 3.0, and 90 min of visible light irradiation.
3.2.5. The Recyclable Ability of S-Co-TiO2 8% Photocatalyst
The stability and reusability of photocatalysts are critical parameters in the study of photocatalysts for use in sustainable wastewater treatment. The S-Co-TiO2 8% photocatalyst was tested for stability and reuse four times. In each test, S-Co-TiO2 8% was centrifuged and then washed and dried before being used in the next cycle under the same experimental conditions for 90 min of visible light irradiation. The reuse test results for S-Co-TiO2 8% photocatalyst are shown in Figure 11. The results showed that the S-Co-TiO2 8% sample had high decolorization efficiency after four reuse cycles, but there was a 44% decrease in decolorization efficiency after four uses. This could be due to the loss of photocatalyst during the iteration process. These findings suggest that the co-doped sample S-Co-TiO2 8% photocatalyst has promising potential and can be used repeatedly to remove dye pollutants.
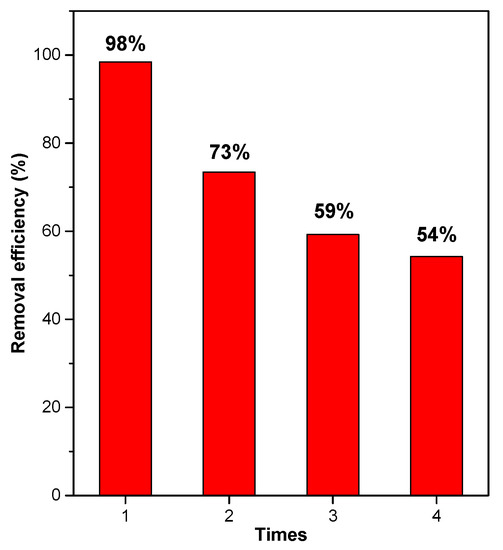
Figure 11.
Recyclability of S-Co-TiO2 8% for RBB removal under visible light illumination, RBB con-centration: 20 mg L−1, initial pH: 3.0, and photocatalyst dosage: 0.6 g L−1.
3.3. Mechanism of RBB Photocatalytic Decolorization
Photocatalytic removal reactions can occur when TiO2 absorbs photons with energies equal to or greater than their band gap energy. S and Co co-dopants create impurity states close to VB and CB, resulting in a narrowing of the TiO2 band gap, thereby increasing photocatalytic visible light activity. The schematic of the S-Co-TiO2 photocatalyst mechanism is presented in Figure S6. The characterization results using XRD, FTIR, SEM-EDX, and SRS UV–vis indicate that the modification of the addition of S and Co co-dopants to TiO2 has been successfully carried out.
When S-Co-TiO2 is exposed to visible light radiation, electrons in the VB are excited towards the CB (eCB−), producing holes (hVB+) in the VB. These excited electron–hole pairs are commonly referred to as excitons [44]. The mechanism that occurs is as follows:
S-Co-TiO2 + hν→ hVB+ + eCB−
The holes can react with adsorbed hydroxyl anion on the TiO2 surface to form hydroxyl radicals, which have high oxidizing power and can decompose organic pollutants, and excited electrons (eCB−) can reduce O2 to form oxygen radicals, which can be converted into hydroxyl radicals in water as follows:
OH− + hVB+ → •OH
•OH + RBB → degradation pollutant (Cl−, NO3−, SO42−, CO2 and H2O)
4. Conclusions
The decolorization of Remazol Black (RBB) was investigated using an S-Co-TiO2 photocatalyst. This photocatalyst was prepared through one-pot synthesis using a single precursor as a source of S and Co dopants. Characterization using XRD, FT-IR, SEM-EDX, and UV–Vis SRS showed that S-and-Co co-doped TiO2 was successfully synthesized and degraded RBB under visible light better than TiO2 or S-TiO2 and Co-TiO2. Eight percent (w/w) of CoSO4 as a single precursor of S and Co provides the best reduction in band gap energy to 2.78 eV and is supported by the best photocatalytic activity when compared to other photocatalysts. After 90 min of temporary visible light, the S-Co-TiO2 8% can degrade 96% of RBB, whereas S-TiO2, Co-TiO2, and undoped TiO2 can decrease to 89%, 56%, and 39%, respectively, and the optimum decolorization results are obtained at pH 3.0. Reuse studies show that S-Co-TiO2 8% has the potential to be used repeatedly for the removal of dye pollutants in the environment.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/photochem1030032/s1, Figure S1: Chemical structure of Remazol Black (RBB); Figure S2: Schematic diagram of photoreactor for photocatalytic experiment; Figure S3: EDX pattern of (a) TiO2, (b) S-TiO2, (c) Co-TiO2, (d) S-Co-TiO2 4%, (e) S-Co-TiO2 6%, and (f) S-Co-TiO2 8%; Figure S4: Absorption spectrum of Remazol Black analyzed by spectrophotometry, Remazol Black concentration: 20 mg L−1; Figure S5: Spectrum of Remazol Black after decolorization by S-Co-TiO2 8% photocatalyst for 150 min visible light irradiation, photocatalyst dose: 1.0 g L−1, initial pH: 5.5, Remazol Black concentration: 20 mg L−1, Figure S6: Schematic diagram of photocatalytic decolorization of RBB by S-Co-TiO2 photocatalyst.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.T.W.; methodology, E.T.W. and R.D.; software, R.D.; validation, E.T.W., R.R. and R.D.; formal analysis, R.D., E.T.W. and R.R.; investigation, R.D., E.T.W. and R.R.; resources, R.D. and E.T.W.; data curation, R.D. and E.T.W.; writing—original draft preparation, R.D.; writing—review and editing, E.T.W., R.R. and R.D.; visualization, R.D., E.T.W. and R.R.; supervision, R.D.; project administration, E.T.W. and R.D.; funding acquisition, E.T.W. and R.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by Kemenristekdikti (Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education) of Indonesia through the Pendidikan Magister menuju Doktor untuk Sarjana Unggul (PMDSU) Scholarship Program (contract No. 2335/UN1/DITLIT/DIT-LIT/PT/2021).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data presented in this study are available in the article.
Acknowledgments
The first author is grateful to the Ministry of Research, Technology, and Higher Education of Indonesia (Kemenristekdikti) for providing a comprehensive scholarship to enable this research to be carried out, as well as to the Department of Chemistry, Universitas Gadjah Mada, which has provided this research facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, and the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Marques, S.M.; Tavares, C.J.; Oliveira, L.F.; Oliveira-Campos, A.M.F. Photocatalytic degradation of C.I. Reactive Blue 19 with nitrogen-doped TiO2 catalysts thin films under UV/visible light. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 983, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Rahman, N.K. Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic of Remazol Brilliant Orange 3R dye adsorption on coffee husk-based activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandham, M.; Sobana, N.; Swaminathan, M. Solar assisted photocatalytic and photochemical degradation of Reactive Black 5. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahel, K.; Perol, N.; Dappozze, F.; Bouhent, M.; Derriche, Z.; Guillard, C. Photocatalytic degradation of a mixture of two anionic dyes: Procion Red MX-5B and Remazol Black 5 (RB5). J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2010, 212, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Cheng, M.C.; Chen, A.H. Photocatalytic decolorization of Remazol Black 5 and Remazol Brilliant Orange 3R by mesoporous TiO2. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 102, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Pereira, L.; Marques Sales, I.; Pereira Zampiere, L.; Silveira Vieira, S.; do Rosário Guimarães, I.; Magalhães, F. Preparation of magnetic photocatalysts from TiO2, activated carbon and iron nitrate for environmental remediation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 382, 111907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnajady, M.A.; Modirshahla, N.; Shokri, M.; Rad, B. Enhancement of photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles by Silver doping: Photodeposition versus liquid impregnation methods. Glob. Nest J. 2008, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.C.; Wu, P.Y.; Lin, T.H.; Lin, T.F. Photocatalytic performance of Cu-doped TiO2 nanofibers treated by the hydrothermal synthesis and air-thermal treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 430, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia, J.J.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Navío, J.A.; Araña, J.; Doña-Rodríguez, J.M. Study of the phenol photocatalytic degradation over TiO2 modified by sulfation, fluorination, and platinum nanoparticles photodeposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 179, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Hsueh, H.T.; Chang, C.W.; Chu, H. The visible light-driven photodegradation of dimethyl sulfide on S-doped TiO2: Characterization, kinetics, and reaction pathways. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 199, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramacharyulu, P.V.R.K.; Praveen Kumar, J.; Prasad, G.K.; Sreedhar, B. Sulphur doped nano TiO2: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic degradation of a toxic chemical in presence of sunlight. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 148, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManamon, C.; O’Connell, J.; Delaney, P.; Rasappa, S.; Holmes, J.D.; Morris, M.A. A facile route to synthesis of S-doped TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic activity. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 406, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, S.A.; Ribeiro, C. A comparative run for visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity of anionic and cationic S-doped TiO2 photocatalysts: A case study of possible sulfur doping through chemical protocol. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 421, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ma, W.; Zhao, J. Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants by Co-Doped TiO2 Under Visible Light Irradiation. Curr. Org. Chem. 2010, 14, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Xi, Z.; Xing, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Tian, B.; Bagwasi, S. Study of synergistic effect of Ce- and S-codoping on the enhancement of visible-light photocatalytic activity of TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 9520–9528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, G.; Liu, S.; Ang, H.M.; Tadé, M.O.; Wang, S. Visible light responsive titania photocatalysts codoped by nitrogen and metal (Fe, Ni, Ag, or Pt) for remediation of aqueous pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ma, Z.; Ban, P.; Xu, X. C, N and S codoped rutile TiO2 nanorods for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singaram, B.; Varadharajan, K.; Jeyaram, J.; Rajendran, R.; Jayavel, V. Preparation of cerium and sulfur codoped TiO2 nanoparticles based photocatalytic activity with enhanced visible light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2017, 349, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinhmar, A.; Setia, H.; Kumar, V.; Sobti, A.; Toor, A.P. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of nickel and nitrogen codoped TiO2 under sunlight. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Xing, M.; Tian, B.; Zhang, J. Improving the visible light photocatalytic activity of nano-sized titanium dioxide via the synergistic effects between sulfur doping and sulfation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 115–116, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yuan, K.; Lu, N.; Xu, H.; Zhang, S.; Takeuchi, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Li, R. The interplay of sulfur doping and surface hydroxyl in band gap engineering: Mesoporous sulfur-doped TiO2 coupled with magnetite as a recyclable, efficient, visible light active photocatalyst for water purification. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 218, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.K.; Godavarthi, S.; Karthik, T.V.K.; Mahendhiran, M.; Hernandez-Eligio, A.; Hernandez-Como, N.; Agarwal, V.; Martinez Gomez, L. Green synthesis of S-doped rod shaped anatase TiO2 microstructures. Mater. Lett. 2016, 183, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, J.; Xiang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Liao, Y. Transition-Metal-Ion (Fe, Co, Cr, Mn, Etc.) Doping of TiO2 Nanotubes: A General Approach. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 12511–12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.M.H.; Bark, C.W. Synthesis of Cobalt-Doped TiO2 Based on Metal-Organic Frameworks as an Effective Electron Transport Material in Perovskite Solar Cells. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 2280–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqa, A.; Masih, D.; Anjum, D.; Siddiq, M. Cobalt and sulfur co-doped nano-size TiO2 for photodegradation of various dyes and phenol. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 37, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mragui, A.; Logvina, Y.; da Silva, L.P.; Zegaoui, O.; da Silva, J.C.G.E. Synthesis of fe-and co-doped TiO2 with improved photocatalytic activity under visible irradiation toward carbamazepine degradation. Materials 2019, 12, 3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, P.; Farhadian, M.; Solaimany Nazar, A.R.; Jeon, B.H. Adsorption and Photodegradation Efficiency of TiO2/Fe2O3/PAC and TiO2/Fe2O3/Zeolite Nanophotocatalysts for the Removal of Cyanide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isari, A.A.; Payan, A.; Fattahi, M.; Jorfi, S.; Kakavandi, B. Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B and real textile wastewater using Fe-doped TiO2 anchored on reduced graphene oxide (Fe-TiO2 /rGO): Characterization and feasibility, mechanism and pathway studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 462, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Liao, Q.; Deng, W.; Huang, Y.; Mao, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, G. The preparation of amorphous TiO2 doped with cationic S and its application to the degradation of DCFs under visible light irradiation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samet, L.; Ben Nasseur, J.; Chtourou, R.; March, K.; Stephan, O. Heat treatment effect on the physical properties of cobalt doped TiO2 sol-gel materials. Mater. Charact. 2013, 85, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Kuo, D.H. Cationic S-doped TiO2/SiO2 visible-light photocatalyst synthesized by co-hydrolysis method and its application for organic degradation. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Sharma, S.N.; Kumar, M.; De, S.K. Morphology dependent luminescence properties of Co doped TiO2 nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 14783–14792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Andersen, J.; Likodimos, V.; Falaras, P.; Linkugel, J.; Dionysiou, D.D. The effect of solvent in the sol-gel synthesis of visible light-activated, sulfur-doped TiO2 nanostructured porous films for water treatment. Catal. Today 2014, 224, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.G.; Kavitha, R. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of sulfur doped TiO2 for the decomposition of phenol: A new insight into the bulk and surface modification. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 143, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugundan, S.; Rajamannan, B.; Viruthagiri, G.; Shanmugam, N.; Gobi, R.; Praveen, P. Synthesis and characterization of undoped and cobalt-doped TiO2 nanoparticles via sol–gel technique. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, J.; Yang, K.; Feng, S.; Tan, W.; Tao, Y.; Mao, H.; Kong, Y. Preparation of S-doped TiO2-three dimensional graphene aerogels as a highly efficient photocatalyst. Synth. Met. 2017, 231, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, S.; Ribeiro, C. An insight toward the photocatalytic activity of S doped 1-D TiO2 nanorods prepared via novel route: As promising platform for environmental leap. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 412, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, S.; Khan, W.; Khan, S.; Husain, S.; Ahmad, A. Consequences of (Cr/Co) co-doping on the microstructure, optical and magnetic properties of microwave assisted sol-gel derived TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 2019, 205, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowoyo, J.O.; Kumar, M.; Jain, S.L.; Shen, S.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, S.S.; Vorontsov, A.V.; Kumar, U. Reinforced photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to fuel by efficient S-TiO2: Significance of sulfur doping. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 17682–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.C.; Ho, W.; Yu, J.; Yip, H.; Po, K.W.; Zhao, J. Efficient visible-light-induced photocatalytic disinfection on sulfur-doped nanocrystalline titania. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Su, Y.L.; Zhang, X.W.; Lei, L.C. Fabrication of visible-light responsive S-F-codoped TiO2 nanotubes. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 1983–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ghoreishian, S.M.; Badii, K.; Norouzi, M.; Rashidi, A.; Montazer, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Vafaee, M. Decolorization and mineralization of an azo reactive dye using loaded nano-photocatalysts on spacer fabric: Kinetic study and operational factors. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.H.; Al-Afify, A.D.; Goher, M.E. Preparation and characterization of graphene—TiO2 nanocomposite for enhanced photodegradation of Rhodamine-B dye. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2018, 44, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Dominguez, A.; Turley, R.S.; Kim, H.; Sultana, K.A.; Shuvo, M.A.I.; Alvarado-Tenorio, B.; Montes, M.O.; Lin, Y.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.; et al. Development of photocatalytic paint based on TiO2 and photopolymer resin for the degradation of organic pollutants in water. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).