Abstract
Due to expansion in infrastructure and increased development of urbanization in Ethiopia, most of the places are covered either by impermeable cement concrete or bitumen that blocks the percolation of water from rainfall. A porous concrete made of zero fine aggregates, creating a pore that permits the concrete to be water permeable, is highly desirable. Similarly, the demand for natural coarse aggregates remains high, while natural resources are being depleted. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the properties of porous concrete using recycled concrete aggregate as a partial replacement for natural coarse aggregate. Experimental tests were conducted on cement setting time, workability of concrete, compressive, split tensile, porosity, and permeability of porous concrete. The properties of porous concrete at different ratios—0, 15, 30, 45 and 60%—revealed that RCA is suitable for use as coarse aggregate. The optimum replacement percentage of recycled aggregate for porous concrete in terms of strength is 30%, with 28th-day compressive strength of 17.37 MPa. However, slight increments were observed in porosity and permeability coefficient. Therefore, the concrete produced in this study is structural concrete, which is suitable for walkways and other concrete flat works, whereby heavy vehicle traffic loads do not exist.
1. Introduction
The production of concrete ingredients commonly implies high energy costs and causes environmental pollution. Therefore, producing sustainable and eco-friendly concrete is highly desirable for reducing the carbon footprint of concrete [1,2]. Additionally, natural resources are being consumed at an increasing rate in today’s world due to rapid urbanization and increased demand [3]. This increased demand for natural resources leads to the depletion of virgin concrete ingredients, which is a critical issue for the construction industry, particularly in developing countries [1]. Moreover, environmentally friendly concrete that uses less energy and emits less carbon during its production than conventional concrete is called green concrete. This concrete is a good alternative to conventional concrete in terms of wise consumption of natural resources. Hence, replacing conventional concrete constituent materials with other alternative raw materials makes green concrete more environmentally friendly. As a result, it is often thought to be cheap to produce concrete with recycled aggregate to avoid extra charges for the disposal of waste, consume less energy, and achieve higher durability [4,5].
Several studies have reported that large quantities of waste are generated every year by the construction industry. The waste continues to instigate serious problems both locally and globally [6,7]. Hence, the trends in the last decade have been to increase the recycling and reuse of construction waste as secondary raw materials in order to enhance their environmental benefits [8]. This waste must be stored in landfill, which does not have a limitless capacity, and solutions are required to be able to reuse materials from demolished buildings such as concrete or mortar [9]. The various construction waste management approaches in decreasing order of environmental impact are disposal, recycling, reuse, and reduction. Moreover, the disposal of waste in landfills is the most detrimental to the environment among all of the waste management approaches [10]. Therefore, strategies for using concrete waste materials such as recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) for the production of porous concrete reduces the amount of demolition waste and the consumption of natural aggregate, which is advantageous for the environment. Therefore, porous concrete is an ideal solution that has been gaining popularity as a tool for sustainable development because of its environmental benefits. Additionally, it is a very special type of concrete with high porosity, being made up of little to no fine aggregates [11]. Conventional concrete has a very low permeability, in which water simply runs off its surface [12]. However, porous or permeable concrete is a special type of concrete that allows water from precipitation and other sources to pass directly through the pores, thereby reducing runoff from the site and recharging the ground water table [13]. It is viable to use it as paving material, pavement sidewalks, secondary roads, parking areas, residential streets, and to achieve good seepage of storm water [14]. Permeable concrete is considered an environmentally friendly construction material, and has been quickly gaining recognition as a green building component. Nevertheless, further attention is needed for construction materials with respect to energy utilization, economy and environmental protection in order to enhance the sustainability and remarkable development in the construction industry, particularly in the context of developing countries.
Many studies have been carried out to investigate the properties of porous concrete and improve its fresh and harden properties. For instance, in the work of Bhutta et al. [15], both the fresh and harden properties of porous concrete made from RCA were improved by adding polymers to the mix. However, in this paper, the properties of porous concrete made from RCA were investigated without admixes or additives. Due to rapid urbanization in recent years, waste is generated during construction and demolition activities, particularly in developing countries. This is commonly disposed in landfills, and only a small quantity is reused for construction. Additionally, the disposal of these wastes causes serious environmental problems and economic impacts. Furthermore, the demand for fresh aggregates for producing concrete is still high, while the availability of natural resources is diminishing. Therefore, recycling construction and demolition waste as an alternative construction material is a sustainable solution for reducing environmental pollution and reducing dependence on natural and non-renewal resources. The outcomes from the research presented here will be beneficial for policymakers and decision makers in preparing guidelines on how to use waste materials effectively, thereby adding to sustainability efforts in the community.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The materials used for this experimental study included cement, coarse aggregate, recycled concrete aggregate, and water. Relevant physical property tests were conducted on the materials before starting the mix design procedures in order to investigate their quality.
2.1.1. Cement
Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) from Dangote cement factory, Oromia, Ethiopia with a grade of 32.5 R, manufactured to satisfy Ethiopian standard ES 1177-1 CEM II/B-P and conforming to ISO-9001:2015, was used in the production of all concrete specimens. The cement class PPC 32.5 R is a versatile all-purpose cement with superior workability, reduced water demand, and superior cohesion, strength and low emissions; it is a rapid-setting cement and provides good early strength. It can also be used to produce low-strength concrete, which is also suitable for porous concrete. The properties of the cement were tested as per ASTM C187, ASTM C191, ASTM C184 and ASTM C188, respectively, and summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Properties of cement.
2.1.2. Normal Coarse Aggregate
Crushed stone gravel of natural basaltic origin conforming to ASTM C 33 was used as coarse aggregate [16]. According to the A.C.I. 522R (2010) committee report, the coarse aggregate size used for porous concrete is either of a single size or with gradings ranging from 19 mm to 9.5 mm. Therefore, aggregates with gradings between 20 mm and 4.75 mm, with a maximum size of 20 mm, were included. Additionally, corrective measures like blending of the aggregate to meet the grading requirements and washing it to make it free from impurities like silt, clay, dirt and inorganic matter were conducted before proceeding to the mix proportion. The particle size distribution of the aggregate was analyzed, and the obtained result fulfilled the ASTM C 33 standard specification of coarse aggregate for concrete production. This test method is mainly used to identify the classification of materials being used as aggregates. The results are shown in Figure 1.
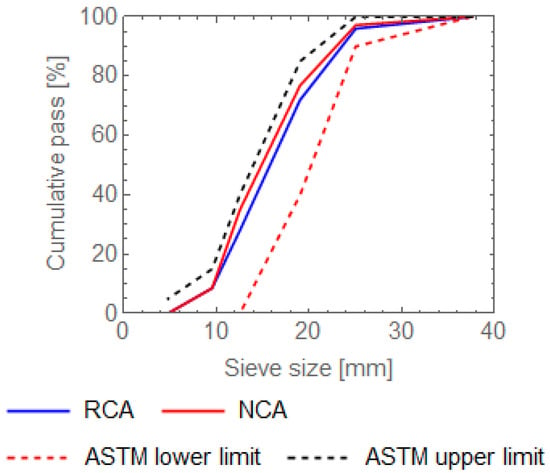
Figure 1.
Aggregate size distribution of normal and recycled aggregates.
2.1.3. Recycled Concrete Aggregate (RCA)
As shown in Figure 2, recycled concrete aggregate obtained from a demolished concrete building at Jimma University’s Hotel and Tourism project site and conforming to ASTM C 33 was used after crushing it to the specified grade, as shown in Table 2. During the recycling process, several impurities were eliminated by sorting the demolished concrete waste from the site before disposal, removing unnecessary attachments, crushing by jackhammer, loading and transporting it to the laboratory, resizing it by hammer to the desired size, and washing it to remove fine particles and some of the old mortar. The grain size distribution for recycled concrete aggregate also fulfilled the requirements of ASTM C 33, as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 2.
Recycled aggregate process: (a) demolished concrete waste; (b) recycled aggregate.

Table 2.
Summary of the properties of aggregates.
Tap water supplied to the Jimma university construction laboratory from the Jimma town water and sewerage authority was utilized in the production, curing and soaking of the samples.
2.2. Methods
Engineering property tests were conducted on the materials to determine their suitability for concrete production. Mix design for the control concrete group and the recycled concrete aggregate replaced concrete group were determined per the A.C.I. 522R, 2010 design standard. Cube molds with dimensions of 150 mm × 150 mm × 150 mm and cylinder molds with dimensions of 200 mm × 100 mm were used to cast the specimen with partial replacement of 0, 15, 30, 45 and 60% normal coarse aggregate with recycled concrete aggregate. According to ACI 522R, (2010), the minimum and maximum compressive strength required for porous concrete made up of natural aggregate ranges between 2.8 and 28 MPa, respectively, with typical values of about 17 MPa, which is suitable for a wide range of applications, such as light-traffic roads, parking lots, residential streets, and pavement sidewalks. In order to obtain a proper mix of RCA, several concrete samples were cast at different mix ratios, and the compressive strength was tested; whereby it was observed that the compressive strength of the concrete decreased significantly when the ratio of RCA was more than 50%, even though it is within the range specified in ACI. Then, it was decided to analyze the effect of the replacement up to 60%. Therefore, a target compressive strength of 17.37 MPa at 30% replacement of RCA is suitable for the intended use. Therefore, 15 to 60% was chosen in order to find the optimum percentage of RCA required for porous concrete. The cast specimens were tested after 7, 14 and 28 days of curing. Destructive test like compressive strength and non-destructive tests like porosity and permeability tests were conducted.
2.3. Mix Proportion
Mix design for porous concrete with strengths ranging between 2.8 and 28 MPa, as per the A.C.I. 522R-2010 recommendations, were used. The mix proportions for normal porous concrete with replacement of various percentages with recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) porous concrete are given in Table 3. The quantity of cement for each experimental group was kept constant, and the water-cement ratio varied with increasing amount of recycled concrete aggregate, due to its higher water absorption capacity. For all tests, three samples were tested, and the mean values are reported.

Table 3.
Mix design proportions.
2.4. Concrete Tests
2.4.1. Workability Test
Workability is the degree of mobility of the concrete and its easiness to work with [17]. Conventionally, it is checked by a vertically uplifting slump cone with a height of 300 mm, a diameter of 200 mm at the top, and a diameter of 100 mm at the bottom. However, this procedure is not appropriate for very wet or very dry concrete mixes. Hence, performing compacting factor tests or testing the density ratio of the weight of partially compacted concrete to the weight of fully compacted concrete is particularly useful for porous concrete mixes with very low Workability. The corresponding compacting factor result is calculated as shown in Equation (1):
2.4.2. Compressive Strength Test
Tests related to the compressive strength of the concrete were conducted at 7, 14, and 28 curing days, as shown in Figure 3. The strength was determined by dividing the maximum load attained for the cross-sectional area of the cube specimen, as shown in Equation (2) [18].
where
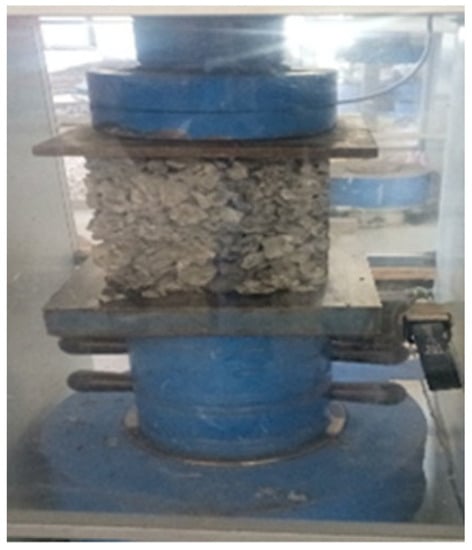

Figure 3.
Compressive strength testing.
- δc = Compressive strength (MPa),
- P = Maximum load (N) and
- A = Cross-sectional area (mm2).
2.4.3. Porosity Test
Porosity is the ratio of voids in the concrete to the total volume (V) of the sample. The test was performed by dividing the difference between the oven-dry weight of the sample (Md) and the weight of the submerged sample in the water tank for a minimum of 30 min (Mw) by the water density (δw) to determine porosity (P) using Equation (3) [19]. The test is shown in Figure 4.
where
Figure 4.
Determination of the porosity of concrete.
- P = Porosity,
- Md = Mass of oven-dried sample,
- Mw = Mass of the submerged sample in the water tank for a minimum of 30 min,
- δw = Density of water,
- V = Total volume of sample.
2.4.4. Permeability Test
The most important feature of the porous concrete is to allow the percolation of water passing through the porous medium. The test was conducted using a constant head method [20]. The coefficient of permeability was obtained using Darcy’s law, as shown in Equation (4), which was preliminarily used as a falling head test to obtain its coefficient as per standard procedures [21].
where
- Q = Quantity of water discharged cm3,
- K = Coefficient of permeability (cm/s),
- L = Length of specimen (cm),
- t = Total time of discharge (s),
- A = Cross-section area of specimen (cm2),
- h = Difference in head on manometer (cm).
3. Results
3.1. Compaction Factor Test Results
Very dry and wet mixes do not enable the correct slump height to be achieved and are not suitable for use with the conventional compaction method. Hence, the compaction factor test was conducted to determine the degree of Workability by allowing the mix to fall through successive hoppers of standard height using a compaction factor test apparatus. This test is a suitable method for testing the compacting factor limits from very low to high Workability, with possible values of 0.78, 0.85, 0.92 and 0.95, which indicate very low, low, medium, and high Workability, respectively as in Table 4.

Table 4.
Test results for compacting factor value.
The results confirmed that, with increasing percentage of recycled aggregate, (1) the water absorption from cement paste increases when the aggregate is dry, due to a the high void ratio; (2) water is released into the interfacial transition zone when the aggregate is moist; and (3) the cement materials penetrate into the pores, in contrast to natural coarse aggregate.
This work highlights the need for a roller compacting technique for a concrete mix that is characterized as harsh.
3.2. Compressive Strength Test Results
The average compressive strength results of cubes for both the natural aggregate mix and the mix with recycled concrete aggregate replacement were determined and evaluated on the 7th, 14th, and 28th curing days by crushing the samples using a Universal Testing Machine. The corresponding mean strength is presented in Figure 5.
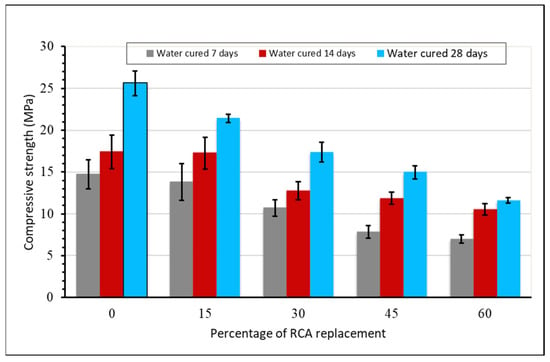
Figure 5.
Compressive strength results for all mixtures, error bars represent the calculated standard deviations for the experimental data.
As shown, with increasing percentage of recycled aggregates in the mixes, there is a decrease in the compressive strength of the cube. For the natural aggregate mix (0% RCA), the 28th-day compressive strength was 25.63 MPa. This mix is considered to be a reference (control) mix for the purpose of comparison with the RCA replaced mix.
As per the A.C.I. 522R 10 guidelines, the compressive strength of natural aggregate porous concrete ranges between 2.8 and 28 MPa, with typical average values of about 17 MPa, which is suitable for a wide range of applications, such as light traffic pavements, parking lots, residential streets, and pavement sidewalks. These experimental results show that for all RCA replacement levels, the compressive strength values fall within the range stipulated in the standard.
For the 45% and 60% RCA replacement levels, the compressive strength results after the 28th day were less than the typical average value of 17 MPa implemented in most required application areas. However, for the 15% and 30% RCA replacement levels, the results were higher than the typical average value of 17 MPa. From this study, the 30% replacement of recycled concrete aggregate was found to provide the optimum level of RCA replacement for porous concrete.
As shown in Figure 5, the compressive strength test results decrease with increasing percentage of recycled aggregate, which reduces the bond strength between cement paste and aggregates. In addition, this affects the strength development of the concrete at the microstructure level by forming different Interfacial Transition Zones (I.T.Z.) during the strength development stages of the concrete [19]. Therefore, the RCA should not have a rough surface structure (old mortar), which is the main drawback to the decreased strength of porous concrete with recycled aggregate replacement.
3.3. Porosity Test Results
The porosity test was performed as per the standard [20], by dividing the difference between the 24 h oven-dried weight of the sample (Md) and the weight of the sample submerged in a water tank for a minimum of 30 min (Mw) by the water density. The corresponding test results on the 28th day for RCA replacements of 0, 15, 30, 45 and 60% were approximately the same, as shown in Figure 6.
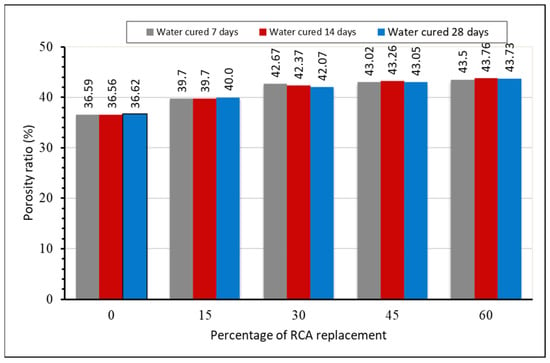
Figure 6.
Porosity of porous concrete.
For every 15% increase in the RCA replacement ratio in the concrete, the porosity ratio of the porous concrete increased. For example, the increment at 28 days with increasing recycled concrete aggregate was 8.45, 12.95, 14.94 and 16.26% for 15, 30, 45 and 60% of RCA, respectively, compared to the control mix. This increment was in the range of approximately 8 to 16% for RCA contents of 15 to 60%. This indicates that porous concrete with recycled aggregate contains not only virgin aggregate, but also hydrated cement paste, which reduces the specific gravity and increases porosity. Additionally, the void ratio of this concrete was beyond the acceptable range of 36–43%, which affects the Workability and strength of the concrete.
3.4. Permeability Test Results
The permeability of porous concrete is an important parameter for evaluating the suitability of using porous concrete for pavement sidewalks, residential streets, tennis courts, light traffic roads, and parking lots. It mainly depends on the size and pore structures of the concrete. The test was conducted by providing sufficient voids through which water could drain or pass safely into the sub-base or subgrade layers of the pavement. Researchers have argued that porous concrete generally has high permeability compared to normal dense concrete, and the permeability test method may not be suitable for testing porous concrete. Keeping this view in mind, a permeability test was conducted to estimate the permeability coefficient of porous concrete. The infiltration test for water to pass through pores of porous concrete was expressed in centimeters per second (cm/s), as per the ASTM-C1701 [21] standard, and the results are shown in Figure 7.
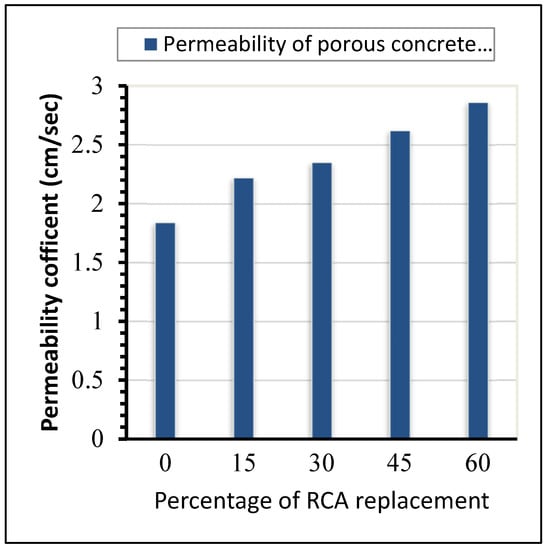
Figure 7.
Permeability coefficient.
With increasing percentage of RCA in the mix, the permeability of the concrete increases due to the increasing void ratio or porosity of the concrete. This shows the direct relationship of porosity and permeability with the RCA replacement amount. Furthermore, Figure 7 shows that the coefficient of permeability (k) increases with every additional 15% inclusion of RCA by anywhere from 17.12 to 35.66%.
3.5. Relationship between the RCA, Strength, Porosity and Permeability Properties of the Concrete
The main challenges encountered during porous concrete mixture proportioning were determining aggregate size, aggregate cement ratio, and water–cement ratio, and the balance between acceptable values of compressive strength, porosity, and water percolation rate. The strength properties of porous concrete decrease with increasing aggregate size [22,23]. However, porosity has a direct relationship with permeability and RCA replacement percentage. Increasing the percentage of RCA increases the porosity, resulting in faster discharge of water through the concrete pores, and consequently, a decrease in compressive strength. As shown on Figure 8, the mean compressive strength of concrete decreases as the percentage of RCA increases, while both porosity and permeability increase. Therefore, by combining all the sizes of coarse aggregates between 20 and 4.75 mm and 30% RCA by weight of natural coarse aggregate, the required compressive strength (17 MPa), sufficient porosity, and permeability requirements were achieved in this study.
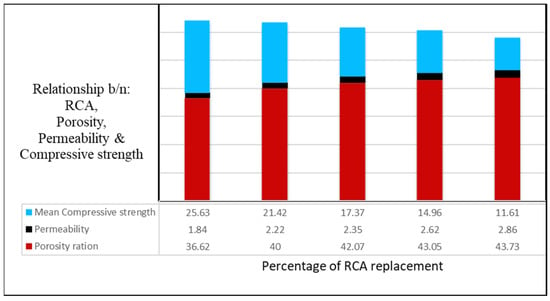
Figure 8.
Relationship between RCA, porosity, permeability, and compressive strength.
4. Discussion
The test results show that the degree of Workability of the concrete slightly decreased from medium to low with increasing amount of recycled concrete aggregate. A similar conclusion was formulated in [24]. For the recycled aggregate mixes, their 28th-day compressive strengths were 21.42, 17.37, 14.96 and 11.61 MPa for 15, 30, 45 and 60% recycled aggregates, respectively. Compared with the control mix, the compressive strengths decreased from 16.43 to 54.70% when the percentages of RCA in the mix was increased from 15 to 60%. The increased amount of RCA affected the strength development of the concrete due to the high void ratio and high water absorption capacity of the old mortars surrounding the RCA. This, in turn, affected the strength development of the concrete by reducing the bond between cement paste and aggregate, as well as the formation of different interfacial transition zones. This finding also confirms the findings reported in previous research [25,26], which concluded that the presence of adhered mortar on the surface of an overwhelmed concrete mixture usually degrades the quality of the recycled mixture, and therefore the fresh and hardened residences of concrete crafted from it compared to natural aggregates. Similar results were reported in [27] and [28], showing that compressive strength decreases with increasing recycled aggregate percentage and porosity.
As shown in Figure 7, the porosity of the concrete increases with increasing ratio of RCA. The cause of this extra porosity is the lack of fine aggregate (sand) and the uniform-sized coarse aggregate in the design of the mix. This, in turn, affects the Workability of the fresh concrete due to the presence of old mortar pores, which absorb a high amount of water during mixing. Therefore, the high-water absorption of RCA results in a decrease in the Workability of fresh concrete and the bonding strength of hardened concrete due to the presence of old mortar on its surface.
This finding was independently confirmed in [29,30], where recycled aggregates were reported to have a higher porosity than natural aggregates, causing a decrease in the mechanical properties and durability of the concrete.
The maximum permeability value of 2.86 cm/s was measured for 60% replacement of RCA by weight of natural coarse aggregate to produce porous concrete. Minimum permeability requirements of 0.2 cm/s to 1.20 cm/s are reported in the standard [31]. The rate of permeability measured during the tests ranges from 1.84 to 2.86 cm/s, demonstrating that good permeability and infiltration capacity have been achieved.
Research conducted on the effect of sand on pervious concrete by [32] argued that the porosity and permeability of pervious concrete decrease with the increase in sand content, but the mechanical properties (strength) of the concrete increase.
5. Conclusions
This research presented experimental studies on the effects of recycled concrete aggregate on the properties of porous concrete. Based on the findings of the study, the following conclusions were drawn:
Increasing the percentage of recycled concrete aggregate decreases the degree of Workability of the porous concrete from medium to low.
The average compressive strength of the porous concrete decreased by between 16.43 and 54.70% for every 15% increase in RCA This is due to the presence of adhered mortar on the RCA, which absorbs the designated mixing water and reduces the amount of cement paste, reducing the bond strength between the cement paste and the coarse aggregate. The cube compressive strengths of 21.42 MPa and 17.37 MPa for 15 and 30% RCA replacement were higher than the typical value (17 MPa) used in non-structural construction applications.
The porosity of the concrete increases slightly with every 15% increase in RCA by an amount in the range of 8 to 16% due to the increased coarseness of aggregate in the mix and the lack of fine aggregates in the mix. This indicates that there is a direct relationship between RCA content and the void ratio of the produced porous concrete.
The permeability of porous concrete increases with increasing RCA content by between 17.12 and 35.66% due to the increased void ratio. The value ranges from 1.84 to 2.86 cm/s, which is high enough to be used as a drainage system. This shows that as the percentage of RCA increases in the mixes, the permeability of the concrete increases.
Increasing the percentage of recycled concrete aggregate increases porosity and permeability and decreases the compressive strength of the porous concrete.
Overall, recycled concrete aggregate has a significant effect on the properties of porous concrete. With increasing percentage of RCA, the higher the porosity, the faster the water permeability rate, and the lower the strength of the final concrete.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.M. and A.M.L.; methodology, M.M.M. and A.M.L.; formal analysis, M.M.M. and A.M.L.; investigation, M.M.M., A.M.L., T.B. and G.U.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.M., A.M.L., T.B. and G.U.; writing—review and editing, A.M.L., T.B. and G.U.; supervision, A.M.L., T.B. and G.U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Warati, G.K.; Darwish, M.M.; Feyessa, F.F.; Ghebrab, T. Suitability of Scoria as Fine Aggregate and Its Effect on the properties of concrete. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, S.; Luhar, I. Rubberized Geopolymer Concrete: Application of Taguchi Method for Various Factors. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2020, 8, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntakal, S.N.; Selvan, S. Application of Pervious Concrete for Pavements: A Review. Rasayan J. Chem. 2017, 10, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadoon, A.S.; Abbas, A.M.; Almayah, A.A. Revision Study of Green Concrete. Basrah J. Eng. Sci. 2019, 19, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Chauhan, A.S.; Jain, A.; Jangid, J.B. Utilization of Waste Material to Make Green Concrete. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2020, 7, 2666–2669. [Google Scholar]
- Admute, A.; Nagarkar, V.; Padalkar, S.; Bhamre, S.; Tupe, A. Experimental Study on Green Concrete. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 4, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Tongo, S.; Aa, O.; Ba, A. Factors Influencing Waste Generation in Buildings Project in South-West, Nigeria. Int. J. Waste Resour. 2020, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etefa, G.; Mosisa, A. Waste Rubber Tires: A Partial Replacement for Coarse Aggregate in Concrete Floor Tile Production. Am. J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 8, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, S.K.; Guntakal, S.K.; Selvan, D.S.S. Experimental Study on behavior of Pervious Concrete in Strength and Permeability by Changing Different Parameters. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2018, 13, 4550–4554. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Thani, S.K.; Park, S. The Case for Sustainable Concrete Waste Management in Qatar. Sustain. Environ. 2019, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Tuan, T. Experimental Study on Mechanical and Hydraulic Properties of Porous Geopolymer Concrete. GEOMATE J. 2020, 19, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Aguayo, F.; Gaedicke, C.; Nerby, C.; Cavazos, M.; Nerby, C. Developing High Strength Pervious Concrete Mixtures with Local Materials. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2020, 9, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaz, A.; Paul, A.; Scholar, P.G. A Review on Influence of Recycled Aggregates in Pervious Concrete. Int. J. Creat. Res. Thoughts 2020, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hase, B.A.; Bhandwalkar, V.; Dere, T.; Patekar, V.; Magar, S. Making Porous Concrete for Rainwater Harvesting and Urban Road. Int. Res. J. Mod. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2020, 2, 411–413. [Google Scholar]
- Bhutta, M.A.R.; Hasanah, N.; Farhayu, N.; Hussin, M.W.; Tahir, M.b.M.; Mirza, J. Properties of porous concrete from waste crushed concrete (recycled aggregate). Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, A. Construction Materials Laboratory Manual; Addis Ababa University: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shetty, M.S. Fresh Concrete. In Concrete Technology Theory and Practice; S. Chand & Co., Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2005; pp. 218–297. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C 39; Standard Test Method for Cylindrical concrete specimens. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1993; Volume 4, pp. 17–21.
- Herki, B.M.A. Lightweight Concrete Using Local Natural Lightweight Aggregate. J. Crit. Rev. 2020, 7, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1754; Standard Test Method for Density and Void Content of Hardened Pervious Concrete. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 1–3.
- ASTM D2434-68; Standard Test Method for Permeability of Granular Soils (Constant head). ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1994; Volume 4, pp. 192–196.
- Zhu, H.; Wen, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, L. Study on the Permeability of Recycled Aggregate Pervious Concrete with Fibers. Materials 2020, 13, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACI522R; Report on Pervious Concrete. ACI Committee 522: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2010.
- Nanera, P.V.; Solanki, J.V. Cost Optimization Through Construction Waste Management. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2020, 7, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Malesev, M.; Radonjanin, V.; Broceta, G. Properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Orig. Sci. Pap. 2014, 2, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, R.-U.; Bhatti, S.S.; Shahin, M.; Hossain, M.; Al Slibi, H.A. Lightweight aggregate concrete produced with crushed stone sand as fine aggregate. Cogent Eng. 2020, 7, 1792219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haripriya, S.; Rajesh, B.; Sudarshan, D.S.; Khan, M.I.; Bhaskar, B. Strength Characteristics of Recycled Aggregate Concrete by Ann. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2020, 9, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Guan, Z.; Guo, L.; Shen, W.; Xue, Z.; Chen, P.; Li, M. Effects of Recycled Aggregate Content on Pervious Concrete Performance. J. Renew. Mater. 2020, 8, 1711–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, N.V.; Dana, S.S.; Pallavi, K.Y. Performance of Recycled Aggregate in Pervious Concrete. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 9, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Al-jabri, H.; Purnell, P. Assessing the role and use of recycled aggregates (R.A.s) in the sustainable management of construction and demolition (C&D) waste via a mini-review and a case study. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 460–471. [Google Scholar]
- García-González, J.; Rodríguez-Robles, D.; Juan-Valdés, A.; Pozo, J.M.M.-D.; Guerra-Romero, M.I. Porosity and pore size distribution in recycled concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramod, S.S.; Pradeep, G.K.; Asundi, V.; Ballari, V.; Patil, S.C. Experimental Investigation on Effect of Sand Content in Pervious Concrete. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 6, 6027–6030. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).