Abstract
The study examines the effects of modifying PG 64-22 asphalt binder with Crumb Rubber Modifier (CRM) and processed oil on its properties. The binder was tested at different temperatures, and different amounts of CRM and processed oil were added to the binder. The modified binders were also aged using different procedures. The study found that adding processed oil to CRM-modified binders reduces viscosity and improves workability, while CRM improves the rutting resistance. However, the addition of processed oil reduces the binder’s rutting performance. The study also found that CRM and processed oil improve the low temperature cracking resistance. The study’s results indicate that co-modifying CRM binders with processed oil resulted in a significant reduction in viscosity values, resulting in improved workability. The results also showed that increasing the processed oil concentration from 6% to 12% caused a viscosity reduction of 27%, 34%, 33%, and 31% for modified binders containing 0, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM, respectively. Even though the addition of processed oil results in a reduction in the rutting performance of asphalt binder, the addition of CRM significantly improved the rutting resistance of asphalt binders. The CRM binder containing processed oil decreased the G*sin δ values, and the content of 6% processed oil containing 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM decreased by 28%, 17%, and 11%, respectively, while the 12% processed oil-modified asphalt binder showed a reduction in G*sin δ by 5%, 13%, and 22%, respectively. The BBR results for modified asphalt binders showed that the incorporation of CRM and processed oil improved the low temperature cracking resistance significantly. The stiffness values with 6% processed oil containing 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM were observed to be 118, 97, and 80 MPa, respectively, while at the same temperature for the same CRM contents with 12% processed oil, the stiffness values were found to be 89, 72, and 56 MPa, respectively.
1. Introduction
Asphalt is a widely used pavement material that is applied on roads due to its viscoelasticity, smoothness, and susceptibility of adhesion while mixing with aggregate. Due to the complexity of asphalt chemical composition, aging has affects in the way of hardening, and makes it brittle. The aging leads asphalt to fatigue, defectiveness, and weakening against temperature shrinkage stress, hydrodynamic stress, and any other harsh situations [1]. On the other hand, the quality of asphalt binders decreases due to the development of refineries and the extraction of most petroleum products. In addition, due to the increment of traffic volumes and dynamic loads, consequently, defects such as cracks due to fatigue, rutting, spalling, and even thermal cracking at low temperatures, are caused [2].
Asphalt binders show linear and nonlinear behaviors of viscoelasticity due to temperature and load changes [3]. A higher viscosity of asphalt binders shows a better resistivity against mentioned defects such as rutting. On the other hand, stiffness properties will have an impact due to the asphalt molecular changes at low temperatures, and the glass transition phenomenon. In aged asphalt binders, the conversion of saturates to asphaltene causes an increment of viscosity in asphalt binders, which makes it susceptible to cracking at low temperatures and different dynamic loads [4].
To overcome the mentioned defects, asphalt modification has been studied for decades to develop and to improve the resistivity of asphalt binders against different loads [5]. A variety of modifiers have been studied in past years, which have increased the resistance of asphalt binder via the improvement of viscosity. Due to the development of industries, populations, and traffic growth, a huge number of disposed tires are considered to be an environmental concern due to the over volume of landfill occupation and safety risks [6]. To dilute the impact of scrap tires on the environment, crumbed rubber modifier (CRM) has been applied since 1930 to prepare rubberized asphalt mixture [7]. The addition of CRM improves the flexibility of asphalt, resulting in a decreased susceptibility to cracking and rutting under heavy loads and extreme temperatures. This enhancement in flexibility also enhances the overall durability of the asphalt, leading to a longer lifespan of the road surface [8]. The integration of CRM into asphalt binder can elevate the quality of asphalt by augmenting its flexibility, durability, and resistance to rutting, cracking, and deformation under heavy loads, as well as improving adhesion [9]. Depending on the project’s specific needs, the granules of CRM are usually sorted to a particular size range [10]. The incorporation of CRM granular as an asphalt modifier is widely acknowledged as an effective method in the industry [11], and the use of it has been demonstrated to have the properties of asphalt and the performance of the road surface is improved [12].
Applying modifiers increases the viscosity, which improves the resistivity of asphalt binders against rutting and allows it to last longer under dynamic loads, while excessive viscosity causes an increment of stiffness at lower temperatures [13]. To reduce stiffness increment at lower temperatures, considering a co-modifier can play an important role in improving resistivity against thermal cracking [14]. To rejuvenate aged asphalt binder, oil compounds are suitable for altering the characteristics of the binder, which decreases based on high solubility and pervasion rate [15]. Processed oil is a subproduct of refineries, which is vulnerable for decreasing viscosity and stiffness consequently at low temperatures [16]. There are insufficient studies to examine the effects of processed oil as a co-modifier with other main modifiers at different ranges of temperatures. On the other hand, recent studies have shown that oil-based compounds can enhance the adhesion between the aggregate and the asphalt, resulting in a more robust road surface with improved resistance to wear and tear [17,18]; however, the effect of processed oil on shear stress, adhesion, and the glass transition of asphalt binder is considerable [19].
This study evaluates the properties of asphalt binders modified using CRM in conjugating processed oil as a co-modifier. The effects on viscosity and stiffness were investigated to find out how the incorporation of different concentrations of CRM and processed oil affect the resistivity of asphalt binders against different defects. Rheological and cracking tests were conducted after short-term and long-term aging through rolling thin film oven (RTFO) and pressure aging vessel (PAV) to compare the characteristics of asphalt binders corresponding to different contents of CRM and processed oil. The viscosities of modified asphalt binders were measured at high temperature via rotational viscometer (RV) along a temperature range of 135 °C to 180 °C with an interval of 15 °C, and the results were reported and compared among the CRM and processed oil contents.
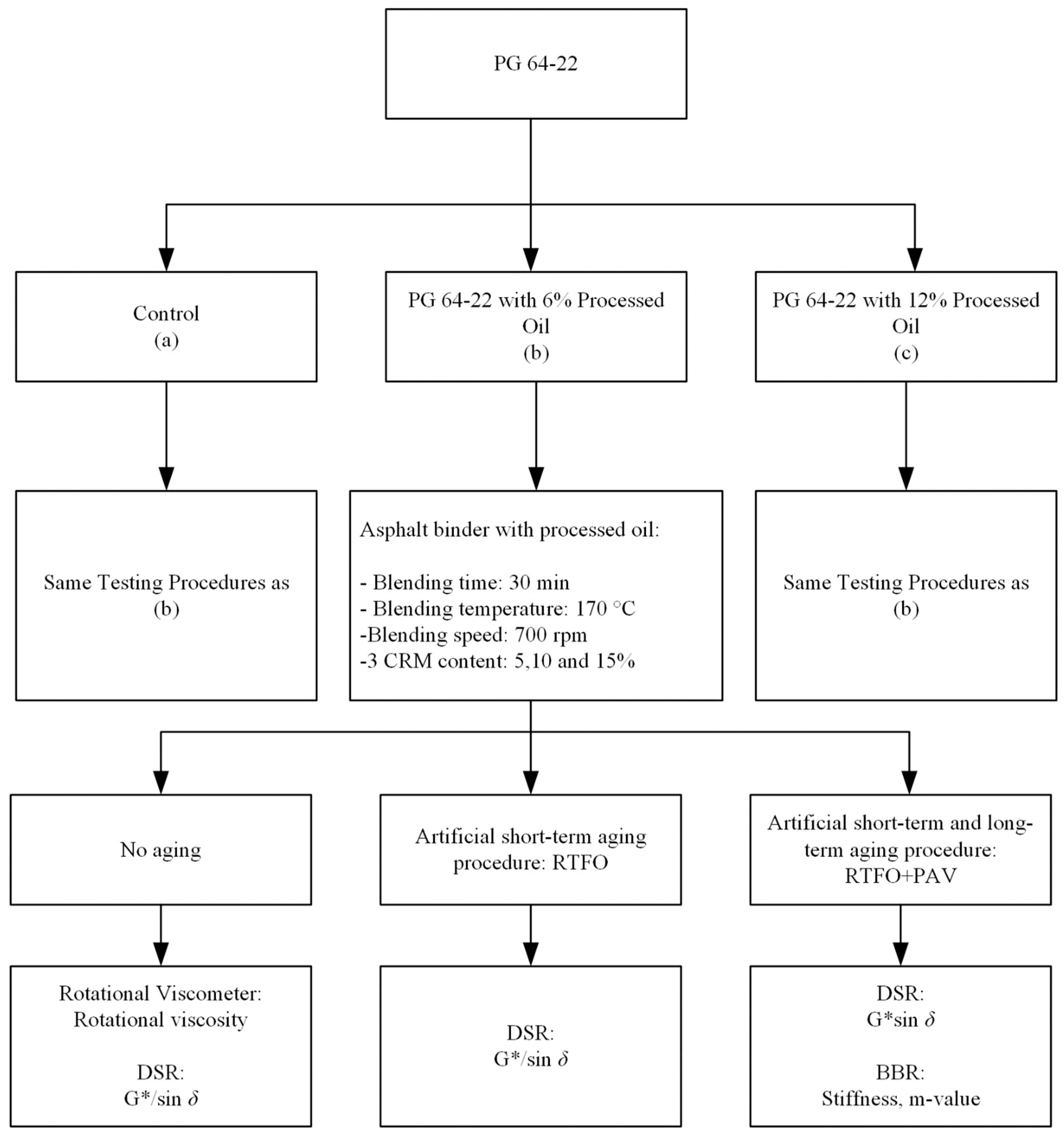
The rutting resistance test was conducted at original state and short-term aged after RTFO through dynamic shear rheometer (DSR), and the results were compared among the different contents of modifier and co-modifier. The fatigue cracking and thermal cracking of the modified asphalt binders were measured after a long-term aging process. The fatigue cracking properties were examined at 25 °C via DSR, and the thermal cracking properties were measured at two temperatures of −12 °C and −24 °C using a bending beam rheometer (BBR). Figure 1 illustrates the experimental design of this study.
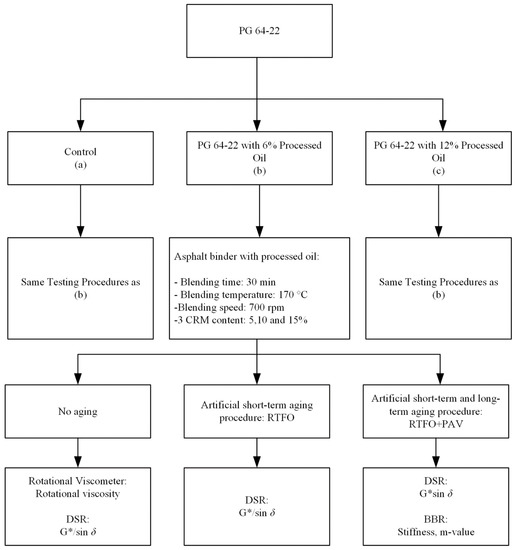
Figure 1.
Flow chart of experimental design procedures.
2. Experimental Design
2.1. Materials
Asphalt binder with a performance grade of 64-22 was chosen as a base binder to be modified using CRM and processed oil. Table 1 presents the properties of the base binder. Table 2 shows the granular sieve analysis of CRM modifier. The properties of co-modifier processed oil are presented in Table 3. Processed oil is a subproduct of the petroleum refinery, with a blackish appearance, and it is mostly used as a mechanical lubricant in different industries. Due to viscosity increment based on the addition of CRM, processed oil is meant to decrease the viscosity value and the stiffness of asphalt binder at low temperatures.

Table 1.
PG 64-22 asphalt binder properties [4].

Table 2.
Gradation of Normal CRM.

Table 3.
Processed oil Properties [4].
2.2. Modification of Asphalt Binders Using CRM-Processed Oil
The asphalt binder samples were prepared through the direct addition of CRM and processed oil in a wet process to the base binders at a mixing temperature of 170 °C with 5 °C tolerance. After reaching the target temperature at 700 revolutions per minute, the processed oil was added and mixed for 10 min. The temperature of the mixing process was monitored manually, so as to not to pass boiling point and lose the binders’ original characteristics, nor to mix at a lower temperature where the mixing process could be destroyed and the materials could be coagulated. The processed oil was added in two contents of 6% and 12% of the base binder sample weight. Due to the high permeation of processed oil at high temperatures, after 10 min, CRM was added to the mixing processed oil asphalt binder at three contents of 5%, 10%, and 15% of the sample weight. To maintain the consistency of the experiment, modifiers and co-modifiers were collected from the same batch. A mixing time span of 30 min was considered to have samples prepared after CRM addition.
The prepared samples were aged artificially in two states of short-term and long-term. The short-term aging process was conducted for 85 min at 163 °C in a rolling thin film oven (RTFO), followed by 20 h of thermal treatment at 100 °C and a pressure of 2.1 MPa in a pressure aging vessel (PAV). After the artificial aging treatment, mentioned tests in the experimental design flowchart were performed to study and to compare the properties of CRM-processed oil-modified asphalt binders.
2.2.1. Basic Characteristics Tests
The rotational viscosity test was conducted along a temperature range of 135 °C to 180 °C at a 15 °C interval for two samples of each composition of modified asphalt binders. To find out the workability of asphalt mixture as one of the main characteristics, 20 rpm was considered as a cylindrical spindle number 27 velocity. A test time span of 20 min was chosen for every individual sample, to have steadily collected data.
The rheological properties of asphalt binders were carried out by measuring the complex shear modulus (G*) and sine of the phase angle (δ) at 82 °C for every sample and calculating G*/sin δ accordingly. Fatigue cracking was evaluated by measuring G* and sin δ at 25 °C, and calculating G*sin δ. Three samples per content of processed oil and CRM were tested to have an average of measurements.
An investigation and comparison between the m-value and stiffness was performed at −12 °C and −24 °C using BBR equipment manufactured by Canon, Huntington, NY, USA, according to the AASHTO T 313. Two samples were poured in molds with dimensions of (125 × 6.35 × 12.7 mm3) per each individual modified asphalt binder with CRM and processed oil according to specifications, and kept in a methanol bath to adjust their temperature, to measure the creep stiffness and m-value of each sample with a load mass of 100 g over 60 s.
2.2.2. Statistical Analysis Method
Statistical analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted using the statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS) by applying Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) comparison and considering α = 0.05. Samples were distributed according to processed oil content, categorized as 6% and 12%, and a CRM content of 5%, 10%, and 15% for each processed oil category. ANOVA was applied to look over significant changes among the means of samples. In the current study, the significance level was 95 (α = 0.05); thereby, each result has a 95% chance of being true. After the determination of uneven means of samples, LSD was calculated. To make a comparison between the two populations, LSD was obtained as the difference between two samples. The comparison was performed between all pairs of samples after the mentioned calculations of LSD. Based on the provided definitions, if the discrepancy between the means of two samples is greater than or equal to the least significant difference (LSD), then it can be inferred that the means of the populations are statistically distinct.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rotational Viscosity
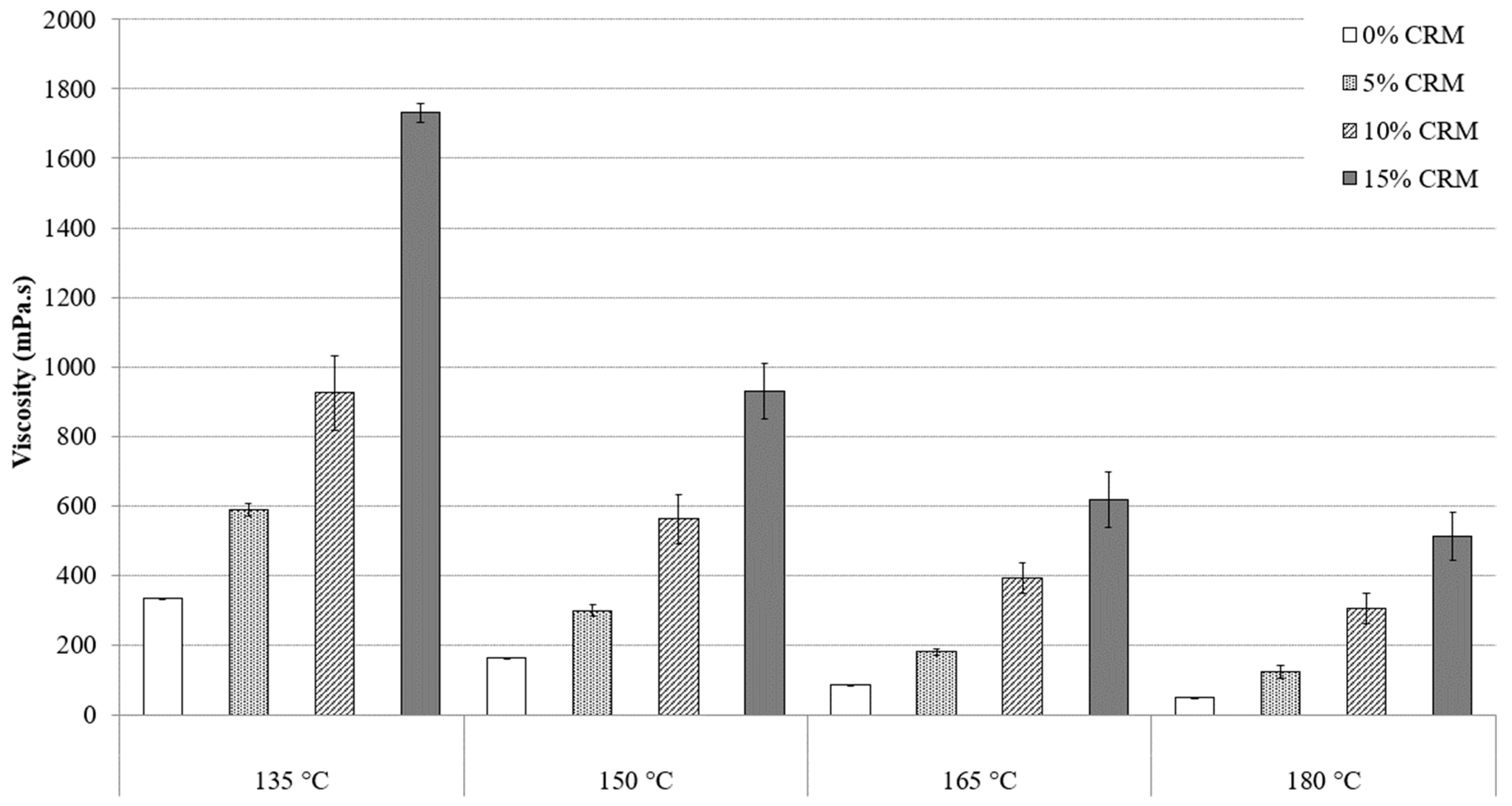
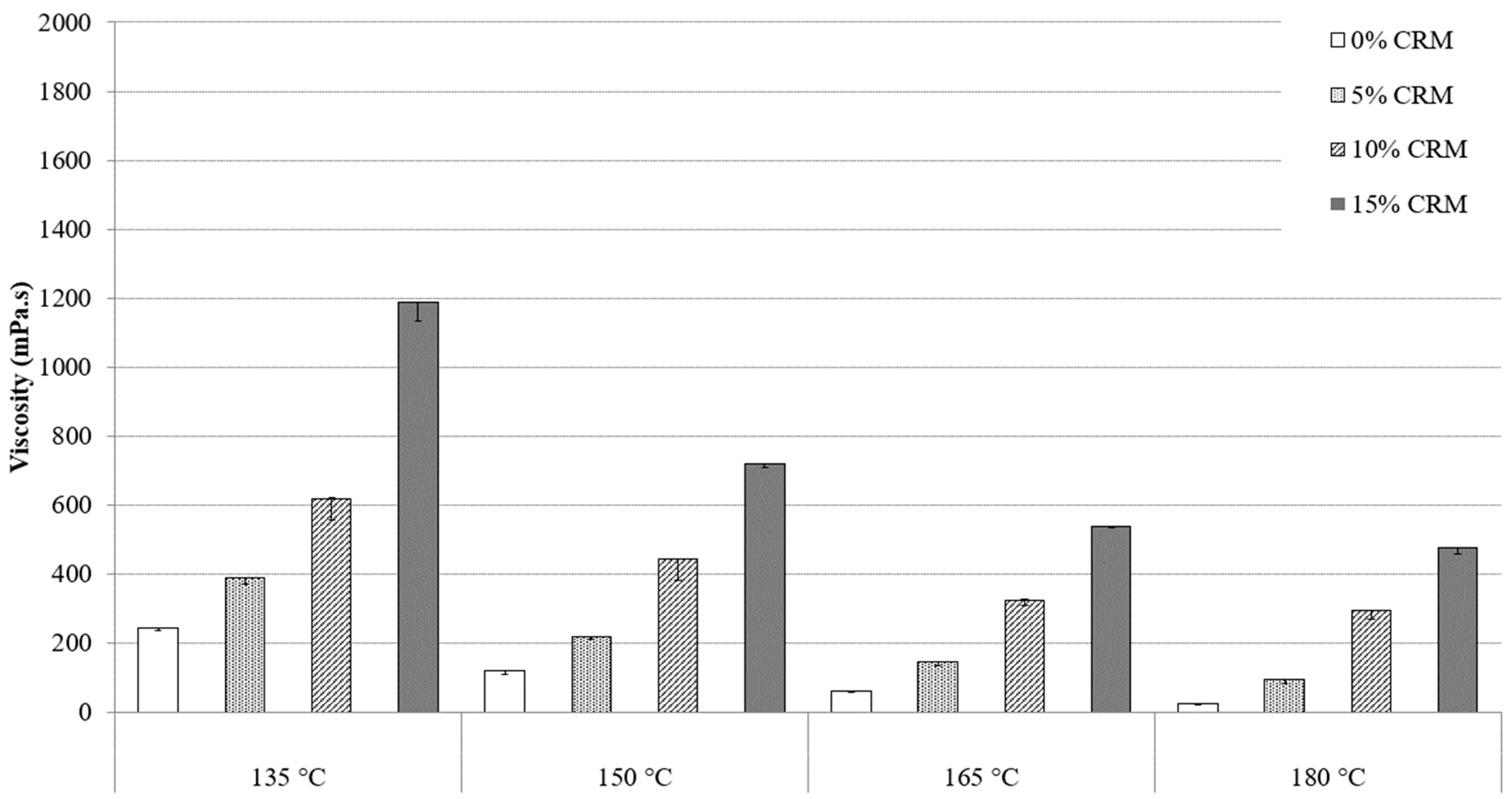
To determine the working conditions, including the preparation temperature and the handling of asphalt mixture on the construction site, it is important to study and to compare the viscosities of asphalt binders at different temperatures. Knowing the viscosity of the binders are vital since pumping through an asphalt plant, the ability of the coating aggregates in a hot mixed asphalt mixture, their susceptibility to being compacted to form a brand-new pavement, are all depended on viscosity values [20]. Figure 2 and Figure 3 present the standard RV test results of PG64-22 modified asphalt binder by 6% and 12% processed oil, containing 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM at 135 °C, 150 °C, 165 °C, and 180 °C. Figure 2 shows the viscosity values of asphalt-modified binder by 6% processed oil in additions of 5%, 10%, and 15% of CRM at the mentioned temperature range. At 135 °C, the viscosity values were observed as 335, 587, 925, and 1730 mPa·s for 0, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM, respectively, at the same temperature. The viscosity measurements of binders modified with 12% processed oil and added with 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM are depicted in Figure 3, with recorded values of 244, 387, 618, and 1187 mPa·s, correspondingly. The results trend showed that increasing the processed oil concentration from 6% to 12%, caused a reduction of 27, 34, 33, and 31% for binders containing 0, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM, respectively, at the same temperature. By increasing the temperature to 150 °C, a reduction on viscosity was observed for all contents of CRM, due to the increment of processed oil from 6% to 12%. Reductions in viscosity values of 26%, 27%, 21%, and 22% were observed for modified asphalt binder with 12% processed oil containing 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM, compared to modified asphalt binder with 6% processed oil. The same reduction patterns of viscosity were observed at 165 °C, subsequently, as well as viscosity values at 180 °C. At 180 °C, the viscosity values of modified asphalt binder with 12% containing 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM were reduced by 50%, 25%, 4%, and 7% compared to modified asphalt binder with the same CRM contents and 6% processed oil.
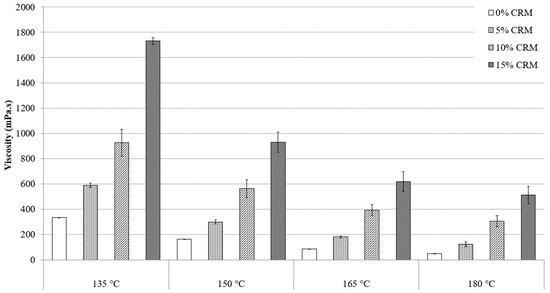
Figure 2.
PG 64-22 viscosity binder with 6% processed oil as a function of CRM content.
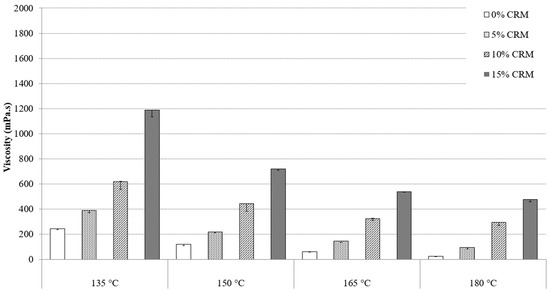
Figure 3.
PG 64-22 viscosity binder with 12% processed oil as a function of CRM content.
The results are evidence of the high penetration of processed oil and its power to restructure the molecular chain of asphaltene, which improves the workability instead. Due to the comparison of results, an excessive concentration of processed oil showed higher effectiveness in viscosity reduction. The results showed how processed oil can improve the workability and handling of modified asphalt binders, while the viscosity improved, based on the addition of CRM. The viscosity of an asphalt binder is mainly specified according to the molecular structure and the intermolecular interactions of the asphaltene molecules network, which represents the rheological properties of the asphalt binder. The presence of processed oil besides the CRM-modified asphalt binder leads to its penetration into the asphaltene network, causing a greater flexibility and a lower viscosity as a result. Both Figure 2 and Figure 3 illustrate the reduction in viscosity to satisfy Superpave Specifications [20], meaning that all modified asphalt binders had viscosities that were lower than 3000 mPa·s. Due to the properties, it seems that the application of processed oil can be effective with most modifiers used, such as SBR, SBS, SIS, CRM, PE, LDPE, etc.
The changes in viscosity values were statistically compared as a result of the processed oil content and the different contents of CRM at a certain temperature range. The significance of changes was observed due to the temperature changes, based on changes in processed oil contents and CRM content changes. Table 4 and Table 5 illustrate the significance of the changes.

Table 4.
Statistical analysis results of viscosity for PG 64-22 with 6% processed oil as a function of CRM content (α = 0.05).

Table 5.
Statistical analysis results of viscosity for PG 64-22 with 12% processed oil as a function of CRM content (α = 0.05).
3.2. Rutting Properties
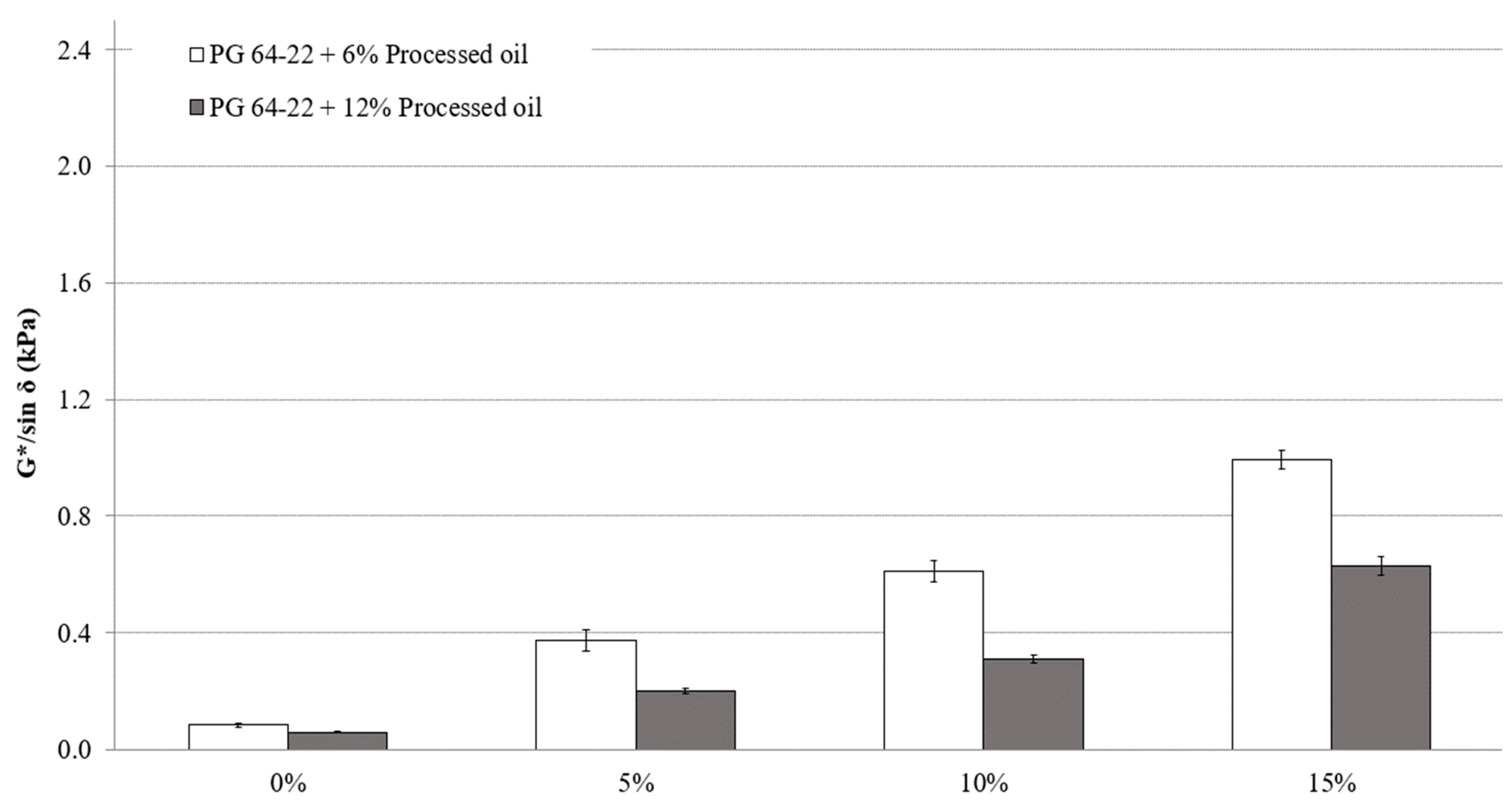
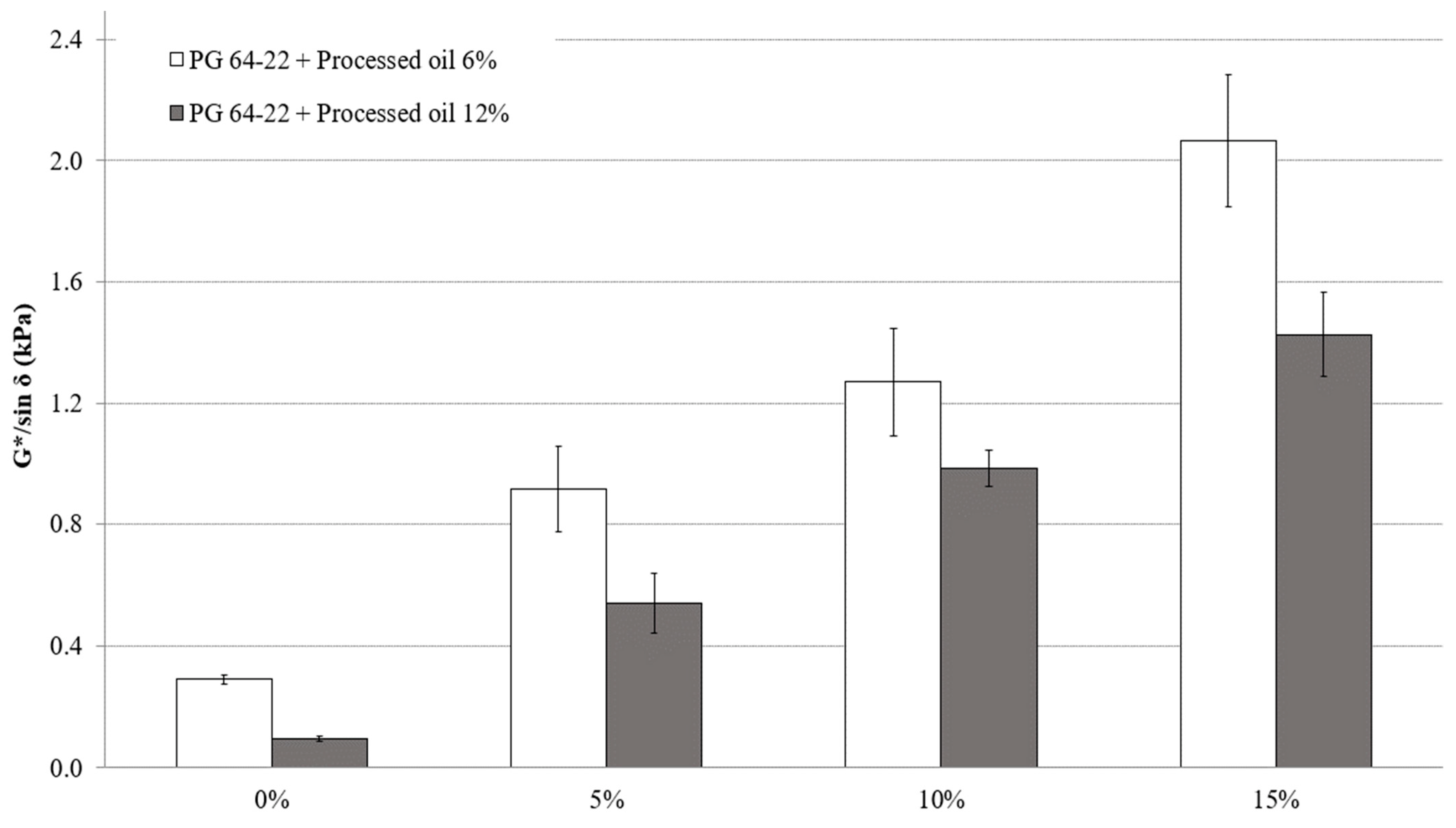
Based on the Superpave Specifications [20], more rutting resistivity and effectiveness can be achieved with higher values of G*/sin δ. G*/sin δ values were measured in two states of original and short-term aging (RTFO) at 82 °C. Figure 4 illustrates the results of the DSR tests for modified asphalt binders in their original state. Although the addition of processed oil results in a significant reduction in the viscosity and rutting resistivity of modified asphalt binders consequently, the addition of CRM improved the resistivity of both modified asphalt binders containing 6% and 12% processed oil, as indicated by the G*/sin δ values. The results are evident, in that the addition of CRM improves rutting resistivity, while the addition of processed oil improves the workability of modified asphalt binders. The addition of CRM to modified asphalt binder with 6% processed oil increased the G*/sin δ values by 388%, 173%, and 171% for the addition rates of 5%, 10%, and 15%, respectively, as demonstrated in Figure 4. On the other hand, the G*/sin δ values of modified asphalt binder with 12% processed oil increased by 323%, 162%, and 211% due to addition of the same contents of 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM, respectively. At the molecular scale, the addition of processed oil to CRM-modified asphalt binder can change the properties that determine its rutting behavior. The rutting properties of asphalt binders are primarily determined by the interactions between the asphalt binder molecules and their surrounding matrix, as well as their ability to maintain their structure and strength under load. Variations in the amount of processed oil added to the binders can modify the molecular structure and interactions of the asphalt binder, leading to alterations in its viscosity, stiffness, and durability. For example, the processed oil can disrupt the intermolecular bonds between the asphalt binder molecules, reducing their strength and leading to a decrease in the binder’s viscosity and resistance to rutting, consequently.
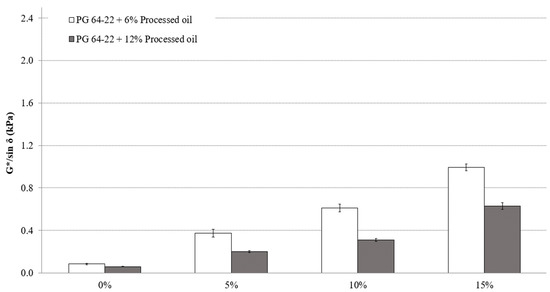
Figure 4.
The relationship between the G*/sin δ of PG 64-22 binder containing processed oil, and the content of CRM at 82 °C.
Statistical analysis and significant changes in G*/sin δ in the original state are presented in Table 6 for both modified asphalt binders containing 6% and 12% processed oil, as well as for the addition rates of 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM. In both asphalt binders modified with 6% and 12% processed oil; significant changes were observed due to the addition of CRM.

Table 6.
Statistical analysis results of G*/sin δ for PG 64-22, with processed oil as a function of CRM content (α = 0.05).
Figure 5 shows the G*/sin δ values for modified asphalt binders containing 6% and 12% processed oil, and varying CRM amounts of 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% at a short-term aging state. When 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM was added to the modified asphalt binder with 6% processed oil, the G*/sin δ values increased by 315%, 138%, and 162%, respectively. In contrast, for the modified asphalt binder with 12% processed oil, the addition of 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM resulted in increases in G*/sin δ values by 569%, 182%, and 144%, respectively. The results observed in Figure 5 evidence that the addition of CRM affects the increase in rutting resistivity, while the existence of processed oil improves the workability and handling of the asphalt binders.
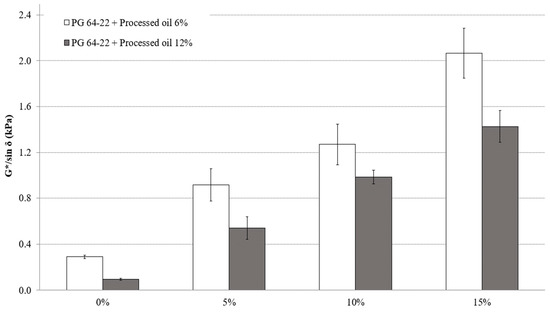
Figure 5.
G*/sin δ value of short-term aged PG 64-22 binder modified with processed oil as a function of CRM content at 82 °C.
Overall, the molecular interactions between the processed oil and the asphalt binder molecules can play a crucial role in determining the binder’s rutting behavior. A detailed understanding of these interactions is important for predicting the optimum conditions of modified asphalt binders in the field, and for designing effective additives to improve their properties.
Table 7 compares the significance of changes in short-term aged asphalt binders resulting from the addition of CRM, in combination with processed oil at different levels. The results indicate that the addition of CRM significantly affects the G*/sin δ values of asphalt binders modified with 6% and 12% processed oil. This is due to the increase in viscosity resulting from a high rate of processed oil penetration that leads to the restructuring of asphaltene molecules and an improvement in workability.

Table 7.
Statistical analysis results of G*/sin δ for RTFO aged PG 64-22, with processed oil as a function of CRM content (α = 0.05).
3.3. Fatigue Cracking
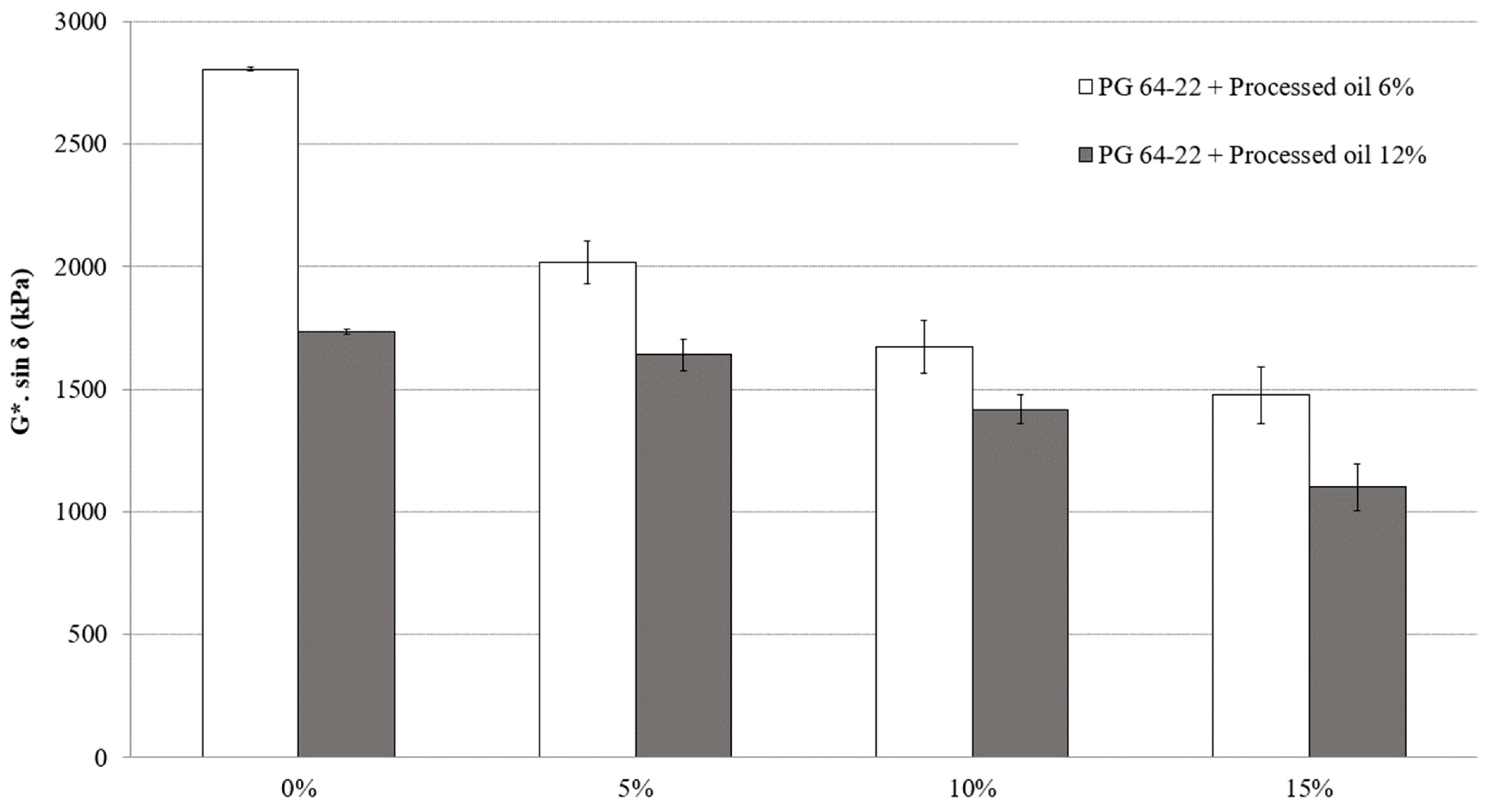
The fatigue cracking characteristics of modified asphalt binders were evaluated at a long-term aging state using the DSR test, which measures G*sin δ. In this context, G represents the stiffness of the binder, while δ represents its viscosity and elasticity. The test was conducted at 25 °C for both modified binders, with 6% and 12% processed oil containing 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM. Figure 6 shows the G*sin δ of all binders. The G*sin δ values of modified asphalt binder with 6% processed oil containing 5%, 10%, and 15% were decreased by 28%, 17%, and 11%, respectively. On the other hand, in a modified asphalt binder with 12% processed oil, the G*sin δ values were reduced by 5%, 13%, and 22% for the CRM contents of 5%, 10%, and 15%, respectively. Fatigue cracking in asphalt pavement occurs because of the repeated loading and unloading of the binder under traffic, which can cause the binder to crack, and eventually leads to pavement failure. Processed oil can weaken the intermolecular bonds between the asphaltene molecules network and result in a reduction in their resistance to cracking, making them more susceptible to fatigue. Improved fatigue cracking resistance was achieved as a result of the restructuring of the asphaltene molecular network and the resulting decrease in G*sin δ, which can be attributed to the high penetration rate of processed oil.
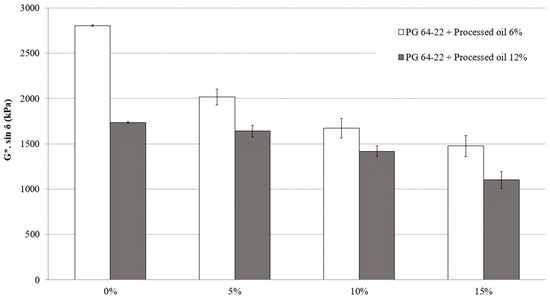
Figure 6.
G*sin δ of RTFO + PAV aged PG 64-22 binder with processed oil as a function of CRM content at 25 °C.
Table 8 presents the significance of changes and the results of statistical comparisons between the two modified asphalt binders with 6% and 12% processed oil, with and without the addition of CRM. The results demonstrate significant changes in all CRM contents, except for the modified asphalt binder with 12% processed oil and 5% CRM, when compared to the base modified binder with 12% processed oil and 0% CRM.

Table 8.
Statistical analysis results (α = 0.05) on the effect of CRM content on G*sin δ for PG 64-22 with processed oil after RTFO + PAV aging.
3.4. Low-Temperature Cracking Characteristics
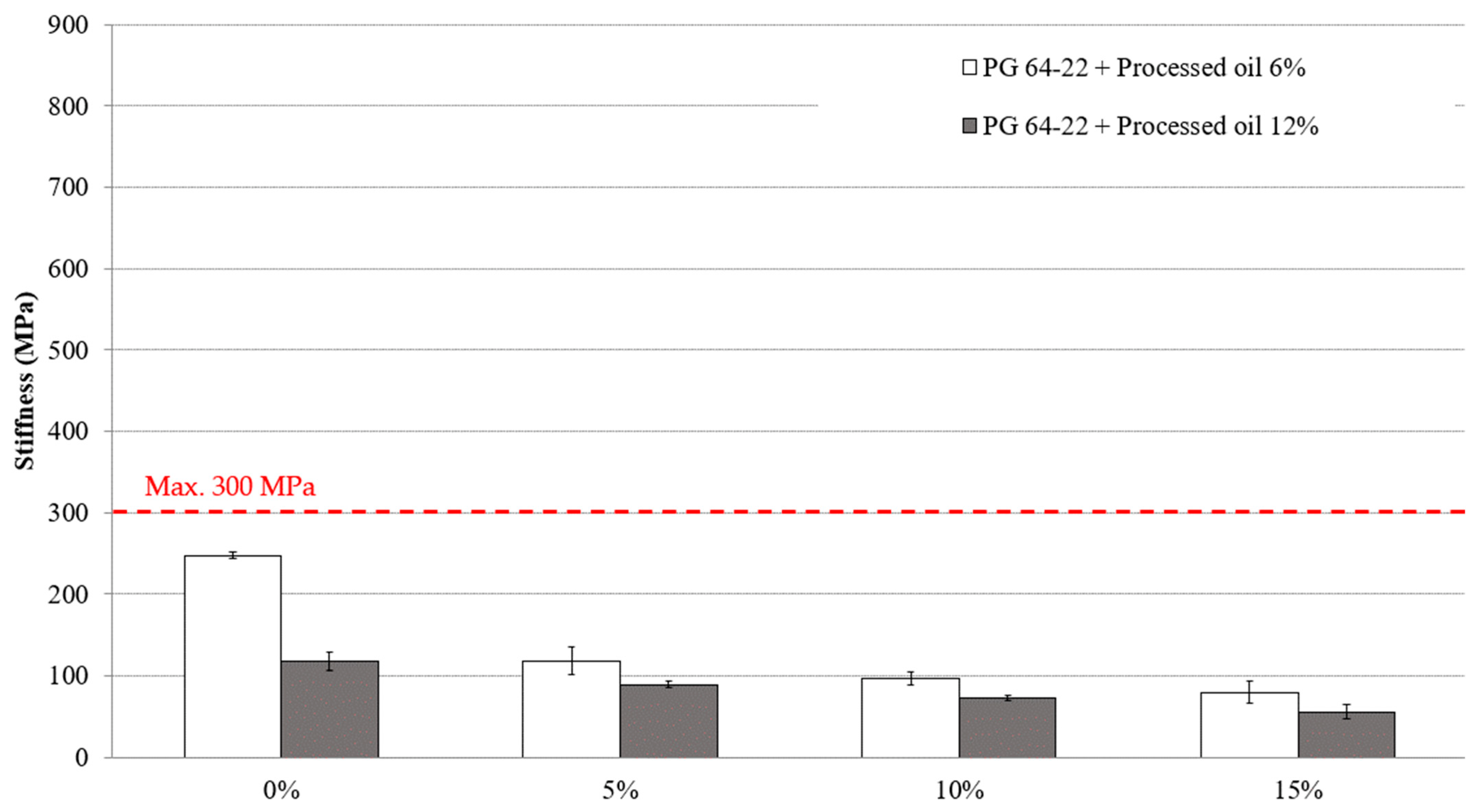
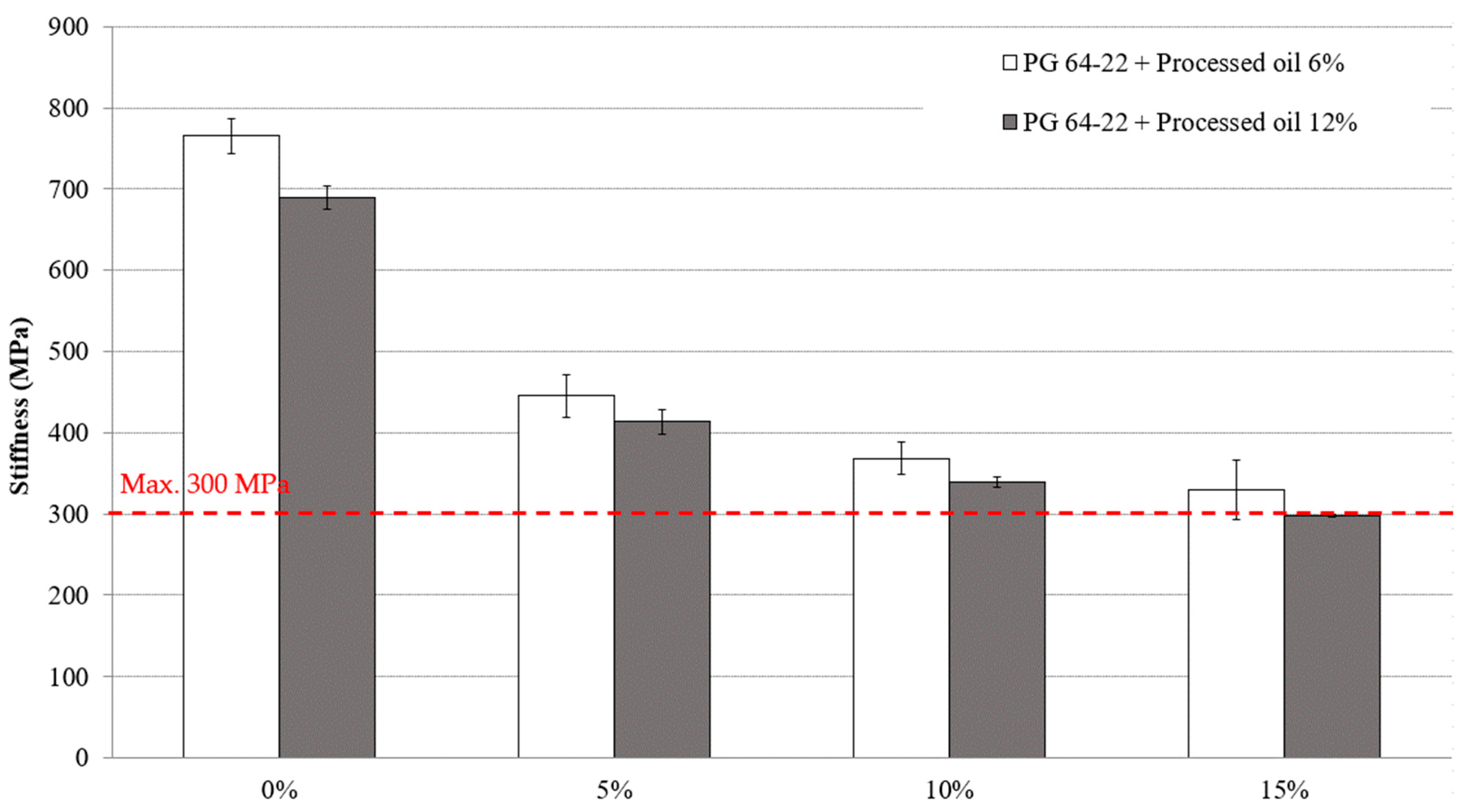
Meeting the Superpave specifications requires the maximum allowable creep stiffness value to be 300 MPa or lower, which is desirable for reducing the tensile stress of the asphalt binder. To evaluate the characteristics of both modified asphalt binders with 6% and 12% processed oil containing 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM, the BBR test was conducted at −12 °C and −24 °C. Figure 7 and Figure 8 illustrate the values of the stiffness of asphalt binders at the mentioned temperatures. At −12 °C, the stiffness values of asphalt binders modified with 6% processed oil and varying CRM amounts of 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% were measured as 247, 118, 97, and 80 MPa, respectively, as shown in Figure 7. In modified asphalt binders containing 12% processed oil, the stiffness values were observed to be 117, 89, 72, and 56 MPa for CRM contents of 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15%, respectively. Comparing the results between the modified asphalt binders with 6% and 12% processed oil and varying the CRM contents shows that the addition of processed oil with CRM reduced the stiffness values. As shown in Figure 8, at −24 °C, the stiffness values of modified asphalt binders with 6% processed oil decreased by 41%, 17%, and 10%, with the addition of 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM, respectively. Similarly, in asphalt binders modified with 12% processed oil, the stiffness values decreased by 40%, 18%, and 12%, with the additions of 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM, respectively. The results show that the modification of asphalt binders using processed oil in conjugating CRM enhances their resistivity against thermal cracking defects. Processed oil can modify the physical properties of the asphalt binder at a molecular scale by altering its viscosity and intermolecular interactions through the restructuring of the asphaltene molecular network during the mixing process. These modifications can have an impact on the stiffness of the binder.
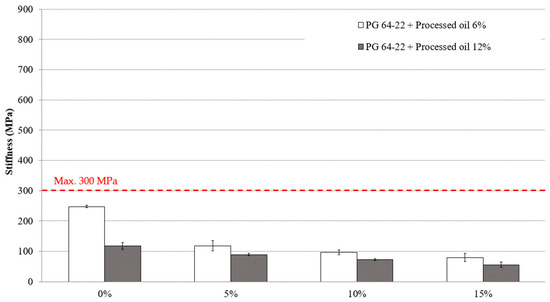
Figure 7.
The effects of various CRM contents on the stiffness of RTFO + PAV aged PG 64-22 binder modified with 6% and 12% processed oil at −12 °C.
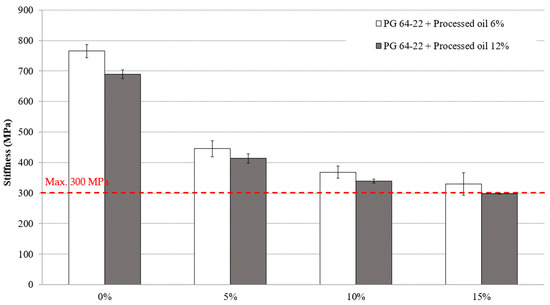
Figure 8.
The effects of various CRM contents on the stiffness of RTFO + PAV aged PG 64-22 binder modified with 6% and 12% processed oil at −24 °C.
Table 9 and Table 10 present the statistical analysis and significance of changes in the stiffness values of modified asphalt binders containing 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM with both 6% and 12% processed oil. The results indicate that most changes are significant with the addition of CRM, except for the modified asphalt binder with 6% processed oil containing 10% and 5% CRM at −12 °C, as well as modified asphalt binders with 12% processed oil containing 10% and 15% CRM, compared to 5% and 10% CRM, respectively. The only non-significant change at −24 °C was observed in 6% modified processed oil with 15% CRM compared to 10% CRM.

Table 9.
Statistical analysis of stiffness for RTFO + PAV aged PG 64-22 binder modified with 6% and 12% processed oil as a function of CRM content at −12 °C (α = 0.05).

Table 10.
Statistical analysis of stiffness for RTFO + PAV aged PG 64-22 binder modified with 6% and 12% processed oil as a function of CRM content at −24 °C (α = 0.05).
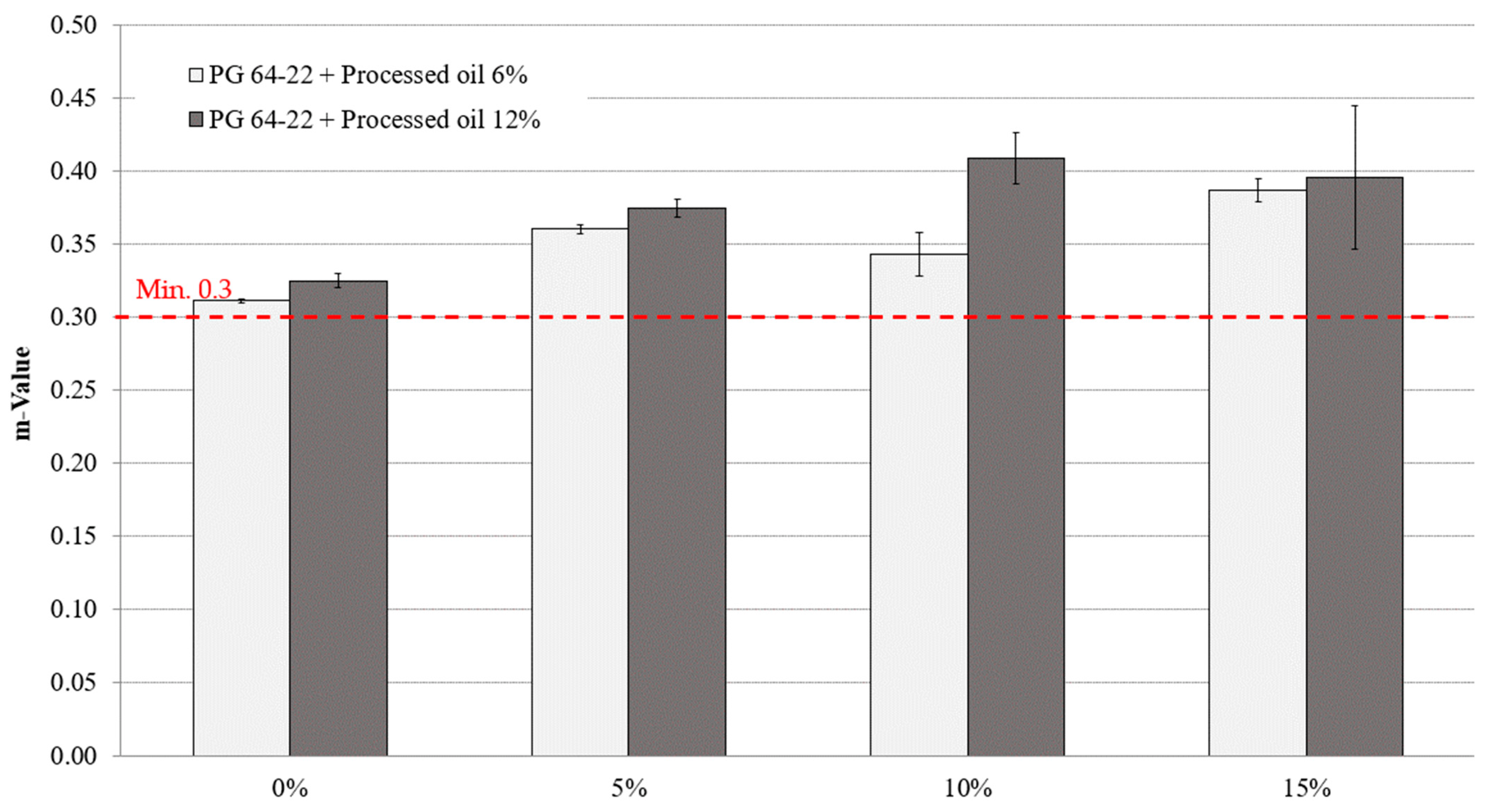
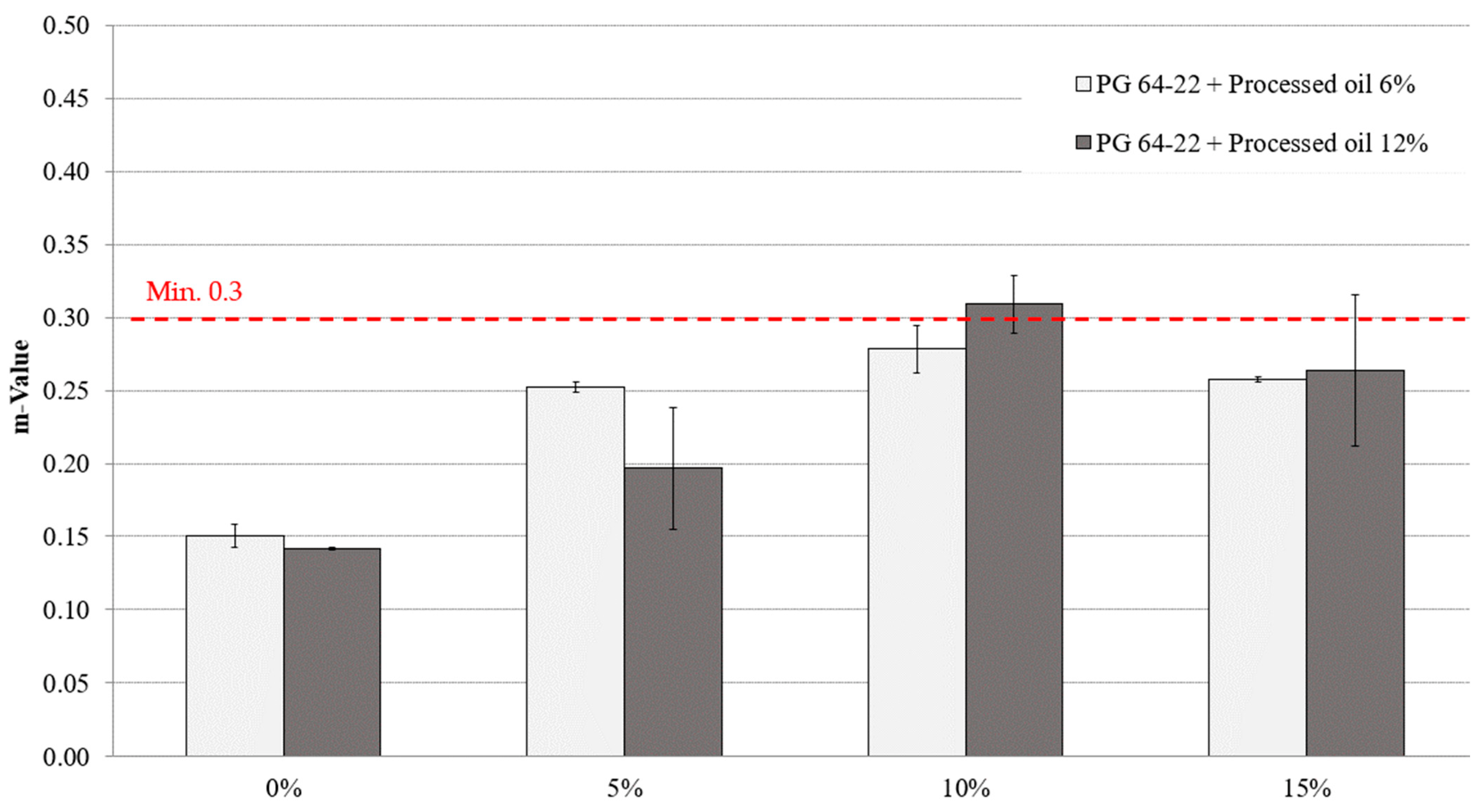
Figure 9 and Figure 10 depict the m-value measurements of modified asphalt binders with both 6% and 12% processed oil and various CRM contents at −12 °C and −24 °C. The addition of CRM resulted in a slight increment of m-values for all modified asphalt binders. At −12 °C, the m-values for modified asphalt binders with 6% processed oil and 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM were 0.311, 0.36, 0.34, and 0.38, respectively, while for modified asphalt binders with 12% processed oil and the same CRM contents, the m-values were 0.324, 0.374, 0.408, and 0.395, respectively. At −24 °C, the m-values of asphalt binders with 6% processed oil and 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% CRM were 0.150, 0.252, 0.278, and 0.257, respectively, while for modified asphalt binders with 12% processed oil and the same CRM contents, the m-values were 0.141, 0.196, 0.309, and 0.263, respectively. It is worth noting that processed oil had a significant impact on viscosity by restructuring the molecular network of asphaltene. Moreover, the increase in CRM content led to an increase in m-values, indicating a reasonable conjugation between the processed oil and the CRM modifiers.
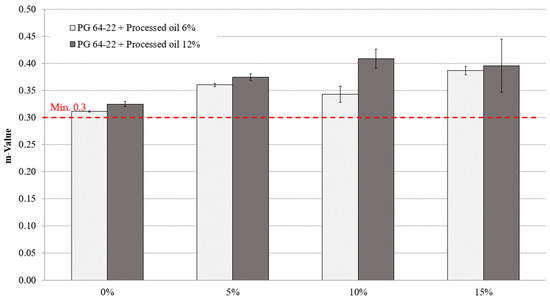
Figure 9.
Effect of CRM content on m-value of processed oil-modified and long-term aged PG 64-22 binder aged at −12 °C.
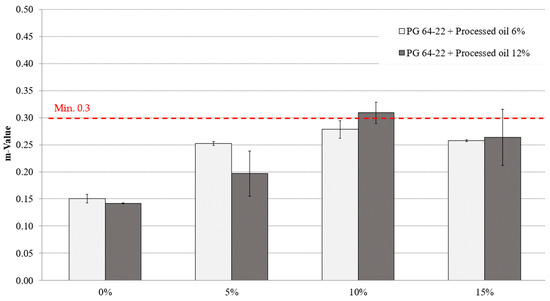
Figure 10.
Effect of CRM content on m-value of processed oil-modified and long-term aged PG 64-22 binder aged at −24 °C.
Table 11 and Table 12 display the statistical analysis of the m-values for modified asphalt binders with varying processed oil and CRM contents. The tables provide a comparison of the significant and non-significant changes observed among the modified asphalt binders.

Table 11.
Statistical analysis results of m-value for RTFO + PAV aged PG 64-22 with processed oil as a function of CRM content −12 °C (α = 0.05).

Table 12.
Statistical analysis results of m-value for RTFO + PAV aged PG 64-22 with processed oil as a function of CRM content −24 °C (α = 0.05).
4. Summary and Conclusions
Physical and rheological tests were performed to assess the properties of modified asphalt binders after the addition of CRM and processed oil, including rotational viscosity, dynamic shear rheometer, and bending beam rheometer tests for characterizing the binders’ characteristics in their original and aged states. The results indicated that adding CRM to asphalt binders increases viscosity, while the addition of processed oil moderates this increment. Modified asphalt binders containing 12% processed oil have a lower viscosity than those with 6% oil, due to the processed oil’s influence on the asphaltene molecules. The processed oil increases the elasticity of the molecules, resulting in reduced viscosity. The more processed oil in the binder, the better its performance at high temperatures and flow properties. Processed oil interacts with asphaltene molecules to produce a stable, low-viscosity system that enhances the overall rheological properties of the modified asphalt binder. The DSR test showed that processed oil improves the rutting resistance of asphalt binders modified with 6% and 12% oil, in contrast to the effect of CRM alone. The results show an improvement in high temperature performance, with a reduced risk of rutting. The reason for this is the restructuring of asphaltene molecules by processed oil, making the binder more elastic and less viscous. This leads to a more stable system and a better overall performance, reducing the risk of rutting. The addition of both processed oil and CRM improved the flexibility of the asphalt binder and reduced the chance of cracking, as revealed by the results of the fatigue test. The cause of this was the processed oil’s restructuring of the asphalt molecules, making the binder more flexible. This improvement in flexibility is crucial for the asphalt binder’s overall performance and longevity. Based on the results obtained from the Bending Beam Rheometer test, the application of processed oil and CRM together made the modified asphalt binders more flexible and less stiff, improving their elasticity based on the obtained m-values, which can be described due to the molecular interactions between the processed oil and the asphaltene molecules. Elasticity is crucial in ensuring that the modified asphalt can handle stresses and deformations from traffic and environmental factors, and the improvement seen in the BBR test is a positive sign for the longevity and performance of the modified asphalt. The observed results showed that the blending of asphalt binders with processed oil and CRM improved their performances and workabilities at both high and low temperatures, and it may reduce the need for high placement temperatures during construction, conserving energy. However, finding the right balance with the amounts of both ingredients used is crucial, as excessive amounts can lead to issues such as excessive rutting or thermal cracking, or a decrement of the softening point of the asphalt. Further exploration using processed oil with other modifiers, such as petroleum resin PE and SBR, is desirable.
Author Contributions
Methodology, S.-J.L.; Investigation, S.-J.L. and M.-S.L.; Data curation, S.V.; Writing—original draft, N.H.; Writing—review & editing, M.M.; Project administration, M.-S.L. and S.-J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from a government funding project (2023 National Highway Pavement Management System).
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sun, X.; Xu, Q.; Fang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, J. Effect Investigation of Ultraviolet Ageing on the Rheological Properties, Micro-Structure, and Chemical Composition of Asphalt Binder Modified by Modifying Polymer. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 7190428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Guo, X.; Hou, F.; Wu, J. Review of intelligent road defects detection technology. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaee, H.A.; Velasquez, R.; Bahia, H.U. Predicting low temperature physical hardening in asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, N.; Yun, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, S.J. Effect of Processed Oil on Asphalt Binder Properties. Materials 2022, 15, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Dong, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C.; Dong, S.; Gu, X. Application of waste oil in asphalt rejuvenation and modification: A comprehensive review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 340, 127784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, Y.; Yu, J.; Dong, N.; Jin, J.; Guo, F. Recycling potential of used crumb rubber for second-round asphalt modification. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Abdelmagid, A.A.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, E.; Chen, Y. Study on the Aging Mechanism and Microstructure Analysis of Rice-Husk-Ash-and Crumb-Rubber-Powder-Modified Asphalt. Polymers 2022, 14, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cui, C.; Temitope, A.A.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, G.; Guo, P. Effect of SBS and crumb rubber on asphalt modification: A review of the properties and practical application. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shi, C.; Yu, Y.; Xu, G.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Qie, L. Mechanical properties evaluation of crumb rubber asphalt mixture for elastic trackbed. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 331, 127048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhu, H.; Kong, L.; Xu, Y.; Ou, L. Stage-aging characteristics and stages division of crumb rubber modified asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 129712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Mazumder, M.; Na, I.H.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, H.H. Evaluation of Effect of Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) on Crumb Rubber Modified (CRM) Asphalt Binder. Materials 2022, 15, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borhan, M.N.; Suja, F.; Ismail, A.; Rahmat RA, O.K. The effects of used cylinder oil on asphalt mixes. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 28, 398–411. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Muhamad-Borhan/publication/237551936_The_Effects_of_Used_Cylinder_Oil_on_Asphalt_Mixes/links/540d7cd70cf2df04e754a887/The-Effects-of-Used-Cylinder-Oil-on-Asphalt-Mixes.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2009).
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Peng, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Liu, H. Preparation and properties of a novel high-viscosity modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 344, 128183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Xia, C.; Yang, Q.; Guo, S.; You, L.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, J. Improvements on high-temperature stability, rheology, and stiffness of asphalt binder modified with waste crayfish shell powder. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadykova, A.Y.; Ilyin, S.O. Bitumen improvement with bio-oil and natural or organ modified montmorillonite: Structure, rheology, and adhesion of composite asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 364, 129919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltwati, A.; Mohamed, A.; Hainin, M.R.; Jusli, E.; Enieb, M. Rejuvenation of aged asphalt binders by waste engine oil and SBS blend: Physical, chemical, and rheological properties of binders and mechanical evaluations of mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Hemmati, N.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, S.J. Laboratory Evaluation of Storage Stability for CRM Asphalt Binders. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.H.; Jakarni, F.M.; Muniandy, R.; Hassim, S. A review on the application of natural rubber as asphalt modifier. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; Volume 1075, p. 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadykova, A.Y.; Ilyin, S.O. Rheological and adhesive properties of nanocomposite bitumen binders based on hydrophilic or hydrophobic silica and modified with bio-oil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asphalt Institute. Individual Asphalt Binder Tests; Asphalt Institute: Lexington, KY, USA, 2003; Available online: https://interstatetesting.com/binder-lab/ (accessed on 19 November 2021).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).