Abstract
Barite, used in mud formulation, is mined in several places to support the industry. However, there is insufficient literature on the downside of mining and associated hazards, especially in the artisanal barite mining sector. This paper contains three parts. The initial section reviews major causes of mining accidents and health hazards in Nigeria. The second section examines existing but weak institutional frameworks and policies for artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) in Nigeria. In the third part, data from questionnaires and heavy metal contamination assessment are compared with health and environmental standards to identify and characterize hazards. It was observed that 54% had health challenges traceable to illicit drugs, and 54% were ignorant about the use of safety kits. The UV-Vis, AAS, and ICP-MS analyses confirmed lead, barium, zinc, copper, and iron in the water samples. Index of geoaccumulation (Igeo) and contamination factor (CF) show that water samples are moderate to highly polluted by Pb2+, Ba2+, and highly contaminated. The chronic daily intake assessment and health quotient analysis revealed that the accumulation of lead and barium is possible and can initiate chronic diseases in humans over a long time. Certain safe mining protocols and controls are recommended.
1. Introduction
Mining is one of the world’s most dangerous occupations [1]. Over the years, many mining-associated accidents have occurred in various parts of the world, often with significant loss of life [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Such mining accidents remind us of how dangerous mining jobs can be and how explicitly hazardous underground mining continues to be [11,12]. Similarly, surface mining blasting-related risks (although not specific to underground mining operations) and their consequences could be worsened and may result in mass widespread accidents [13,14,15].
Mining accidents and fatalities among the Artisanal and Small-scale miners (ASMs) occur in the process of mining metals, minerals, and energy materials (i.e., not construction materials), as shown in Table 1. Thousands of miners die from these mining accidents each year, especially in coal and hard rock mining [16]. Although surface mining is usually less hazardous than underground mining [2,17,18], the participation of artisanal and small-scale miners in barite mining fields has increased the number of mining fatalities across the upper and middle Benue Trough. Artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) in Nigeria employed about 0.5 million as of 2015 [19], and in 2021 over 2 million. These miners’ and mining communities’ contribution to societal development is vital. Both occupational and environmental health and safety issues must be addressed at the mines and workplaces objectively.

Table 1.
Some cases of mining hazards in Nigeria.
Heavy metal contamination due to mining and mineral processing (washing) has become one of the most silent but significant environmental side effects [28,29]. Studies in the literature have reported on acidification and acid mine drainage associated with the mining of coal, gold, and other minerals containing pyrite and galena (FeS2 and PbS) [27,30]. Barite is one mineral or ore that has not been examined to pose such a threat [28]. Barite mineral, although non-carcinogenic, may be associated with lead sulphide (PbS) and encrusted with pyrite or iron pyrite microcrystal [31,32]. Sulphuric acid mine runoff is unavoidable when barite tailings containing sulphide minerals are exposed to water and oxygen. The consequence is acidification of water and can increase the release of other heavy metals such as iron, zinc, copper, lead, cadmium, arsenic, and barium.
Previous reviews on safety and risk analysis have shown the relevance of workplace safety models in the safety-critical assessment of risks, either at mines or in any other activities where dangerous tools are used. Several safe assessment methods have been developed to address the quality and productivity of workers that sustain severe accidents at work and uncovered the adverse effect of heavy metal contaminants and other critical environmental threats to human health [33,34,35,36,37]. Researchers have examined ways to domesticate some of these advanced safe mining methods in Nigeria but with little positive results [36,38]. This is because many local miners believed the “advance” safe mining strategies have no direct correlation and cannot provide solutions to the type of mining hazard peculiar to them [19,39]. Moreover, nothing much seems to have changed regarding miners’ and government attitudes to mineral exploration. Miners appear to have nothing to worry about despite the dozens of unreported cases of mining accidents. The significance of wearing safety kits such as mining boots, hand gloves, eye goggles, and clothes specifically designated for mining only at the site should be communicated again. There is also a claim that the institutional policy guilds’ activities of artisanal and small-scale miners (ASM) caters to chemical contamination due to barite mining. However, the miners’ and mining sites’ managers are unaware of the safety data sheet, which is a minimum requirement for the operation of mines. Therefore, it is helpful to engage these local miners in discussing prevalent mining accidents and fatalities that have profound health implications and develop safe assessment methods, processes, and programs to prevent the reoccurrence of mining hazards.
This paper reviews mining activities by the artisanal and small-scale miners in Nigeria and presents safe mining strategies. It identifies mining accidents that are peculiar to artisanal and small-scale miners (ASMs), revises existing but weak and inadequate mining policy, and assesses potential mining risks to human health due to mining and social lifestyles of the miners. Questionnaires were administered to local miners (part-time and full-time) within the middle Benue Trough of Nigeria to identify hazards. Water from barite ponds and effluents was also analyzed to characterize associated risks and recommend safe mining protocols and controls, especially for the barite mining sector. Two research questions were investigated in the study. These are: (1) Certain mining accidents and their adverse effect on miners are traceable to miners’ refusal to use safe mining kits and (2) Artisanal barite mining contributes to severe heavy metal contamination. Field survey and heavy metal contamination assessment of water in barite ponds and recycled wastewater at barite mine sites validated the research questions.
2. A Review of Status of Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining (ASM) and Safe Mining Practices in Nigeria
2.1. Legal, Regulatory, and Institutional Frameworks of Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining
There are legal and regulatory documents and institutions that govern the activities of artisanal and small-scale miners in Nigeria. Figure 1 and Figure 2 show the existing legal, regulatory, and institutional frameworks for Nigeria’s mining sector. Aside from the frameworks, policy objectives guide the everyday activities within the mineral value-chain. These objectives include but are not limited to comprehensive actions on the acquisition of rights, mine ownership requirement and restrictions, minerals processing and export, transfer mineral rights, land use, environmental, mineral titles, health and safety, and constitutional law. Despite these frameworks, Nigeria’s mining sector is yet to reach its full potential [40,41,42].

Figure 1.
Legal framework for mining in Nigeria (adapted from [40]).
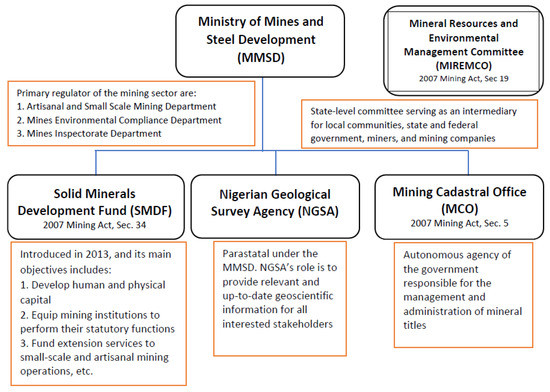
Figure 2.
Institutional framework for mining in Nigeria (Modified from [40]).
Research has shown that enacting an Act and introducing laws or policies to drive Nigeria’s mining sector can strengthen the regulatory frameworks [40,41,43,44]. However, there were no prior works on health, mine safety, and mining hazard prevention procedures until March 2016, when the Nigerian government acknowledged mercury and lead (Pb) health risks. Mining accidents are not limited to chemical hazards. It also includes every form of harm against the miners, mining communities, and resources located within the mining environment. This set of rules is mandatory and must be enforced by every player within the mining and mineral business [41,42,44].
2.2. Mining Hazards in Nigeria
The sources of hazards associated with the sector include chemical, physical, and mechanical [21,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53]. Major mining accidents occur due to the use of crude and sharp tools by artisanal and small-scale miners to extract minerals. Some of past and current mining hazards or accidents in different parts of Nigeria are shown in Table 2 and Figure 3. These hazards are traceable to the illegal mining and mineral extraction practices done by artisanal miners in Nigeria. Stone quarrying and solid minerals exploration dominate artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) activities in Nigeria [45], as shown in Table 2 and Figure 3.

Table 2.
Some mining activities and accidents in communities within the Nigerian States.
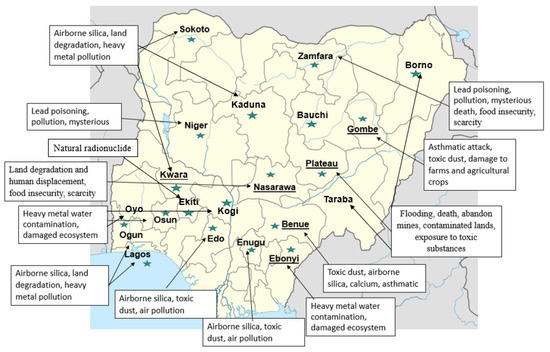
Figure 3.
Mining Hazard Map of Nigeria [24,54,56].
2.3. Safe Mining Methods for Local and Global Mining: Precautions and Control Measures
Within the last 25 years, there have been increased safety regulations, safer machinery development, training, and education initiatives for miners in Nigeria and Africa in general. However, this has not changed the fact that mining is still a dangerous profession [1]. Before discussing potential accidents and risks in mining, it is vital to consider the average miner work shift based on human resource management. Typically, miners work in a 12 h shift at the underground mine while others work throughout the whole week or remain at a mining camp for months before returning home [17]. Miners are expected to be physically, mentally, and psychologically sound and healthy to achieve overall safety in mines. Strict adherence to safety procedures such as the use of respirators, ventilation systems, and ear protectors will go a long way to reduce cases of mining accidents, injuries, and fatalities [2]. Some of the safety practices and challenges include those involving behavioural guidelines, communication, vehicle interactions, explosives, and the role of enforcement agencies [2,17,57,58,59,60,61,62].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Survey of Miners
The state of hazards within the barite mining industry was examined using surveying tools. Thirty-eight (38) unstructured questionnaires were distributed to miners who specialize in barite mining. Twenty-seven (27) out of thirty-five (~35) barite miners in the community completed and returned the questionnaires. The questionnaire was designed strictly as safety information-seeking procedures based on the major objective of the safety training. The questionnaire also serves as a pre-training/pre-workshop tool or quiz used to identify and assess miners’ health concerns, and to develop training manual(s)/choose efficient communication method(s) that address the peculiar needs of the miners under the study.
Approval for the research was obtained from relevant authorities. No medical procedures were observed, as no human body fluids or organs were used for any form of analysis or medical tests. The survey examines why miners refused to use mining boots, gloves, goggles, and clothes contained in the safety mining kits. The entire study attempts to assess and characterize potential health hazards caused by artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) activities. Questions were read to miners who could not read.
3.2. Chemical Analysis and Risk Assessment
Quantitative risk assessment and health hazard analysis were done in accordance with environmental standards and procedures. Water samples were collected from abandoned barite ponds and wastewater from barite washing and stored in polyethylene bottle (PET) at room temperature. Two ml of the water samples were measured into the cuvette and filled to a mark. The dissolved elements in water samples such as Pb2+, Ba2+, Zn2+, Fe2+, and Cu2+ were analyzed colorimetrically using a Shimadzu UV-1900 UV-Vis Spectrophotometer. Tailings effluents was prepared in accordance to standards reported in [63]. The metallic content in the water samples were analyzed using atomic absorption spectrophotometer (AAS), Model: A-Analys 100. The liquid-liquid extraction method (LLEM) was employed in the absorption or digestion of the sample [64]. The elemental composition of the samples was measured using PerkinElmer ICP mass spectrometer, NexIONTM 350X. The digestates of barite tailings or extracts were diluted to 1% (100 times).
The index of geoaccumulation (Igeo), contamination factor (CF), chronic daily intake (CDI), and health risk (HQ & HI) are computed for Pb2+, Ba2+, Zn2+, Fe2+, and Cu2+ using the data from the USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) and DEA (South Africa Department of Environmental Affairs). Igeo, CDI, CF, and HQ, were computed according to procedures reported in the literature. Each parameter was calculated using Equations (1)–(4) [48,56,65,66,67,68,69,70,71]
where is the concentration of metal in water samples, is the metal concentration in water before the introduction of metals due to mining activities, is the concentration of heavy metals in water, , and are the body weight and daily water ingestion rate, HQ is hazard quotient, RfD: reference dose factor, NOAEL: No-Observable Adverse effect level.
4. Results
4.1. Characteristics of Survey Respondents
Figure 4 revealed the level of awareness of mineworkers about the minimum safety required during the mining operations. More than 92% of the miners surveyed were male, and ~64% of the miners who answered the survey were above 25 years-old. It was clear that most miners are young adults, and over 50% of the barite artisanal miners in the study have only basic school education or had no formal education. The miners’ biodata showed that many miners only understand local languages and may need to be trained on safe mining methods using local language to communicate essential details.
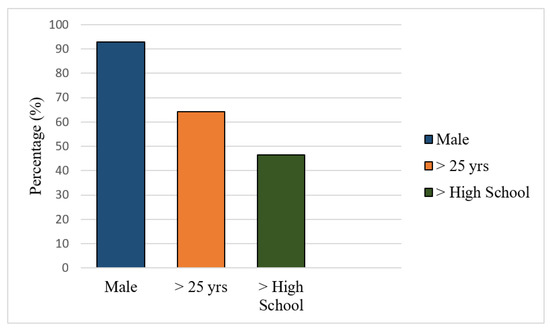
Figure 4.
Characteristics of survey respondents (barite miners) showing human participation and performance at the barite mining site.
4.2. Health Hazards of Miners
Part of the survey sought to know the previous and present health challenges of miners within the barite field under the study. Figure 5 shows that ~54% of the miners that responded to the survey agreed they have health challenges traceable to illicit drug intake such as stimulants; 17.9% of the respondents had experienced specific symptoms such as headache, stomach-ache, body weakness, and difficulty breathing. Such health issues may be traceable to rigorous mining activities and exposure to poisonous substances [72,73]. In comparison, 28.7% argued that they do not have any health issues. Also, 53.6% of the miners were ignorant of the benefits of using safety kits for mining, while 46.4% of the miners use safety kits but not at all times. Mine workers were exposed to certain risks, either knowingly or ignorantly, and become most vulnerable to sickness, air-borne diseases, and perhaps death because of insufficient knowledge about the risks associated with the mining profession.
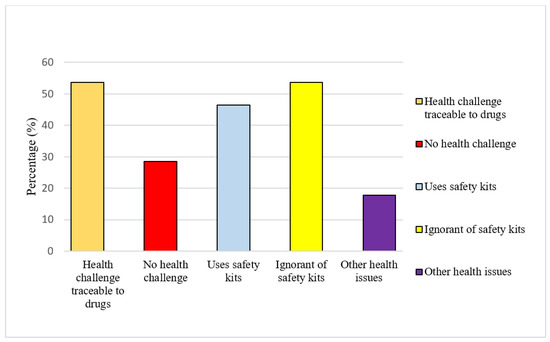
Figure 5.
Health and safety issues in the mining sites under study.
Miners are subjected to long-time exposure to heavy metals contamination. Water used for washing minerals accumulates in ponds near the mining sites and are used for domestic purpose. Potential oral and dermal ingestion are assessed by analyzing water from barite ponds and tailings.
The ultraviolent-visible (UV-Vis) spectra in Figure 6 identify absorbance bands showing the weak d-d transition of some identified transition metal complexes in the water samples. This indicates the formation of complexes of the transition metals in the octahedral fields as the d-orbital splits. The calibrated UV-visible spectrophotometer signifies and matches the transition metals in solution using the colour of the d-block compound. The peak absorbance wavelength of 675 nm is assigned to Cu2+, and the visible absorbance band that stretches from 960–980 nm indicates electronic excitations for Fe2+, V4+, and Ni2+. Similarly, the atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) identifies and measures the concentration of Zn2+, Pb2+, Cd2+, Fe2+, and Cu2+, as shown in Table 3. The result indicates that Zn2+, Pb2+, Cd2+, Fe2+, and Cu2+ as transition metal ions may be present in the water samples associated with the mining site, as indicated by the barite tailings. However, the concentration of copper and cadmium available in the site is less when compared with the World Health Organization (WHO) Standards or limits. The available concentration of lead and iron were 113.8 mg/kg and 15.6 mg/kg, respectively. In contrast, the WHO limits for these elements are pretty small, as shown in Table 3. Fe, Pb, and Cu exceed the WHO allowable limit and remain a potential threat to the mine workers and the host community.
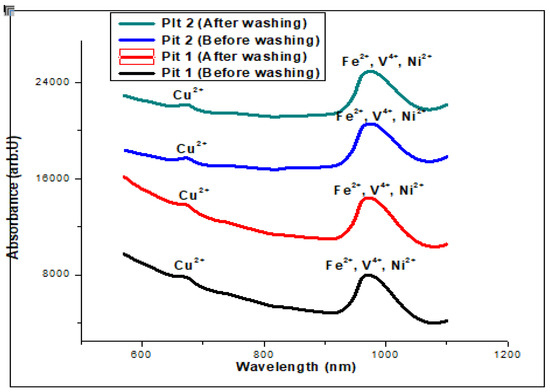
Figure 6.
UV-Vis spectrograph for the elemental composition of water from the mined pits (UV-visible spectra of transition metals complexes identified in the water samples showing weak d-d absorbance bands at 675 nm and is assigned to Cu2+, and absorption bands that stretch from 960 to 980 nm posted to Fe2+, V4+, and Ni2+, respectively).

Table 3.
AAS analysis water sample TB (completely leached tailings) showing the concentration of heavy metals at barite mining sites in the Middle Benue Trough, Nigeria (Results were compared to WHO data in [3,17]).
The inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS) results in Figure 7 shows that zinc, copper, and cadmium are below the maximum allowable limit set by World Health Organization (WHO), European Union (EU), Nigerian Industrial Standards (NIS), United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), and China Ministry of Health National Standards (CMHNS) for ecological and health safety. However, the content of Fe in TB1 is relatively higher than the maximum allowable limits set by the governing standards. Similarly, Pb in TB1 is above the health and environmental risk levels recommended by the local and international agencies. This outcome indicates that the water used in the ore washing will result in water pollution and heavy metals’ ingestion if returned to rivers and streams used by people. On the contrary, there was no evidence of cadmium contamination in the digestates of mine tailings or tailing effluents in the current study, as shown in Figure 7.
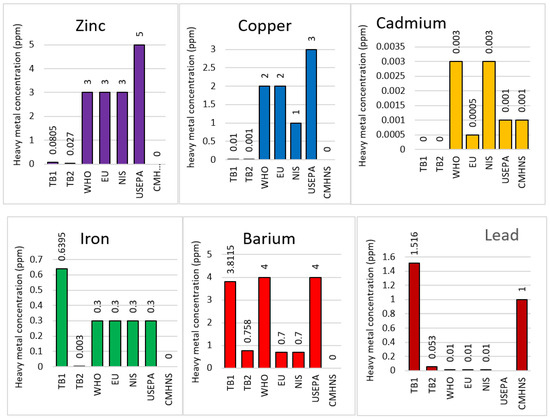
Figure 7.
ICPMS Analysis. The concentration of heavy metals associated with artisanal barite mining (ABM) at some mining sites within the Middle Benue Trough, Nigeria. WHO (World Health Organization); EU (European Union); NIS (Nigerian Industrial Standard); USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency); CMHNS (China Ministry of Health National Standards).
Contamination assessment of mine water samples in Table 4 shows that the index of geoaccumulation (Igeo) for Ba, Cu, and Fe in TB1 is between 0 and 1. The barite ponds and rivers are moderately polluted by Ba, Cu, and Fe. Similarly, Igeo of Pb in TB1 is above 6 (≥6). This indicates Pb extremely pollutes the ponds. The contamination factor (CF) of Ba in TB2 and Fe in TB2, Zn, and Cu in both samples are less than 1 (CF < 1). This implies that the water samples are lowly contaminated by Ba, Fe, Zn, and Cu and cannot pose any substantial risk to the health of miners and residents of the mining sites.

Table 4.
Contamination Assessment of Heavy metals in mines water and tailing effluents.
On the other hand, the CF for Ba in TB1 and Fe in TB1 is between 1 and 2.999, and Pb in TB1 also exceeds 6 (>6). Pb moderately contaminates the barite ponds and other water resources. Also, the chronic daily intake (CDI) for Ba, Pb, Zn, Fe, and Cu in barite ponds or mine water and tailing effluents is between 1.17 × 10−5 mg/kg day and 4.47 × 10−2 mg/kg day for an adult, 1.10 × 10−5 mg/kg day, and 4.17 × 10−2 mg/kg day for children. The result presents the possible consequence of long-term exposure to heavy metals and classifies the toxicity level as acute or chronic.
Table 5 indicates that health quotients (HQs) of Zn, Cu, and Fe for the tailings (TB1 & TB2) are less than 0.1. Such HQ is classified as No risk (HQ < 0.1) and cannot lead to adverse health implications in a short time. The presence of Ba and Pb in TB2 poses a relatively low risk to health which shows that some precautionary measures should be taken to avert negative health consequences. However, Pb in TB1 contributes medium to high risk (for 1 < HQ < 4, and HQ > 4). Thus, an adverse effect non-carcinogenic risk is expected. Table 5 also shows that health indexes (HIs) of heavy metals in TB2 for adults and children are below 1. However, HIs for TB1 are greater than 1. For children and adults that drink up to 2 L of water from water sources contaminated by TB1, a cumulative HI of 5.81 indicates elevated non-carcinogenic risks (Table 5).

Table 5.
Risk characteristics [Hazard Quotient (HQ) and health index (HI)] of Heavy metals in mines water and tailing effluents.
5. Discussion
The survey results shown in Figure 4 agree that artisanal barite mining is dominated by men (mostly young adults) and has a lower literacy level as reported on the general status of artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) in Nigeria. Previous research has shown that artisanal miners of gold, gemstones, diamond, galena, limestone, zinc have similar gender distribution and are exposed to peculiar risks and difficult tasks associated with their profession. Miners are predominantly unskilled and semi-skilled, as observed with artisanal miners that specialize in gold, gemstone, granite, and sand mining. This agrees with the general state of several mining sites managed by artisanal and small-scale miners in Nigeria [19,74,75,76,77,78].
In the current survey, it was quite true that some of the miners felt their present medical conditions are due to factors other than mining, as shown in Figure 5. Several works reported in the literature have shown that all miners are vulnerable to mining hazards aside from previous medical conditions, except for those using complete protective kits during mining [45,73]. Artisanal miners are exposed to dust risk, which lowers the Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV) and Forced Vital Capacity (FVC). Such results have shown that miners that abuse drugs as stimulants may not experience reduced lung function (fibrosis), defective oxygen diffusion, and impaired pulmonary function in the short term. However, exposure to heavy metal contamination would further worsen the present medical conditions [19,45,73,79,80,81].
Post-survey discussion with miners reveals that artisanal barite miners do not have the financial capacity to fund bills of medical examinations. Most artisanal miners earn lower than the cost of medical treatment. They would prefer self-medication or visit a traditional medical practitioner for medical consultation and treatment as no medical facilities and personnel available. Miners illicitly use nicotine to fight body weakness and other symptoms that requires an adequate medical examination. Also, it is uncertain whether owners of mining sites offer medical care to miners as there is no part of the mining policy or institutional frameworks that compelled or enforced employers to provide for the medical care of miners. Miners are encouraged to use safety kits during mining and seek medical attention when necessary. The need for annual medical outreach to mining sites is recommended for medical counseling, diagnosis, treatments, and referral of miners with severe medical conditions to access medical facilities.
High values of HQs for Ba and Pb increase HI’s value for water sample TB1. However, the case is different for sample TB2, posing no observable hazard to human health. The use of such water for various applications and eating aquatic lives such as fishes loaded with heavy metals is unsafe. Also, the heavy metal contamination risk assessment revealed that water from barite ponds and wastewater returned into the river are contaminated by lead and barium. The chronic daily intake (CDI), health quotient (HQ), and health index (HI) for these heavy metals in the water samples suggest that an adverse effect due to non-carcinogenic risk is expected. The use of affordable water filters such as carbon filters specifically designed to remove lead and Ba will help to reduce the quantity of heavy metals consumed in drinking water.
5.1. Major Inhibitors to Safe Mining Methods in Nigeria
The foremen, managers, and owners of mining sites, mineral processors within the mining industries, and academia, as stakeholders, were interviewed verbally to identify major inhibitors to safe mining in Nigeria. The inhibitors identified include funding, lack of enforcement, infrastructural needs, and insecurity.
Project Funding: The Nigerian government has done a lot through the Federal Ministry of Mines and Steel Development (MMSD) in the reform of institutional framework, establishment of ASM Directorate, Solid Minerals Development Fund (SMDF), Mineral Sector Support for Economic Diversification Project. However, some of the stakeholders in the industry and research institutions complained that funds for the projects hardly get to the mine inspectors to develop safety procedures and protocols.
Regulations and Sanctions: Although many regulations and sanctions have been established, implementation has been lacking. Mine inspectors hardly visit mine sites, and minimal awareness is created among the miners on safety and health hazards.
Infrastructural Collapse and Decay: The infrastructural imbalance within the country has completely paralyzed the power, transportation, mines, and minerals sector of the economy. However, the outright privatization of electricity generation and distribution and rail transportation should encourage investments in mining equipment importation for local mineral beneficiation and development of mines.
Security and illegal mining: Most recent and ongoing security challenges within the middle belt, Northeastern and Niger-delta regions of Nigeria can be addressed by developing a robust corporate social responsibility program to alleviate the suffering of the people living within the mineral mining and processing communities. The enactment of the mining act and collaborations among the foreign investors and experts will assist the Nigerian government in the development of a workable mining framework and a road map significantly required for relevance within an acceptable safe mining operation [17,82].
5.2. Impact of COVID-19 on Health of Miners
The first official case of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic was announced in Nigeria on February 27, 2020 [83,84]. In the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, Nigeria’s mining industry experienced sudden downtime, reducing its contribution to the national gross domestic product (GDP). The recent drop-in commercial activities and demand for minerals has also worsened the situation. Also, there are cohorts of individuals facing health and financial challenges during the pandemic. Aside from the older people, miners and mining community’ respiratory health is at stake due to the fact that some miners have pre-existing medical complications [73,80,85]. There is, however, no specific data or literature on incidents of COVID-19 related cases or the death of miners. Other subsidiary concerns among the artisanal and small-scale miners, who do not have a stable income for feeding and medical tests, surround the ability to continue routine medical examination and treatment during the pandemic. Therefore, the participation of private health providers and global aid agencies is critical at this point.
In the real sense, the right time to implement innovative and strategic plans, cultivate safety information-seeking behavior in artisanal and small-scale miners (ASMs), and enforce safe mining practices to ensure that miners and the mining activities are safe, is now. Such plans are not limited to remote collaboration, adoption of digital capabilities, safety training on the use of safe mining kits, strict observance of work ethics, occupational and environmental health safety protocols, and personal hygiene in addition to local CDC protocols on COVID-19 prevention, and vaccination of miners. Also, in collaboration with the Capstone team in the United Kingdom, the Nigerian government is reassessing the existing roadmap for mineral exploration amidst new challenges and opportunities due to the pandemic [40,86,87].
5.3. Policy Imperatives and Strategies for Fostering Safe Mining
Mining in Nigeria is regulated by the Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999, the Nigerian Minerals and Mining Acts, 2007. The Nigerian Minerals and Mining Regulations, 2011 are the significant regulations and policies that control the artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) activities in Nigeria. These policies directly address issues related to mineral exploration, environmental protection, and safety [19,88,89,90]. Policies on the environment, health, and safety have been the focus of this study. Although laws should enforce strict observance of these policies for all miners, only legal holders of mineral titles can be tracked. There are reports on Nigeria’s government effort to formalize over 1.5 million artisanal and small-scale miners (ASMs) into cooperative groups [40,89,91]. However, information available to miners is limited.
Mine Inspectors and Mine Cadastral Officer are responsible for information dissimilation, but their ratio to ASMs is about 1:200 to 1:10,000. There is an urgent need to strengthen information aids and sources to formalize artisanal and small-scale miners in Nigeria. An information sharing framework can be supported by government declaration for a Miners’ Day, a public holiday entirely given to massive sensitization on safe mining issues, safety education and awareness, medical outreaches, and miners networking. Considering mining as a hazardous endeavor, formalizing ASMs into groups will ensure adequate operations management and encourage the participation of relevant stakeholders such as Medical Doctors and Paramedics, rock mechanics, and mining engineering experts. Given the above, existing policies should guarantee safe mining at all mining sites in Nigeria.
There exists a generalized future mining plan in Nigeria called Nigerian Mining Road Map, but the content only speaks to the public without any commitment to ensure its compliance. As earlier mentioned, owners of mining sites and the government are more concerned with the business of mining and not the quality of mineral extraction, safety of life, and the mining environment. The road map proposes the path to mining prosperity and not to ensuring a responsible and sustainable mineral extraction. However, as part of the plan to diversify the economy due to the pandemic, the Ministry of Mines and Solid Minerals Development (MMSD) is considering using Science and Technology in solid mineral exploitation. This includes the use of satellites for mining data acquisition for solid mineral exploration and Artificial Intelligence (Al) to ensure mining safety and efficiency of mineral processing methods. There is a need to adopt an automated safe mining strategy or incorporate mine-based technology such as mine remoting and an automated mining system. This is key to envisioning sustainable barite mining; however, a stable power supply (electricity) is needed to drive this technology contained in the mining road map.
6. Conclusions
This study identifies and reviews mining accidents peculiar to artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) to re-iterate that mining accidents have severe consequences on miners and their environment. It revises existing but weak and inadequate mining policy, assessing potential mining risks to human health due to the mining and social lifestyles of the miners. Results show that artisanal miners are exposed to polluted water, air, and farmland. The consumption of water from barite ponds poses a relatively high risk to human health over a long period of time. Therefore, it can be concluded that mineworkers are exposed to a certain level of risks either knowingly or ignorantly due to artisanal barite mining. Adverse non-carcinogenic risks due to Pb and Ba in water and a worsening of health via illicit drug intake are expected. Operational therapy and practices such as sensitization on the danger of drugs to health, the importance of taken sufficient rest, and the use of safety tools and affordable water filter have been recommended to ensure safer artisanal mining activities. To envision the future of barite mining, detailed recommendations on the need for annual medical outreach to mining sites and the use of technology (Al) for future mining were presented. Some peculiar safe mining protocols and controls to reduce the daily chronic intake (CDI) of heavy metals in water (barite pond and tailings) are also mentioned.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.O.A. and A.P.O.; Data curation, D.O.A.; Formal analysis, D.O.A. and A.R.A.; Funding acquisition, D.O.A.; Investigation, D.O.A. and A.R.A.; Methodology, D.O.A.; Project administration, A.P.O.; Supervision, C.M.E. and R.K.A.; Validation, D.O.A.; Writing—original draft, D.O.A.; Writing—review & editing, D.O.A., A.P.O., C.M.E., A.R.A., M.T. and R.K.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study (Ph.D. program for the first author) was funded by Regional Scholarship Innovation Fund (RSIF).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Institutional approval was obtained from the African University of Science and Technology prior to the study.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data from the study is available on request.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the support of Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI), USA, African University of Science and Technology (AUST), Nigeria, and Pan African Material Institute (PAMI), Nigeria.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence any part of this work as reported in the paper.
References
- Amponsah-Tawiah, K.; Ntow, M.A.O.; Mensah, J. Occupational Health and Safety Management and Turnover Intention in the Ghanaian Mining Sector. Saf. Health Work 2016, 7, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIOSH. Injuries, Illnesses, and Hazardous Exposures in the Mining Industry, 1986–1995: A Survelliance Report; NIOSH: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 1–141.
- Donoghue, A.M. Occupational health hazards in mining: An overview. Occup. Med. 2004, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringemeier, D. Inrush and mine inundation—A real threat to Australian coal mines. In Proceedings of the International Mine Water Association, Annual Conference, Bunbury, Australia, 30 September–4 October 2012; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, D.; Wadsworth, E.J.K.; Johnstone, R.; Quinlan, M. A Study of the Role of Workers Representatives in Health and Safety Arrangements in Coal Mines in Queensland; Cardiff University Press: Cardiff, UK, 2014; pp. 1–115. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, F.; Saleh, J.H. Challenging the emerging narrative: Critical examination of coalmining safety in China, and recommendations for tackling mining hazards. Saf. Sci. 2015, 75, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwe, K.C.; Duru, C.B.; Iwu, A.C.; Merenu, I.A.; Uwakwe, K.A.; Oluoha, U.R.; Ogunniyan, T.B.; Madubueze, U.C.; Ohale, I. Occupational hazards, safety and hygienic practices among timber workers in a South Eastern State, Nigeria. Occup. Dis. Environ. Med. 2016, 4, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Duarte, A.L.; DaBoit, K.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; Teixeira, E.C.; Schneider, I.L.; Silva, L.F.O. Hazardous elements and amorphous nanoparticles in historical estuary coal mining area. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Berre, S.; Bretesché, S. Having a high-risk job: Uranium miners’ perception of occupational risk in France. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2020, 7, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, B. Another Two Mine Fatalities Brings 2020 Total to 58 Deaths. 2021. Available online: https://www.miningweekly.com/ (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Hopkins, A.; Maslen, S. Risky Rewards: How Company Bonuses Affect Safety; Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.: Surrey, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, M. Ten Pathways to Death and Disaster: Learning from Fatal Incidents in Mines and Other High Hazard Workplaces; Federation Press: Alexandria, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdevari, S.; Shahriar, K.; Esfahanipour, A. Human health and safety risks management in underground coal mines using fuzzy TOPSIS. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, P.L. Environmental impacts of coal mining and associated wastes: A geochemical perspective. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2004, 236, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.; Balluz, L.; Malilay, J. Natural and technologic hazardous material releases during and after natural disasters: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 322, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Younger, P.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Q.; Dai, T.; Kong, S.; Jin, K.; Yang, Q. Addressing the CO2 emissions of the world’s largest coal producer and consumer: Lessons from the Haishiwan Coalfield, China. Energy 2015, 80, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansah, K.J.; Yalley, A.B.; Dumakor-Dupey, N. The hazardous nature of small scale underground mining in Ghana. J. Sustain. Min. 2016, 15, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzode, V.V.; Maiti, J.; Ray, P.K. A methodology for evaluation and monitoring of recurring hazards in underground coal mining. Saf. Sci. 2011, 49, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oramah, I.T.; Richards, J.P.; Summers, R.; Garvin, T.; McGee, T. Artisanal and small-scale mining in Nigeria: Experiences from Niger, Nasarawa and Plateau states. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2015, 2, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daburum, N.H.; Songden, S.D.; Mangset, E.W. Assessment of Radiation Dose with Excess Life Cancer Risk of Mining Dumpsites of Wase, Plateau State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Med. Phy. Biomed. Eng. Sci 2019, 6, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- JohnPaul, A.A.; Ayodeji, L.T.; Tangfu, X.; Ning, Z.; Liu, Y. Toxicity, uptake, potential ecological and health risks of Thallium (Tl) in environmental media around selected artisanal mining sites in Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosun, M.M.; Usikalu, M.R.; Oyewumi, K.J.; Achuka, J.A. Radioactivity levels and transfer factor for granite mining field in Asa, North-central Nigeria. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesfeld, P.; Tirima, S.; Anka, S.M.; Fotso, A.; Nota, M.M. Reducing lead and silica dust exposures in small-scale mining in northern Nigeria. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2019, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anka, S.A.; Bello, T.S.; Waziri, A.F.; Muhammad, A.S.; Bello, I.; Nasiru, A.M. Environmental effect of lead combination of mining communities in Zamfara State, Nigeria: A review. J. Biol. Today World 2020, 9, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Disaster Waste Management Guidelines; Joint UNEP/OCHA Environment Unit: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Aluko, T.; Njoku, K.; Adesuyi, A.; Akinola, M. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil from the iron mines of Itakpe and Agbaja, Kogi State, Nigeria. Pollution 2018, 4, 527–538. [Google Scholar]
- Adewumi, A.J.P.; Laniyan, T.A.; Xiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Ning, Z. Exposure of children to heavy metals from artisanal gold mining in Nigeria: Evidences from bio-monitoring of hairs and nails. Acta Geochim. 2020, 39, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, C.I.; Nganje, T.N.; Edet, A. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment associated with abandoned barite mines in Cross River State, southeastern Nigeria. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2015, 3, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, C.I.; Nganje, T.; Edet, A. Hydrochemical assessment of pond and stream water near abandoned barite mine sites in parts of Oban massif and Mamfe Embayment, Southeastern Nigeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3793–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laniyan, T.A.; Adewumi, A.J. Evaluation of contamination and ecological risk of heavy metals associated with cement production in Ewekoro, Southwest Nigeria. J. Health Pollut. 2020, 10, 200306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeleg, E.; Janeczek, J.; Metelski, P. Native selenium as a byproduct of microbial oxidation of distorted pyrite crystals: The first occurrence in the Carpathians. Geol. Carpathica 2013, 64, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melekestseva, I.Y.; Tret’yakov, G.A.; Nimis, P.; Yuminov, A.M.; Maslennikov, V.V.; Maslennikova, S.P.; Kotlyarov, V.; Beltenev, V.; Danyushevsky, L.; Large, R. Barite-rich massive sulfides from the Semenov-1 hydrothermal field (Mid-Atlantic Ridge, 13 30.87′ N): Evidence for phase separation and magmatic input. Mar. Geol. 2014, 349, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunjó, J.; Fthenakis, V.; Vílchez, J.A.; Arnaldos, J. Hazard and operability (HAZOP) analysis. A literature review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wu, C.; Kang, L.; Reniers, G.; Huang, L. Work safety in China’s Thirteenth Five-Year plan period (2016–2020): Current status, new challenges and future tasks. Saf. Sci. 2018, 104, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shen, Y.; Saravanan, V.; Luhach, A.K. Workplace safety and risk analysis using Additive Heterogeneous Hybridized Computational Model. Aggress Violent Behav. 2021, 101558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ding, B.; Li, Z. Impact of sand mining on the carbon sequestration and nitrogen removal ability of soil in the riparian area of Lijiang River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, B.; Anderson, A. Sustainable resolutions for environmental threat of the acid mine drainage. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, A.; Buresi, M.; Lembo, A.; Lin, H.; McCallum, R.; Rao, S.; Schmulson, M.; Valdovinos, M.; Zakko, S.; Pimentel, M. Hydrogen and methane-based breath testing in gastrointestinal disorders: The North American consensus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warra, A.A.; Prasad, M.N.V. Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Waste Rehabilitation with Energy Crops and Native Flora-A Case Study from Nigeria; Elsevier Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ango, M.; Erdenebat, B.; Tang, K.Y. Creation of a Sustainable Mining Program through Formalization of Artisanal and Small Scale Miners; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Heffron, R.J. The role of justice in developing critical minerals. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2020, 7, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, K.; Lund, M.; Blanchette, M.; Mccullough, C. Regulation of artisanal small scale gold mining (ASGM) in Ghana and Indonesia as currently implemented fails to adequately protect aquatic ecosystems. In Proceedings of the International Mine Water Association Symposium, Xuzhou, China, 18–22 August 2014; pp. 401–405. [Google Scholar]
- Akper, P.T.; Ani, L. Legal and Policy Issues in the Development of Nigeria’s Mining Sector: Charting the Way Forward. SSRN 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wireko-Gyebi, R.S.; King, R.S.; Braimah, I.; Lykke, A.M. Local knowledge of risks associated with artisanal small-scale mining in Ghana. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwibo, A.N.; Ugwuja, E.I.; Nwambeke, N.O.; Emelumadu, O.F.; Ogbonnaya, L.U. Pulmonary problems among quarry workers of stone crushing industrial site at Umuoghara, Ebonyi State, Nigeria. IJOEM 2012, 3, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taiwo, A.M.; Awomeso, J.A. Assessment of trace metal concentration and health risk of artisanal gold mining activities in Ijeshaland, Osun State Nigeria—Part 1. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 177, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, U.; Asuku, A.; Umar, A.; Ahmed, Y.A.; Adam, U.S.; Abdulmalik, N.F.; Yunusa, M.H.; Abubakar, A.R. Assessment of Radon Concentration And Associated Health Implications In Ground Water And Soil Around Riruwai Mine Site, Kano State, Nigeria And Its Environs. Fudma J. Sci. 2020, 4, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, A.J.; Laniyan, T.A. Ecological and human health risks associated with metals in water from Anka Artisanal Gold Mining Area, Nigeria. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2021, 27, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvholm, B.; Silverman, D. Lung cancer in heavy equipment operators and truck drivers with diesel exhaust exposure in the construction industry. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 60, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njinga, R.L.; Tshivhase, V.M. Major chemical carcinogens in drinking water sources: Health implications due to illegal gold mining activities in Zamfara State-Nigeria. Expo Health 2019, 11, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Article, O. Prevalence of Cough among Adults in An Urban Community in Nigeria. West Afr. J. Med. 2011, 30, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Kyari, F.; Alhassan, M.B.; Abiose, A. Pattern and outcome of paediatric ocular trauma–A 3-year review at National Eye Centre, Kaduna. Niger. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 8, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakpa, A.; Argungu, G.M.; Muawiya, S.; Wase, M.M.; Shuaibu, L.M. Assessment of Mineral Resources in Federal Capital Territory (FCT) Abuja, Nigeria. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2019, 7, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merem, E.C.; Twumasi, Y.; Wesley, J.; Isokpehi, P.; Shenge, M.; Fageir, S.; Crisler, M.; Romorno, C.; Hines, A.; Hirse, G.; et al. Assessing the ecological effects of mining in West Africa: The case of Nigeria. Int. J. Min. Eng. Miner. Process. 2017, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP/OCHA. Environment and Humanitarian Action: Increasing Effectiveness, Sustainability and Accountability; UNEP/OCHA Environment Unit: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, S.; Tahir Shah, M.; Khan, S. Health risk assessment of heavy metals and their source apportionment in drinking water of Kohistan region, northern Pakistan. Microchem. J. 2011, 98, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.K.; Harrison, J. Effects of vibration on the hand-arm system of miners in India. Occup. Med. 1996, 46, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, S.; Allsop, A.; Davies, M.; Al, E. The Prevention and Control of Fire and Explosion in Mines; Health & Safety Executive: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- Frank, T.; Bise, C.J.; Michael, K. A hearing conservation program for coal miners. Occup. Health Saf. 2003, 72, 106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manley, L. Should States Serve as Laboratories for Mine Safety Regulation. Ariz St. LJ 2009, 41, 379. [Google Scholar]
- Orogbu, L.O.; Onyeizugbe, C.U.; Chukwuma, E. Safety practice and employee productivity in selected mining firms in Ebonyi State, Nigeria. J. Res. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2018, 10, 1964–1970. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, B.; Pan, X.; Love, P.E.D.; Sun, J.; Tao, C. Hazard analysis: A deep learning and text mining framework for accident prevention. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 46, 101152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpan, I.O. Effect of sample treatment on trace metal determination of Nigerian crude oils by Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) Technique. Afr. J. Environ. Pollut. Health 2005, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ibe, K.A.; Ogeleka, D.F.; Ani, I.C.; Uyebi, G.O. Suitability of Nigerian barite as a weighting agent in drilling mud. Int. J. Min. Miner. Eng. 2016, 7, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geo. J. 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA; ABD. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund; Volume I: Human health evaluation manual (Part A); EPA/540/1-89/002; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Camp Dresser & McKee, Inc. Guidelines for Water Reuse, US Environmental Protection Agency; EPA/625/R-04/108; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- EPA, US. Fact Sheet PFOA & PFOS Drinking Water Health Advisories; EPA 800-F-16-003; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Shah, I.; Khan, T.; Hanif, M.; Shah, A.; Siddiqui, S.; Khattak, S.A. Environmental aspects of selected heavy and trace elements of Cherat Coal deposits. J. Himal. Earth Sci. 2016, 49, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Adewumi, A.J.; Laniyan, T.A. Contamination, sources and risk assessments of metals in media from Anka artisanal gold mining area, Northwest Nigeria. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessel, G.K.; Sluis-Cremer, P.A. Hearing loss in white South African goldminers. S. Afr. Med. J. 1987, 71, 354–367. [Google Scholar]
- Babatunde, O.; Ayodele, L.; Elegbede, O.; Babatunde, O.; Ojo, O.; Alawode, D.; Ademol, O.; Oluwasey, A. Practice of occupational safety among artisanal miners in a rural community in Southwest Nigeria. Int. J. Sci. Environ. Technol. 2013, 2, 622–633. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Environmental and Occupational Health Hazards Associated with Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining; World Health Organization HQ: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tirima, S.; Bartrem, C.; von Lindern, I.; von Braun, M.; Lind, D.; Anka, S.M.; Abdullahi, A. Environmental remediation to address childhood lead poisoning epidemic due to artisanal gold mining in Zamfara, Nigeria. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwagwu, W.E. Job Satisfaction of Information Technology Artisans in Nigeria. Mousaion 2018, 36, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Melodi, M.M.; Opafunso, Z.O. An Assessment of Existing Production and Revenue Capacities for Artisanal and Small-Scale Granite Mining in Southwest Nigeria. J. Min. World Express 2014, 3, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.M.; Oruonye, E.D. Socioeconomic impact of artisanal and small scale mining on the Mambilla Plateau of Taraba State, Nigeria. World J. Soc. Sci. Res. 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Olley, B.O.; Abikoye, G.E. Predicting Intentions and Continuous Cannabis Use among Smokers. In Perspectives on Drugs, Alcohol and Society in Africa; Obot, I.S., Abikoye, G.E., Eds.; Centre for Research and Information on Substance Abuse (CRISA): Jos, Nigeria, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Azodo, C.C.; Omuemu, V.O. Perception of spirituality, spiritual care, and barriers to the provision of spiritual care among undergraduate nurses in the University of Lagos, Nigeria. J. Clin. Sci. 2017, 14, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, O.; Gilles, N.; Fon, N.; Luma, H.; Greg, N. Impact of Artisanal Gold Mining on Human Health and the Environment in the Batouri Gold District, East Cameroon. Acad. J. Interdiscip. Stud. 2018, 7, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Esheya, S.E.; Okoye, P.C.U.; Nweze, P.N.J.; Okonkwo, N.A. Socio-Economic Effects of Chemical Pollution on Agricultural Production in Mineral Mining Communities of South-East Nigeria. Merit Res. J. Bus. Manag. 2017, 5, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kalu, B. COVID-19 in Nigeria: A disease of hunger Respiratory health in athletes: Facing the COVID-19 challenge. Lancet Respir. 2020, 8, 556–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebowale, A.S.; Fagbamigbe, A.F.; Akinyemi, J.O.; Obisesan, O.K.; Awosanya, E.J.; Afolabi, R.F.; Alarape, S.A.; Obabiyi, S.O. The spread of COVID-19 outbreak in the first 120 days: A comparison between Nigeria and seven other countries. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laniyan, T.A.; Adewumi, A.J.P. Potential ecological and health risks of toxic metals associated with artisanal mining contamination in Ijero, southwest Nigeria. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2020, 55, 858–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amzat, J.; Aminu, K.; Kolo, V.I.; Akinyele, A.A. Coronavirus outbreak in Nigeria: Burden and socio-medical response during the first 100 days. Int. J. Infect Dis. 2020, 98, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwagwu, W.E.; Igwe, E.G. Safety information-seeking behaviour of artisanal and small-scale miners in selected locations in Nigeria. Libri 2015, 65, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolayan, D.O.; Adetunji, A.R.; Peter, A.; Oghenerume, O.; Amankwah, R.K. Characterization of barite reserves in Nigeria for use as weighting agent in drilling fluid. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallo, S.J. Mitigating the Activities of Artisanal and Small-Scale Miners in Africa: Challenges for Engineering and Technological Institutions. IJMER 2012, 2, 4714–4725. [Google Scholar]
- Mensah, A.K.; Mahiri, I.O.; Owusu, O.; Mireku, O.D.; Wireko, I.; Kissi, E.A. Environmental Impacts of Mining: A Study of Mining Communities in Ghana. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, J.H.; Cummings, A.M. Safety in the mining industry and the unfinished legacy of mining accidents: Safety levers and defense-in-depth for addressing mining hazards. Saf. Sci. 2011, 49, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).