Isopanduratin A Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α-Induced Nuclear Factor κB Signaling Pathway by Promoting Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase-Dependent Ectodomain Shedding of TNF Receptor 1 in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Antibodies
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Transfection
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
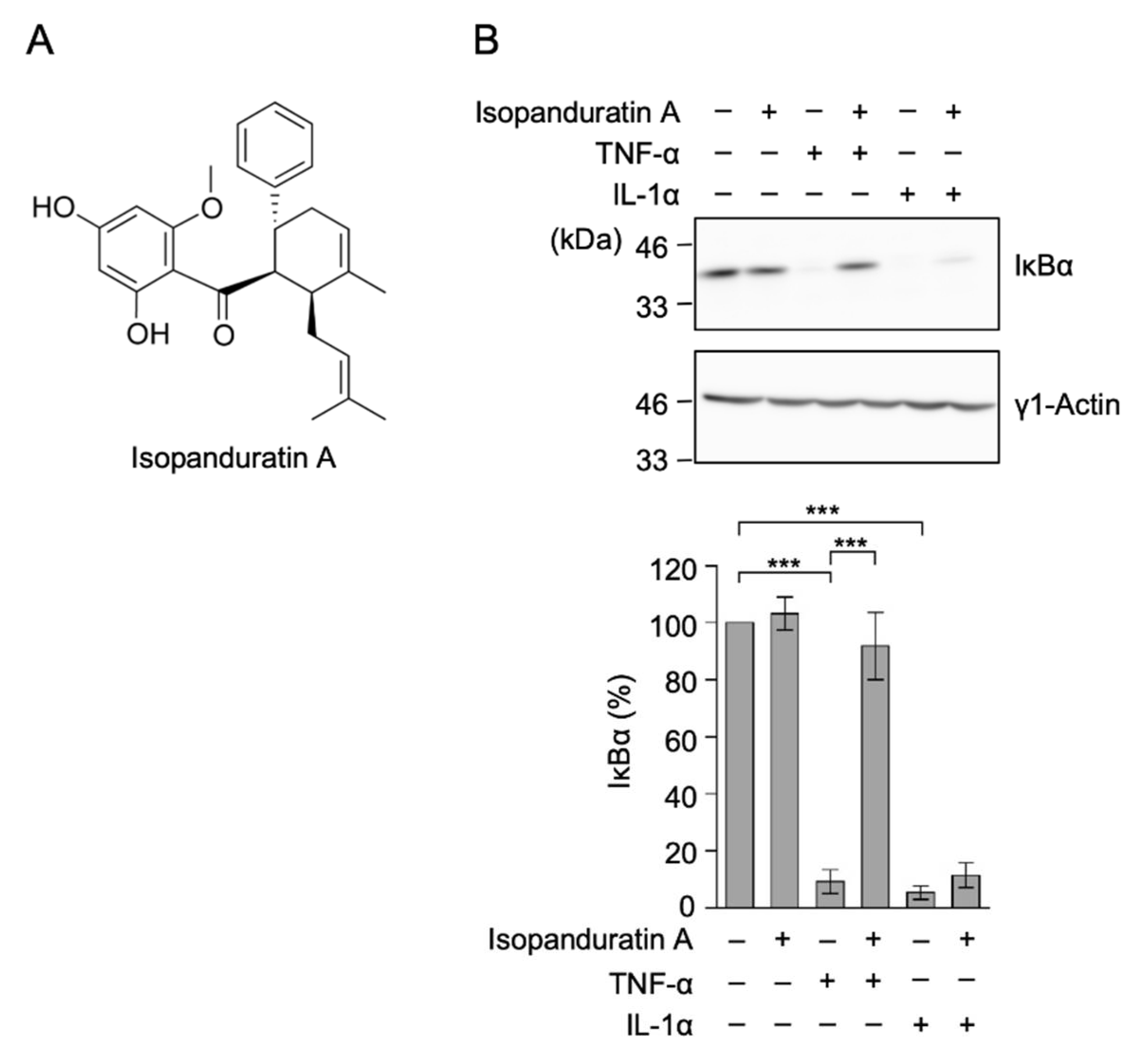
3.1. Isopanduratin A Inhibited IκB Degradation Induced by TNF-α, but Not IL-1α
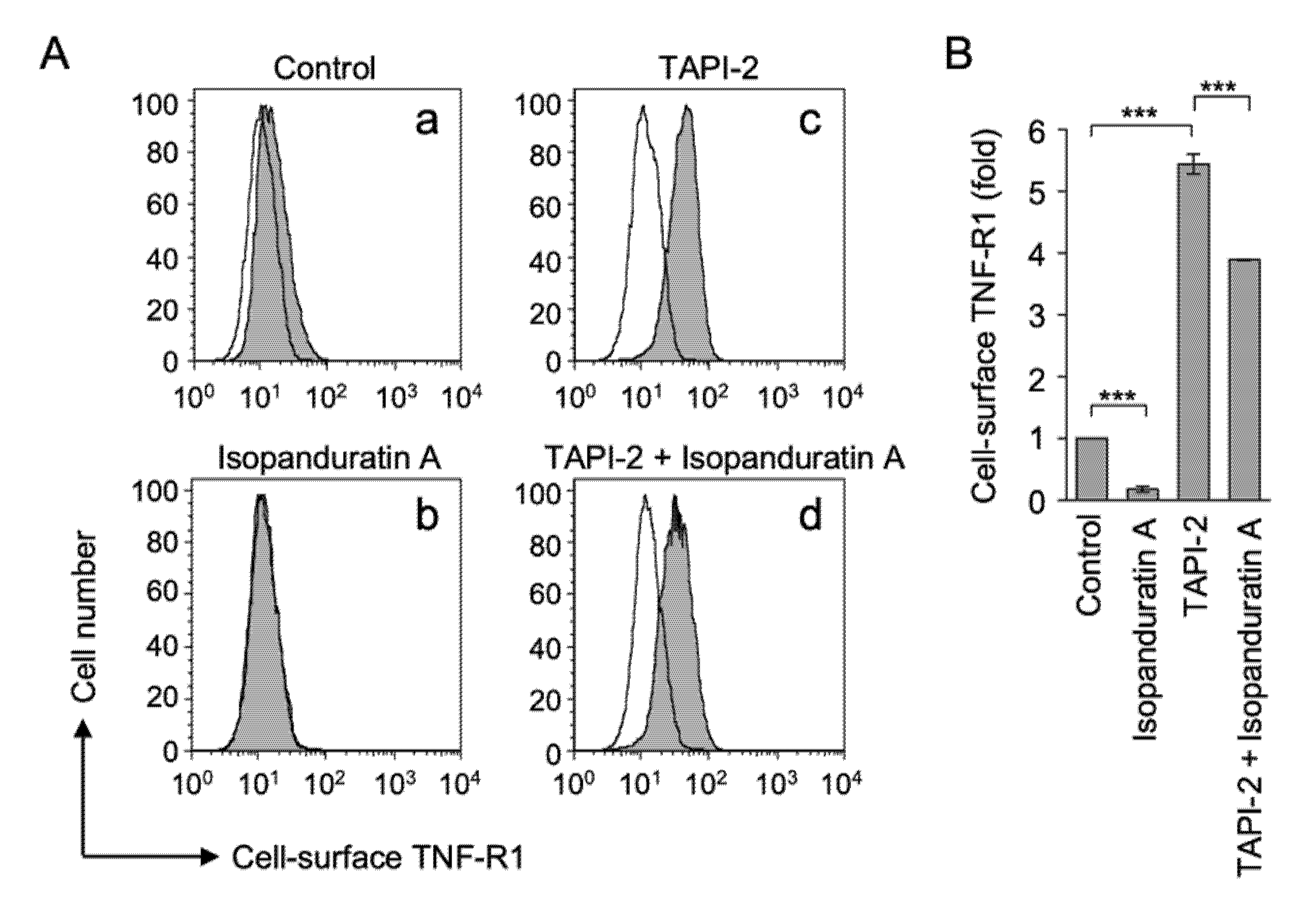
3.2. Isopanduratin A Decreased the Expression of TNF-R1
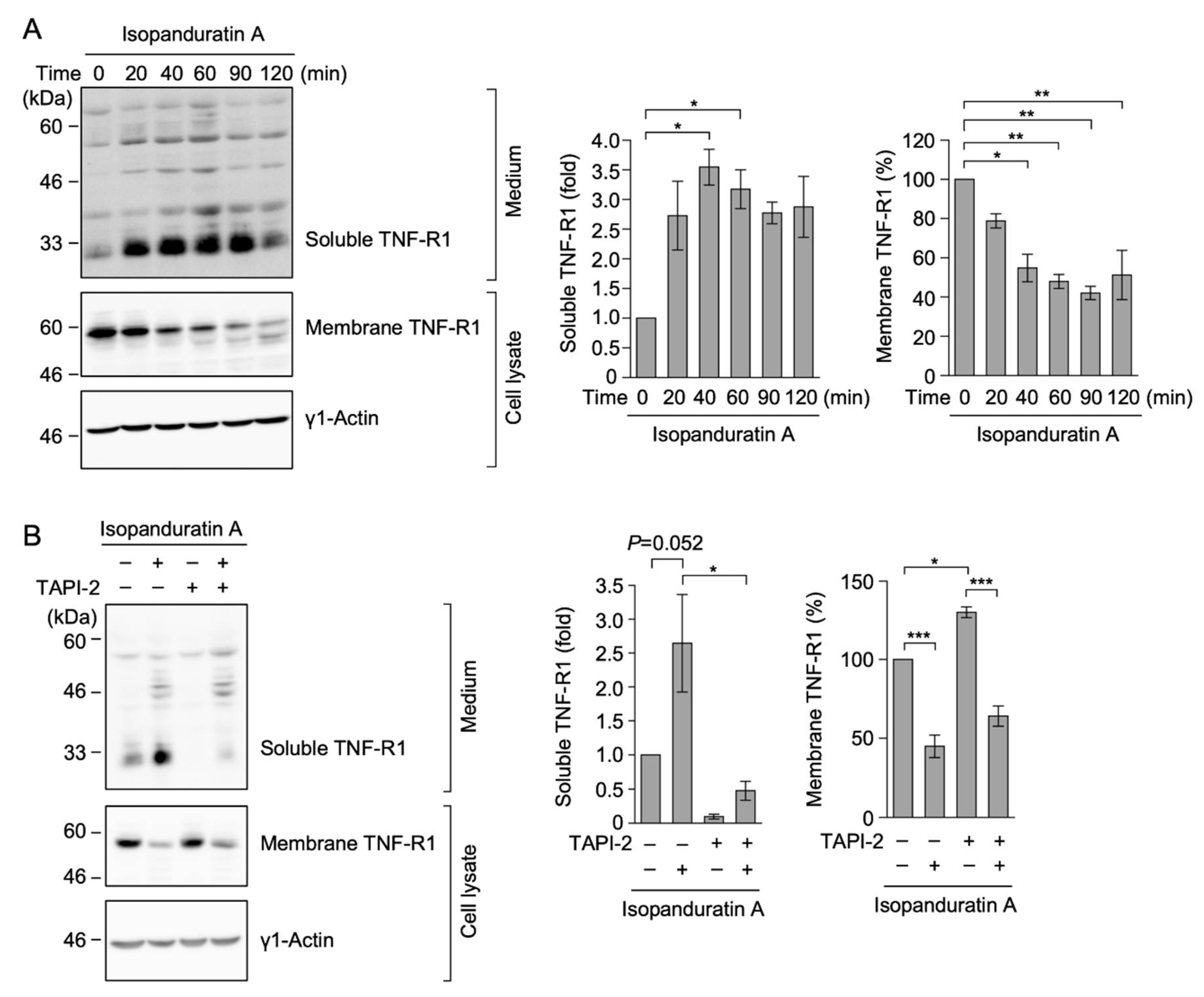
3.3. Isopanduratin A Induced the Ectodomain Shedding of TNF-R1
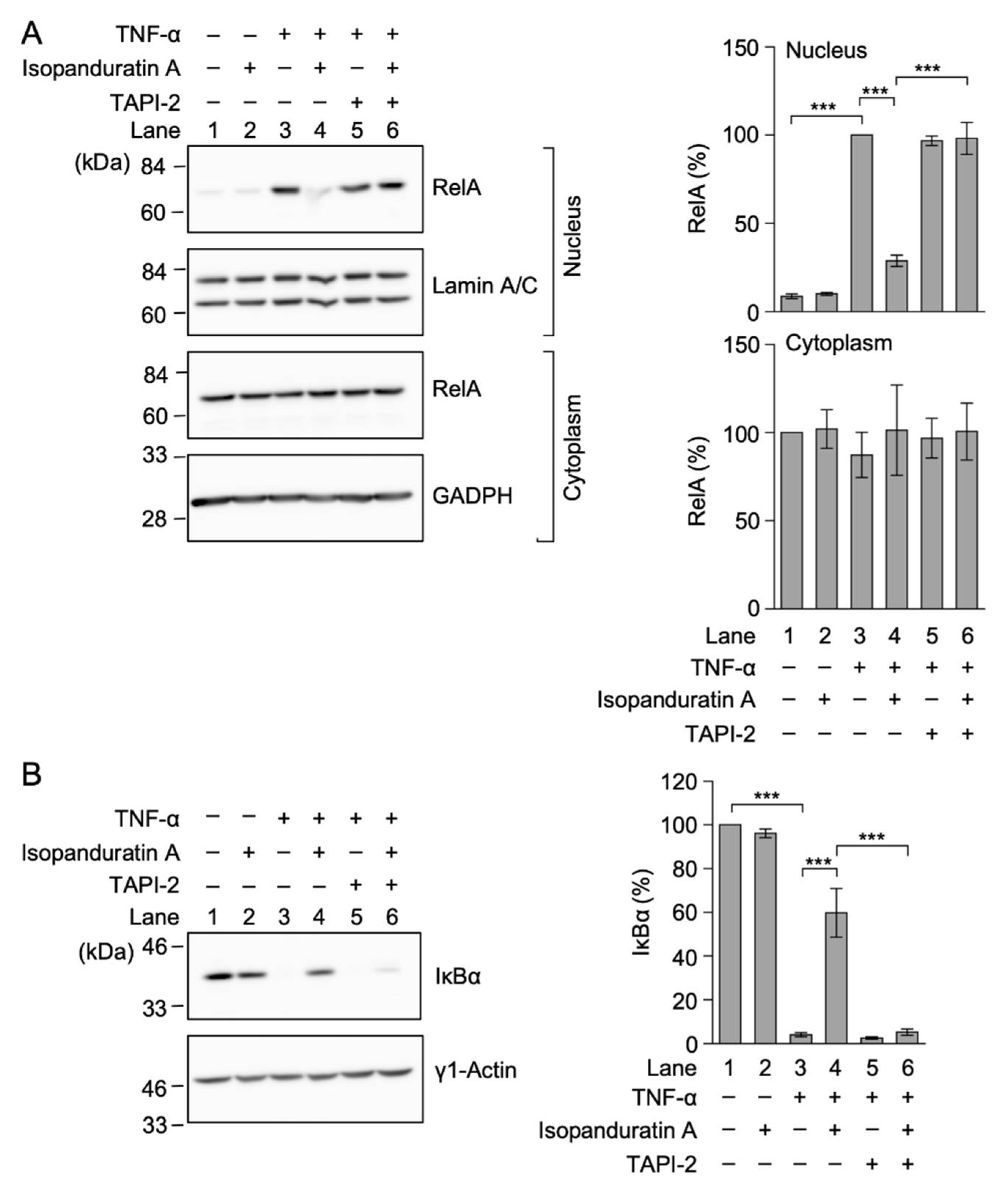
3.4. Isopanduratin A Inhibited the TNF-α-Induced NF-κB Signaling Pathway by Inducing the Ectodomain Shedding of TNF-R1
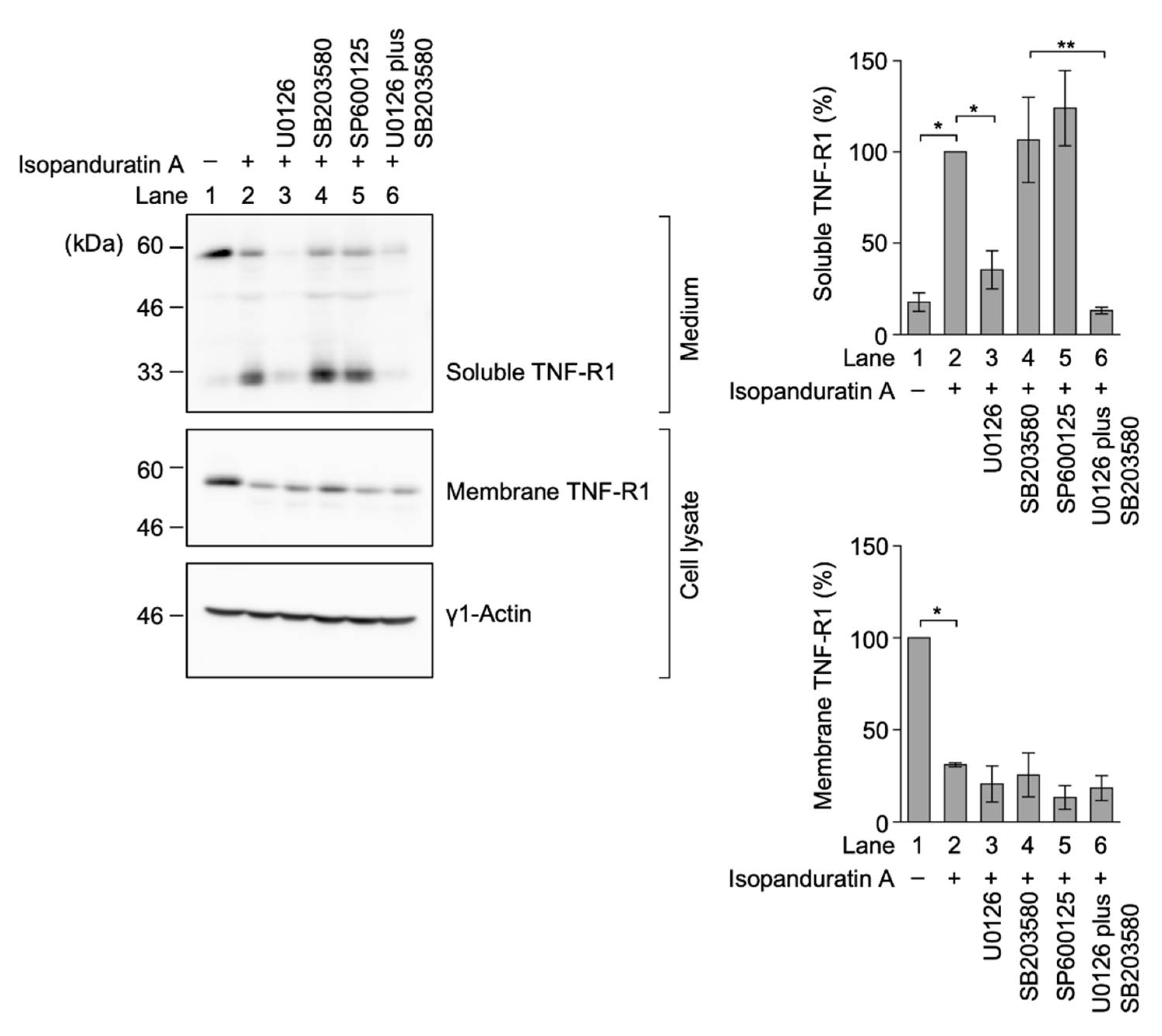
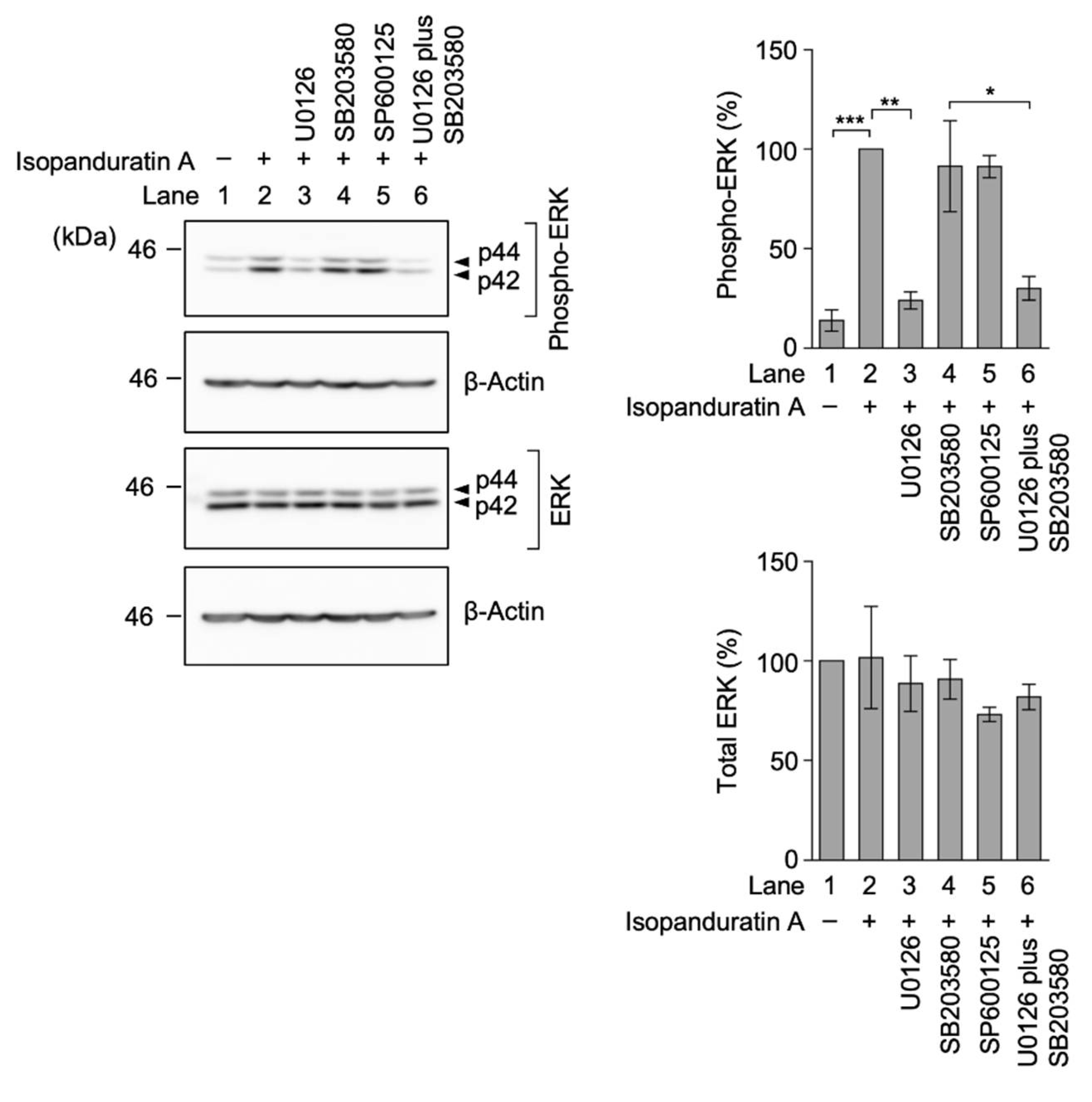
3.5. Isopanduratin A Induced the Ectodomain Shedding of TNF-R1 by ERK Activation
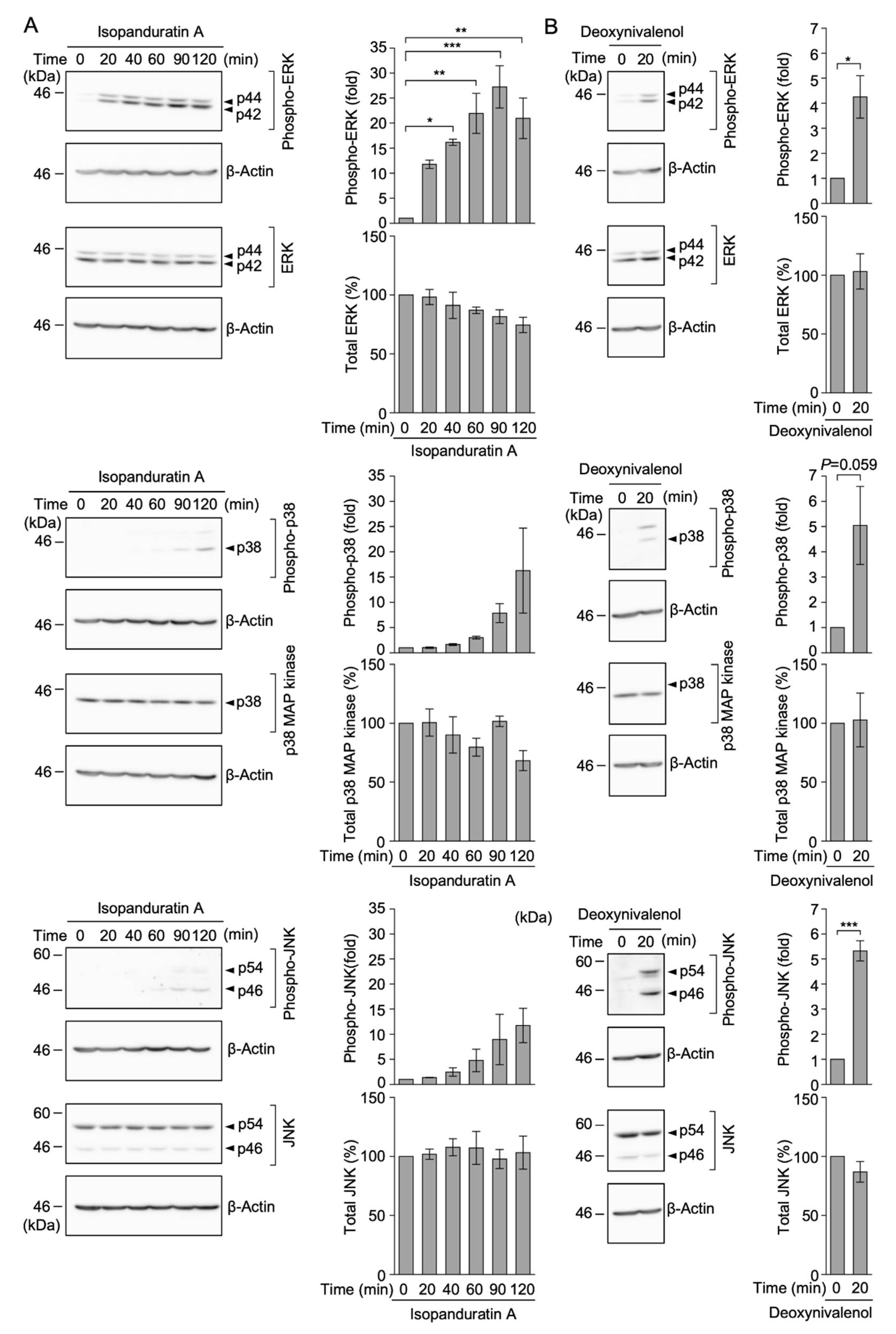
3.6. Isopanduratin A Induced the Rapid Phosphorylation of ERK, but Not p38 MAP Kinase or JNK
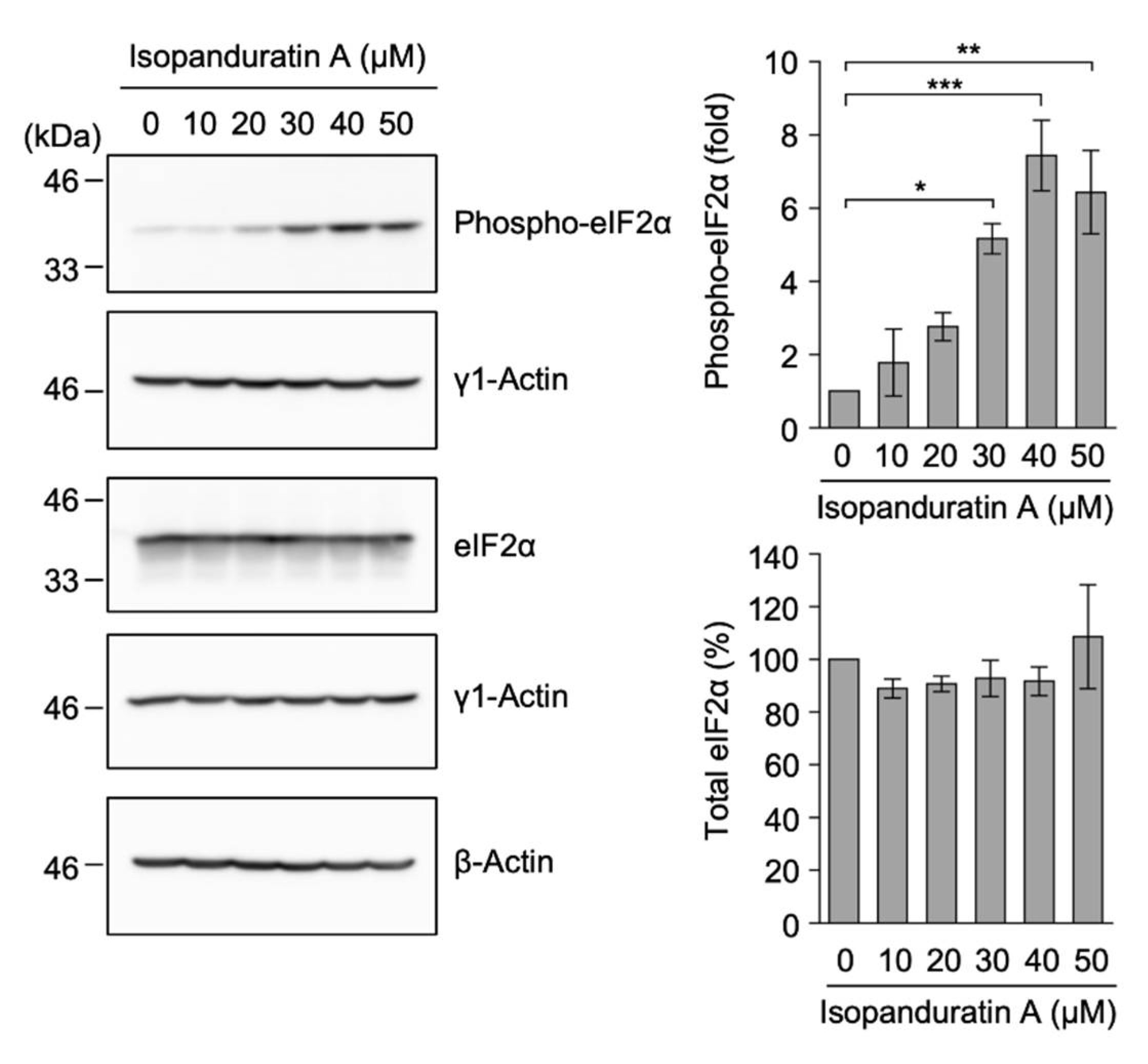
3.7. Isopanduratin A Promoted eIF2α Phosphorylation
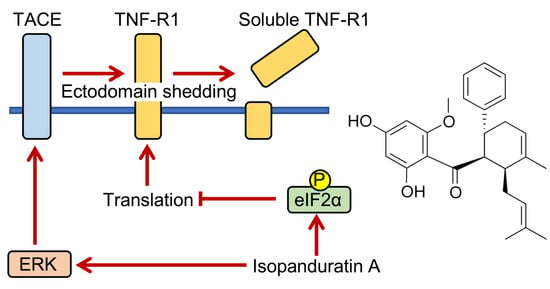
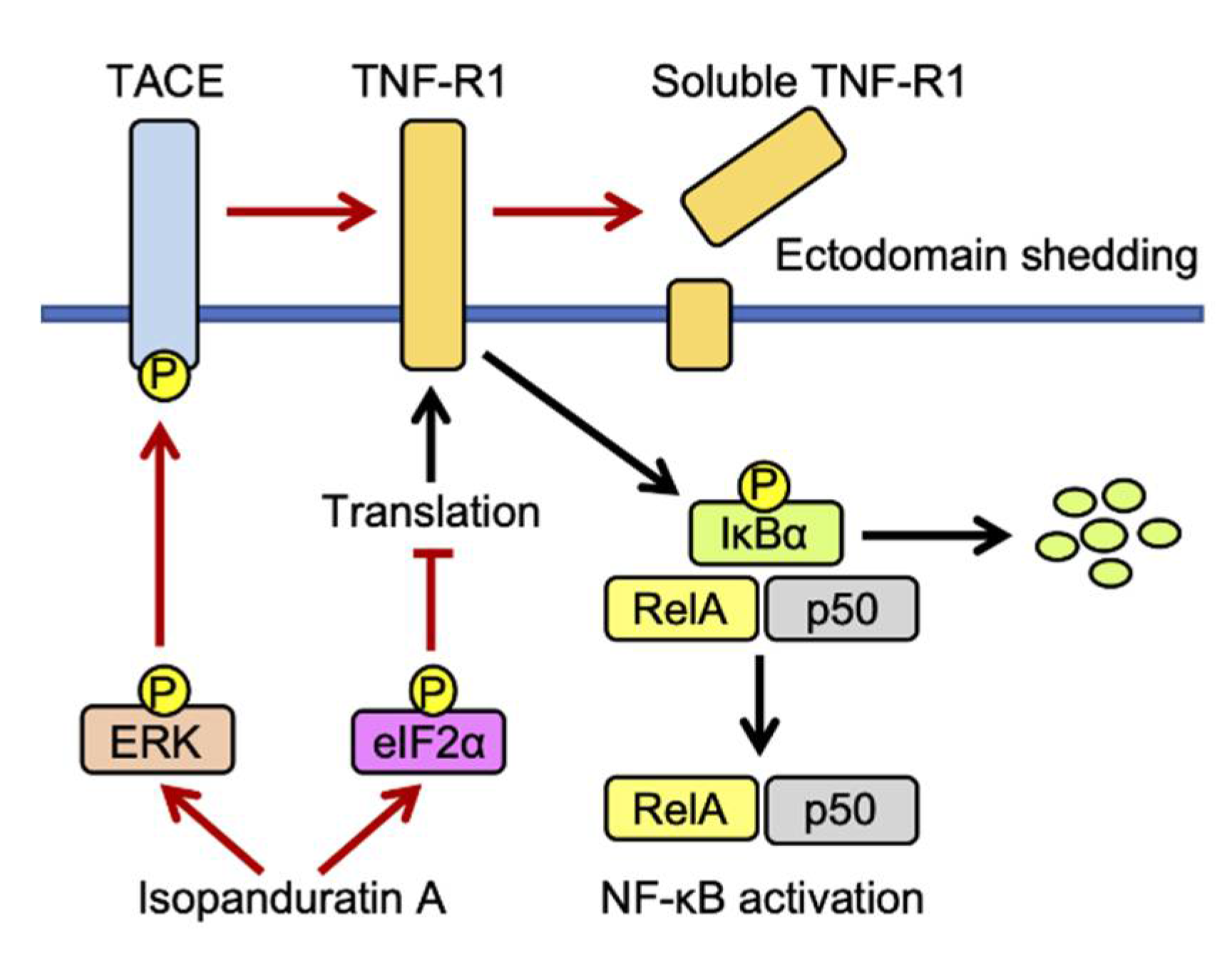
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.-A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajant, H.; Scheurich, P. TNFR1-induced activation of the classical NF-κB pathway. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Regulation of NF-κB by TNF family cytokines. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhoj, V.G.; Chen, Z.J. Ubiquitylation in innate and adaptive immunity. Nature 2009, 458, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Iwai, K. Roles of linear ubiquitinylation, a crucial regulator of NF-κB and cell death, in the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 266, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. NF-κB: Linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, V.; Karin, M. Is NF-κB a good target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2009, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gooz, M. ADAM-17: The enzyme that does it all. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 45, 146–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Garbers, C.; Rose-John, S. ADAM17: A molecular switch to control inflammation and tissue regeneration. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Rodríguez, E.; Montero, J.C.; Esparís-Ogando, A.; Yuste, L.; Pandiella, A. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylates tumor necrosis factor-α-converting enzyme at threonine 735: A potential role in regulated shedding. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 2031–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soond, S.M.; Everson, B.; Riches, D.W.H.; Murphy, G. ERK-mediated phosphorylation of Thr735 in TNFα-converting enzyme and its potential role in TACE protein trafficking. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Xu, P.; Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. TACE-mediated ectodomain shedding of the type I TGF-β receptor downregulates TNF-β signaling. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.; Derynck, R. Direct activation of TACE-mediated ectodomain shedding by p38 MAP kinase regulates EGF receptor-dependent cell proliferation. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kataoka, T. Chemical Biology of inflammatory cytokine signaling. J. Antibiot. 2009, 62, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kataoka, T. Translation inhibitors and their unique biological properties. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 676, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogura, H.; Tsukumo, Y.; Sugimoto, H.; Igarashi, M.; Nagai, K.; Kataoka, T. Ectodomain shedding of TNF receptor 1 induced by protein synthesis inhibitors regulates TNF-α-mediated activation of NF-κB and caspase-8. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, H.; Tsukumo, Y.; Sugimoto, H.; Igarashi, M.; Nagai, K.; Kataoka, T. ERK and p38 MAP kinase are involved in downregulation of cell surface TNF receptor 1 induced by acetoxycycloheximide. Inter. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Taketani, S.; Osada, H.; Kataoka, T. Cytotrienin A, a translation inhibitor that induces ectodomain shedding of TNF receptor 1 via activation of ERK and p38 MAP kinase. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 667, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Kataoka, T. Deoxynivalenol induces ectodomain shedding of TNF receptor 1 and thereby inhibits the TNF-α-induced NF-κB signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 701, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.; Quach, H.T.; Watanabe, T.; Kanoh, N.; Iwabuchi, Y.; Usui, T.; Kataoka, T. Irciniastatin A, a pederin-type translation inhibitor, promotes ectodomain shedding of cell-surface tumor necrosis factor receptor 1. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, H.T.; Hirano, S.; Fukuhara, S.; Watanabe, T.; Kanoh, N.; Iwabuchi, Y.; Usui, T.; Kataoka, T. Irciniastatin A induces potent and sustained activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and thereby promotes ectodomain shedding of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 in human lung carcinoma A549 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozmer, Z.; Perjési, P. Naturally occurring chalcones and their biological activities. Phytochem. Rev. 2016, 15, 87–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, H.A.; Yusof, R.; Rahman, N.A. A search for vaccines and therapeutic for Dengue: A review. Curr. Comput. Aided. Drug Des. 2007, 3, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.-H.; Wang, R.-F.; Guo, S.-Z.; Lin, B. An update on antitumor activity of naturally occurring chalcones. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 815621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synchrová, A.; Koláriková, I.; Žemlička, M.; Šmejkal, K. Natural compounds with dual antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 1471–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-K.; Chung, J.-Y.; Baek, N.-I.; Park, J.-H. Isopanduratin A from Kaempferia pandurata as an active antibacterial agent against cariogenic Streptococcus mutans. Inter. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 23, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.-S.; Shim, J.-S.; Gwon, S.-H.; Lee, C.-W.; Kim, H.-S.; Hwang, J.-K. Antibacterial activity of panduratin A and isopan-duratin A isolated from Kaempferia pandurata Roxb. against Acne-causing microorganisms. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 17, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Shim, J.-S.; Cho, Y.; Baek, N.-I.; Lee, C.-W.; Kim, H.-S.; Hwang, J.-K. Depigmentation of melanocytes by isopandu-ratin A and 4-hydroxypanduratin A isolated from Kaempferia Pandurata Roxb. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 2141–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morikawa, T.; Funakoshi, K.; Ninomiya, K.; Yasuda, D.; Miyagawa, K.; Matsuda, H.; Yoshikawa, M. Medicinal foodstuffs. XXXIV. Structures of new prenylchalcones and prenylflavannones with TNF-α and aminopeptidase N inhibitory activities from Bosenbergia rotunda. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatsumpun, N.; Sritularak, B.; Likhitwitayawuid, K. New biflavonoids with α-glucosidase and pancreatic lipase inhibitory activities from Bosenbergia rotunda. Molecules 2017, 22, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, M.T.T.; Nguyen, H.X.; Dang, P.H.; Dibwe, D.F.; Esumi, H.; Awale, S. Constituents of the rhizomes of Boesenbergia pandurata and their antiausterity activities against the PANC-1 human pancreatic cancer line. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, N.N.; Awale, S.; Esumi, H.; Tezuka, Y.; Kadota, S. Bioactive secondary metabolites from Boesenbergia pandurata of Myanmar and their preferential cytotoxicity against human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cell line in nutrient-deprived medium. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1582–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.T.; Do, N.M.; Tran, D.H.-K.; To, N.B.; Vo, P.H.; Nguyen, M.T.T.; Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, H.X.; Truong, K.D.; Pham, P.V. Isopanduratin A isolated from Boesenbergia pandurata reduces HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation in both monolayer and three-dimensional cultures. Av. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 3, 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Tanigaki, R.; Takahashi, R.; Nguyen, M.T.T.; Nguyen, N.T.; Do, T.V.N.; Nguyen, H.X.; Kataoka, T. 4-Hydroxypanduratin A and isopanduratin A inhibit tumor necrosis factor α-stimulated gene expression and the nuclear factor κB-dependent signaling pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yun, J.-M.; Kwon, H.; Hwang, J.-K. In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of panduratin A isolated from Kaempferia pandurata in RAW264.7 cells. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheah, S.-C.; Appleton, D.R.; Lee, S.-T.; Lam, M.-L.; Hadi, A.H.A.; Mustafa, M.R. Panduratin A inhibits the growth of A549 cells through induction of apoptosis and inhibition of NF-kappaB translocation. Molecules 2011, 16, 2583–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, S.-C.; Lai, S.-L.; Lee, S.-T.; Hadi, A.H.A.; Mustafa, M.R. Panduratin A, a possible inhibitor in metastasized A549 cells through inhibition of NF-kappaB translocation and chemoinvasion. Molecules 2013, 18, 8764–8778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.-B.; Kim, C.; Hwang, J.-K. Inhibitory effects of panduratin A on periodontitis-induced inflammation and osteoclastogenesis through inhibition of MAPK pathways in vitro. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kondo, T.; Takeda, K.; Muko, R.; Ito, A.; Chang, Y.-C.; Magae, J.; Kataoka, T. 4-O-Methylascochlorin inhibits the prolyl hydroxylation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, which is attenuated by ascorbate. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, K.; Kuwada, S.; Nakao, A.; Li, X.; Okuda, N.; Nishida, A.; Mitsuda, S.; Fukuoka, N.; Kakeya, H.; Kataoka, T. Different localization of lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1) in mammalian cultured cell lines. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 153, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuda, S.; Yokomichi, T.; Yokoigawa, J.; Kataoka, T. Ursolic acid, a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid, inhibits intracellular trafficking of proteins and induces accumulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 linked to high-mannose-type glycans in the endoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Open Bio. 2014, 4, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quach, H.T.; Tanigaki, R.; Yokoigawa, J.; Yamada, Y.; Niwa, M.; Hirano, S.; Shiono, Y.; Kimura, K.; Kataoka, T. Allantopyrone A interferes with multiple components of the TNF receptor 1 complex and blocks RIP1 modifications in the TNF-α-induced signaling pathway. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, N.T.; Sasaki, S.; Miyake, Y.; Nguyen, N.T.; Dang, P.H.; Nguyen, M.T.T.; Kataoka, T. α-Conidendrin inhibits the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 induced by tumor necrosis factor-α in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 890, 173651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiono, Y.; Yokoi, M.; Koseki, T.; Murayama, T.; Aburai, N.; Kimura, K. Allantopyrone A, a new α-pyrone metabolite with potent cytotoxicity from an endophytic fungus, Allantophomopsis Lycopodina KS-97. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonenberg, N.; Hinnebusch, A.G. Regulation of translation initiation in eukaryotes: Mechanisms and biological targets. Cell 2009, 136, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merrick, W.C.; Pavitt, G.D. Protein synthesis initiation in eukaryotic cells. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a033092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.-M.; Kwon, H.; Mukhtar, H.; Hwang, J.-K. Induction of apoptosis by panduratin A isolated from Kaempferia pandurata in human colon cancer HT-29 cells. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.-M.; Kweon, M.-H.; Kwon, H.; Hwang, J.-K.; Mukhtar, H. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by a chalcone panduratin A isolated from Kaempferia pandurata in androgen-independent human prostate cancer cells PC3 and DU145. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanlangenakker, N.; Bertrand, M.J.M.; Bogaert, P.; Vandenabeele, P.; Vanden Berghe, T. TNF-induced necroptosis in L929 cells is tightly regulated by multiple TNFR1 complex I and II members. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, B.-K.; Kim, C.; Kim, M.-B.; Hwang, J.-K. Panduratin A prevents tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced muscle atrophy in L6 rat skeletal muscle cells. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: A double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seals, D.F.; Courtneidge, S.A. The ADAMs family of metalloproteases: Multidomain proteins with multiple functions. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donnelly, N.; Gorman, A.M.; Gupta, S.; Samali, A. The eIF2α kinases: Their structures and functions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3493–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakos-Zebrucka, K.; Koryga, I.; Mnich, K.; Ljujic, M.; Samali, A.; Gorman, A.M. The integrated stress response. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 1374–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, S.-L.; Wong, P.-F.; Lim, T.-K.; Lin, Q.; Mustafa, M.R. Cytotoxic mechanisms of panduratin A on A375 melanoma cells: A quantitative and temporal proteomics analysis. Proteomics 2015, 15, 1608–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestka, J.J.; Zhou, H.-R.; Moon, Y.; Chung, Y.J. Cellular and molecular mechanisms for immune modulation by deoxynivalenol and other trichothecenes: Unraveling a paradox. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 153, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestka, J.J. Mechanisms of deoxynivalenol-induced gene expression and apoptosis. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2008, 25, 1128–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moriwaki, C.; Tanigaki, R.; Miyake, Y.; Vo, N.T.; Nguyen, M.T.T.; Nguyen, N.T.; Do, T.N.V.; Nguyen, H.X.; Kataoka, T. Isopanduratin A Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α-Induced Nuclear Factor κB Signaling Pathway by Promoting Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase-Dependent Ectodomain Shedding of TNF Receptor 1 in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells. BioChem 2021, 1, 174-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1030014
Moriwaki C, Tanigaki R, Miyake Y, Vo NT, Nguyen MTT, Nguyen NT, Do TNV, Nguyen HX, Kataoka T. Isopanduratin A Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α-Induced Nuclear Factor κB Signaling Pathway by Promoting Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase-Dependent Ectodomain Shedding of TNF Receptor 1 in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells. BioChem. 2021; 1(3):174-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1030014
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoriwaki, Chihiro, Riho Tanigaki, Yasunobu Miyake, Nghia Trong Vo, Mai Thanh Thi Nguyen, Nhan Trung Nguyen, Truong Nhat Van Do, Hai Xuan Nguyen, and Takao Kataoka. 2021. "Isopanduratin A Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α-Induced Nuclear Factor κB Signaling Pathway by Promoting Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase-Dependent Ectodomain Shedding of TNF Receptor 1 in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells" BioChem 1, no. 3: 174-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1030014
APA StyleMoriwaki, C., Tanigaki, R., Miyake, Y., Vo, N. T., Nguyen, M. T. T., Nguyen, N. T., Do, T. N. V., Nguyen, H. X., & Kataoka, T. (2021). Isopanduratin A Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α-Induced Nuclear Factor κB Signaling Pathway by Promoting Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase-Dependent Ectodomain Shedding of TNF Receptor 1 in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells. BioChem, 1(3), 174-189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biochem1030014