Abstract
Due to increasing anthropogenic activities, trace metals (TM) remain a major concern particularly in semi-arid countries with limited water resources. In this context, the present study aims to understand the geochemistry of trace metals in bottom sediments from the Sebou basin, representing 1/3 of the surface water resources of Morocco. Total concentrations of trace metals (As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) and some physicochemical parameters were measured in the fraction < 63 µm. The order of abundance of the elements was Zn > Cr > Cu > Ni > Pb > Co > As > Cd. The enrichment factor calculation showed that 70% of the samples were naturally concentrated in trace metals, especially As and Ni, as well as Cd and Pb, except at some stations. On the contrary, the most enriched elements were Cr, Zn, and Cu. Chromium presented an enrichment higher than 5 and toxicity risks at some stations, such as the downstream Fez city known for its important tannery activities. A multivariate analysis of the data evidenced the strong link between the identified natural elements (As, Co, Ni) with clays and Fe and Al oxides, whereas elements (Cd, Cu, Cr, Pb, Zn) mainly derived from anthropogenic activities (industrial and domestic waste, agricultural inputs) were linked to phosphorus and, to a lesser extent, particulate organic carbon.
1. Introduction
The development of anthropogenic activities (agricultural, mining, industrial, artisanal, domestic, etc.) has a very visible impact on the quality of aquatic environments. This impact is more important when effluents are discharged without any pre-treatment [1]. The input of contaminants, especially trace metals (TM), affects benthic species and human health because of their persistence, toxicity, and capacity to be bioaccumulated through the food chain [2,3]. One of the best ways to assess the contamination of rivers by trace metals from natural and anthropogenic sources is to investigate bottom sediments [4,5,6]. Indeed, sediments have a high retention capacity of trace metals and act as a sink for pollutants [7,8]. The components of sediments (iron and manganese oxides, clays, organic matter, carbonates, and the residual fraction) mainly control these elements [9]. However, the behavior of trace metals in sediments depends on several biogeochemical processes [10]. Under certain physicochemical conditions, such as pH, dissolved oxygen, or redox potential, they can be released in the dissolved phase and become bioavailable [11,12]. Semi-arid basins, characterized by long, dry, low-water periods, are mostly sensitive to trace metal contamination [13,14], which is the case of the Sebou basin.
The Sebou basin includes one of the most important hydrographic networks in Morocco, representing 1/3 of the surface water resources of the country [15]. However, the rapid development of artisanal and industrial activities, population growth, modernization, and intensification of agriculture have decreased the quality of the Sebou River [16]. Today, it is considered as one of the most polluted rivers in Morocco [17]. Several studies have been carried out to identify trace metal contamination in the Sebou basin, but most of them have been focused on the biological and physicochemical study of the water and sediments in the Fez sub-basin [1,12,18,19,20,21].
The present study aimed to investigate the origin and controlling factors of trace metals in the river bottom sediments at the basin scale, especially the fluvial part of the Sebou basin during various seasonal conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Sebou basin is located in the northwest of Morocco (Figure 1). The fluvial part of our concern extends over an area of 26,200 km2. It is a carbonate basin characterized by calcareous rocks, dolomites, marls, marly calcareous rocks, and evaporites. Three geomorphological units can be distinguished [22]: the Upper (Middle Atlas), Middle (Rif and Pre-Rif mountains), and Lower Sebou basin (Gharb plain). The climate is Mediterranean type with an oceanic influence. The average rainfall varies between 600 and 1000 mm, and the temperature varies between 10 and 20 °C.
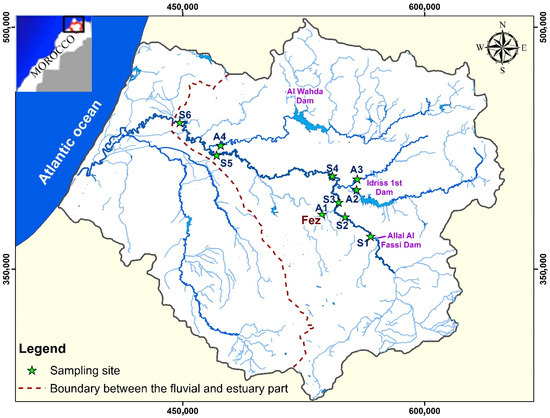
Figure 1.
The Sebou basin (northwest of Morocco) and location of the sampling stations from upstream to downstream: along the Sebou main course (from S1 to S6) and the tributaries (from A1 to A4). The red dashed line delimits the considered sub-basin at Machraa Bel Ksiri city (S6).
The annual surface water inflow of the Sebou River (5600 million m3·year−1) is very irregular in space and time. The hydrological regime depends strongly on the main tributaries’ right bank (the Lben, the Inaouen, and the Ouergha, Figure 1). Ten main dams are located in the Sebou basin, the most important one being Al Wahda, with a storage capacity of 3714 million m3 [16].
The suitable agricultural area is about 1.9 million hectares (around 20% of the national potential). The principal crops concern cereals, vegetables, cane sugar, sugar beet, oleaginous plants, citrus, and vineyards [16]. The most important anthropogenic units are quarries, paper industries, sugar refineries, oil extraction, and tanneries.
Around 86% of domestic wastewater is discharged into the watercourse [17]. The city of Fez alone generates 40% of these discharges [1]. The main identified polluting activities are tanneries, textiles, and paper industries, which produce copper, lead, nickel, and sulfides. Liquid wastes from food processing industries (oil, sugar, dairy products, etc.) generate biological inhibition in the aquatic ecosystem due to the high level of organic matter concentration [1]. During the periods of those liquid discharges, dam releases are carried out to dilute the pollutant load in order to improve the water quality of the Sebou River.
2.2. Sampling and Pre-Treatment of Samples
Four spatial sampling campaigns were carried out in 2018 and 2019 during contrasted hydrological periods and seasons (March 2018: high flow; July 2018, April 2019, July 2019: low flow, where the discharge during these four campaigns at the outlet station (S6) was 486.53, 50.1, 5.2, and 24.1 m3·s−1, respectively).
Surface sediments (0–5 cm) were taken from 10 stations on the Sebou River (code S) and its tributaries (Fez, Innaouen, Lben, and Ouergha) (code A, Figure 1). These stations were selected in order to survey the main water course of the Sebou River (from upstream to downstream), and the changes occurring after the confluence with the tributaries. The surface sediment samples were collected from the border of the river, under water, and they were stored in polyethylene bottles. Once in the laboratory, the samples were air dried, quartered, gently disaggregated in an agate mortar, and sieved into three fractions (2000–200 µm, 200–63 µm, and ≤63 µm).
2.3. Physicochemical Treatments and Analysis
At the Laboratoire écologie fonctionnelle et environnement (Toulouse, France), a microgranulometric analysis was performed on the total fraction (≤2 mm) and the fine fraction (≤63 µm) with a Horiba LA 950 laser microgranulometer. Total concentrations of major and trace metals were measured in the fine fraction (<63 µm), after complete dissolution using the alkaline fusion method with lithium metaborate [23], with an inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (ICP-MS) at the Service d’Analyse des Roches et des Minéraux (SARM) of the Centre for Petrographic and Geochemical Research (CRPG, Nancy, France). Blanks and certified standard sediments were used following standardized and validated methods [24]. Particulate organic carbon (POC) was analyzed with a ThermoFisher Flash 2000, after an inorganic carbon removal with hydrochloric acid (HCL, 2N) on a hot plate (60 °C).
2.4. Enrichment Level Assessment
The assessment of trace metal concentrations in sediments is necessary, but it is not a sufficient way to identify the contamination level and origin [25,26]. Many authors have used the enrichment factor, Equation (1) [26], as an indicator of the anthropogenic contribution of trace metal concentrations [5,27,28].
where (X/R)Sample and (X/R)Background are the ratios between the concentrations of the trace metal and the normalizing element in the sample and in the reference material, respectively.
EF = (X/R)Sample/(X/R)Background
In this study, aluminum (Al) was selected as the normalizing element because it is a rather conservative element and a major constituent of clay minerals and exhibits a very significant correlation with most of the trace metals [29]. UCC is used worldwide as a reference material, but it may lead to misinterpretation because of regional bedrock particularities [5]. Considering the absence of the local reference material for the Sebou basin, we used the bedrock composition of the close Tafna basin (northwest Algeria, [14]).
Five levels of trace metal enrichment in sediments can be defined [30]: 0 to 2: deficiency to low; 2 to 5: moderate enrichment; 5 to 20: significant enrichment; 20 to 40: very rich enrichment; ≥40: extremely high enrichment.
2.5. Data Treatement
Data treatment was carried out using Excel (2010) and SPSS statistic 21 software (SPSS, IBM, International Business Machines Corporation, New-York, NY, USA). The maps were generated using ArcMap 10.2.2 (ESRI, International Business Machines Corporation, Redlands, CA, USA). The data used for the principal component analysis were centered and reduced by SPSS software.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sediment Texture and Elemental Composition
Particle size analysis of the total fraction (≤2 mm) showed that 76% of the measured samples contained more than 57% of the fine fraction ≤63 µm (fine silts, coarse silts, and clays). This fraction (≤63 µm) was dominated by fine silts with mean values of 70% and 61% during the spring and summer periods, respectively. The particulate organic carbon (POC) in the sediments was low (0.9%), with no variation between seasons. No relationship was found between POC and the sediment texture, or with major and trace metals, except for Pb (avoiding two outliers: r = 0.79, n = 32, p < 0.05).
The analytical results show that Si, Al, Fe, Ca, Mg, K, and Na constituted more than 75% of the geochemical composition of the sediments. This is consistent with the Sebou basin lithology, which is essentially composed of carbonates and marl rocks characterized by a dominance of limestone and aluminosilicates.
The order of abundance of trace metals in sediments was Zn > Cr > Cu > Ni > Pb > Co > As > Cd (Figure 2). The mean trace metal contents of the Sebou sediments were compared to other rivers flowing through carbonate basins [31]. Concentrations in the Sebou basin were higher than those observed in the North African Tafna basin (northeast Algeria, [14]) except for Pb, but they were lower, for example, than those observed in the Upper Pearl River basin (China, [32]). The standard deviation indicates a higher dispersion of concentrations for Zn, Cr, and Pb. The highest average concentrations for Cd, Cu, Cr, Zn, and Pb were found at S3, for As at S1, for Ni at A1, and for Co at A3 and A4 stations (Figure 2).
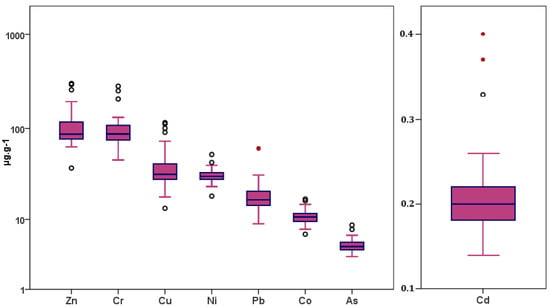
Figure 2.
Box plot of the TE concentrations in bottom sediments from the Sebou basin. Notice that concentrations are expressed in log, except for Cd.
3.2. Enrichment Factor (EF)
The EF showed that 70% of the samples were naturally enriched in trace metals (EF ≤ 1.5, deficiency to low), especially As and Ni, as well as Cd and Pb, if we exclude some stations (Figure 3). Even for some elements, the EF was lower than one, indicating a natural enrichment of the sediments compared to the Tafna bedrock.
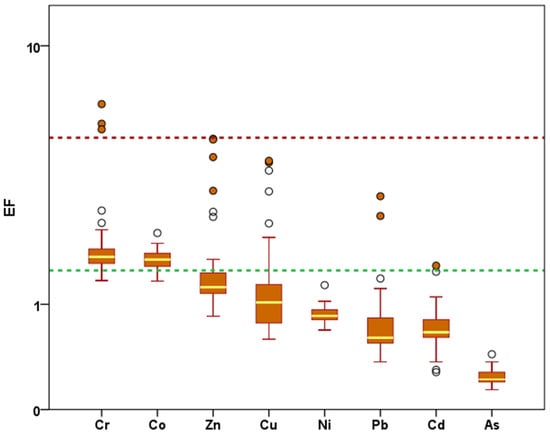
Figure 3.
Enrichment factor of trace metals in sediments from the Sebou basin normalized to the Tafna bedrock [29]. The upper outliers (above 1.5) are for stations S3, S4, and A1. Mostly the orange circles indicate the Fez station (S3). The dashed green and red lines indicate the EF values of 1.5 and 5, respectively.
The highest EF values of Zn, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn were observed at site S3 (Figure 3). High enrichment was also observed at station A1 for Zn, Cu, and Pb and at S4 for Cu and Cr. The enrichment of trace metals at the S3 station might be due to the liquid discharge of Fez city, which is known to be very concentrated with these contaminants [1]. The authors of [1] mentioned very high concentrations of some major (SO4) and trace metals (Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb) due to the use of some chemicals in the manufacturing process in the tannery discharges and/or in the metal finishing facility discharges [1]. The very low pH (between 3.2 and 4.2, [1]) for effluents registered from tanneries, metal finishing facilities, and oil mills favored metal dispersion downstream. Moderate enrichment of Cr and Co was observed at almost all sampled stations, which can be related either to the presence of impurities (naturally present in the raw materials) in phosphate fertilizers, or to an overestimation regarding the chosen reference material. However, to evaluate the risk of these metals’ enrichment, it is necessary to evaluate their availability using extraction procedures [9,31].
3.3. Origin and Controlling Factors of Trace Metals
Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed on the average concentrations of trace metals and major elements, with some key parameters (clay, fine silt (FS), coarse silt (CS), and POC content) in the sediments, to identify the controlling factors (Figure 4).
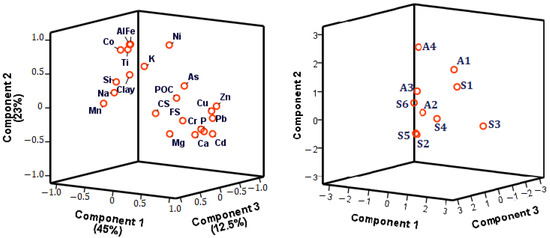
Figure 4.
Three-dimensional representation of PCA for the three main components, considering trace metals and major elements, clay, fine silt (FS), coarse silt (CS), and POC content in bottom sediments of the Sebou basin.
Three principal components were selected, which explained 80% of the total variance. The first component, accounting for 45% of the total variance, distinguished strongly positively linked trace metals that are the most anthropogenically influenced (Zn, Cr, Cu, Pb, Cd) and also P, whereas clay, K, and Mn are the opposite, indicating non-major control by clay and manganese oxides. These trace metals mostly originated from domestic wastewater and industrial discharge. Station S3 mentioned above for its contamination origin is strongly linked to this axis. It was supposed that Cr mostly originated from artisanal activity due to Fez city effluent discharge [1]. For the second component, accounting for 23% of the total variance, nickel and Co, as well as Al, Fe, and Ti, were strongly positively related to this axis, whereas Ca was the opposite. This indicates that the least anthropogenically influenced metals (Ni and Co) are mainly controlled by Al and Fe oxides. Finally, As and Ca were negatively linked to axis 3 (12.5% of the variance), where Si, Na, and CS were positively linked to this axis. This means that evaporites (from which Na mainly originates) did not control any metals, and that As has a natural origin since it is very common in the sedimentary bedrock [5,14], and it was associated with carbonate, which is the dominant bedrock in the Sebou basin.
4. Conclusions
The different tools used in this study allowed us to understand the geochemical behavior of trace metals (As, Cd, Co, Cu, Cr, Ni, Pb, and Zn) in the Sebou basin sediments in natural and anthropogenic contexts. Overall, the results obtained do not show alarming concentrations, except for Cr, Zn, and Cu at some stations, particularly the downstream Fez city. However, to assess the real risks of metal availability, it is imperative to evaluate their labile fraction.
Principal component analysis (PCA) allowed us to identify the most anthropized elements (Zn, Cr, Cu, Pb, Cd) which were linked to phosphorus, those which were less impacted by anthropic activity (Co and Ni) controlled by iron and aluminum oxides, and, finally, those with a natural origin (As) linked to carbonate (the dominant bedrock in the Sebou basin).
Author Contributions
S.E., S.H., J.-L.P. and A.P. conceived and designed the experiments; S.E., S.H., J.-L.P. and A.P. performed the experiments; S.E., A.P. and S.H. analyzed the data; S.E., S.H., J.-L.P. and A.P. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; S.E. and A.P. wrote the paper. S.H. and J.-L.P. read and approved the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the PHC-Toubkal program (N° TBK/18/69) via Campus France (N° 38944PF) as well as by a CNRS contribution in France and the Agence de l’eau Artois-Picardie (Grant N° 5745800), which supported analysis costs in the framework of the O’Sebou observatory. S.E. received financial support from PHC-Toubkal via Campus France.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request due to restrictions. The data presented in this study are available on request and under conditions from the corresponding author (A.P.). The data are not publicly available because S.E. has not yet defended her Ph.D.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the technical teams of the laboratory écologie fonctionnelle et environnement from different analytical platforms and the BIZ team for their assistance and help with physicochemical analysis and part of the sample preparation. This work is a part of the cotutelle Ph.D. (Ibn Tofail University-Toulouse INP) research of S.E. and of the PHC-Toubkal project O’Sebou. S.E. received financial support from PHC-Toubkal via Campus France, and the analysis costs were supported by the PHC project as well as by a CNRS contribution in France.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviation
| ABHS | Agence du Bassin hydraulique du Sebou |
References
- Hayzoun, H.; Garnier, C.; Durrieu, G.; Lenoble, V.; Le Poupon, C.; Angeletti, B.; Ouammou, A.; Mounier, S. Organic carbon, and major and trace element dynamic and fate in a large river subjected to poorly-regulated urban and industrial pressures (Sebou River, Morocco). Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, M.; La Cara, F.; Volpe, F.; De Mattia, A.; Serino, V.; Petitto, F.; Zavalloni, C.; Limone, F.; Pellecchia, R. Heavy metal uptake in the enological food chain. Food Chem. 2009, 117, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.W. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals both in wild and mariculture food chains in Daya Bay, South China. Estuar. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 163, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; Tueros, I.; Borja, A.; Belzunce, M.; Franco, J.; Solaun, O.; Valencia, V.; Zuazo, A. Maximum likelihood mixture estimation to determine metal background values in estuarine and coastal sediments within the European Water Framework Directive. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’guessan, Y.M.; Probst, J.-L.; Bur, T.; Probst, A. Trace elements in stream bed sediments from agricultural catchments (Gascogne region, SW France): Where do they come from? Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2939–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, M.M.C.; Silva, M.M.; da Silva, E.A.F.; Dinis, P.A.; Rocha, F. Transfer processes of potentially toxic elements (PTE) from rocks to soils and the origin of PTE in soils: A case study on the island of Santiago (Cape Verde). J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 183, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Mohan, D.; Singh, V.K.; Malik, A. Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—A tributary of the Ganges, India. J. Hydrol. 2005, 312, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G.J. Determination of sediment metal background concentrations and enrichment in marine environments—A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leleyter, L.; Probst, J.-L. A new sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace elements in river sediments. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1999, 73, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charriau, A.; Lesven, L.; Gao, Y.; Leermakers, M.; Baeyens, W.; Ouddane, B.; Billon, G. Trace metal behaviour in riverine sediments: Role of organic matter and sulfides. J. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, J.; Rosas, H.; Solé, M.; Lao, C. Heavy metals and metalloids in sediments from the Llobregat basin, Spain. J. Environ. Geol. 2003, 44, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Hassimi, H.; Taleb, A.; Bouezmarni, M.; Karzazi, O.; Taleb, M.; Kherbeche, A.; Debbaut, V. The effect of the physicochemical conditions variations on the behavior of heavy metals trapped in polluted fluvial system sediments: The case of Oued Sebou, Morocco. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.R.A.; Andrade, E.M.; Palácio, H.A.Q.; Sales, M.M.d.; Maia, A.R.S. Influence of land use/occupation on water quality in the Trussu river valley, Ceará, Brazil. Rev. Ciênc. Agron. 2017, 48, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Benabdelkader, A.; Taleb, A.; Probst, J.-L.; Belaidi, N.; Probst, A. Anthropogenic contribution and influencing factors on metal features in fluvial sediments from a semi-arid Mediterranean river basin (Tafna River, Algeria): A multi-indices approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamhasni, N.; Chillasse, L.; Abba, H.; El Haouat, S.; El Madani, M. Typologie des eaux de surface du bassin du Sebou par multi-approche: Corrélation entre indice biologique global des réseaux de contrôle et de surveillance (IBG-RCS) et l’approche physicochimique et microbiologique. Afr. Sci. Rev. Int. Sci. Technol. 2013, 9, 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, J.-L.; Raïs, N.; Chahinian, N.; Moulin, P.; Ijjaali, M. Water quality assessment of highly polluted rivers in a semi-arid Mediterranean zone Oued Fez and Sebou River (Morocco). J. Hydrol. 2014, 510, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABHS. Inventaire du Degré de Pollution des Ressources en eau Dans le Bassin du Sebou. Mission 2: Rapport de L’inventaire du Degré de Pollution de Sebou; ABHS: Fez, Morocco, 2014; p. 174. [Google Scholar]
- De Waele, J.; Di Gregorio, F.; El Wartiti, M.; Fadli, D.; Follesa, R.; Marini, A.; Melis, M.T. Geo-environmental risk in the upper valley of the Oued Sebou (Fes, Central Morocco): A preliminary approach. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2004, 39, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukal, B.; Dominik, J.; Vignati, D.; Arpagaus, P.; Santiago, S.; Ouddane, B.; Benaabidate, L. Assessment of water quality and toxicity of polluted Rivers Fez and Sebou in the region of Fez (Morocco). J. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 131, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalami, A.E.O.; Merzouki, M.; El Hillali, O.; Maniar, S.; Koraichi, S.I. Pollution des eaux de surface de la ville de Fès au Maroc: Typologie, origine et conséquences. Larhyss J. 2011, 9, 2521–9782. [Google Scholar]
- El Gaidoumi, A.; Tanji, K.; Chaouni Benabdallah, A.; Taleb, A.; Kherbeche, A. Characterization and quantification of heavy metals in Oued Sebou sediments. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 7496576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoussi, M.; Haïda, S.; Imassi, S. Effects of the construction of dams on the water and sediment fluxes of the Moulouya and the Sebou Rivers, Morocco. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2002, 3, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzanti, E.; Andò, S.; France-Lanord, C.; Vezzoli, G.; Censi, P.; Galy, V.; Najman, Y. Mineralogical and chemical variability of fluvial sediments: 1. Bedload sand (Ganga–Brahmaputra, Bangladesh). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 299, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carignan, J.; Hild, P.; Mevelle, G.; Morel, J.; Yeghicheyan, D. Routine Analyses of Trace Elements in Geological Samples using Flow Injection and Low Pressure On-Line Liquid Chromatography Coupled to ICP-MS: A Study of Geochemical Reference Materials BR, DR-N, UB-N, AN-G and GH. J. Geostand. Newsletter 2001, 25, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, N.; Yao, M. Normalisation and heavy metal contamination in mangrove sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 216, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, R.; Stoner, J. Pb in particulates from the lower atmosphere of the eastern Atlantic. J. Nat. 1973, 245, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounouira, H.; Embarch, K.; Amsil, H.; Bounakhla, M.; Foudeil, S.; Benyaich, F.; Haddad, M.; Said, F. Study of heavy metal assessment in the Gharb plain along Sebou river (Morocco) using k0-NAA method at the Moroccan Triga Mark II research reactor. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2018, 16, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; de Caritat, P. Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: Regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 337, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussiez, V.; Ludwig, W.; Probst, J.-L.; Monaco, A.J.E.P. Background levels of heavy metals in surficial sediments of the Gulf of Lions (NW Mediterranean): An approach based on 133Cs normalization and lead isotope measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 138, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, R. Depth variation in copper, lead, and zinc concentrations and mass enrichment ratios in soils of an urban watershed. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mrissani, S.; Haida, S.; Probst, J.-L.; Probst, A. Multi-Indices Assessement of Origin and Controlling Factors of Trace Metals in River Sediments from a Semi-Arid Carbonated Basin (the Sebou Basin, Morocco). Water 2021, 13, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wu, W.; Nel, W.; Ji, J. The behavior of metals/metalloids during natural weathering: A systematic study of the mono-lithological watersheds in the upper Pearl River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).