Abstract
The study presents results of the research project ASPIRE (atmospheric parameters affecting spectral solar irradiance and solar energy). A new dataset has been created for Athens, Greece, for one year (December 2020–November 2021), consisting of detailed measurements of spectral solar irradiance (SSI) from 300 to 1020 nm and its influencing parameters (clouds, aerosols, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, water vapor). The new dataset is explored, and major results are presented. The datasets are available to scientists from interdisciplinary scientific communities for research and education purposes. Here, we present an overview of different studies within ASPIRE, dealing with effects of different aerosol types on solar measurements and PV-related outputs and also the evaluation of a nowcasting solar model under different atmospheric conditions.
1. Introduction
While the solar radiation reaching the top of the Earth’s atmosphere is relatively constant, the radiation at a certain location at the Earth’s surface varies significantly due to: (i) solar elevation (related to the location coordinates and height above sea level) and (ii) atmospheric effects, including local atmospheric variations related to cloud reflectance and attenuation, absorption and scattering from aerosols, water vapor and absorbing trace gases. Assessing the impact of all the above parameters on the total solar radiation measured at the ground level is a complex procedure. The source of this complexity is the fact that the mentioned atmospheric parameters have different effects on different parts of the solar spectrum and different efficiencies for different solar elevations because of changes in the path of photons through, for example, clouds, aerosols, trace gases, etc., that are linked with the solar (zenith) incident angle.
The ASPIRE project had four specific objectives: (a) to investigate the effects of atmospheric composition (clouds, aerosols, water vapor, trace gases) in different solar spectral regions of the solar radiation reaching the surface; (b) to assess the impact of atmospheric composition on ultraviolet index (UVI), the effective doses for the production of vitamin D in human skin (hereinafter vitamin D dose) and photosynthetically active radiation (PAR); (c) to estimate the efficiency of different photovoltaic (PV) materials based on spectral solar irradiance measurements for various atmospheric composition cases; (d) and to evaluate the performance of the solar energy nowcasting system (SENSE) using measured solar spectra. In this study, we describe the solar radiation data collected during the 12-month experimental campaign of the ASPIRE project and present results from objectives (c) and (d). The results presented for objective (c) are for August 2021 while the results presented for objective (d) are for measurements from the entire campaign.
2. Experimental Campaign Data
A 12-month intensive measurement experimental campaign was carried out in Athens from December 2020 to November 2021 in order to investigate all possible atmospheric parameters that affect the spectral solar Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI) and Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI). Athens provides a variety of such parameters, as in the city’s atmosphere, we can find a diversity of aerosol types (urban local pollution, transported dust, marine aerosols, biomass burning) and their mixtures that are frequently recorded. Also, the total ozone column (TOC) in Athens is representative for mid-latitudes [1] and in some cases, it can be influenced by changes in the tropospheric ozone [2]. Water vapor and clouds can vary significantly during the year and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) concentrations can be from zero to relatively high for European cities’ levels. At the same time, the SENSE pilot system simulated GHI and DNI real-time measurements and archived SENSE energy output products together with model inputs (cloud properties, aerosol properties, trace gases, water vapor). Numerous state-of-the-art instruments were employed in the campaign, as summarized in Table 1, together with their measurement capabilities.

Table 1.
Instruments used in the ASPIRE experimental campaign.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solar Radiation Doses under High-Aerosol Conditions
In August 2021, significant wildfires took place in northern Euboea, Peloponnese and Attica. Very high aerosol concentrations were measured in the Greater Area of Athens (GAA) based on Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Level 1.5 data from AERONET (Figure 1).
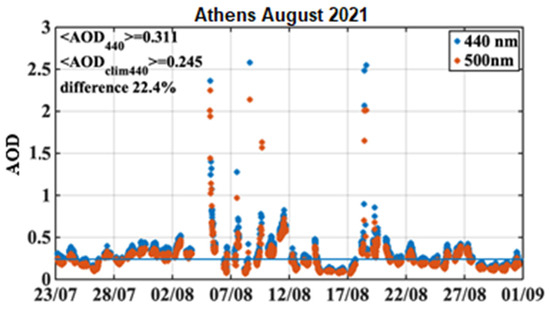
Figure 1.
Time series of AOD at 440 nm and 500 nm in August 2021 from AERONET Level 1.5 data. Mean AOD at 440 nm in August 2021 was 0.311 while AOD at 440 nm from climatology is 0.245.
Recent findings, based on ASPIRE campaign data, showed that smoke and dust aerosols during August 2021 led to reductions in UVI in Athens by up to 53%, in vitamin D dose by up to 50%, in PAR up to 21% and in GHI up to 17%, with potential implications for health, agriculture and energy [3]. The above results indicate that solar radiation biological doses, e.g., UV index, vitamin D and PAR, can be significantly affected by high-aerosol loads in sun-rich countries like Greece even in the summer months.
The available GHI was less affected relative to other radiometric quantities, but its reduction can be significant for solar energy production systems, such as PVs. In view of the GHI reduction of up to 17% in the GAA during August 2021 [3], we have estimated the efficiency of different PV materials based on spectral solar irradiance measurements for different aerosol conditions. More specifically, we have analyzed measurements from two days: an aerosol-free day (16 August) and a day with very high aerosol load from smoke (18 August). The results are presented in the following section.
3.2. Efficiency of Different PV Materials
The performance of PV cells and systems is known to be highly dependent on the spectral distribution of the incident solar irradiance and, therefore, the parameters that affect it. Precise solar spectral irradiance (SSI) measurements in the spectral range 300–1014 nm (W/m2/nm) were conducted by a precision spectroradiometer (PSR) (Table 1) in order to achieve a better understanding of the influence of the spectral variations of the incident solar irradiance on the performance of PV modules for some cases under clear-sky (cloudless) conditions from the ASPIRE campaign.
The spectral sensitivity of each PV module is different and depends highly on the semiconductor material used. The optimum absorption of the two technologies under study, gallium arsenide (GaAs) and cadmium telluride (CdTe), is mainly observed in the visible area of the spectrum. GaAs is sensitive to a wider spectral area, while both technologies experience their maximum absorption at approximately 800 nm, where the intensity of the SSI is lower (Figure 2).
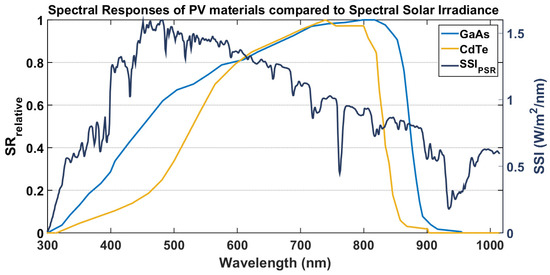
Figure 2.
The relative spectral response of GaAs and CdTe (left y-axis), compared to a reference spectrum derived from PSR under clear-sky conditions (right y-axis).
The spectral responses, SR (A W−1), of the two aforementioned technologies (GaAs, and CdTe) were considered in order to observe their performance under aerosol-free (e.g., 16 August 2021) and high-AOD conditions (e.g., 18 August 2021) when the air quality over the city of Athens was burdened by wildfires that occurred in the surrounding areas [3]. Their performance was calculated using Equation (1) and is illustrated in Figure 3. The relative difference between the two technologies for the two cases was calculated using Equation (2) and is shown in the same figure (right y-axis):
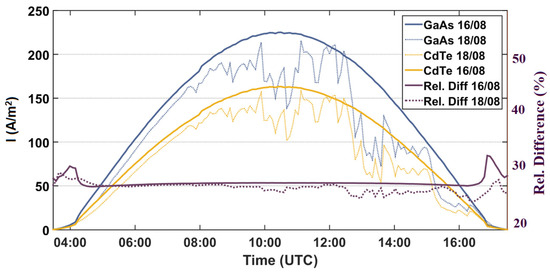
Figure 3.
The performance of the two technologies (GaAs and CdTe) during 16 August 2021 (low-aerosol load) and 18 August 2021 (high-AOD, smoke). The right y-axis shows the relative differences between GaAs and CdTe PV performance during the daytime.
In the case of low AOD (16 August), the difference between the performance of the under-study technologies remains stable during the day, at approximately 27%, whereas the presence of smoke in the atmosphere (18 August) decreases both technologies’ performance. The decrease is larger for GaAs (by 3–4% relative to CdTe) after ~9:00 UTC, following the increase in AOD (as recorded by AERONET). This can be explained by its higher sensitivity at shorter wavelengths (Figure 2) and more specifically between 300 nm and 500 nm, where the effect of smoke aerosols is stronger.
3.3. Evaluation of the Solar Energy Nowcasting System (SENSE)
SENSE is an advanced operational system designed to deliver up-to-the-minute nowcasting of GHI and DNI for Europe and North Africa. Operating at a spatial resolution of approximately 5 km, SENSE utilizes sophisticated radiative transfer model calculations. By considering the sun’s precise position and integrating the aerosol forecast obtained from the Copernicus Atmospheric Service (CAMS), which provides AOD forecasts at 550 nm every 3 h, SENSE generates estimations of GHI and DNI under clear-sky conditions. Complementary variables such as Ångström Exponent, Precipitable Water Vapor (PWV) and Single Scattering Albedo (SSA) are derived from local climatology records. Additionally, SENSE promptly retrieves cloud information from the SEVIRI (Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager) instrument onboard MSG (Meteosat Second Generation) satellites, every 15 min. To extract cloud optical thickness from these data, a cloud modification factor (CMF) is applied to refine its clear sky estimates [4].
During the ASPIRE campaign, SENSE was especially tailored to produce spectral irradiance and specific spectral integrals of GHI and DNI corresponding to the ASNOA station’s closest grid point, ensuring compatibility with the spectral regions recorded by PSR and broadband instruments. More specifically, GHI Tot refers to the GHI integral at 285–2800 nm, DNI Tot refers to 200 to 4000 nm, GHI PSR and DNI PSR refer to 300–1020 nm and GHI Vis (from PSR spectral measurements) refers to 400–700 nm. A scatterplot of all SENSE estimations against the corresponding measured data is shown in Figure 4. GHI Tot is particularly compared with the average of ±3 min around the SENSE time, DNI Tot is compared at the exact time of SENSE and those extracted from PSR data are compared with the closest PSR measurement if there is one in the ±3 min range. As expected, GHI has better agreement than DNI. This is explained by the higher attenuation of DNI by aerosols and especially clouds, which results in the largest error propagation when forecasts/satellite images deviate from real-cloud conditions.
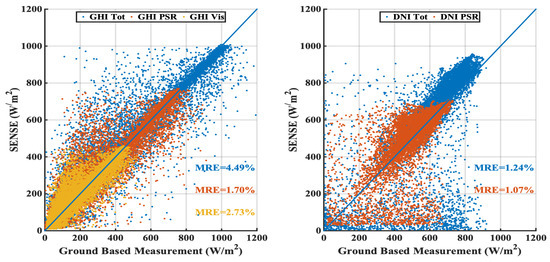
Figure 4.
SENSE nowcasting estimations of GHI (left) and DNI (right) at different spectral regions against ground-based measurements of the same variables, for the whole duration of the ASPIRE campaign. Mean relative error (MRE) is also shown as percentage.
GHI Vis has the best agreement due to the fact that CAMS AOD is in this region (550 nm), resulting in a more accurate simulation via SENSE. The general performance of SENSE is sufficient, considering the limitations of available input data. A comparison over longer periods provides even better statistics, which could be adequate for the evaluation of the system to be used for many applications. Point-by-point comparisons are the ones most affected by the variability of the clouds and the fact that AOD input data are provided on a 3 h timescale. The integration of GHI and DNI components from instantaneous to hourly and daily values improves the statistics as cloud variability effects are smoothed out.
4. Conclusions
We have assessed the impact of aerosols on solar irradiance and solar energy in Athens, Greece, using the ASPIRE dataset. Our main findings can be summarized as follows:
- Combined smoke and dust events significantly affect air quality and solar irradiance in Greece. Biologically effective doses (e.g., UVI, vitamin D, PAR) can be significantly affected by high loads of aerosol even in sun-rich countries like Greece, even in the summer months.
- PV performance estimation shows a strong dependence on atmospheric parameters such as aerosol amounts. The materials used play an essential role, and considering the high variability of the outdoor conditions, especially in countries like Greece, where dust events and wildfires occur, could cause a considerable deviation of the predicted power generation from large-scale installations.
- SENSE performs at satisfactory levels, with low mean relative differences for both GHI and DNI. DNI estimations are more difficult than GHI, due to the higher influence of aerosols and clouds. The best SENSE performance is observed in the visible spectral range, where the input data are more detailed.
Data from the project ASPIRE are available to scientists and end users from interdisciplinary scientific communities (energy, health, agriculture, biology, marine sciences, atmospheric chemistry) for research and education purposes and can be accessed through the project’s website https://aspire.geol.uoa.gr (accessed on 18 August 2023).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.E. and S.K.; methodology, K.E., S.K., I.-P.R. and D.K.; software, I.-P.R., D.K., I.F., C.B. and K.P.; validation, I.-P.R., D.K., I.F. and K.P.; formal analysis, I.-P.R. and D.K.; investigation, K.E., S.K., I.-P.R., I.F. and D.K; resources, K.E., S.K., B.E.P., D.F., A.K. and A.R.; data curation, I.-P.R., D.K., C.B., B.E.P., D.F., A.K. and A.R.; writing—original draft preparation, K.E., I.-P.R. and D.K.; writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, I.-P.R. and D.K.; supervision, K.E. and S.K.; project administration, K.E.; funding acquisition, K.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research work was funded by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (H.F.R.I.) under the “First Call for H.F.R.I. Research Projects to support Faculty members and Researchers and the procurement of high-cost research equipment grant” (Atmospheric parameters affecting spectral solar irradiance and solar energy (ASPIRE), project number 300).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
Klaus Gierens from DLR-IPA for the provision of satellite cloud data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Eleftheratos, K.; Kouklaki, D.; Zerefos, C. Sixteen Years of Measurements of Ozone over Athens, Greece with a Brewer Spectrophotometer. Oxygen 2021, 1, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerefos, C.S.; Kourtidis, K.A.; Balis, D.; Bais, A.; Calpini, B. Photochemical Activity Over the Eastern Mediterranean Under Variable Environmental Conditions. Phys. Chem. Earth (C) 2001, 26, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoom, A.; Fountoulakis, I.; Kazadzis, S.; Raptis, I.-P.; Kampouri, A.; Psiloglou, B.; Kouklaki, D.; Papachristopoulou, K.; Marinou, E.; Solomos, S.; et al. Investigation of the effects of the Greek extreme wildfires of August 2021 on air quality and spectral solar irradiance. EGUsphere 2023. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Kazadzis, S.; Taylor, M.; Raptis, P.I.; Keramitsoglou, I.; Kiranoudis, C.; Bais, A.F. Assessment of surface solar irradiance derived from real-time modelling techniques and verification with ground-based measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).