Abstract
This work aimed to develop a parameterized, two-dimensional field model of a switched reluctance motor (SRM). The main task of the developed model was to calculate the value of the electromagnetic torque for various positions of the rotor. Based on these calculations, the characteristics of the electromagnetic torque were determined depending on the position of the rotor angle φ for the current function I (T = f (φ, I)). Using the model, it was possible to additionally observe the phenomena occurring in the motor winding, e.g., distributions, isolines of magnetic potential, induction, and to calculate the values of the temperature. The parameterized structural elements that made up the entire model can be freely changed and, thus, the results for various structures can be obtained. Thanks to this, it was possible to evaluate and compare motor of different designs. To validate the model, measurements were conducted on real-scale reluctance motors, and families of electromagnetic torque characteristics were obtained for various design cases. The results received from the tested motors were juxtaposed with simulation results procured via the model. Based on this comparison, it was possible to determine the accuracy of the model’s operation.
Keywords:
reluctance motor; FEM; motor modelling; electric motor; Ansys Motor-CAD; versatile; validation 1. Introduction
The switched reluctance motor (SRM) can be considered one of the simplest electric motors. This motor consists of a stator and a rotor made of a package of electromagnetic sheets with prominent poles distributed around the circumference. The number of stator and rotor poles is even and different from each other (except for single-phase motors). On the opposite poles of the stator, there are coils connected to each other, which form an independent circuit called the phase band. SRM motors are characterized by a simple structure and the necessity to use a control system for the correct operation of the device. The advantages and disadvantages (features) of SRM motors are presented below:
- Low production cost;
- High durability and reliability of work;
- Encouraging heat dissipation properties (most heat is generated in the stator);
- Resistance to high temperatures;
- Low power losses generated by the rotor;
- Wide range of rotation speed regulation;
- Large ripple of torque;
- High acoustic noise and vibrations; and
- High costs related to the control system.
Switched reluctance motors, thanks to their advantages, are increasingly used in machines and devices. They are most common in solutions used for ventilation, household appliances, fans, pumps, washing machines, vacuum cleaners, blowers, dryers, etc. Additionally, it is worth mentioning a few strictly industrial applications for those motors: mining machine drives, mill drives, forklift drives, and air conditioning equipment drives. With the further development of science and technology, SRM motors can be used in the maritime industry as linear drives, as well as displacing and replacing induction motors used in machines and devices. Some of the chosen applications for SRM motors are shown in Figure 1 below.

Figure 1.
Applications employing switched reluctance motors: (a) Dyson DC31 [1]; (b) reluctance motor with its control system, hand dryer by Hishine [2].
With the further development of science and technology, SRM motors can be used in the maritime industry as linear drives, as well as a replacement for induction motors used in machines and devices. As was indicated, the SRM electrical motors are viable solutions for a vast number of applications. Therefore, it is worth conducting research that is aimed at developing better and more efficient SRM motors. The approach taken by our team concerned mostly the modelling and FEM simulation works with proper validation concerning those devices. The main task of the developed model was to calculate the value of the electromagnetic torque for various positions of the rotor. Based on these calculations, the characteristics of the electromagnetic torque were determined depending on the position of the rotor angle φ for the current function I (T = f (φ, I)). Using the model, it was possible to additionally observe the phenomena occurring in the motor winding, e.g., distributions, isolines of magnetic potential, induction, and the temperature on different elements, and to calculate the value of the magnetic flux. The model’s advantages and novelties can be highlighted by the bullet list presented below.
- It is fully customizable. There is a vast number of elements that can be changed in order to examine different scenarios.
- It has a versatile tool for checking the motor measurement results and also to improve and optimize various types of motor designs.
- The didactic feature can be used to observe the distribution of the magnetic flux isolines, the intensity of the magnetic field, or the distribution of the potential in the motor for different variants.
- It is more accurate than analytical calculations; moreover, it is possible to observe the shape of the modelled motor and phenomena occurring during the analysis.
- It can be validated by experimental results derived during work with real-scale SRM motors.
2. State of the Art
Permanent magnet DC electric machines are currently used in most electric vehicle and robotics’ applications. Due to the declining resources of the rare earth metals, the need to implement alternative solutions is significant. Reluctance machines can become the best alternative to permanent magnet motors. The importance of the development of electrical reluctance machines is evidenced by many publications [3]. In robotics, electromobility and space technology, due to the constant output power, good temperature management, and resistance to damage, can find a desirable application. Moreover, SRM has the advantages of low weight, high efficiency, small size, low cost, and high torque at low velocities. Many precise and high-resolution sensorless rotor position estimation techniques have been published in the past literature for switched reluctance motor (SRM) drives. This paper presents a simplified, coarse rotor position estimation method suitable for a low-cost SRM drive such as water pumps, washing machines, and electric vehicles. The proposed method is applicable where speed control is achieved by PWM or hysteresis current controller. This method utilizes flux-linkage characteristics of the motor to estimate rotor position. It requires information about the magnetic curve only at one rotor position instead of the entire magnetic characteristics of the motor. The simulation results for the sensorless SRM drive validate the feasibility of the proposed method [4].
In publication [5], the authors presented a novel simulation approach to analyze the performance of an in-wheel SRM with two separate models of the SRM system dedicated to an electric vehicle. A reactive load diagram for simulating the SRM drive is provided with two separate models of the SRM system and the vehicle system. The presented diagram can be used to analyze the performance of any electric machine. The authors [6] presented an interesting and insightful work on velocity estimation. Compensated torque and electromechanical differential equations were used. The software in the form of the MATLAB/SIMULINK programs was used. In another paper [7], the authors compared the performance of the SRM with different combinations of poles/slots and the number of flux barriers, proposed an SRM topology with 4-pole/36-slot combinations, and distributed windings and a three-layer flux barrier. Then, an oblique rotor with flow asymmetry barriers and flat tips was used. In addition, the Taguchi method, the differential evolution algorithm, and Pareto evaluation were integrated to implement multi-criteria optimization of the sequence subspace, yielding the proposed SRM design scheme. It is worth mentioning that the control systems for reluctance machines are developing very dynamically at the same time.
Many researchers [8] built a multi-level converter topology for a switched reluctance motor (SRM) drive. SRM has the advantages of a simple structure, high reliability, high fault tolerance, and low production cost. However, large torque fluctuations, vibration during operation, and acoustic noise are the main disadvantages of the SRM. The proposed theory of the multi-level converter for the five-phase SRM drive overcomes these disadvantages and turns them into advantages such as high torque range, low torque ripple, and vibration-free response with flexible speed control. The article presents the theory of operation and simulation results of a five-phase multilevel converter for a SRM drive [9,10,11]. As a result, as the number of phases increases, the performance of the system increases, too, but without increasing the number of switches. The comparison is presented on the basis of the torque characteristics of the motor supplied from the proposed converter and the asymmetric half-bridge converter for various conditions. This analysis concludes that the proposed converter topology has advantages over the conventional converter topology, especially for high-speed responses [12,13,14]. For the optimal design of a Synchronous Reluctance Motor (SynRM), the rotor topology and the selection of multiple design variables remain a significant challenge. Basically, the SynRM rotor is designed in the axial or radial direction only, and the design variables are reduced based on experience; however, the above process is time consuming [15,16,17]. Hence, the authors of this publication believe that the approach to designing the structure of electromechanical electric machines should be expressed through a multispectral approach using the latest computer tools. As already mentioned, the decreasing amount of rare earth metals causes the development of the structure, and the standard approach is time consuming and cost consuming and increases the consumption of materials. Many publications cited by the authors of this publication are valuable; but it is worth noting how our team approached the construction of electric machines in a different way. Of course, this procedure can be scaled in terms of motor power and types.
3. Theoretical Part
3.1. The Principle of Torque Generation in SRM Motors
The mechanism for generating torque in switched reluctance motors is based on the fact that when the winding of a given phase band is energized (current flows through it), the rotor ought to take the position in which the main magnetic circuit of the motor has the lowest reluctance [18]. The lowest reluctance occurs when the poles of the stator and the poles of the rotor are in the coaxial position. The torque produced in this way is called the reluctance torque. In short, it can be described that the rotor (the pair of rotor poles) in the SRM motor, being in a misalignment position with the stator poles, will turn to the energized pair of stator poles, obtaining the coaxiality of the poles because the flux reluctance is then the smallest (iron has a much lower reluctance than air). The described principle is shown in Figure 2 below.

Figure 2.
Movement of the rotor during SRM motor operation: (a) While energizing the phase band, the rotor will move by the angle φ aiming at the coaxial position; (b) rotor position after moving by the angle φ.
3.2. Design Solutions for SRM Motors
The basic parameters characterizing switched reluctance motors (in addition to construction dimensions such as stator or rotor diameters, motor length, or pole dimensions) are:
- Number of stator poles, Ns;
- Number of rotor poles, Nr; and
- Number of stator winding bands, m.
Due to the optimal design of the drive, the most frequently constructed motors are motors with an even number of stator and rotor poles, of which the energized poles of the stator and rotor are opposite. Depending on the number of supplied pole pairs (phase bands), we can divide these motors into groups, described below.
3.2.1. Single-Phase Reluctance Motors
Single-phase motors are characterized by a simple structure and the ability to obtain high rotational speeds [19,20,21,22]. Their biggest disadvantage is the difficulty of starting up, as well as the possibility of the rotor turning in the wrong direction than intended. One solution to these problems is to use a magnet. The magnet positions the rotor in such a way that, while starting, the motor will generate torque in the required direction. This solution can be used when the load on the shaft is small: The magnetic field of the magnet will pull the rotor to the correct position despite the load. The magnetic field of the magnet does not affect the motor during operation. Another way is to use a special type of motor design. Exemplary cross-sections of single-phase motors are shown in Figure 3 below.
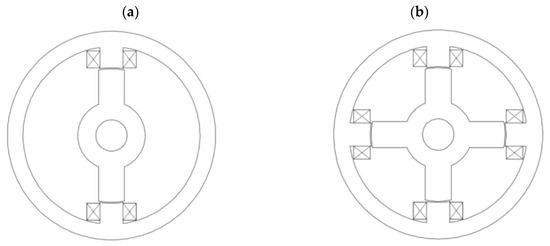
Figure 3.
Exemplary cross-sections of different single-phase reluctance motor types: (a) 2/2; (b) 4/4, number of pole pairs per phase p = 2.
3.2.2. Two-Phase Reluctance Motors
Two-phase reluctance motors have two-phase bands, which make the rotor rotate by appropriate band switching. Those have better speed control than single-phase models and a more complex control system. Problems can arise in this design, as in single-phase motors with engine start, while the stator and rotor poles are coaxial. As for single-phase motors, a magnet can be used for starting. Various types of special construction motors are also used, e.g., the use of rotor or stator asymmetry [23,24,25].
3.2.3. Three-Phase Reluctance Motors
The greatest advantage of three-phase SRM motors compared to single- and two-phase motors is the ease of starting (the motor will start regardless of the initial rotor position) and the ease of changing the rotation direction of the rotor [26,27,28,29]. Additionally, the torque ripple on the motor shaft is smaller due to the greater number of switched bands. The following shows a three-phase (12/8) switched reluctance motor with two pairs of poles for each phase, p = 2. Two pairs of stator poles are supplied as one string. The operation of the SRM motor with two pole pairs per phase is shown in Figure 4 below.

Figure 4.
Movement of the rotor during 12/8 SRM motor operation: (a) While energizing the phase band, the rotor will move by the angle φ aiming at the coaxial position; (b) rotor position after moving by the angle φ.
3.2.4. Multi-Phase Reluctance Motors
Four-phase and five-phase motors, as well as those with a greater number of phases due to a more complicated control system (more switching of individual phase bands per revolution), develop lower rotational speeds. At the same time, due to the greater number of switched bands, they have an even characteristic of the electromagnetic torque and lower ripple. Examples of cross-sections of four- and five-phase engines are shown in Figure 5 below.
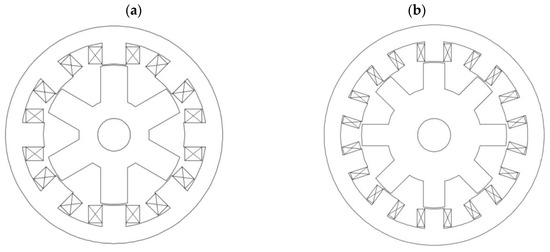
Figure 5.
Exemplary cross-sections of different multi-phase reluctance motor types: (a) four-phase, 8/6; (b) five-phase, 5/8.
3.3. Control Methods of SRM Motors
Appropriate control enables the motor to operate in a wide range of rotational speed regulations. For this purpose, there are three basic ways of controlling the SRM motor:
- Current control;
- Voltage control;
- Single-pulse control; and
- Direct torque control (theoretically the most difficult control method).
Depending on the control method, the motor obtains various parameters. Figure 6 presents the mechanical characteristics of the SRM engine divided into zones depending on the control method.
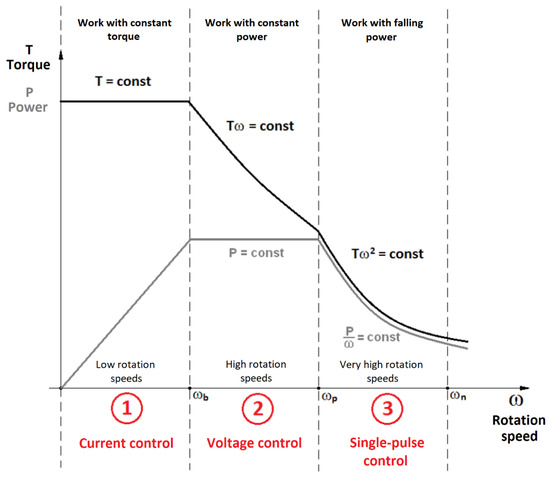
Figure 6.
Simplified mechanical characteristics of the SRM motor with marked properties: scope of work and control system.
3.3.1. The Operation Principle of the SRM Motor with the Control System
A switched reluctance motor needs an appropriate control system to function properly. An exemplary block diagram of an SRM motor is shown in Figure 7 below.

Figure 7.
Block diagram of the proposed SRM drive.
A classical SRM drive consists of three essential elements:
- The angular position sensor of the shaft, e.g., encoder, resolver, or non-contact sensor, that determines the angular position of the shaft/rotor and transmits it to the control system;
- The control system, an electronic system that receives signals from the transducer/angular position sensor that controls the power converter; and
- The power converter, an electronic commutator that switches on the individual phase bands, causing the motor to be in constant motion. The schematic diagram of the converter for one phase band is shown in Figure 8.
 Figure 8. A power converter for controlling one phase band, where Vdc is the DC voltage source, T1 and T2 are the transistors connected by the control circuit, D1 and D2 are the diodes, and L is the motor phase band.
Figure 8. A power converter for controlling one phase band, where Vdc is the DC voltage source, T1 and T2 are the transistors connected by the control circuit, D1 and D2 are the diodes, and L is the motor phase band.
The windings marked in the Figure 9 on the diagram (marked with the letter L) are a simplification of one phase band in the motor, that is, two windings on opposite poles (on the A1 pole and A2 pole) connected in series with the lead and the end.
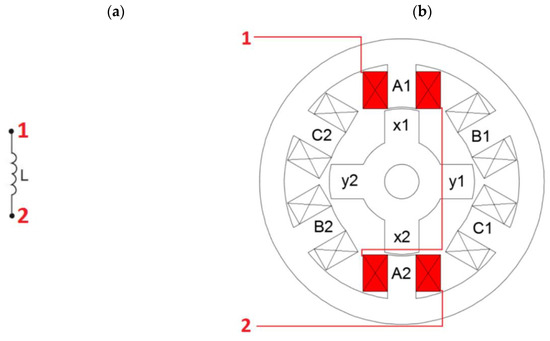
Figure 9.
Simple schematic showing switched reluctance motor winding: (a) Symbol of winding, L. (b) A simplified diagram of the phase winding of an SRM motor.
A single motor cycle for one of the phase bands consists of four stages. Those stages are described in Table 1 below.

Table 1.
A single motor cycle for single-phase band with description.
3.3.2. Current Control: Constant Torque Operation
In this operating range, the motor obtains high torque values and low rotational velocities. Due to the low velocities, the duration of one phase band switching cycle is relatively long. The current value must be limited to the load capacity of the phase windings. The current is limited by current regulators (e.g., hysteresis regulators). When such a regulator is used, the current in the phase winding changes between the Imax and Imin levels: When Imax is reached, the system disconnects the current. While at Imin, the system turns on the power and, thus, the current has a fixed value (with a hysteresis deviation). An example of the current, inductance, and voltage waveforms for current control as a function of the position of the rotor rotation angle concerning the stator is shown in Figure 10 below.

Figure 10.
Current control. The waveform of current i, voltage U (PWM), and Phase inductance L of the SRM motor as a function of the position of the angle of the rotor poles in relation to the stator poles φ [30].
3.3.3. Voltage Control: Constant Power Operation
In this operating range, the motor obtains average torque values and high rotational velocities. The voltage control is based on the adjustment of the duty cycle (width) of the PWM (Pulse-width modulation) voltage supplying the winding of a given phase. An example of the current, inductance, and voltage waveforms with current control as a function of the position of the rotor rotation angle with respect to the stator is shown in Figure 11.

Figure 11.
Voltage control. The waveform of current i, voltage U (PWM), and Phase inductance L of the SRM motor as a function of the position of the angle of the rotor poles in relation to the stator poles φ [30].
3.3.4. One-Pulse Control: Operation with Falling Power
When the duty cycle of the PWM voltage signal is k = 1 (at ωp speed), the motor works in the range of single-pulse control. In this range, the torque (and, hence, the power) drops sharply with increasing rotational speed. The speed is regulated by changing the value of the control angles θon and θoff. An example of the current, inductance, and voltage waveforms in single-pulse control as a function of the position of the rotor rotation angle concerning the stator is shown in Figure 12.

Figure 12.
One-pulse control. The waveform of current i, voltage U (PWM), and Phase inductance L of the SRM motor as a function of the position of the angle of the rotor poles in relation to the stator poles φ [30].
4. Simulation Part
Nowadays, with the developing computer technology, i.e., due to computers with more and more computing power and more complex specialized computer programs, it is possible to carry out complex calculations related to materials and machines [8,9,10]. This technology allows, among others, the development of designs and models of electrical machines by performing special calculations. It aids scientists to determine the parameters and properties of those devices [11,12,13,14]. The biggest advantage of creating electric machines’ field models is the ability to determine the properties of the machine without actually having to construct it. Due to this, it is possible to obtain data and check whether it will meet the established assumptions and properties. If the results would be unsatisfactory, the changes and improvements can be implemented to the model until the desired results are met [15,16,17,18]. Covering this solution, a project that meets the assumptions and conditions is obtained. Modeling also has disadvantages [19,20,21,22,23]. Despite the increasingly accurate and sophisticated model development programs, the inaccuracy of the results obtained from the model is greater than the inaccuracy of the results obtained while measuring parameters’ values on the real machines (errors related to the results are small, but will almost always be less accurate than those made by measuring the parameters on real-scale electric machine) [24,25,26]. This is related to the inaccuracy of recreating the real model (all phenomena occurring in reality, as well as the actual structure of the motor) [27,28,29,30]. The data from the models can be verified by comparison with the results obtained during the testing of real motors; in this way, errors can be eliminated in the event of wrong modeling of the machine, and the model can be used, for example, as a tool for improving the structure to achieve better values of certain parameters. For conducting this work, two FEM (Finite Element Method) programs were used to provide model simulations: ANSYS MotorCad and Opera 2D.
4.1. Model Geometry
The first step was to model the regions by calculating the appropriate sections and construction angles. With the help of these parameters, there were, among others, settable coordinates of start and endpoints of regions, rotational coordinates, or offsets by specific segments. The geometries were calculated for three types of motors implemented in the model: 6/4, 8/6, and 10/8. The exemplary setting of construction parameters of the design sections and angles while creating stator-related regions are shown in Figure 13 below.

Figure 13.
Exemplary construction geometry determination process for 8/6 SRM motor: (a) stator fragment with marked design parameters, (b) 3D ANSYS representation of modeled 8/6 SRM motor.
4.2. The 6/4 Motor Simulations’ Results
With the usage of a procured model, it was possible to determine the torque values for different motor designs (different sets of parameters). An example of a set of parameters for a three-phase SRM 6/4 motor with characteristics for 24 angles ranging from 0° to 45° is shown in Table 2 and Figure 14. Table 3 shows the obtained torque values for individual rotor position angles. The graph was created presenting this characteristic and it is shown in Figure 15 below. After introducing a different set of input parameters, the characteristic of the static torque as a function of the rotor angle position φ depending on the flowing current I was obtained. It is worth noting that the main parameters (apart from the given design parameters) were the parameters z, number of turns, and k, coil fill factor. Those significantly affect the coil. While designing a model, when it is not possible to clearly define these parameters, it is viable to perform calculations for one rotor position angle and, thus, check whether the introduced parameters, z and k, correspond in reality.

Table 2.
Parameters used for model procurement of a 6/4 motor.
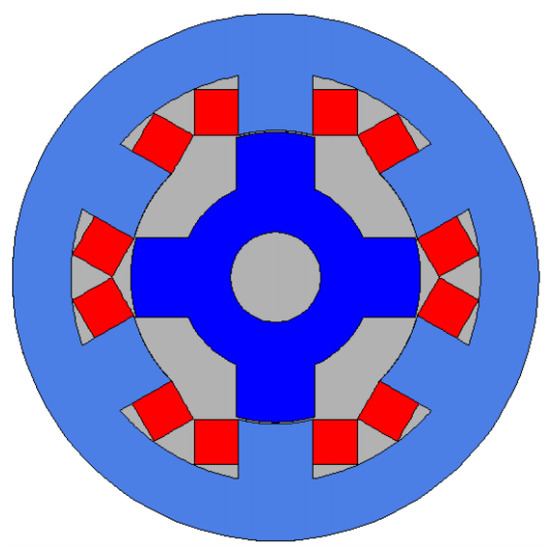
Figure 14.
A 2D model of a 6/4 motor.

Table 3.
A 6/4 motor: torque values for individual angles derived from the model.

Figure 15.
Torque characteristic of the modeled SRM 6/4 motor. The characteristics are based on data from Table 2.
4.3. The 8/6 Motor Simulations’ Results
The SRM 8/6 motor was modelled in a very similar way as the 6/4 motor. Figure 16 shows a graphical representation of the 2D model. Table 4 presents the modeled parameters of the SRM motor. Table 5 presents torque values for different angles and current values. The 8/6 motor type is a quite popular device used in industries.

Figure 16.
A 2D Model of an 8/6 motor.

Table 4.
Parameters used for model procurement of the 8/6 motor.

Table 5.
The 8/6 motor: torque values for individual angles’ and currents’ values derived from the model.
Therefore, our team procured additional simulations of electrical parameters, such as magnetic induction and magnetic field strength, which are shown in Figure 17 below. Moreover, thermal analysis was conducted during the motor operation. It is shown in Figure 18 and Figure 19 below.

Figure 17.
Magnetic properties simulations of an 8/6 motor: (a) magnetic flux density [Wb/m2]; (b) magnetic induction [T].
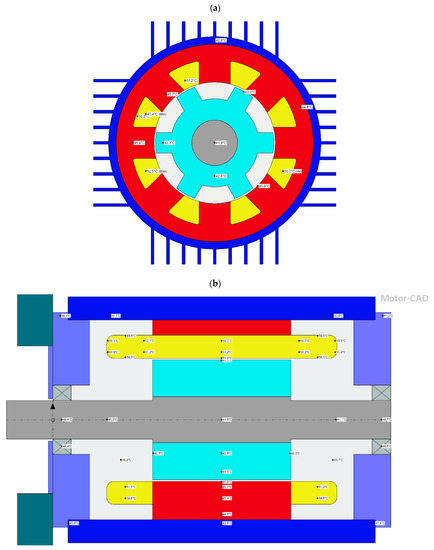
Figure 18.
Thermal properties simulations of an 8/6 motor: (a) Temperature distribution for different regions of the motor during its operation [°C]; (b) Temperature distribution, motor cross-section [°C].

Figure 19.
Schematic diagram of the adopted equivalent lumped-parameter thermal circuit of the SRM.
4.4. The 10/8 Motor Simulations’ Results
The SRM 10/8 motor was modelled as with previous motors. Figure 20 shows a graphical representation of the 2D model. Table 6 presents the modeled parameters of the SRM motor. Table 7 presents torque values for different angles and current values.

Figure 20.
A 2D Model of a 10/8 motor.

Table 6.
Parameters used for model procurement of a 10/8 motor.

Table 7.
The 10/8 motor: torque values for individual angles’ and currents’ values derived from the model.
Impact of Changes in Rotor Parameters on the Torque Value
The developed model can be used as a tool for optimizing motor performance. By changing the parameters, the user can obtain interesting motor properties (e.g., the highest torque with the smallest possible dimensions of the motor–economic costs). The impact of changing the geometrical dimensions of the rotor on the torque characteristics is shown below on Figure 21. The characteristic will be determined for a five-phase 10/8 motor employing two different rotors.

Figure 21.
A 10/8 motor model with a modified rotor: (a) Motor model for the rotor #1 with bps = 18, hps = 16.8; (b) Motor model for the rotor #2 with bps = 12, hps = 12.8.
Figure 22 shows that changes in parameters affect the shape of the characteristic. The value of the maximum torque is at a similar level, while the shape of the angular characteristic is different for these cases. By changing the geometric parameters, the user can get the best solution for the motor: Get the best performance.
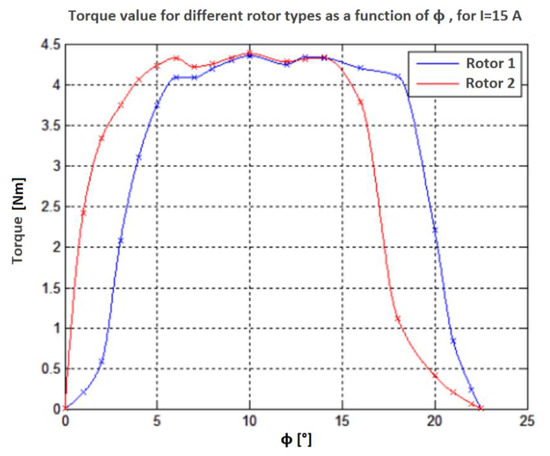
Figure 22.
Comparison of torque characteristics obtained for two different rotors.
5. Results’ Validation
Before the implementation of this model, laboratory measurements were performed: measurements of the static electromagnetic torque of the switched reluctance motor. These measurements consisted of building a power supply and measurement system. The measuring system consisted of a special arm mounted on the motor shaft, which pressed on the electronic scale. Then, using calculations, the torque value was obtained. These measurements were carried out for two different motors (each with two different rotors), for different values of the supply current, I, and different arm deflection angles (different angles of the rotor position relative to the stator). Additionally, the characteristics were determined as torque value as a function of flowing current I, for a constant value of angle φ. Torque values for different rotors used in the same motor were calculated and compared. Design parameters were used to verify that the model was working properly, as the real-scale SRM motors. Characteristics were compared with the obtained characteristics from laboratory measurements. Diagrams of torque families’ characteristics and a comparison of the characteristics on one diagram for two different motors (two sets of parameters) are shown below to validate the procured model (Table 8 and Table 9).

Table 8.
An 8/6 motor: torque values for individual angles’ and currents’ values derived from laboratory measurements.

Table 9.
A 10/8 motor: torque values for individual angles’ and currents’ values derived from laboratory measurements.
Comparing the two families of characteristics (Figure 23 and Figure 24), it can be concluded that the calculated values of the torque from the model are similar to those obtained from laboratory measurements. The obtained maximum torque values are comparable for both cases. For both determined characteristics, however, errors appear related to the build-up of the torque (especially for the case of the 8/6 motor for the current 25 A in the range from 5° to 15°). This is related to the inaccuracy of the geometric representation of the model concerning the real-scale motor and with the given magnetization characteristics, which will not reflect fully the real magnetization of the motor sheet.
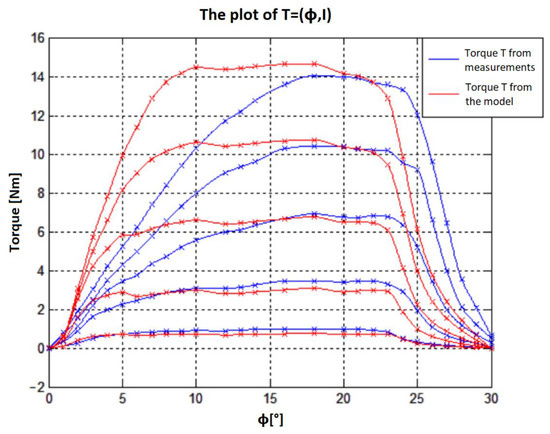
Figure 23.
An 8/6 motor: juxtaposition of the torque characteristics between those from the model and those from laboratory measurements.

Figure 24.
The 10/8 motor: juxtaposition of the torque characteristics between those from the model and those from laboratory measurements.
Figure 25 below shows a tested 10/8 SRM motor during laboratory measurements.

Figure 25.
Tested 10/8 SRM motor during laboratory measurements.
6. Summary and Conclusions
This work aimed to develop a parameterized, two-dimensional field model of a switched reluctance motor for calculating the static torque, thermal effects, and other electrical properties essential for SRM electric motors. The work aim was achieved: The model, depending on the entered parameters, was created correctly, and the characteristics determined with its help corresponded to the actual characteristics. Thanks to parameterization, it is possible to obtain all kinds of motor designs, e.g., three-phase (e.g., 6/4 motor) and four-phase (8/6), as well as designs with more phases (five and up). The model can be made for a two-phase (e.g., 4/2) and a one-phase (2/2) structure, but errors related to the winding may appear: By automatically drawing, the region may be drawn incorrectly. In this case, it is possible to make minimal changes and enter the coil width and height manually. It is also possible to create a model for more pole pairs per phase (2 or 3). After making the model and calculations, the determined torque characteristic is consistent with that one determined by the measurements.
Several options and additions were developed for the model. Using the application, the user can determine the entire torque characteristics for the full range of the rotor angle (from coaxial position to the maximum deflection) or the torque for a single rotor angle. Input data, parameters for the model and angles’ rotor position, can be entered through previously prepared files or by using a convenient interface created inside the program. The user decides for what and how many angles the program is to determine the characteristics. If you intend to determine the pictorial characteristic, it is possible to enter, for example, 10 angles within the full position angle φ of the rotor. To obtain the most accurate characteristics, it is possible to enter a very large number of angles (e.g., rotation every 0.5°).
The main task of the developed model was to calculate the value of the electromagnetic torque for various angles φ between the stator pole and the rotor pole and to determine the electromagnetic torque characteristics depending on the position of the rotor angle φ for the flowing current function I (T = f (φ, I)). Comparing the obtained characteristics with the examples from the literature, it can be seen that the shape of these characteristics is correct. To check the correctness of the model more precisely, the characteristics obtained from the model were compared with the characteristics obtained from the measurements conducted in the laboratory. This comparison is shown in Figure 23 and Figure 24. On the charts presented there, it can be observed that the maximum value of the torque was similar in both cases and the discrepancies occurred for a certain range of angles. The differences can be observed in the steepness of the torque rise for the 8/6 motor, especially for the current I = 25 A for the angle in the range from 0° to 10°. This is related to the inaccuracy of the model representation with the real geometry of the motor, as well as with the phenomena that occur in the real motor (magnetization of the stator core and rotor, the influence of temperature, etc.). A very significant cause of the error is also the inaccurate representation of the loaded plate magnetization characteristics with the magnetization characteristics in a real motor. The real magnetization characteristics were worse than those assumed in the calculations: The saturation effect was greater than in the actual motor.
By verifying the results (torque values from the model and torque values from laboratory measurements), it can be concluded that the obtained torque values from the model are correct. The model can, therefore, be used as a tool to check the measurement results, as well as to improve and optimize various types of motor design to obtain better performance. The model can be used as a teaching tool. It can be used to observe the distribution of the magnetic flux isolines, the intensity of the magnetic field, or the distribution of the potential in the motor. Compared to the analytical model, it takes longer to obtain the results (it can be shortened by parameterizing the calculation mesh). The advantages of the field model in relation to the analytical model are that more accurate results are derived and the phenomena occurring in the motor can be observed, as well as the shape of the modeled motor. The model that was made is valid; however, further improvements and optimization may make the model even better. The model is universal for most designs of SRM motors. For motors with two or four stator poles, it may not be correct due to the way the coil region is modeled. Nevertheless, the mentioned motors designs were not the main aim for the model. The solution is to create an appropriate routine that would draw the coil regions correctly for these designs. Another suggestion to improve the model is to optimize the code characterizing energized coils with more pole pairs per p phase. The current procedure works optimally; the improvement would be related to code clarity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K. and H.C.; data curation, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K and H.C.; formal analysis, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K. and H.C.; investigation, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K. and H.C.; methodology, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K. and H.C.; project administration, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K. and H.C.; resources, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K. and H.C.; supervision, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K. and H.C.; validation, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K. and H.C.; visualization, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K. and H.C.; writing—original draft preparation, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K. and H.C.; writing—review and editing, K.B., M.S., S.Ł., Ł.K. and H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This publication was created within the II edition of the competition/grant of the Scientific Council for the Discipline Automatics, Electronics, Electrical engineering of the Warsaw University of Technology.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The English proofreading of the text was done by Iwona Elżbieta Kolimas.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Data Sheet. Available online: http://www.cadget.com/dyson-dc31-vacuum-cleaner-104000-rpm-of-raw-suction (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Data Sheet. Available online: https://hishinetech.en.ecplaza.net/products/300w-11000rpm-hand-dryer-bldc-motor_3916921 (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Tong, J.; Zou, Y. Design of a fuse-time testing system on STM32. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Computer Sciences and Applications, Wuhan, China, 17–19 October 2013; pp. 406–409. [Google Scholar]
- Makwana, J.A.; Pramod, A.; Srivastava, S.P. Automation and Signal. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Energy, Bhubaneswar, India, 28–30 December 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hongbo, M.; Hongmei, L.; Liwen, L.; Mingna, M.; Zhiwei, C. SRM Design Based on the Sequence Sub-space Multi-Objective Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Jeju, Korea, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hadke, V.V.; Thakre, M.P. Integrated Multilevel Converter Topology for Speed Control of SRM Drive in Plug in-Hybrid Electric Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Infor-matics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 23–25 April 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, A.R.; Babu, E.; Kumaravel, S. Performance Analysis of Grid Powered Asymmetrical Bridge Converter Driven SRM. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th IEEE India Council International Conference, Coimbatore, India, 16–18 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lotiya, J. Thermal analysis and optimization of temperature rise in busbar joints configuration by FEM. In Proceedings of the 2014 6th IEEE Power India International Conference (PIICON), Delhi, India, 5–7 December 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yaman, G. A thermal analysis for a switchgear system. J. BAUN Inst. Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kolimas, Ł.; Łapczyński, S.; Szulborski, M.; Świetlik, M. Low voltage modular circuit breakers: FEM employment for modeling of arc chambers. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2020, 68, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Song, Z.; Fu, P.; Jiang, L.; Wang, M.; Dong, L. Prediction of Temperature Rise in Water-Cooling DC Busbar through Coupled Force and Natural Convection Thermal-Fluid Analysis. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2016, 44, 3346–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.K.; Thompson, J.M. ANSYS Mechanical APDL for Finite Element Analysis; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-812981-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kolimas, Ł.; Łapczyński, S.; Szulborski, M. Tulip contacts: Experimental studies of electrical contacts in dynamic layout with the use of FEM software. Int. J. Electr. Eng. Educ. 2019, I, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Deng, Y. Initial Rotor Position Estimation and Sensorless Control of SRM Based on Coordinate Transformation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 1004–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Masi, A.; Danisi, A.; Losito, R.; Perriard, R. Characterization of magnetic immunity of an ironless inductive position sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongdae, K.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, Y.H. Design and preliminary evaluation of high-temperature position sensors for aerospace applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 4018–4025. [Google Scholar]
- Khoshnoud, F.; Silva, C.W. Recent advances in MEMS sensor technology mechanical applications. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2012, 15, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.B.; Fielke, J.M. Recent developments in strored grain sensors, monitoring and management technology. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2017, 20, 32–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaney, M.J.; Eren, L. Detecting motor bearing faults. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2004, 7, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Ding, F.; Li, Q. Novel High-Response Electromagnetic Actuator for Electronic Engraving System. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Honda, T.; Kasamura, K.; Nakashima, Y.; Nakano, K.; Kondo, K.; Higaki, H. Bio-inspired shaft seal in coolant pump for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA), Birmingham, UK, 20–23 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.E.; Jewell, G.W.; Forrest, S.J.; Rens, J.; Maerky, J. Design Features for Enhancing the Performance of Electromagnetic Valve Actuation Systems. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ding, F.; Wang, C. Novel bidirectional linear actuator for electrohydraulic valves. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 2199–2201. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, P.; Wen, H.; Meng, Z. Magnetic force analysis and experiment of novel permanent magnet axial thrust balance structure in canned motor pump. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Conference on Advanced Computer Control, Shengyang, China, 27–29 March 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Chang, J. A New Electromagnetic Linear Actuator for Quick Latching. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 1849–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Tozzi, P.; Hurni, M.; Segesser, Ł.K. No drive line, no seal, no bearing and no wear: Magnetics for impeller suspension and flow assessment in a new VAD. Interact. Cardiovas. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 3, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Seethaler, R.J. A fully flexible valve actuation system for internal combustion engines. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 16, 36–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdalyan, B.; Dogan, O. Effect of a semi electro-mechanical engine valve on performance and emissions in a single cylinder spark ignited engine. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2010, 11, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taji, B.; Chan, A.D.C.; Shirmohammadi, S. Effect of Pressure on Skin-Electrode Impedance in Wearable Biomedical Measurement Devices. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 1900–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, P.; Korkosz, M. Switched Reluctance Motor—Theoretical Basis; Electric Drives Control Laboratory: Warsaw, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).