Abstract
With respect to widely evaluating and elementally assaying the comprehensive possible applications of Internet of Things (IoT) technology for efficiently advancing administrative and operating performances during the implementation of community development missions, this research attempts to initially analyze the various means of employing Internet of Things (IoT) technology by assessing the affairs and activities of 6918 contemporary community associations in Taiwan in order to inductively construct the most effective Internet of Things (IoT) digital system, not only to update their original documentary administrative system to easily and conveniently implement and record administrative missions, activities, and services but also to handle and display the bulk of news and information from most community residents and the Taiwanese government (such as the Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan). However, after conducting a systematic survey on research related to the Internet of Things (IoT) technology in recent years, there is no one able to directly analyze the shortages and challenges of the diversified applications of Internet of Things (IoT) technology in administrative performance. Specifically, the greatest challenges are the Taiwanese individual information protection regulations and the laws regarding the various applications of digital data (such as the Taiwan Personal Data Protection and Telecommunication Acts), which apparently hinder the development of Internet of Things (IoT) technology in the enhancement of community associations in Taiwan. Therefore, the suggestion contributed by this research is to institute basic digital data using ACT for all 6918 community associations in Taiwan in order to directly force the application of IoT technology to advance the performances and achievements of community development associations.
1. Introduction
The briefest administrative programs of the Executive Yuan, which is the highest administrative government department, include “live and work in peace and contentment”, “continuous reproduction breed in an endless succession”, and “balanced development in Taiwan”. Therefore, in order to improve population loss in the outermost districts of the city, the rapid establishment of community development associations has become the one of local revitalization practices of these administrative programs in an attempt to achieve the “live and work in peace and contentment”, “continuous reproduction breed in an endless succession”, and “balanced development in Taiwan” goals.
In order to strengthen rural development and improve population aging issues, the Taiwanese government’s Ministry of Health and Welfare began to institute and administer the Regulations on Community Development Work on 18 September 2014 to improve current Taiwanese communities, enhance the welfare of residents, and construct a wonderful, aggressive, integrated, and interdependent modern group and entire society. According to Article 12 of the Regulations on Community Development Work: “The community development associations shall devise community development plans, prepare budgets and actively promote community development according to community characteristics and the needs of residents, in addition to being in line with government policies and projects originally designed by the community.” Based on the basic purpose of the development of a community development association in Article 12 of the Regulations on Community Development Work [1], projects receiving government funds must respect government policies, as stated above. The 13 principles are listed as:
- The construction of public facilities:
- (1)
- The construction or repair of community centers.
- (2)
- Protecting the environment and improving sanitation in communities.
- (3)
- The maintenance of roads and gutters in communities.
- (4)
- The collation of and increase in parking facilities.
- (5)
- Community greening and beautification.
- (6)
- Other matters relating to the construction of public facilities.
- The development of production and welfare:
- (1)
- The establishment of community production and construction funds.
- (2)
- The promotion of social welfare.
- (3)
- The establishment of community nurseries.
- (4)
- Promoting the development of community businesses.
- (5)
- Other matters relating to the development of production and welfare.
- Spiritual and ethical development:
- (1)
- Important measures for improving the ethos of society as well as advocating and promoting models of public etiquette.
- (2)
- The maintenance and promotion of rural culture and traditional crafts.
- (3)
- The establishment of traffic safety in the community.
- (4)
- The establishment of community pacts.
- (5)
- The promotion of civil defense.
- (6)
- The establishment of art and recreation teams.
- (7)
- The establishment of community senior citizens’ clubs.
- (8)
- The establishment of community growth classrooms.
- (9)
- The establishment of community volunteer service teams.
- (10)
- The establishment of community libraries.
- (11)
- Advocating for community-wide activities.
- (12)
- Promoting community disaster reporting and prevention drills.
- (13)
- Other matters relating to spiritual and ethical development.
Therefore, Figure 1 illustrates the 13 principles of Article 12 of the Regulations on Community Development Work as:
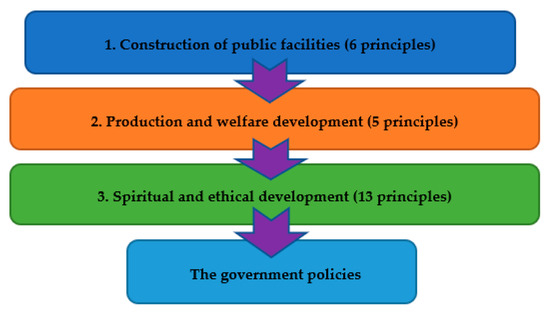
Figure 1.
The 13 principles of the government policies.
However, as an urgent and serious issue, aging populations in remote or special needs areas of Taiwan require the most significant services and activities provided from all Taiwanese community development associations, which have had the most severe lack of useful methods, tools, and technologies to support them in advancing their operational effectiveness and implementing efficiency in the majority of Taiwanese community development associations, especially those in remote or special needs regions. Therefore, with the 100 percent coverage rate of fourth-generation mobile networks and the more than 50 percent coverage rate of the fifth-generation mobile networks, the majority of empirical industrialists have recommended considering employing wireless and internet technologies to directly construct unique digital connections for Taiwanese community development associations via the Internet [2,3,4,5].
These digital connections between community development associations will not only advance the efficiency of internal services and activities, such as providing the elderly with meals at community care locations (places) and providing entertainment services at community clubs for the elderly (places), etc., but will also strengthen the operational effectiveness of external services and activities, such as the development of tourism, the promotion of local culture, marketing regional agricultural productions, etc. [6].
Based on the rapidly spreading infections of contemporary global contagious diseases, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2003 and the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in 2019, the majority of educational and on-the-job training courses were implemented though a series of virtual wireless connections using the IoT technology [7,8,9,10], as shown in Figure 2:

Figure 2.
The main research concept.
2. Conceptual Literature
Significantly, in view of the accumulation of outcomes and performances, the number of Taiwanese community development associations has been greater than 6918 since 2020, based on the official statistics from the Ministry of Health and Welfare. Subsequently, since 2019, the number of directors and supervisors (persons) of community development associations was up to 108,524 individuals, including the 6918 director generals, 75,440 directors, and 26,166 supervisors. The number of people serviced was 22,014,889, and they were served by the 145,935 members comprising all Taiwanese community development associations. Momentously, up to 12,612,351 people were attended to through welfare services or activities for some specific communities’ services and activities, such as community care locations offering meal services for the elderly (places), elderly entertainment services, activities for the elderly hosted by community clubs (places), meal services, and family entertainment services, such as community common rooms for mothers (classes), the promotion of local tourism, cultural development activities for folk, literature, and art (teams), regional security services from community mutual-help programs (teams), etc.
Eventually, the fundamental aspects developed were directly created and comprehensively instituted, and these developed aspects related to production and development, such as financial and economic development for industries located in community development associations; life aspects, such as cultural and living developments for regional residents in community development associations; and ecological aspect, such as environmental introduction, protection, and education for in-depth circumstantial understanding in community development associations. There were still some various outstanding services and activities in multiple aspects, such as tourism development, including economic living, transportation, and shopping demands, the regional cultural promotion of guidelines for living, and extensive environmental introduction, education, and protection propaganda, etc. [11,12,13,14].
In order to directly complete the organizational structure, positively enhance the service functions, and aggressively establish the community activities of community development associations in Taiwan, all Taiwanese community development associations must obtain the strongest and most powerful methods to be able to not only reinforce the current functions and services but also to satisfy a series of accumulated deficiencies. Furthermore, in association with the swift and sustainable development of services and activities in all Taiwanese community development associations, virtual methods, digital tools, and vital systems have been desired for each Taiwanese community development association.
As a result, Internet of Things (“IoT”) technology has been considered a supporting digital technology to advance the administrative effectiveness and operating efficiency of the diversified services and activities of the 6918 current Taiwanese community development associations, according to its virtual, digital, and systematical characteristics. This is because the IoT is a type of digital computed connection that can transfer various data in association with a series of 3C (“computer, communication and consumer”) electronic diversified devices such as smart phones, individual notebooks, and personal computers. In addition, IoT technology is definitely able to comprehensively connect the diversified devices and humans via integrating the complicated digital data collected from each universally unique identifier (“UUID”) from the electronic devices with digital connection functions. Recently, with the rapid development of wireless and internet technologies, the coverage rate of the fourth-generation mobile networks has reached 100 percent since 2018, and the fifth-generation mobile networks have up to 49 percent coverage since 2020, based on the official 2020 report of the National Communication Commission (“NCC”) in Taiwan.
3. Conclusions and Future Direction
With respect to widely evaluating and elementally analyzing the various possibilities and diversified applications of IoT technology for strengthening the internal administrative performances and implementation efficiencies of the services and activities provided by the current 6918 community development associations in Taiwan, these Taiwanese community development associations obviously demand a large, powerful, stable, and highly compatible digital system to assist them in handling large volumes of data and information in order to advance the implementation of community services and activities. In particular, the digital system can not only directly advance the efficiency of the community associations but could also assist the Taiwanese government in supporting and understanding the situation and consequences of implementing a digital system for the current 6918 community development associations. Extraordinarily, with respect to the hyper-speed and hyper-connected characteristics of the IoT technology, each 6918 community association could update the efficiency of their administrative performance and their efficiency in implementing services and activities through the diversified applications of the IoT technology by means of sharing more news and information between each Taiwanese community development association.
However, with respect to recent research [15,16] in IoT-technology-related fields in association with the administrative performances of community development associations, the most critical shortages and challenges are obviously the individual digital data protection and security regulations and rules (such as the Taiwan Personal Data Protection and Telecommunication Acts). After the executing a series of preliminary analyses, the empirical suggestion is to institute rules for the application of basic digital data in all 6918 current Taiwanese community development associations in order to easily introduce IoT technology into each community development association in order to successfully confront a series of threats due to serious global contagious diseases.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-C.M.L. and M.-Y.H.; methodology, M.-Y.H.; validation, J.-C.M.L.; formal analysis, M.-Y.H.; investigation, J.-C.M.L.; resources, J.-C.M.L. and C.-L.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.-Y.H. and C.-L.W.; writing—review and editing, M.-Y.H.; visualization, J.-C.M.L.; supervision, M.-Y.H.; project administration, M.-Y.H.; funding acquisition, and C.-L.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the research supporting research projects (MOST 110-2420-H-002-003-MY3-Y11209) of Ministry of Science and Technology and (NTCU111103) from the National Taichung University of Education.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research did not execute the questionnaires and interview and hence, this research did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable because this research did not involve any humans.
Data Availability Statement
No new data was created.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- The Article 12 of the Regulations on Community Development Work; Ministry of Health and Welfare: Taipei, Taiwan, 2014.
- Hsieh, M.-Y. Interdisciplinarily Exploring the Most Potential IoT Technology Determinants in the Omnichannel E-Commerce Purchasing Decision-Making Processes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.Y. The Most sustainable niche principles of social media education in a higher education contracting era. Sustainability 2020, 12, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-M.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Usak, M. A Multi-Criteria Study of Decision-Making Proficiency in Student’s Employability for Multidisciplinary Curriculums. Mathematics 2020, 8, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-K.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Usak, M. A Concrete Study on Social-Media Connection of Global Literacy Abilities in MOOCs under the Dual Impacts of Lower Birth-Rate and COVID-19. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usak, M.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Chan, Y.-K. A Concretizing Research on Making Higher-Education Sustainability Count. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, M.; Usak, M.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Uygun, H. A New Perspective on Pedagogical Content Knowledge: Intellectual and Emotional Characteristics of Science Teachers. Rev. de Cercet. si Interv. Sociala 2021, 72, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-L.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Min, K.-W.; Yu, M.-T.; Ho, C.-T. Use of Sensor Technologies in Online Courses in Post-COVID-19 Era. Sensors Mater. 2021, 33, 2045–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Chan, Y.-K.; Hsieh, M.Y. The Determinants of ESG for Community LOHASism Sustainable Development Strategy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-K.; Hsieh, M.-Y. An Empirical Study on Higher Education C-ESG Sustainable Development Strategy in Lower-Birth-Rate Era. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-Y. Online learning era: Exploring the most decisive determinants of MOOCs in Taiwanese higher education. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2016, 12, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-M. Employing MCDM methodology to verify correlationship between social media and service quality in the dynamic m-commerce era. J. Internet Technol. 2018, 19, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-M.; Usak, M. High Education Radical Transformation Era: How Teachers’ Competency can Enhance the Students’ Employability. Rev. Cercet. Interv. Soc. (RCIS) 2020, 68, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-M.; Hsieh, M.-Y. An Interdisciplinary Research on Students’ Employability in Technology Education to Advance Higher Education Enrollment Sustainability. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-Y. The Sustainable Development and Strategic Approaches for Contemporary Higher Education. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Chan, Y.-K.; Hsieh, M.Y. Preliminary Research on the Sustainable Determinants of Taiwanese Ecotourism with the International Standards. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).