Abstract
Chazence is a subsidiary of Zence Object Technology Company in the Greater Bay Area of China. It is a sustainable enterprise that combines tea industry consumables (tea residue) with fiber composite technology to replace traditional materials and conduct product practices. Their core philosophy aligns with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly Goals 9 and 12, emphasizing industrial innovation, the sustainable management of natural resources, and the promotion of sustainable consumption and production patterns. However, the current system of tea recycling is extensive and requires precise data management and back-end human resource allocation to ensure efficient collaboration between professionals and grassroots staff. Currently, the system does not have a user-friendly interface for human resource allocation, data management, resource management, and visual information. Therefore, we optimized the interface and functional design of the warehouse system to improve the efficiency of resource management of Chazence by understanding its approach to tea recycling. Through surveys and interviews, employee needs and user experiences were analyzed, and the results guide the design of a sustainable enterprise management system from a user experience (UX) perspective.
1. Introduction
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) comprise 17 global objectives established by the United Nations. These goals explicitly call on enterprises to leverage their innovative capabilities to advance sustainable development through investment, solution development, and business practices. Zence Object Technology Company, a sustainability-focused enterprise based in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China, has launched “Chazence,” an innovative brand that produces environmentally friendly products by recycling tea waste and applying fiber composite materials. They integrate fiber composite material into consumables. However, as the brand continues to expand, the effective management of production and human resources has become a significant challenge, as Xiao Qidong, the principal of Chazence, noted in an interview. The effectiveness of enterprise strategy implementation largely depends on the development of its information system. The system plays a pivotal role in resource management. This information system directly affects the enterprise’s ability to formulate subsequent strategic and tactical objectives aimed at enhancing competitiveness and ensuring sustainable development [1].
Amid the wave of digital transformation, the integration of user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design has become a critical factor in enterprise management systems. In the systems, managing and optimizing user experience has become crucial for maintaining and enhancing competitive advantage in an increasingly competitive environment [2]. For a company such as Zence Object Technology, which specializes in tea leaf recycling and regeneration for rural economic sustainability, an intuitive and efficient management system designed based on employee user experience enhances internal operational efficiency and cross-departmental collaboration, thereby improving the accuracy and timeliness of decision-making. Therefore, this study aims to design an enterprise management system interface for Zence Object Technology’s tea brand based on user experience principles, to address challenges such as resource allocation difficulties, understaffing, and inefficiencies in cross-departmental collaboration encountered in the company’s daily operations.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Sustainable Enterprise and SDGs
Under SDGs, enterprise competitiveness is no longer defined solely by profit maximization, but rather by the ability to balance environmental protection, social responsibility, and economic performance [3]. Sustainable development is essential for the long-term growth of enterprises, global ecological sustainability, and social progress. Since the United Nations introduced the SDGs, an increasing number of enterprises have incorporated sustainability into their strategic objectives. For example, in 2017, the Japan Business Federation (Keidanren) incorporated the SDGs into its Corporate Action Charter, encouraging enterprises to explore sustainable business models. The BAMX Food Bank, for example, recycles imperfect vegetables from farmers and surplus food from enterprises, processing them into affordable ingredients for low-income families. The Bank provides skills training and employment opportunities. For sustainable enterprises, innovation refers to companies leveraging technological and product advancements to reduce resource waste and minimize environmental impact. Wells, taking the automotive industry as an example, emphasizes that corporate innovation includes business models to enhance sustainability through approaches such as the circular economy and ecological design beyond products [4].
2.2. Management Information
The concept of management information systems was initially proposed in the 1930s. Subsequently, Simon emphasized the pivotal role of information in management and decision-making, focusing on information collection and management. Effective management systems effectively reduce time lags in information synchronization, improve the efficiency of information management, and resolve issues related to information inconsistency [5]. Over the past several decades, enterprise management systems have matured with well-defined theoretical frameworks and technical solutions. Since the 1980s, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems have been widely used. In the 21st century, the advent of the Internet, cloud computing, and big data has further accelerated the evolution of enterprise management systems. Even without significant upgrades, the usage rate of management systems in 2021 remained higher than in 2013 [6]. Under the new economic paradigm, enterprise management systems need to be continuously updated. For such an update, conceptual models to integrate different systems, such as enterprise risk management (ERM) and Property Management Systems (PMS), have been proposed based on different methodologies to create economic benefits [7].
2.3. System Interface Design
The concept of user-centered design (UCD) serves as a fundamental principle in user interface design, emphasizing the role of user needs and experiences throughout the entire design process [8]. In enterprise-level management systems, design principles are critical to address the inherent complexity of enterprise operations and ensure an optimal user experience and system stability. Key design considerations, such as user-centricity, interface consistency, optimized information presentation, visual guidance, esthetic appeal, and cross-platform adaptability, significantly enhance the user’s browsing experience and overall satisfaction. Hany et al. proposed an innovative interface design approach based on four dimensions: understanding the usage environment, identifying user requirements, designing appropriate solutions, and evaluating the design. The design resulted in an 83.6% increase in satisfaction among student users [9]. Internet service companies serve enterprises or merchants. Their core objective is to meet users’ requirements by systematizing and digitizing traditional offline operations, enabling efficient enterprise collaboration, and reducing operational costs. An enterprise-centered design emphasizes the connections between role scenarios and efficient interactive experiences, ensuring the enhancement of enterprise operational efficiency [10].
2.4. Summary
Based on the literature review and analysis, we adopted UCD and enterprise management system design principles and optimized the interface architecture of the Chazence enterprise management system. Modular information layouts, streamlined interaction flows, and enhanced data visualization improved the system’s usability, accessibility, and operational efficiency for enterprise users.
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Subjects
To analyze the needs and experience expectations of internal employees and management in the enterprise management system of Zence Object Technology, we conducted a semi-structured interview method for preliminary needs assessment. The questionnaire consisted of ten questions in four dimensions (Table 1). The interviewees were the founder and the project manager of Zence Object Technology, both of whom possessed in-depth knowledge of the operation and requirements of enterprise management systems. The interviews were conducted between November and December 2024, with each session lasting approximately one hour. These interviews yielded in-depth insights into employees’ needs and functional expectations, as well as directions for improvement in system interaction and information architecture. The findings served as a foundation for the subsequent optimization of the enterprise management system interface.

Table 1.
Questionnaire structure.
3.2. Research Instruments
The interview questions were refined based on the user needs interview framework. A semi-structured interview method was employed to analyze the needs, expectations, and user experiences of the Chazence enterprise management system. The advantages of structured and unstructured interviews were considered for the collection of qualitative data.
3.3. Interview
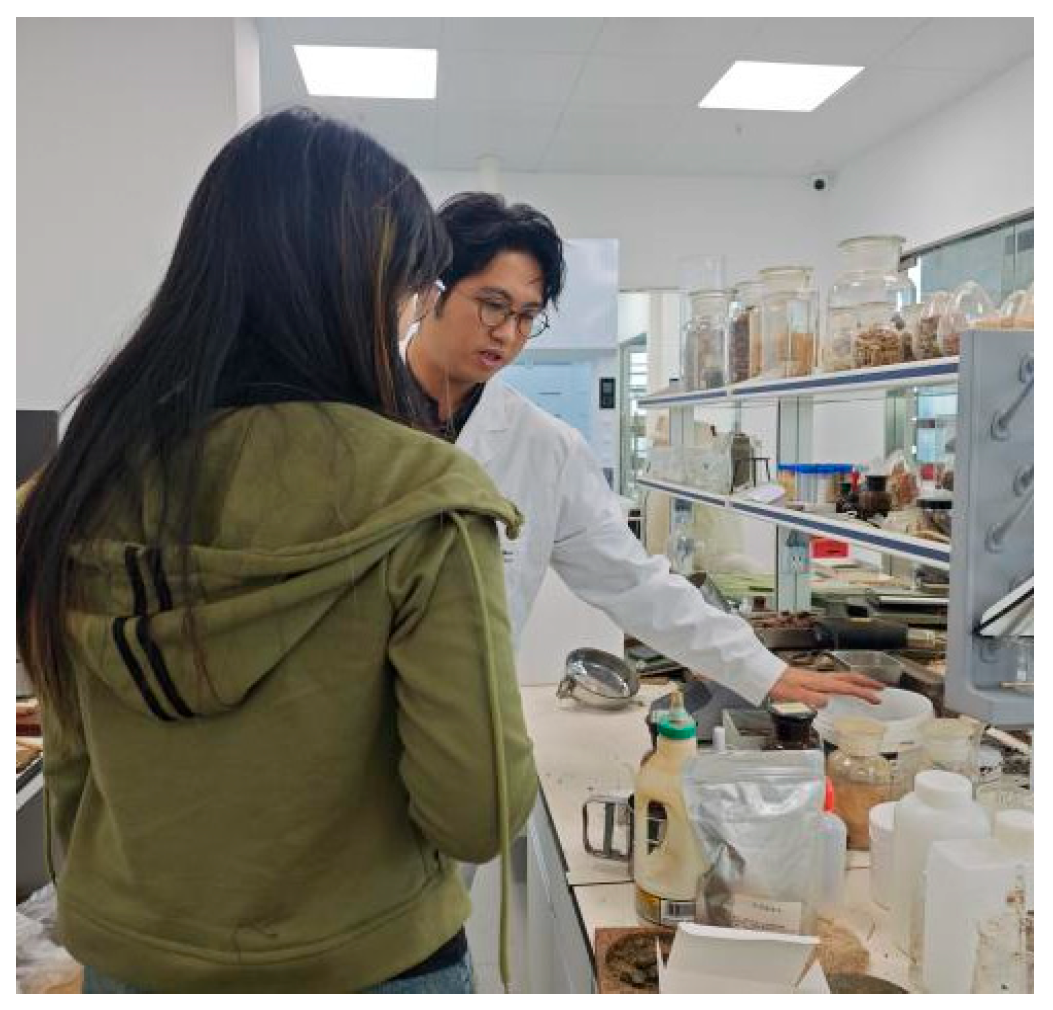
The interviews lasted approximately one hour. Before the interviews, the participants were introduced to the purpose and process of the study, followed by questions about user background, existing challenges, functional requirements, and interface design preferences (Figure 1). The interviewees provided examples, such as warehouse staff manually entering data, which led to errors and made it difficult to accurately track inventory changes in specific raw materials. These examples offered basic information for the subsequent system design (Figure 2). To ensure data integrity, the interviews were audio recorded, and notes were taken with the interviewees’ consent. The results were analyzed for the design and optimization of the management system to improve operational usability and data management efficiency.

Figure 1.
Visit to Chazence laboratory.
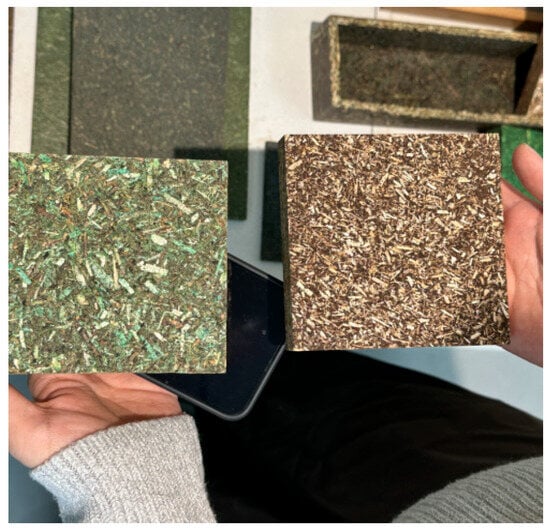
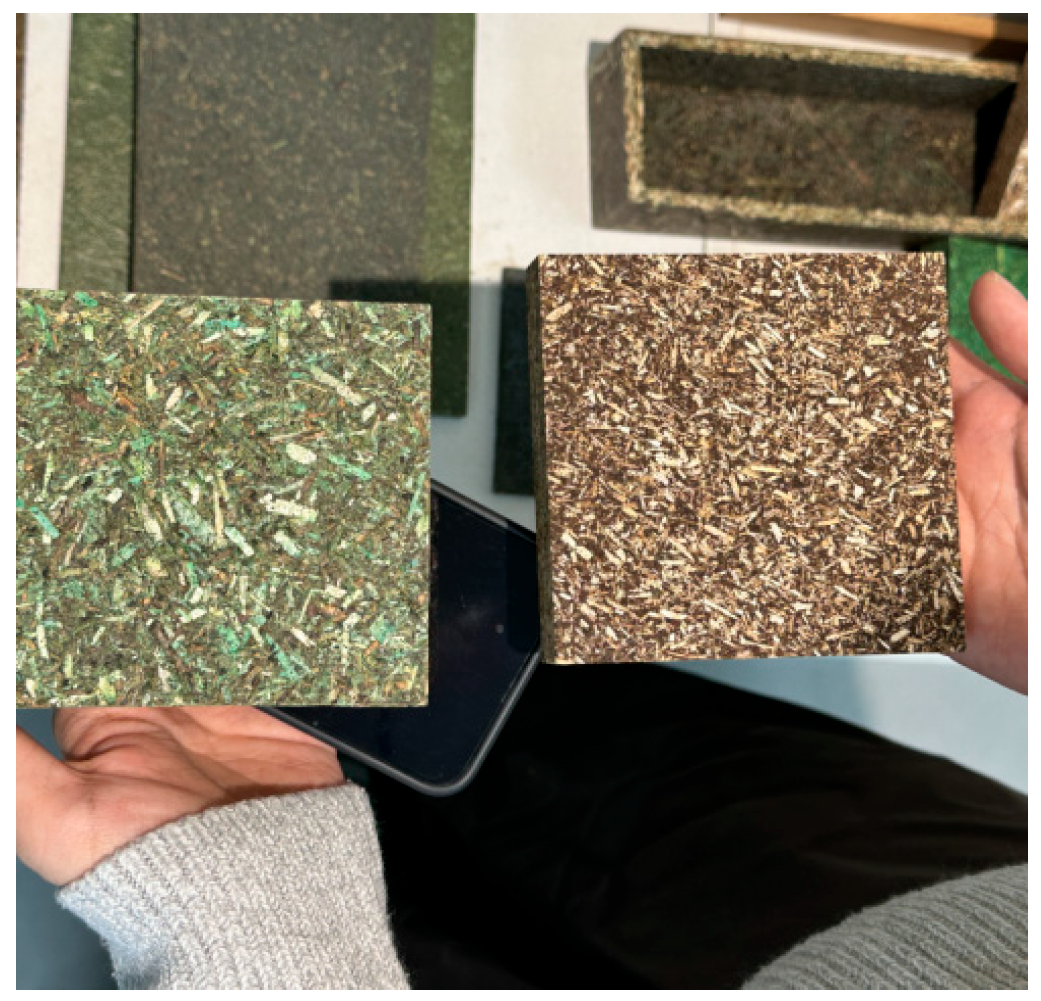
Figure 2.
Categories of boards produced by Chazence.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. User Requirements
Two stakeholders of the Chazence enterprise management system—the founder of Chazence and the project manager—were interviewed. Both participants played central roles in the development and implementation of the system and provided comprehensive and professional insights into the enterprise’s requirements. Based on the interview, the following key points were identified.
- Existing challenges: Chazence enterprise management processes lack systematization, with data requiring manual verification, which is prone to errors and negatively impacts operational efficiency and accuracy.
- Functional requirements: Digitization is needed in production and inventory management, particularly in raw material stock management and production tracking. The implementation of barcode-based inbound and outbound scanning can improve resource management efficiency and minimize human error.
- Interface design preferences: The system interface must be simple and intuitive, minimizing complex operations to ensure that employees at all levels can quickly become proficient in its use. For factory workers, a mobile interface is appropriate, enabling real-time operation and rapid data entry.
- Core design principles: The system design must prioritize usability, incorporating a streamlined interface design and efficient functional modules to accommodate the operational needs of diverse users. This is especially important for older employees, for whom overly complex operations must be avoided. Interaction methods need to be convenient and efficient—for instance, barcode scanning can significantly improve task execution speed.
Based on the results, we adopted a mobile platform architecture (targeted at warehouse and production staff) to ensure that the system met the requirements of different roles. The emphasis was placed on portability and real-time operation. Core features include barcode-based inbound processing, inventory management, and mobile-end workflows.
4.2. Interface Design
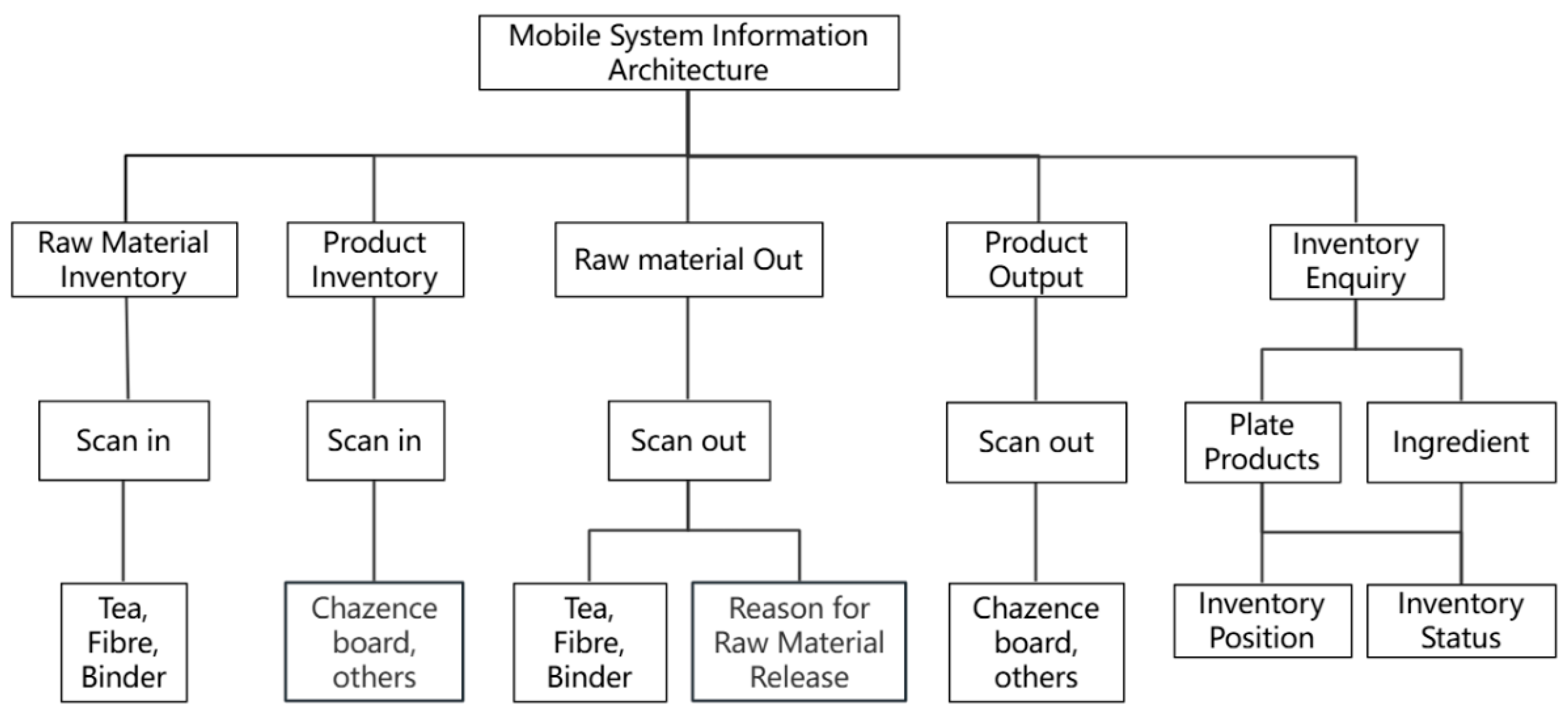
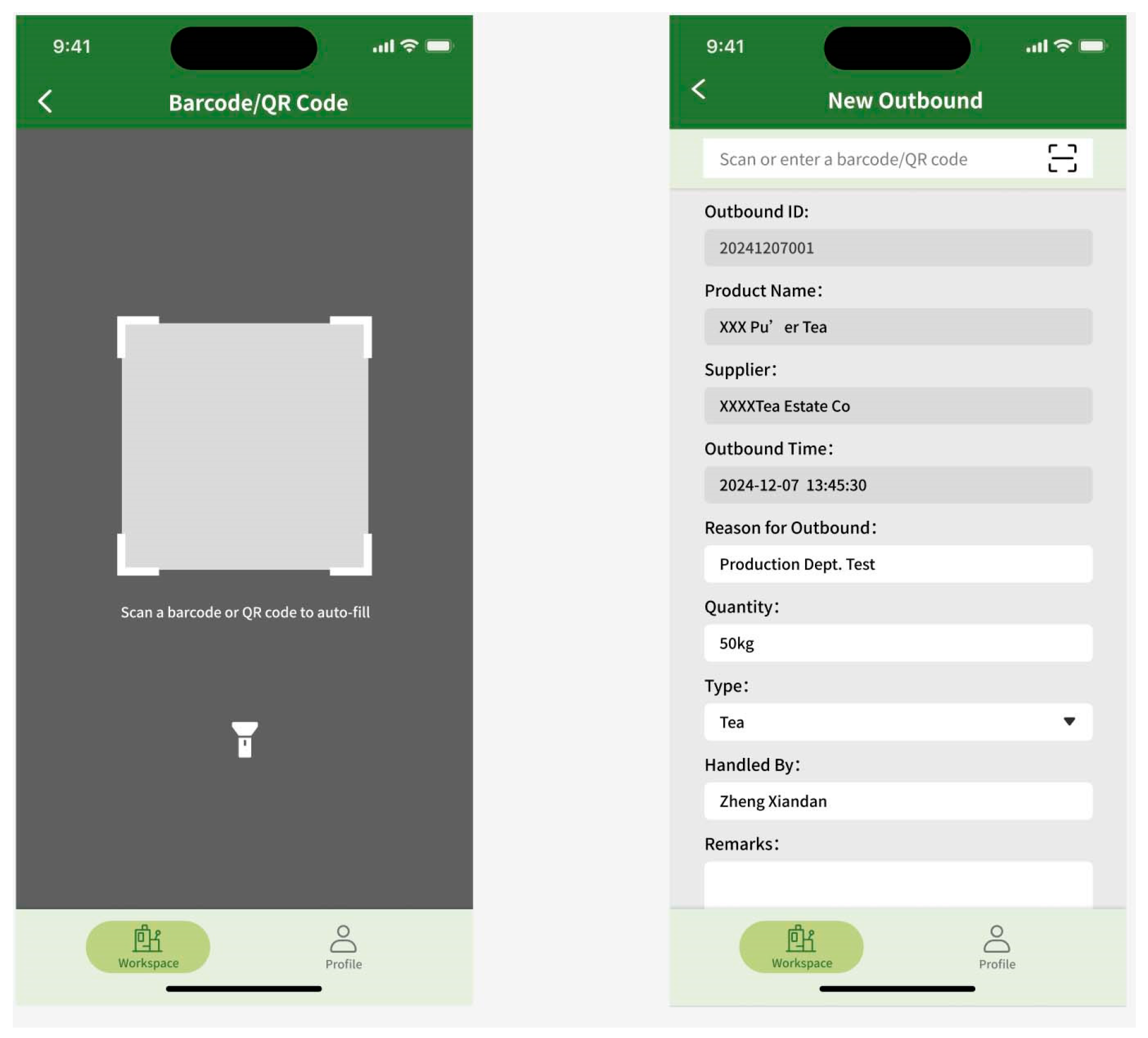
The mobile interface was designed for on-site factory operators, enabling them to perform inbound and outbound inventory operations through barcode scanning. The data is synchronized in real-time with the system’s backend, enabling immediate accessibility to both the production department and management personnel. Considering the complex factory environment and the difficulties that factory workers encounter when using mobile devices, the mobile interface features a simple functional architecture (Figure 3).
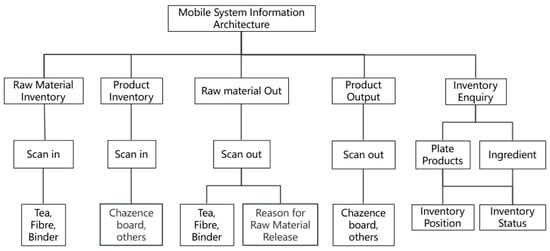
Figure 3.
Information architecture of enterprise management system.
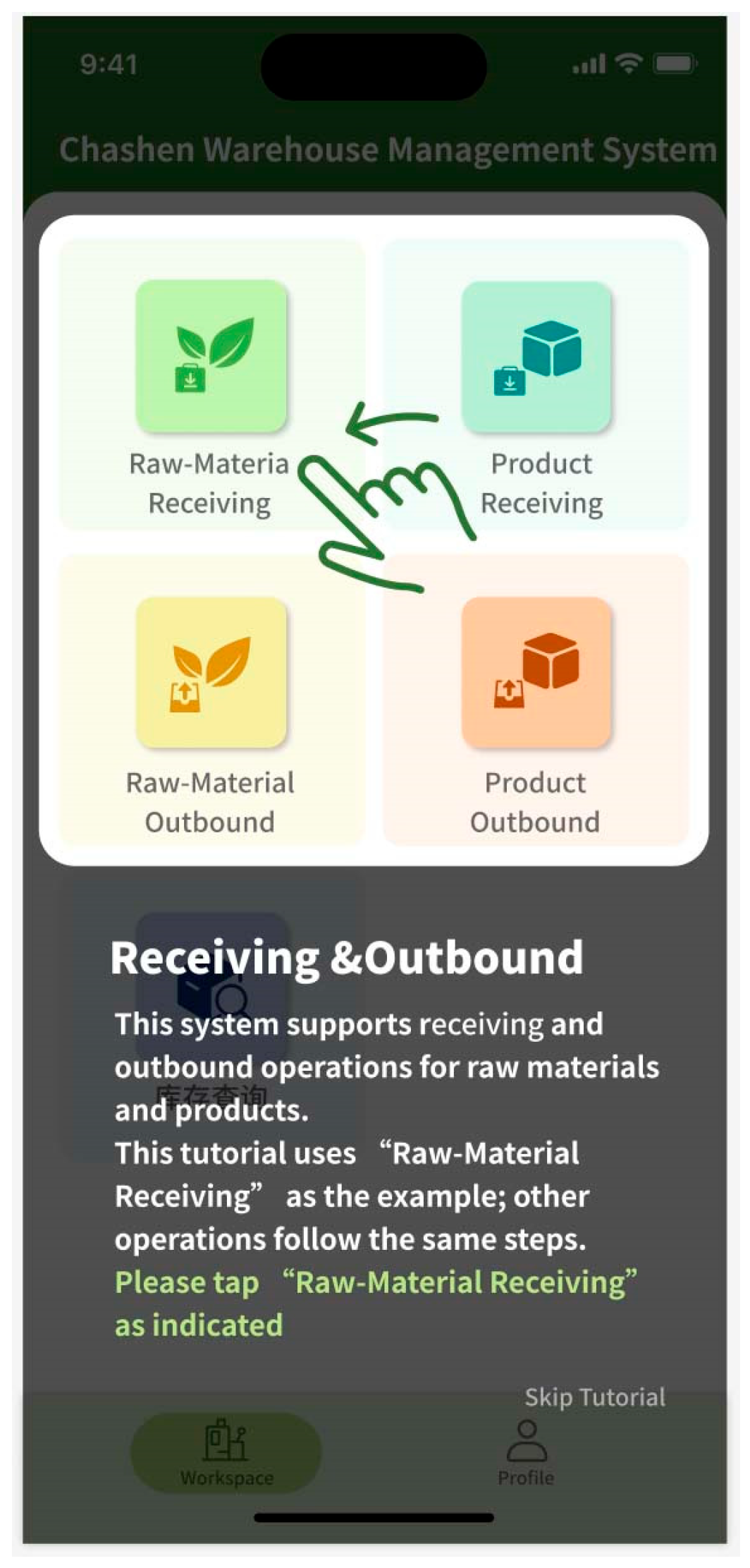
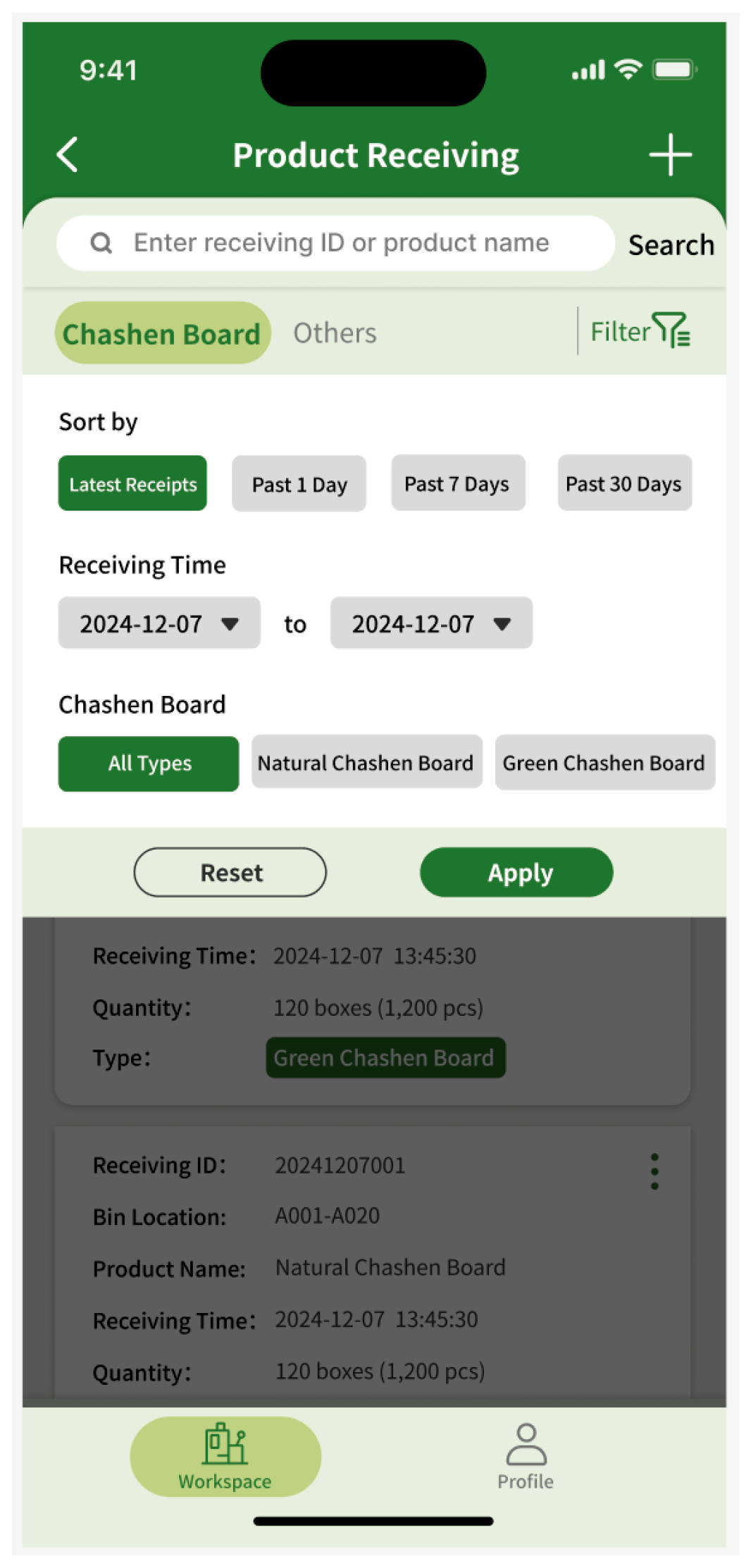
The mobile prototype design is tailored to meet the operational requirements of factory personnel, featuring core functionalities including barcode-based inbound and outbound inventory processing and inventory queries. The design enables operational convenience and efficiency. The navigation bar at the bottom of the home interface consists of two main sections: Workbench and My Profile. The Workbench section facilitates inventory management functions, including check-in and check-out operations, while the My Profile section enables users to configure account settings. The streamlined navigation and functional layout enhance user experience by allowing users to quickly familiarize themselves with the system (Figure 4 and Figure 5). Based on user requirements, the mobile interface design incorporates quick response (code) or barcode scanning functions. The system automatically populates relevant information based on scanned barcodes, thereby minimizing errors in manual data entry and enhancing inventory operation efficiency. To maintain data integrity, users must document the reason for material dispatch during outbound processes, preventing data inconsistencies resulting from special circumstances such as testing procedures or material shrinkage (Figure 6).
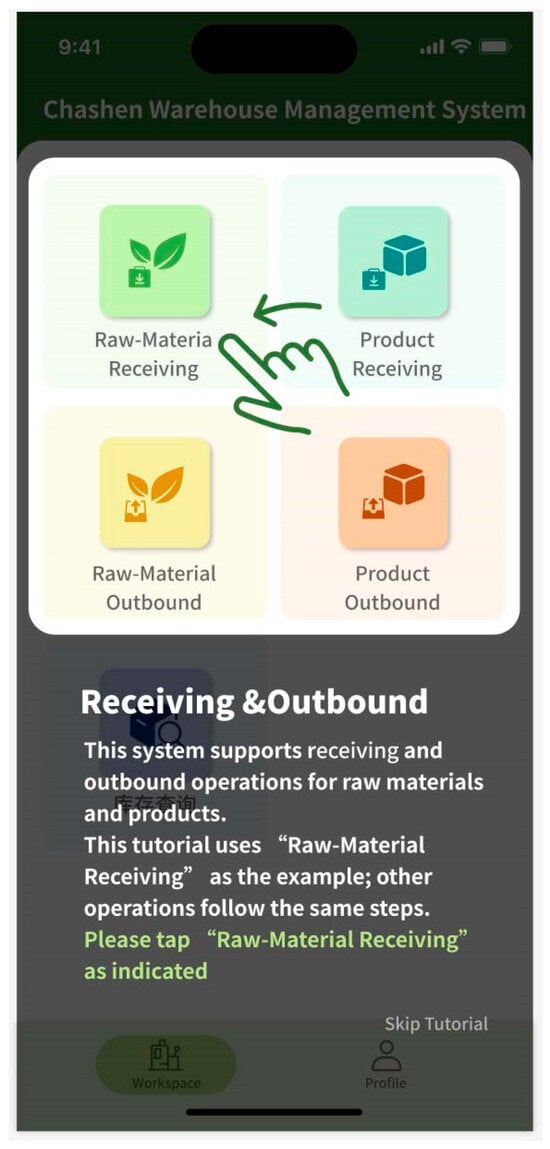
Figure 4.
User guide.
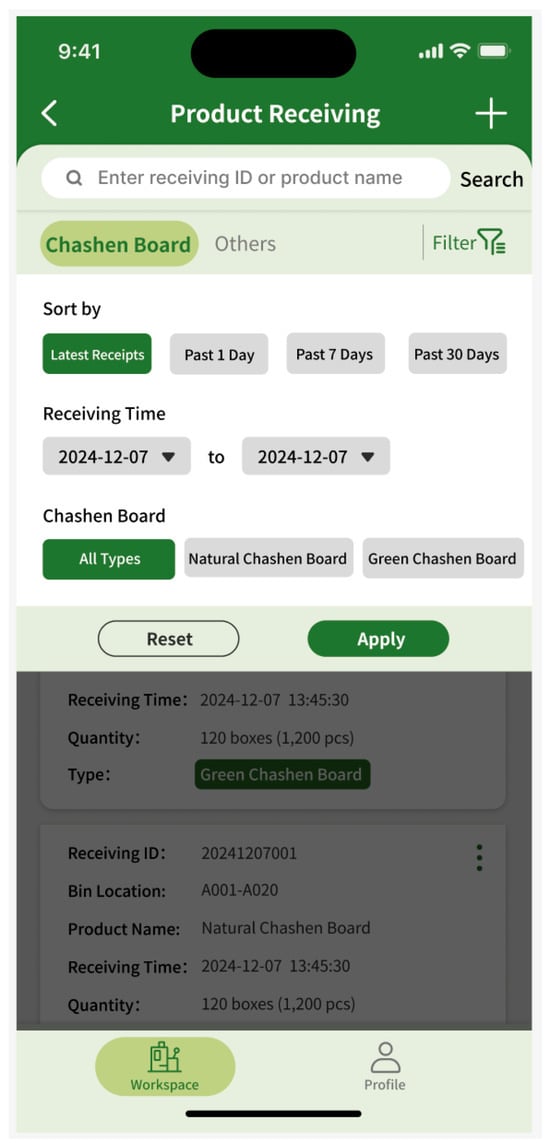
Figure 5.
Category filter.
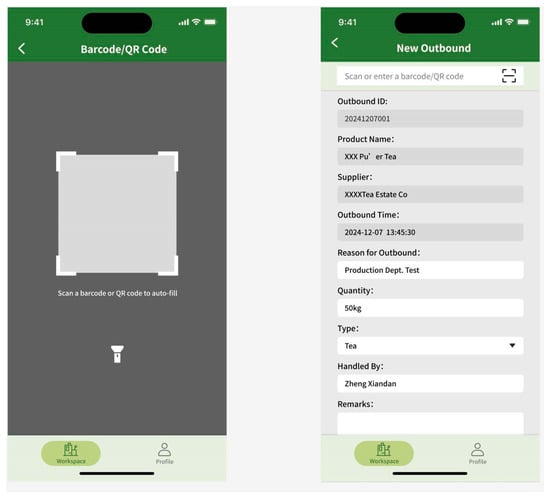
Figure 6.
Barcode-based inbound/outbound processing.
5. Conclusions
We developed the interface design for the Chazence enterprise management system, focusing on the Chazence brand under Zence Object Technology Company. The system was designed according to user experience principles to optimize resource management efficiency and enhance cross-departmental collaboration while promoting organizational sustainability. Guided by user requirements, the designed mobile interface prioritizes convenience and real-time functionality, allowing workers to efficiently manage barcode-based inbound and outbound processing, inventory tracking, and data queries. It is still necessary to collect user experience (UX) feedback on system implementation through qualitative interviews. The results lead to the enhancement of the system’s interaction logic, data management protocols, visual hierarchy, and adaptability to meet diverse enterprise management requirements while supporting long-term organizational sustainability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-T.M. and P.-W.H.; methodology, H.-T.M. and P.-W.H.; software, H.-T.M.; validation, H.-T.M. and P.-W.H. and Q.-F.H.; formal analysis, H.-T.M. and P.-W.H.; investigation, H.-T.M.; resources, H.-T.M.; data curation, H.-T.M.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-T.M.; writing—review and editing, H.-T.M. and P.-W.H.; visualization, H.-T.M.; supervision, P.-W.H.; project administration, P.-W.H. and Q.-F.H.; funding acquisition, P.-W.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund, FDCT. Funding Number 0045/2023/ITP2.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are obtained in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Asaul, A.; Voynarenko, M.; Dzhulii, L.; Yemchuk, L.; Skorobohata, L.; Mykoliuk, O. The latest information systems in the enterprise management and trends in their development. In Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Advanced Computer Information Technologies (ACIT), České Budějovice, Czech Republic, 5–7 June 2019; pp. 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Li, Y. Research on user experience optimization methods for web-based enterprise management information systems. Electron. Technol. Softw. Eng. 2014, 24, 185–186. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X. International practice and future prospects of sustaining competitive and responsible enterprises (SCORE). China Emerg. Manag. 2024, 5, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, P. Sustainable business models and the automotive industry: A commentary. IIMB Manag. Rev. 2013, 25, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y. Application and development trends of enterprise management systems. Electron. Technol. Softw. Eng. 2018, 18, 149. [Google Scholar]
- Pawliczek, A.; Kolos, P.; Lenort, R.; Kolumber, S.; Wicher, P. Management tools and systems-usage in logistics companies in the Czech Republic. Acta Logist. 2022, 9, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, I.; Camilli, R.; Chirico, A.; Mechelli, A. The integration between enterprise risk management and performance management system: Managerial analysis and conceptual model to support strategic decision-making process. Prod. Plann. Control 2022, 35, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, D.A.; Draper, S.W. User Centered System Design: New Perspectives on Human-Computer Interaction; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hany, E.; Setiawan, A.; Ardhy, F.; Rizki, F. Evaluasi dan perancangan user interface (UI) untuk meningkatkan user experience (UX) menggunakan metode human centered design (HCD) pada aplikasi Sitabsis di SMPN 03 Gading Rejo. Aisyah J. Inform. Electr. Eng. 2023, 5, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, J.; Zhou, H. B-end interface design of live e-commerce platforms based on user experience. Ind. Des. 2023, 1, 95–97. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).