Application of Machine Learning for Optimizing Chemical Vapor Deposition Quality †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
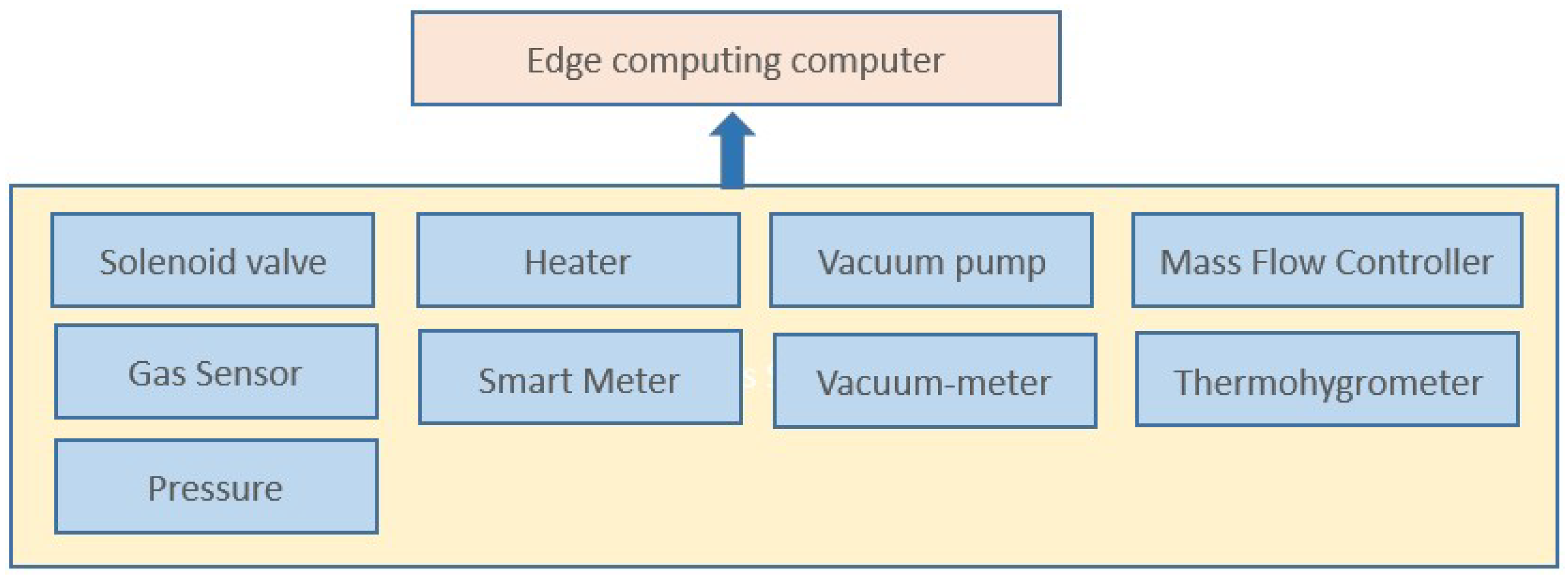
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Feature Selection
2.4. Model Construction, Validation, and Optimization
2.4.1. Logistic Regression
2.4.2. Random Forest
2.4.3. XGBoost
2.4.4. SVR
3. Result
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Hong, T.; Piette, M.A. Building thermal load prediction through shallow machine learning and deep learning. Appl. Energy 2020, 263, 114683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yuan, J.; Chen, L. Short-term load forecasting using EMD-LSTM neural networks with a Xgboost algorithm for feature importance evaluation. Energies 2017, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery And Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, D.; Elzarka, H. Advanced machine learning techniques for building performance simulation: A comparative analysis. J. Build. Perform. Simul. 2019, 12, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]




| Combination | Mean | Standard Deviation (SD) | Combination | Mean | SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lasso | L.R | 0.875 | 0.725 | PCA | L.R | 0.538 | 0.182 |
| XGB | 0.940 * | 0.926 * | XGB | 0.745 | 0.8 | ||
| R.F | 0.658 | 0.801 | R.F | 0.097 | 0.522 | ||
| SVR | −0.324 | −0.263 | SVR | −0.308 | −0.214 | ||
| Anova | L.R | 0.211 | 0.427 | Mutual- Info | L.R | −0.649 | 0.429 |
| XGB | −0.165 | 0.746 | XGB | 0.657 | 0.912 | ||
| R.F | −0.340 | 0.454 | R.F | 0.423 | 0.752 | ||
| SVR | −0.271 | −0.287 | SVR | −0.201 | −0.257 | ||
| Combination | Mean | SD | Combination | Mean | SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lasso | L.R | 0.546 | 0.233 | PCA | L.R | −0258 | −0.793 |
| XGB | 0.523 | 0.886 * | XGB | 0.73 | 0.807 | ||
| R.F | 0.771 * | 0.587 | R.F | 0.697 | 0.18 | ||
| SVR | 0.089 | 0.016 | SVR | 0.13 | −0.058 | ||
| Anova | L.R | 0.124 | 0.083 | Mutual- Info | L.R | 0.017 | −0.299 |
| XGB | 0.467 | 0.338 | XGB | 0.523 | 0.736 | ||
| R.F | 0.255 | −0.177 | R.F | 0.284 | 0.078 | ||
| SVR | 0.033 | −0.329 | SVR | 0.085 | −0.176 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-W.; Wang, J.-H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, W.-L.; Tu, H.-K. Application of Machine Learning for Optimizing Chemical Vapor Deposition Quality. Eng. Proc. 2025, 108, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025108005
Lin C-Y, Chen C-W, Wang J-H, Wang C-Y, Wang W-L, Tu H-K. Application of Machine Learning for Optimizing Chemical Vapor Deposition Quality. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 108(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025108005
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chen-Yu, Chun-Wei Chen, Jung-Hsing Wang, Chung-Ying Wang, Wei-Lin Wang, and Hao-Kai Tu. 2025. "Application of Machine Learning for Optimizing Chemical Vapor Deposition Quality" Engineering Proceedings 108, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025108005
APA StyleLin, C.-Y., Chen, C.-W., Wang, J.-H., Wang, C.-Y., Wang, W.-L., & Tu, H.-K. (2025). Application of Machine Learning for Optimizing Chemical Vapor Deposition Quality. Engineering Proceedings, 108(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025108005






