Abstract
Different countries in Europe have proposed some restrictions about bisphenol A (BPA), considered an endocrine disruptor, for the production of food packing and toys for children, for example, Denmark, France, Sweden, Belgium, Austria and Norway. However, it is still being found in wastewater effluents. In this study, BPA was degraded by catalytic wet air oxidation employing ruthenium-impregnated carbon nanosphere catalysts (CNS). The catalyst was synthesized with a mixture of resorcinol and formaldehyde and later, a pyrolysis treatment was impregnated by 1, 2, 5, 7 and 10% of ruthenium and activated with hydrogen at 350 °C. The experimental installation was a batch Hastelloy high-pressure reactor of 100 mL of volume with an electrical jacket and a variable-speed magnetic drive. The concentration of BPA was followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. After the study of different experiment variables (temperature (110–150 °C), pressure (20–50 bar), initial concentration of BPA (5–30 mg L−1) and catalyst mass (50–300 mg)) in a batch reactor of 100 mL of volume, two different potential models (r = k CaBPA and r = k CaBPA Pb Cc Ru) were used for simulating the kinetic behavior of BPA from the adjustment of the experimental data obtained for CWAO reactions. It also tested different loads of ruthenium (1–10%) in BPA degradation. Both adjustments had a correlation factor of 0.98 and reproduced all the experiments well, being better than those ones with 20 mg L−1 of initial concentration of BPA. BPA degradation was above 97% at 90 min of reaction time from 2% of Ru in the catalyst.
1. Introduction
Bisphenol A (BPA) has been widely used of high production volume (more than 5 tonnes per year) for the plastic of polycarbonate fabrication and epoxy resins in many industries [1,2]. Then, BPA can be found in pacifiers, bottle nipples, tin cans, soft drinks, polyvinyl chloride, epoxy-based paints, plastic sports equipment, medical devices, surface coatings, printing inks and thermal paper commonly used in cash register receipts, among others. BPA can migrate in small amounts to food and beverages contained in these containers, especially when they are not used correctly. Humans appear to be exposed through different pathways: food, through the migration of packaging liners; beverages, also due to coatings or contamination; and environmental, by dust in suspension and cosmetics. For this reason, different countries have proposed some restrictions and laws about BPA, considered an endocrine disruptor, for the production of food packing and toys for children, for example, Denmark, France, Sweden, Belgium, Austria, and Norway. However, only France has adopted a complete ban on the handling of BPA [3,4]. The conventional treatments of the wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are insufficient to eliminate this compound from the water, having found between values of μg L−1 to ng L−1, and the non-elimination of BPA affects other ecosystems. In Lyon, BPA has been reported to be between 136 and 156 ng L−1 in the effluent of a WWTP [5]. In Quebec, BPA has been found in the sludge from a WWTP with 270–360 μg kg−1 dry weight [5].
Advanced oxidation processes have emerged to degrade refractory compounds, such as bisphenol A, that other conventional processes cannot eliminate. There are many processes inside this group, one of them being the catalytic wet air oxidation (CWAO). It is crucial for a good selection of the catalyst for the process to keep active after several reactions. As the catalytic support confers a large part of the properties to the catalyst, the correct choice of support is essential. Throughout history, different materials have been employed for this aim, such as zeolites, clays, resins, carbon-based materials, etc. However, nanomaterials are the most employed nowadays, such as nanotubes, nanofibers and nanospheres [6,7,8,9].
This research work aims to degrade BPA with CWAO using a ruthenium carbon nanosphere-based catalyst.
2. Methods
Bisphenol A (BPA) (CAS 80-05-7) was supplied by Sigma-Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany), in an analytical purity (>99.99%) and employed for BPA solutions by diluting stock solutions to the required concentrations.
Resorcinol (99 wt.%), Pluronic F127 powder, formaldehyde solution (37 wt.% in water, stabilized with 15 wt.% methanol) and RuCl3 H2O were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. HNO3 (69.5 wt.%) was provided by Carlo Erba and HCl (37 wt.%) by Honeywell Fluka. Fischer Chemical supplied ethanol absolute.
The synthesis of the carbon nanospheres (CNS) was prepared by mixing resorcinol and formaldehyde in a polycondensation reaction with Pluronic F127 as a template. The synthesis of the CNS−Ru catalysts was accomplished by incipient wetness impregnation method and activation with hydrogen following the procedures described by Serra-Pérez et al. [10]. Catalysts were prepared with a content of 1, 2, 5, 7, and 10% in weight of Ru.
WAO and CWAO experiments were carried out in a 100 mL Hastelloy high-pressure batch reactor equipped with a magnetically driven stirrer set at 700 rpm to avoid any mass transfer limitations in the liquid phase of the reaction. It was also provided an electrical jacket to heat the reactor. The reactor is also connected to the bottles of nitrogen and air. The gas and cooling water feed, a pressure gauge and a rupture disk were located at the top of the reactor. Two thermocouples indicate the temperature inside the reactor and inside the jacket to have control of them. A total of 100 mL of BPA solution was loaded into the reactor with catalyst (CWAO) in a typical run. After purging with nitrogen to remove any trace of air, the reactor was heated to the desired temperature while the agitator was already working. The air was introduced until the work pressure was achieved when the desired temperature was reached. The first withdrawn sample was taken when the pressure was introduced, considering it as reaction zero time. Samples were collected at regular time intervals and then were cooled in water and immediately analyzed in duplicate, after being filtered through 0.45 μm PTFE filters and centrifuged for 10 min at 4500 rpm. Additionally, all the reaction tests were repeated three times, obtaining a 3% of experimental error.
Different reaction variables were modified in the oxidation experiments with the CNS−Ru(2%) catalyst, such as temperature (110–150 °C), pressure (20–50 bar), catalyst dose (0.5–3.0 g∙L−1), initial BPA concentration (5–30 mg∙L−1), following Table 1. The variables were optimized sequentially and in the order previously mentioned. At the optimal conditions, different loads of Ru in the catalyst were tested.

Table 1.
Sequence of experiments.
3. Results and Discussion
The optimal conditions were achieved with 130 °C, 20 bar, 0.04 gRu L−1 (2.0 g L−1 of CNS−Ru (2%)) and an initial concentration of 20 mg L−1, where the BPA degradation was above 97% [10].
Two potential models were employed to adjust the experimental results.
3.1. Kinetic Degradation: One-Factor Potential Model
In this model, only reactions varying temperature and initial concentration of BPA (experiments 1–4 and 11–13 from Table 1) were adjusted to a nonlinear potential model, Equation (1).
where r (mmol g Ru−1 min−1) was the reaction rate, CBPA (mmol L−1) was the BPA concentration, a was the order for the BPA concentration and also the total order of the reaction. The constant k (mmol1−a La gRu−1 min−1 for CWAO) was the kinetic constant, which was described by the Arrhenius equation, Equation (2):
where k0 (same units of k) was the pre-exponential factor, Ea (kJ mol−1) was the activation energy, R the gas constant (8.314 10−3 kJ mol−1 K−1) and T (K) the temperature.
r = k(T) CaBPA
k = k0 e(−Ea/(RT))
For the application of the equations, some assumptions were taken: the volume is constant, the catalyst mass is constant and the reaction system is heterogeneous, Equation (3):
where V was the reaction volume, and W (gRu) was the mass of the contained metal in the used catalyst.
r = (V/W) (−dCBPA/dt)
The experimental data were fitted to the integrated Equation (1) through Origin 2019, employing the iteration algorithm of Levenberg–Marquardt. BPA initial concentration, reaction time and temperature were selected as independent variables. The correlation coefficient of the adjustment was 0.98, Equation (4):
r = 8606 e(−31.03/(RT)) C0.98BPA
The experiments with an initial concentration of 20 mg L−1 fitted the model better than with the other concentrations. The activation energy was 31 kJ mol−1.
3.2. Kinetic Degradation: Complex Potential Model
In this model, all the experiments from Table 1 were considered for Equation (5):
r = k(T) CaBPA Pb CcRu
The employed reactor equation was Equation (3) as in the previous case and the experimental data were adjusted by Origin 2019. In this case, reaction time, initial concentration of NPR, temperature, oxygen pressure and concentration of Ru were considered the independent variables in the adjustment. The correlation coefficient of the adjustment was 0.98, Equation (6):
r = 1013 e(−31.60/(RT)) C0.99BPA P0.55 C0.78Ru
The experiments with an initial concentration of 20 mg L−1 fitted the model better than with the other concentrations, Figure 1. As in the previous model, the activation energy was 31 kJ mol−1.
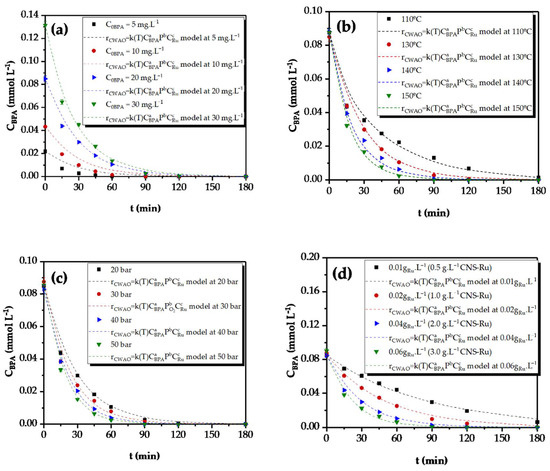
Figure 1.
Fitted experimental data to Equation (6) for (a) different initial BPA concentrations in the reaction (130 °C, 20 bar, 2.0 g L−1 of CNS−Ru(2%); (b) different reaction temperatures (20 bar, 2.0 g L−1 of CNS−Ru(2%), C0BPA = 20 mg L−1); (c) different pressures (130 °C, C0BPA = 20 mg L−1, 2.0 g L−1 CNS−Ru); (d) different Ru concentration values (130 °C, 20 bar, C0BPA = 20 mg L−1).
3.3. Effect of the Ruthenium Load in the CNS−Ru Catalyst
At the optimal conditions, different loads of Ru were tested to determine the most effective load of Ru in the CNS−Ru catalyst. The conversion in 90 min of reaction time was 84% for 1 wt.% of Ru, while the conversion for 2 wt.% of Ru was above 97%. The BPA degradation with 10 wt.% of Ru was 97% in 60 min of reaction time. However, increasing the percentage of Ru from 2 to 10% is not worthwhile from an economic point of view.
4. Conclusions
Two potential models were successfully employed for the adjustment of the experimental data simulating the behavior of the BPA degradation by CWAO with ruthenium carbon nanospheres (R2 = 0.98). The activation energy was in both models 31 kJ mol−1.
In the test of the ruthenium load in the catalyst, the first percentage that allowed a BPA conversion above 97% was 2 wt.% in Ru in the CNS−Ru catalyst.
Author Contributions
E.S.-P.: formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft, methodology. G.O.: writing—review and editing, J.G.: conceptualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Project REMTAVARES (S2018/EMT-4341) and the European Social Fund.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Regional Government of Madrid provided through Project REMTAVARES (S2018/EMT-4341) and the European Social Fund. Estrella Serra-Pérez thanks the Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades for a Grant (FPU2015/04075).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rubin, B.S.; Bisphenol, A. An endocrine disruptor with widespread exposure and multiple effects. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 127, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deblonde, T.; Cossu-Leguille, C.; Hartemann, P. Emerging pollutants in wastewater: A review of the literature. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2017/2018. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials; Enzymes; Flavourings and Processing Aids (CEF). Scientific Opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, J.; Kristofco, L.A.; Steele, W.B.; Yates, B.S.; Breed, C.S.; Williams, E.S.; Brooks, B.W. Global assessment of bisphenol a in the environment: Review and analysis of its occurrence and bioaccumulation. Dose-Response Int. J. 2015, 13, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erjavec, B.; Kaplan, R.; Djinović, P.; Pintar, A. Catalytic wet air oxidation of bisphenol A model solution in a trickle-bed reactor over titanate nanotube-based catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 132, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaccallo, Y.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Marín, M.P.; Gil, M.V.; Larriba, M.; Águeda, V.I.; Ovejero, G.; García, J. Magnetic Fe3O4/multi-walled carbon nanotubes materials for a highly efficient depletion of diclofenac by catalytic wet peroxideoxidation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 22372–22388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.-T.; Teng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X. Heterogeneous activation of persulfate by carbon nanofiber supported Fe3O4@carbon composites for efficient ibuprofen degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Perez, E.; Ferronato, C.; Giroir-Fendler, A.; Alvarez-Torrellas, S.; Ovejero, G.; Garcia, J. Highly Efficient Ru Supported on Carbon Nanosphere Nanoparticles for Ciprofloxacin Removal: Effects of Operating Parameters, Degradation Pathways, and Kinetic Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 15515–15530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Pérez, E.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Águeda, V.I.; Delgado, J.A.; Ovejero, G.; García, J. Insights into the removal of Bisphenol A by catalytic wet air oxidation upon carbon nanospheres-based catalysts: Key operating parameters, degradation intermediates and reaction pathway. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).