Abstract
Obesity represents a global health challenge, with a critical and urgent need for long-term, sustainable management strategies. Tirzepatide is a novel dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. At first approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, tirzepatide represents one of the latest clinically approved and commercially available pharmacological options for obesity management. This narrative review aimed to synthesize existing clinical evidence on the efficacy and safety of tirzepatide in non-diabetic obese individuals. A comprehensive literature search was conducted using the PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, ClinicalTrials.gov, and Google Scholar databases to identify relevant clinical trials, meta-analyses, and original studies assessing the weight-loss impact of tirzepatide from 2022 onwards. Synthesized evidence indicated that tirzepatide achieved up to 20.9% weight loss over 72 weeks (SURMOUNT-1), 18.4% after lifestyle intervention (SURMOUNT-3), 17.5% in Chinese adults (SURMOUNT-CN), and 25.3% with continued treatment over 88 weeks (SURMOUNT-4). Meta-analyses confirmed higher odds of ≥5–20% weight loss versus semaglutide and liraglutide, significantly reducing body mass index, waist circumference, blood pressure, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk. Health-related quality of life improved with greater weight loss, and gastrointestinal side effects (nausea, diarrhea, constipation) were common but mild to moderate, with <5% treatment discontinuation. Tirzepatide achieved significant weight loss, cardiometabolic benefits, and improved quality of life in non-diabetic obese individuals, but further research is needed on long-term efficacy, safety, and clinical application.
1. Introduction
Obesity is a rapidly growing global epidemic, with an estimated 1 billion adult males and 1.1 billion adult females affected by overweight and obesity as of 2021 [1,2,3]. A recent study by the GBD 2021 Adult BMI Collaborators indicated that between 1990 and 2021, the global prevalence of obesity increased by 155% in males and 105% in females [3]. The most dramatic rise in obesity prevalence was reported in the Middle East and North Africa region, where rates in males more than tripled [3]. Several countries in Oceania, North Africa, and the Middle East now report adult overweight and obesity prevalence exceeding 80%, which highlights the urgent need for effective, scalable, and sustainable weight management strategies [3,4,5].
Obesity has been well-recognized as a primary risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), hypertension, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk, and many other disorders [6,7,8,9]. Its pathophysiological role is mediated through complex metabolic, inflammatory, and hormonal mechanisms that contribute to insulin resistance, endothelial dysfunction, and systemic inflammation [8,10,11]. Beyond its clinical consequences, obesity imposes a substantial economic burden on healthcare systems, primarily due to the long-term management of its associated comorbidities [12,13,14]. Therefore, the economic impact of obesity highlights the necessity for effective clinical management strategies to alleviate its financial burden [15,16].
In light of these clinical and economic consequences, the effective management of obesity has become a public health imperative [17,18]. While lifestyle interventions remain the cornerstone of management [19], pharmacological therapies play an increasingly important adjunctive role, particularly in countering the complex interplay of environmental, genetic, and epigenetic contributors to obesity [20,21,22,23]. Currently, only a limited number of long-term pharmacological agents have received approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for obesity management, although several promising agents are in various stages of clinical development and regulatory evaluation [24,25,26].
Among the pharmacological agents approved for long-term obesity management, tirzepatide—a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist—has demonstrated notable weight-reduction efficacy in recent clinical trials [27,28,29]. Initially approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, tirzepatide has since received regulatory authorization by the U.S. FDA for chronic weight management [30]. It has been authorized for individuals who are categorized as obese, which is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m2 or higher, or for those who are classified as overweight and possess at least one weight-related health condition, such as hypertension, elevated cholesterol levels, T2DM, obstructive sleep apnea, or ASCVD [31].
Tirzepatide is a dual incretin receptor agonist that targets both GIP and GLP-1 receptors [32,33]. The proposed mechanisms of action involve multiple metabolic pathways, including a decrease in hunger and energy intake, an increase in energy expenditure, an increase in thermogenic activity, inhibition of gastric emptying, and increased glucose metabolism [34,35]. Synergistic action on the targets of GLP-1 and GIP strengthens the role of tirzepatide as an efficacious pharmaceutical agent for obesity treatment [36,37,38,39].
Although tirzepatide was originally developed to improve glycemic control in individuals with T2DM [40,41], its evident weight-reducing effects have led to growing interest in its use among non-diabetic individuals with obesity [42,43,44,45]. Preliminary evidence suggests that the magnitude of weight loss may be even greater in non-diabetic populations, potentially due to differences in insulin sensitivity, neuroendocrine regulation, and baseline metabolic function [46,47]. Moreover, the safety profile may differ in this group, with a reduced risk of hypoglycemia but possible variation in gastrointestinal tolerability and long-term cardiometabolic effects [48,49]. These distinctions underscore the need to evaluate tirzepatide efficacy and safety specifically in non-diabetic populations, independent of its role in T2DM management [50,51].
Given the growing off-label interest and the expanding number of clinical trials evaluating tirzepatide in non-diabetic individuals, there is a continued need for comprehensive reviews that elucidate its efficacy and safety profile within this specific population. As such, key questions regarding tirzepatide’s standalone utility for weight management in non-diabetic individuals remain an area which need further research. Therefore, this narrative review aimed to advance the field of pharmacotherapy of obesity by consolidating and appraising the most recent clinical evidence to inform both practice and research. Specifically, this review aimed to evaluate tirzepatide efficacy and safety as a pharmacotherapeutic agent in non-diabetic adults with obesity which aligns with emerging clinical guidelines for obesity management [52,53,54].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This narrative review followed a structured approach for narrative literature reviews [55,56,57,58]. Specifically, this narrative review was developed in accordance with the scale for the assessment of narrative review articles (SANRA), a validated quality assessment tool designed to enhance the scientific rigor, clarity, and transparency of non-systematic reviews [59].
The importance of the review topic was established by addressing the global burden of obesity and the growing use of tirzepatide in non-diabetic populations. The review objective—to synthesize current evidence on tirzepatide efficacy and safety in this group—was clearly defined. To address this objective, we conducted a focused literature search across five major databases, limited to peer-reviewed, English-language studies published from 2022 to March 2025. Priority was given to randomized controlled trials (RCTs), meta-analyses, and systematic reviews assessing tirzepatide clinical outcomes. Gray literature and non-peer-reviewed sources were excluded to maintain data synthesis reliability. Study designs and levels of evidence were considered qualitatively during synthesis but no formal risk of bias tool was applied, in line with the narrative nature of this review.
2.2. Review Question
In alignment with the SANRA guidelines, which emphasize a clear and well-justified aim, this review focused on evaluating tirzepatide as a novel pharmacological intervention for weight management in non-diabetic individuals with obesity. While initially approved for glycemic control in T2DM, tirzepatide has demonstrated substantial weight loss effects independent of glycemic benefit, prompting clinical interest in its use for non-diabetic populations [60]. Given the evolving nature of current evidence, the aim of this review was to synthesize and appraise the available literature on its efficacy and safety in this specific population. The guiding research question was as follows: what is the current clinical evidence on the efficacy and safety of tirzepatide for weight loss in non-diabetic obese individuals?
2.3. Literature Search Strategy
To ensure transparency and reproducibility in accordance with the SANRA standards, a structured literature search was conducted across the following five major databases: PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, ClinicalTrials.gov, and Google Scholar. The search aimed to identify peer-reviewed studies reporting on the efficacy and safety of tirzepatide in non-diabetic individuals with obesity. Search terms included combinations of relevant keywords such as “Tirzepatide”, “obesity management”, “dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist”, “weight loss treatment”, and “clinical outcomes in obesity”. Boolean operators were applied using combinations, such as “Tirzepatide” OR “GLP-1” OR “peptide” OR “medication” OR “weight loss” OR “obesity”, to expand sensitivity. Filters were applied to include only human studies, published in English, from 2022 onward. Google Scholar was used to identify additional peer-reviewed literature while gray literature, preprints, and non-peer-reviewed sources were excluded to ensure the scientific integrity of the included data. The final search was completed on 1 March 2025.
2.4. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
In accordance with the SANRA guidelines emphasizing clarity and relevance in evidence selection, this review included studies that evaluated the efficacy and safety of Tirzepatide in non-diabetic, overweight or obese individuals. Eligible sources were restricted to peer-reviewed clinical trials, meta-analyses, systematic reviews, and observational studies published between 2022 and 2025. Studies were required to report at least one relevant outcome related to weight loss such as BMI reduction, waist circumference, or metabolic parameters, including blood pressure, lipid profile, or ASCVD risk scores. Additional endpoints of interest included treatment discontinuation rates, gastrointestinal adverse effects, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) to allow for a comprehensive synthesis of tirzepatide clinical utility.
To ensure methodological robustness, studies with a relatively small sample size were excluded. This threshold was informed by standard sample sizes in phase 2–3 obesity pharmacotherapy trials and was intended to reduce the risk of bias and to enhance generalizability. This approach also aligns with the SANRA framework, which emphasizes the quality and relevance of endpoint data.
Further exclusions included studies conducted primarily in individuals with T2DM, as well as animal studies, in vitro experiments, case reports, editorials, opinion pieces, and conference abstracts. Articles lacking sufficient data on efficacy or safety outcomes, those with short follow-up durations, unclear methodologies, or duplicated or overlapping datasets were also omitted to maintain the scientific integrity of the synthesis.
2.5. Data Collection and Analysis
Following the initial title and abstract screening by the first and senior authors, full-text articles were assessed for eligibility based on the aforementioned predefined inclusion criteria. Data extraction focused on key record characteristics, including the authors, year, design, population demographics, tirzepatide dose, intervention duration, and primary outcomes (e.g., percentage weight loss, cardiometabolic changes, adverse events, and treatment discontinuation). The synthesis was performed narratively to report on efficacy trends across the included records, safety profiles, and real-world implications.
3. Results
3.1. Overview of the Included Records
The initial database search retrieved 465 articles. Following the screening and filtering process based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria and a consensus among the four authors, 17 records were deemed eligible and included in this narrative review. These studies were organized chronologically from the earliest publication in 2022 to the most recent in 2025, ensuring a structured presentation of evolving clinical evidence. The detailed list of the selected studies is presented in (Table 1). The 17 studies included in this narrative review span a range of designs, including phase 3 randomized controlled trials, systematic reviews, and network meta-analyses, with a total of about 26,090 participants. These studies primarily assessed the efficacy and safety of tirzepatide in overweight and obese adults, with a few focusing on specific comorbidities such as inflammatory bowel disease and obstructive sleep apnea. The doses of tirzepatide varied, ranging from 5 mg to 15 mg once weekly, with treatment durations spanning from 16 weeks to 88 weeks.

Table 1.
Overview of included studies evaluating tirzepatide for weight management in non-diabetic obese individuals.
3.2. Efficacy of Tirzepatide Based on the Included Records
Across the 17 included records, tirzepatide was consistently reported to show substantial efficacy in inducing weight loss among adults with overweight or obesity. Selected findings from four key trials are summarized in (Figure 1), highlighting both absolute and categorical weight loss outcomes across diverse clinical contexts. In the landmark SURMOUNT-1 trial by Jastreboff et al., the mean weight loss at 72 weeks was −15.0%, −19.5%, and −20.9% with tirzepatide 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg, respectively, compared to −3.1% with placebo [61]. Moreover, 91% of participants on the 15 mg dose achieved ≥ 5% weight loss, and 57% achieved ≥ 20% weight loss, compared to 35% and 3% in the placebo group, respectively [61].
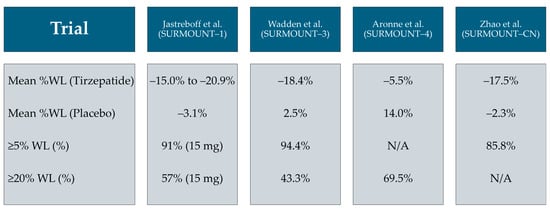
Figure 1.
Summary of mean percentage weight loss (WL) and the percentage of participants achieving ≥ 5% and ≥20% total WL in four selected tirzepatide trials among non-diabetic individuals with obesity/overweight [61,62,65,66].
Similarly, the SURMOUNT-3 trial by Wadden et al., which included a 12-week intensive lifestyle intervention lead-in, showed an additional −18.4% weight loss over 72 weeks in the tirzepatide group versus a 2.5% gain with placebo; 94.4% of participants achieved ≥ 5% additional loss and 43.3% achieved ≥ 20% [62]. In the SURMOUNT-4 maintenance trial by Aronne et al., continued tirzepatide therapy after a 36-week open-label lead-in period resulted in a sustained mean weight loss of −5.5% versus a +14.0% rebound in the placebo group (p < 0.001); notably, 69.5% of participants maintained ≥ 20% total weight loss at 88 weeks [65]. In the SURMOUNT-CN study among Chinese adults by Zhao et al., tirzepatide 15 mg achieved a −17.5% mean weight reduction versus −2.3% with placebo at 52 weeks, with ≥5% weight loss attained in 85.8% versus 29.3%, respectively [66].
Pooled meta-analyses further supported tirzepatide efficacy. Qin et al. found that tirzepatide 15 mg achieved a mean body weight change of −11.8% (95% confidence interval (CI) −14.5 to −9.1) across seven randomized controlled trials (RCTs), while Liu et al. reported the consistent superiority of tirzepatide over a placebo in non-diabetic populations [67,68]. The systematic review by Rochira et al. showed a mean reduction in fat mass of −6.6 kg and waist circumference reductions of up to −18.5 cm with 15 mg doses [69]. In the SUMMIT trial by Packer et al., adults with obesity and heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction receiving tirzepatide experienced a −13.5% mean weight loss and a 6.9-point greater improvement in the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire–Clinical Summary Score versus a placebo at 52 weeks (p < 0.001) [76].
3.3. Benefits of Tirzepatide on Cardiometabolic Function
Across the included records, tirzepatide consistently improved multiple cardiometabolic parameters beyond weight loss, including a reduction in systolic blood pressure, fasting insulin, glycated hemoglobin, and an improved lipid profile, as illustrated in (Figure 2). In SURMOUNT-1, Jastreboff et al. reported significant reductions in waist circumference (−14.0 to −18.5 cm across doses), systolic blood pressure (−6.6 to −7.7 mmHg), fasting insulin (−33.3% to −43.6%), and triglycerides (−20.1% to −24.8%) [61].
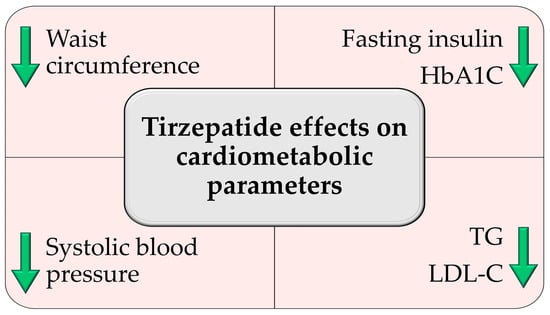
Figure 2.
Tirzepatide-induced improvements in cardiometabolic parameters based on the included records. HbA1c: glycated hemoglobin; TG: triglycerides; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Green arrows indicate a decrease in the parameter described.
A post hoc analysis by Hankosky et al. demonstrated a 23.5% relative reduction in the 10-year predicted ASCVD risk score in participants receiving tirzepatide versus a 12.7% increase with placebo (p < 0.001) [71]. In the SURMOUNT-3 trial, Wadden et al. observed favorable effects on metabolic syndrome components, with tirzepatide reducing BMI by −7.7 kg/m2 and waist circumference by −11.3 cm compared to a placebo [62]. Meta-analyses by Qin et al. reaffirmed these benefits, with tirzepatide significantly lowering fasting glucose (mean difference: −0.47 mmol/L), systolic blood pressure (−4.4 mmHg), LDL cholesterol (−0.25 mmol/L), and improving HDL cholesterol (mean increase: +0.09 mmol/L) [67].
Liu et al. reported consistent reductions in blood pressure and improvements in lipid profiles among non-diabetic patients [68]. Rochira et al. reported marked reductions in visceral adipose tissue and total fat mass (−6.6 kg) with a preservation of lean body mass, suggesting targeted cardiometabolic improvement [27]. In patients with obesity and heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction, Packer et al. demonstrated that tirzepatide improved cardiac function, with a −6.9-point improvement in the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire–Clinical Summary Score at 52 weeks [76]. Malhotra et al. further reported reductions in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and systolic blood pressure among individuals with obstructive sleep apnea [74].
3.4. Safety of Tirzepatide Based on the Included Records
Across the included clinical trials and meta-analyses, tirzepatide demonstrated a generally favorable safety profile, with adverse events largely mild to moderate and predominantly gastrointestinal in nature. In the SURMOUNT-1 trial by Jastreboff et al., nausea, diarrhea, and constipation were the most frequently reported adverse effects, occurring in 31% to 35% of participants, particularly during dose escalation [61]. Treatment discontinuation due to adverse events occurred in 4.3%, 7.1%, and 6.2% of participants in the 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg groups, respectively, compared to 2.6% in the placebo group [61].
In the SURMOUNT-3 study, gastrointestinal side effects remained the leading cause of withdrawal, but only 4.1% of participants discontinued due to adverse events over 72 weeks of treatment [62]. Similarly, in the SURMOUNT-4 trial, 6.3% of tirzepatide-treated individuals discontinued due to adverse events versus 1.4% with placebo [65]. The SURMOUNT-CN trial in Chinese adults mirrored these patterns, with <5% discontinuation and most side effects occurring during dose escalation [66].
Meta-analyses by Qin et al. [67] and Liu et al. [68] confirmed that gastrointestinal events were more common with tirzepatide than a placebo (odds ratios ranging from 3.6 to 8.3 for nausea and vomiting), but the incidence of serious adverse events and hypoglycemia was low and not significantly increased. Notably, in trials involving comorbid populations, such as those with obstructive sleep apnea [74] or heart failure with preserved ejection fraction [76], tirzepatide was well tolerated without unexpected adverse events.
4. Discussion
As obesity remains a major global health challenge, the demand for pharmacological interventions that offer substantial, sustained weight reduction with an acceptable safety profile has intensified [1,78,79,80,81,82,83]. The current narrative review concisely evaluated current available evidence regarding tirzepatide efficacy and safety in non-diabetic obese individuals, synthesizing findings from multiple high-quality clinical trials and meta-analyses. As a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, tirzepatide demonstrates clinically significant weight loss, with notable results compared to those seen with bariatric interventions [62,84,85,86,87]. However, direct equivalence to surgical approaches should be interpreted with caution due to differences in the population, intervention mechanisms, and follow-up duration.
The unique mechanism of action of tirzepatide and its ability to drive clinically relevant improvements in weight and metabolic parameters represent an important addition to the arsenal of obesity pharmacotherapy, though not a definitive solution [39,77,88]. While weight loss remains its most striking benefit, tirzepatide also offers potential benefits in glycemic control, a tolerability profile consistent with GLP-1 receptor agonists, and emerging evidence of acceptable adherence in early real-world studies [29,38]. Real-world comparative studies suggest greater efficacy than semaglutide in inducing clinically significant weight loss, with similar tolerability, although head-to-head evidence remains limited [72,89,90,91,92]. The discussion that follows examines the depth of its clinical impact, key considerations for its role in long-term obesity management, and the remaining gaps in knowledge that warrant further investigation.
In this review, tirzepatide has been shown to provide significant and sustained weight loss in multiple randomized controlled trials. The SURMOUNT-1 trial, a cornerstone in this evolution, highlighted tirzepatide’s considerable efficacy in non-diabetic individuals with obesity [61]. In the 72-week, placebo-controlled trial involving non-diabetic individuals with obesity, participants treated with 15 mg of tirzepatide achieved a mean weight reduction of 20.9%, overshadowing the modest 3.1% decline observed in the placebo group [61]. These outcomes were remarkable in obesity pharmacotherapy compared to traditional drugs [26]. Nevertheless, the extent of tirzepatide-induced weight loss remains notably lower than that achieved through bariatric surgery, which continues to represent the gold standard in terms of both absolute magnitude and the long-term sustainability of weight reduction [86,93,94,95]. This distinction is important, particularly in populations with high-risk obesity or metabolic syndrome where surgical outcomes may confer greater long-term benefit. However, the emergence of tirzepatide among other GLP-1 receptor agonists narrows the gap between pharmacological and surgical interventions, highlighting a notable progress in the medical management of obesity [20,96,97].
The current review showed that tirzepatide efficacy lies in its adaptability across various clinical contexts. For example, the SURMOUNT-3 trial evaluated tirzepatide in individuals who had already lost ≥5% of their baseline weight through a 12-week intensive lifestyle program. Over the subsequent 72 weeks, those randomized to tirzepatide achieved an additional mean weight reduction of 18.4%, compared to a weight gain in the placebo arm [62]. These findings support tirzepatide’s potential role as not only a stand-alone agent but also as a pharmacologic adjunct to lifestyle-based approaches, a strategy that remains foundational in long-term obesity care [98,99,100]. The generalizability of tirzepatide efficacy was equally notable in SURMOUNT-CN, conducted among Chinese adults with obesity [66]. In SURMOUNT-CN, tirzepatide 15 mg yielded a mean weight reduction of 17.5% over 52 weeks compared to 2.3% with a placebo, demonstrating its tirzepatide efficacy across diverse ethnic and genetic backgrounds [66].
The most compelling argument for tirzepatide’s potential role in modern obesity management may lie in the SURMOUNT-4 trial, which addressed the often-ignored aspect of weight maintenance [65]. After an open-label 36-week run-in with tirzepatide and significant weight reduction, participants were randomized to either continue tirzepatide or switch to a placebo [65]. The divergence was notable, with those maintained on tirzepatide losing an additional 5.5% whereas those who switched to the placebo regaining 14.0%, offsetting a substantial portion of the initial benefit [65]. This finding serves as a reminder that obesity is a chronic, relapsing disease and its pharmacologic management must be approached through sustained therapy which would yield sustained benefit [26,101,102].
The management of obesity extends beyond the initial induction of weight loss to include its long-term maintenance—an area often marked by physiological and behavioral challenges [64,103]. The SURMOUNT-4 trial provides supporting evidence on the importance of continued pharmacological intervention [65]. Specifically, participants who remained on tirzepatide therapy for a total of 88 weeks achieved a sustained mean weight reduction of 25.3%, underlining tirzepatide capacity to support prolonged weight loss. In contrast, those who transitioned to placebo following a 36-week lead-in period exhibited substantial weight regain, highlighting the relapse-prone nature of obesity in the absence of ongoing treatment [65].
These findings align with longstanding data demonstrating that weight regain after initial loss is frequently driven by counter-regulatory biological mechanisms [104,105]. Reductions in energy expenditure, increases in appetite-regulating hormones such as ghrelin, and diminished levels of leptin collectively contribute to a state that favors weight regain [106,107]. Tirzepatide’s dual agonistic action on GIP and GLP-1 receptors may help counteract these compensatory mechanisms by improving insulin sensitivity, enhancing satiety, and modulating energy balance [33,108]. Nevertheless, the observed rebound upon treatment cessation in SURMOUNT-4 supports the conceptualization of obesity as a chronic, relapsing disease requiring sustained therapeutic intervention [65].
In this review, the included meta-analyses have positioned tirzepatide as one of the most effective pharmacological agents currently available for the treatment of overweight and obesity in non-diabetic populations [63,67,68,72,73]. A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials confirmed that tirzepatide induced greater weight loss than semaglutide and liraglutide, with higher odds of achieving ≥5–20% weight loss [63]. However, direct comparative trials remain limited, and dose equivalence across different agents may vary, warranting cautious interpretation. Another meta-analysis evaluating dose-dependent efficacy found that 15 mg of tirzepatide achieved the highest efficacy in weight reduction, outperforming GLP-1 receptor agonists in absolute weight loss and metabolic improvements [73]. Nonetheless, longer-term data and real-world effectiveness studies are still needed to clarify whether these benefits are sustained over time and across diverse patient populations [109].
Beyond weight loss, the effects of tirzepatide on body composition represent an important dimension of its clinical utility. For example, an included systematic review found that tirzepatide significantly reduced total fat mass, visceral adipose tissue, and waist circumference, outperforming other GLP-1 receptor agonists and dual hormone receptor agonists, although its effect on fat-free mass remains less clearly defined [69,110]. In obesity management, the preservation of lean mass is critical for metabolic health and physical function, particularly in older adults, and this area warrants further investigation [111,112,113].
In addition, tirzepatide appears to exert potentially beneficial cardiometabolic effects as shown in the current review findings [114,115,116,117]. A post hoc analysis of the SURMOUNT-1 trial revealed that tirzepatide therapy led to a statistically significant reduction in the 10-year predicted risk of ASCVD [71]. This reduction was not a byproduct of weight loss alone but was accompanied by notable improvements in lipid parameters, reductions in systolic blood pressure, and declines in HbA1c, even in participants without T2DM [71]. Given the high prevalence of cardiovascular complications in obesity, this finding suggests that tirzepatide may offer long-term cardioprotective benefits. However, the absence of long-term cardiovascular outcomes data from the included records in this review limits our ability to definitively establish the cardioprotective benefit of tirzepatide.
In the same vein of tirzepatide’s potential cardiometabolic benefits, a study evaluating tirzepatide’s impact on metabolic parameters in non-diabetic patients with IBD found that BMI and total body weight significantly decreased, with no significant changes in liver enzymes or inflammatory markers, supporting its potential metabolic benefits beyond obesity [70]. While these findings suggest a metabolic benefit that may extend beyond classical obesity phenotypes, the small sample size and observational nature of the data limit broad generalization.
Moreover, tirzepatide’s therapeutic impact appears to extend into pathophysiological domains where obesity drives multisystem dysfunction. In patients with moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnea, tirzepatide therapy was associated with significant reductions in the apnea–hypopnea index, body weight, and systemic inflammatory markers [74]. In patients with heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction, tirzepatide reduced the risk of cardiovascular mortality and disease progression while also improving health status scores [76]. These findings highlight its potential beyond weight loss in managing obesity-related complications [118]. While these outcomes appear promising, the variability in studies’ duration and patient heterogeneity underscores the need for further longitudinal and comparative investigations to fully define tirzepatide’s role in obesity-related comorbidities.
In this review, tirzepatide has demonstrated a consistent and clinically relevant, though still emerging, impact on HRQoL, a key secondary endpoint in obesity management [119,120]. In a post hoc analysis of the SURMOUNT-1 trial, Gudzune et al. reported that participants receiving tirzepatide who achieved greater weight loss experienced proportionally greater improvements across multiple validated HRQoL instruments [75]. Specifically, participants achieving ≥20% weight loss exhibited the most pronounced gains in physical functioning, psychosocial well-being, and general health perception. These findings align with the existing literature indicating that moderate weight loss is required to achieve clinically significant improvements in HRQoL measures [121,122]. However, these improvements appear to be weight-dependent rather than pharmacologically unique to tirzepatide, and therefore may also be observed with other high-potency anti-obesity agents [123].
Importantly, the safety profile of tirzepatide, as reported across the included records in the current review, aligns with known class effects of incretin-based therapies and appears generally favorable [124,125,126]. Gastrointestinal adverse events—notably nausea, diarrhea, and constipation—were the most frequently reported side effects, consistent across the SURMOUNT-1, SURMOUNT-3, SURMOUNT-CN, and SURMOUNT-4 trials [61,62,65,66]. These events were predominantly mild to moderate in severity and transient in nature, typically occurring during dose escalation [109].
Meta-analytical evidence further supports the tolerability of tirzepatide as shown by Qin et al. and Xie et al. [67,72]. These reviews showed that while tirzepatide was associated with a higher incidence of gastrointestinal events compared to a placebo and other GLP-1 receptor agonists, the rates of serious adverse events and treatment withdrawals remained low and comparable across interventions [67,72,109,127,128]. To optimize the tolerability of tirzepatide and other incretin-based therapies, clinical guidance recommends gradual dose escalation, dietary modifications, and supportive management for gastrointestinal adverse events [129,130,131]. Drawing from expert consensus across specialties, strategies include eating smaller, low-fat meals, maintaining hydration, and slowing the dose-escalation schedule when necessary [132]. In cases of persistent nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, temporary dose-delay or symptomatic treatment may be employed [132]. These approaches have been shown to reduce the incidence and severity of gastrointestinal adverse events and improve adherence, ultimately ensuring that patients can benefit from the full therapeutic potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists without premature discontinuation [130,132].
Despite the reassuring short-to-medium term data on tirzepatide’s safety, the duration of follow-up in most trials (ranging from 52 to 88 weeks) limits the comprehensive assessment of long-term safety, particularly regarding cardiovascular, renal, and endocrine outcomes [38,133]. Furthermore, concerns about potential risks related to gallbladder disease, pancreatitis, and thyroid neoplasia, among other possible adverse events observed in some GLP-1 receptor agonists, warrant continued pharmacovigilance [124,134,135,136]. Thus, long-term observational data and post-marketing surveillance are essential to confirm tirzepatide safety across broader populations and over extended durations of use [137,138].
While tirzepatide has emerged as a pharmacologic agent in the management of obesity, its clinical trajectory remains under active refinement. Several critical areas necessitate further investigation to fully elucidate its role within the therapeutic landscape of obesity pharmacotherapy. First, comparative efficacy studies are required to delineate the relative benefits of tirzepatide against emerging polyagonists, such as retatrutide—a novel triple agonist of GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptors [63,139,140]. Second, long-term tirzepatide weight durability beyond 88 weeks remains an unresolved challenge. While SURMOUNT-4 demonstrated a 25.3% weight reduction sustained through continuous tirzepatide therapy, participants randomized to the placebo experienced substantial weight regain, underscoring the chronic relapsing nature of obesity [65]. As with T2DM pharmacotherapy, research must now explore whether long-term benefits of tirzepatide can be maintained with dose tapering, intermittent reinitiation, or structured de-escalation protocols—none of which are currently supported by evidence [65,141]. Third, body composition outcomes require clarification. Although tirzepatide robustly reduces total and visceral adipose tissue, concerns remain about concomitant lean mass loss [69]. Fourth, tirzepatide’s real-world effectiveness and implementation science must catch up with efficacy data, as recently highlighted by Thomsen et al. [29]. Adherence in randomized controlled trials likely overestimate patient behavior in routine clinical settings, where factors such as injection aversion, cost, insurance coverage, and patient education significantly affect long-term outcomes [142,143,144,145,146]. Finally, the range of tirzepatide’s metabolic impact warrants expansion beyond weight-centric endpoints. While preliminary studies suggest potential benefits in conditions such as obstructive sleep apnea [74], and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction [76], large-scale, disease-specific trials with organ-specific outcomes and mechanistic biomarkers are necessary to validate and quantify these observations among patients with other chronic diseases [147].
This narrative review must acknowledge its limitations and the broader scientific uncertainties that persist regarding tirzepatide safety and efficacy as follows. The current review was largely based on the results of controlled environments of randomized clinical trials. These conditions, while methodologically sound, may not mirror the complexities of real-world clinical practice, where comorbidities, adherence variability, and socio-economic constraints reshape therapeutic outcomes. Foremost among the uncertainties is the long-term safety profile of tirzepatide. Additionally, the economic sustainability of tirzepatide is another frontier requiring empirical investigation. Moreover, tirzepatide applicability in pediatric populations remains wholly speculative. The epidemiological rise in childhood obesity and its sequelae necessitate pediatric trials that go beyond simple dose adjustments to examine the agent’s developmental, endocrinologic, and psychological effects. Until such data are available, tirzepatide must be viewed as an investigational agent in this demographic [148]. Finally, the rapid emergence of next-generation agents, such as retatrutide and cagrilintide–semaglutide combinations, demands that tirzepatide be continuously evaluated not only against placebos but also in head-to-head comparative effectiveness trials [149,150,151]. The therapeutic bar is rising and while tirzepatide has thus far cleared it, its enduring relevance will hinge on superior or at least equivalent performance across efficacy, safety, cost, and quality of life metrics [152,153].
5. Conclusions
As shown in the included records in this review, tirzepatide stands at the forefront of contemporary pharmacologic strategies for obesity management, demonstrating notable efficacy in inducing weight-loss—approaching a 20% mean reduction in several high-quality trials—alongside marked improvements in cardiometabolic health and health-related quality of life in non-diabetic populations. Its dual agonist mechanism targeting GIP and GLP-1 receptors confers a unique metabolic advantage over traditional monotherapies. Despite a favorable safety profile, particularly regarding the low rate of serious adverse events, gastrointestinal side effects remain the most common tolerability concern. The evidence also underscores a recurring theme: sustained treatment is necessary to maintain therapeutic gains and prevent weight regain. Key findings from this review underscore tirzepatide’s promise in addressing both obesity and its related comorbidities. However, long-term safety, durability of effects, comparative effectiveness against newer agents such as retatrutide, and cost-effectiveness in real-world settings remain essential areas for future investigation. As the global burden of obesity continues to rise, there is a growing imperative to evolve therapeutic paradigms. While tirzepatide is not a universal solution, current evidence positions it as a promising agent within the emerging landscape of pharmacologic obesity treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S. (Mohammed Sallam) and M.S. (Malik Sallam); methodology, M.S. (Mohammed Sallam); software, M.S. (Malik Sallam); validation, M.S. (Mohammed Sallam), J.S. and S.E.G.; formal analysis, M.S. (Mohammed Sallam) and M.S. (Malik Sallam); investigation, M.S. (Mohammed Sallam) and S.E.G.; resources, M.S. (Mohammed Sallam) and S.E.G.; data curation, M.S. (Malik Sallam) and J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S. (Mohammed Sallam); writing—review and editing, M.S. (Malik Sallam), J.S. and S.E.G.; supervision, M.S. (Mohammed Sallam); project administration, M.S. (Mohammed Sallam). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors express gratitude to the Mediclinic Group and the Mohammed Bin Rashid University of Medicine and Health Sciences (MBRU) for fostering an environment that supports research initiatives.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| FDA | The U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| GIP | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| HRQoL | Health-related quality of life |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| RCTs | Randomized controlled trials |
| SANRA | Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
References
- Koliaki, C.; Dalamaga, M.; Liatis, S. Update on the Obesity Epidemic: After the Sudden Rise, Is the Upward Trajectory Beginning to Flatten? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutari, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. A 2022 update on the epidemiology of obesity and a call to action: As its twin COVID-19 pandemic appears to be receding, the obesity and dysmetabolism pandemic continues to rage on. Metab.-Clin. Exp. 2022, 133, 155217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Adult BMI Collaborators. Global, regional, and national prevalence of adult overweight and obesity, 1990–2021, with forecasts to 2050: A forecasting study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 813–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruh, S.M. Obesity: Risk factors, complications, and strategies for sustainable long-term weight management. J. Am. Assoc. Nurse Pract. 2017, 29, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Word Health Organization. Health Service Delivery Framework for Prevention and Management of Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240073234 (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Valenzuela, P.L.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Castillo García, A.; Lieberman, D.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Lucia, A. Obesity and the risk of cardiometabolic diseases. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Qiu, T.; Li, L.; Yu, R.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Proud, C.G.; Jiang, T. Pathophysiology of obesity and its associated diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2403–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C. The Related Metabolic Diseases and Treatments of Obesity. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaifa, I.K.; Bahari, H.; Yong, Y.K.; Noor, S.M. Endothelial Dysfunction in Obesity-Induced Inflammation: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity. Front. Med. 2013, 7, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.; Rachel, N.; Garrison, S.; Johanna, R.; John, W. Economic impacts of overweight and obesity: Current and future estimates for eight countries. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e006351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.; Rachel, N.; Garrison, S.; Jaynaide, P.; Johanna, R.; John, W. Economic impacts of overweight and obesity: Current and future estimates for 161 countries. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 7, e009773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweis, N. The economic burden of obesity in 2024: A cost analysis using the value of a statistical life. Crit. Public Health 2024, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laddu, D.; Neeland, I.J.; Carnethon, M.; Stanford, F.C.; Mongraw-Chaffin, M.; Barone Gibbs, B.; Ndumele, C.E.; Longenecker, C.T.; Chung, M.L.; Rao, G. Implementation of Obesity Science Into Clinical Practice: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 150, e7–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlas, S.J.; Kim, K.; Nhan, E.; Touchette, D.R.; Moradi, A.; Agboola, F.; Rind, D.M.; Beaudoin, F.L.; Pearson, S.D. Medications for obesity management: Effectiveness and value. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2023, 29, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apovian, C.M.; Aronne, L.; Barenbaum, S.R. Clinical Management of Obesity; Professional Communications, Inc.: 400 Center Bay Drive West Islip, NY, USA, 2023; ISBN 9781545756898. [Google Scholar]
- Hoey, H.; Roche, E. Obesity a triple pandemic, the trillion dollar disease: Prevention is imperative. Glob. Pediatr. 2024, 7, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornier, M.A. A review of current guidelines for the treatment of obesity. Am. J. Manag. Care 2022, 28, S288–S296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Blüher, M.; Tschöp, M.H.; DiMarchi, R.D. Anti-obesity drug discovery: Advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Tronieri, J.S.; Butryn, M.L. Lifestyle modification approaches for the treatment of obesity in adults. Am. Psychol. 2020, 75, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; Finucane, F.M. Structured lifestyle modification as an adjunct to obesity pharmacotherapy: There is much to learn. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 49, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. The future of obesity: New drugs versus lifestyle interventions. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 17, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmaleh-Sachs, A.; Schwartz, J.L.; Bramante, C.T.; Nicklas, J.M.; Gudzune, K.A.; Jay, M. Obesity Management in Adults: A Review. JAMA 2023, 330, 2000–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Chakhtoura, M.; Haber, R.; Ghezzawi, M.; Rhayem, C.; Tcheroyan, R.; Mantzoros, C.S. Pharmacotherapy of obesity: An update on the available medications and drugs under investigation. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 58, 101882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohani, P.; Malekpour Alamdari, N.; Bagheri, S.E.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Sohouli, M.H. The effects of subcutaneous Tirzepatide on obesity and overweight: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1230206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, M.; Snygg, J.; Allam, D.; Kassem, R. Shifting the Scales: Tirzepatide’s Breakthrough in Obesity Management. Cureus 2024, 16, e60545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, R.W.; Mailhac, A.; Løhde, J.B.; Pottegård, A. Real-world evidence on the utilization, clinical and comparative effectiveness, and adverse effects of newer GLP-1RA-based weight-loss therapies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 66–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Approves New Medication for Chronic Weight Management. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-medication-chronic-weight-management (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Abbasi, J. FDA Green-Lights Tirzepatide, Marketed as Zepbound, for Chronic Weight Management. JAMA 2023, 330, 2143–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, F.S.; Douros, J.D.; Gabe, M.B.; Showalter, A.D.; Wainscott, D.B.; Suter, T.M.; Capozzi, M.E.; van der Velden, W.J.; Stutsman, C.; Cardona, G.R.; et al. Tirzepatide is an imbalanced and biased dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e140532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; D’Alessio, D.A. Tirzepatide, a dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor co-agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with unmatched effectiveness regrading glycaemic control and body weight reduction. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanlikian, G. How Tirzepatide Works? Available online: https://www.genemedics.com/tirzepatide (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Chavda, V.P.; Ajabiya, J.; Teli, D.; Bojarska, J.; Apostolopoulos, V. Tirzepatide, a New Era of Dual-Targeted Treatment for Diabetes and Obesity: A Mini-Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.K. Mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications of GLP-1 and dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonists. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1431292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samms, R.J.; Coghlan, M.P.; Sloop, K.W. How May GIP Enhance the Therapeutic Efficacy of GLP-1? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokary, S.; Bawadi, H. The promise of tirzepatide: A narrative review of metabolic benefits. Prim. Care Diabetes 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.M.; Ferreira, A.C.; de Paula Barbosa, A. Injectables Pharmacotherapies for Obesity: Mechanisms, Efficacy, and Aesthetic Implications. Obesities 2025, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- France, N.L.; Syed, Y.Y. Tirzepatide: A Review in Type 2 Diabetes. Drugs 2024, 84, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheen, A.J. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes: Pleiotropic Cardiometabolic Effects and Add-on Value of a Combined Therapy. Drugs 2024, 84, 1347–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera Gutierrez, R.; Tama, E.; Bechenati, D.; Castañeda Hernandez, R.; Bennett, P.K.; McNally, A.W.; Fansa, S.; Anazco, D.; Acosta, A.; Hurtado Andrade, M.D. Effect of Tirzepatide on Body Weight and Diabetes Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes and Overweight or Obesity. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2025, 100, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, C.J.; Ingelfinger, J.R. Shifting Tides Offer New Hope For Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.B. In adults with obesity without diabetes, adding tirzepatide to a lifestyle intervention increased weight loss at 72 wk. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, Jc116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, S. Tirzepatide: A New Anti-Obesity Medication. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, S.; Pollicino, C.; Maggio, D.; Torres, A.; Argano, C. Tirzepatide against obesity and insulin-resistance: Pathophysiological aspects and clinical evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1402583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardar, M.B.; Nadeem, Z.A.; Babar, M. Tirzepatide: A novel cardiovascular protective agent in type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Papamargaritis, D.; Sargeant, J.A.; Davies, M.J. Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Management. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 32, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.; Pelletier, J.; Koyfman, A.; Bridwell, R.E. GLP-1 agonists: A review for emergency clinicians. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 78, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zweihary, A.M. Safety and Effectiveness of Tirzepatide Use in Obesity Without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cureus 2024, 16, e51788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaore, S.; B, B.; Khasbage, S.; Atal, S. Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide on Glycaemic and Non-Glycaemic Outcomes in Diabetes: A Systematic Review of Meta-Analyses. Cureus 2024, 16, e56939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mesquita, Y.L.L.; Pera Calvi, I.; Reis Marques, I.; Almeida Cruz, S.; Padrao, E.M.H.; Carvalho, P.E.d.P.; da Silva, C.H.A.; Cardoso, R.; Moura, F.A.; Rafalskiy, V.V. Efficacy and safety of the dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide for weight loss: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Pan, X.-H.; Chew, H.S.J.; Goh, R.S.J.; Lin, C.; Anand, V.V.; Lee, E.C.Z.; Chan, K.E.; Kong, G.; Ong, C.E.Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide for treatment of overweight or obesity. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndubuisi, J.; Panjiyar, B. Efficacy and Safety of GLP-1RAs including Tirzepatide, in the Management of Obesity in Nondiabetic Patients: A Systematic Review. Preprints 2024, 2024, 072397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Bhatia, G. Writing and appraising narrative reviews. J. Clin. Sci. Res. 2021, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R. Writing narrative style literature reviews. Med. Writ. 2015, 24, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.N.; Johnson, C.D.; Adams, A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: Secrets of the trade. J. Chiropr. Med. 2006, 5, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motevalli, M. Comparative Analysis of Systematic, Scoping, Umbrella, and Narrative Reviews in Clinical Research: Critical Considerations and Future Directions. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2025, 2025, 9929300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baethge, C.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Mertens, S. SANRA—A scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles. Res. Integr. Peer Rev. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Kamrul-Hasan, A.B.M.; Nagendra, L.; Bhattacharya, S. Efficacy and Safety of Novel Twincretin Tirzepatide, a Dual GIP/GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, as an Anti-obesity Medicine in Individuals Without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Touchrev Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadden, T.A.; Chao, A.M.; Machineni, S.; Kushner, R.; Ard, J.; Srivastava, G.; Halpern, B.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide after intensive lifestyle intervention in adults with overweight or obesity: The SURMOUNT-3 phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2909–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhezi, O.S.; Alahmed, A.A.; Alfayez, O.M.; Alzuman, O.A.; Almutairi, A.R.; Almohammed, O.A. Comparative effectiveness of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the management of obesity in adults without diabetes: A network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Roux, C.W.; Zhang, S.; Aronne, L.J.; Kushner, R.F.; Chao, A.M.; Machineni, S.; Dunn, J.; Chigutsa, F.B.; Ahmad, N.N.; Bunck, M.C. Tirzepatide for the treatment of obesity: Rationale and design of the SURMOUNT clinical development program. Obesity 2023, 31, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronne, L.J.; Sattar, N.; Horn, D.B.; Bays, H.E.; Wharton, S.; Lin, W.Y.; Ahmad, N.N.; Zhang, S.; Liao, R.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Continued Treatment with Tirzepatide for Maintenance of Weight Reduction in Adults with Obesity: The SURMOUNT-4 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 331, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, R.; Yuan, Y.; Li, X. Tirzepatide for Weight Reduction in Chinese Adults with Obesity: The SURMOUNT-CN Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Yang, J.; Ni, Y.; Deng, C.; Ruan, Q.; Ruan, J.; Zhou, P.; Duan, K. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly tirzepatide for weight management compared to placebo: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis including the latest SURMOUNT-2 trial. Endocrine 2024, 86, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shi, H.; Xie, M.; Sun, Y.; Nahata, M.C. Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide versus placebo in overweight or obese adults without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2024, 46, 1268–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochira, V.; Greco, C.; Boni, S.; Costantino, F.; Dalla Valentina, L.; Zanni, E.; Itani, L.; El Ghoch, M. The Effect of Tirzepatide on Body Composition in People with Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review of Randomized, Controlled Studies. Diseases 2024, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Pierre, J.; Klein, J.; Choi, N.K.; Fear, E.; Pannain, S.; Rubin, D.T. Efficacy and Safety of GLP-1 Agonists on Metabolic Parameters in Non-Diabetic Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2024, 69, 4437–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankosky, E.R.; Wang, H.; Neff, L.M.; Kan, H.; Wang, F.; Ahmad, N.N.; Griffin, R.; Stefanski, A.; Garvey, W.T. Tirzepatide reduces the predicted risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and improves cardiometabolic risk factors in adults with obesity or overweight: SURMOUNT-1 post hoc analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zheng, G.; Liang, Z.; Li, M.; Deng, W.; Cao, W. Seven glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and polyagonists for weight loss in patients with obesity or overweight: An updated systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Metabolism 2024, 161, 156038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.H.; Tan, B.; Chin, Y.H.; Lee, E.C.Z.; Kong, G.; Chong, B.; Kueh, M.; Khoo, C.M.; Mehta, A.; Majety, P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and other weight loss drugs in overweight and obesity: A network meta-analysis. Obesity 2024, 32, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Grunstein, R.R.; Fietze, I.; Weaver, T.E.; Redline, S.; Azarbarzin, A.; Sands, S.A.; Schwab, R.J.; Dunn, J.P.; Chakladar, S.; et al. Tirzepatide for the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudzune, K.A.; Stefanski, A.; Cao, D.; Mojdami, D.; Wang, F.; Ahmad, N.; Ling Poon, J. Association between weight reduction achieved with tirzepatide and quality of life in adults with obesity: Results from the SURMOUNT-1 study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.; Zile, M.R.; Kramer, C.M.; Baum, S.J.; Litwin, S.E.; Menon, V.; Ge, J.; Weerakkody, G.J.; Ou, Y.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamza, M.; Papamargaritis, D.; Davies, M.J. Tirzepatide for overweight and obesity management. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2025, 26, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi Beshir, S.; Ahmed Elnour, A.; Soorya, A.; Parveen Mohamed, A.; Sir Loon Goh, S.; Hussain, N.; Al Haddad, A.H.I.; Hussain, F.; Yousif Khidir, I.; Abdelnassir, Z. A narrative review of approved and emerging anti-obesity medications. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023, 31, 101757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janić, M.; Janež, A.; El-Tanani, M.; Rizzo, M. Obesity: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunvald, E.; Shah, R.; Hernaez, R.; Chandar, A.K.; Pickett-Blakely, O.; Teigen, L.M.; Harindhanavudhi, T.; Sultan, S.; Singh, S.; Davitkov, P. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Pharmacological Interventions for Adults With Obesity. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 1198–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congdon, P.; Amugsi, D. Editorial: The obesity epidemic: Causes, context, prevention. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1030180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.B.; Yahya, T.; Satish, P.; Laird, R.; Agatston, A.S.; Cainzos-Achirica, M.; Patel, K.V.; Nasir, K. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists: A Medication for Obesity Management. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2022, 24, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandfon, S.; Eylon, A.; Khanna, D.; Parmar, M.S. Advances in Anti-obesity Pharmacotherapy: Current Treatments, Emerging Therapies, and Challenges. Cureus 2023, 15, e46623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabah, S.; Al-Khairi, I.; Jamal, M.; Qaddoumi, M.; Alajmi, F.; Kumar, J.; Abukhalaf, N.; Cherian, P.; Madhu, D.; Arefanian, H.; et al. Effect of Dual Glucagon-Like Peptide 1/Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptor Agonist (Tirzepatide) versus Bariatric Surgery on Weight Loss and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Med. Princ. Pract. 2024, 33, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobkovich, A.; Kale-Pradhan, P.; Lipari, M. Incretin Analogs for Weight Management in Adults Without Diabetes. Ann. Pharmacother. 2023, 58, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Palcu, P. Weight loss between glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and bariatric surgery in adults with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity 2022, 30, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, F.; Dokmak, G.; Bader, M.; Karaman, R. A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications. Life 2023, 13, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melson, E.; Miras, A.D.; Papamargaritis, D. Future therapies for obesity. Clin. Med. 2023, 23, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.J.; Goodwin Cartwright, B.M.; Gratzl, S.; Brar, R.; Baker, C.; Gluckman, T.J.; Stucky, N.L. Semaglutide vs Tirzepatide for Weight Loss in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. JAMA Intern. Med. 2024, 184, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andraos, J.; Muhar, H.; Smith, S.R. Beyond glycemia: Comparing tirzepatide to GLP-1 analogues. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, J.P.; Davies, M.J.; Rosenstock, J.; Pérez Manghi, F.C.; Fernández Landó, L.; Bergman, B.K.; Liu, B.; Cui, X.; Brown, K. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Várkonyi, T.T.; Pósa, A.; Pávó, N.; Pavo, I. Perspectives on weight control in diabetes–Tirzepatide. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 202, 110770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicker, D.; Sagy, Y.W.; Ramot, N.; Battat, E.; Greenland, P.; Arbel, R.; Lavie, G.; Reges, O. Bariatric Metabolic Surgery vs Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Mortality. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2415392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, E.; Ottosson, J.; Cao, Y.; Sundbom, M.; Näslund, E. Cardiovascular and diabetes outcomes among patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes after metabolic bariatric surgery or glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist treatment. Br. J. Surg. 2024, 111, znae221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, L.; Sharif, G.; Eda, S.; Raju Tullimalli, I.; Amin, A.; Riyalat, A.A.; Alrashid, F.F.; Abdelrahim, A.A. Comparative Effectiveness of Bariatric Metabolic Surgery Versus Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Cardiovascular Outcomes and Mortality: A Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e71684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, S.A.; El-Tanani, M.; Matalka, I.I.; Rangraze, I.R.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Khan, M.A.; Tambuwala, M.M. Tirzepatide: Unveiling a new dawn in dual-targeted diabetes and obesity management. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 19, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macêdo, A.P.; Vieira, R.F.; Brisque, G.D.; Abud, G.F.; Pauli, J.R. Liraglutide and Exercise: A Possible Treatment for Obesity? Obesities 2022, 2, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olateju, I.V.; Ogwu, D.; Owolabi, M.O.; Azode, U.; Osula, F.; Okeke, R.; Akabalu, I. Role of Behavioral Interventions in the Management of Obesity. Cureus 2021, 13, e18080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, M.; Dobbie, L.J.; Ciudin, A.; Halil, M. Behaviour therapy for obesity in older adults. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 130, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avenell, A.; Brown, T.J.; McGee, M.A.; Campbell, M.K.; Grant, A.M.; Broom, J.; Jung, R.T.; Smith, W.C. What interventions should we add to weight reducing diets in adults with obesity? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials of adding drug therapy, exercise, behaviour therapy or combinations of these interventions. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2004, 17, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, G.A.; Kim, K.K.; Wilding, J.P.H. Obesity: A chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World Obesity Federation. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbraccia, P.; Dicker, D. Obesity is a chronic progressive relapsing disease of particular interest for internal medicine. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2023, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, K.D.; Kahan, S. Maintenance of Lost Weight and Long-Term Management of Obesity. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochner, C.N.; Barrios, D.M.; Lee, C.D.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X. Biological mechanisms that promote weight regain following weight loss in obese humans. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 120, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, P.S.; Bergouignan, A.; Cornier, M.A.; Jackman, M.R. Biology's response to dieting: The impetus for weight regain. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 301, R581–R600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, M.D.; Jakobsdottir, S.; Drent, M.L. The role of leptin and ghrelin in the regulation of food intake and body weight in humans: A review. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, B.; Wang, Y. Appetite regulation and weight control: The role of gut hormones. Nutr. Diabetes 2012, 2, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.K.; Nikooienejad, A.; Bray, R.; Cui, X.; Wilson, J.; Duffin, K.; Milicevic, Z.; Haupt, A.; Robins, D.A. Dual GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Tirzepatide Improves Beta-cell Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, A.B.; Gulkarov, S.; Lau, R.; Klek, S.P.; Srivastava, A.; Renna, H.A.; De Leon, J. Weight Reduction with GLP-1 Agonists and Paths for Discontinuation While Maintaining Weight Loss. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.; Robinson, K.; Thomas, S.; Williams, D.R. Dietary intake by patients taking GLP-1 and dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonists: A narrative review and discussion of research needs. Obes. Pillars 2024, 11, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, D.; Sizoo, D.; Bakker, S.J.L.; van Beek, A.P. Obesity management strategies should cut fat, not muscle. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 1039–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeland, I.J.; Linge, J.; Birkenfeld, A.L. Changes in lean body mass with glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies and mitigation strategies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26 (Suppl. 4), 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linge, J.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Neeland, I.J. Muscle Mass and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists: Adaptive or Maladaptive Response to Weight Loss? Circulation 2024, 150, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezza, T.; Víctor, V.M. Beyond Weight Loss: Evaluating Cardiovascular Advantages of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2024, 24, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Almeida, G.; Nienkötter, T.F.; Balieiro, C.C.A.; Pasqualotto, E.; Cintra, J.B.; Carvalho, H.C.P.; Silva, A.L.S.; Kabariti, J.C.; Minucci, B.S.; Bertoli, E.D.; et al. Cardiovascular Benefits of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients Living with Obesity or Overweight: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2024, 24, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cao, Q.; Lin, L.; Lu, J.; Bi, Y.; Chen, Y. Efficacy of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist-Based Therapies on Cardiovascular Events and Cardiometabolic Parameters in Obese Individuals Without Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Diabetes 2025, 17, e70082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hu, J.; Zhao, C.; Liu, H.; He, C. Comparative efficacy of incretin drugs on glycemic control, body weight, and blood pressure in adults with overweight or obesity and with/without type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1513641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, J.; Shah, N.P.; Agarwala, A.; Khan, M.S.; Butler, J. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Cardiovascular Disease: What Do Clinicians Need to Know? Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2024, 26, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolotkin, R.L.; Andersen, J.R. A systematic review of reviews: Exploring the relationship between obesity, weight loss and health-related quality of life. Clin. Obes. 2017, 7, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, D.A.; Rejeski, J.; Lang, W.; Van Dorsten, B.; Fabricatore, A.N.; Toledo, K. Impact of a weight management program on health-related quality of life in overweight adults with type 2 diabetes. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, R.L.; Wadden, T.A.; Tronieri, J.S.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Chao, A.M.; Alamuddin, N.; Leonard, S.M.; Carvajal, R.; Bakizada, Z.M.; Pinkasavage, E.; et al. Short- and Long-Term Changes in Health-Related Quality of Life with Weight Loss: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Obesity 2018, 26, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, J.; Smith, C.M.; Kearns, B.; Haywood, A.; Bissell, P. The association between obesity and quality of life: A retrospective analysis of a large-scale population-based cohort study. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, K.S.; Sapin, H.; Dong, W.; Williamson, S.; Lee, C.J.; Thieu, V.T. Improved Glycaemic and Weight Management Are Associated with Better Quality of Life in People with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Tirzepatide. Diabetes Ther. 2023, 14, 1867–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, I.; Di Gioia, L.; Di Molfetta, S.; Caporusso, M.; Cignarelli, A.; Sorice, G.P.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. The real-world safety profile of tirzepatide: Pharmacovigilance analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2024, 47, 2671–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempesis, I.G.; Liu, J.; Dalamaga, M. The catcher in the gut: Tirzepatide, a dual incretin analog for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Metabol. Open 2022, 16, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Yu, B.; Ling, B.; Lv, G.; Shang, H.; Zhao, X.; Jie, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Weight loss efficiency and safety of tirzepatide: A Systematic review. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghusn, W.; Hurtado, M.D. Glucagon-like Receptor-1 agonists for obesity: Weight loss outcomes, tolerability, side effects, and risks. Obes. Pillars 2024, 12, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiz, A.; Filion, K.B.; Toutounchi, H.; Tsoukas, M.A.; Yu, O.H.Y.; Peters, T.M.; Eisenberg, M.J. Efficacy and Safety of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Weight Loss Among Adults Without Diabetes: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 2025, 178, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, F.; Al-Najim, W.; le Roux, C.W. Health Benefits Beyond the Scale: The Role of Diet and Nutrition During Weight Loss Programmes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, S.; Davies, M.; Dicker, D.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Rubino, D.M.; Pedersen, S.D. Managing the gastrointestinal side effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists in obesity: Recommendations for clinical practice. Postgrad. Med. 2022, 134, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, A.; Ingersoll, A.B. Patient initiation and maintenance of GLP-1 RAs for treatment of obesity: A narrative review and practical considerations for primary care providers. Postgrad. Med. 2021, 133, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgojo-Martínez, J.J.; Mezquita-Raya, P.; Carretero-Gómez, J.; Castro, A.; Cebrián-Cuenca, A.; de Torres-Sánchez, A.; García-de-Lucas, M.D.; Núñez, J.; Obaya, J.C.; Soler, M.J.; et al. Clinical Recommendations to Manage Gastrointestinal Adverse Events in Patients Treated with Glp-1 Receptor Agonists: A Multidisciplinary Expert Consensus. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; McGuire, D.K.; Pavo, I.; Weerakkody, G.J.; Nishiyama, H.; Wiese, R.J.; Zoungas, S. Tirzepatide cardiovascular event risk assessment: A pre-specified meta-analysis. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Xu, J.; Mu, X.; Shi, Y.; Fan, H.; Li, S. Safety issues of tirzepatide (pancreatitis and gallbladder or biliary disease) in type 2 diabetes and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1214334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayless, D.; Singh, J.; Park, B.U.; Sweetser, S. Tirzepatide-Associated Colonic Ischemia. ACG Case Rep. J. 2024, 11, e01551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Ma, M.; Liao, X. Data mining study on adverse events of tirzepatide based on FAERS database. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, A.; Rabbani, S.A.; El-Tanani, M.; Arora, M.K.; Sharma, S.; Dubey, H.; Aljabali, A.A.; Tambuwala, M.M. Safety profile of tirzepatide: A real-world pharmacovigilance analysis of EudraVigilance database. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2024, 30, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, F.A.; Altaf, R.; Bashir, T.; Asghar, F.; Altaf, R.; Tousif, S.; Goyal, A.; Mohammed, A.; Mohammad, M.F.; Anan, M.; et al. Effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists on weight and cardiovascular outcomes: A review. Medicine 2024, 103, e40364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Kaplan, L.M.; Frías, J.P.; Wu, Q.; Du, Y.; Gurbuz, S.; Coskun, T.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; Hartman, M.L. Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity—A Phase 2 Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstock, J.; Frias, J.; Jastreboff, A.M.; Du, Y.; Lou, J.; Gurbuz, S.; Thomas, M.K.; Hartman, M.L.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; et al. Retatrutide, a GIP, GLP-1 and glucagon receptor agonist, for people with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, double-blind, placebo and active-controlled, parallel-group, phase 2 trial conducted in the USA. Lancet 2023, 402, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, R.; Desai, K.; Teng, C.C.; Reznor, G.; Stockbower, G.; Grabner, M.; Benneyworth, B.D. Characteristics and Dosing Patterns of Tirzepatide Users with Type 2 Diabetes in the United States. Diabetes Ther. 2025, 16, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, L.; Clifford, S.; Mulick, A.; Jackson, C.; Vrijens, B. How the EMERGE guideline on medication adherence can improve the quality of clinical trials. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Berry, S.; Malkin, S.J.P.; Hunt, B.; Sharma, A. Evaluating the Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness of Once-Weekly Semaglutide 1 mg Versus Liraglutide 1.8 mg: A Health Economic Analysis in the UK. Diabetes Ther. 2023, 14, 1005–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoulias, D.; Koufakis, T.; Ruža, I.; El-Tanani, M.; Rizzo, M. Therapeutic Advances in Obesity: How Real-World Evidence Impacts Affordability Beyond Standard of Care. Pragmat. Obs. Res. 2024, 15, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.M.; Staff, M.; Bain, S.C.; Min, T. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Analogues for the Treatment of Obesity. Eur. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.J.; Zhang, V.; Gratzl, S.; Do, D.; Goodwin Cartwright, B.; Baker, C.; Gluckman, T.J.; Stucky, N.; Emanuel, E.J. Discontinuation and Reinitiation of Dual-Labeled GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Among US Adults with Overweight or Obesity. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e2457349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.R.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.X.; Cao, Y.; Yu, X.; Samuel, R.; Ali, B.; Desiderio, R.; Cholankeril, G.; et al. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Risk for Cirrhosis and Related Complications in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2024, 184, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.; Li, X.; Ma, G. Prediction of pediatric dose of tirzepatide from the reference adult dose using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1326373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, D.; Nagendra, L.; Harish, B.G.; Sharma, M.; Joshi, A.; Hathur, B.; Kamrul-Hasan, A. Efficacy and Safety of Cagrilintide Alone and in Combination with Semaglutide (Cagrisema) as Anti-Obesity Medications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 28, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Conlon, J.M. Multifunctional incretin peptides in therapies for type 2 diabetes, obesity and associated co-morbidities. Peptides 2025, 187, 171380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztanek, F.; Tóth, L.I.; Pető, A.; Hernyák, M.; Diószegi, Á.; Harangi, M. New Developments in Pharmacological Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes-Beyond and Within GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.P.; Hardaswani, D.; Patel, J.; Saiyed, F.; Goswami, R.J.; Saiyed, T.I.; Patel, H.; Amin, T.H. Comparative Effectiveness of Semaglutide, Liraglutide, Orlistat, and Phentermine for Weight Loss in Obese Individuals: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2025, 17, e80321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsbad, S.; Holst, J.J. The promise of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) for the treatment of obesity: A look at phase 2 and 3 pipelines. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2025, 34, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).