Abstract
The emergence of generative AI has caused a major dilemma—as higher education institutions prepare students for the workforce, the development of digital skills must become a normative aim, while simultaneously preserving academic integrity and credibility. The challenge they face is not simply a matter of using AI responsibly but typically of reconciling two opposing duties: (A) preparing students for the future of work, and (B) maintaining the traditional role of developing personal academic skills, such as critical thinking, the ability to acquire knowledge, and the capacity to produce original work. Higher education institutions must typically balance these objectives while addressing financial considerations, creating value for students and employers, and meeting accreditation requirements. Against this need, this multiple-case study of fifty universities across eight countries examined institutional response to generative AI. The content analysis revealed apparent confusion and a lack of established best practices, as proposed actions varied widely, from complete bans on generated content to the development of custom AI assistants for students and faculty. Oftentimes, the onus fell on individual faculty to exercise discretion in the use of AI, suggesting an inconsistent application of academic policy. We conclude by recognizing that time and innovation will be required for the apparent confusion of higher education institutions in responding to this challenge to be resolved and suggest some possible approaches to that. Our results, however, suggest that their top concern now is the potential for irresponsible use of AI by students to cheat on assessments. We, therefore, recommend that, in the short term, and likely in the long term, the credibility of awards is urgently safeguarded and argue that this could be achieved by ensuring at least some human-proctored assessments are integrated into courses, e.g., in the form of real-location examinations and viva voces.
1. Introduction
The question of the responsible use of artificial intelligence (AI) in education has become a flashpoint following the public release of chatbots in 2022 and their subsequent adoption [1,2,3,4] by students, instructors, and academic administrators. While one might intuitively, and perhaps naively, agree that using technology responsibly is preferable to using it irresponsibly, this question is not easily answered. In the absence of a clearly defined notion of responsibility, it becomes a question of value rather than a question of fact. The generative AI revolution caught academia by surprise. A recent UNESCO [4] survey of over 450 schools and universities describes it as the “[f]astest spreading digital application of all time” and underscores a gap by noting that “[l]ess than 10% of schools and universities have formal guidance on AI”, further stressing that “[w]hile schools and universities appear to be taking their time to make recommendations and lay down rules, students and teachers are not waiting”.
The results of a recent survey of n = 224 chief business officers [5] and n = 380 presidents [6] at U.S. colleges and universities, conducted by Inside Higher Ed and Hanover Research, paint a similar picture. The report notes that while “relatively few presidents’ institutions (18 percent) have published or adopted a policy or policies governing the use of AI, including in teaching and research” [5] (p. 6), the technology is being widely used, with 33% of business officers using AI to make job-related decisions, and 45% of presidents reporting using AI virtual chat assistants and chatbots. The number of academic leaders who felt optimistic about the emerging technology was much higher than those who were concerned, where over half—55% of business officers and 50% of presidents—“describe themselves as somewhat or very optimistic”. In contrast, fewer respondents—6% of presidents and 4% of business officers—expressed concern about AI’s impact on higher education. And, while only 13% of officers have confidence in the higher education sector’s preparedness to manage the rise of AI, 24% of officers and 17% of presidents are confident that their own institution has a grip on the situation.
In this paper, as instructors in Western universities, we focus on generative artificial intelligence, defined here as a set of computer algorithms that simulate intelligent human behaviors [7], and examine its impact on the academic processes.
One may argue that generative AI is just another technological tool—a more advanced learning and teaching aid [8]; if we find the latter useful and allow its use in the classroom, there is no reason we should deny the use of the former. This technology has tremendous potential to improve the learning environment; it can fillin the gaps in student and faculty support, providing a personalized learning experience, on-demand tutoring, and immediate feedback, as well as automating assignment grading and streamlining course creation and research activities [9,10,11].
However, this argument leads to a conundrum. On the one hand, information technologies have long played a vital role in supporting teaching, learning, and research in education. On the other hand, the gold standard of learning is akin to Plato’s dialogues—pondering minds testing each other’s assumptions about reality; technology has no place in this. Critical thinking skills and the ability to produce original work have largely been the hallmark—and obsession—of academia. Communication and computational devices are often banned, with the focus placed on individual achievement, and collaboration may be misconstrued as collusion [12]. Examinations have been conducted in strictly controlled environments, as if the subjects were tested in a lab where exposure to contaminants could skew the results. The technological space where learning takes place differs from the realities outside the classroom.
One might further argue that generative AI is not just another technological tool because it represents a notable leap forward. While earlier algorithms were primarily used to analyze human-produced data, the new class of algorithms is capable of logical reasoning and generating its own data [13,14]; it can take the human out of the loop—generate bespoke essays, conference papers, course outlines, and computer code, allowing students, instructors, and researchers to delegate much of their work to AI assistants. Ifenthaler et al. [15] stressed that “AI is omnipresent in education” and noted that “new roles and profiles are emerging beyond traditional ones”. The public release of generative AI tools such as ChatGPT was met with excitement. Within the first few months, it attracted millions of users [2]. According to a recent survey conducted by Tyton partners and sponsored by Turnitin of 1600 students and 1000 faculty members across more than 600 institutions, the use of generative AI is growing, and many students would continue using the tools even if they were banned [1]. This may be viewed as alarming and a reason for concern. A recent study demonstrated that AI can be “the brightest student in the class” who scores higher on assignments than human counterparts [16]. Another, a study of UK Open University assessment by Richards et al. [17], concluded the following: “[p]erhaps the most significant finding…is not that ChatGPT behaves as an outstanding student across some of the undergraduate modules, but that it performs consistently as an ‘adequate undergraduate student’—able to pass assessment without drawing undue attention to itself” (p. 15).
A further study also using blind marking of AI-produced examination scripts at a British university [18] concluded that “the grades awarded to our AI submissions were on average half a grade higher than that achieved by real students”. Also, it concluded that “across modules there was an 83.4% chance that the AI submissions would outperform a random selection of the same number of real student submissions”. Worryingly, they found that 94% of their AI submissions were undetected. Similarly, a study by Fleckenstein at al. [19] found that “…with relatively little prompting, current AI can generate texts that are not detectable for teachers, which poses a challenge to schools and universities in grading student essays”. This evidence should not be ignored by higher education institutions.
A further challenge that generative AI poses to the academic process is that, while the originality requirement can be satisfied with little effort [20,21], algorithms are biased toward linguistic diversity [22], which may lead to false accusations [23]. This opens a door to a whole new array of issues relating to authenticity and ownership [24]. For instance, admission portfolios, grant and patent applications, among other works expected to be produced by humans, can be generated in-part by machines and presented as original works created by humans. This leads to a peculiar situation where human-produced artifacts are compared and ranked against the machine-generated content. Considering that generative models can be trained on award-winning artifacts, there are implications for justice, as some may gain an unfair advantage by using the machine, thereby skewing the outcome. In this case, the winners are likely to be those with technology skills, rather than those with the ability to produce original work. This raises the questions of whether using AI to achieve a desired outcome is morally justifiable and whether academia’s obsession with the originality of one’s work has, in the light of technological advancements, been rendered obsolete.
The literature and media debates indicate that generative AI has sown seeds of distrust among teaching staff, who are on the lookout for machine-assisted plagiarism, and in the absence of adequate means of detection, may falsely accuse students of using ChatGPT [23]. A growing body of literature raises concerns about the potential misuse of AI and about the gaps in the traditional checks and balances [20,21,25,26]. In one interview, when asked about ChatGPT, Dr. Noam Chomsky described the technology as “high-tech plagiarism” and a “way of avoiding learning” [27]. The opinion of New York City’s Department of Education tallies with that of Chomsky, as it “announced a ban on the wildly popular chatbot ChatGPT–which some have warned could inspire more student cheating –from its schools’ devices and networks” [28]. Moreover, technology that provides on-demand answers promotes overreliance on technological aid, whereby one deprives oneself of an opportunity to learn from their own mistakes, to find one’s own style, and to think critically. These threats will likely be exacerbated in the future as wearable AI devices become more ubiquitous.
All this has implications for academic processes including teaching, learning and research, and therefore, it prompts a revision of the concepts of learning, integrity, authenticity, and originality and raises questions about the future of the teaching profession and the value higher education is expected to provide. It is ironic that the absence of policies governing the use of AI does not prevent some academic leaders from using the technology to make decisions pertaining to academic processes [5,6]. This highlights that while academia as an institution may adhere to traditional values, academia as an industry, driven by the need for efficiency and economic viability, may adopt a more flexible, technology-driven approach.
However, it could be argued that if AI tools are good enough for academic leaders to keep courses and research programs running, they should also be considered acceptable for students to use in completing assignments. Similarly, it could be argued that the former have no moral right to punish the latter for practices they themselves partake in if, after all, one role of institutions of higher education is viewed as being to prepare students for the future of work, which is becoming predominantly technological.
In the next section, we explicate the research aims and questions and then provide an overview of the related literature, describe the study methodology, present the results, discuss the findings, and conclude with discussing future research directions.
Research Aims and Questions
The overarching objective of this study is to examine how higher education institutions are confronting the new reality of generative AI. It is motivated by the gap in the literature on institutional responses and their commitment to doing the proverbial “right thing”.
This research is important and timely for several reasons. First, there is some evidence to suggest a disparity between the adoption rates of AI and the policies governing its use [6], which is a cause for concern. Moreover, the novelty of the issue, coupled with its growing adoption rates, makes the matter even more urgent. For instance, ChatGPT alone reached 100 million monthly active users in the two months after its launch [2]. The impact of generative AI on academic processes is largely unknown and therefore warrants examination. To this end, we posed one research question: what can academic guidelines tell us about the responsible use of AI in higher education?
2. Background
In November 2021, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) issued its first global standard on AI ethics, titled the Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence [29]. This document may serve as the foundation for the responsible use of AI. It argues that the role of AI technologies in the academic context should be to “support the learning process without reducing cognitive abilities”, and highlights the importance of “research initiatives on the responsible and ethical use of AI technologies in teaching, teacher training and e-learning, among other issues” [29] (p. 34). The document further calls on member states to promote the acquisition of “media and information literacy skills to strengthen critical thinking and competencies needed to understand the use and implication of AI systems, in order to mitigate and counter disinformation, misinformation and hate speech” [29] (p. 35),and stresses the importance of developing “‘prerequisite skills’ for AI education…as well as critical and creative thinking, teamwork, communication, socio-emotional and AI ethics skills” (p. 33). It also noted that a system of checks and balances is needed “to effectively report on the benefits and harms of AI systems” [29] (p. 35).
At the 2024 World Economic Forum Annual Meeting, Partovi and Yongpradit [3] discussed seven principles for the responsible use of AI in education. These include explicitly connecting the use of AI to educational goals, affirming adherence to existing policies, promoting AI literacy, realizing the benefits of AI while addressing the associated risks, promoting academic integrity, maintaining human decision-making, and continuously assessing the impact of AI.
Decades before generative algorithms became a staple of everyday life, academic institutions were exploring the possibilities of using intelligent systems for student support, improving learning and teaching outcomes, and mitigating cheating, among other use cases. This is evidenced in a study by Bozkurt et al. [30], which reviews the application of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies in education over a span of 50 years, from 1970 to 2020.
What constitutes responsible use of AI depends on the presuppositions about the role of education as a societal institution. For instance, consider the argument made by Ferguson et al. [31], who noted that the role of education is to “train people for employment, to develop good citizens, to socialize people within a community, and to develop happy, rounded individuals” (p. 6). If one accepts these premises as the raison d’être, or ultimate goals, of the educational process, then the responsible and ethical use of AI would be any action taken to achieve these objectives. Studies of the response of higher education institutions to Generative AI include Dabis, and Csáki [32], who concluded that “[r]egarding human oversight, the typical response identified by the study involves a blend of preventive measures (e.g., course assessment modifications) and soft, dialogue-based sanctioning procedures”. Also, a study by Chan and Hu [33] focused on students’ perceptions of generative AI technologies in higher education and included the recommendation that “…higher education institutions should consider rethinking their policy, curricula and teaching approaches to better prepare students for a future where GenAI technologies are prevalent”. A novel “thing ethnography approach” by Michel-Villarreal et al. [34] asked ChatGPT to explain the challenges and opportunities of Generative AI for higher education and found “… the urgent need for clear policies, guidelines, and frameworks to responsibly integrate ChatGPT in higher education” (p. 1). A study by Chan [35] proposed a six-point policy framework to manage the use of AI in higher education, as follows: (1) provide training to all stakeholders, (2) developing ethical use and risk management guidelines, (3) complement human work with AI rather than replace it, (4) use AI to teach new skills, (5) ensure the transparency of the AI environment, and (6) ensure data privacy and security.
The issue of bias in generative AI is well explored in the literature and ranges from historical biases [36,37] to toxic or harmful language [38,39] and from medical diagnostic errors [40,41] to gender bias [42]. When machine-generated content is integrated into student essays, course syllabi, and research papers, the inherent bias in data will be perpetuated as a result. Townson [43] proposed a three-stop approach to managing bias by (1) deciding on data and design, (2) checking the model outputs, and (3) monitoring for problems. However, one may dismiss such a proposal as impractical due to the sheer scale of the data that need to be processed and updated with every societal change.
The full scope of risks related to machines that can imitate human artifacts remains unknown, and thus, the concerns are well-warranted. Technology that relies on big data suffers from what Lazer et al. [44] described as “big data hubris”. Typically, the process of model creation is not transparent, and once created it remains a black box. Large datasets, particularly of public discourse scraped from the Internet, may contain incomplete or inaccurate information. Big data entails significant effort in preparing and monitoring a model’s performance to ensure that it will not carry out what it was not designed to carry out. Even when the scope of data is narrowed to scientific information, there is no guarantee that the model will be reliable or produce a valid output every time. A case in point is Meta’s scientific LLM, Galactica, which was taken down three days after its release. Although the model produced a human-readable output, it failed in its core objective—to provide factual information [45]. One should not accept a model’s output at face value. This, in turn, limits the useful scope of the application of generative AI in education, where the pursuit of truth is the core objective.
3. Method
This qualitative study employs a multiple-case study design to examine the institutional response to generative AI and its impact on their respective stakeholders as indicated in their publicly available written sources. Our aim was to provide a high-level overview of the institutional response to emergent generative AI through a content analysis of these sources. Halkias et al. [46] noted that “the multiple case study design is a valuable qualitative research tool in studying the links between the personal, social, behavioral, psychological, organizational, cultural, and environmental factors that guide organizational and leadership development”. This method is often applied in educational research to examine the inner workings of academic institutions, as it allows researchers to draw comparisons and identify common denominators, not only across different institutional environments but also organizational functions and actions, as well as their policies and initiatives [47,48,49]. This method provides a structured framework to achieve the study’s objectives and identify patterns in institutional responses to the emergence of generative AI.
The data collection and analysis process, depicted in Figure 1, was divided into five phases. We began data collection with purposive sampling, using the QS World University Rankings [50] as a primary data source. The rationale for using the QS World University Rankings was its extensive use in previous research [51,52]. The 2024 list was composed of 1498 institutions across 104 countries. Data collection and analysis were conducted between February and April 2024.
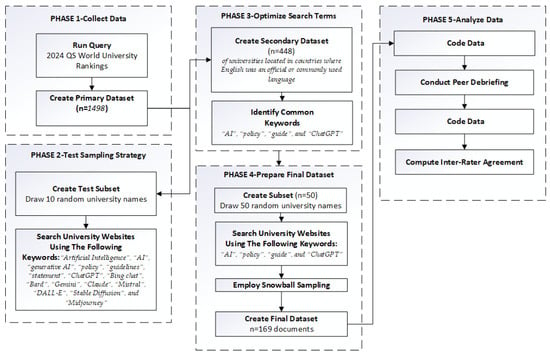
Figure 1.
The data collection and analysis process.
Second, as a pilot, to assess the viability of the sampling strategy, a random subset of 10 university names was drawn from the primary data source and their respective website search conducted. The preliminary list of search terms included the following: “Artificial Intelligence”, “AI”, “generative AI”, “policy”, “guidelines”, “statement”, “ChatGPT”, “Bing chat”, “Bard”, “Gemini”, “Claude”, “Mistral”, “DALL-E”, “Stable Diffusion”, and “Midjourney”. The preliminary analysis revealed that while all landing pages of universities in the subsample were in English or had an English translation, some documents containing these terms were only available in the languages of the countries or territories where the universities are located.
Third, to optimize search terms, the primary dataset (n = 1498) was limited to universities located in countries where English was an official or commonly used language. This included Australia, Canada, Ireland, the United States, the United Kingdom, New Zealand, Nigeria, India, the Philippines, South Africa, Hong Kong, and Singapore, which yielded a list of 448 institutions, hereafter referred to as the secondary dataset. Furthermore, we restricted the search terms to “AI”, “policy”, “guide”, and “ChatGPT” since these terms were more commonly present in the documents of interest.
Fourth, a random subsample of n = 50 universities was drawn from the secondary dataset. To avoid duplication, as may occur with universities having multiple campuses (e.g., University of California, Los Angeles, and University of California, Berkeley), only the first campus location that appeared on the list was included in the analysis. Canadian universities whose guidelines were only available in French were excluded from the analysis. To compensate for these exclusions, the random drawing continued until 50 universities were reached. University websites were then searched using keywords identified in phase 3, to locate information relevant to institutional response to generative AI. The inclusion criteria for the documents were as follows: institutional guidelines were publicly accessible, written in English, and at least one implication related to generative AI was discussed. Snowball sampling was employed to obtain additional relevant information, because some documents contained links to others. For example, some teaching guidelines included a link to an academic integrity policy. A total of n = 169 documents were collected for final analysis, hereafter referred to as the final dataset. The geographic distribution of the universities in the sample was as follows: Australia (6), Canada (1), Hong Kong (1), Ireland (3), India (5), Nigeria (1), the United Kingdom (8), and the United States (25).
Fifth, an inductive coding approach was employed, starting with identifying and labeling recurring ideas, followed by identifying relationships among the labels, and integrating them into categories. The sources were analyzed for manifest content, where the meaning was explicit. The units of content analysis were phrases (see examples in Table 1) which were labeled and subsequently organized into overarching categories (e.g., academic integrity).

Table 1.
Results summary.
Furthermore, drawing on the literature, the data were classified along the threat–opportunity binary, serving as a proxy for responsible and irresponsible use of AI. Corresponding reasons and proposed actions to each implication of generative AI were also identified and recorded. Implications that appeared across multiple documents (e.g., privacy concerns appeared in the teaching guide, privacy policy, and academic integrity policy) were counted once per institution. Implications were included if they appeared in at least two documents from different institutions. The data were independently coded by two coders. The inter-rater agreement was measured by Krippendorff’s alpha coefficient [53], yielding a reliability score of 0.81. Peer debriefing [54] was employed to enhance the credibility and trustworthiness of the data analysis by verifying the researchers’ interpretations [55]. To this end, three colleagues, each with over ten years of experience in both teaching and research, participated in iterative discussions to refine the codes and categories.
Limitations
The limitations of this study include the modest sample size, the limited and variable public availability of documents which suited our enquiry, our restriction to English language documents, and the dynamic nature of the current response of universities to AI.
4. Results
The documents varied in scope and breadth; among them were AI-specific guidelines and statements, as well as academic integrity policies, library resources, research guides, study guides, workshop outlines, presentations, and teaching resources. Some documents provided a broad overview of AI technology, while others provided specific use cases.
4.1. Identifying Universities’ Concerns About AI (And Academic Integrity)
The results summary is presented in Table 1, and Figure 2 depicts the frequency of each implication, also expressed as a percentage of the total mentions in the document corpus. Proposed actions ranged widely from observing the situation to banning it outright to fully embracing the technology. The general trend, however, was toward threat mitigation, to curb the irresponsible use of generative AI, with a less frequent emphasis on opportunities and benefits.
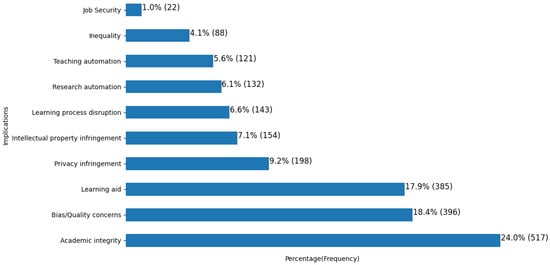
Figure 2.
Ranked order of mentions and percentage for each implication.
The top concern was the impact of large language models (LLMs) on academic integrity, due to their potential for irresponsible use by students to cheat on assignments. To address the problem, four overlapping strategies were discussed, including communication, the detection of AI misuse, referencing and acknowledgment of AI-generated content, and disincentivizing AI use. Teaching staff were advised to update their syllabi, communicate expectations, redesign assignments, familiarize themselves with students’ writing styles, and remain vigilant about the potential misuse of AI tools. Some library guides provided examples and links to detection tools and resources explaining how to acknowledge the use of and cite ChatGPT [56]. Teaching staff were also advised to AI-proof assessments by requesting rough drafts to track work progress, replacing essays with authentic assessments, and incorporating in-class writing exercises and group activities. A related concern stemmed from depriving students of opportunities to practice their critical thinking skills. In response, instructors were advised to engage with and support students, and to ban the use of AI when necessary. Moreover, students and instructors were warned about the limitations of generative models and advised to approach an LLM’s output with caution as algorithms are known to generate biased and inaccurate responses, and in the case of computer code, bugs and security vulnerabilities. AI’s potential to undermine equality, as not everyone has access to these tools, was mentioned, although it was not a top concern. The level of concern about AI was higher among universities in Western countries.
Privacy was the fourth-highest concern; sharing confidential information with AI platforms was considered irresponsible due to the potential to undermine privacy and violate intellectual property rights. The results suggest that privacy concerns came in the way of academic integrity because submitting students’ work to plagiarism detection services without permission could constitute an infringement of privacy or intellectual property, thereby creating a unique dilemma. Instructors have a duty to uphold the values of academic integrity and a duty to use AI responsibly; however, the guidelines were not explicit about which duty or concern claims priority or how the dilemma should be resolved. Having discretionary powers to assign relative importance when making decisions about responsible use in an ad hoc fashion is likely to result in confusion or, worse, inconsistent policy application.
4.2. Universities’ Efforts to Innovate Whilst Preserving the Status Quo: Some Examples
While it is reassuring that many institutions in our sample acknowledged the emergence of AI as a unique challenge, efforts to address it, by reconciling the two seemingly conflicting goals of innovation and preserving the status quo, inevitably create inconsistencies in decision-making. Let us now turn to some examples of institutional guidelines where this issue is particularly salient.
Concordia University’s Guidelines for teaching with generative artificial intelligence stipulate that (1) “Material drawn from ChatGPT or other AI tools must be acknowledged; representing as one’s own an idea, or expression of an idea, that was AI-generated will be considered an academic offense…” and (2) that “Students may use artificial intelligence tools for generating ideas, creating an outline for an assignment, or polishing language, but the final submitted assignment must be the student’s own work” [57].
Australian National University’s Best Practice When Using Generative AI provides the following advice regarding referencing AI-generated content: “Generative AI is not an academic source, hence may be inappropriate to cite or use in an assignment”. However, the guide warns that students should not “neglect to reference generative AI used in research” [58].
The Generative AI Usage Guidance of The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill reads “AI should help you think. Not think for you. Use these tools to give you ideas, perform research…and analyze problems. Do not use them to do your work for you, e.g., do not enter an assignment question into ChatGPT and copy & paste the response as your answer” [59].
The question that arises is this: when a machine generates ideas that students are allowed to integrate into their assignments and submit for credit, helps them compile research literature, explains findings, and analyzes problems, how much thinking is left for the students to perform on their own if the intelligent machine shoulders much of the cognitive load? Considering that modern tools such as word processors and search engines have AI at the back end, this becomes a question of degree rather than kind.
The term “help you think” is rather broad. When a policy is not specific enough to define the concept of originality and avoids setting a hard limit on the level of assistance a student can receive for the submitted work to be considered original, the irresponsible use of AI becomes a gray area. While ChatGPT was the most common tool described in the sample, other LLMs, such as Elicit for conducting research tasks [60], Dall-E and Midjourney for generating images from text prompts [61], Google’s Bard and Microsoft’s Bing chat [62], GitHub Co-pilot, and Perplexity AI, among others, were also discussed. Three universities in our sample (Arizona State University, Duke University, and the University of Michigan) have announced the integration of their own AI assistants for learning, teaching, or research.
AI has been proposed as a learning and teaching aid to help students improve the quality of their writing, summarize text, provide on-demand feedback, answer questions, and brainstorm ideas for course projects. AI image generators may prove useful in visualizing data and ideas. Likewise, instructors may use generative models to teach AI ethics and discuss moral issues arising from the use of technology; they may also use AI tools to automate teaching tasks, such as creating lesson plans, and research tasks, such as extracting data from and summarizing research papers.
While AI can automate some academic tasks and provide personalized learning experiences and on-demand support, it could also potentially displace teaching staff; tasks such as assignment grading and tutoring might be delegated to machines, further making academic careers more precarious. However, losing jobs to AI was the least concerning issue discussed in our sample.
5. Discussion
In this section, we first discuss the findings and then proceed to answer the research question of what can academic guidelines tell us about the responsible use of AI in higher education.
5.1. Universities’ Concerns About AI and Academic Integrity
While advancements in AI are a cause for celebration of human intellectual achievement and undoubtedly mark the dawn of true human–machine collaboration, they also present both risks and opportunities, driving us into uncharted waters. Our analysis of institutional guidelines, and more specifically their corresponding proposed actions, suggests that the line between responsible and irresponsible use of AI is blurry, due to the difficulty in reconciling apparently conflicting commitments.
A ban on AI, even a partial one, would undermine a commitment to prepare students for the future of work. As such, UNESCO’s and WEF’s recommendations—to “empower students and teachers and enhance their experience”, “to improve access to information and knowledge”, to “promote the acquisition of ‘prerequisite skills’ for AI education” [29], to “promote AI literacy”, and to “explicitly connect the use of AI to educational goals” [3]—would likely not be met. By the same token, allowing the use of AI without viable strategies to prevent misuse—exemplified by the limited efficacy of detection methods [63,64] and concerns over user privacy and copyright laws—creates a situation where academic integrity and learning quality could be compromised, while also violating the stipulated principles of responsible use [3,35].
In our sample, academic integrity was identified as the largest single issue of concern, and it is justified. Large language models can summarize, paraphrase, and generate text passages, as well as perform reasoning tasks and answer assignment questions, thereby offering personalized learner support on demand [13,14,16]. Considering that large language models can produce new content, traditional plagiarism detection strategies are rendered ineffective. LLMs can imitate writers’ idiosyncratic patterns and speak in their voice [65]. While instructors are encouraged to keep an extra eye on students, detecting AI-generated content is a challenging endeavor. To ensure compliance with integrity policy, some institutions advise their faculty to use stylometric detection tools and share lists of detection services. While many institutions acknowledge the limitations of authorship verification tools—citing their unreliability, potential violations of students’ privacy and intellectual property rights, and propensity for false accusations—these tools are often permitted for use at the instructor’s discretion.
Our results denote that instructors are often given discretion regarding how they maintain the integrity of their assessments and discretion to encourage or discourage the use of AI tools to foster digital skills. This approach is problematic for several reasons. First, this creates a peculiar situation where the same course, taught by different instructors, may promote and ban the use of AI, depending on who is teaching it. This creates unnecessary inconsistency and confusion in the application of academic integrity policy. We have already seen a similar situation arise in the case of student collaboration and collusion, where the same help-seeking behavior is punished or rewarded depending on the instructor’s stance [12,66].
Exemptions from a policy developed to ensure the responsible use of AI can undermine the very policy by allowing its inconsistent application. However, having a policy alone does not guarantee its effectiveness, and the examples in the Section 4 underscore just that. Relying solely on instructors’ discretion without comprehensive, enforceable guidelines for the use of AI in education is arguably insufficient. While this approach may be seen as a quick and easy fix to reconcile conflicting goals, beliefs, and values, this strategy fails to consider the full complexity of how technology affects students and the overall quality of education.
It would be unreasonable to expect all faculty to have the necessary expertise to address related legal, ethical, psychological, as well as privacy issues that technology creates. This has been evident with remote proctoring technologies, which, once hailed as a viable solution to the security of online assessments, failed to meet the legal threshold of privacy [67]. But despite legal challenges, these technologies have not been completely abandoned and are often used at the instructors’ discretion. To ensure consistency and compliance with regulatory standards, it is important to invest in research and develop institutional or even national-level policies that explicitly stipulate how and when technology can be used, thereby striving to protect the stakeholders.
Because bias is inherent in the model training process, all generated output should be interpreted with caution [45,68]. A study by Liang et al. [22] examined the performance of popular AI-generated text detectors, concluding that they are biased and flag the writings of non-native English speakers as AI-generated. Moreover, OpenAI has taken its similarity detector down due to accuracy concerns [69]. This unfortunate predicament is likely to lead to the creation of another administrative process, thereby increasing the administrative burden, to address false accusations [23,70,71]. Moreover, AI assistants are now available not only on smartphones but also on wearable devices. Due to their growing ubiquity, one would need to conduct all assessments securely to measure students’ knowledge in its pure form, untainted by the technological environment, but this creates logistical challenges [64,72].
The results suggest that many institutions are familiar with technological limitations and are skeptical about the automatic detection of AI-generated content. For example, in guidance on AI detection at Vanderbilt University, it is noted that, “there is a larger question of how Turnitin detects AI writing and if that is even possible. To date, Turnitin gives no detailed information as to how it determines if a piece of writing is AI-generated or not” [73]. The research guide of George Washington University maintains that “plagiarism tools feed the beast: they create huge datasets of student writing that can be sold to help train AI software. One reason that tools like ChatGPT are so good at generating plausible student writing is that they have been trained on a large corpus of work from college students”. Their solution is to rely on instructors to validate authorship veracity. “Advocating for smaller classes, better compensation, and other improved working conditions is part of disincentivizing unwanted use of AI generators” [74].
Because the detection process aims to identify generated content in submitted assignments by offering instructors a probability score that reflects the likelihood of machine authorship, rather than assessing the stylistic consistency of a student’s writing or behavioral patterns [75,76,77], this results in a limitation of the current approach.
However, maintaining a high level of integrity comes with a hefty price tag, and the associated opportunity costs should also be taken into consideration. Smaller classes and reduced teaching loads would require the hiring of more staff. The bigger question here is about the ethical commitment of individual faculty members and the institutional barriers that may hinder the effective implementation of academic integrity processes [72,78]. By ignoring AI’s potential to automate learning and teaching tasks such as assessments, academic leaders would be neglecting their duty to exercise fiscal prudence. Conversely, the automation of tutoring and assessment tasks, among others, would make many academic professions precarious and assignments easier to cheat on. The proverbial Pandora’s box has been left open; regardless of whether the use of AI is authorized by instructors or not, there is an inherent possibility that AI technology will be used without permission. The pace of adoption tends to outpace that of policy, setting in motion a game of proverbial whack-a-mole, whereby unintended consequences must be perpetually addressed, adding an additional burden on academic administrators and faculty.
Much of the literature argues that institutional credibility will be irreparably damaged if students are allowed to claim credits for work they did not complete. However, the scope of this argument is limited to ethical considerations, presenting a simple binary of good versus evil—buying essays from essay mills is wrong, whereas doing your own homework is the only right thing to do. When the use of generative AI is allowed in coursework, under the banners of career readiness or digital literacy, one unwittingly extends this argument to quality considerations, shifting the focus from individuals engaged in questionable conduct that violates integrity policy to the institutional ability to foster an effective learning experience.
What follows is that institutional credibility is now affected not only when students are involved in cheating scandals [79,80] but also when students and researchers delegate some of their work to AI assistants. One may argue that in the age of intelligent machines, institutional credibility becomes commensurate with the level of automation. Imagine two identical courses taught using the same learning materials; however, one allows students to integrate the output of large language models in the assessments, and the other does not. The issue here is not that students in both courses have completed assessments and met learning objectives, which were identical in both courses, but that learning outcomes completed with the help of AI assistants cannot be considered equivalent to learning outcomes completed without any external assistance. There is a fundamental difference between “I can solve this problem on my own” and “I cannot solve this problem on my own”. Which of these is being assessed needs to be clear to both the student and the assessor.
5.2. What Can Academic Guidelines Tell Us About the Responsible Use of AI in Higher Education?
The academic guidelines surveyed present a very variable and confusing response to this new challenge. For the most part, they do not face up to the hugely increased opportunities for academic misconduct even though they identify it as a main threat. This is worrying because if students are unable to generate ideas on their own, instead relying on AI to create an outline for an assignment and asking the AI to polish the language, how much of it all is the actual student’s own work? Given that much of what is being submitted for course credit was performed by AI, how will the work be assessed, provided it was designed by humans for humans? And the most important question to ask here is whether feeding prompts to an algorithm and stitching its outputs together would be considered learning.
By the same token, the academic guidelines do not generally address the issue of AI tools being used to assist instructors with providing student feedback, generating course materials, and evaluating student papers—while students use AI to generate ideas and content—in which case the once-pure human dialogue between student and instructor would be replaced by machine-to-machine communication. The temptation to reduce the teaching load and automate student assessment may lead to a scenario where AI-generated essays, submitted by students, are passed by instructors to the same AI systems that generated them. This might sound ironic or outright absurd, but this scenario is not far-fetched and should be clearly addressed by higher education institutions.
One cannot help but notice that the opportunities identified in our analysis revolve around personal productivity. AI tools allow students and faculty to learn and work more efficiently, automate menial tasks, and focus on more important ones, all to be successful in their roles—whether that means obtaining better grades, marking assignments faster, or publishing more papers. However, not a single document in our sample discussed how to use AI to detect scientific fraud, which is nonetheless an important issue, despite some significant work being carried out on that front [81,82,83]. These apparent shortcomings provide good reason to support the recommendation of studies such as that by Richards et al. [17] in respect of the UK Open University’s response to generative AI, i.e., that “in the short term, a return to face-to-face examinations is a straightforward way of retaining credible assessment, with a longer-term strategy requiring a rethink of the role of assessment as well as how it is conducted, potentially including the greater use of viva-voce examinations, live presentations, and increased reliance on personal portfolios of work” (p. 28). This seems to be the only responsible response and should have been clearly addressed in the guidelines, but, mostly, it was not.
6. Conclusions
This study examined how the emergence of generative AI prompted academic institutions to confront a new reality by analyzing a modest sample of 50 institutional guidelines and identifying issues related to teaching, learning, research, and academic administration. The findings suggest that academic institutions are struggling to find the right balance between mitigating risks and leveraging opportunities.
Most significantly, AI is seen as a threat to academic integrity and quality, challenging established assessment and detection strategies while raising important ethical, social, and pedagogical implications. For instance, reliance on AI tools may hinder students’ ability to think critically, affecting their capacity for creative expression, independent problem-solving, and decision-making. This blurs the line between responsible and irresponsible use; even if the intent is good, the long-term effects are unknown and could be devastating. This raises the question of whether the traditional academic values of integrity and originality impede the relevance of education to workforce needs?
Future research should also examine the extent to which the established academic processes need to be preserved and how. Or, put another way, how should the teaching, learning, research, and administration practices be retrofitted to keep pace with technological change? Another topic for future research is to examine why academic institutions responded to the issue of generative AI the way they did. The literature describes the lack of formal guidance on AI, despite its widespread adoption [4,6], as a simple problem—just write the policy and follow it. However, the absence of a policy may serve as a strategic compromise to avoid the pitfall of violating the very rules one has established. To this end, a survey of key stakeholders in the policymaking process should be conducted to explore why some concerns are prioritized over others and why certain opportunities are forfeited. One may argue that the effort to fit AI use into the existing normative framework focuses on the question of how to preserve the status quo and distracts from the question of why. We conclude that the integration of generative AI into higher education will have an impact that stretches beyond merely the need to prevent academic misconduct and minimize privacy and copyright infringement.
In response to this apparent confusion, we argue that the considerable challenge for higher education institutions is to ensure the responsible use of AI to “support the learning process without reducing cognitive abilities” as recommended by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization [29]. Our study suggests that whilst this could usefully be based on the foundations set by UNESCO [4,29], it will require time and innovation. Our study, however, showed that the top concern now of the 50 higher education institutions whose documents we surveyed is the impact of large language models (LLMs) on academic integrity, due to their potential for irresponsible use by students to cheat on assessments. In what is often viewed as an arms race between those who would cheat and those who would seek to stop them, we therefore also recommend that, in the short term (and probably still in the long term), the credibility of awards is urgently safeguarded. This could be achieved by ensuring at least some human-proctored assessments are integrated into courses, e.g., in the form of real-location examinations and viva voces.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A. and D.J.P.; methodology, A.A.; formal analysis, A.A.; data curation, A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.; writing—review and editing, A.A. and D.J.P.; visualization, A.A. and D.J.P.; project administration, A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study employed post hoc secondary data analysis and did not involve any human participants.
Informed Consent Statement
This study employed post hoc secondary data analysis and did not involve any human participants.
Data Availability Statement
All data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. We are grateful to our colleagues and reviewers for their valuable and constructive feedback.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Coffey, L. Students Outrunning Faculty in AI Use. Available online: https://www.insidehighered.com/news/tech-innovation/artificial-intelligence/2023/10/31/most-students-outrunning-faculty-ai-use (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Hu, K. ChatGPT Sets Record for Fastest-Growing User Base—Analyst Note; Reuters: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Partovi, H.; Yongpradit, P. 7 Principles on Responsible AI Use in Education. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/stories/2024/01/ai-guidance-school-responsible-use-in-education/ (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- UNESCO. UNESCO Survey: Less than 10% of Schools and Universities Have Formal Guidance on AI. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/en/articles/unesco-survey-less-10-schools-and-universities-have-formal-guidance-ai (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Flaherty, C.; Lederman, D. 2024 Survey of College and University Chief Business Officers; Inside Higher Ed: 2024. Available online: https://www.insidehighered.com/reports/2024/07/16/2024-survey-college-and-university-chief-business-officers (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Flaherty, C.; Lederman, D. 2024 Survey of College and University Presidents; Inside Higher Ed: 2024. Available online: https://www.insidehighered.com/reports/2024/02/27/2024-survey-college-and-university-presidents (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Hwang, G.-J.; Xie, H.; Wah, B.W.; Gašević, D. Vision, Challenges, Roles and Research Issues of Artificial Intelligence in Education. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2020, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigud, A. Post-Traditional Learning Analytics: How Data and Information Technology Transform Learning Environment. In Emerging Trends in Learning Analytics; Brill Sense: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Khan, S.; Khan, I.H. Unlocking the Opportunities through ChatGPT Tool towards Ameliorating the Education System. BenchCouncil Trans. Benchmarks Stand. Eval. 2023, 3, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshetri, N. The Economics of Generative Artificial Intelligence in the Academic Industry. Computer 2023, 56, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Huang, A.Y.; Lu, O.H. Artificial Intelligence in Intelligent Tutoring Systems toward Sustainable Education: A Systematic Review. Smart Learn. Environ. 2023, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland-Smith, W. Crossing the Line: Collusion or Collaboration in University Group Work? Aust. Univ. Rev. 2013, 55, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Frieder, S.; Pinchetti, L.; Griffiths, R.-R.; Salvatori, T.; Lukasiewicz, T.; Petersen, P.; Berner, J. Mathematical Capabilities of Chatgpt. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2023/hash/58168e8a92994655d6da3939e7cc0918-Abstract-Datasets_and_Benchmarks.html (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Hagendorff, T.; Fabi, S.; Kosinski, M. Human-like Intuitive Behavior and Reasoning Biases Emerged in Large Language Models but Disappeared in ChatGPT. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2023, 3, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifenthaler, D.; Majumdar, R.; Gorissen, P.; Judge, M.; Mishra, S.; Raffaghelli, J.; Shimada, A. Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Teaching and Learning: Implications for School Leaders, Teachers, Policymakers and Learners. In Proceedings of the Moving Forward to New Educational Realities in the Digital Era, Kyoto, Japan, 29 May–1 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Cano, E.; Ramírez-Hurtado, J.M.; Sáez-López, J.M.; López-Meneses, E. ChatGPT: The Brightest Student in the Class. Think. Ski. Creat. 2023, 49, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.; Waugh, K.; Slaymaker, M.; Petre, M.; Woodthorpe, J.; Gooch, D. Bob or Bot: Exploring ChatGPT’s Answers to University Computer Science Assessment. ACM Trans. Comput. Educ. 2024, 24, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarfe, P.; Watcham, K.; Clarke, A.; Roesch, E. A Real-World Test of Artificial Intelligence Infiltration of a University Examinations System: A “Turing Test” Case Study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0305354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, J.; Meyer, J.; Jansen, T.; Keller, S.D.; Köller, O.; Möller, J. Do Teachers Spot AI? Evaluating the Detectability of AI-Generated Texts among Student Essays. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2024, 6, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Cui, W. Evade ChatGPT Detectors via a Single Space. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.02599. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, D.R.; Cotton, P.A.; Shipway, J.R. Chatting and Cheating: Ensuring Academic Integrity in the Era of ChatGPT. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2023, 61, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Yuksekgonul, M.; Mao, Y.; Wu, E.; Zou, J. GPT Detectors Are Biased against Non-Native English Writers. PATTER 2023, 4, 100779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorichanaz, T. Accused: How Students Respond to Allegations of Using ChatGPT on Assessments. Learn. Res. Pract. 2023, 9, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, B. AI-Generated Art Cannot Receive Copyrights, US Court Says; Reuters: London, UK, 2023; Available online: https://www.reuters.com/legal/ai-generated-art-cannot-receive-copyrights-us-court-says-2023-08-21/ (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Khalil, M.; Er, E. Will ChatGPT Get You Caught? Rethinking of Plagiarism Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.04335. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, M. Academic Integrity Considerations of AI Large Language Models in the Post-Pandemic Era: ChatGPT and Beyond. J. Univ. Teach. Learn. Pract. 2023, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open Culture. Noam Chomsky on ChatGPT: It’s “Basically High-Tech Plagiarism” and “a Way of Avoiding Learning”; Open Culture: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2023; Available online: https://www.openculture.com/2023/02/noam-chomsky-on-chatgpt.html (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Rosenblatt, K. ChatGPT Banned from New York City Public Schools’ Devices and Networks. Available online: https://www.nbcnews.com/tech/tech-news/new-york-city-public-schools-ban-chatgpt-devices-networks-rcna64446 (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- UNESCO. UNESCO’s Recommendation on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence: Key Facts 2023. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/en/artificial-intelligence/recommendation-ethics (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Bozkurt, A.; Karadeniz, A.; Baneres, D.; Guerrero-Roldán, A.E.; Rodríguez, M.E. Artificial Intelligence and Reflections from Educational Landscape: A Review of AI Studies in Half a Century. Sustainability 2021, 13, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.; Barzilai, S.; Ben-Zvi, D.; Chinn, C.; Herodotou, C.; Hod, Y.; Kali, Y.; Kukulska-Hulme, A.; Kupermintz, H.; McAndrews, P. Innovating Pedagogy 2017: Exploring New Forms of Teaching, Learning and Assessment, to Guide Educators and Policy Makers. Open University Innovation Report 6; Open University: Milton Keynes, UK, 2017; Available online: https://oro.open.ac.uk/52761/ (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Dabis, A.; Csáki, C. AI and Ethics: Investigating the First Policy Responses of Higher Education Institutions to the Challenge of Generative AI. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.Y.; Hu, W. Students’ Voices on Generative AI: Perceptions, Benefits, and Challenges in Higher Education. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2023, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel-Villarreal, R.; Vilalta-Perdomo, E.; Salinas-Navarro, D.E.; Thierry-Aguilera, R.; Gerardou, F.S. Challenges and Opportunities of Generative AI for Higher Education as Explained by ChatGPT. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.Y. A Comprehensive AI Policy Education Framework for University Teaching and Learning. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2023, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edenberg, E.; Wood, A. Disambiguating Algorithmic Bias: From Neutrality to Justice. 2023, pp. 691–704. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3600211.3604695 (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Jo, A. The Promise and Peril of Generative AI. Nature 2023, 614, 214–216. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A. GPT-3 and InstructGPT: Technological Dystopianism, Utopianism, and “Contextual” Perspectives in AI Ethics and Industry. AI Ethics 2023, 3, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, I. Keeping Tabs on GPT-SWE: Classifying Toxic Output from Generative Language Models for Swedish Text Generation. 2022. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A1704893&dswid=-1709 (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- King, M. Harmful Biases in Artificial Intelligence. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meskó, B.; Topol, E.J. The Imperative for Regulatory Oversight of Large Language Models (or Generative AI) in Healthcare. NPJ Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wei, M.; Sun, Y.; Suh, Y.J.; Shen, L.; Yang, S. Smiling Women Pitching Down: Auditing Representational and Presentational Gender Biases in Image Generative AI. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.10566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townson, S. Manage AI Bias Instead of Trying to Eliminate It. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2023, 64, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Lazer, D.; Kennedy, R.; King, G.; Vespignani, A. The Parable of Google Flu: Traps in Big Data Analysis. Science 2014, 343, 1203–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaven, W.D. Why Meta’s Latest Large Language Model Survived Only Three Days Online. MIT Technol. Rev. 2022, 15, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Halkias, D.; Neubert, M.; Thurman, P.W.; Harkiolakis, N. The Multiple Case Study Design: Methodology and Application for Management Education; Routledge: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 1-00-324493-9. [Google Scholar]
- Waheed, Z.; Hussin, S.; Bin Megat Daud, M.A.K. The Best Practices for School Transformation: A Multiple-Case Study. J. Educ. Adm. 2018, 56, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigud, A. Institutional Level Identity Control Strategies in the Distance Education Environment: A Survey of Administrative Staff. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2013, 14, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, R. A Multiple Case Design for the Investigation of Information Management Processes for Work-Integrated Learning. Int. J. Work. Integr. Learn. 2018, 19, 223–235. [Google Scholar]
- QS World University Rankings QS World University Rankings: Top Global Universities. Available online: https://www.topuniversities.com/qs-world-university-rankings (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Estrada-Real, A.C.; Cantu-Ortiz, F.J. A Data Analytics Approach for University Competitiveness: The QS World University Rankings. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. IJIDeM 2022, 16, 871–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowter, B.; Reggio, D.; Hijazi, S. QS World University Rankings. In Research Analytics; Auerbach Publications: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 121–136. Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.1201/9781315155890-7/qs-world-university-rankings-ben-sowter-david-reggio-shadi-hijazi (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Krippendorff, K. Agreement and Information in the Reliability of Coding. Commun. Methods Meas. 2011, 5, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, Y.S.; Guba, E.G. Naturalistic Inquiry; SAGE: New York, NY, USA, 1985; ISBN 978-0-8039-2431-4. Available online: https://www.google.ca/books/edition/Naturalistic_Inquiry/2oA9aWlNeooC?hl=en&gbpv=0 (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Stahl, N.A.; King, J.R. Expanding Approaches for Research: Understanding and Using Trustworthiness in Qualitative Research. J. Dev. Educ. 2020, 44, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- McAdoo, T. How to Cite ChatGPT. Available online: https://apastyle.apa.org/blog/how-to-cite-chatgpt (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Concordia University. Generative AI Teaching Guidelines. Available online: https://www.concordia.ca/content/concordia/en/ctl/tech-tools/teach-with-technology/guidelines-gen-ai.html (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Australian National University. Best Practice When Using Generative AI. Available online: https://www.anu.edu.au/students/academic-skills/academic-integrity/best-practice-principles/best-practice-when-using (accessed on 6 April 2024).
- UNC Chapel Hill. Student Generative AI Usage Guidance. Available online: https://provost.unc.edu/student-generative-ai-usage-guidance/ (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Whitfield, S.; Hofmann, M.A. Elicit: AI Literature Review Research Assistant. Public Serv. Q. 2023, 19, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyadi, M.; Rafi, M.; Shan, W.; Lucky, H.; Moniaga, J.V. Accuracy and Fidelity Comparison of Luna and DALL-E 2 Diffusion-Based Image Generation Systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Industry 4.0, Artificial Intelligence, and Communications Technology (IAICT), Bali, Indonesia, 13–15 July 2023; pp. 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Steele, C. 7 ChatGPT Alternatives Ready to Answer Your Burning Questions. Available online: https://www.pcmag.com/news/chatgpt-alternatives-ai-chatbots-ready-to-answer-your-burning-questions (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Thomson, S.; Amigud, A.; Huijser, H. Authenticity, Originality, and Beating the Cheats. In Technology-Enhanced Learning and the Virtual University; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Amigud, A.; Arnedo-Moreno, J.; Daradoumis, T.; Guerrero-Roldan, A.-E. An Integrative Review of Security and Integrity Strategies in an Academic Environment: Current Understanding and Emerging Perspectives. Comput. Secur. 2018, 76, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, U.; Keenan, K.; Somers, G.; Sorenson, S. Large Language Models: A Deep Dive: Bridging Theory and Practice; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; ISBN 978-3-031-65646-0. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, R.; Cox, A.L. ‘At Least They’Re Learning Something’: The Hazy Line between Collaboration and Collusion. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2005, 30, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holpuch, A.; Rubin, A.; Remote Scan of Student’s Room Before Test Violated His Privacy, Judge Rules. The New York Times. 25 August 2022. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2022/08/25/us/remote-testing-student-home-scan-privacy.html (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Vynck, G.D.; Tiku, N. Google Takes down Gemini AI Image Generator. Here’s What You Need to Know. Washington Post, 22 February 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Coldewey, D. OpenAI Scuttles AI-Written Text Detector over “Low Rate of Accuracy”. TechCrunch, 25 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, G.A. Analysis | We Tested a New ChatGPT-Detector for Teachers. It Flagged an Innocent Student. Washington Post, 1 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Klee, M. She Was Falsely Accused of Cheating With AI—And She Won’t Be the Last. Rolling Stone, 6 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Amigud, A.; Pell, D.J. Virtue, Utility and Improvisation: A Multinational Survey of Academic Staff Solving Integrity Dilemmas. J. Acad. Ethics 2022, 20, 311–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, M. Guidance on AI Detection and Why We’re Disabling Turnitin’s AI Detector. Available online: https://www.vanderbilt.edu/brightspace/2023/08/16/guidance-on-ai-detection-and-why-were-disabling-turnitins-ai-detector/ (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Atias, D. Research Guides: Responding to Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools. Available online: https://libguides.gwu.edu/c.php?g=1294883&p=9510493 (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Amigud, A.; Arnedo-Moreno, J.; Daradoumis, T.; Guerrero-Roldan, A.-E. A Robust and Non-Invasive Strategy for Preserving Academic Integrity in an Open and Distance Learning Environment. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 17th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT), Timisoara, Romania, 3–7 July 2017; pp. 530–532. [Google Scholar]
- Monaco, J.V.; Stewart, J.C.; Cha, S.-H.; Tappert, C.C. Behavioral Biometric Verification of Student Identity in Online Course Assessment and Authentication of Authors in Literary Works. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Sixth International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Arlington, VA, USA, 29 September–2 October 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Amigud, A.; Arnedo-Moreno, J.; Daradoumis, T.; Guerrero-Roldan, A.-E. Open Proctor: An Academic Integrity Tool for the Open Learning Environment. In Proceedings of the 9th Int. Conference on Intelligent Networking and Collaborative Systems (INCoS 2017), Toronto, Canada, 24–26 August 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; pp. 262–273. [Google Scholar]
- Pell, D.J.; Amigud, A. The Higher Education Dilemma: The Views of Faculty on Integrity, Organizational Culture, and Duty of Fidelity. J. Acad. Ethics 2022, 21, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hextrum, K. Operation Varsity Blues: Disguising the Legal Capital Exchanges and White Property Interests in Athletic Admissions. High. Educ. Politics Econ. 2019, 5, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, L. MyMaster Essay Cheating Scandal: More than 70 University Students Face Suspension. The Sydney Morning Herald, 18 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Fu, W.; Liang, G.; Qiu, J. AI-Enabled Image Fraud in Scientific Publications. Patterns 2022, 3, 100511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N. How Journals Are Fighting Back against a Wave of Questionable Images. Nature 2024, 626, 697–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, A. AI Beats Human Sleuth at Finding Problematic Images in Research Papers. Nature 2023, 622, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).