Abstract
Introduction: Early-life neurological and inflammatory disorders significantly affect long-term cognitive, social, and emotional development. The ‘Developmental Origins of Health and Disease’ hypothesis states that an adverse intrauterine environment may predispose offspring to chronic health conditions due to altered growth and development. Factors measured in umbilical cord blood can provide information about the status of the in utero environment during development. Evidence indicates that umbilical cord blood adipokines, namely leptin and adiponectin, may influence fetal programming and could be useful in predicting offspring health outcomes. Leptin and adiponectin are crucial in energy homeostasis, immune response, and placental function, and some studies suggest that altered concentrations may increase the risk of developing inflammatory and neurological disorders in later life. Further, limited studies have demonstrated sex-specific differences in adipokine concentrations and disease risk. Conclusions: Understanding the role of umbilical cord blood adipokines in fetal programming could offer new insights into early risk prediction and intervention strategies, promoting better health outcomes for children at risk of neurological and inflammatory diseases due to an adverse maternal environment during pregnancy.
1. Introduction
Child neurological and inflammatory disorders significantly impact cognitive, social, and emotional development, as well as the quality of life of individuals through childhood and throughout life. Neurological diseases account for over 20% of the disease burden, with the most commonly diagnosed in childhood being autism, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), learning abilities, epilepsy and seizures, and movement disorders including cerebral palsy. Asthma is the fifth leading cause of total health burden among infants aged 0–5 [1]. In Australia, an estimated 10%—approximately 460,000—of children aged 0–14 were reported to have asthma as a long-term condition in 2017–2018 [1]. Neurological and inflammatory disorders are associated with genetic predispositions, infections, immune system dysregulation, maternal health conditions, environmental exposures, and adverse environmental influences during the perinatal stage [2]. Leptin and adiponectin are key adipokines that contribute to neurodevelopment, energy metabolism, and immune function in utero, making them potential biomarkers for an adverse maternal environment that may impact early-life health outcomes [3]. Therefore, the aim of this narrative review was to summarize the research data implying a relationship between leptin and adiponectin and the diagnosis of neurological and inflammatory diseases in early childhood.
2. Developmental Origins of Health and Disease
During pregnancy, the female body undergoes immense physiological challenges to nurture and support the developing fetus [4]. Fetal organ development during pregnancy is a highly regulated process, beginning with organogenesis in the first trimester, where key organ systems start to form. As the pregnancy progresses, these organs mature, with organogenesis in humans completed at the time of birth [5]. Thus, the in utero environment is critical for normal fetal growth and development. The ‘Developmental Origins of Health and Disease (DOHaD)’ hypothesis postulates that exposure to an adverse in utero environment during critical periods of development and growth can significantly impact an individual’s growth, and thus their short- and long-term health [6]. Central to this concept is the idea of developmental programming, where the developing fetus undergoes physiological and structural adaptations in response to the condition within the uterine environment [7]. In uncomplicated pregnancies, adaptation ensures the optimal survival of the fetus in the given intrauterine environment and later after birth. However, in adverse intrauterine environments, the consequent adaptations may be unsuitable for the environment after birth, potentially predisposing the individual to health challenges when such conditions do not persist [8]. Environmental impacts on fetal development can be mediated by the placenta, which forms an interface between maternal and fetal systems. Environmental perturbations, such as maternal nutrition, stress, and toxin exposure, can impact placental function, altering growth and thus impacting the programming of fetal organ development [9] (Figure 1). Adipokines, which are cytokines primarily excreted by adipose tissue, play a number of tant roles during pregnancy. Adipokine concentrations can be modulated by environmental, physiological, or pathological changes, which impact placental function, subsequently affecting fetal growth and development. These interactions may increase the infant’s vulnerability to a range of disorders that may emerge later in life.
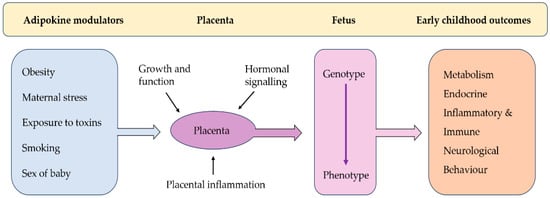
Figure 1.
(Modified from Burton et al. (2016)) [9] Pathways linking adipokine modulators to early childhood outcomes via placental and fetal development.
2.1. Role of the Placenta in DoHAD
The placenta is a multifunctional and transient organ that serves as the master regulator of the intrauterine environment via nutrient transfer, metabolism, gas exchange, neuroendocrine signaling, growth hormone production, and immunologic surveillance [9]. Due to its strong influence on fetal growth and development, the placenta is central to the DOHaD hypothesis. More specifically, the placenta contributes to the impact of the in utero environment on lifelong child health outcomes, including the risk of common, non-communicable health conditions [10]. The placenta undergoes structural and functional adaptations to mitigate adverse maternal factors, such as nutrient deprivation, drugs or toxin exposure, or hypoxia. However, when normal placental function is impaired, or the organ’s capacity for adaptation is exceeded, then the fetal milieu may be disturbed, with significant life-long health consequences for the infant [11].
2.2. Umbilical Cord Blood as a Child Health Indicator
Umbilical cord blood is a non-invasive surrogate indicator of human fetal development. While the placenta contains both maternal and fetal cells, umbilical cord blood is solely derived from the fetus. Consequently, biomarkers in umbilical cord blood may predict the impact of an adverse maternal environment during development, and thus the risk of poor health outcomes on the offspring. Thus, measuring adipokine concentrations in the umbilical cord as an indicator of fetal serum adipokines may help to reflect the child’s metabolic state in utero [12].
3. Adipokines in Pregnancy
During the important stages of development, adipokines may impact the development of the fetus [13]. Leptin and adiponectin are primarily adipocyte-secreted hormones known to play critical roles in energy homeostasis, immune response, appetite, insulin sensitivity, and inflammation in adults [3]. As adiponectin and leptin are almost exclusively expressed in adipose tissue, meaning that their effects can be more confidently described as specific downstream effects of adiposity, leptin and adiponectin appear to be particularly promising candidate biomarkers of offspring risk that may help to define the mechanisms through which birthing parent adiposity influences fetal development [12]. Both leptin and adiponectin concentrations are influenced by a range of factors, including maternal body composition, placental function/dysfunction, and maternal metabolic changes. Leptin concentrations increase with maternal fat mass and placental secretion, peaking in the third trimester. Adiponectin peaks in the first trimester, and then decreases for the remainder of the pregnancy, potentially due to the increase in insulin resistance [14]. Adiponectin was thought to be produced by the placenta, but the findings are not consistent [14]. Both adipokines may be further affected by maternal diet and exercise, inflammation, and hormonal shifts, which can impact fetal growth and development [14]. While their roles in fetal and neonatal development are less well understood, emerging evidence shows they are critical during pregnancy for uterine and placental functioning [15,16,17]. These adipokines help regulate placental insulin sensitivity, nutrient delivery, vascular function, and the inflammatory response, making them vital for placental growth and thus fetal growth and development [10]. However, the role of adipokines in fetal and neonatal growth requires further research [18].
4. Role of Leptin and Adiponectin in Pregnancy
Leptin, the most widely studied adipokine, is the 16-kDa product of the obese (ob) gene and has been shown to regulate energy homeostasis in adults by relaying information about the body’s energy and nutrient stores from the periphery to the brain [19]. Leptin is primarily secreted by adipose tissue; however, during human pregnancy, it is also secreted by the placenta, which is the second most significant source of leptin in humans. Leptin is recognized as a key signalling molecule in the reproductive system, playing a role in regulating gonadotrophin production, blastocyte formation and implantation, normal placentation, and communication between the fetus and placenta. Leptin crosses the placenta via specific leptin receptors that are primarily expressed in the syncytiotrophoblast layer of the placenta [20]. Leptin plays a crucial role during the first stages of pregnancy, with maternal plasma leptin concentrations rising in the first and second trimesters and peaking during the third trimester, before then returning to pre-pregnancy concentrations before parturition [21]. The leptin peak corresponds to the completion of organogenesis [18,22]. During pregnancy, leptin modulates critical processes such as proliferation, protein synthesis, invasion, and apoptosis in placental cells [17].
Research in animal models has demonstrated that leptin is involved in the development and maturation of several organs during pregnancy, including the heart, brain, kidneys, and pancreas [23,24]. Despite its critical roles, maternal leptin concentrations can vary significantly based on several factors. Elevated maternal BMI is associated with hyperleptinemia due to increased adipose tissue mass and reduced leptin sensitivity. Obese pregnant women often exhibit heightened leptin resistance, which can impair placental and fetal growth by disrupting nutrient and inflammatory signalling [10]. Additionally, the dysregulation of leptin correlations has been correlated with the pathogenesis of various disorders associated with reproduction and gestation, including polycystic ovary syndrome, recurrent miscarriage, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), pre-eclampsia, and intrauterine growth restriction [17]. Alterations in maternal–placental–fetal leptin exchange may modify the development of the fetus and contribute to an increased risk of developing disease in adulthood. Alterations in leptin during development may be associated with an increased risk of developing several adulthood diseases, including cardiovascular, metabolic, and renal diseases, via altered fetal development and organogenesis [18]. In rats, organogenesis is completed after pregnancy. Attig et al. [25] found that postnatal leptin, in the window before the completion of organogenesis, is essential for the maturation of numerous organs, including the pancreas, kidney, thymus, and ovary, and for hypothalamic development in newborn rats. Antagonism of leptin during this critical early postnatal period in rats impairs organ maturation and disrupts physiological functions, highlighting leptin’s pivotal role in early-life development and long-term health outcomes.
Adiponectin is an adipokine exclusively produced by adipose tissue. Circulating maternal adiponectin does not cross the placenta, although adiponectin receptors (ADIPOR1 and ADIPOR2) are present in the placenta [26,27]. These receptors play a role in placental signaling, influencing nutrient transfer and fetal development [28]. Adiponectin appears to function separately within the maternal and fetal systems, signaling through placental receptors on trophoblast cells [14,27,29]. While maternal adiponectin concentrations decrease throughout gestation, fetal adiponectin concentrations increase, promoting fat deposition and fetal growth [30]. Fetal adiponectin is postulated to have the opposite effect of circulating adiponectin in adults, promoting fetal growth and adipose deposition [14], and often shows an inverse relationship with leptin concentrations [13,31]. In pregnancies complicated by obesity or gestational diabetes, lower maternal adiponectin concentrations have been linked to impaired glucose metabolism and altered placental function [32]. This dysregulation may affect insulin sensitivity and nutrient transport across the placenta, potentially leading to adverse fetal outcomes, including an increased risk of excessive fetal growth, insulin resistance, and long-term metabolic disorders [33].
Rodent studies have found that fetal adiponectin plays a role in modulating fetal growth and development, with multiple studies suggesting that adiponectin promotes adiposity [30,34,35]. The administration of adiponectin increased litter size and decreased neonatal size in mice [36]. This suggests that maternal adiponectin regulates fetal growth, potentially downregulating placental amino acid transport and insulin/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling [36,37]. In contrast to maternal adiponectin, fetal adiponectin serves to promote fetal growth and adipose deposition, possibly by increasing fetal insulin resistance [38]. The effect of adiponectin on fetal growth is proposed to be a consequence of altered placental nutrient transport; as adiponectin does not cross the placenta itself [39]. Thus, the impact of exogenous adiponectin on fetal growth is likely limited by nutrient availability [28]. Moreover, rodent studies have shown that fetal adiponectin plays a role in fat metabolism through controlling adiponectin-modulating enzymes and pathways that enhance fatty acid oxidation and reducing triglyceride accumulation [40]. Unlike adiponectin from the mother, fetal adiponectin increases circulating free fatty acids and increases the activity of genes in the liver that promote fat production, such as sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c), fatty acid synthase (FAS), and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) [30]. When rodent mothers are obese, their offspring accumulate more body fat and show higher adipose adiponectin [41]. This suggests that the mother’s condition can influence how adiponectin concentrations are regulated in her offspring. However, the observation that, at birth, umbilical cord blood adiponectin is as much as seven times higher than maternal serum concentrations but decreases significantly within the first year of life reflects the dynamic changes in adiponectin regulation during early development [42].
In humans, very few studies have investigated sex-specific differences in umbilical cord blood adipokines, but often these findings are contradictory. For example, females have higher leptin concentrations in cord blood compared with males [43], while adiponectin concentrations were not impacted by sex [43,44]. Another study found, at term, no difference in cord leptin in offspring born to normoglycemic mothers, while in male offspring born to mothers with Gestational Impaired Glucose Tolerance, leptin was increased [45]. Interestingly, Ashley-Martin et al. [46] observed sex-specific differences in the associations between umbilical cord blood adipokines and child growth. Specifically, umbilical cord blood adiponectin concentrations were positively associated with modest increases in body mass index (BMI) z-scores and the sum of skinfolds in boys and not girls [46]. Several mechanisms may underlie the observed differences according to sex regarding the associated effects of adiponectin growth. The higher serum estrogen observed in females may protect them from the adverse effects of maternal obesity-associated hormone dysregulation during fetal development due to the role of estrogen in the epigenetic regulation of adipogenic genes [47]. Dearden et al. [48] proposed that the male placenta may also be more vulnerable to damage from adverse in utero conditions such as maternal obesity or undernutrition compared to the female placenta. This vulnerability is thought to be attributed to the reduced antioxidant capacity, lower reserve capacity for environmental changes, and lower expression of protective genes like O-GIcNAc transferase (OGT), which compromises the male placenta’s ability to maintain functional resilience [49]. These differences could explain why adiponectin-related mechanisms vary between sexes, while leptin-related mechanisms do not. Males and females may react differently to adipokine hormones due to differences in fat distribution, with males typically having more visceral fat and females having more subcutaneous fat. For instance, studies in rats show that male brains are more responsive to insulin than female brains [50].
However, other studies have found that umbilical cord blood leptin is higher in females compared to males [51,52]. Sex differences in adipokine concentration may lead to differences in offspring regarding the development of inflammatory and neurological disorders [53]. Sex differences therefore need to be considered when understanding the complex interplay in the development of placental function, fetal growth, and development of disorders.
5. Role of Leptin and Adiponectin in Early Childhood Health
5.1. Child Inflammatory Disease
Both leptin and adiponectin play essential roles in regulating immune responses and inflammation [54]. Leptin is a pro-inflammatory adipokine which enhances immune responses and promotes the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, contributing to macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue and heightened placental inflammation [55,56,57]. In contrast, adiponectin generally exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokine production [58]. The inflammatory state during pregnancy is highly regulated, shifting between pro- and anti-inflammatory phases to accommodate the needs of each trimester; however, adverse maternal factors can influence the balance between these adipokines [6,59]. Elevated leptin levels can lead to increased systemic and placental inflammation, and this inflammatory state may expose the fetus to higher inflammatory mediators in utero, affecting immune system development [60]. Chronic exposure to elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines can influence fetal immune programming, which may contribute to an increased risk of inflammatory diseases in early childhood [61]. This intrauterine environment, characterized by heightened inflammation, could predispose the infant to immune dysregulation, potentially leading to conditions such as asthma, chest infections, gastroenteritis, and meningitis in childhood [62]. The mechanisms behind this increased risk are believed to stem from the early shaping of the infant’s immune system, influenced by the inflammatory environment during gestation [58].
5.2. Early Childhood Neurological Disease
Evidence indicates an association between adverse pregnancy environment and infant risk for neurodevelopmental disorders [63]. The mechanisms underlying the relationship between fetal environment and neurodevelopmental outcomes remain complex and poorly understood, but emerging research points to the role of altered adipokine concentrations during pregnancy. Adipokines, specifically leptin and adiponectin, are critical regulators of metabolic, inflammatory, and developmental pathways, and may play a pivotal role in shaping brain development. Alterations in the concentrations of these adipokines could lead to imbalanced inflammatory states, potentially interfering with the critical processes of brain maturation and function [63,64].
The biological effects exerted by leptin during the early phases of development and organ maturation remain largely unknown [25]. Evidence suggests that leptin plays a critical role in fetal brain development, potentially through its ability to activate pro-inflammatory cytokines. These cytokines influence key neurotransmitter systems involved in regulating behaviour, highlighting leptin’s potential impact on neural function and behavioural outcomes [53]. Moreover, studies have provided insights into leptin’s mechanisms of action within the brain. Lee et al. [65] demonstrated that leptin modulated neural excitability by influencing potassium channels in regions critical for cognition, memory, motor control, and emotional regulation, such as the amygdala, hippocampus, cerebellum, and substantia nigra. Similarly, Smith et al. [66] highlighted leptin’s role in enhancing synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis within the hippocampus, a key region for learning and memory. These findings collectively suggest that leptin acts as a neuromodulator during early development, with its effects extending across multiple brain regions and influencing both the structural and functional aspects of neural maturation.
Rodent studies suggest that adipokines may play a crucial role in fetal neurodevelopment [67]. In young adult mice, short-term leptin infusions were found to enhance memory and learning abilities [68,69]. However, elevated leptin concentrations can result in leptin resistance in the brain, potentially impairing cognitive function in young adult rodents [70,71]. Adiponectin protects the brain by regulating inflammatory responses. In adult rodents, adiponectin demonstrated neuroprotective properties by exerting anti-inflammatory effects through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines and a reduction in microglial activation, thereby mitigating neuroinflammation [72]. Additionally, adiponectin enhances neuronal survival and function by promoting energy homeostasis and activating signalling pathways such as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and the PI3K/Akt pathway, which are crucial for cellular repair and neurogenesis [73]. However, reductions in adiponectin may increase pro-inflammatory cytokine concentrations, leading to neuroinflammation and subsequent cognitive impairments [74,75].
Adiponectin has been implicated in the metabolic programming of infants exposed to maternal obesity [14]. One potential mechanism is altered adiponectin signalling affecting the fetal mTOR of the placenta, a critical regulator of autophagy sensitive to nutritional status [76]. Although maternal adiponectin does not cross the blood–placental barrier, it influences placental cells by inhibiting glucose and amino acid transporters, thereby restricting nutrient availability for the fetus [77]. Human studies have correlated umbilical cord blood adiponectin with a higher full-scale and performance intelligence quotient (IQ) and higher working memory composite scores in children seven years of age [67].
Studies investigating the relationship between leptin, adiponectin, and neurodevelopment in children, especially older children, have yielded inconsistent results (Table 1). Elevated leptin has been associated with a 30% increased risk of asthma in children born to obese mothers [78], yet shows no association with wheezing disorders [43] or IQ development. Interestingly, reduced leptin concentrations are linked to lower neurodevelopmental scores at 12 months of age [79], whereas elevated leptin appears to have no significant impact on overall neurodevelopmental outcomes [64]. Similarly, adiponectin shows variable outcomes, with elevated concentrations increasing the risk of asthma or obstructive bronchitis [43] and negatively affecting motor skill development at 12 months [64]. These findings suggest that while adipokine concentrations may influence early health outcomes, further research is needed to strengthen these associations. Currently, assessments of adipokines are not routinely conducted, resulting in there being insufficient data to support more comprehensive systematic reviews. What remains uncertain is whether umbilical cord blood leptin and adiponectin are associated with neurodevelopment in very young children, how they might predict early childhood neurological outcomes, and whether there is a sex effect. Interestingly, no studies reported the birth weight of infants or the gestational age, which would significantly impact the adipokine concentrations. There is a significant knowledge gap regarding the impact of these adipokines on fetal environment and their potential influence on child neurodevelopment at one year of age. Further research is needed to clarify these associations.

Table 1.
Association between human umbilical cord blood adipokines and early child neurological and immune health outcomes.
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
In utero adipokine exposure to leptin and adiponectin, which can be estimated by measurement in umbilical cord blood at delivery, is increasingly recognized as pivotal in shaping early childhood health by influencing fetal development and programming. While much of the existing research has focused on their correlation with child adiposity, growing evidence suggests that these adipokines may also impact neurological and inflammatory disorders. Notably, limited evidence suggests that these adipokines have sex-specific effects, with variations in concentration and response contributing to disparities in susceptibility to neurological and inflammatory disorders between male and female infants. Importantly, despite sex acting as a biological variable [80], very few studies report sex differences. This may be partly due to a lack of (unreported) sex differences, or a failure to separate the data based on sex. Further, the sample size of the cohort for a number of studies may be insufficient to detect small effects in the data [78]. Another consideration in the analyses of neurological and inflammatory disorders is the lack of standardisation for diagnosis, as well as potential variations in the methods of collecting and processing samples for analysis [78]. Future research should ensure that data are sufficiently powered and separated based on sex, and that there is clinical/physician diagnosis of disease, with standardised sample processing and analysis.
Thus, further research is needed to clarify leptin and adiponectin’s mechanisms and their role in the development of these disorders. Understanding potential correlations between altered concentrations of leptin and adiponectin in utero and early childhood diagnosis of neurological and inflammatory disorders is crucial for early risk prediction and intervention to improve child outcomes and provide the most effective treatment options for these children.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.J.H. and D.H.H.; methodology, O.J.H. and D.H.H.; validation, O.J.H. and D.H.H.; formal analysis, A.M.B.; investigation, A.M.B., O.J.H. and D.H.H.; data curation, A.M.B., O.J.H. and D.H.H.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M.B., O.J.H. and D.H.H.; writing—review and editing, All authors; supervision, D.H.H.; project administration, D.H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Australia’s Children. 2022. Available online: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/children-youth/australias-children (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Han, V.X.; Patel, S.; Jones, H.F.; Dale, R.C. Maternal immune activation and neuroinflammation in human neurodevelopmental disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 564–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, U.; Gressner, A.M. Endocrine Regulation of Energy Metabolism: Review of Pathobiochemical and Clinical Chemical Aspects of Leptin, Ghrelin, Adiponectin, and Resistin. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 1511–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma-Pillay, P.; Nelson-Piercy, C.; Tolppanen, H.; Mebazaa, A. Physiological changes in pregnancy. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2016, 27, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardi, G.; Cetin, I. Human fetal growth and organ development: 50 years of discoveries. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 194, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J. The fetal and infant origins of adult disease. Bmj 1990, 301, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabadán-Diehl, C.; Nathanielsz, P. From Mice to Men: Research models of developmental programming. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2013, 4, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandy, M.; Nyirenda, M. Developmental Origins of Health and Disease: The relevance to developing nations. Int. Health 2018, 10, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.J.; Fowden, A.L.; Thornburg, K.L. Placental Origins of Chronic Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1509–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, K.R.; Powell, T.L. Effects of maternal obesity on placental function and fetal development. Reproduction 2017, 153, R97–R108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Freedman, A.N.; Avula, V.; Harris, R.; Liu, W.; Pan, C.; Lusis, A.J.; Joseph, R.M.; Smeester, L.; Hartwell, H.J.; et al. Placental genomics mediates genetic associations with complex health traits and disease. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, E.L.; Molloy, K.R.; Dunn, G.A.; Balanzar, A.L.; Young, A.S.; Loftis, J.M.; Ablow, J.C.; Nigg, J.T.; Gustafsson, H.C. Adipokines measured during pregnancy and at birth are associated with infant negative affect. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 120, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ippolito, S.; Tersigni, C.; Scambia, G.; Di Simone, N. Adipokines, an adipose tissue and placental product with biological functions during pregnancy. Biofactors 2012, 38, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aye, I.L.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Review: Adiponectin—The missing link between maternal adiposity, placental transport and fetal growth? Placenta 2013, 34, S40–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauguel-de Mouzon, S.; Lepercq, J.; Catalano, P. The known and unknown of leptin in pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 194, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, M.C.; Castracane, V.D. Leptin in Pregnancy. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 63, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Perez, A.; Toro, A.; Vilarino-Garcia, T.; Maymo, J.; Guadix, P.; Duenas, J.L.; Fernandez-Sanchez, M.; Varone, C.; Sanchez-Margalet, V. Leptin action in normal and pathological pregnancies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.F.; McAinch, A.J.; Romano, T.; Wlodek, M.E.; Hryciw, D.H. Leptin in pregnancy and development: A contributor to adulthood disease? Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E335–E350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.M. Leptin and the endocrine control of energy balance. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challier, J.; Galtier, M.; Bintein, T.; Cortez, A.; Lepercq, J.; Hauguel-de Mouzon, S. Placental Leptin Receptor Isoforms in Normal and Pathological Pregnancies. Placenta 2003, 24, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubring, C.; Englaro, P.; Siebler, T.; Blum, W.F.; Demirakca, T.; Kratzsch, J.; Kiess, W. Longitudinal Analysis of Maternal Serum Leptin Levels during Pregnancy, at Birth and Up To Six Weeks after Birth: Relation to Body Mass Index, Skinfolds, Sex Steroids and Umbilical Cord Blood Leptin Levels. Horm. Res. 1999, 50, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, M.E.; Collado-Pérez, R.; Frago, L.M.; Barrios, V. Recent Advances in the Knowledge of the Mechanisms of Leptin Physiology and Actions in Neurological and Metabolic Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emilsson, V.; Liu, Y.L.; Cawthorne, M.A.; Morton, N.M.; Davenport, M. Expression of the functional leptin receptor mRNA in pancreatic islets and direct inhibitory action of leptin on insulin secretion. Diabetes 1997, 46, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoggard, N.; Hunter, L.; Duncan, J.S.; Williams, L.M.; Trayhurn, P.; Mercer, J.G. Leptin and leptin receptor mRNA and protein expression in the murine fetus and placenta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11073–11078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attig, L.; Larcher, T.; Gertler, A.; Abdennebi-Najar, L.; Djiane, J. Postnatal leptin is necessary for maturation of numerous organs in newborn rats. Organogenesis 2011, 7, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminos, J.E.; Nogueiras, R.; Gallego, R.; Bravo, S.; Tovar, S.; García-Caballero, T.; Casanueva, F.F.; Diéguez, C. Expression and regulation of adiponectin and receptor in human and rat placenta. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 4276–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tan, B.; Karteris, E.; Zervou, S.; Digby, J.; Hillhouse, E.W.; Vatish, M.; Randeva, H.S. Secretion of adiponectin by human placenta: Differential modulation of adiponectin and its receptors by cytokines. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyce Gruber, B.L.; Dolinsky, V.W. The Role of Adiponectin during Pregnancy and Gestational Diabetes. Life 2023, 13, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, E.A.; Wolfe, M.W. Adiponectin Attenuation of Endocrine Function within Human Term Trophoblast Cells. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 4358–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Yoo H s Madon, A.; Kinney, B.; Hay, W.W., Jr.; Shao, J. Adiponectin Enhances Mouse Fetal Fat Deposition. Diabetes 2012, 61, 3199–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Laborde-Cárdenas, C.C.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The Role of Adipokines in Health and Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.C.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Placental function in maternal obesity. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrettini, S.; Caroli, A.; Torlone, E. Nutrition and Metabolic Adaptations in Physiological and Complicated Pregnancy: Focus on Obesity and Gestational Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 611929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, L.M.; Porter, K. Longitudinal changes in serum proinflammatory markers across pregnancy and postpartum: Effects of maternal body mass index. Cytokine 2014, 70, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N.; Vaughan, O.R.; Haro, M.; Cooper, W.N.; Musial, B.; Charalambous, M.; Pestana, D.; Ayyar, S.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C.; Burton, G.J.; et al. An obesogenic diet during mouse pregnancy modifies maternal nutrient partitioning and the fetal growth trajectory. Faseb J. 2013, 27, 3928–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, F.J.; Schumacher, M.A.; Jiang, J.; Kanai, Y.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Chronic maternal infusion of full-length adiponectin in pregnant mice down-regulates placental amino acid transporter activity and expression and decreases fetal growth. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1495–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, T.; Aye, I.L.; Goberdhan, D.C. The emerging role of mTORC1 signaling in placental nutrient-sensing. Placenta 2012, 33, e23–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napso, T.; Yong, H.E.; Lopez-Tello, J.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N. The role of placental hormones in mediating maternal adaptations to support pregnancy and lactation. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aye, I.L.; Rosario, F.J.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Adiponectin supplementation in pregnant mice prevents the adverse effects of maternal obesity on placental function and fetal growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12858–12863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.D. Adiponectin: Role in Physiology and Pathophysiology. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayol, S.A.; Simbi, B.H.; Bertrand, J.; Stickland, N.C. Offspring from mothers fed a ‘junk food’ diet in pregnancy and lactation exhibit exacerbated adiposity that is more pronounced in females. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 3219–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, Y.; Yokota, I.; Kitamura, S.; Matsuda, J.; Naito, E.; Kuroda, Y. Plasma adiponectin levels in newborns are higher than those in adults and positively correlated with birth weight. Clin. Endocrinol. 2004, 61, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenbacher, D.; Weyermann, M.; Fantuzzi, G.; Brenner, H. Adipokines in cord blood and risk of wheezing disorders within the first two years of life. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajantie, E.; Hytinantti, T.; Hovi, P.; Andersson, S. Cord plasma adiponectin: A 20-fold rise between 24 weeks gestation and term. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 4031–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oken, E.; Morton-Eggleston, E.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Switkowski, K.M.; Hivert, M.F.; Fleisch, A.F.; Mantzoros, C.; Gillman, M.W. Sex-Specific Associations of Maternal Gestational Glycemia with Hormones in Umbilical Cord Blood at Delivery. Am. J. Perinatol. 2016, 33, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley-Martin, J.; Karaceper, M.; Dodds, L.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Ettinger, A.S.; Fraser, W.D.; Muckle, G.; Monnier, P.; Fisher, M.; Kuhle, S. An examination of sex differences in associations between cord blood adipokines and childhood adiposity. Pediatr. Obes. 2020, 15, e12587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjune, J.I.; Stromland, P.P.; Jersin, R.A.; Mellgren, G.; Dankel, S.N. Metabolic and Epigenetic Regulation by Estrogen in Adipocytes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 828780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, L.; Bouret, S.G.; Ozanne, S.E. Sex and gender differences in developmental programming of metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2018, 15, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howerton, C.L.; Bale, T.L. Targeted placental deletion of OGT recapitulates the prenatal stress phenotype including hypothalamic mitochondrial dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9639–9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, D.J.; Riedy, C.A.; Smith, K.A.; Benoit, S.C.; Woods, S.C. Differential sensitivity to central leptin and insulin in male and female rats. Diabetes 2003, 52, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laml, T.; Hartmann, B.W.; Preyer, O.; Ruecklinger, E.; Soeregi, G.; Wagenbichler, P. Serum leptin concentration in cord blood: Relationship to birth weight and gender in pregnancies complicated by pre-eclampsia. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tome, F.M.; Chateau, D.; Helbling-Leclerc, A.; Fardeau, M. Morphological changes in muscle fibers in oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 1997, 7 (Suppl. 1), S63–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valleau, J.C.; Sullivan, E.L. The impact of leptin on perinatal development and psychopathology. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2014, 61–62, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Ianiro, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Adolph, T.E. Adipokines: Masterminds of metabolic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.; Gollapudi, S.; Su, H.; Gupta, S. Leptin Activates Human B Cells to Secrete TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-10 via JAK2/STAT3 and p38MAPK/ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleffi, S.; Petrai, I.; Bertolani, C.; Parola, M.; Colombatto, S.; Novo, E.; Vizzutti, F.; Anania, F.A.; Milani, S.; Rombouts, K. Upregulation of proinflammatory and proangiogenic cytokines by leptin in human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denizli, M.; Capitano, M.L.; Kua, K.L. Maternal obesity and the impact of associated early-life inflammation on long-term health of offspring. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 940937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijóo-Bandín, S.; Aragón-Herrera, A.; Moraña-Fernández, S.; Anido-Varela, L.; Tarazón, E.; Roselló-Lletí, E.; Portolés, M.; Moscoso, I.; Gualillo, O.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; et al. Adipokines and Inflammation: Focus on Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Raya, B.; Michalski, C.; Sadarangani, M.; Lavoie, P.M. Maternal Immunological Adaptation During Normal Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, V.X.; Patel, S.; Jones, H.F.; Nielsen, T.C.; Mohammad, S.S.; Hofer, M.J.; Gold, W.; Brilot, F.; Lain, S.J.; Nassar, N.; et al. Maternal acute and chronic inflammation in pregnancy is associated with common neurodevelopmental disorders: A systematic review. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, P. The role of adipokines in chronic inflammation. Immunotargets Ther. 2016, 5, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabic, D.; Koenig, J.M. A perfect storm: Fetal inflammation and the developing immune system. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 87, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundakovic, M.; Jaric, I. The Epigenetic Link between Prenatal Adverse Environments and Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Genes 2017, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Vargas, Z.; Zhao, A.; Baltazar, P.I.; Friedman, J.F.; McDonald, E.A. Cord blood adiponectin and leptin are associated with a lower risk of stunting during infancy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Kang, G.M.; Kim, M.S. Leptin directly regulate intrinsic neuronal excitability in hypothalamic POMC neurons but not in AgRP neurons in food restricted mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 681, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.M.; Brzezinska, P.; Hubert, F.; Mimee, A.; Maurice, D.H.; Ferguson, A.V. Leptin influences the excitability of area postrema neurons. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R440–R448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Muckle, G.; Lanphear, B.P.; Boivin, M.; Chen, A.; Dodds, L.; Fraser, W.D.; Ouellet, E.; Seguin, J.R.; et al. Associations of cord blood leptin and adiponectin with children’s cognitive abilities. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 99, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, S.A.; Banks, W.A.; Morley, J.E. Effects of leptin on memory processing. Peptides 2006, 27, 1420–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oomura, Y.; Hori, N.; Shiraishi, T.; Fukunaga, K.; Takeda, H.; Tsuji, M.; Matsumiya, T.; Ishibashi, M.; Aou, S.; Li, X.L.; et al. Leptin facilitates learning and memory performance and enhances hippocampal CA1 long-term potentiation and CaMK II phosphorylation in rats. Peptides 2006, 27, 2738–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, J.R.; Jolivalt, C.G.; Reagan, L.P. Food for thought: The role of appetitive peptides in age-related cognitive decline. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, C.D. Leptin signaling in brain: A link between nutrition and cognition? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1792, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.T.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S.; et al. Adiponectin protects hippocampal neurons against kainic acid-induced excitotoxicity. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 61, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, M.; Izumiya, Y.; Higuchi, A.; Shibata, R.; Qiu, J.; Kudo, C.; Shin, H.K.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Ouchi, N. Adiponectin prevents cerebral ischemic injury through endothelial nitric oxide synthase dependent mechanisms. Circulation 2008, 117, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnoldussen, I.A.; Kiliaan, A.J.; Gustafson, D.R. Obesity and dementia: Adipokines interact with the brain. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 1982–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, J.M.; Milton, A.J.; Smith, A.E.; Laezza, F.; Taglialatela, G.; Hommel, J.D.; Abate, N. Cognitive deficits associated with a high-fat diet and insulin resistance are potentiated by overexpression of ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase phosphodiesterase-1. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2018, 64, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merabova, N.; Ugartemendia, L.; Edlow, A.G.; Ibarra, C.; Darbinian, N.; Tatevosian, G.; Goetzl, L. Maternal obesity: Sex-specific in utero changes in fetal brain autophagy and mTOR. Obesity 2024, 32, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberger, E.; Larsson, A.; Kunovac Kallak, T.; Sundstrom Poromaa, I.; Wikstrom, A.K.; Osterroos, A.; Ahlsson, F. Maternal early mid-pregnancy adiponectin in relation to infant birth weight and the likelihood of being born large-for-gestational-age. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Rodriguez, J.A.; Forno, E.; Casanello, P.; Padilla, O.; Krause, B.J.; Uauy, R. Leptin in Cord Blood Associates with Asthma Risk at Age 3 in the Offspring of Women with Gestational Obesity. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Xiao, X.; Song, X.; Qi, Z.; Li, Y. Prediction of cord blood leptin on infant’s neurodevelopment: A birth cohort in rural Yunnan, China. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2023, 148, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltz, A.M.; Beery, A.K.; Becker, J.B. Analysis of sex differences in pre-clinical and clinical data sets. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 2155–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).