Resilient Anomaly Detection in Fiber-Optic Networks: A Machine Learning Framework for Multi-Threat Identification Using State-of-Polarization Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. State of Polarization (SOP) as a Sensing Mechanism
2.1. Eavesdropping
2.2. Simultaneous Events
2.3. State-of-Polarization-Based Vibration Monitoring
3. Vibration Emulation and State-of-Polarization Sensing Setup
4. Machine Learning Model Architecture
4.1. Machine Learning Classifiers
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
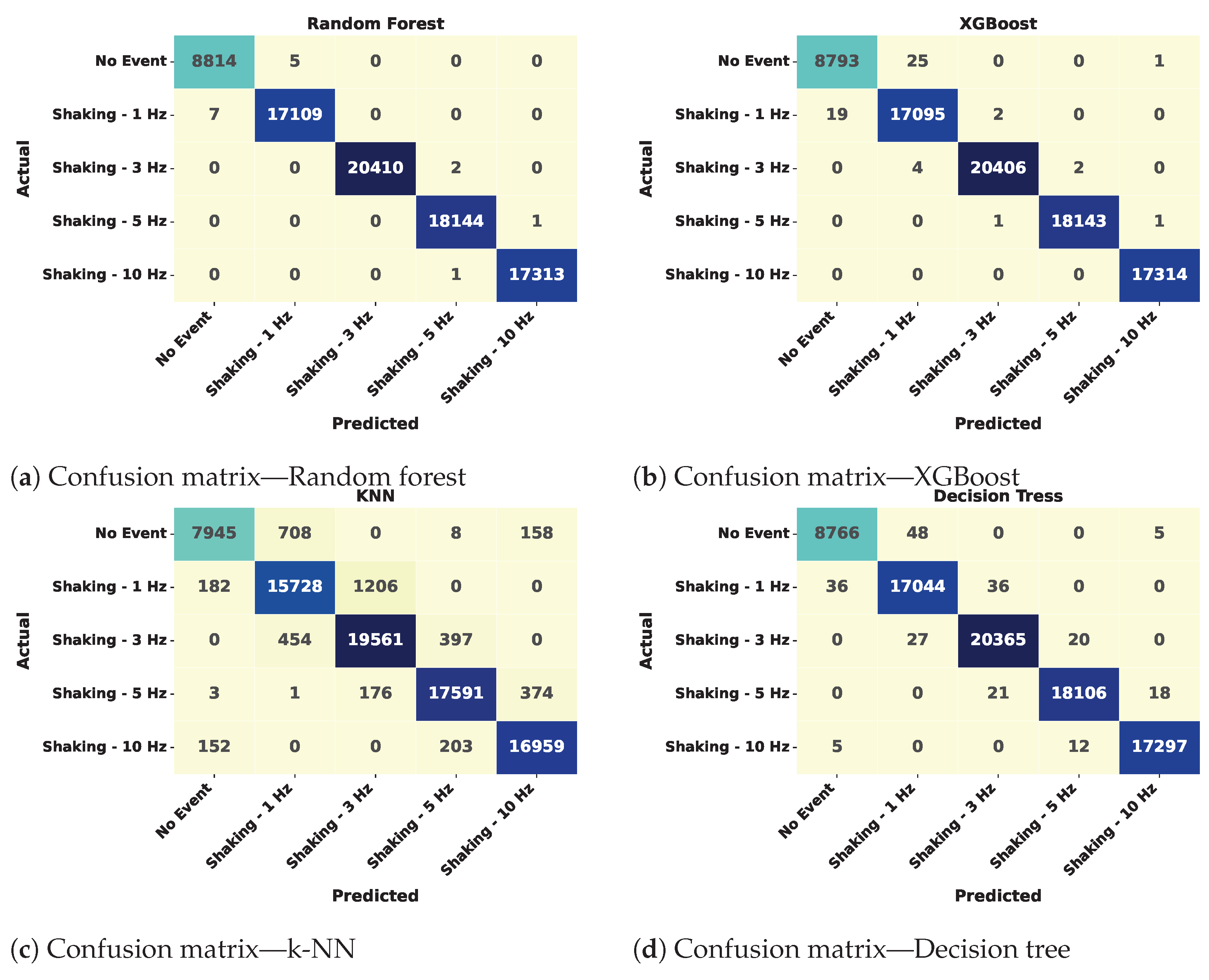
4.2.1. Confusion Matrix
4.2.2. Accuracy
4.2.3. Precision
4.2.4. Recall
4.2.5. F-1 Score
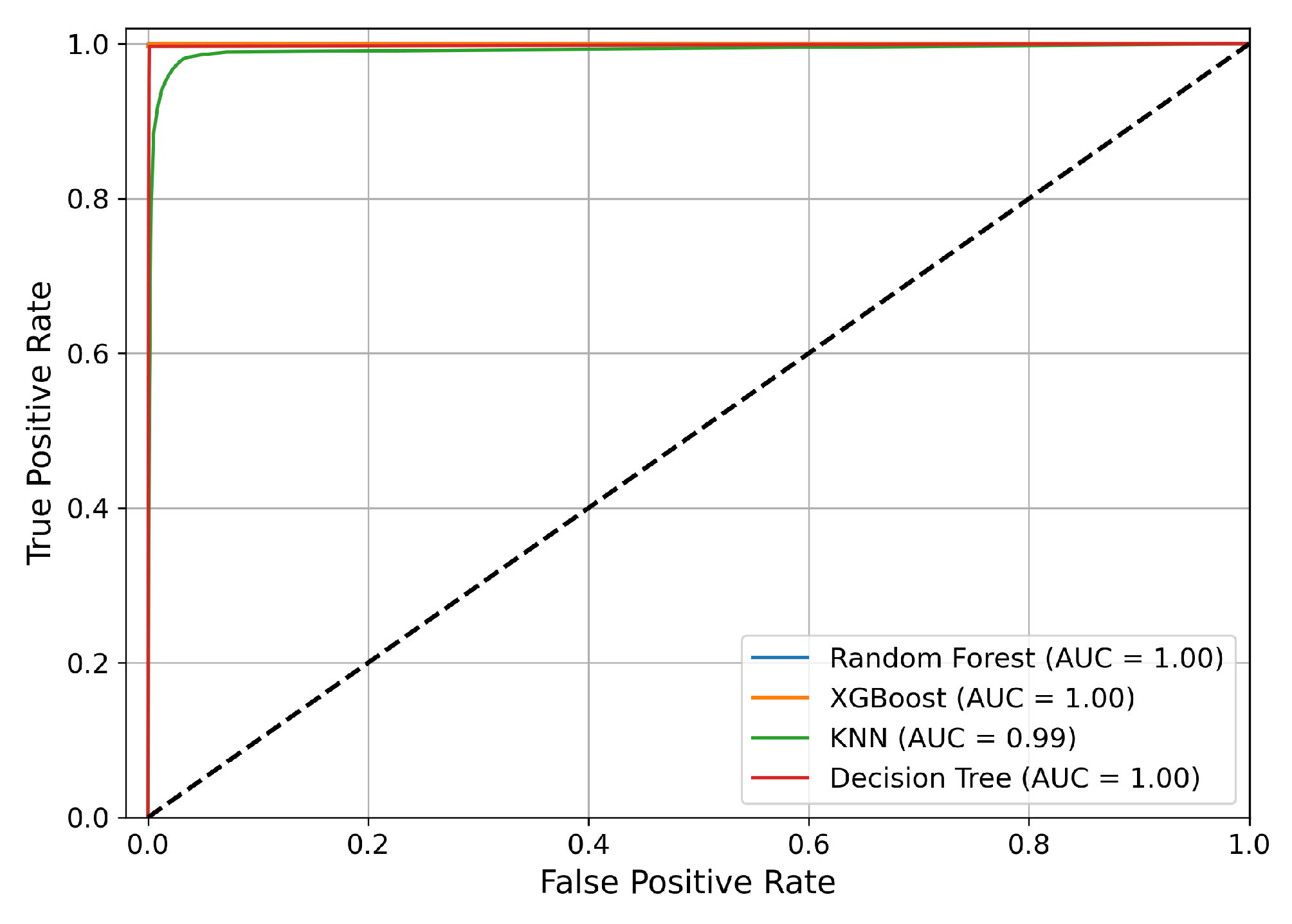
4.2.6. AUC-ROC Curve
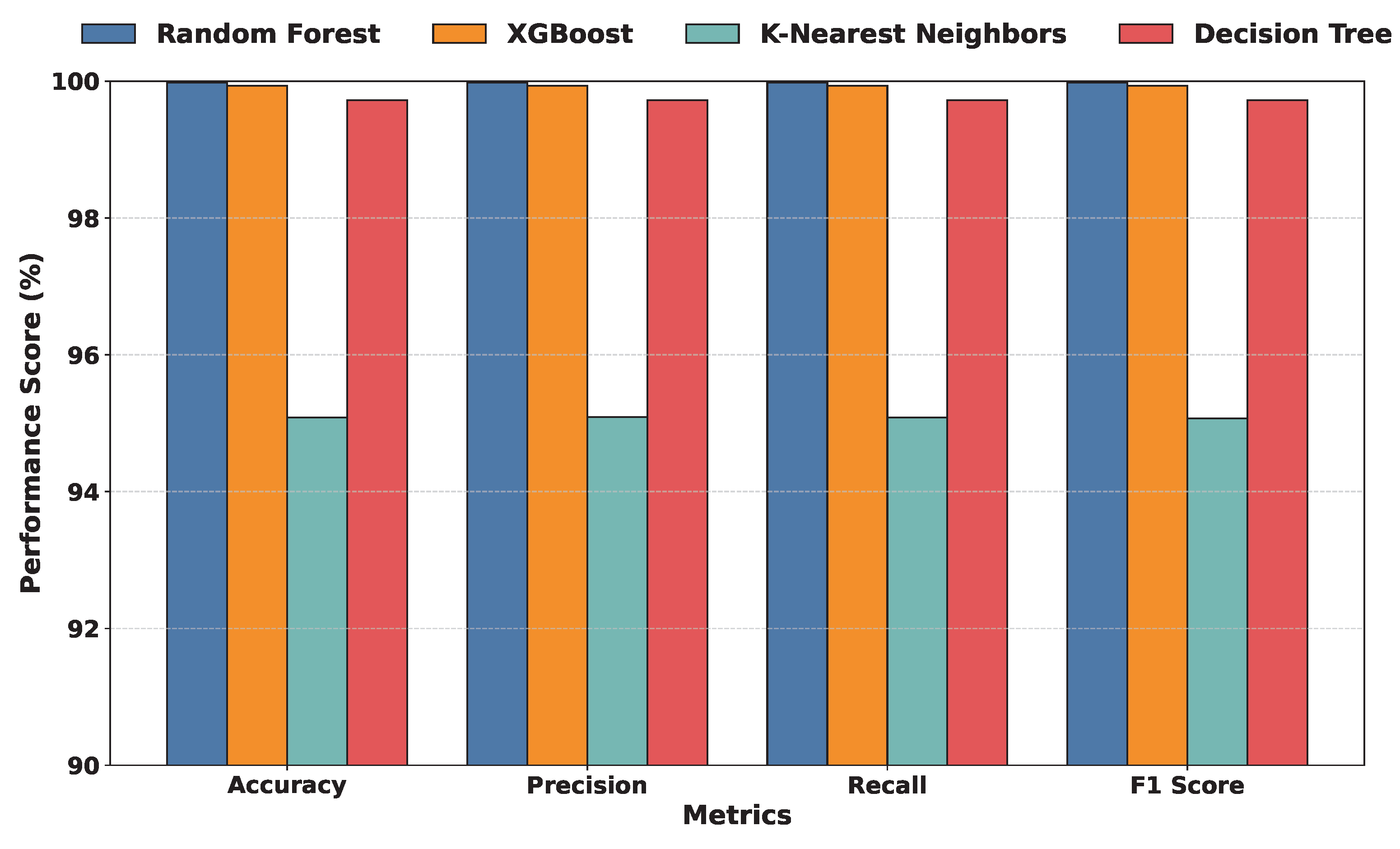
5. Performance Analysis of Machine Learning Model
5.1. Performance Evaluation of Model Classification Scores
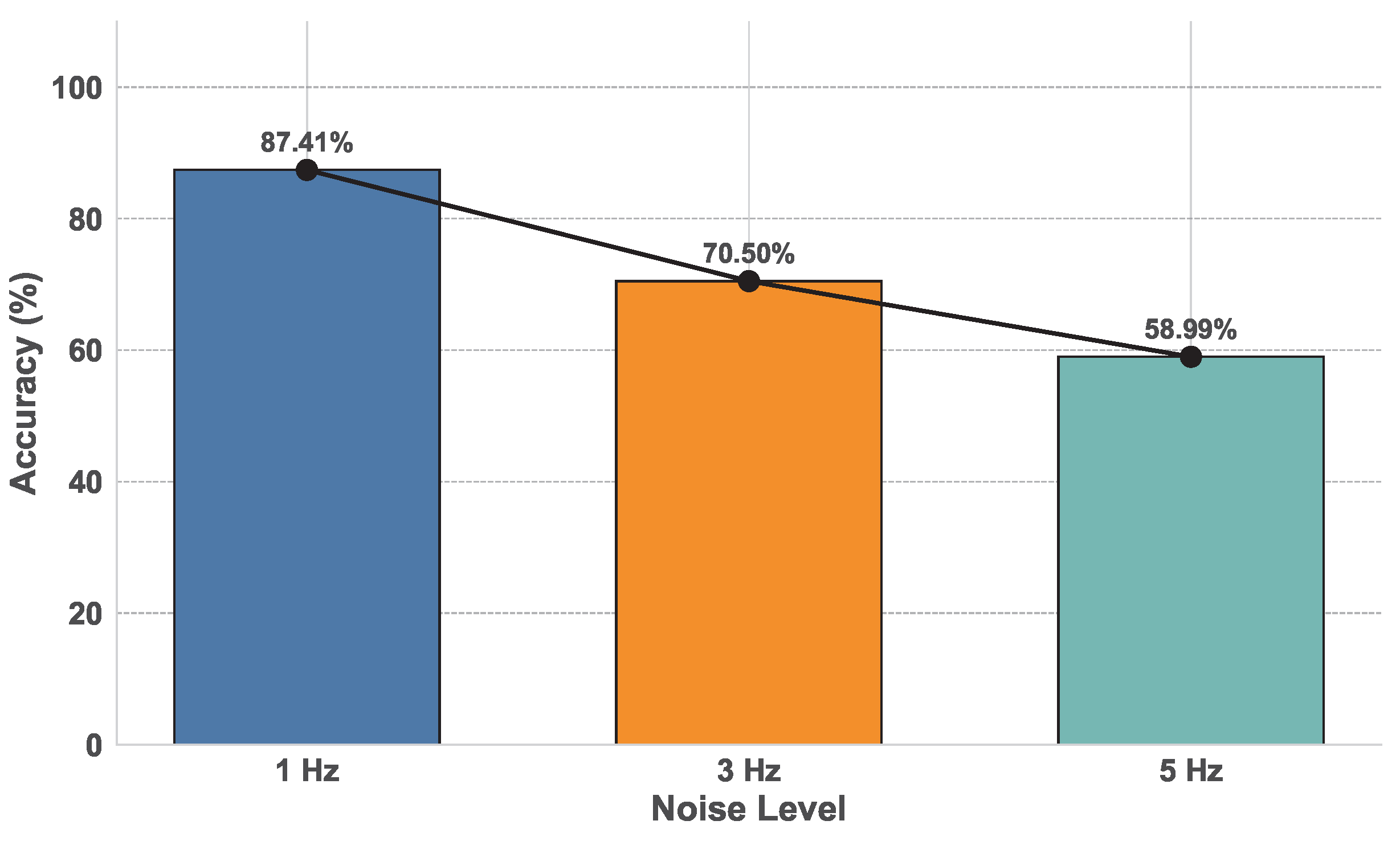
5.2. Performance Evaluation of ML Models Using Weighted Metrics
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOP | State of Polarization |
| SOPAS | State-of-Polarization Angular Speed |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| OTDR | Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer |
| DAS | Distributed Acoustic Sensing |
| DOP | Degree of Polarization |
| OFI | Optical Fiber Identification |
| SMF | Single Mode Fiber |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| BiGRU | Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit |
| DCM | Data Clustering Module |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| PCB | Printed Circuit Board |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| k-NN | k-Nearest Neighbor |
| RF | Random Forest |
| WPM | Weighted Performance Metric |
| TP | True Positive |
| TN | True Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| FN | False Negative |
| AUC | Area Under Curve |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| FPR | False Positive Rate |
| OvR | One-vs-Rest |
| TPR | True Positive Rate |
| AUC-ROC | Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| 1D-CNN | One-Dimensional CNN |
References
- Malik, G.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, A. Merging Engine Implementation with Co-Existence of Independent Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation Algorithms in Virtual Passive Optical Networks. In Proceedings of the Asia Communications and Photonics Conference 2021, Shanghai, China, 24–27 October 2021; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; p. T4A.273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalou, M.; Mohammed Amin, T.; Kheddouci, H. The Critical Node Detection Problem in networks: A survey. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2018, 28, 92–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Chen, G.; Meng, W.; Tang, F.; Chen, Y. Kilometer-Long Optical Fiber Sensor for Real-Time Railroad Infrastructure Monitoring to Ensure Safe Train Operation. In Proceedings of the 2015 Joint Rail Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 23–26 March 2015. ASME/IEEE Joint Rail Conference. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edme, P.; Paitz, P.; Walter, F.; van Herwijnen, A.; Fichtner, A. Fiber-optic detection of snow avalanches using telecommunication infrastructure. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.12649. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, H.; Usmani, F.; Virgillito, E.; Bratovich, R.; Proietti, R.; Straullu, S.; Pastorelli, R.; Curri, V. A Machine Learning-Driven Smart Optical Network Grid for Earthquake Early Warning. In Proceedings of the 2024 24th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Bari, Italy, 14–18 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifta, R.; Munster, P.; Sysel, P.; Horvath, T.; Novotny, V.; Krajsa, O.; Filka, M. Distributed fiber-optic sensor for detection and localization of acoustic vibrations. Metrol. Meas. Syst. 2015, 22, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendão, C.; Silva, I. Optical Fiber Sensors and Sensing Networks: Overview of the Main Principles and Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner, A.; Bogris, A.; Nikas, T.; Bowden, D.; Lentas, K.; Melis, N.S.; Simos, C.; Simos, I.; Smolinski, K. Theory of phase transmission fibre-optic deformation sensing. Geophys. J. Int. 2022, 231, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiqiang, Z.; Biondi, E.; Li, J.; Yin, J.; Ross, Z.; Zhan, Z. Seismic Arrival-time Picking on Distributed Acoustic Sensing Data using Semi-supervised Learning. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, N.; Yuan, S.; Lellouch, A.; Gualtieri, L.; Lecocq, T.; Biondi, B. City-Scale Dark Fiber DAS Measurements of Infrastructure Use During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, S.; Dong, Y.; Biondi, B.; Noh, H. TelecomTM: A Fine-Grained and Ubiquitous Traffic Monitoring System Using Pre-Existing Telecommunication Fiber-Optic Cables as Sensors. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2023, 7, 64:1–64:24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalino, C.; Schiano, M.; Di Giglio, A.; Wosinska, L.; Furdek, M. Experimental Study of Machine-Learning-Based Detection and Identification of Physical-Layer Attacks in Optical Networks. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 4173–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecozzi, A.; Cantono, M.; Castellanos, J.C.; Kamalov, V.; Muller, R.; Zhan, Z. Polarization sensing using submarine optical cables. Optica 2021, 8, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelli, K.; Cho, J.Y.; Azendorf, F.; Griesser, H.; Tropschug, C.; Pachnicke, S. Machine-learning-based anomaly detection in optical fiber monitoring. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2022, 14, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boitier, F.; Lemaire, V.; Pesic, J.; Chavarria, L.; Layec, P.; Bigo, S.; Dutisseuil, E. Proactive Fiber Damage Detection in Real-time Coherent Receiver. In Proceedings of the 2017 European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC), Gothenburg, Sweden, 17–21 September 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelli, K.; Lonardi, M.; Gripp, J.; Olsson, S.; Boitier, F.; Layec, P. Breaking boundaries: Harnessing unrelated image data for robust risky event classification with scarce state of polarization data. In Proceedings of the 49th European Conference on Optical Communications (ECOC 2023), Hybrid Conference, Glasgow, UK, 1–5 October 2023; Volume 2023, pp. 924–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelli, K.; Lonardi, M.; Gripp, J.; Olsson, S.; Boitier, F.; Layec, P. Computer Vision for Anomaly Detection in Optical Networks with State of Polarization Image Data: Opportunities and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2024 24th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Bari, Italy, 14–18 July 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyarko-Boateng, O.; Adekoya, A.; Weyori, B. Predicting the Actual Location of Faults in Underground Optical Networks using Linear Regression. Eng. Rep. 2020, 3, eng212304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelli, K.; Grießer, H.; Ehrle, P.; Tropschug, C.; Pachnicke, S. Reflective fiber fault detection and characterization using long short-term memory. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2021, 13, E32–E41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Peng, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. A deep convolutional neural network with new training methods for bearing fault diagnosis under noisy environment and different working load. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 100, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighi, L.; Karlsson, S.; Natalino, C.; Wosinska, L.; Ruffini, M.; Furdek, M. Deep Learning for Detection of Harmful Events in Real-World, Noisy Optical Fiber Deployments. J. Light. Technol. 2025, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, B.; Proietti, R.; Zhu, Z.; Yoo, S.J.B. Self-Taught Anomaly Detection With Hybrid Unsupervised/Supervised Machine Learning in Optical Networks. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 1742–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasov, A.; Dejdar, P.; Munster, P.; Horvath, T.; Barcik, P.; Da Ros, F. Enhancing fiber security using a simple state of polarization analyzer and machine learning. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 167, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighi, L.; Karlsson, S.; Natalino, C.; Furdek, M. Machine Learning-Based Polarization Signature Analysis for Detection and Categorization of Eavesdropping and Harmful Events. In Proceedings of the 2024 Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC), San Diego, CA, USA, 24–28 March 2024; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Sadighi, L.; Karlsson, S.; Natalino, C.; Wosinska, L.; Ruffini, M.; Furdek, M. Detection and Classification of Eavesdropping and Mechanical Vibrations in Fiber Optical Networks by Analyzing Polarization Signatures Over a Noisy Environment. In Proceedings of the ECOC 2024; 50th European Conference on Optical Communication, Frankfurt, German, 22–26 September 2024; pp. 527–530. [Google Scholar]
- Sadighi, L.; Karlsson, S.; Wosinska, L.; Furdek, M. Machine Learning Analysis of Polarization Signatures for Distinguishing Harmful from Non-harmful Fiber Events. In Proceedings of the 2024 24th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Bari, Italy, 14–18 July 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, G.; Masood, M.U.; Dipto, I.C.; Mohamed, M.C.; Straullu, S.; Bhyri, S.K.; Galembirti, G.M.; Pedro, J.; Napoli, A.; Wakim, W.; et al. SOP-Based Anomaly Detection Leveraging Machine Learning for Proactive Optical Restoration. In Proceedings of the Optical Network Design and Modelling ONDM, Pisa, Italy, 6–9 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, G.; Masood, M.U.; Mohamed, M.C.; Straullu, S.; Bhyri, S.K.; Galembirti, G.M.; Pedro, J.; Napoli, A.; Wakim, W.; Curri, V. Machine Learning for Predictive Multi-Event Detection in Fiber Optic Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning for Communication and Networking (ICMLCN), Barcelona, Spain, 26–29 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, G.; Masood, M.U.; Dipto, I.C.; Mohamed, M.C.; Straullu, S.; Bhyri, S.K.; Galembirti, G.M.; Pedro, J.; Napoli, A.; Wakim, W.; et al. Intelligent Detection of Overlapping Fiber Anomalies in Optical Networks Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Summer Topicals, Berlin, Germany, 21–23 July 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, C.; Lin, J. Support vector machines for anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the 2006 6th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Dalian, China, 21–23 June 2006; Volume 1, pp. 2594–2598. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelli, K.; Lonardi, M.; Gripp, J.; Correa, D.; Olsson, S.; Boitier, F.; Layec, P. Anomaly detection and localization in optical networks using vision transformer and SOP monitoring. In Optical Fiber Communication Conference; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2024; p. Tu2J.4. [Google Scholar]
- Collett, E. Field Guide to Polarization; SPIE Digital Library; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, S.; Rizzelli, G.; Barla, M.; Gaudino, R. Algorithm optimization for rockfalls alarm system based on fiber polarization sensing. IEEE Photonics J. 2023, 15, 7100709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, D.; Sypabekova, M.; Bekmurzayeva, A.; Molardi, C.; Dukenbayev, K. 2—Principles of fiber optic sensors. In Optical Fiber Biosensors; Tosi, D., Sypabekova, M., Bekmurzayeva, A., Molardi, C., Dukenbayev, K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 19–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar Iqbal, M.; Fathallah, H.; Belhadj, N. Optical fiber tapping: Methods and precautions. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on High-Capacity Optical Networks and Emerging Technologies, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 19–21 December 2011; pp. 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Lin, R.; Li, Y.; Lei, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wosinska, L.; Monti, P.; Zhang, J. Machine-learning-based method for fiber-bending eavesdropping detection. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 3183–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.K.; Deniz, A.; Yuksel, H. Experimental Optical Setup to Measure Power Loss versus Fiber Bent Radius for Tapping into Optical Fiber Communication Links. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Energy Technologies (ICECET), Cape Town, South Africa, 9–10 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Li, Y.; Song, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Multi-intensity Bending Eavesdropping Detection and Identification Scheme Based on the State of Polarization. In Proceedings of the 2023 Opto-Electronics and Communications Conference (OECC), Shanghai, China, 2–6 July 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurny, V.; Dejdar, P.; Tomasov, A.; Munster, P.; Horvath, T. Eavesdropping Vulnerabilities in Optical Fiber Networks: Investigating Macro-Bending-Based Attacks Using Clip-on Couplers. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Workshop on Fiber Optics on Access Networks (FOAN), Gent, Belgium, 30–31 October 2023; pp. 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Guan, L.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M. Cause-aware failure detection using an interpretable XGBoost for optical networks. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 31974–31992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruzes, S. Failure Management Overview in Optical Networks. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 169170–169193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Introduction to machine learning: K-nearest neighbors. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, J.R. Learning decision tree classifiers. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 1996, 28, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
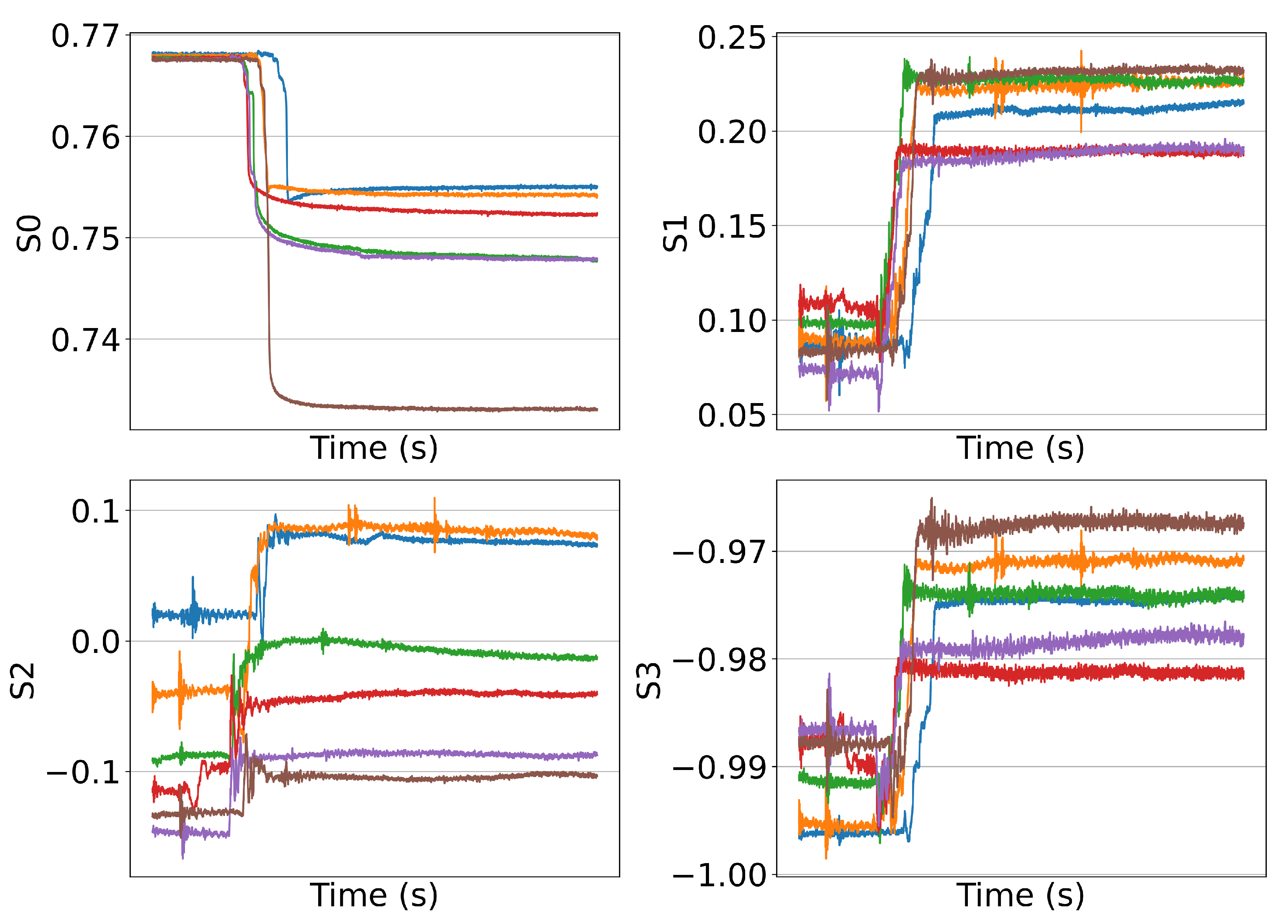
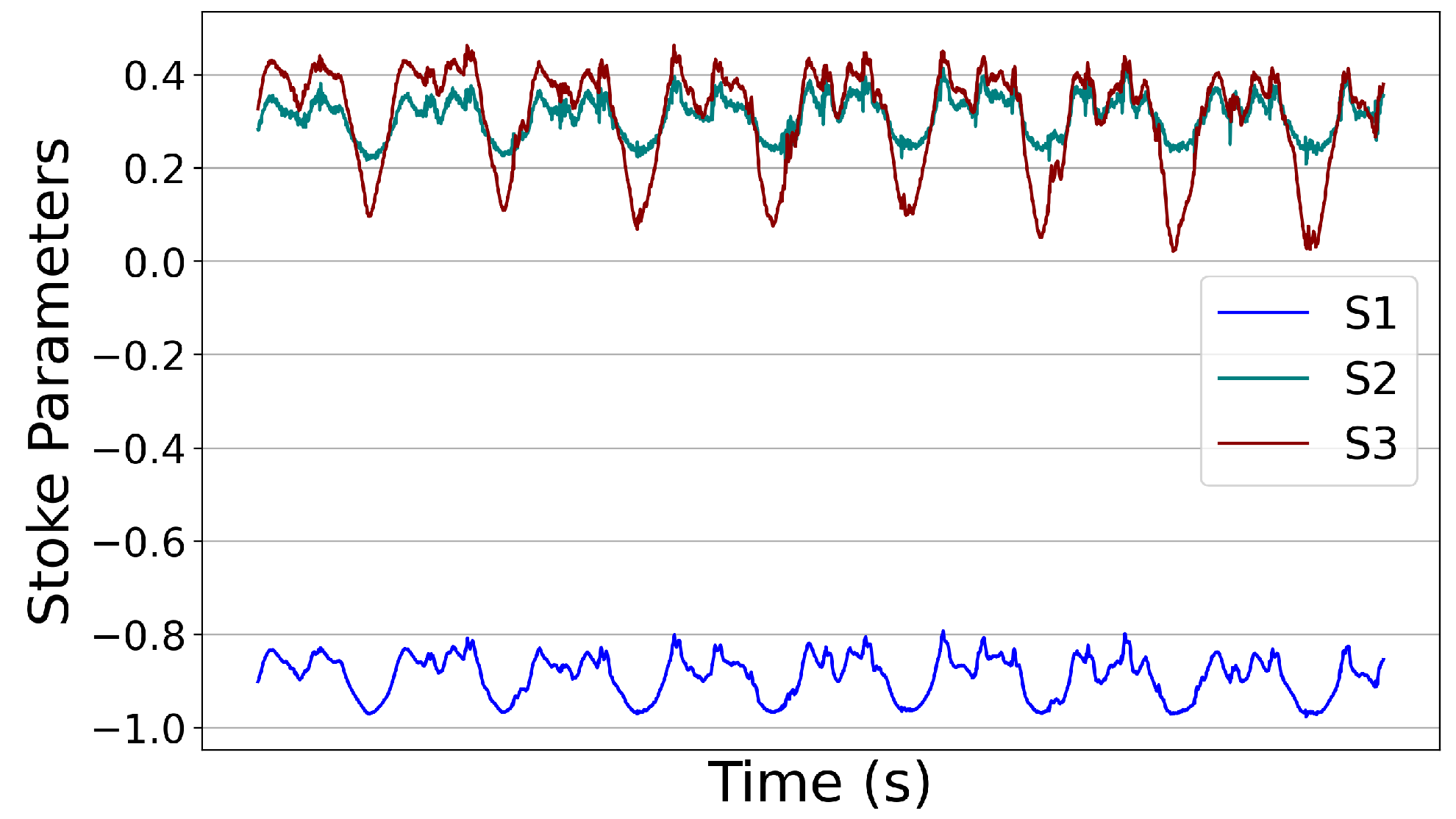
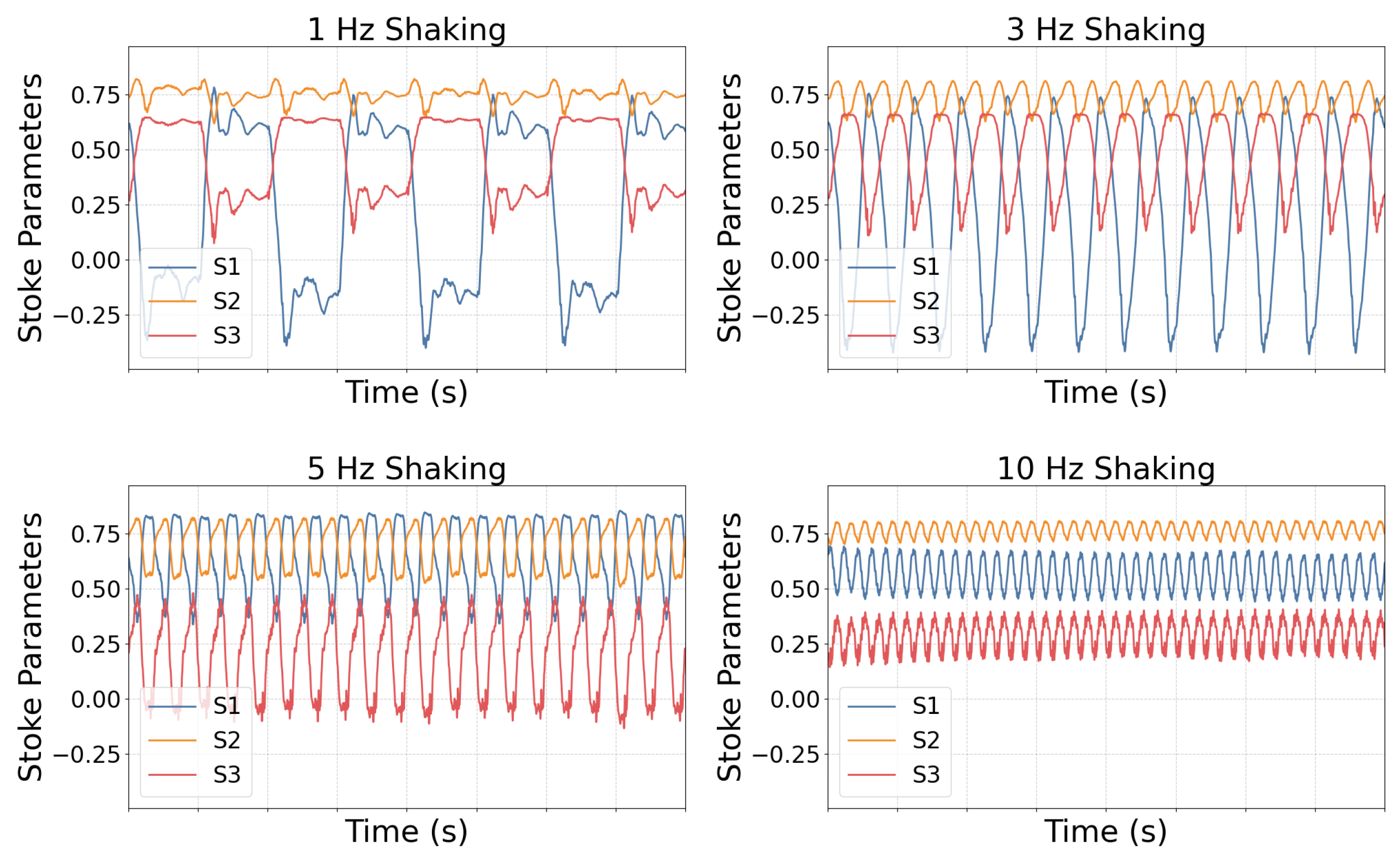
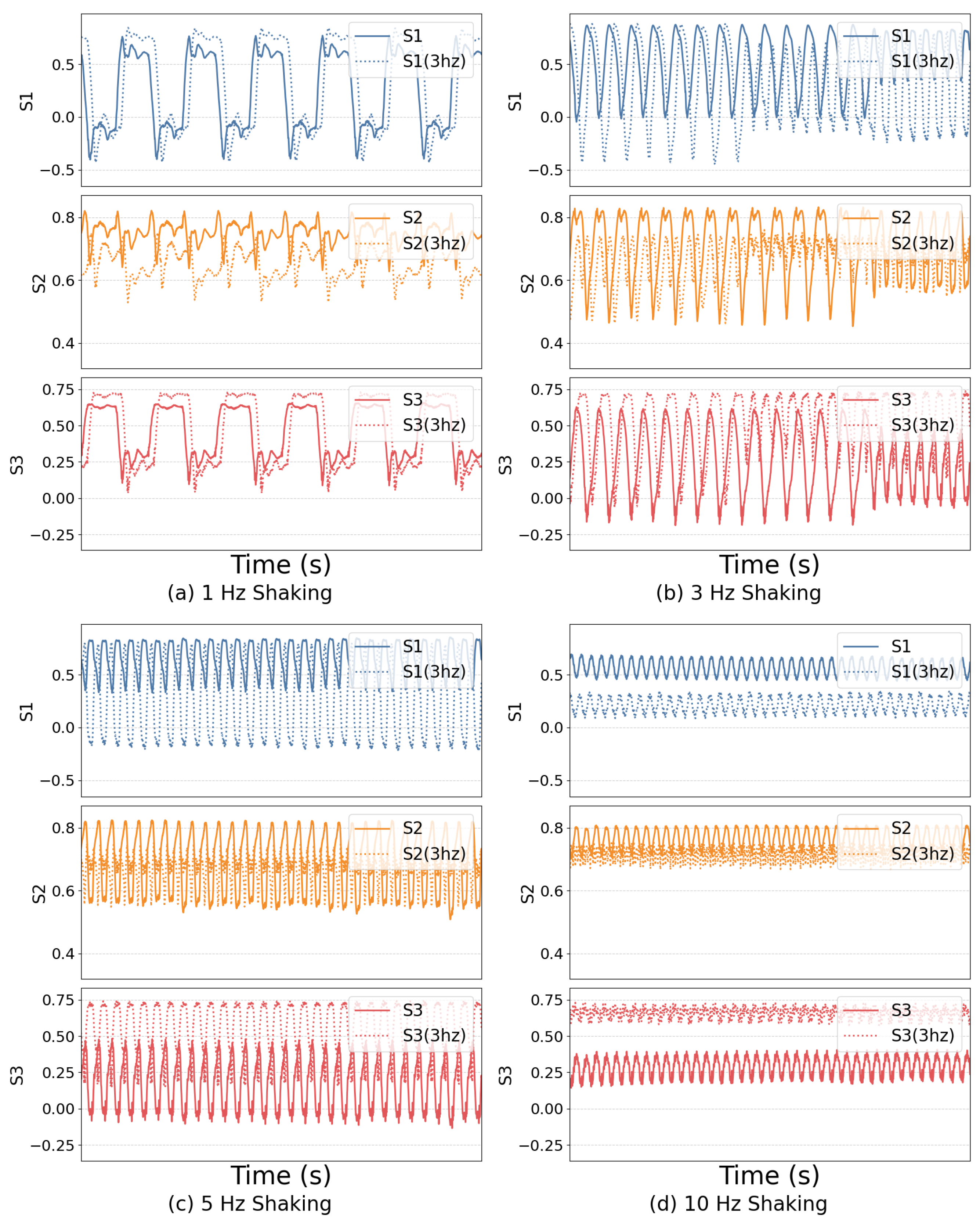

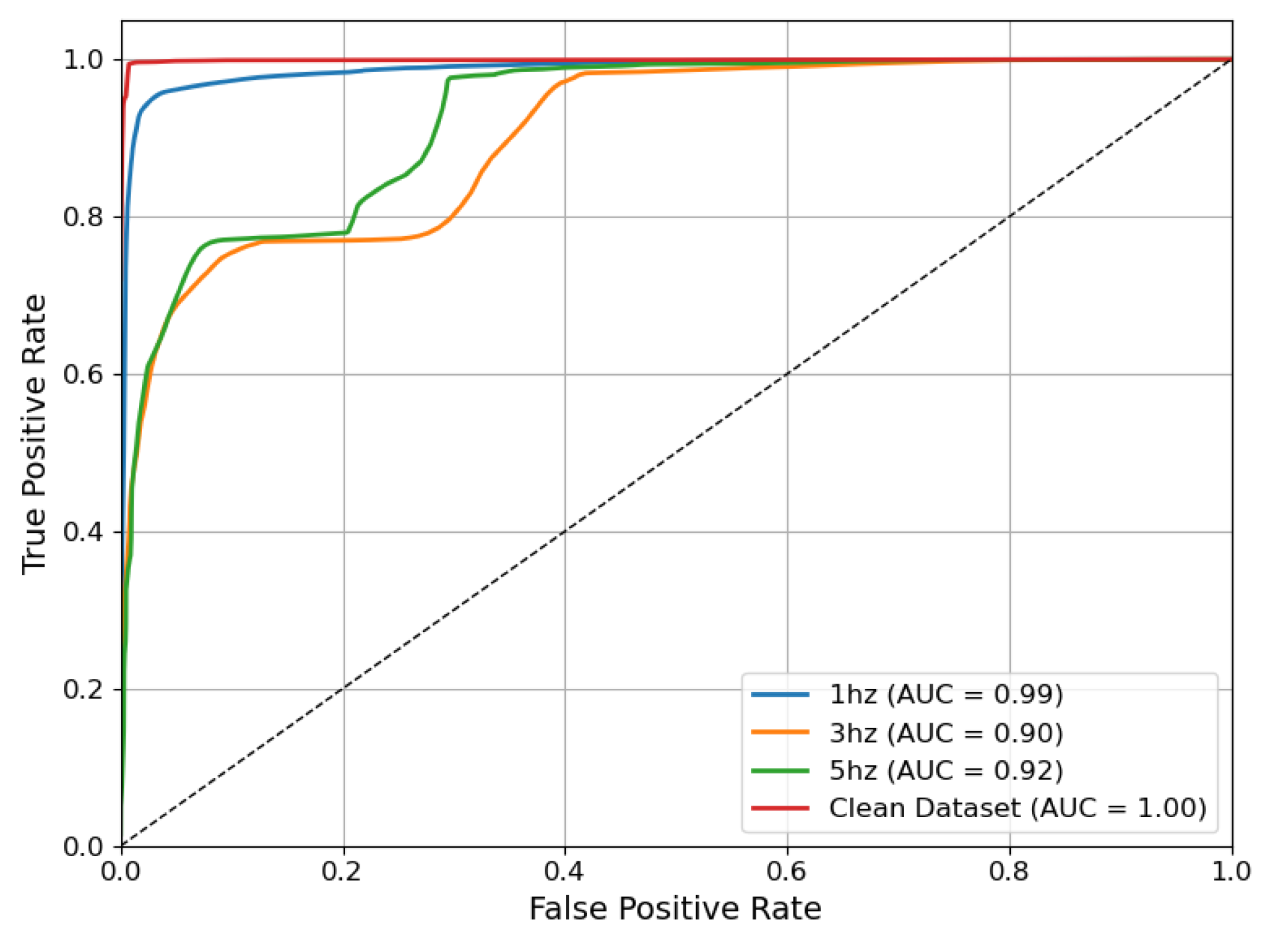
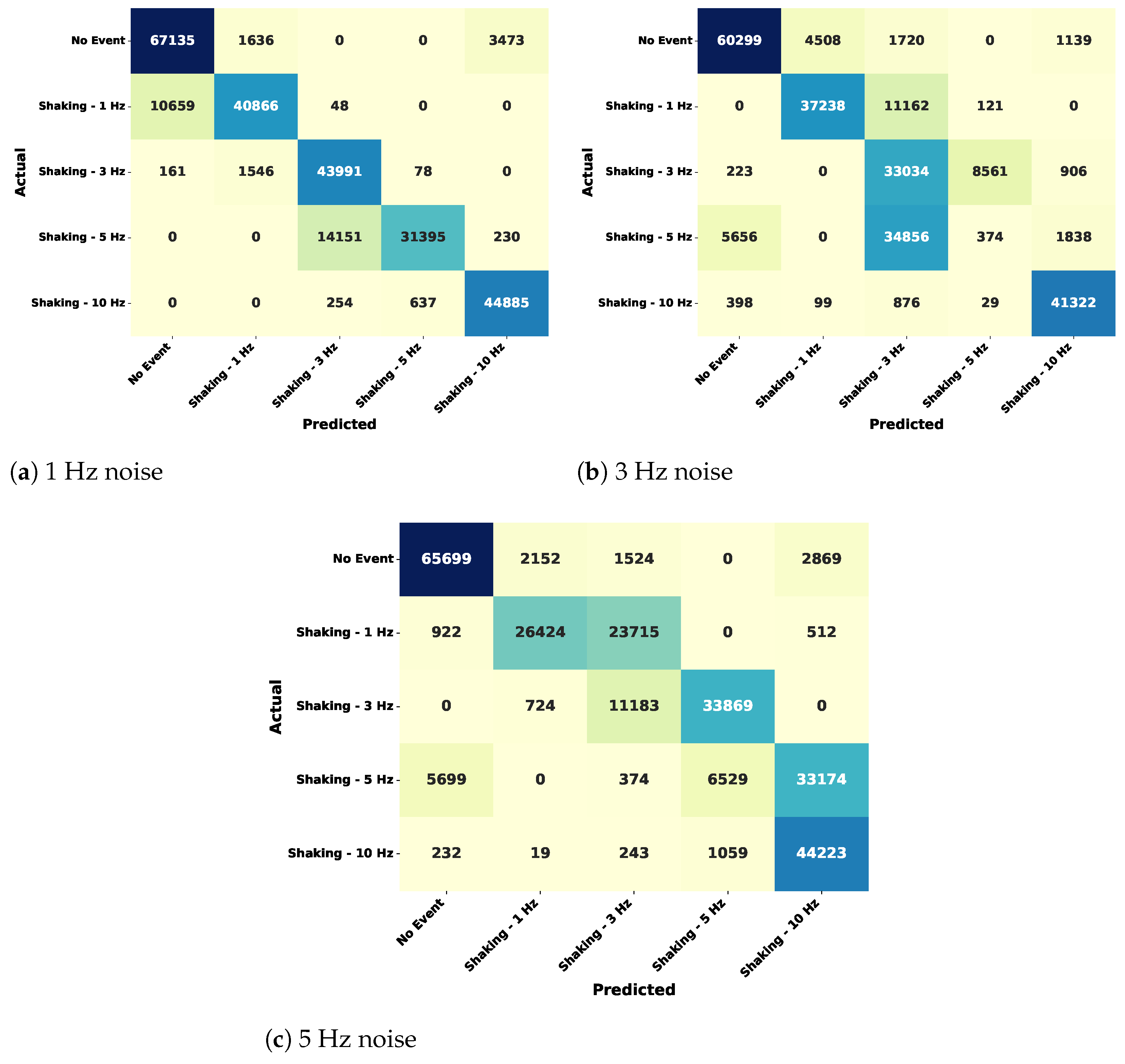
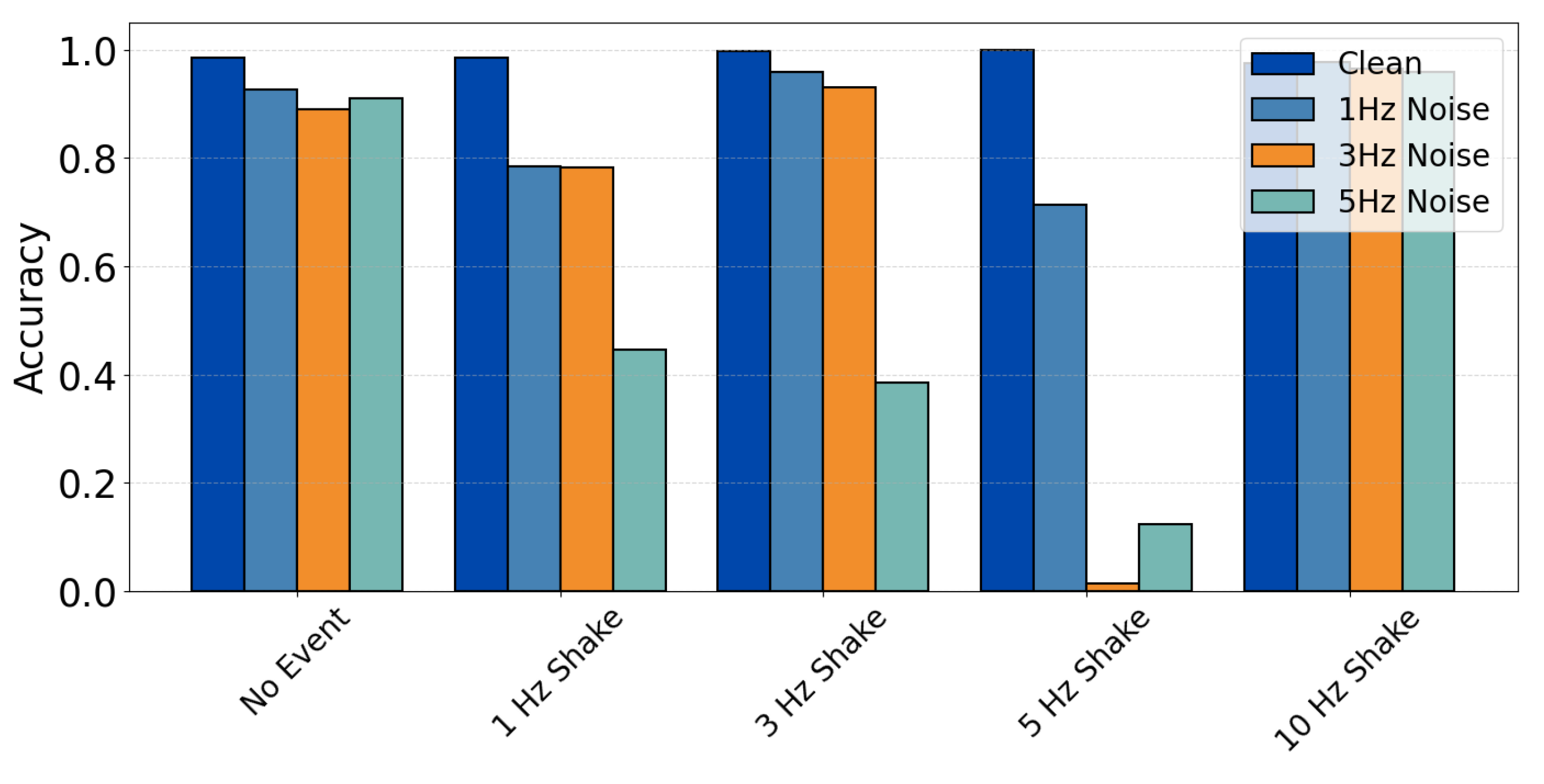
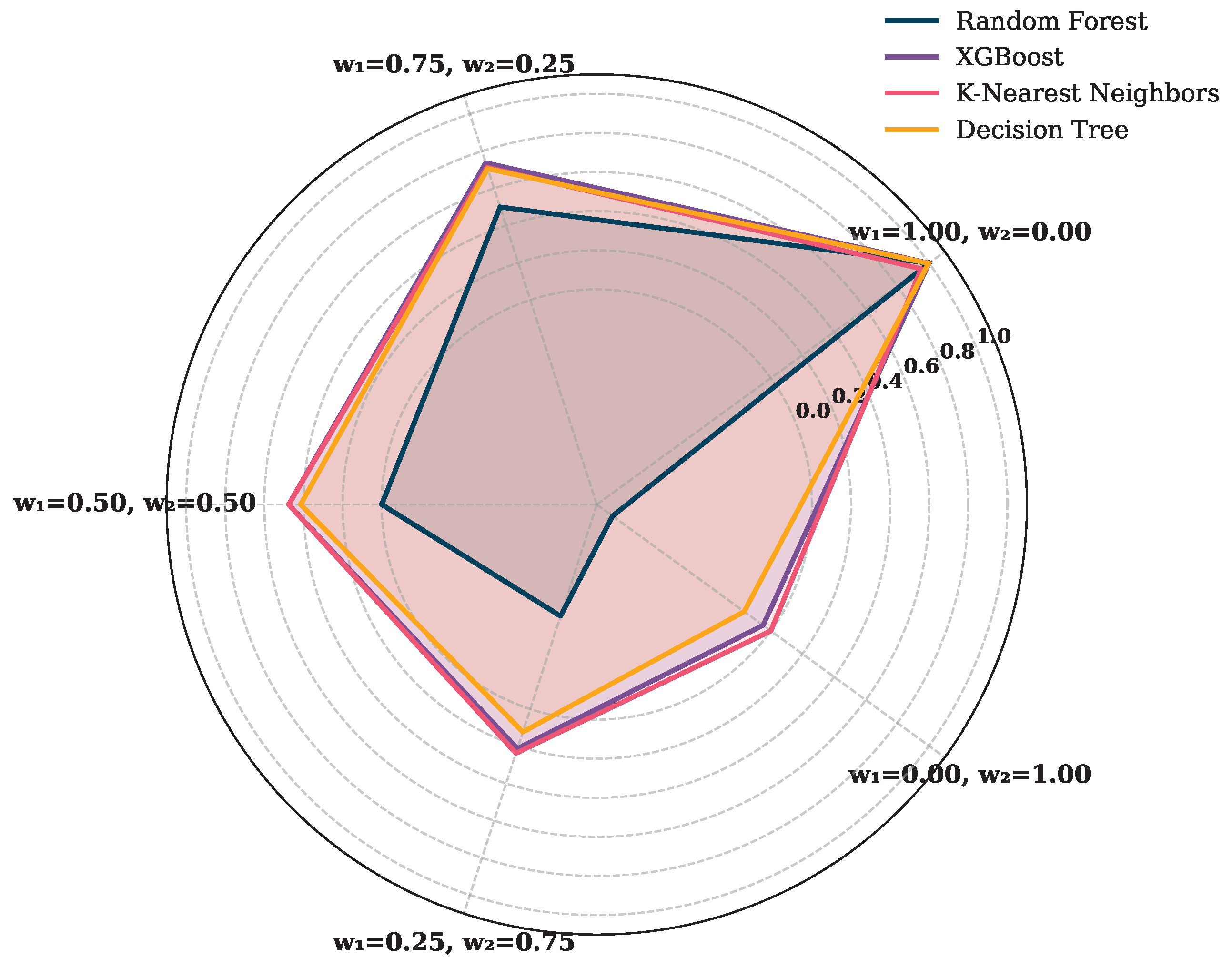
| Event Type | Severity Level | Description |
|---|---|---|
| No event | None | Normal operations with no impact on fiber integrity |
| Shaking (1 Hz) | Low | Ambient noise due to environmental activities |
| Shaking (3 Hz) | Moderate | Minor disturbances caused by nearby environment |
| Shaking (5 Hz) | High | Sustained mechanical stress |
| Shaking (10 Hz) | Critical | Critical intrusion |
| Feature Type | Variable Type | Feature Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Input Features | , , , | |
| Rolling Mean (Win = 500, 1000) | ||
| Rolling Std Dev (Win = 500, 1000) | ||
| Lag Features (Lag = 1, 2, 3) |
| Predicted Positive | Predicted Negative | |
|---|---|---|
| Actual Positive | TP | FN |
| Actual Negative | FP | TN |
| Accuracy (%) | F-1 Score | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario | RF | XGBoost | k-NN | DT | RF | XGBoost | k-NN | DT |
| No noise | 99.98 | 99.93 | 95.08 | 99.72 | 0.9998 | 0.9993 | 0.9507 | 0.9972 |
| 1 Hz noise | 87.5 | - | - | - | 0.873 | - | - | - |
| 3 Hz noise | 70.50 | - | - | - | 0.699 | - | - | - |
| 5 Hz noise | 58.99 | - | - | - | 0.578 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malik, G.; Dipto, I.C.; Masood, M.U.; Mohamed, M.C.; Straullu, S.; Bhyri, S.K.; Galimberti, G.M.; Napoli, A.; Pedro, J.; Wakim, W.; et al. Resilient Anomaly Detection in Fiber-Optic Networks: A Machine Learning Framework for Multi-Threat Identification Using State-of-Polarization Monitoring. AI 2025, 6, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6070131
Malik G, Dipto IC, Masood MU, Mohamed MC, Straullu S, Bhyri SK, Galimberti GM, Napoli A, Pedro J, Wakim W, et al. Resilient Anomaly Detection in Fiber-Optic Networks: A Machine Learning Framework for Multi-Threat Identification Using State-of-Polarization Monitoring. AI. 2025; 6(7):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6070131
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalik, Gulmina, Imran Chowdhury Dipto, Muhammad Umar Masood, Mashboob Cheruvakkadu Mohamed, Stefano Straullu, Sai Kishore Bhyri, Gabriele Maria Galimberti, Antonio Napoli, João Pedro, Walid Wakim, and et al. 2025. "Resilient Anomaly Detection in Fiber-Optic Networks: A Machine Learning Framework for Multi-Threat Identification Using State-of-Polarization Monitoring" AI 6, no. 7: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6070131
APA StyleMalik, G., Dipto, I. C., Masood, M. U., Mohamed, M. C., Straullu, S., Bhyri, S. K., Galimberti, G. M., Napoli, A., Pedro, J., Wakim, W., & Curri, V. (2025). Resilient Anomaly Detection in Fiber-Optic Networks: A Machine Learning Framework for Multi-Threat Identification Using State-of-Polarization Monitoring. AI, 6(7), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6070131









