Ocean Circulation Drives the Variability of the Carbon System in the Eastern Tropical Atlantic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
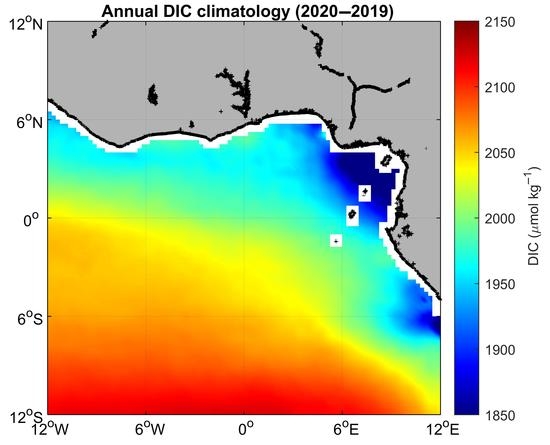
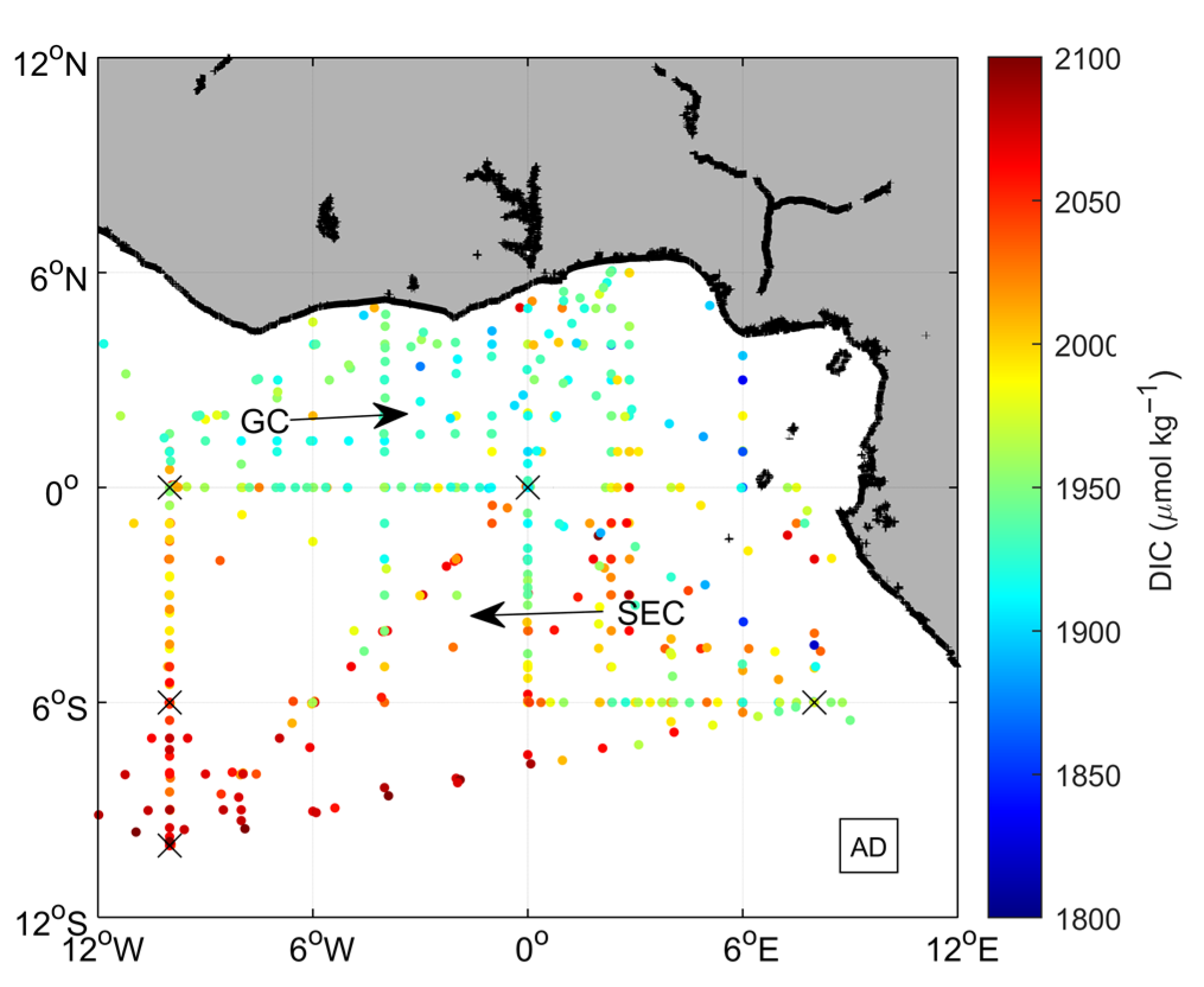
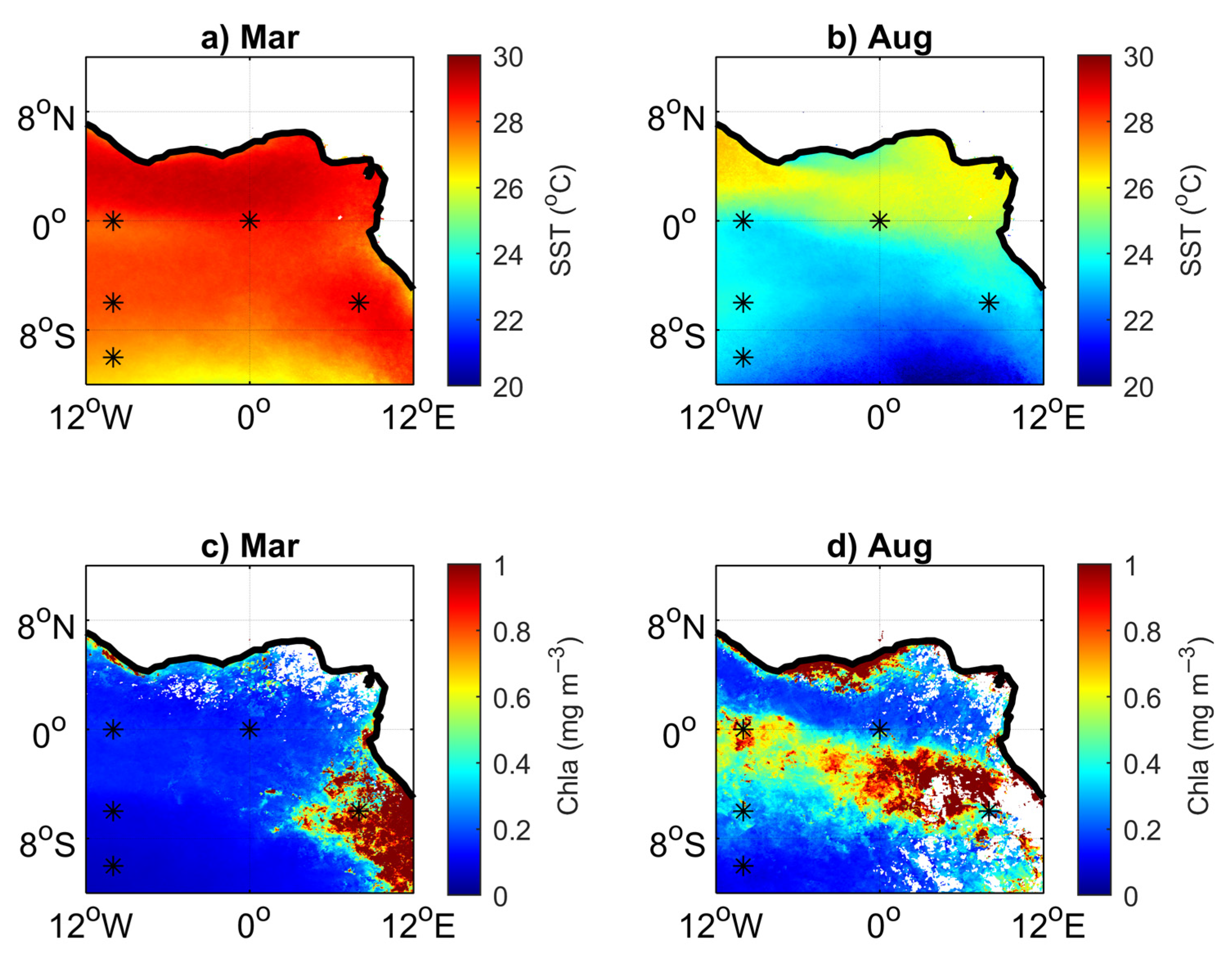
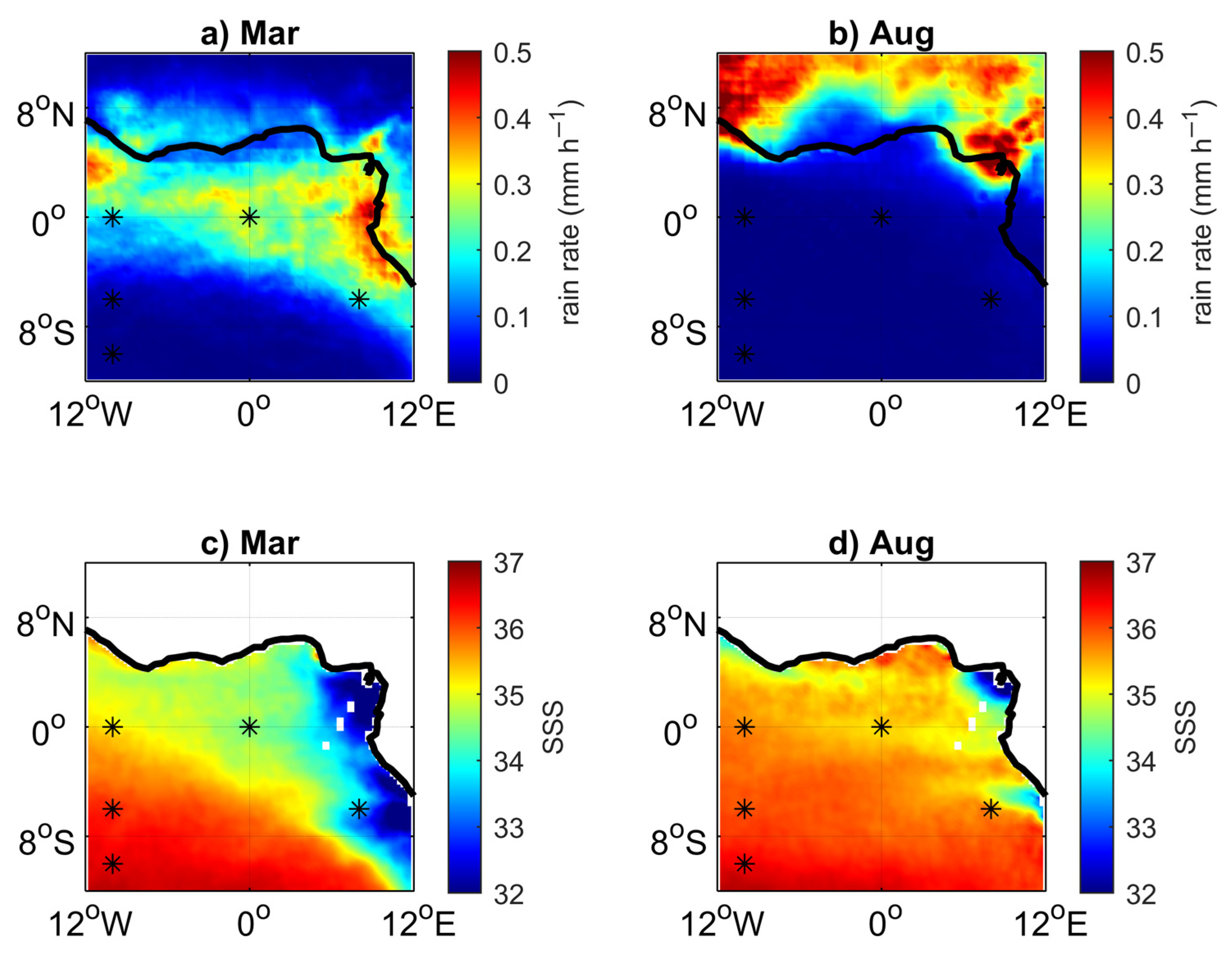
3.1. Environmental Setting
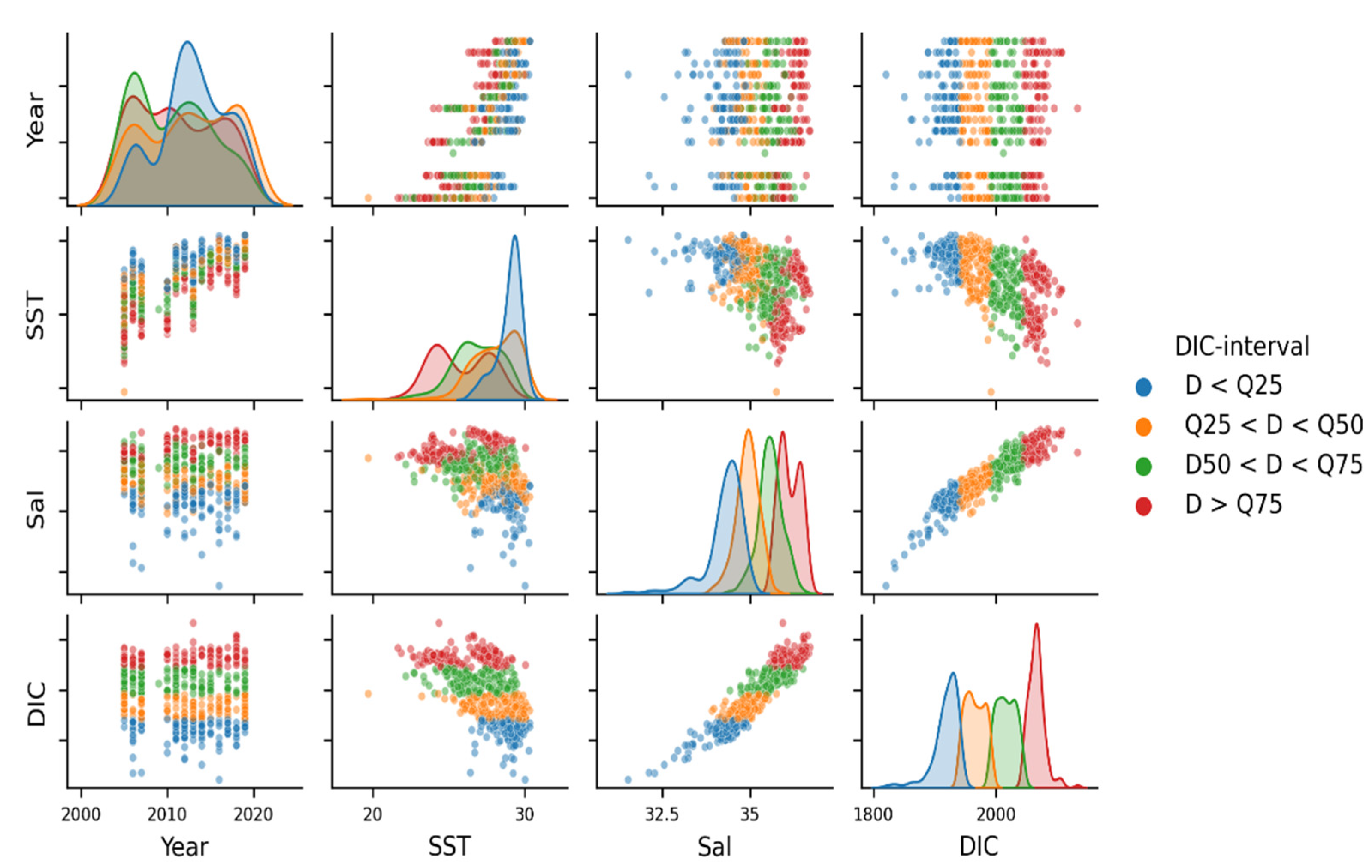
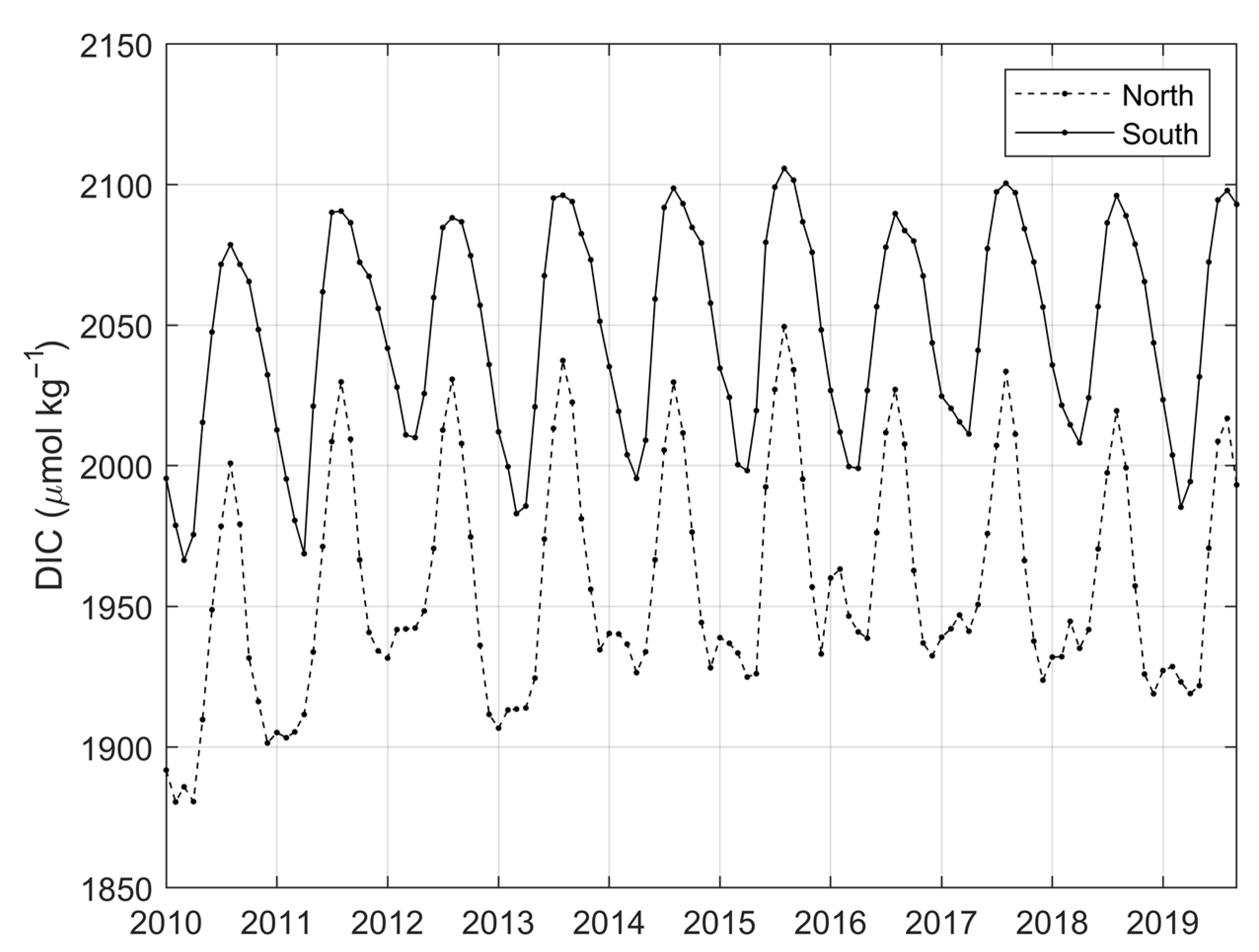
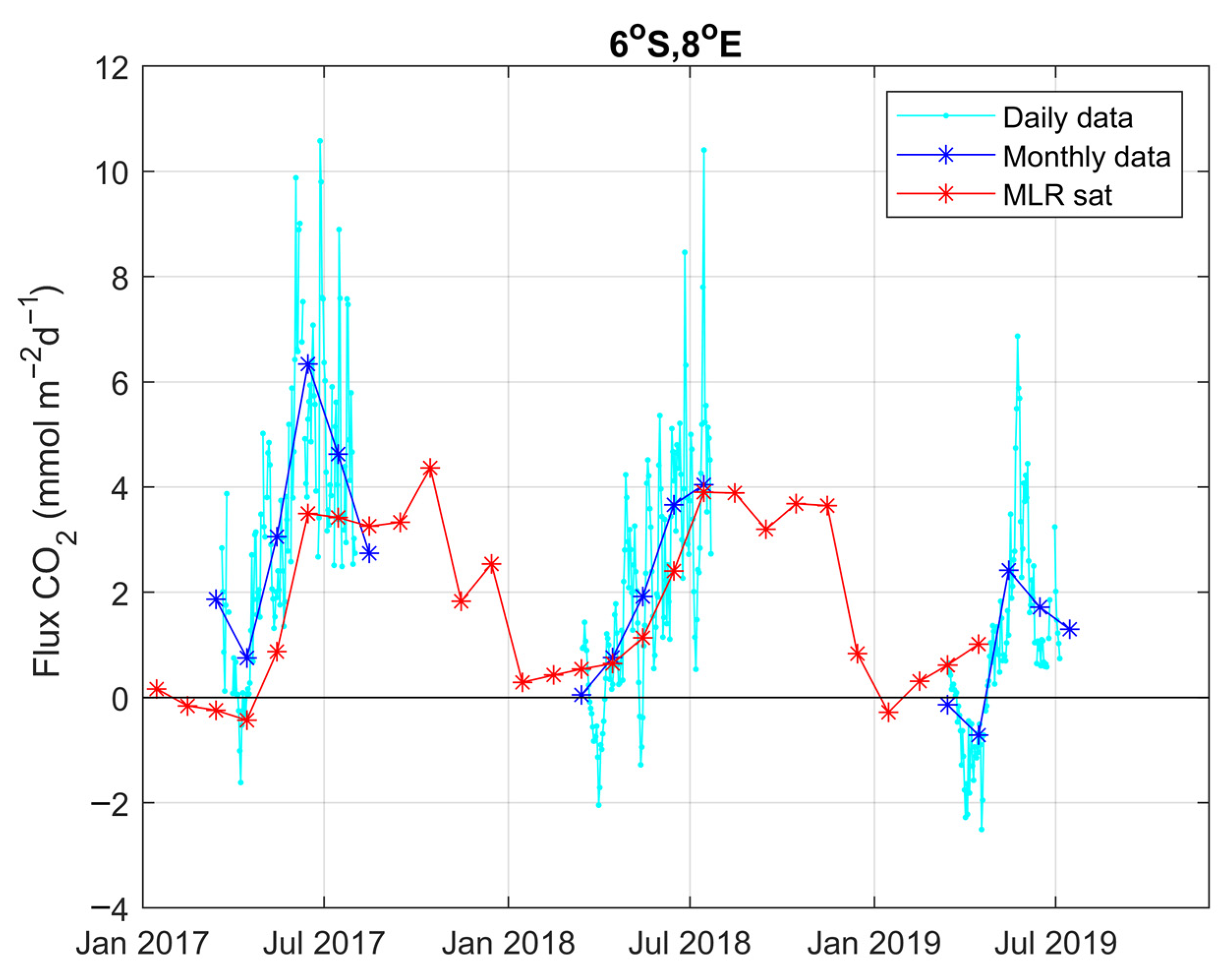
3.2. Variability and Drivers of the Carbon System
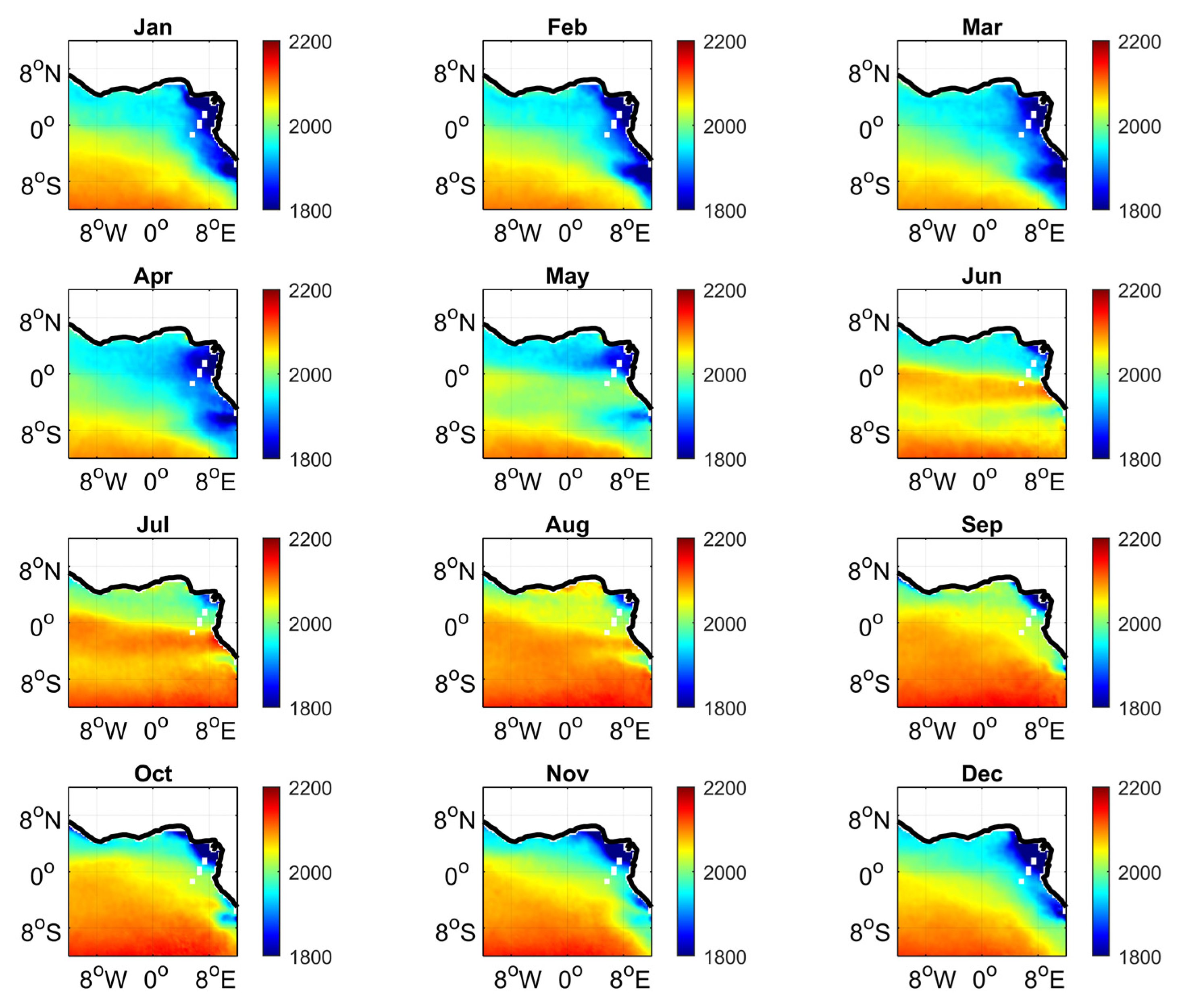
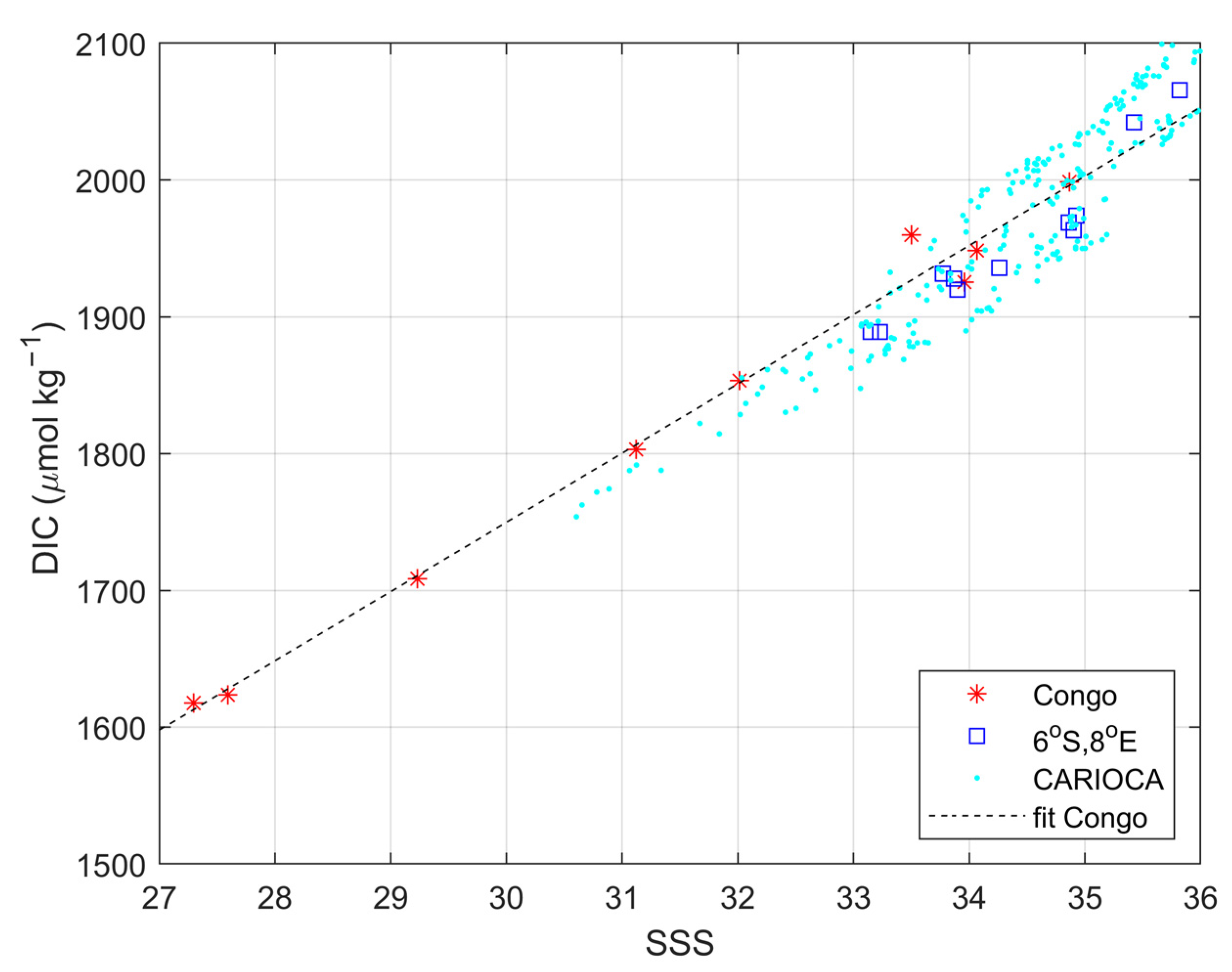
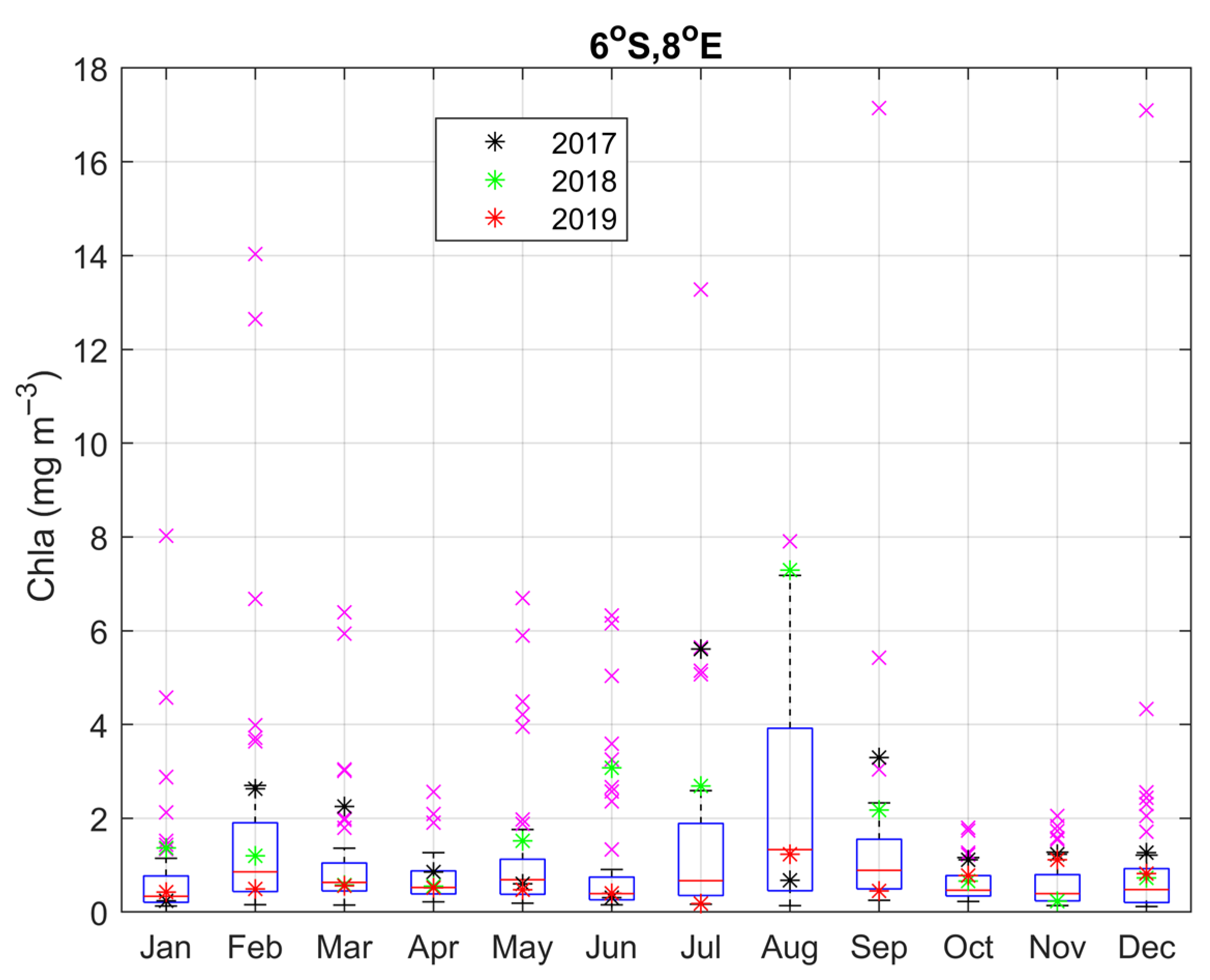
3.3. Impact of the Congo Plume
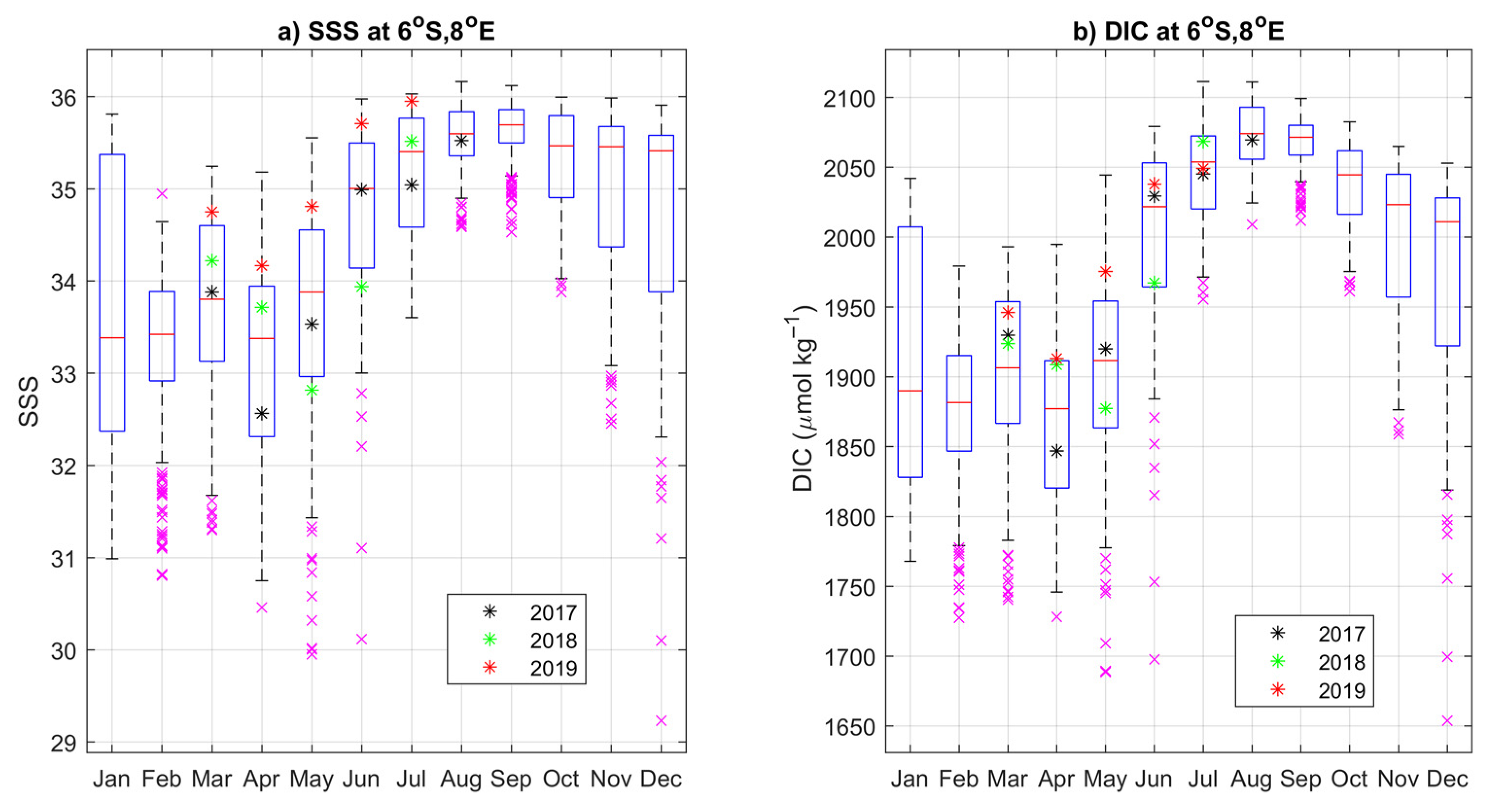
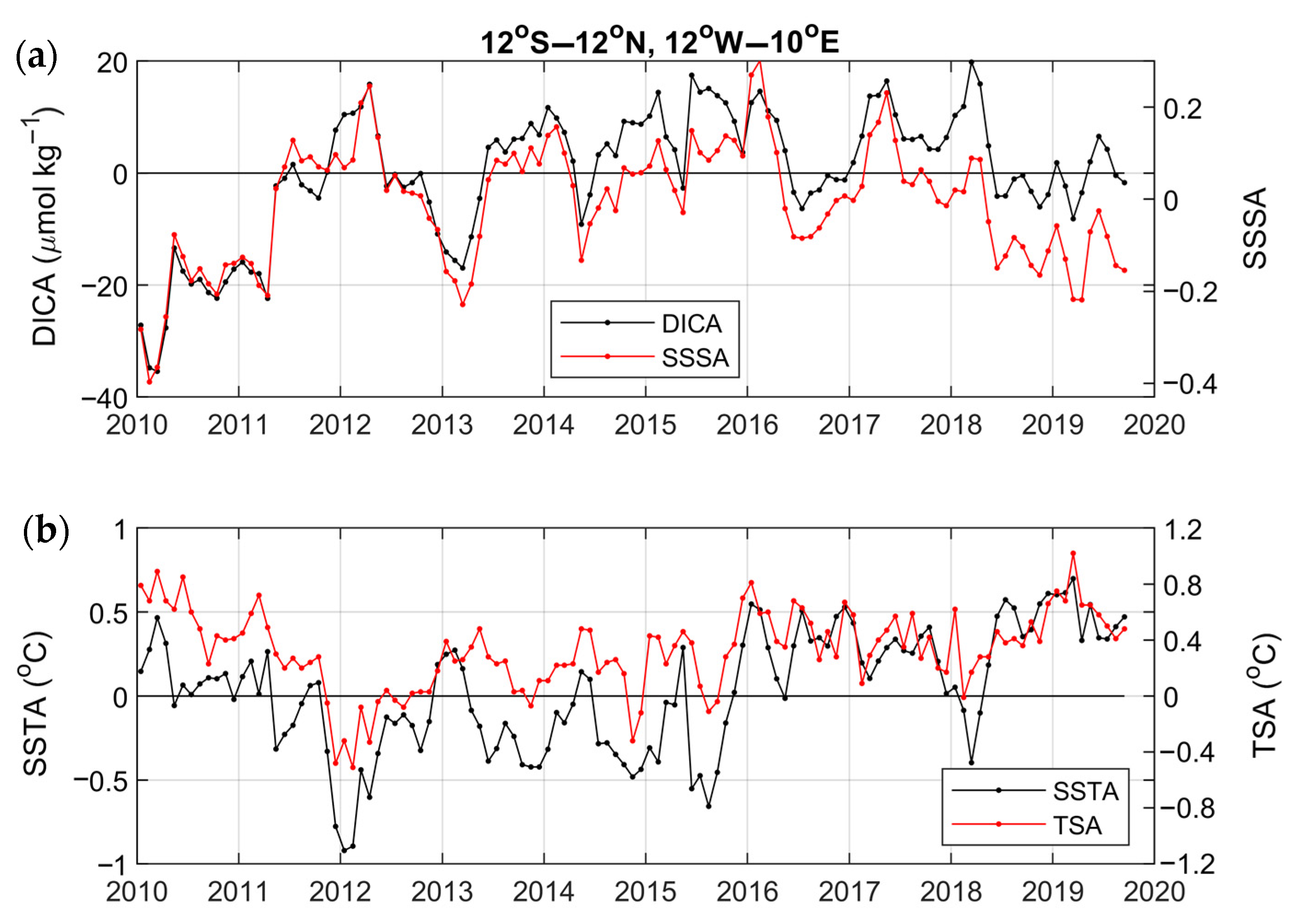
3.4. Year-to-Year Variability of the Carbon Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Features of the Carbon Parameters
4.2. Year-to-Year Variability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Regression Methods and Results
| Meta-Parameters | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Input variables | Year, SST, SSS, SinDoY, CosDoY |
| Output variables | DIC |
| Train/Val | DIC 4 quantiles (1/6 for Val from each quant.) |
| Normalization | Center-reduction (both Input and Output) |
| Architecture | Layers size: Input: 5, Hidden: 15, Output: 1 |
| Condition | N | NTrain | NVal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIC < Q25 | DIC < 1941.1 | 159 | 132 | 27 |
| Q25 < DIC < Q50 | 1941.1 ≤ DIC < 1992.2 | 159 | 132 | 27 |
| Q50 < DIC < Q75 | 1992.2 ≤ DIC < 2044.6 | 158 | 132 | 26 |
| DIC > Q75 | DIC ≥ 2044.6 | 161 | 135 | 27 |
| Mooring or Cruise | Regression Method | DIC < Q25 | Q25 < DIC < Q50 | Q50 < DIC < Q75 | DIC > Q75 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE [µmol kg−1] | RMSE [µmol kg−1] | RMSE [µmol kg−1] | RMSE [µmol kg−1] | ||
| 6° S, 10° W | MLR | NaN | 13.8 | 7.2 | 7.8 |
| NN | NaN | 13.4 | 7.3 | 7.0 | |
| 6° S, 8° E | MLR | 18.0 | 15.0 | 12.7 | 9.4 |
| NN | 14.0 | 15.0 | 11.5 | 8.9 | |
| EGEE 3 | MLR | 7.1 | 8.3 | 12.5 | 18.1 |
| NN | 4.8 | 7.5 | 9.9 | 14.1 | |
| PIRATA-FR-29 | MLR | 11.2 | 8.1 | 4.8 | 6.9 |
| NN | 8.1 | 11.1 | 5.3 | 9.2 |
| Mooring or Cruise | Regression Method | RMSE (mol kg−1) | r | N | Time Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6° S, 10° W | MLR | 7.7 | 0.96 | 6611 | 2006–2017 |
| DT | 14.1 | 0.87 | |||
| RF | 9.8 | 0.94 | |||
| NN | 7.3 | 0.97 | |||
| 6° S, 8° E | MLR | 14.8 | 0.98 | 239 | 2017–2019 |
| DT | 25 | 0.95 | |||
| RF | 24 | 0.95 | |||
| NN | 12.8 | 0.99 | |||
| EGEE 3 | MLR | 11.8 | 0.97 | 6895 | 2006 |
| DT | 14 | 0.96 | |||
| RF | 10 | 0.98 | |||
| NN | 9.3 | 0.98 | |||
| PIRATA FR-29 | MLR | 8.1 | 0.99 | 4462 | 2019 |
| DT | 11 | 0.98 | |||
| RF | 9 | 0.98 | |||
| NN | 9.4 | 0.99 |
References
- Le Quéré, C.; Orr, J.C.; Monfray, P.; Aumont, O.; Madec, G. Interannual variability of the oceanic sink of CO2 from 1979 through 1997. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2000, 14, 1247–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Murtugudde, R.; Hackert, E.; Wang, J.; Beauchamp, J. Seasonal to decadal variations of sea surface pCO2 and sea-air CO2 flux in the equatorial oceans over 1984–2013: A basin-scale comparison of the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2015, 29, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, S.R.; Coles, V.J.; Subramaniam, A.; Yager, P.L. Seasonal variations in the Amazon plume-related atmospheric carbon sink. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2007, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, S.R.; Yager, P.L. Physical and biological contributions to the western tropical North Atlantic Ocean carbon sink formed by the Amazon River plume. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, A.; Yager, P.L.; Carpenter, E.J.; Mahaffey, C.; Björkman, K.; Cooley, S.; Kustka, A.B.; Montoya, J.P.; Sañudo-Wilhelmy, S.A.; Shipe, R.; et al. Amazon River enhances diazotrophy and carbon sequestration in the tropical North Atlantic Ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10460–10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternon, J.F.; Oudot, C.; Dessier, A.; Diverrès, D. A seasonal tropical sink for atmospheric CO2 in the Atlantic Ocean: The role of the Amazon River discharge. Mar. Chem. 2000, 68, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körtzinger, A. A significant sink of CO2 in the tropical Atlantic Ocean associated with the Amazon River plume. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, N.; Flores, M.M.; Gaspar, F.L.; Rocha, C.; Jiang, S.; Araujo, M.; Ibánhez, J.S.P. Net heterotrophy in the Amazon continental shelf changes rapidly to a sink of CO2 in the outer Amazon plume. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibánhez, J.S.P.; Araujo, M.; Lefèvre, N. The overlooked tropical oceanic CO2 sink. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3804–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibánhez, J.S.P.; Diverrès, D.; Araujo, M.; Lefèvre, N. Seasonal and interannual variability of sea-air CO2 fluxes in the tropical Atlantic affected by the Amazon River plume. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2015, 29, 1640–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.; Farrara, J.D.; Schumann, G.; Andreadis, K.M.; Moller, D. Sea surface salinity variability in response to the Congo river discharge. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 99, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorini, S.R.; Murtugudde, R.G.; McClain, C.R.; Christian, J.R.; Picaut, J.; Busalacchi, A.J. Biological and physical signatures in the tropical and subtropical Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1999, 104, 18367–18382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, D.C.E.; De Baar, H.J.W.; De Jong, E. Dissolved carbon dioxide in tropical East Atlantic surface waters. Phys. Chem. Earth 1999, 24, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lefèvre, N. Low CO2 concentrations in the Gulf of Guinea during the upwelling season in 2006. Mar. Chem. 2009, 113, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caniaux, G.; Giordani, H.; Redelsperger, J.-L.; Guichard, F.; Key, E.; Wade, M. Coupling between the Atlantic cold tongue and the West African monsoon in boreal spring and summer. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisard, P. Variations saisonnières à l’équateur dans le golfe de Guinée. Cah. ORSTOM Sér. Océanograph. 1973, 11, 349–358. [Google Scholar]
- Hardman-Mountford, N.J.; McGlade, J.M. Seasonal and interannual variability of oceanographic processes in the Gulf of Guinea: An investigation using AVHRR sea surface temperature data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 3247–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbland, A.; Le Borgne, R.; Le Bouteiller, A.; Voituriez, B. Structure hydrologique et production primaire dans l’Atlantique tropical oriental (Hydrological structure and primary production in the eastern tropical Atlantic Ocean). Océanograph. Trop. 1983, 18, 249–293. [Google Scholar]
- Djagoua, É.V.; Affian, K.; Larouche, P.; Saley, B. Variabilité saisonnière et interannuelle de la chlorophylle en surface de la mer sur le plateau continental de la Côte d’Ivoire à l’aide des images de SeaWiFS de 1997 à 2004. Télédétection 2006, 6, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, K.; Mélin, F. Variability of chlorophyll-a concentration in the Gulf of Guinea and its relation to physical oceanographic variables. Prog. Oceanogr. 2017, 151, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, J.; Brown, B.; Ajao, E.A.; Donkor, S. Local to regional polycentric levels of governance of the Guinea Current Large Marine Ecosystem. Environ. Dev. 2016, 17, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radenac, M.H.; Jouanno, J.; Tchamabi, C.C.; Awo, M.; Bourlès, B.; Arnault, S.; Aumont, O. Physical drivers of the nitrate seasonal variability in the Atlantic cold tongue. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanno, J.; Marin, F.; Du Penhoat, Y.; Molines, J.M.; Sheinbaum, J. Seasonal Modes of Surface Cooling in the Gulf of Guinea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2011, 41, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voituriez, B.; Herbland, A. Etude de la production pélagique de la zone équatoriale de l’Atlantique à 4oW: I—Relations entre la structure hydrologique et la production primaire. Cah. ORSTOM. Sér. Océanograph. 1977, 15, 313–331. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, J.R.; Murtugudde, R. Tropical Atlantic variability in a coupled physical–biogeochemical ocean model. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2003, 50, 2947–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrié, C.; Oudot, C.; Genthon, C.; Merlivat, L. CO2 fluxes in the tropical Atlantic during FOCAL cruises. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 11741–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudot, C.; Ternon, J.F.; Lecomte, J. Measurements of atmospheric and oceanic CO2 in the tropical Atlantic: 10 years after the 1982–1984 FOCAL cruises. Tellus 1995, 47, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Parard, G.; Lefèvre, N.; Boutin, J. Sea water fugacity of CO2 at the PIRATA mooring at 6oS, 10oW. Tellus B 2010, 62, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, N.; Veleda, D.; Araujo, M.; Caniaux, G. Variability and trends of carbon parameters at a time series in the eastern tropical Atlantic. Tellus B 2016, 68, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourlès, B.; Araujo, M.; McPhaden, M.J.; Brandt, P.; Foltz, G.R.; Lumpkin, R.; Giordani, H.; Hernandez, F.; Lefèvre, N.; Nobre, P.; et al. PIRATA: A Sustained Observing System for Tropical Atlantic Climate Research and Forecasting. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 577–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, N.; Guillot, A.; Beaumont, L.; Danguy, T. Variability of fCO2 in the Eastern Tropical Atlantic from a moored buoy. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, C01015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmond, J.M. High precision determination of titration alkalinity and total carbon dioxide content of seawater by potentiometric titration. Deep Sea Res. 1970, 17, 737–750. [Google Scholar]
- Stramma, L.; Schott, F. The mean flow field of the tropical Atlantic Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part II 1999, 46, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heuven, S.; Pierrot, D.; Rae, J.W.B.; Lewis, E.; Wallace, D.W.R. MATLAB Program Developed for CO2 System Calculations; Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrbach, C.; Culberson, C.H.; Hawley, J.E.; Pytkowicz, R.M. Measurement of the apparent dissociation constants of carbonic acid in seawater at atmospheric pressure. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1973, 18, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, A.G.; Millero, F.J. A comparison of the equilibrium constants for the dissociation of carbonic acid in seawater media. Deep Sea Res. 1987, 34, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, K.; Weisberg, S.B.; Dickson, A.G.; Hofmann, G.E.; Newton, J.A.; Aseltine-Neilson, D.; Barton, A.; Cudd, S.; Feely, R.A.; Jefferds, I.W.; et al. Core Principles of the California Current Acidification Network: Linking Chemistry, Physics, and Ecological Effects. Oceanography 2015, 28, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J.; Byrne, R.H.; Wanninkhof, R.; Feely, R.A.; Clayton, T.; Murphy, P.; Lamb, M.F. The internal consistency of CO2 measurements in the equatorial Pacific. Mar. Chem. 1993, 44, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, C.; Gloor, E.; Jacobson, A.R.; Key, R.M.; McKinley, G.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Wanninkhof, R. Constraining global air-sea gas exchange for CO2 with recent bomb14C measurements. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2007, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.F. CO2 in water and seawater: The solubility of a non-ideal gas. Mar. Chem. 1974, 2, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.J.J.; Scott, R.; Hoffman, M.; Leidner, R.; Atlas, J.A. Remote Sensing Systems Cross-Calibrated Multi-Platform (CCMP) 6-Hourly Ocean Vector Wind Analysis Product on 0.25 deg Grid; Version 2.0.; Remote Sensing Systems: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2015; Available online: www.remss.com/measurements/ccmp (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Koffi, U.; Lefèvre, N.; Kouadio, G.; Boutin, J. Surface CO2 parameters and air-sea CO2 flux distribution in the eastern equatorial Atlantic Ocean. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 82, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J.; Lee, K.; Roche, M. Distribution of alkalinity in the surface waters of the major oceans. Mar. Chem. 1998, 60, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enfield, D.B.; Mestas, A.M.; Mayer, D.A.; Cid-Serrano, L. How ubiquitous is the dipole relationship in tropical Atlantic sea surface temperatures? J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 7841–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, Y.; Dandonneau, Y.; Voituriez, B. Variabilité, Circulation et Chlorophylle Dans la Région du Dôme d’Angola en Février-Mars 1971; Documents Scientifiques; Centre de Recherches Océanographiques: Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire, 1974; Volume 5, pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.A.; Bienvenu, D.J.; Mann, P.J.; Hoering, K.A.; Poulsen, J.R.; Spencer, R.G.M.; Holmes, R.M. Inorganic carbon speciation and fluxes in the Congo River. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, J.; Lucas, M.; Dufau, C.; Sutton, M.; Stum, J.; Lauret, O.; Channelliere, C. Detection and variability of the Congo River plume from satellite derived sea surface temperature, salinity, ocean colour and sea level. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materia, S.; Gualdi, S.; Navarra, A.; Terray, L. The effect of Congo River freshwater discharge on Eastern Equatorial Atlantic climate variability. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 39, 2109–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonou, F.K.; Noriega, C.; Lefèvre, N.; Araujo, M. Distribution of CO2 parameters in the Western Tropical Atlantic Ocean. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2016, 73, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangriesheim, A.; Pierre, C.; Aminot, A.; Metzl, N.; Baurand, F.; Caprais, J.-C. The influence of Congo River discharges in the surface and deep layers of the Gulf of Guinea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2009, 56, 2183–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.V.N.; Giordani, H.; Caniaux, G.; Araujo, M. Seasonal and Interannual Mixed-Layer Heat Budget Variability in the Western Tropical Atlantic From Argo Floats (2007–2012). J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 5298–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibánhez, J.S.P.; Flores, M.; Lefèvre, N. Collapse of the tropical and subtropical North Atlantic CO2 sink in boreal spring of 2010. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Marchine Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. Networks for Pattern Recognition; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Keras. 2015. Available online: https://github.com/keras-team/keras (accessed on 31 October 2020).
- Dean, J.; Monga, R. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. 2015. Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org/ (accessed on 31 October 2020).


| Pair | Calculated Parameter | RMSE | r |
|---|---|---|---|
| TA–DIC | fCO2 | 11.7 atm | 0.90 |
| DIC–fCO2 | TA | 7.4 mol kg−1 | 0.99 |
| fCO2–TA | DIC | 5.9 mol kg−1 | 0.99 |
| Mooring or Cruise | RMSE * | r | N | Time Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6° S, 10° W | 9.7 mol kg−1 | 0.96 | 6611 | 2006–2017 |
| 6° S, 8° E | 14.4 mol kg−1 | 0.99 | 239 | 2017–2019 |
| EGEE 3 | 9.8 mol kg−1 | 0.98 | 6895 | 2006 |
| PIRATA FR-29 | 10.0 mol kg−1 | 0.99 | 4462 | 2019 |
| Mixing Equation | Salinity Range | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| DIC = 50.6 (±2.0) ∗ SSS + 231.7 (±62.2) | S > 27 | This work |
| DIC = 54.0 ∗ S + 109 | S > 33 | [13] |
| DIC = 46.5 (±1) ∗ SSS + 355 (±48) | S > 22 | [49] |
| Site | CO2 Flux | ΔfCO2 | DIC | SSS | SST | Wind |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mmol m−2d−1) | (atm) | (mol kg−1) | (°C) | (m s−1) | ||
| 6° S, 8° E | 3.06 ± 1.74 | 59 ± 28 | 1973 ± 87 | 34.3 ± 1.1 | 26.6 ± 2.8 | 5.0 ± 0.6 |
| 6° S, 10° W | 5.61 ± 1.49 | 55 ± 16 | 2047 ± 27 | 35.9 ± 0.2 | 26.9 ± 1.7 | 7.1 ± 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lefèvre, N.; Mejia, C.; Khvorostyanov, D.; Beaumont, L.; Koffi, U. Ocean Circulation Drives the Variability of the Carbon System in the Eastern Tropical Atlantic. Oceans 2021, 2, 126-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans2010008
Lefèvre N, Mejia C, Khvorostyanov D, Beaumont L, Koffi U. Ocean Circulation Drives the Variability of the Carbon System in the Eastern Tropical Atlantic. Oceans. 2021; 2(1):126-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans2010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleLefèvre, Nathalie, Carlos Mejia, Dmitry Khvorostyanov, Laurence Beaumont, and Urbain Koffi. 2021. "Ocean Circulation Drives the Variability of the Carbon System in the Eastern Tropical Atlantic" Oceans 2, no. 1: 126-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans2010008
APA StyleLefèvre, N., Mejia, C., Khvorostyanov, D., Beaumont, L., & Koffi, U. (2021). Ocean Circulation Drives the Variability of the Carbon System in the Eastern Tropical Atlantic. Oceans, 2(1), 126-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/oceans2010008