Abstract
With interest in camel milk growing due to its nutrients and biologically active compounds, research into methods of processing and drying it is crucial. In recent decades, extensive studies have explored its chemical composition and health benefits with a focus on drying techniques and their effects on its properties. This review systematically summarizes the available literature on camel milk drying processes and their effects on its chemical composition with a view to shortening the drying time. To achieve this goal, we meticulously reviewed numerous studies published between 2014 and 2024 to identify optimal drying methods that maximize the preservation of camel milk’s nutrient components and bioactive compounds. Our analysis revealed significant findings: freeze drying preserves nutrients better than spray drying, but is less efficient. Spray drying, while faster, tends to compromise some nutritional values. Conclusively, optimizing drying parameters can improve production efficiency and nutrient retention.
1. Introduction
Dried milk products are widely applied in various industries, especially in confectionery, infant formulas, and bakery products. These characteristics make them highly suitable for international trade [1]. According to the IDF Dairy Bulletin, the production of SPM is growing every year and will have increased by 1.3% to 5,000,000 tonnes in 2022 [2]. However, the optimal duration and choice of regimes in the drying process have not been studied sufficiently, especially for non-traditional types of milk.
Camel milk (CM) boasts notably elevated concentrations of iron, vitamin C, and protein while possessing a lower level of lactose compared to cow milk [3]. Additionally, camel milk is rich in various minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, magnesium, manganese, zinc, and B vitamins [4], and contains a group of proteins with antiviral, antifungal, and antibacterial properties [5]. The distinctive composition of its omega-3 fatty acids allows camel milk to undergo freezing and thawing processes without changing its texture or experiencing curdling, a frequent problem encountered with cow’s milk ([4]).
As such, camel milk is a fascinating dairy product believed to offer various health advantages and potentially combat human health conditions such as diabetes, cancer, hypertension, and autism [6,7].
Camel milk, sourced predominantly from regions in Asia and Africa [4] that are characterised by hot climates, requires strategies to preserve its quality and extend its shelf life, especially considering the potential absence of refrigeration facilities during storage. Given these circumstances, milk drying has emerged as a viable alternative for preservation and storage, ensuring the longevity of the product without compromising its quality.
Dehydration and the production of milk powders are common practices used to stabilise milk constituents for storage and transportation. Parameters like feed solid concentration, milk flow rate, inlet temperature, outlet temperature, and nozzle air pressure significantly affect the properties of milk/dairy powders [8].
The production of dairy powder involves several processing stages, such as pasteurisation, concentration, and dehydration [9]. The heat treatments administered at each stage can induce alterations in the characteristics of dairy powder, such as the stability of different milk components (proteins, vitamins, minerals, etc.), solubility, and other physical attributes. Analysing the quality of dairy powder products is crucial for understanding and managing potential changes that may arise during storage or transportation [1].
The industry faces challenges primarily associated with creating distinct powdered dairy products while maximising production efficiency to minimise energy usage and product wastage. Among the various methods used to reduce water content on a large scale, two operations stand out: atomisation/pulverisation (commonly known as spray drying) and freeze-drying processes. Therefore, the aim of this review is to systematically summarise the available literature data on CM drying processes and their effects on CM’s chemical composition in terms of reducing the drying time.
The consumption of dried dairy products has increased significantly worldwide due to their convenience, food safety, and long shelf life. Despite this, optimal drying methods for non-traditional milk types like camel milk are not well studied. This review addresses this gap by exploring camel milk drying processes. Current strategies include freeze drying and spray drying, each with unique advantages and drawbacks. This study proposes optimizing these methods to enhance nutrient retention and production efficiency. Camel milk contains higher iron, vitamin C, and protein levels compared to cow’s milk, along with lower lactose. For instance, camel milk has 3.82% fat, 4.46% lactose, and notable levels of calcium and potassium. In contrast, cow’s milk often contains less of these nutrients and more saturated fats, leading to issues such as poor digestibility and allergenicity.
These initial observations highlight the unique nutritional benefits of camel milk and the need to explore optimal drying techniques. Our study aims to systematically review the literature on camel milk drying methods, compare their efficiency and effects on milk composition, and suggest improvements to enhance the drying process’s efficiency and nutrient preservation.
2. Materials and Methods
This semi-systematic review used a monographic approach to texts written in English to summarize the available literature on the chemical composition of camel milk and possible differences between drying methods for the period encompassing 2003 to 2022. We reviewed the literature on camel milk drying technology and chemical composition during drying and investigated methods used to reduce drying time. In this review, we analysed existing studies on different camel milk drying methods including freeze drying and spray drying, as well as their effects on milk powder quality. We also evaluated the effects of various factors on camel milk composition during the drying process, such as temperature, drying time, and storage conditions. Our work aims to identify optimal drying methods that maximize the retention of camel milk nutrients and bioactive components and to explore ways to reduce drying time to improve production efficiency. To conduct this analysis, we studied the scientific databases Scopus, Google Scholar, and PubMed to cover a wide range of published research results on milk compounds. To search for relevant information, the following key terms were used: vacuum freeze drying, camel milk, and reduced drying time. This review considered 224 full-text articles from Scopus’ ScienceDirect database and 1380 from the Google Scholar database, of which 52 were relevant. We used a wide range of synonyms to find the most relevant literature.
Figure 1 shows the optimised search results for the last 10 years (2014–2024) for articles found using the keyword camel milk powder; 46 articles were relevant. A search with the same keyword yielded more results in Google Scholar, while 13 results were found in PubMed using the same keyword.
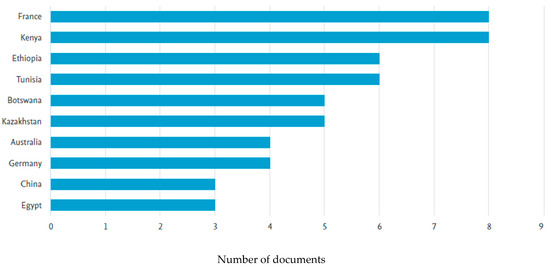
Figure 1.
Analysis in Scopus.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Camel Milk Characterisation and Importance
3.1.1. Chemical Composition of Camel Milk
Camel milk (CM) boasts notably elevated concentrations of iron, vitamin C, and protein while possessing a lower level of lactose compared to cow milk. Camel milk contains 12.47 ± 1.53% total solids, 4.46 ± 1.03% lactose, 3.82 ± 1.08% fat, and 3.35 ± 0.62% protein, alongside various minerals. Its unique composition includes higher levels of long-chain fatty acids, lower saturated fatty acids, and beneficial bioactive proteins [10]. Consequently, numerous studies [11,12,13,14] have been conducted on CM fat content, which ranges from 2.46 to 5.70% [10], and its potential effects on human health. The elevated melting point (41.9 °C) of CM is attributed to its fat composition—a high level of long-chain fatty acids, a scarcity of short-chain fatty acids, and trans 18:1 isomers. Furthermore, CM demonstrates lower saturated fatty acid (SFA) content (46.0–66.0%) alongside higher levels of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) (25.7–49.3%) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) (2.7–8.5%) compared to cow milk (Bakry et al. 2021) and smaller fat globules, with an average diameter of 2.61 μm [14]. This feature suggests that CM is more easily digestible by humans, presenting a potential advantage in terms of gastrointestinal processing.
The prevalence of long-chain fatty acids (LC-FAs) and unsaturated fatty acids in CM significantly contributes to its capacity to reduce the incidence of fat-related cardiovascular ailments by an estimated 35–50%. Intriguingly, CM fat boasts a richer concentration of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) in comparison to human milk [14]. The average cholesterol level of CM is 37.15 mg·100 g−1, varying within the wide range of 25.61 to 50.42 mg·100 g−1, and was found to be lower than that of cow milk. These investigations have unveiled a positive correlation between CM consumption and human well-being, revolutionising perceptions of CM fat as a health-promoting food source.
Protein concentrations in CM range from 2.15% to 4.80%. CM predominantly consists of caseins, comprising from 52.0% to 87.0% of its total protein content, with αS1-casein, αS2-casein, β-casein, and kappa-casein constituting 21%, 10%, 65%, and 3.47%, respectively [11]. Notably, β-casein contributes to CM’s easy digestibility in human infants due to its susceptibility to peptide hydrolysis. Compared to bovine milk caseins, camel caseins exhibit a similar amino acid composition, albeit with lower cysteine and higher proline content [15].
In addition to caseins, CM whey proteins contain α-lactalbumin, serum albumin, immunoglobulins, lactophorin (GlyCAM-1), and lactoferrin at concentrations of 2.01, 0.40, and 1.74 mg mL−1, respectively [11,16]. These proteins’ physiochemical properties and bioactivities, including those of their peptides released during fermentation/digestion, have been extensively reviewed by [7]. The absence of β-lactoglobulin in CM, similar to human milk, positions it as a promising alternative protein source to human milk and in infant formula owing to its reduced allergenicity [11,17]. The presence of β-LG in bovine whey enhances its heat stability, resulting in the poor stability of CM at temperatures up to 140 °C in contrast to cow’s milk [11]. On the other hand, α-lactalbumin (α-LA) constitutes the primary component of camel whey, while bovine whey contains only 25% of this protein. Both camel and human milk are recognised for their high contents of α-LA and lactoferrin (Lf) [8,18]. Whey proteins such as IgGs, Lf, lactoperoxidase, lysozyme, and other enzymes are potent antimicrobial components in CM [19,20]. The antimicrobial properties of CM are attributed to the high levels of protective proteins in the whey fraction, known for their superior thermostability [21]. Consequently, camel whey proteins serve as a novel source of proteins capable of generating bioactive peptides with potential health benefits [22].
CM exhibits a lactose content similar to that of bovine milk, ranging from 2.40% to 5.80%. With free access to drinking water, the average lactose content in camels rises to 5%, whereas in dehydrated camels, it decreases to 2.9%. Fluctuations in lactose concentration in CM have been linked to variations in taste, from occasionally sweet to bitter [8]. Notably, CM appears to be a safer and healthier option for individuals with lactose intolerance, possibly due to factors such as its lower casomorphin concentration, which slows intestinal motility and allows lactase action over an extended period [23]. Additionally, CM’s reduced lactose intolerance compared to bovine milk may be attributed to its high L-lactate content in its raw form, which surpasses that of bovine milk by 100 times [8].
The average ash content in CM resembles that of bovine milk but surpasses human milk by a significant margin, ranging from 0.60% to 1.05%. Major mineral concentrations in CM include calcium (111.4 mg 100 g−1), varying from 30.0 to 250.0 mg 100 g−1; magnesium (6.7 mg 100 g−1), from 4.5 to 20.0 mg 100 g−1; phosphorus (81.2 mg), from 34.0 to 100.0 mg 100 g−1; sodium (57.8 mg), from 22.0 to 69.0 mg 100 g−1; and potassium (156.3 mg), from 52.0 to 180.0 mg 100−1 [24]. In comparison, bovine milk shows higher concentrations of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus of 119.9 mg, 13.4 mg, and 95.0 mg, respectively. The calcium-to-phosphorus (Ca:P) ratios for camel and bovine milk stand at 1.50 and 1.29, respectively [8]. Moreover, CM boasts a significantly higher iron (from 10 to 20 mg 100 g−1) concentration compared to bovine milk, this being six times higher [24].
CM also hosts a variety of vitamins, including A, C, D, E, and the B group. The mean vitamin A value is 100 µg L−1 with a range of 50 to 140 µg L−1 [25]. Significantly higher compared with bovine milk is the vitamin D concentration—15.6 ng ml−1. The concentration of vitamin E (27.6 µg 100 mL−1) in CM is lower compared to the 33.5 µg 100 mL−1 in bovine milk.
Notably, CM is renowned for its elevated vitamin C content, this being three to five times higher than that of bovine milk [17]. According to Zhao et al. [26], consuming one cup of Bactrian camel milk (250 g) provides enough vitamin C to meet 100% of the daily human requirements [26]. The concentration of vitamin B2 in CM is similar to that found in bovine milk, at 156 µg 100 mL−1 [25]. The vitamin B3 concentration (391.2 µg 100 mL−1) in CM is notably higher compared to that in bovine milk, whereas bovine milk contains more of vitamins A and B2 [8]. The vitamin B1 and B6 levels are similar in both camel and bovine milk [25].
3.1.2. Functional Properties of Camel Milk
In regions abundant with camels, CM has been traditionally consumed for the treatment of diabetes, with notable success. Studies have demonstrated a significantly lower prevalence of diabetes in CM-consuming communities compared to non-consuming ones (0% vs. 5.5%) [8]. Numerous clinical trials have underscored the anti-diabetic effects of CM. The authors of [27] reported that type I diabetes patients required 66% less insulin after three months of CM consumption, with long-term efficacy and safety confirmed in 1- and 2-year trials [28]. Additionally, CM appears beneficial for controlling insulin levels in type II diabetes patients, as evidenced by a significant increase observed after two months of CM consumption [26].
In terms of antimicrobial effects, CM demonstrates notable antibacterial activity against a spectrum of bacteria, encompassing both Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains such as Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhimurium, Klebsiella pneumonia, and Clostridium perfringens [8]. It was proved that CM could protect against the harmful effects caused by S. aureus and E. coli in rats. Scientists found that CM, when used in conjunction with ciprofloxacin, worked synergistically to combat S. aureus and E. coli, thereby reducing bacterial resistance and allowing for a decrease in the dosage of antibiotics needed [28,29]. This antibacterial property of CM holds promise for combating diseases caused by bacterial infections, including tuberculosis (TB) and Crohn’s disease, and viruses (rotavirus, hepatitis C) [30,31]. Lactoferrin, lysozyme, and immunoglobulins, which are abundant in CM, primarily contribute to its antibacterial activity. Examinations using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) displayed alterations in the structure of bacterial cells when exposed to lactoferrin. Different forms of lactoferrin demonstrated dose-dependent cytotoxicity against the A549 human lung cancer cell line, indicating potential anticancer properties [32]. Furthermore, the enzymatic hydrolysis of camel whey proteins enhances their antimicrobial potency, hinting at the release of peptides with heightened antimicrobial effects post-digestion [33]. Additionally, antifungal and antiparasitic activities have also been attributed to CM.
Camels possess a distinctive and robust immune system, characterised by antibodies that are significantly smaller in size compared to those in humans. Notably, CM contains unique IgG2 and IgG3 antibodies lacking light chains [34]. These antibodies are highly effective when targeting specific antigens, exhibiting complete neutralising activity against toxins like tetanus toxin and serving as superior inhibitors of enzyme antigens. The underlying mechanisms of autism could potentially include an excess of naturally occurring or externally introduced opioid peptides, which may originate from dietary sources such as cow’s milk proteins. Certain patients exhibit inadequate intestinal breakdown of casein proteins, resulting in the production of beta-casomorphins, short neuroactive peptides derived from casein. These peptides, notably beta-casomorphin [12], have been implicated as a potential risk factor for autism [5,12,17,33]. Remarkably, CM therapy has shown promising effects on the behaviour of autistic children, potentially linked to its ability to combat oxidative stress. After two weeks of CM consumption, autistic children exhibited significant increases in plasma concentrations of glutathione, myeloperoxidase, and superoxide dismutase, indicative of improved oxidative stress control. The rehabilitative effect of CM’s immunoglobulins is believed to contribute to alleviating potential dairy food allergies in autistic children, further highlighting its therapeutic potential [35].
Bovine milk allergy represents a significant concern among both children and adults, with clinical symptoms ranging from mild to severe. With over 20 proteins capable of triggering allergic reactions, casein fractions, particularly αS1-casein, and β-lactoglobulin have been identified as the most potent allergens within bovine milk [5]. In contrast, human milk composition lacks β-lactoglobulin, and αS1-casein is present in low concentrations, while β-casein is notably abundant [8]. The protein profile of CM closely resembles that of human milk, indicating its potential as a viable alternative for individuals with bovine milk allergies. Promising outcomes from clinical trials support the use of CM in treating milk allergies in children. Moreover, CM has been suggested as a preferable option for those with lactose intolerance due to its rapid lactose digestion [5,8]. However, broader-scale trials are necessary to substantiate these claims further.
3.2. Drying Methods for CM
3.2.1. Spray Drying
Spray drying has been found to have a lower impact on the physical properties of milk powder compared to freeze drying. However, the process must be optimized to retain the nutritional properties and techno-functional characteristics of the powder. Spray-dried camel milk powder typically contains 29–45% lactose, with protein content around 26%. Spray drying can be considered a dehydration process due to the properties of its encapsulation technique. Depending on the set-up parameters, spray-dried powder can be classified as either small-size (1–5 μm), medium-size (5–25 μm), or large-size (10–60 μm) crystals. The main impact on crystal size is the atomisation condition, such as droplet size [36]. The spray drying of CM has been found to have a lower impact on the physical properties of milk powder compared to freeze drying [3]. However, the process must be optimised to retain the nutritional properties and techno-functional characteristics of the powder [37]. The spray drying conditions, such as inlet temperature and atomisation pressure, can affect the yield and nutritional components of the milk powder [37]. The changes in physico-chemical, functional, moisture sorption, and morphological characteristics of CM powder due to spray drying have also been investigated [38]. It has been found that the inlet drying air temperature and milk flow rate influenced the thermal, optical, and physical properties of laboratory spray-dried powders [39].
Compared to bovine milk powder, spray-dried CM powder has been found to have a lower extent of protein denaturation and different water sorption properties [40].
Spray-dried CM (camel milk) powder typically contains 29–45% lactose, as shown in Table 1. This range is influenced by various factors such as geographical origin, breed, and lactation stage.

Table 1.
Composition of spray-dried camel milk powder.
CM powder is a rich source of protein, with a composition that includes α-lactalbumin, lactoferrin, serum albumin, and caseins [43]. The protein content of CM powder, based on the data shown in Table 1, is around 26 w/w, which is lower than that of cow and buffalo milk powder [44]. However, the specific amount of protein in CM powder may vary depending on the processing method and the addition of other ingredients. CM powder also contains a significant amount of fat, with Table 1 reporting a range of 20 to 29 (w/w) fat content. The fat in CM is primarily composed of triacylglycerols, with a high proportion of saturated fatty acids. This makes CM powder a rich source of healthy fats, which can be beneficial for those consumers who are looking to increase their fat intake. The findings of Ogolla et al. [39]’s report indicated that inlet drying air temperatures significantly influenced the moisture content and colour properties of the powders [39].
Several parameters influence the quality of spray-dried camel milk, as detailed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Parameters influencing spray-dried camel milk.
To achieve the most effective moisture removal, an appropriately high inlet temperature should be chosen, but should not impact or cause thermal damage to the active compounds in milk. Additionally, a high inlet temperature also helps to prevent particle agglomeration, particle adhesion on the walls of the drying chamber, and microstructure collapse. Outlet temperature depends mainly on product properties and the processes that occur during drying, such as gas inlet temperature, gas flow rate, enthalpy of evaporation, and concentration of milk solids. Feed rate has a direct effect on particle size; the higher the feed rate, the larger the particles.
The kinetics of the spray-drying process are complicated and challenging. The particle size and characteristics are dependent on numerous factors during this process.
3.2.2. Freeze-Drying Method
Freeze drying preserves the integrity of bioactive chemicals at low drying temperatures, protecting the end product’s quality. Freeze-dried camel milk powder contains higher levels of total protein, casein, whey proteins, lactose, and ash (Table 3).

Table 3.
Comparison of Nutrient Composition in Spray-Dried and Freeze-Dried Camel Milk Powder.
Freeze drying is a common process used to produce CM powder because it may preserve the integrity of bioactive chemicals at low drying temperatures, protecting the end product’s quality. This method is essential for improving the usability and accessibility of CM in a range of applications. It has been discovered that the nutritional qualities of freeze-dried CM are significantly different from those of fresh milk, having increased levels of total protein, casein, whey proteins, lactose, and ash [45]. Significant modifications in CM powder’s physico-chemical, functional, moisture sorption, and morphological characteristics have been identified in studies examining the specific impacts of freeze drying [38]. This method improves the powder’s colour features, insolubility index, and flowability [41]. The specific parameters of freeze-dried camel milk are listed in Table 4.

Table 4.
Parameters of freeze-dried camel milk.
The process of freeze drying CM offers several benefits. Freeze drying can stop the Maillard process and denaturation of whey protein while preserving heat-sensitive chemicals [38]. On the other hand, there is a high possibility that using the freeze-drying process in combination with a vacuum will significantly reduce the thermolability of protein and the amino acid composition of CM [3]. The process can also create milk powder particles which are difficult to disintegrate and that cannot achieve full solubility [3].
Compared to other dehydration techniques, freeze drying takes longer, which might impact turnaround time and production efficiency. While many of the nutritional and practical qualities of CM are retained during the freeze-drying process, some of the volatile chemicals that give the milk its flavour and aroma may be lost. This may have an impact on the finished product’s sensory attributes, possibly resulting in variations in flavour when compared to fresh milk [46]. Optimising the freeze-drying process of camel milk is key to improving production efficiency and maintaining the quality of the final product. Thus, optimising the freeze-drying process will reduce production time, improve the quality of the final product, and provide more consistent organoleptic characteristics. The composition of freeze-dried camel milk powder is provided in Table 5.

Table 5.
Composition of freeze-dried camel milk powder.
According to a previous study, freeze-dried CM possessed greater amounts of iron and calcium than spray-dried milk (15.3 and 0.012 g/kg, respectively) [38]. Freeze drying eliminates moisture, which stops enzyme activity and microbiological growth—two main causes of food degradation. As a result, the product has a longer shelf life than fresh milk and may be stored for a long time without needing to be refrigerated [48]. There are multiple processes involved in the process of freeze drying, and temperature, pressure, and other variables must be carefully monitored at all times.
Vacuum dehydration is usually combined with freeze drying to take place at slightly higher temperatures, with a notably elevated medium pressure, and without the need for the material to be freeze-dried first. This results in good final product quality and notable energy efficiency. The characteristics of heat transfer during vacuum drying are typically determined by the vacuum level, which is usually in the medium-to-low range [52].
Tastemirova and co-authors revealed that drying CM causes a partial denaturation of its amino acid composition, which results in a decrease in the amount of low-molecular-weight protein fractions and an increase in higher-molecular-weight protein fractions. The amounts of other nonessential amino acids decreased as follows—13.16 times for glycine, 2 times for proline, 6.34 times for alanine, and 2.26 times for serine—whereas the amount of arginine increased by 2.53 times. The components of whey protein like albumin and globulin fractions are particularly vulnerable to denaturation alterations, which disrupt the hydration membranes of proteins on the surface and cause slight variations in the composition of amino acids [3].
The amount of saturated fatty acids in CM powder was shown to decrease during vacuum freeze drying at a sublimation temperature of −15 °C, except for capric, tridecylic, and heneicosanoic acids. An increase in the amount of unsaturated fatty acids was noted, which was related to structural variations in the fatty acid phase of CM during the vacuum freeze-drying process [3].
Additionally, when this drying method is used, insignificant changes in the contents of vitamins and macroelements occur. For instance, vitamin B1 (thiamine) is decreased by 7.69%, while vitamin B2 (riboflavin) is more than doubled and vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is decreased by 22.22%. The major losses are seen in vitamin C (ascorbic acid), which is decreased by more than three-fold [3].
Table 6 above lists some of the worldwide companies that manufacture and sell CM powder. The powder is produced using either spray- or freeze-drying technology, emphasising the quality, purity, and nutritional properties of their products. Overall, the camel milk freeze-drying process continues to attract attention as a potentially important method of preservation and transportation.

Table 6.
Brands offering camel milk powders.
However, it is important to consider the loss of certain vitamins and important nutrients during the drying process, which could potentially affect the nutritional value of the final product. It is also important to note that there are many companies offering camel milk powder on the market, indicating a growing interest in this product and its popularity among consumers.
Overall, further research and technology development in the production and drying of camel milk powder can help improve the quality and preservation of this product, which in turn can lead to the expansion of its potential applications and market popularity.
4. Conclusions
The development of new technology for camel milk drying holds significant importance and potential for the food industry. Camel milk possesses unique nutritional properties and is utilized in various food products and beverages, but its drying process is complex and energy-intensive. Introducing new drying technologies based on advanced computational methods and innovative approaches can significantly improve production efficiency and environmental sustainability. Optimizing drying parameters, particularly in spray drying and freeze-drying methods, can enhance nutrient retention and production efficiency.
Our review of the literature reveals that most studies focus on comparing the physico-chemical parameters, protein quality, and phenolic composition of dried camel and cow milk. While several articles delve into creating mixtures with dried camel milk for infant feeding or exploring differences in milk composition based on drying methods, few address the selection of freeze-drying modes based on changes in camel milk composition or the reduction in drying times.
Further research in this field is crucial for advancing camel milk drying technology. Continued studies on computational fluid dynamics, multiphysics modelling, and material properties are essential to create more accurate models of the drying process. Practical implementation of these research findings will enable the successful integration of developed technologies into production processes, yielding tangible benefits.
Reducing camel milk drying time is not only economically advantageous but also technically feasible with the use of new information technologies. Ongoing research, the development of new methods, and their practical applications are necessary to achieve more efficient and environmentally friendly camel milk drying. Additionally, further studies are needed to determine the optimal sublimation temperature, balancing the preservation of nutritional substances with energy efficiency. This will ensure the highest product quality while optimizing resource utilization, ultimately leading to improved product quality and enhanced market competitiveness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, A.R., F.D.; methodology J.Z., K.M.; verification, J.Z., K.M., D.T.; research, N.A.; sources, A.Y., N.A.; writing—drafting, D.T.; writing—reviewing and editing, D.T., K.M.; supervision, A.R.; project management, F.D.; obtaining funding, The article is based on the results of the programme BR21881957 “Development of deep processing technology and equipment for vacuum sublimation drying of mare and camel milk”. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been/was/is funded by the Committee of Science of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan (Grant No. BR21881957).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Fatima Dikhanbayeva was employed by the company U. Joldasbekov Institute of Mechanics and Engineering and AlmatyTechnological University. Author Dinara Tlevlessova was employed by the company U. Joldasbekov Institute of Mechanics and Engineering and Kazakh Scientific Research Institute LLP, Almaty, 050000, Kazakhstan. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest”. The authors declare that this study received funding from the Committee of Science of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication”.
References
- Rosa, E.; Schwinden, P.E. A Comprehensive Approach about Comparison between Drying Technologies and Powdered Dairy Products. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulletin_527_WDSR_2023.Pdf. 22 October 2023. Available online: https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0636/7991/files/SKY2856_2857_2858_Instruction_v4.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Ukilim, T.; Ciprovica, I.; Shingisov, A. The Comparison of the Spray-Drying and Freeze-Drying Techniques for Camel milk: A Review. Res. Rural. Dev. 2020, 35, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahida, S.; Henning, A.; Alexey, S.; Golik, B.; Pandiselvam, R.; Venkidasamy, B.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Maqsood, S. Traditional and Commercial Dairy Products from Yak, Camel, Zebu-Brahma, Mithun, Reindeer and Sow—A Review on Current Research Status. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 152, 105879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibhavana, S.; Vasukhi, S.M.; Ramesh, S.; Rajakumari, R.; Abhijith, A.S.; Krishna, S.A.; Prakash, G.; Raida Nair, A.V.; Prashanth, A.; Pran, M.; et al. Prospective Nutritional, Therapeutic, and Dietary Benefits of Camel milk Making It a Viable Option for Human Consumption: Current State of Scientific Knowledge. J. Exp. Biol. Agric. Sci. 2023, 11, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akli, M.A.; Yap, P.G.; Mudgil, P.; Khan, F.B.; Anwar, I.; Muhammad, K.; Gan, C.Y.; Maqsood, S. Invited Review: Camel Milk–Derived Bioactive Peptides and Diabetes—Molecular View and Perspectives. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 649–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devendra, K.; Verma, A.K.; Chatli, M.K.; Singh, R.; Kumar, P.; Mehta, N.; Malav, O.P. Camel milk: Alternative Milk for Human Consumption and Its Health Benefits. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 46, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, L.; Worku, M. Recent perspective on cow’s milk allergy and dairy nutrition. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7503–7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.M.; Ton, T.T.; Gaiani, C.; Bhandari, B.R.; Bansal, N. Changes in surface chemical composition relating to rehydration properties of spray-dried Camel milk powder during accelerated storage. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konuspayeva, G.; Faye, B.; Loiseau, G. The Composition of Camel milk: A Meta-Analysis of the Literature Data. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2009, 22, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayman, A.S.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Abdo, M.; Ombarak, R.A.; Hussein, E.O.S.; Suliman, G.; Alhimaidi, A.R.; Ammari, A.A.; Ba-Awadh, H.; Taha, A.E.; et al. Nutritional, Antimicrobial and Medicinal Properties of Camel’s Milk: A Review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3126–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyassu, S. Camel milk Products: Innovations, Limitations and Opportunities. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2023, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narmuratova, M.; Konuspayeva, G.; Loiseau, G.; Serikbaeva, A.; Nathalie, B.; Didier, M.; Faye, B. Fatty Acids Composition of Dromedary and Bactrian Camel milk in Kazakhstan. J. Camel Pract. Res. 2006, 13, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.B.; Yang, L.; Farag, M.A.; Korma, S.A.; Khalifa, I.; Cacciotti, I.; Ziedan, N.I.; Jin, J.; Jin, Q.; Wei, W.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of the Composition, Nutritional Value, and Functional Properties of Camel milk Fat. Foods 2021, 10, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, W.P.; Haenlein, G.F.W. Milk and Dairy Products in Human Nutrition; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thao, M.H.; Zou, Z.; Bansal, N. Camel milk: A review of its nutritional value, heat stability, and potential food products. Food Res. Int. 2022, 153, 110870. [Google Scholar]
- Seifu, E. Recent advances on camel milk: Nutritional and health benefits and processing implications—A review. AIMS Agric. Food 2022, 7, 777–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizhayeva, A.; Oleinikova, Y.; Saubenova, M.; Sadanov, A.; Amangeldi, A.; Aitzhanova, A.; Alybaeva, A.; Yelubaeva, M. Impact of probiotics and their metabolites in enhancement the functional properties of whey-based beverages. AIMS Agric. Food 2020, 5, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, G.; Ramadan, N.K.; Sayed, L.H.; Badr, B.M.; Omar, H.M.; Selamoglu, Z. Why whey? Camel whey protein as a new dietary approach to the management of free radicals and for the treatment of different health disorders. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2017, 20, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.U.; Selamoglu, Z. Nutritional and Medical Perspectives of Whey Protein: A Historical Overview. J. Pharm. Care 2019, 7, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Niaz, B.; Saeed, F.; Ahmed, A.; Imran, M.; Maan, A.A.; Khan, M.K.I.; Tufail, T.; Anjum, F.M.; Hussain, S.; Suleria, H.A.R. Lactoferrin (LF): A natural antimicrobial protein. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1626–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, I.; Dell’Anno, M.; Canala, B.; Magnaghi, S.; Petrali, B. Evaluation of hydration with lactoferrin on late-instar Tenebrio molitor larvae performance and functional properties of obtained meal. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 22, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguita-Ruiz, A.; Aguilera, C.M.; Gil, Á. Genetics of Lactose Intolerance: An Updated Review and Online Interactive World Maps of Phenotype and Genotype Frequencies. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaukhar, K.; Faye, B.; Bengoumi, M. Mineral Status in Camel milk: A Critical Review. Anim. Front. 2022, 12, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, F.; Konuspayeva, G.; Bengoumi, M. Vitamins of Camel milk: A Comprehensive Review. J. Camelid Sci. 2019, 12, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.B.; Bai, Y.H.; Niu, Y.W. Composition and Characteristics of Chinese Bactrian CAMEL MILK. Small Rumin. Res. 2015, 127, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmiran, P.; Ejtahed, H.S.; Angoorani, P.; Eslami, F.; Azizi, F. Camel Milk Has Beneficial Effects on Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 15, e42150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehadeh, K. Importance of CM for Human Health. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2016, 28, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, E.; Saneei, B.; Alizadeh, M.; Hosseini, S.S.; Zahedi Bialvaei, A.; Taheri, K. Isolation of probiotic bacteria from raw camel’s milk and their antagonistic effects on two bacteria causing food poisoning. New Microbes New Infect. 2018, 27, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelazez, A.; Melak, S.; Abdelmotaal, H.; Alshehry, G.; Al-Jumayi, H.; Algarni, E.; Meng, X.C. Potential antimicrobial activity of camel milk as a traditional functional food against foodborne pathogens in vivo and in vitro. Food Sci. Technol. Int. Cienc. Y Tecnol. Aliment. Int. 2024, 30, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaban, A.M.; Raslan, M.; Sharawi, Z.W.; Abdelhameed, M.S.; Hammouda, O.; El-Masry, H.M.; Elsayed KN, M.; El-Magd, M.A. Antibacterial, Antifungal, and Anticancer Effects of Camel Milk Exosomes: An In Vitro Study. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhulaifi, M.M.; Alosaimi, M.M.; Khan, M.S.; Tabrez, S.; Shaik, G.M.; Alokail, M.S.; Hassan, M.A.; Awadalla, M.E.; Husain, F.M. Assessment of Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial, Antibiofilm, and Anticancer Potential of Lactoferrin Extracted from Camel Milk. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 1464–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepide, B.; Saadat, S.; Memarzia, A.; Sarir, H.; Folkerts, G.; Boskabady, M.H. The Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Camel milk. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 855342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Falzarano, D. Unique aspects of adaptive immunity in camelids and their applications. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 134, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AL-Ayadhi Laila, Y.; Elamin, N.E. Camel Milk as a Potential Therapy as an Antioxidant in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 602834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñón-Balderrama, C.I.; Leyva-Porras, C.; Terán-Figueroa, Y.; Espinosa-Solís, V.; Álvarez-Salas, C.; Saavedra-Leos, M.Z. Encapsulation of Active Ingredients in Food Industry by Spray-Drying and Nano Spray-Drying Technologies. Processes 2020, 8, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtegebriel, H.; Edward, D.; Wawire, M.; Sila, D.; Seifu, E. Effect of operating parameters on the surface and physico-chemical properties of spray-dried Camel milk powders. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 112, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshwal, G.K.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, D.; Sharma, H. Effect of spray and freeze drying on physico-chemical, functional, moisture sorption and morphological characteristics of Camel milk powder. LWT 2020, 134, 110117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogolla, J.A.; Kulig, B.; Bădulescu, L.; Okoth, M.W.; Esper, G.; Breitenbach, J.; Hensel, O.; Sturm, B. Influence of inlet drying air temperature and milk flow rate on the physical, optical and thermal properties of spray-dried Camel milk powders. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 751–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouari, A.; Mtibaa, I.; Triki, M.; Jridi, M.; Zidi, D.; Attia, H.; Ayadi, M.A. Effect of spray-drying parameters on the solubility and the bulk density of Camel milk powder: A response surface methodology approach. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2020, 73, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, A.M.E.; Elamin, O.M.; Elkhalifa, E.A.; Laleye, L. Comparison of physicochemical properties of spray-dried camel’s milk and cow’s milk powder. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. Eng. 2014, 4, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Habtegebriel, H.; Edward, D.; Wawire, M.; Seifu, E.; Gaukel, V. Surface fat and insolubility of whole Camel milk powders as affected by spray drying operating parameters. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 128, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.; Harbourne, N.; Oruna-Concha, M.J. Quantification of major Camel milk proteins by capillary electrophoresis. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 58, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoganandi, J.; Mehta, B.M.; Wadhwani, K.N.; Darji, V.B.; Aparnathi, K.D. Evaluation and comparison of Camel milk with cow milk and buffalo milk for gross composition. J. Camel Pract. Res. 2014, 21, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, W.H.; Khalifa, E.H. Chemical and microbiological quality of camel’s milk sold in the United Arab Emirates. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harizi, N.; Madureira, J.; Zouari, A.; Ayadi, M.A.; Cabo Verde, S.; Boudhrioua, N. Effects of Spray Drying, Freeze Drying and Gamma Irradiation on the Antioxidant Activities of Camel and Cow Milk Fractions. Processes 2023, 11, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Al-Hakmani, H.; Al-Alawi, A.; Al-Marhubi, I. Thermal characteristics of freeze-dried Camel milk and its major components. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 549, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Duley, J.A.; Cowley, D.M.; Reed, S.; Arachchige, B.J.; Bhandari, B.; Shaw, P.N.; Bansal, N. Physicochemical properties and whey proteomes of Camel milk powders produced by different concentration and dehydration processes. Foods 2022, 11, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunooj, K.V.; George, J.; Kumar, V.S.; Radhakrishna, K.; Bawa, A.S. Thermal degradation and decomposition kinetics of freeze dried cow and Camel milk as well as their constituents. J. Food Sci. Eng. 2011, 1, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Aralbayev, N.; Dikhanbayeva, F.; Serikbayeva, A.; Yusof, Y.A.; Manaf, Y.N.A. Comparative study of amino acid composition of raw and dry Camel Milk and shubat (Camelus dromedaries). EurAsian J. BioSciences 2019, 13, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar]
- Aralbayev, N.; Dikhanbayeva, F.; Yusof, Y.A.B.; Tayeva, A.; Smailova, Z. Devising Optimal Technological Parameters for Spray Drying to Produce Whole Camel Milk Powder (30 August 2021). East. Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2021, 4, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhytkul, A.; Volodymyr, P.; Nurlan, K.; Azret, S.; Bayan, K. Determination of Heat Transfer Mechanisms during Vacuum Drying of Solid-Moist and Liquid-Viscous Materials (30 December 2022). East. Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2022, 6, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).