Abstract
Concrete sewer pipes can be corroded by the biogenic sulfuric acid (H2SO4) generated from microbiological activities in a process called biocorrosion or microbiologically induced corrosion (MIC). In this study, inhibitors that can reduce Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans growth and thus may reduce the accumulation of biofilm components responsible for the biodegradation of concrete were used. D-tyrosine, tetrakis hydroxymethyl phosphonium sulfate (THPS) and TiO2 nanoparticles were investigated as potential inhibitors of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) growth. Results showed that most of the chemicals used can inhibit SOB growth at a concentration lower than 100 mg/L. TiO2 nanoparticles exhibited the highest biocide effect and potential biocorrosion mitigation activity, followed by D-tyrosine and THPS.
1. Introduction
Concrete pipes are still being used for the construction of sewer networks worldwide. However, concrete sewer pipes are corroded by the biogenic sulfuric acid (H2SO4) generated from microbiological activities in a process called biocorrosion or microbiologically induced corrosion (MIC). The biogenic H2SO4 reacts with cementitious materials in concrete, resulting in structural failures of sewers [1,2]. Deterioration of concrete due to biocorrosion is very costly annually, and on a global scale, it has been identified as the lead cause of sewer deterioration [3]. There is a necessity for novel approaches for biocorrosion mitigation in concrete sewers. Concrete sewer corrosion is a complex process, involving microbial sulfide oxidation, which leads to H2SO4 production, chemical reactions between acids and cementitious materials and concrete deterioration due to chemical and biochemical reactions between H2SO4 and the cementitious materials [4]. One of the biocorrosion’s last steps involves the formation of biofilms mainly from acidophilic microbial communities, and more specifically, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans is the most known strain responsible for severe biogenic corrosion [5,6]. The Thiobacillus genus, as a key bacterial manifestation onto concrete sewers, leads to the concrete’s deterioration [7,8]. The product of their metabolism (i.e., sulfuric acid) results in attacks that lead to concrete degradation. Before the formation of H2SO4 by thiobacillus, sulfate-reducing bacteria convert sulfate into sulfide (e.g., H2S) under anaerobic conditions. Later, with emission into the sewer atmosphere, H2S is oxidized to sulfur and sulfur compounds, thus providing an ideal catalyst for the thiobacillus bacteria to metabolize it to sulfuric acid. A detailed explanation of the biocorrosion process in the sewers can be found in [9,10]. Concrete sewer system biocorrosion problems can be addressed with various methods such as the application of protective coatings onto the concrete surface [11,12], biocides and chemical dosing [1]. O2 dosing with pH elevation using Mg(OH)2 can the SRB activities and control H2S emissions. The success of many control methods depends on pH, but the adjustment of pH is complex [13]. The majority of the typical chemical dosing procedures require continuous chemical addition in order to achieve effective sulfide control at all times, incurring high chemical consumption and operational costs [14].
A highly interesting solution that the research can be directed to is the investigation of natural or green biocides, which will effectively address the problem of biocorrosion. Microorganisms that disrupt intercellular communication (quorum quenching (QQ)) and thus reduce the accumulation of biofilm components responsible for biocorrosion can be used as natural biocides [15]. In this study, D-tyrosine, tetrakis hydroxymethyl phosphonium sulfate (THPS) and their combination were used as quorum quenchers, and their efficiency in the reduction of SOB microorganisms was evaluated. D-tyrosine has been widely applied as an inhibitor in various applications, such as in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries as a depigmentation agent, while it has been found that it inhibits biofilm formation [16]. Moreover, THPS has been widely recognized as an environmentally friendly antimicrobial reagent with zero toxicity. Some studies found that the combination of D-tyrosine and THPS could play a synergistic role to effectively prevent SRB biofilm formation [17]. However, no research has been performed regarding their effect on SOB bacteria.
Antimicrobial concrete, with the addition of diverse antimicrobial agents against microorganisms involved in biocorrosion, especially in sewer systems, has been extensively studied in the literature [18]. Cement containing nano-TiO2 could inhibit the growth of microorganisms and is studied in the current work as a possible microorganism inactivator [19]. In most cases, however, municipal wastewater treatment companies are trying to maintain the existing concrete sewer pipes, and since the majority of them are not made of antimicrobial concrete, an inhibitor that can be inserted in the liquid phase or sprayed onto the surface is a more feasible alternative.
MIC can be managed by dealing with sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) with various methods [20]. When the concrete surface is already exposed to SOBs, high-pressure water can be applied onto the surface for the removal of the slime layer (i.e., the layer on the concrete surface where SOBs exist) [21]. Moreover, MgOH2 application increases surface pH [11] and inhibits SOB growth. Deactivation of SOB can be achieved with the addition of biocides or inhibitors [22,23]. Na2WO4 is a strong growth inhibitor of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans [22]. SOB growth was completely inhibited by formates at 50 mM concentration [23]. Biocides and inhibitors should be used in small concentrations for cost and environmental reasons.
In this paper, a corrosion inhibition study took place, in order to study possible concrete corrosion inhibitors. Special emphasis was given to inhibitors that can reduce Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans growth and the subsequent sulfate production, as well as the accumulation of biofilm components responsible for biodegradation of concrete. The inhibition efficiencies of three different inhibitors (i.e., D-tyrosine, THPS and TiO2) and some of their combinations are tested.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism, Experimental Media and Growth Conditions
Experiments were carried out with pure cultures of the Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans DSM9463 strain, purchased from DSMZ-German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures GmbH. For the experiments, two culture media were used: an Acidiferrobacter medium recommended from DSMZ (known as M-sulfur) and a medium of mineral salts (known as M-thiosulfate) free of calcium, iron, aluminum, and sulfate ions previously described by [24]. M-Sulfur was prepared according to DSMZ instructions. Briefly, 2.00 g (NH4)2SO4, 0.25 g MgSO4 × 7H2O, 0.10 g K2HPO4 and 0.10 g KCl were dissolved in 1 L of distilled water and sterilized by autoclaving for 15 min at 121 °C (a typical standard for steam sterilization is achieved after 15 to 30 min once all surfaces have reached a temperature of 121 °C). pH was adjusted to 3.5 with H2SO4 before autoclaving. Before use, 5.00 g/L of powdered sulfur sterilized by steaming for 3 h on each of the 3 successive days was added into the medium. Culture M-thiosulfate was composed of NH4Cl (2.43 g/L), MgCl2 × 6H2O (0.41 g/L), KH2PO4 (3.00 g/L) and Na2S2O3 × 5H2O (5.00 g/L). The optimized volume of the inoculum in its culture medium was 10 v/v (%) toward the end of the logarithmic phase of bacterial growth. The bacterial strain was kept in a refrigerator at 4 °C in the above-described liquid media and was recultivated every week. The bacterial strain was cultured at least three times at 30 °C before experimental use. All the chemicals used were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.2. Growth, Sulfate and pH Kinetics of A. Thiooxidans
The growth and pH kinetics of the A. thiooxidans DSM9463 strain were determined by inoculating 10 v/v (%) of the bacterial cultures into 10 mL of M-sulfur or M-thiosulfate. The optical density (O.D. 630 nm) was determined every day (Elisa Microplate Reader EL-10A, BIOBASE) for a total period of 7 days, and the results were used to identify the exponential and stationary growth phase of the bacterial strain. Sulfate was determined using a Hach Lange sulfate kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The pH of the bacterial suspensions was determined by a pH meter (PH-2002 EDGE, Hanna Instruments).
2.3. Inhibition Assays
D-Tyrosine, THPS and TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) were investigated as potential inhibitors of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria growth. D-Tyrosine and THPS were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Stock solutions of D-tyrosine (500 mg/L) and THPS (1000 mg/L) were prepared in deionized water and filter sterilized. From this stock solution, serial dilutions were prepared in M-sulfur or M-thiosulfate to obtain concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 100 mg/L (D-tyrosine) and 0.1 to 200 mg/L (THPS). The synergistic inhibition effect of D-tyrosine and THPS was also investigated. Two biocide mixes consisting of the combination of D-tyrosine/THPS 1:1 and 1:5 with concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 200 mg/L were tested. In order to avoid acidity due to THPS addition to the culture medium, the stock solution of THPS was neutralized to pH 5.8 by adding a sodium hydroxide solution as previously described [17]. A stock suspension of TiO2 NPs (100 mg/L) (CAS Number: 13463-67-7, nanopowder, 21 nm primary particle size (TEM), ≥99.5% trace metals basis, Sigma-Aldrich) was prepared in deionized water and sonicated at 130 W for 10 min (Imgen Technologies LLC) [25]. Working concentrations of TiO2 NPs (0.1, 1, 10 and 20 mg/mL) were prepared by adding adequate volumes from the stock suspension into the M-sulfur or M-thiosulfate. For inhibition assays, an equal volume of A. thiooxidans DSM9463 cell suspensions was obtained from M-sulfur or M-thiosulfate cultures at the exponential growth phase during the maximum growth rate (96 h) and resuspended into 10 mL of the corresponding medium containing TiO2 NPs, D-tyrosine and/or THPS. The optical density and pH were determined every day for a total period of 7 days.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean ± SD of at least three replicates. Statistical significance was determined using unpaired Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA when comparing three or more groups. Values of p < 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant (* symbol in the figures). Relative IC50 was calculated by nonlinear regression curve fitting. Analysis was carried out using GraphPad Prism 6.01 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Growth, Sulfate and pH Kinetics
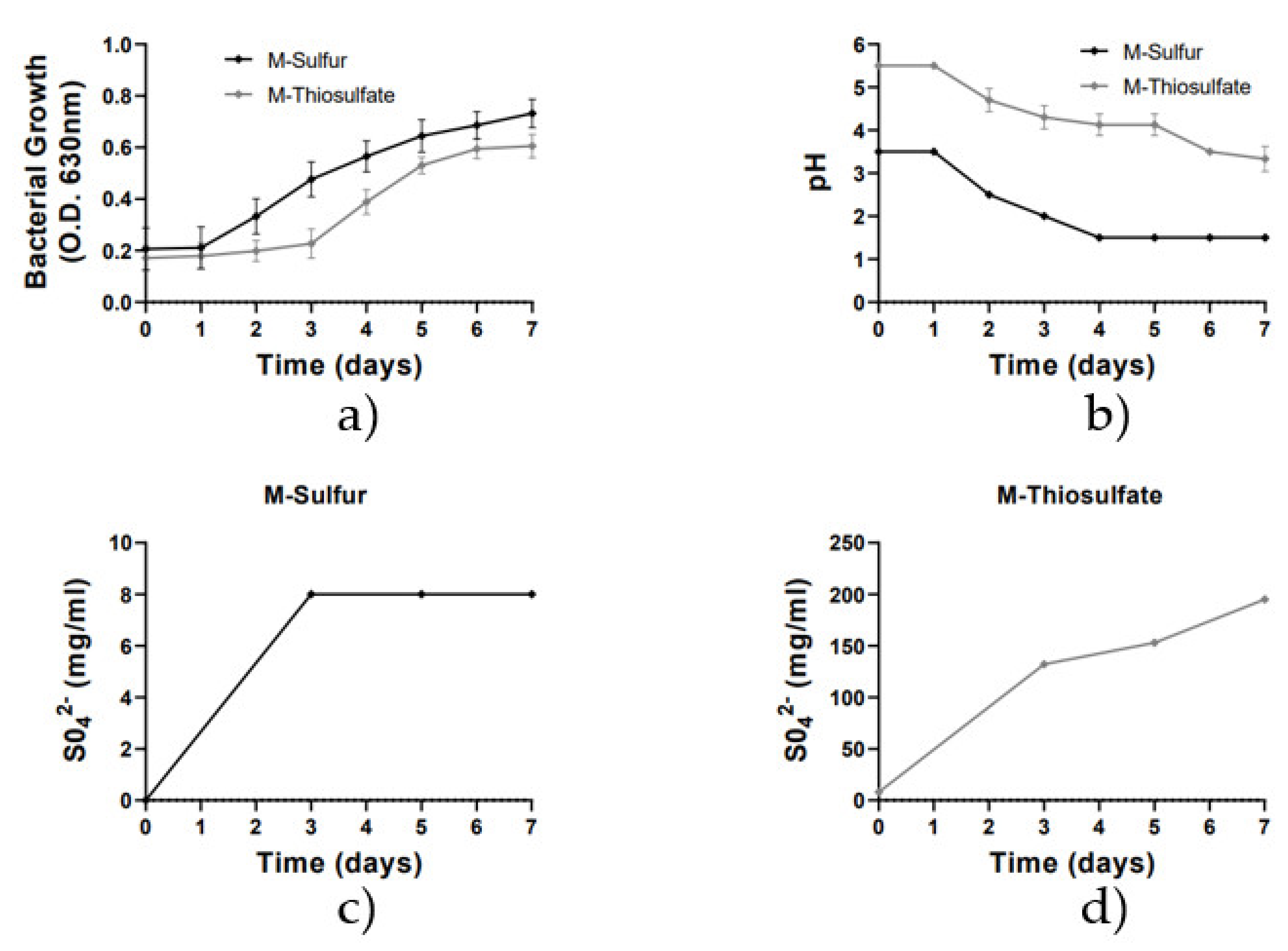
In this study, the growth and sulfur-oxidizing activity of the A. thiooxidans DSM9463 strain were investigated using two liquid culture media containing either powder sulfur (M-sulfur) or thiosulfate ions (M-thiosulfate) as the required energy for the bacterial growth. According to bacterial growth curves (Figure 1a), A. thiooxidans showed a slightly higher growth rate in the presence of powder sulfur (M-sulfur) than in the presence of thiosulphate ions (M-thiosulfate). In M-Sulfur, A. thiooxidans entered the exponential growth phase at Day 1, reaching the maximum growth rate at Days 5–6 (O.D. = 700 nm). In contrast, in Medium_2, the bacterial strain entered the exponential growth phase at Day 3, reaching the maximum growth rate at Day 7 (O.D. = 560 nm). Once the bacterial strain was in its log phase (approximately at Day 3), a decrease occurred in pH of both culture media (Figure 1b) in association with an increase in sulfate ion concentrations (Figure 1c,d). According to these results, it is evident that the sulfur-oxidizing A. thiooxidans consumed sulfur and thiosulfate ions as a source of energy and converted them into sulfate ions, decreasing the pH in the culture media. Specifically, pH was decreased from 3.5 to 1.5 and from 5.5 to 3.0 in M-sulfur and M-thiosulfate, correspondingly (Figure 1b). Similarly, sulfate ion concentration was increased up to 150 mg/mL in M-thiosulfate, while only a low increase in the produced sulfate ions (8 mg/mL) was determined in M-sulfur. According to previously published results [24,26], the presence of powder sulfur may create problems, such as low sensitivity in measuring sulfate ion concentration, while thiosulfate liquid culture media with no ions, similar to cement, such as M-thiosulfate, has been characterized as the most suitable medium for the study of A. thiooxidans activity and cement biodegradation. On the other hand, lowering of the pH has been positively associated with the increase in sulfate ion concentrations and thus is used as an indicator of the sulfur-oxidizing activity of A. thiooxidans. Therefore, both culture media were used in our later experiments to investigate potential biocides of A. thiooxidans DSM9463.
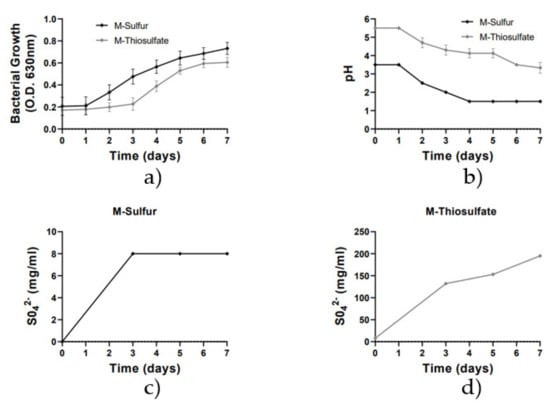
Figure 1.
Growth rate analysis of A. thiooxidans DSM9463 strain, pH and sulfate concentration variation for the 2 media. Line graphs depict mean values (±SD). (a) Growth rate for the 2 media; (b) pH variation for the 2 media; (c) sulfate concentration variation for M-Sulfur; (d) sulfate concentration variation for M-Thiosulfate.
3.2. Inhibitors’ Effect
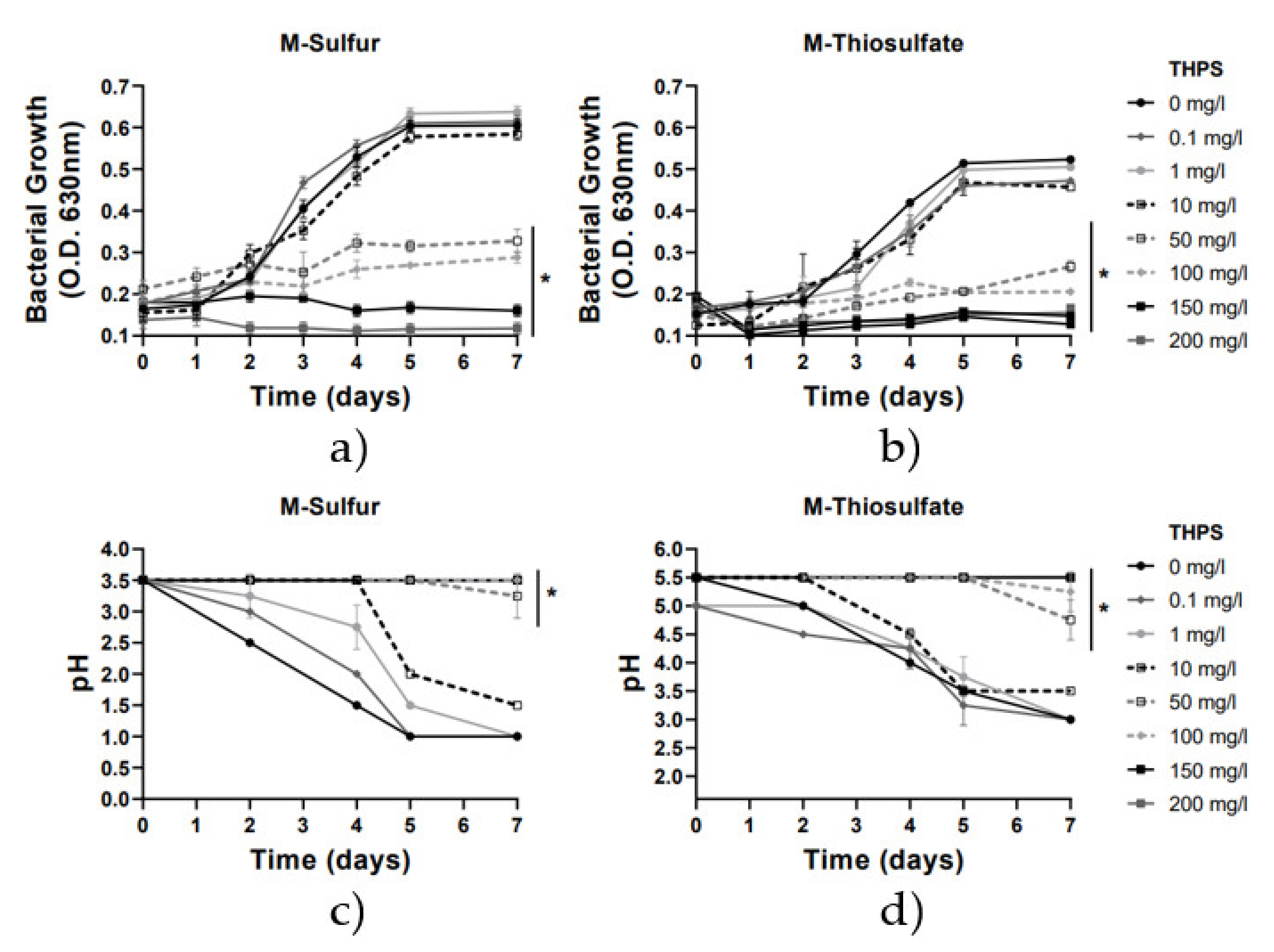
To investigate the biocide effect of THPS, various doses ranging from 0.1 to 200 mg/L were inoculated in the culture media of the A. thiooxidans DSM9463 strain. Bacterial cell density and pH variation were recorded daily. According to the results presented in Figure 2, THPS inhibited the growth of the A. thiooxidans strain, in M-sulfur and in M-thiosulfate, at doses up to 50 mg/L, reaching the maximum inhibitory effect at doses of 100–200 mg/L, where an approximately 80% inhibition was observed in bacterial growth, in both media, in comparison with the corresponding control samples. Similarly, pH variations positively correlated with the growth activity of the A. thiooxidans strain in the presence of THPS doses. At doses up to 50 mg/L, pH remained stable at pH 3.5–3.0 and pH 5.50–5.00 in M-sulfur and M-thiosulfate, correspondingly, showing that the bacterial strain was unable to oxidize sulfur or thiosulfate to produce sulfate ions.
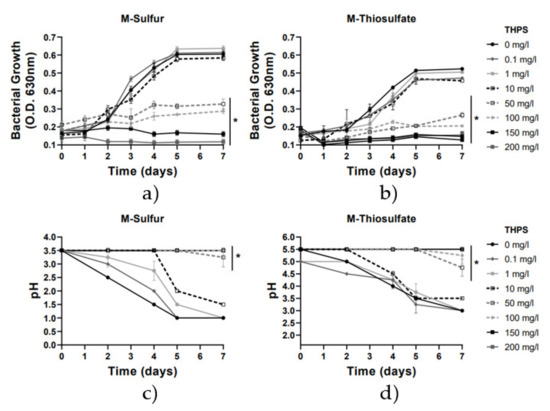
Figure 2.
Growth rate and pH variations vs. time for the 2 media with the addition of THPS (0–200 mg/L). Line graphs depict mean values (±SD). (*) denotes p < 0.05. (a) Growth rate for M-Sulfur; (b) Growth rate for M-Thiosulfate, (c) pH variation for M-Sulfur; (d) pH variation for M-Thiosulfate.
THPS is one of the most widely used biocides in large-scale applications such as in the oil and gas industry, as it is biodegradable and effective against a broad spectrum of microorganisms [27]. THPS was found to be an effective bactericide against sulfate-reducing bacteria such as Desulfovibrio vulgaris, while its main mechanism of action includes the disruption of the cell membranes and disulfide bond in microbial enzymes [17]. In this study, for the first time, THPS was characterized as a promising biocide of sulfate-oxidizing bacteria and a potential agent for biocorrosion mitigation in sewer systems.
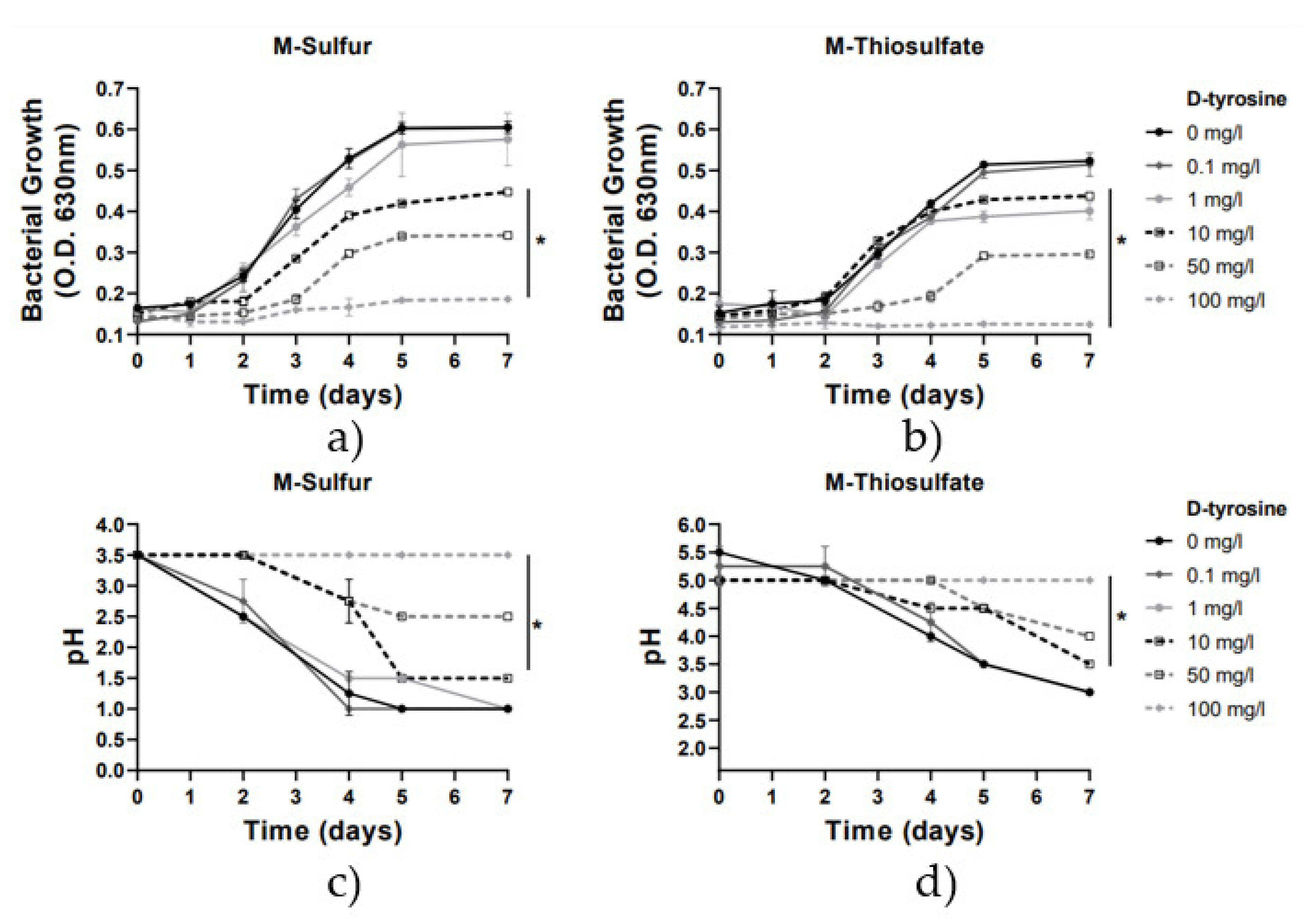
The effect of D-tyrosine on the growth and sulfur-oxidizing activity of A. thiooxidans was investigated using doses ranging from 0.1 to 100 mg/L. According to our results (Figure 3), D-tyrosine bactericidal activity was dose responded, exhibiting a statistically significant inhibitory effect from concentrations up to 10 mg/L in M-sulfur and up to 1 mg/L in M-thiosulfate, in comparison with the control samples. Inoculation of 10 mg/L, 50 mg/L and 100 mg/L of D-tyrosine in the culture M-sulfur resulted in 30%, 50% and 70% inhibition of A. thiooxidans cell density, respectively. The addition of 1–10 mg/L, 50 mg/L and 100 mg/L of D-tyrosine in the culture M-thiosulfate resulted in 25%, 60% and 85% inhibition of A. thiooxidans growth, respectively, showing a slightly stronger inhibitory effect in M-thiosulfate in comparison with M-sulfur. Considering the metabolic activity of bacterial strain, pH was decreased at the low concentrations of 0.1–1 mg/L of D-tyrosine, similarly to the control samples (pH 1.0 in M-sulfur and pH 3.0 in M-thiosulfate at Day 7), while also, a slight pH reduction was observed at 10–50 mg/L of D-tyrosine, ranging from pH 2.50–1.50 to 4.0–3.5 in M-sulfur and M-thiosulfate at Day 7, respectively. Furthermore, pH remained stable at the highest tested concentration of 100 mg/L (pH 3.50 in M-sulfur, pH 5.00 in M-thiosulfate at Day 7). According to the above results, although D-tyrosine exhibited stronger bactericidal activity than THPS (Figure 2), it did not entirely inhibit the sulfur-oxidizing activity of the remaining viable cells (Figure 3). One possible cause of such discrepancies may include the multiple biochemical pathways involved in D-tyrosine’s mechanism of action. It was recently demonstrated that D-tyrosine can modify the composition of bacterial extracellular protein and polysaccharides matrix (EPS) and could also inhibit cell attachment and biofilm formation. However, the specific effect of D-tyrosine on bacterial growth varies widely depending on the type of bacterial strains and D-tyrosine concentration [28].
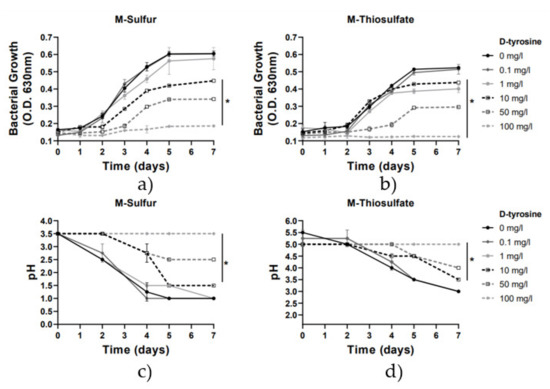
Figure 3.
Growth rate and pH variation vs. time for the 2 media with the addition of D-tyrosine (0–100 mg/L). Line graphs depict mean values (±SD). (*) denotes p < 0.05. (a) Growth rate for M-Sulfur; (b) Growth rate for M-Thiosulfate; (c) pH variation for M-Sulfur; (d) pH variation for M-Thiosulfate.
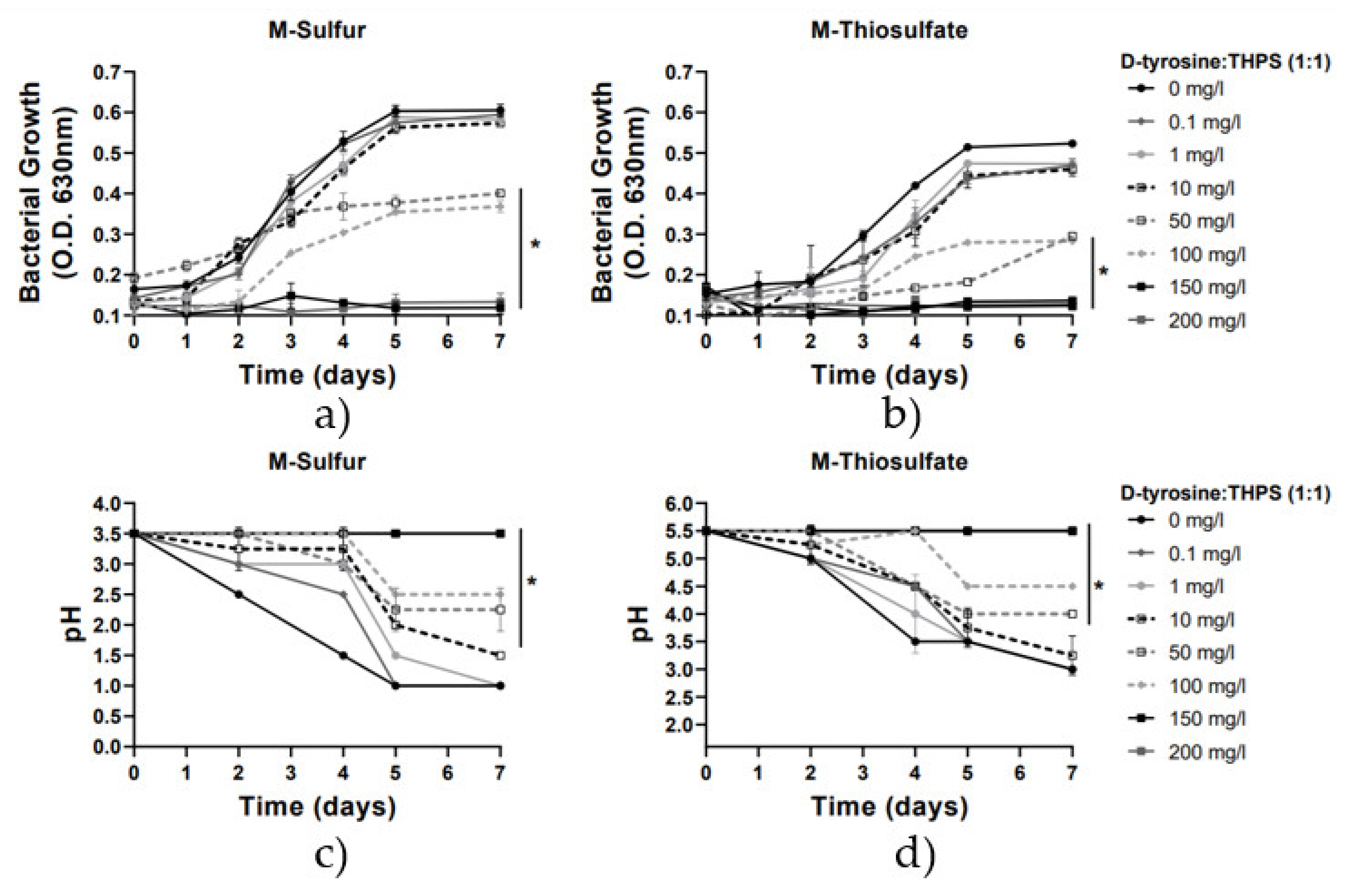
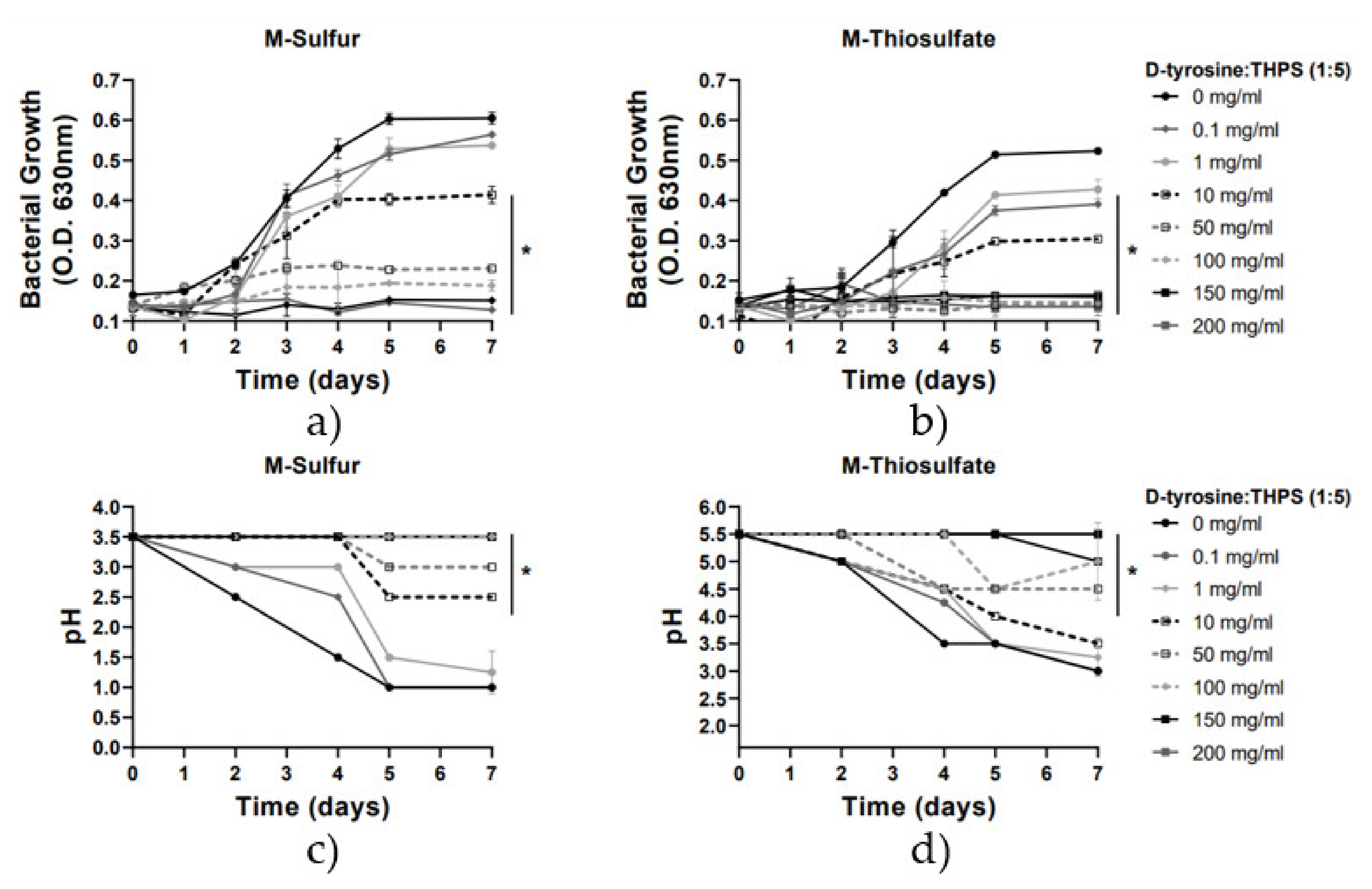
Furthermore, in this study, the efficacy of the combination of concentrations of D-tyrosine and THPS in the prevention of A. thiooxidans growth and sulfate ions production was investigated. Results presented in Figure 4 and Figure 5 show that D-tyrosine considerably enhanced THPS bactericidal activity. The biocide cocktail consisting of D-tyrosine/ΤHPS 1:5 (Figure 5) was far more effective than THPS and D-tyrosine alone and their binary combination 1:1 (Figure 4). For instance, the binary concentration of 10 mg/L D-tyrosine/THPS 1:5 was found to be highly effective in the inhibition of A. thiooxidans DSM9463 and the prevention of sulfur-oxidation, resulting in an approximately 50% growth inhibition activity in both media, while only a low reduction in pH values was observed (Figure 5). In contrast, the inoculation of the binary concentration of 10 mg/L D-tyrosine/THPS 1:1 (Figure 4), as well as the addition of a dose of 10 mg/L of THPS alone, did not lead to a statistically significant reduction (Figure 2). The maximum inhibitory effect (>80%) of the cocktail of D-tyrosine/THPS in the 1:5 combination was estimated at 50 mg/L, while the maximum inhibitory effect of the combination of D-tyrosine/THPS 1:1 (Figure 4), as well as of THPS (Figure 2) and D-tyrosine (Figure 3) alone, was estimated above 100 mg/L. All the above results reveal an efficient synergy between D-tyrosine and THPS to reduce the THPS dosage while achieving equal or stronger biocide activity.
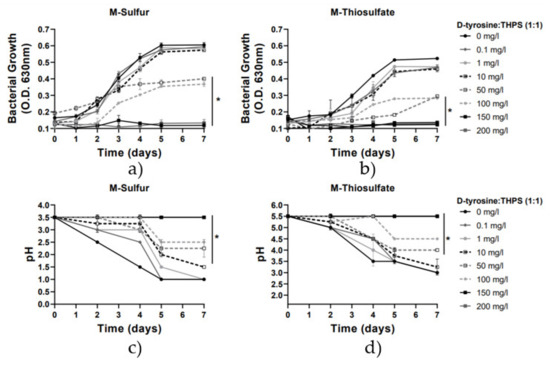
Figure 4.
Growth rate and pH variation vs. time for the 2 media with the addition of D-tyrosine/THPS (1:1) (0–200 mg/L). Line graphs depict mean values (±SD). (*) denotes p < 0.05. (a) Growth rate for M-Sulfur; (b) Growth rate for M-Thiosulfate; (c) pH variation for M-Sulfur; (d) pH variation for M-Thiosulfate.
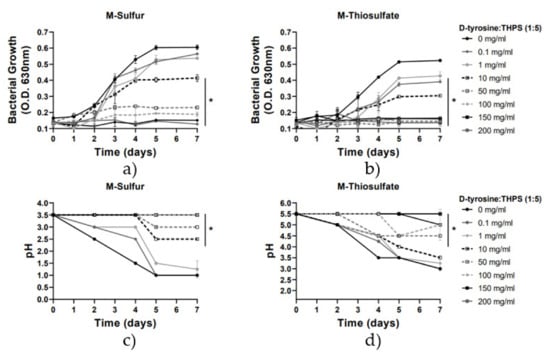
Figure 5.
Growth rate and pH variation vs. time for the 2 media with the addition of D-tyrosine/THPS (1:5) (0–200 mg/L). Line graphs depict mean values (±SD). (*) denotes p < 0.05. (a) Growth rate for M-Sulfur; (b) Growth rate for M-Thiosulfate; (c) pH variation for M-Sulfur; (d) pH variation for M-Thiosulfate.
In this study, for the first time, we demonstrated that D-tyrosine could be used as a potential enhancer of the THPS microbiocide against A. thiooxidans strains, leading to biocorrosion mitigation in sewer systems. Although THPS has been characterized as an environmentally friendly biocide, repeated uses of high doses of THPS have been associated with the promotion of resistant microbes, thus causing dosage escalation and increasing costs [29]. Since the choices of biocides for large-scale field applications are very limited, the use of biocide enhancer, such as D-amino acids (D-methionine, D-tyrosine, D-tryptophan, and D-leucine), has been suggested as a potentially attractive approach to prevent biofilms [30]. D-tyrosine has been shown to inhibit the growth of several bacterial species, including Desulfovibrio vulgaris, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis, due to alterations in their peptidoglycan synthesis in the cell walls [28,31], as well as it was demonstrated to enhance the efficacy of THPS and alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride (ADBAC) biocides in the mitigation of the Desulfovibrio vulgaris biofilm [30,32].
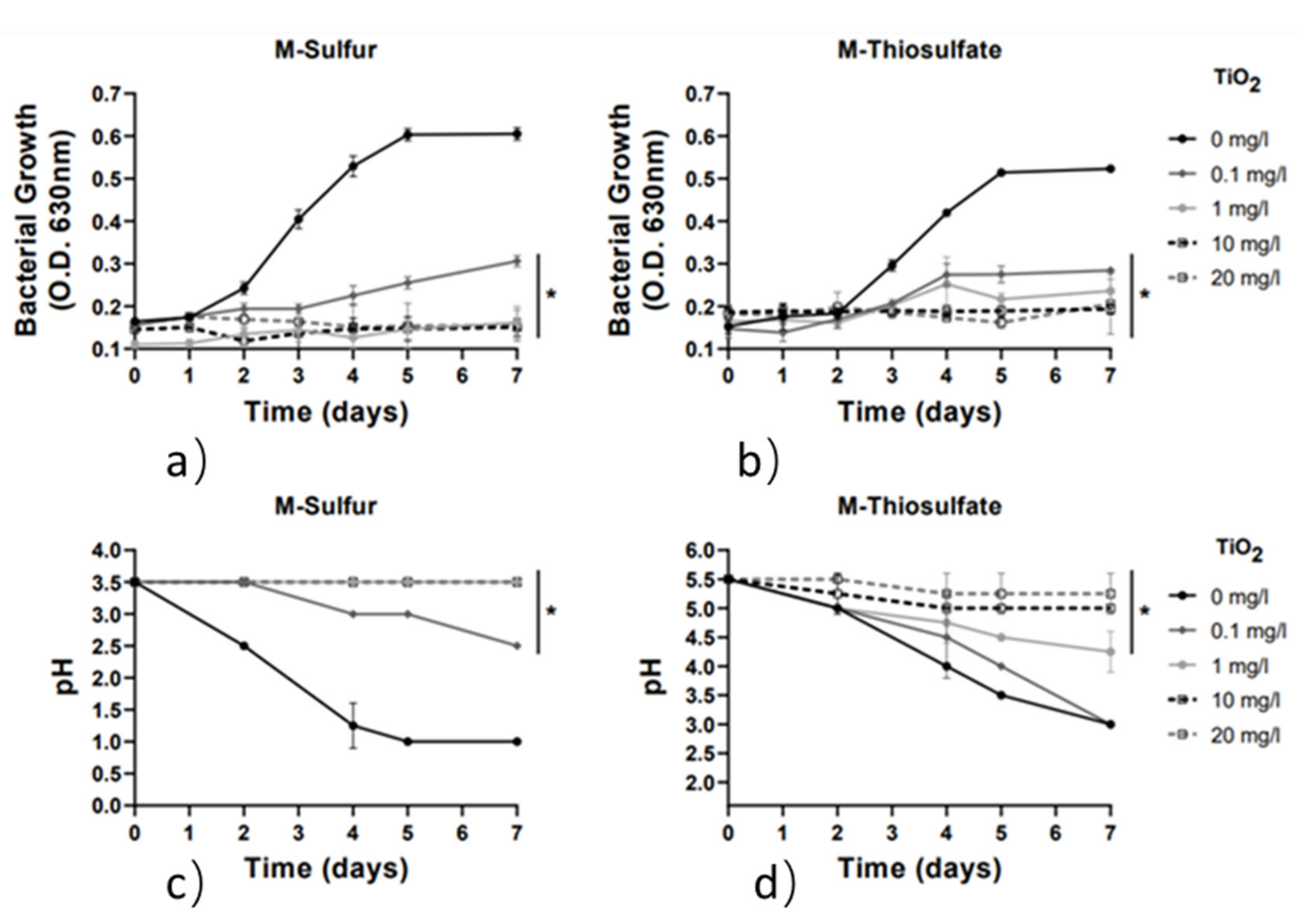
Finally, the effect of low-exposure concentrations (0.1, 1, 10 and 20 mg/L) of TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) on the growth of A. thiooxidans DSM9463 strain and its capacity to oxidize sulfur and thiosulphate ions was investigated. Results, presented in Figure 6, indicate that TiO2 NPs exhibited a strong biocide effect on the A. thiooxidans DSM9463 strain. Interestingly, at very low concentrations of 0.1 mg/L and 1 mg/L, TiO2 nanoparticles caused up to a 50% and 80% inhibition effect in bacterial strain growth in both media, respectively. Additionally, the capacity of A. thiooxidans to oxidize sulfur and thiosulfate ions and subsequently reduce pH was inhibited in both media at a concentration of 1 mg/L. In agreement with our results, several previous studies have highlighted the capacity of TiO2 NPs to reduce the bacterial growth rate of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial species, including Mycobacterium smegmatis, Shewanella oneidensis, Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli, at concentrations lower than 1 mg/L [33,34].
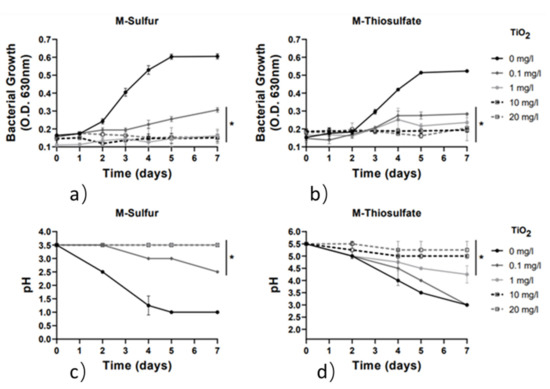
Figure 6.
Growth rate and pH variation vs. time for the 2 media with the addition of TiO2 nanoparticles (0–20 mg/L). Line graphs depict mean values (±SD). (*) denotes p < 0.05. (a) Growth rate for M-Sulfur; (b) Growth rate for M-Thiosulfate; (c) pH variation for M-Sulfur; (d) pH variation for M-Thiosulfate.
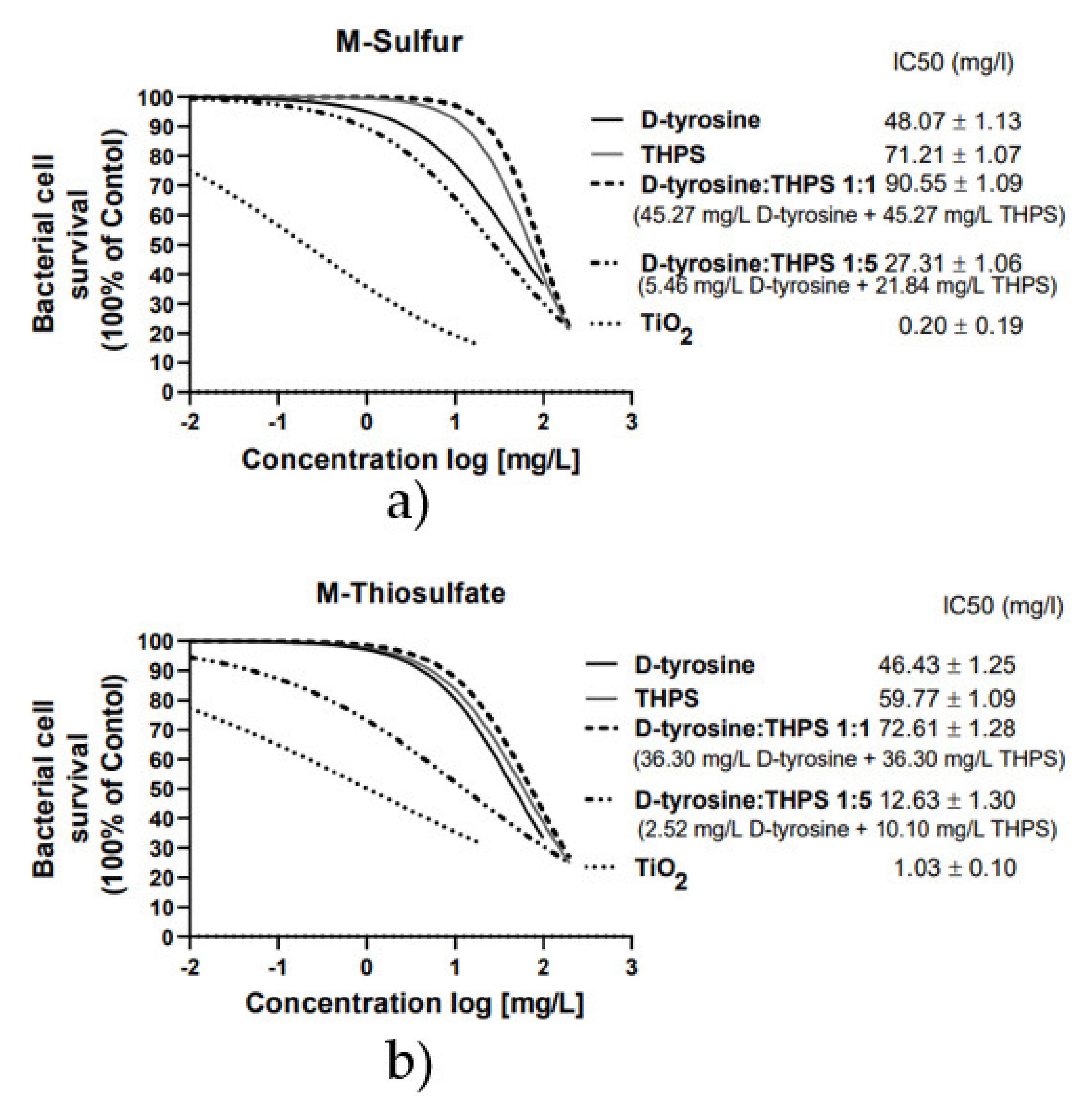
Taking into consideration all the above data, TiO2 NPs exhibited the highest biocide effect and potential biocorrosion mitigation activity, followed by D-tyrosine and THPS. According to the data presented in Figure 7, the IC50 concentration of TiO2 NPs, D-tyrosine and THPS was estimated at 0.2 mg/L ± 0.19, 48 mg/L ± 1.13 and 71 mg/L ± 1.09 in M-sulfur, and at 1.03 mg/L ± 0.10, 46.43 mg/L ± 1.25 and 59.77 mg/L ± 1.09 in M-thiosulfate, respectively. Slight differences observed between the two media may be due to the different growth rates of the A. thiooxidans strain in the two media (Figure 1), as well as due to the different metabolic pathways involved in the use of powder sulfur (M-sulfur) or thiosulfate ions (M-thiosulfate) as an energy source for the growth of bacterial stain. Moreover, D-tyrosine was characterized as a potential biocide enhancer of THPS. The binary cocktail of D-tyrosine and THPS, in a combination of 1:1, reduced significantly the THPS concentration needed to reduce bacterial cell density at 50% (IC50) from 71 mg/L to 45.27 mg/L in M-sulfur and from 59.77 mg/L to 12.63 mg/L in M-thiosulfate, revealing the enhancing effect of D-tyrosine on THPS activity. In contrast, the IC50 concentration of D-tyrosine during the application of the binary cocktail of D-tyrosine/THPS 1:1 remained at the same level as when it was used alone at 40 mg/L. Finally, the application of the binary cocktail in a combination of D-tyrosine/THPS 1:5 reduced the IC50 concentration of both bactericidal agents below 20 mg/L, revealing their synergetic activity. This synergistic approach using THPS, a green biocide, and a naturally occurring chemical, D-tyrosine, may lead to their large-scale application on concrete sewer pipes to reduce corrosion caused by the sulfuric acid, which is mainly produced by sulfur-oxidizing bacteria such as A. thiooxidans.
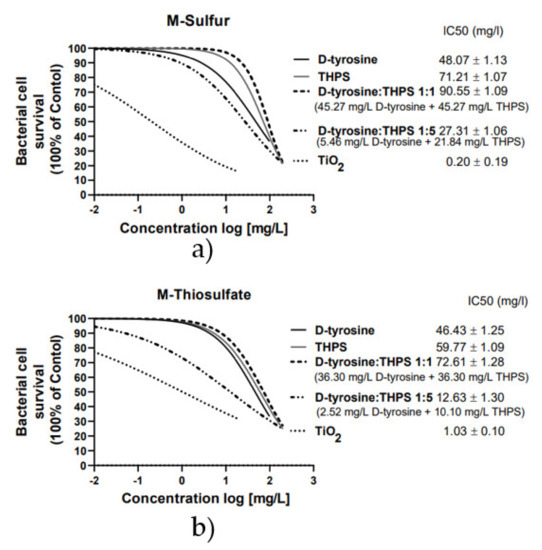
Figure 7.
Determination of the IC50 concentration of the tested potential biocides by nonlinear regression analysis for (a) M-Sulfur and (b) M-Thiosulfate. Curves shows log (concentration) of the tested compound vs. bacterial growth survival determined as % of the corresponding survival of the control samples at day 7.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, biocides and inhibitors (i.e., THPS, D-tyrosine, D-tyrosine/THPS 1:1, D-tyrosine/THPS 1:5 and TiO2 NPs) were examined under their potential use in SOB inhibition. Results showed promising potential use for the most tested chemicals even in relatively small concentrations. TiO2 NPs can inhibit SOBs with the minimum concentration. The application of D-tyrosine/THPS 1:5 may be a promising alternative for concrete sewer inhibition. For future work, the performance of these chemicals and the potential of their joint use with TiO2 NPs could be tested on large-scale concrete surfaces in order to examine the effect on biofilm formation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.F., D.B. and P.S.; methodology, G.F., D.B. and E.D.; investigation, G.F., D.B. and E.D.; data curation, E.P.; writing—original draft preparation, G.F., D.B. and E.D.; writing—review and editing, E.P., M.Y. and P.S.; supervision, P.S. and M.Y.; project administration, P.S.; funding acquisition, P.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been co-financed by the European Union and Greek national funds through the Operational Program Human Resource Development, Education and Lifelong Learning, under the call research support with emphasis on young researchers, PHASE B (Development of an innovative quorum quenching method to reduce biocorrosion of sewers).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, L.; Hu, C.; Liu, W.V. The Sustainability of Concrete in Sewer Tunnel—A Narrative Review of Acid Corrosion in the City of Edmonton, Canada. Sustainability 2018, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fytianos, G.; Tsikrikis, A.; Anagnostopoulos, C.A.; Papastergiadis, E.; Samaras, P. The Inclusion of Acidic and Stormwater Flows in Concrete Sewer Corrosion Mitigation Studies. Water 2021, 13, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikaar, I.; Sharma, K.R.; Hu, S.; Gernjak, W.; Keller, J.; Yuan, Z. Reducing sewer corrosion through integrated urban water management. Science 2014, 345, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Zhou, M.; Chiu, T.H.; Sun, X.; Keller, J.; Bond, P. Wastewater-Enhanced Microbial Corrosion of Concrete Sewers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8084–8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, S.; Odagiri, M.; Ito, T.; Satoh, H. Succession of Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria in the Microbial Community on Corroding Concrete in Sewer Systems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Kappler, U.; Jiang, G.; Bond, P. The Ecology of Acidophilic Microorganisms in the Corroding Concrete Sewer Environment. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.; Nonaka, T.; Tazaki, K.; Koga, M.; Hikosaka, Y.; Noda, S. Interactions of nutrients, moisture and pH on microbial corrosion of concrete sewer pipes. Water Res. 1992, 26, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, M.; McNally, C.; Richardson, M. Biochemical attack on concrete in wastewater applications: A state of the art review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytianos, G.; Baltikas, V.; Loukovitis, D.; Banti, D.; Sfikas, A.; Papastergiadis, E.; Samaras, P. Biocorrosion of Concrete Sewers in Greece: Current Practices and Challenges. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Wang, T.; Wu, K.; Kan, L. Microbiologically induced corrosion of concrete in sewer structures: A review of the mechanisms and phenomena. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 117813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydney, R.; Esfandi, E.; Surapaneni, S. Control concrete sewer corrosion via the crown spray process. Water Environ. Res. 1996, 68, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merachtsaki, D.; Fytianos, G.; Papastergiadis, E.; Samaras, P.; Yiannoulakis, H.; Zouboulis, A. Properties and Performance of Novel Mg(OH)2-Based Coatings for Corrosion Mitigation in Concrete Sewer Pipes. Materials 2020, 13, 5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, D.; Bal Krishna, K.C.; Kastl, G.; Sathasivan, A. The role of pH on sewer corrosion processes and control methods: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Sun, J.; Sharma, K.R.; Yuan, Z. Corrosion and odor management in sewer systems. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarascia, G.; Wang, T.; Hong, P.-Y. Quorum Sensing and the Use of Quorum Quenchers as Natural Biocides to Inhibit Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. Antibiotics 2016, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zolghadri, S.; Bahrami, A.; Khan, M.T.H.; Munoz-Munoz, J.; Garcia-Molina, F.; Garcia-Canovas, F.; Saboury, A.A. A comprehensive review on tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 279–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Gu, T. A synergistic d-tyrosine and tetrakis hydroxymethyl phosphonium sulfate biocide combination for the mitigation of an SRB biofilm. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 3067–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Dong, S.; Ashour, A.; Han, B. Antimicrobial concrete for smart and durable infrastructures: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 120456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganji, N.; Allahverdi, A.; Naeimpoor, F.; Mahinroosta, M. Photocatalytic effect of nano-TiO2 loaded cement on dye decolorization and Escherichia coli inactivation under UV irradiation. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 5395–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jiang, G.; Bond, P.L.; Keller, J.; Yuan, Z. A novel and simple treatment for control of sulfide induced sewer concrete corrosion using free nitrous acid. Water Res. 2015, 70, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islander, R.L.; Devinny, J.S.; Mansfeld, F.; Postyn, A.; Shih, H. Microbial Ecology of Crown Corrosion in Sewers. J. Environ. Eng. 1991, 117, 751–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, A.; Muraoka, T.; Maeda, T.; Takeuchi, F.; Kanao, T.; Kamimura, K.; Sugio, T. Growth Inhibition by Tungsten in the Sulfur-Oxidizing BacteriumAcidithiobacillus thiooxidans. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, T.; Aso, I.; Togashi, S.; Tanigawa, M.; Shoji, K.; Watanabe, T.; Watanabe, N.; Maki, K.; Suzuki, H. Corrosion by bacteria of concrete in sewerage systems and inhibitory effects of formates on their growth. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2636–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, A.; Allahverdi, A.; Hejazi, P. Accelerated biodegradation of cured cement paste by Thiobacillus species under simulation condition. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 86, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, A.; Bhuvaneshwari, M.; Babu, S.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. The effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on sulfate-reducing bacteria and their consortium under anaerobic conditions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3741–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, A.; Hejazi, P.; Allahverdi, A. Evaluation of Effective Strategies for Cultivation of Acidithiobacillus Thiooxidans as Cement-Degrading Bacteria. Iran. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 10, 55–66. Available online: http://www.ijche.com/article_10232.html (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Silva, P.; Oliveira, S.H.; Vinhas, G.M.; Carvalho, L.J.; Baraúna, O.S.; Filho, S.L.U.; Lima, M.A.G. Tetrakis hydroxymethyl phosphonium sulfate (THPS) with biopolymer as strategy for the control of microbiologically influenced corrosion in a dynamic system. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2021, 160, 108272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Wen, D.; Liu, C.; Li, Q. Inhibition of biofilm formation by d-tyrosine: Effect of bacterial type and d-tyrosine concentration. Water Res. 2016, 92, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, R.; Yang, D.; Rahman, H.B.A.; Gu, T. Laboratory testing of enhanced biocide mitigation of an oilfield biofilm and its microbiologically influenced corrosion of carbon steel in the presence of oilfield chemicals. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 125, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wen, J.; Fu, W.; Gu, T.; Raad, I. d-amino acids for the enhancement of a binary biocide cocktail consisting of THPS and EDDS against an SRB biofilm. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wu, J.; Zin, G.; Di Luccio, M.; Wen, D.; Li, Q. d-Tyrosine loaded nanocomposite membranes for environmental-friendly, long-term biofouling control. Water Res. 2018, 130, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jia, R.; Al-Mahamedh, H.H.; Xu, D.; Gu, T. Enhanced Biocide Mitigation of Field Biofilm Consortia by a Mixture of D-Amino Acids. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.K.; Lyon, D.Y.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Comparative eco-toxicity of nanoscale TiO2, SiO2, and ZnO water suspensions. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3527–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Huang, R.; Sahu, M.; Feng, X.; Biswas, P.; Tang, Y.J. Bacterial responses to Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).