Evaluation of the Anticancer and DNA-Binding Characteristics of Dichloro(diimine)zinc(II) Complexes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
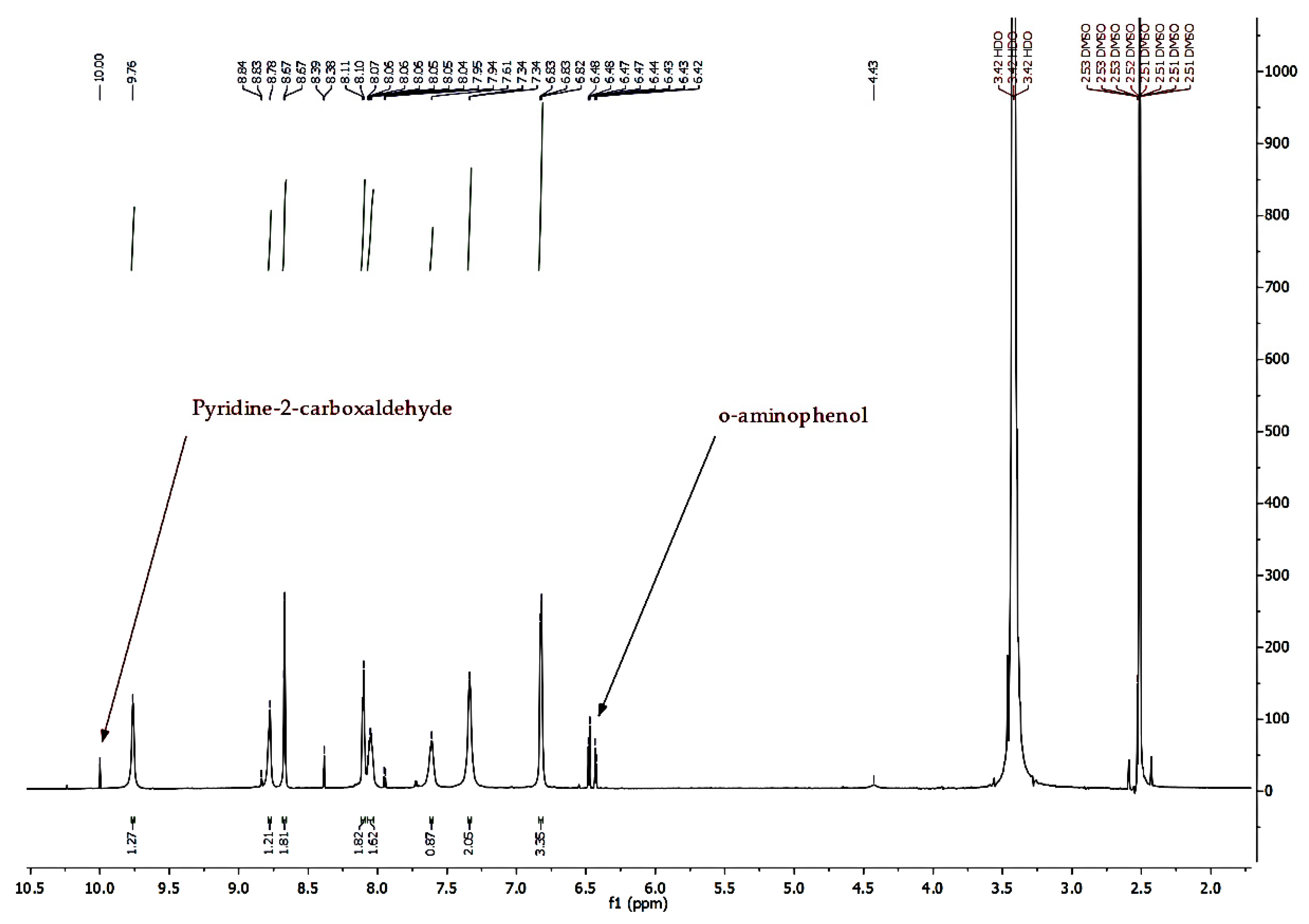
2.2. Methods and Instrumentation
2.3. DNA Binding Studies
2.4. Molecular Docking Studies
2.5. Anticancer Activity and Cytotoxicity
3. Results
3.1. DNA-Binding Studies
3.2. Docking Studies
3.3. Anticancer Activities
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CT-DNA | calf-thymus DNA |
| COLO 205 | human colon adenocarcinoma cancer cell line |
| RCC-PR | human kidney clear cell carcinoma cancer cell line |
| LLC-MK2 | rhesus monkey kidney epithelial normal cell line |
References
- Wang, D.; Lippard, S.J. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasetto, L.M.; Andrea, M.R.D.; Brandes, A.A.; Rossi, E.; Monfardini, S. The development of platinum compounds and their possible combination. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2006, 60, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.; Giandomenico, C.M. Current Status of Platinum-Based Antitumor Drugs. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2451–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabik, C.A.; Dolan, M.E. Molecular mechanisms of resistance and toxicity associated with platinating agents. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2007, 33, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heffeter, P.; Jungwirth, U.; Jakupec, M.; Hartinger, C.; Galanski, M.; Elbling, L.; Micksche, M.; Keppler, B.; Berger, W. Resistance against novel anticancer metal compounds: Differences and similarities. Drug Resist. Updates 2008, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatzschneider, U. Chapter 14: Metallointercalators and metalloinsertors: Structural requirements for DNA recognition and anticancer activity. In Metallo-Drugs: Development and Action of Anticancer Agents; Sigel, A., Sigel, H., Freisinger, E., Sigel, R.K.O., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 387–436. [Google Scholar]
- Pages, B.J.; Ang, D.L.; Wright, E.P.; Aldrich-Wright, J.R. Metal complex interactions with DNA. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 3505–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.K.-W. Luminescent Rhenium (I) and Iridium (III) Polypyridine Complexes as Biological Probes, Imaging Reagents, and Photocytotoxic Agents. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2985–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.P.; Holtkamp, H.U.; Meier, S.M.; Hartinger, C.G. Chapter 10: The Analysis of Therapeutic Metal Complexes and Their Biomolecular Interactions. In Inorganic and Organometallic Transition Metal Complexes with Biological Molecules and Living Cells; Lo, K.K.-W., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 355–386. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, D.H.; Scott, P. Chapter 7: Antimicrobial Metallodrugs. In Inorganic and Organometallic Transition Metal Complexes with Biological Molecules and Living Cells; Lo, K.K.-W., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 205–243. [Google Scholar]
- D’Cruz, O.J.; Uckun, F.M. Metvan: A novel oxovanadium (IV) complex with broad spectrum anticancer activity. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2002, 11, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scrivens, P.J.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A.; Giannini, G.; Wang, T.; Loignon, M.; Batist, G.; Sandor, V.A. Cdc25A-inhibitory properties and antineoplastic activity of bisperoxovanadium analogues. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2003, 2, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Tu, C.; Wei, H.; Yang, Z.; Lin, L.; Ding, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z. A novel cytotoxic ternary copper (II) complex of 1,10-phenanthroline and l-threonine with DNA nuclease activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004, 98, 2099–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendiran, V.; Karthik, R.; Palaniandavar, M.; Stoeckli-Evans, H.; Periasamy, V.S.; Akbarsha, M.A.; Srinag, B.S.; Krishnamurthy, H. Mixed-ligand copper (II)-phenolate complexes: Effect of coligand on enhanced DNA and protein binding, DNA cleavage, and anticancer activity. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 8208–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagababu, P.; Barui, A.K.; Thulasiram, B.; Devi, C.S.; Satyanarayana, S.; Patra, C.R.; Sreedhar, B. Antiangiogenic Activity of Mononuclear Copper (II) Polypyridyl Complexes for the Treatment of Cancers. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 5226–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashat, K.; Babgi, B.A.; Hussien, M.A.; Arshad, M.N.; Abdellattif, M. Synthesis, structures, DNA-binding and anticancer activities of some copper(I)-phosphine complexes. Polyhedron 2019, 158, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babgi, B.A.; Mashat, K.H.; Abdellattif, M.H.; Arshad, M.N.; Alzahrani, K.A.; Asiri, A.M.; Du, J.; Humphrey, M.G.; Hussien, M.A. Synthesis, structures, DNA-binding, cytotoxicity and molecular docking of CuBr (PPh3)(diimine). Polyhedron 2020, 192, 114847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaedi, S.; Babgi, B.A.; Abdellatif, M.H.; Arshad, M.N.; Emwas, A.; Jaremko, M.; Humphrey, M.G.; Asiri, A.M.; Hussein, M.A. DNA-Binding and Cytotoxicity of Copper(I) Complexes Containing Functionalized Dipyridylphenazine Ligands. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mital, M.; Ziora, Z. Biological applications of Ru (II) polypyridyl complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 375, 434–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gorle, A.K.; Sundaraneedi, M.K.; Keene, F.R.; Collins, J.G. Kinetically-inert polypyridylruthenium (II) complexes as therapeutic agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 375, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapdi, A.R.; Fairlamb, I.J.S. Anti-cancer palladium complexes: A focus on PdX2L2, palladacycles and related complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4751–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, F.; Hadadzadeh, H.; Simpson, J.; Shahpiri, A. A water-soluble Pd(ii) complex with a terpyridine ligand: Experimental and molecular modeling studies of the interaction with DNA and BSA; and in vitro cytotoxicity investigations against five human cancer cell lines. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 9081–9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, I. On the medicinal chemistry of gold complexes as anticancer drugs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messori, L.; Abbate, F.; Marcon, G.; Orioli, P.; Fontani, M.; Mini, E.; Mazzei, T.; Carotti, S.; O’Connell, T.; Zanello, P. Gold (III) Complexes as Potential Antitumor Agents: Solution Chemistry and Cytotoxic Properties of Some Selected Gold (III) Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3541–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markov, D.; Naryshikina, T.; Mustaev, A.; Severinov, K. A zinc-binding site in the largest subunit of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase is involved in enzyme assembly. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2439–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.; Cui, C.; Luo, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Ko, J.K.; Huo, X.; Ma, J.; Fu, L.W.; Souza, R.F.; Korichneva, I.; et al. Selective inhibitory effects of zinc on cell proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through Orai1. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fong, L.Y.; Nguyen, V.T.; Farber, J.L. Esophageal cancer prevention in zinc-deficient rats: Rapid induction of apoptosis by replenishing zinc. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadizadeh, S.; Amirnasr, M.; Tirani, F.F.; Mansouri, A.; Schenk, K. DNA-BSA interaction, cytotoxicity and molecular docking of mononuclear zinc complexes with reductively cleaved N2S2 Schiff base ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2018, 483, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikneswaran, R.; Eltayeb, N.E.; Ramesh, S.; Yahya, R. New alicyclic thiosemicarbazone chelated zinc (II) antitumor complexes: Interactions with DNA/protein, nuclease activity and inhibition of topoisomerase-I. Polyhedron 2016, 105, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovala-Demertzi, D.; Yadav, P.N.; Wiecek, J.; Skoulika, S.; Varadinova, T.; Demertzis, M.A. Zinc (II) complexes derived from pyridine-2-carbaldehyde thiosemicarbazone and (1E)-1-pyridin-2-ylethan-1-one thiosemicarbazone. Synthesis, crystal structures and antiproliferative activity of zinc (II) complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arion, V.B. Coordination chemistry of S-substituted isothiosemicarbazides and isothiosemicarbazones. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 387, 348–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khathami, N.D.; Al-Rashdi, K.S.; Babgi, B.A.; Hussien, M.A.; Arshad, M.N.; Eltayeb, N.E.; Elsilk, S.E.; Lasri, J.; Basaleh, A.S.; Al-Jahdali, M. Spectroscopic and biological properties of platinum complexes derived from 2-pyridyl Schiff bases. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2019, 23, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muranishi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Odoko, M.; Okabe, N. (2,2’-Biquinoline-κ2N,N′)dichloropalladium(II), -copper(II) and -zinc(II). Acta Crystallograph. C: Cryst. Struct. Commun. 2005, C61, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.A.; Puzyk, M.V.; Balashev, K.P. Spectroscopic and electrochemical properties of dichlorobiquinoline complexes of Au (III), Pt (II), and Pd (II). Opt. Spectrosc. 2006, 101, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, M.; Baghlaf, A.O.; Al-Mouty, A.; Al-Dousry, M. Preparation and characterization of 2,2’-dipyridylamine, 2,2’-dipyridylketone and 2,2’-dithiodipyridine complexes of copper (II), zinc (II), nickel (II) and uranium (VI) metal ions. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 1992, 14, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Annibale, G.; Canovese, L.; Cattalini, L.; Natile, G.; Biagini-Cingi, M.; Manotti-Lanfredi, A.M.; Tiripicchio, A. Reversible addition of protic molecules to coordinated di-2-pyridyl ketone in palladium (II), platinum (II), and gold (III) complexes. X-ray crystal structures of dichloro(dihydroxydi-2-pyridylmethane) palladium (II) and dichloro(dihydroxydi-2-pyridylmethane) gold (III) chloride. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. Inorg. Chem. 1981, 12, 2280–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.S.; Saha, P.; Mitra, P.; Maity, S.S.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, P. Unsymmetrical diimine chelation to M(II) (M = Zn, Cd, Pd): Atropisomerism, pi-pi stacking and photoluminescence. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 7375–7384. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantari, R.; Asadi, Z. DNA/BSA binding of a new oxovanadium (IV) complex of glycylglycine derivative Schiff base ligand. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1219, 128664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferoğlu, Z.; Mahmoud, M.M.A.; Ihmels, H. Studies of the binding interactions of dicationic styrylimidazo [1, 2-a] pyridinium dyes with duplex and quadruplex DNA. Dyes Pigment. 2016, 125, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muanza, D.N.; Kim, B.W.; Euler, K.L.; Williams, L. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Nine Medicinal Plants from Zaire. Int. J. Pharmacog. 1994, 32, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzuto, J.M.; Che, C.-T.; McPherson, D.D.; Zhu, J.-P.; Topcu, G.; Erdelmeier, C.A.J.; Cordell, G.A. DNA as an Affinity Probe Useful in the Detection and Isolation of Biologically Active Natural Products. J. Natur. Prod. 1991, 54, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skehan, P.; Storeng, R.; Scudiero, D.; Monks, A.; McMahon, J.; Vistica, D.; Warren, J.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Boyd, M. New Colorimetric Cytotoxicity Assay for Anticancer-Drug Screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescifina, A.; Zagni, C.; Varrica, M.G.; Pistara, V.; Corsaro, A. Recent advances in small organic molecules as DNA intercalating agents: Synthesis, activity, and modeling. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 74, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, G.; Terenzi, A.; Lauria, A.; Almericom, A.M.; Leal, J.M.; Busto, N.; Garcia, B. DNA-binding of nickel (II), copper (II) and zinc (II) complexes: Structure–affinity relationships. Coord. Che. Rev. 2013, 257, 2848–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, B.; Rajendiran, V.; Maheswari, P.U.; Stoeckli-Evans, H.; Palaniandavar, M. Structures, spectra, and DNA-binding properties of mixed ligand copper (II) complexes of iminodiacetic acid: The novel role of diimine co-ligands on DNA conformation and hydrolytic and oxidative double strand DNA cleavage. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Busto, N.; Martínez-Alonso, M.; Leal, J.M.; Rodríguez, A.M.; Domínguez, F.; Acuña, M.I.; Espino, G.; García, B. Monomer–Dimer Divergent Behavior toward DNA in a Half-Sandwich Ruthenium (II) Aqua Complex. Antiproliferative Biphasic Ac-tivity. Organometallics 2015, 34, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Morán, O.A.; Villarreal, M.L.; Álvarez-Berber, L.; Meneses-Acosta, A.; Rodríguez-López, V. Cytotoxicity, Post-Treatment Recovery, and SelectivityAnalysis of Naturally Occurring Podophyllotoxins from Bursera fagaroides var. fagaroides on BreastCancer Cell Lines. Molecules 2016, 21, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudev, T.; Lim, C. Tetrahedral vs Octahedral Zinc Complexes with Ligands of Biological Interest: A DFT/CDM Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11146–11153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
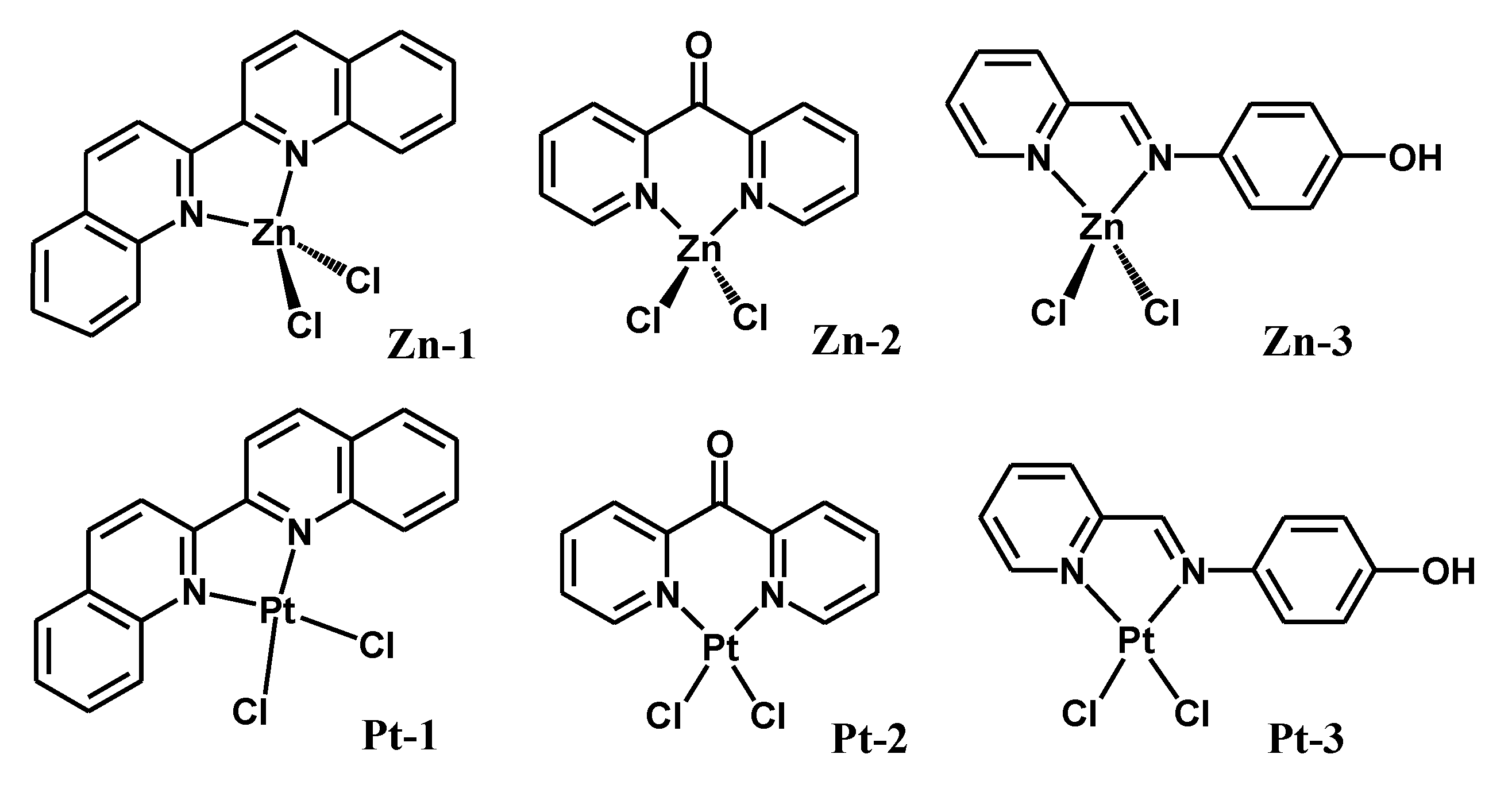
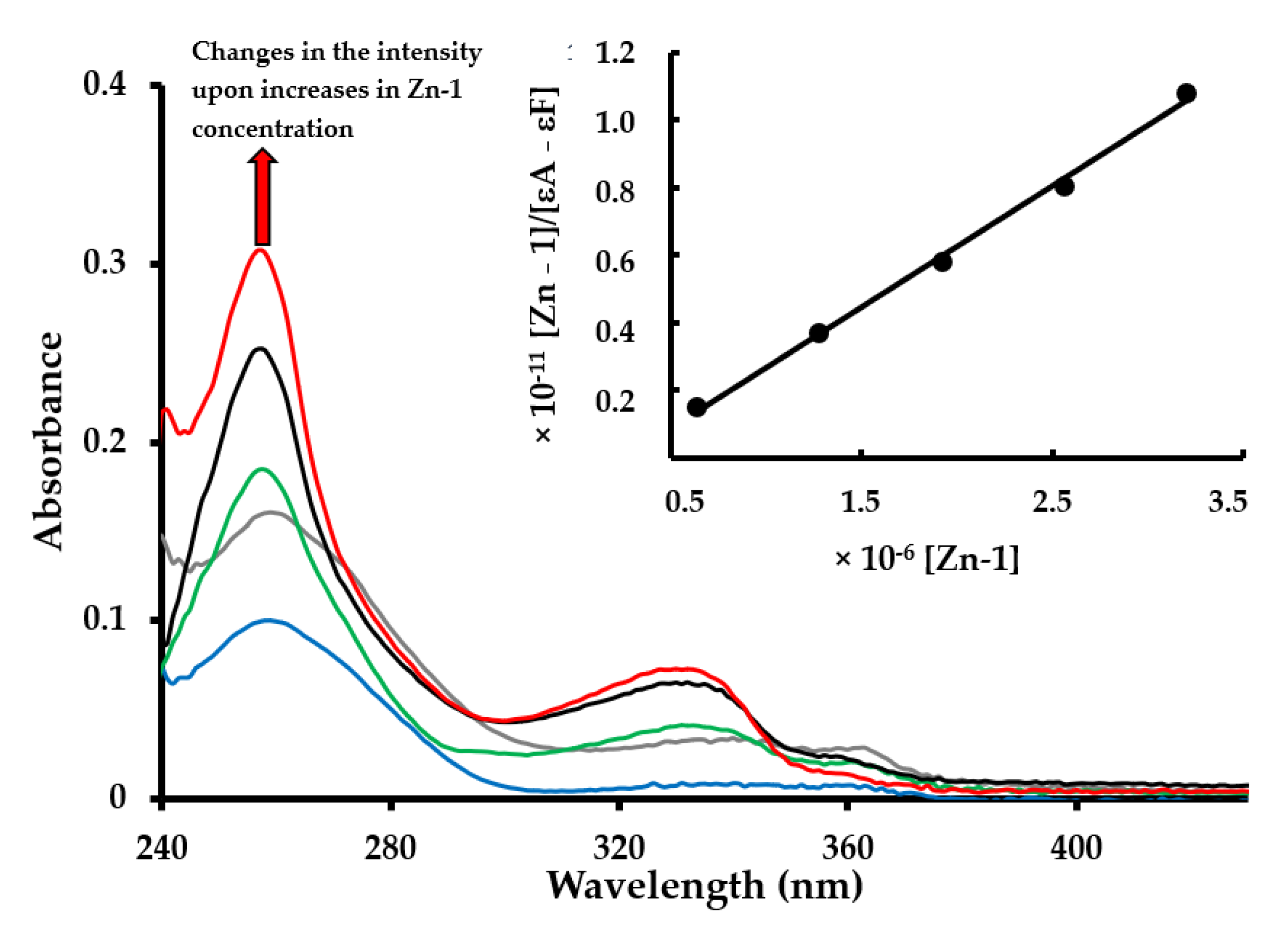
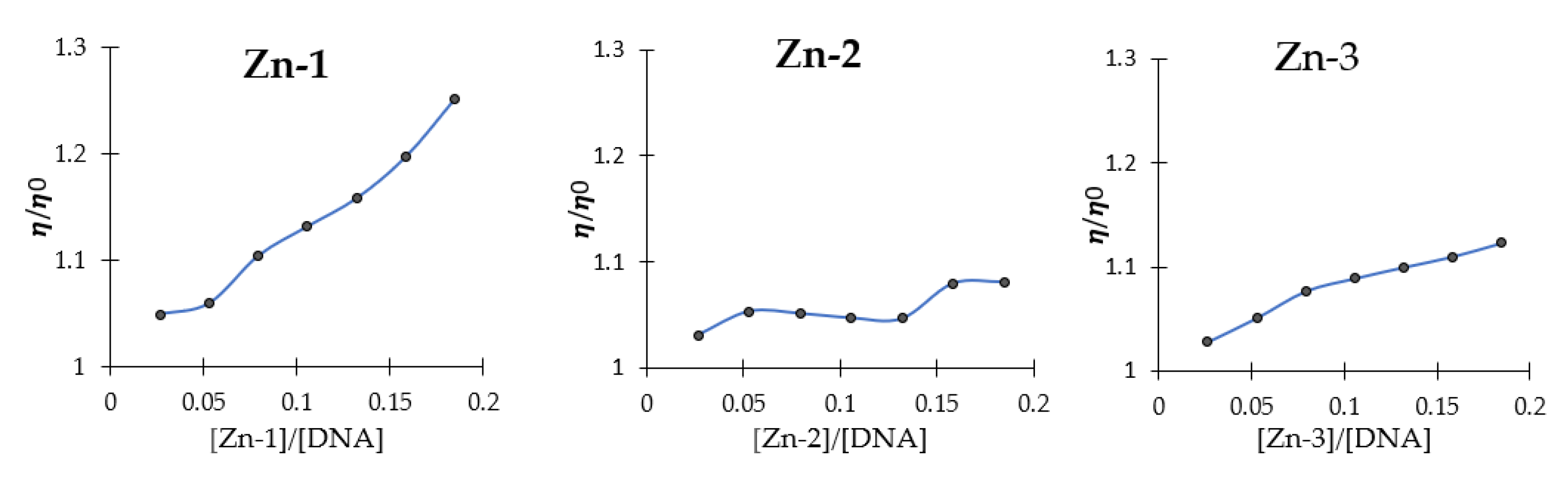
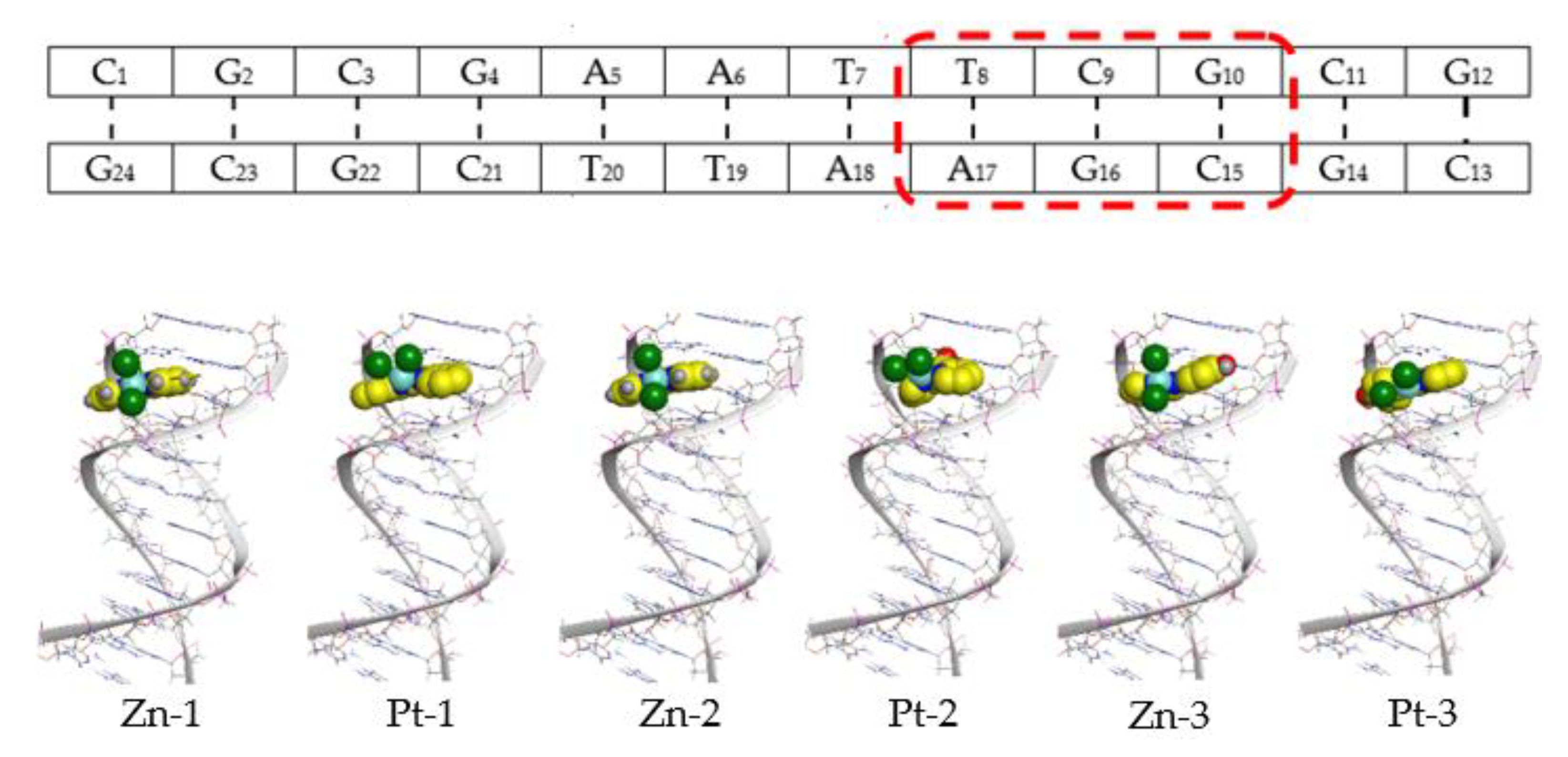
| Compound | Kb (Intrinsic Binding Constant) | Docking Scores | Proposed Interaction by Docking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn-1 | 6.67 × 106 | −3.45 | H-π (G16—biquinoline) H-π (A17—biquinoline) |
| Pt-1 | 4.44 × 106 | −3.34 | None |
| Zn-2 | 5.00 × 105 | −4.78 | H-acceptor (G10—dipyridylketone) H-π (A17—dipyridylketone) |
| Pt-2 | 1.00 × 106 | −5.52 | H-acceptor (G14—dipyridylketone) |
| Zn-3 | 1.00 × 106 | −5.42 | H-acceptor (G16—Cl) |
| Pt-3 | 5.00 × 105 | −4.58 | None |
| Compound | COLO 205 | RCC-PR | LLC-MK2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn-1 | 9.46 ± 0.02 | 15.54 ± 0.77 | 695.37 ± 42.89 |
| Pt-1 | 21.43 ± 0.04 | 17.81 ± 0.14 | 453.77 ± 6.99 |
| Zn-2 | 8.10 ± 0.08 | 14.41 ± 0.10 | 627.17 ± 37.36 |
| Pt-2 | 14.82 ± 0.06 | 18.69 ± 0.04 | 397.30 ± 12.26 |
| Zn-3 | 8.18 ± 0.01 | 13.54 ± 0.03 | 534.37 ± 37.23 |
| Pt-3 | 14.69 ± 0.02 | 15.47 ± 0.04 | 472.87 ± 17.81 |
| Cisplatin | 12.59 ± 0.04 | 11.07 ± 0.07 | 378.50 ± 31.84 |
| Sunitinib | 9.22 ± 0.01 | 8.74 ± 0.04 | 548.13 ± 61.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babgi, B.A.; Domyati, D.; Abdellattif, M.H.; Hussien, M.A. Evaluation of the Anticancer and DNA-Binding Characteristics of Dichloro(diimine)zinc(II) Complexes. Chemistry 2021, 3, 1178-1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3040086
Babgi BA, Domyati D, Abdellattif MH, Hussien MA. Evaluation of the Anticancer and DNA-Binding Characteristics of Dichloro(diimine)zinc(II) Complexes. Chemistry. 2021; 3(4):1178-1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3040086
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabgi, Bandar A., Doaa Domyati, Magda H. Abdellattif, and Mostafa A. Hussien. 2021. "Evaluation of the Anticancer and DNA-Binding Characteristics of Dichloro(diimine)zinc(II) Complexes" Chemistry 3, no. 4: 1178-1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3040086
APA StyleBabgi, B. A., Domyati, D., Abdellattif, M. H., & Hussien, M. A. (2021). Evaluation of the Anticancer and DNA-Binding Characteristics of Dichloro(diimine)zinc(II) Complexes. Chemistry, 3(4), 1178-1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemistry3040086








