Abstract
The characteristics of Food Supply Chains (FSC) make them hard to manage properly, and many efforts have been conducted to alleviate the difficulties related to their management, especially when it comes to integrating the latest Information and Communications Technologies. The Internet of Things (IoT) has shown to be very beneficial in providing a holistic and real-time vision of FSCs. Blockchain, with its decentralization and immutability, is another promising technology, that is showing a great potential in managing FSCs. A lot of research has been carried out to prove the advantages of each of these technologies on its own. However, the research investigating their adoption together is still not enough. Our paper presents a study of recent advances in the integration of IoT and Blockchain in Food Supply Chain Management (FSCM) over the past five years. We identify key research trends, analyze the benefits and limitations of IoT–blockchain integration, and highlight major challenges hindering large-scale adoption. Finally, we propose future research directions to address these challenges and improve the adoption of IoT–blockchain solutions in FSCs. This study aims to serve as a reference for researchers and practitioners seeking to understand and advance the integration of these emerging technologies in FSCM.
1. Introduction
One of the most critical global challenges today is meeting the food needs of the world’s population. Governments and private organizations have invested and still invest a tremendous amount of effort and resources to cope with this challenge, both at the corporate and academic levels. FSCs are a key pillar in achieving this goal.
In general, the goal of supply chain management is to deliver to the consumer the expected product. This has become very difficult, due to the fact that consumers are now more demanding than ever, in terms of product quality. Supply chains have some common goals and characteristics, but depending on the product or service in the center of the chain, more specific goals and characteristics can arise.
In particular, FSCs, when compared to other supply chains, have special characteristics, most importantly the fact that the majority of food products are perishable and have limited shelf life. The shelf life is the period during which the decrease in quality of perishables remains acceptable to end users; in simpler words, it is the period of time food can be kept before it should be disposed of [1]. This explains why in FSCs, in addition to focusing on reducing costs, minimization of food waste and loss is considered while trying to comply with health and safety regulations in all phases of the supply chain [2]. Another characteristic of FSCs is that they span wide geographic areas and include multiple stakeholders, which adds to the complexity of their management. To deal with these challenges, there is a need for developing adequate monitoring and traceability systems for FSCs [1]. This is why a significant part of the resources invested in the FSC market is intended to explore new technological solutions that go beyond the limits of existing ones.
Using the SWOT framework, Table 1 analyzes the challenges encountered at each stage of the food supply chain by identifying key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The analysis highlights that investing in advanced technologies throughout the supply chain presents substantial opportunities to improve efficiency, enhance traceability, promote sustainability, and strengthen resilience, effectively addressing critical weaknesses.

Table 1.
SWOT Analysis on Food Supply Chain Management Challenges.
IoT, with its ubiquitous interconnection, sensing capabilities, and computing model, proved to be a practical solution for many problems. That is why its application in the FSCM seemed logical. Indeed, there are many examples of IoT adoption in FSCM, with more promising future applications. While IoT can provide real-time product monitoring and traceability, it cannot ensure the transparency of the supply chain and the trust between its participants. This is where the Blockchain technology can help. This Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) has the potential of tracking FSCs’ transactions and maintaining its data integrity. Additionally, it enhances transparency, security, and collaboration within the supply chain actors [17].
The integration of these two advanced technologies together in FSCM has been investigated in recent years. This paper’s goal is to provide a brief overview of these two technologies, and analyze the work that has been conducted in this area in the last five years. To establish the necessity of this survey and position our contribution within the existing body of research, we summarize previous reviews on the integration of IoT and Blockchain in FSCM over the past five years in Table 2. The analysis reveals that only a limited number of studies have examined the application of these two emerging technologies together and their impact on FSCM. Furthermore, these reviews primarily covered research conducted before 2022. In contrast, our study presents a comprehensive survey focusing on English peer-reviewed articles published between January 2020 and July 2025, making it an up-to-date reference for researchers and practitioners aspiring to work in this field.

Table 2.
Existing review papers on the integration of IoT and Blockchain in FSCM.
To that end, our survey will try to answer the following research questions:
RQ1: What research has been done on the adoption of Blockchain and IoT in FSCM?
RQ2: What are the advantages of combining Blockchain and IoT in FSCM?
RQ3: What are the key challenges that hinder the adoption of these two technologies in the FSCM?
The structure of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 outlines the methodology adopted in this study. Section 3 presents an overview of IoT and Blockchain technologies. Section 4 analyzes the limitations of IoT within the context of FSCM. Section 5 provides a detailed discussion on the integration of Blockchain with IoT as a means to address these limitations. Section 6 highlights the key challenges that hinder the adoption of both technologies in managing FSCs. Section 7 discusses potential avenues for future research. Finally, Section 8 offers concluding remarks and emphasizes directions for further investigation.
2. Methodology
The literature search for this systematic review was conducted using a structured, keyword-based strategy. Key search terms included: “Internet of Things in food supply chain”, “Blockchain in food supply chain”, “Blockchain and IoT integration”, “traceability in agri-food using blockchain”, and “smart food logistics”. These keywords were used to query major academic databases such as Scopus, Web of Science, IEEE Xplore, SpringerLink, and ScienceDirect.
To ensure the relevance and quality of the included studies, the following inclusion criteria were applied:
- Publication period: Only articles published between January 2020 and July 2025 were considered.
- Language: Articles had to be written in English.
- Type of publication: Only peer-reviewed journal articles were included.
Following the initial search, the titles and abstracts of all retrieved articles were screened to assess their relevance to the study objectives. Articles that did not address the adoption, integration, or application of IoT and Blockchain technologies in the food supply chain were excluded at this stage. Screening at the title and abstract level facilitated the efficient removal of out-of-scope or irrelevant studies prior to full-text review.
3. Background
3.1. The Internet of Things
IoT is a rapidly growing technological paradigm that is transforming our lives. The term Internet of Things was first used by Kevin Ashton in 1999 to describe a network of objects connected using Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) [22]. IoT can be simply seen as a large network of connected things communicating data between each other, and some computer databases, along with protocols, standards, platforms, and more, that help establish this interconnection [23]. Some IoT enabling technologies are RFID, Wireless Sensors Networks (WSNs), Cloud computing, and Data Analytics [22]. Figure 1 shows how RFID is used within IoT.
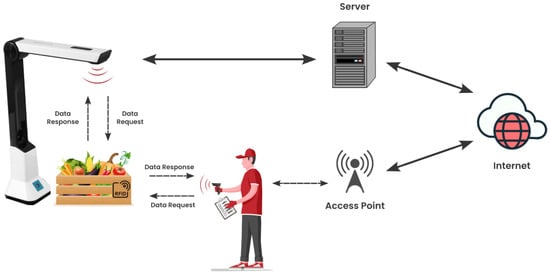
Figure 1.
The Common Architecture of Identification Systems in IoT-Enabled Environments [24].
Since IoT’s introduction, there has been no standard architecture, to be adopted by everyone, despite the numerous research that have been conducted. We can find in the literature different architecture proposals; some of them are more used than others, namely the three-layer, four-layer, and five-layer architectures [25,26,27,28].
The three-layer architecture is a basic imagination of IoT, where the perception layer is responsible for collecting real-time information through sensors, and conducting actions through actuators. The collected data is communicated via the network layer, and the information are finally put to use in the application layer [25,26,27].
The rise in popularity of IoT and its adoption to more complex systems motivated the proposition of more detailed and comprehensive architectures. The four-layer architecture, for example, which in addition to the components of the three-layer architecture, introduces another new layer. The processing layer, which intermediates the network and the application layers, relies on the cloud and edge computing technologies to perform data aggregation, computation, storage, and analysis [28].
Moreover, after the integration of IoT in real world businesses, researchers proposed to add a fifth layer, creating the five-layer architecture (shown in Figure 2). This fifth layer is called the business layer, and it is placed on top of the application layer, with the aim to translate technical outcomes into strategic decisions and actionable insights, to create business value [25,27].
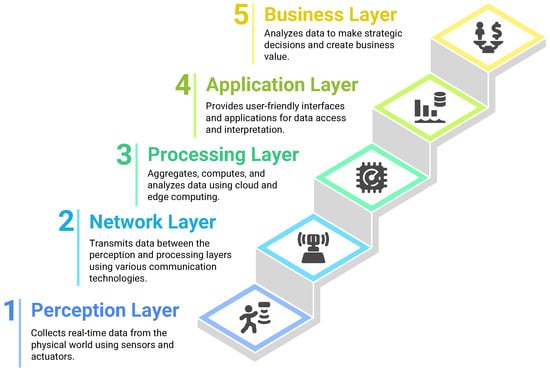
Figure 2.
Five-layer IoT architecture.
IoT is revolutionizing the way devices, machines, systems, and humans interact, significantly enhancing efficiency, productivity, and quality of life. Its applications include smart homes and cities, smart transportation and logistics, smart manufacturing and industries, smart healthcare, smart safety and security, smart grids, smart retailing, and smart agriculture, among others [26,29,30]. Figure 3 illustrates the most common applications of IoT.
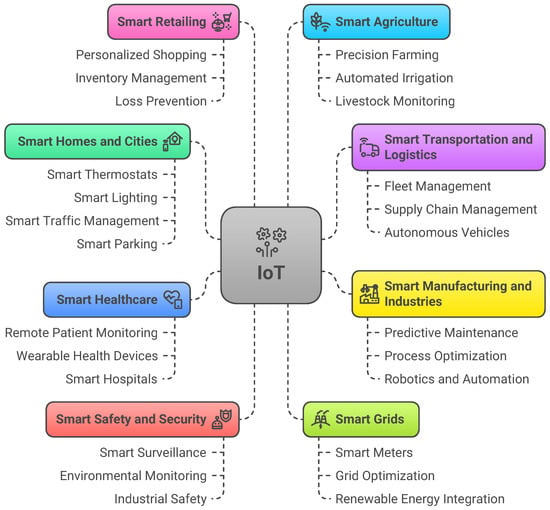
Figure 3.
Most common applications of the IoT.
3.2. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a tamper-proof, append-only, distributed ledger, shared on a peer-to-peer network, storing in a cryptographically secure way a set of transactions that are logically ordered. Transactions are only committed when a consensus on their validity is reached by the network peers [31,32]. Each time transactions are validated, a new block is created and added to the chain, thus leading to the name Blockchain. Blocks are composed of two major parts, i.e., a header and a body. The block’s header contains metadata about the block, including information facilitating its linkage to other blocks in the chain, along with a timestamp, a nonce, and a merkle tree [32]. The block’s body contain the transactions, which represent a transfer of value from one Blockchain address to another [31]. It is worth noting that the structure’s details might change from one Blockchain platform to another, while keeping the defining blocks in place. Figure 4 represents the basic structure of a Blockchain.
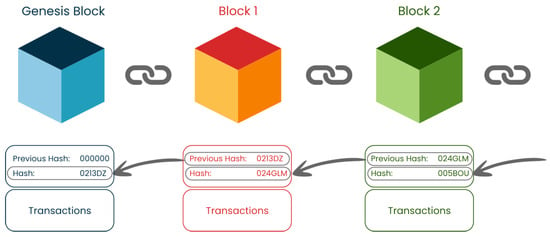
Figure 4.
The basic structure of a Blockchain.
Since its first introduction by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008, Blockchain has attracted a lot of attention from researchers and industry practitioners alike, thanks to its defining features. Blockchain is immutable, which means that when data is added, it cannot be modified or deleted [33]. Additionally, Blockchain is decentralized, both in data storage and decision making, and it does not require any central authority to function [34,35]. Moreover, the security of Blockchain is guaranteed by multiple techniques put in place, from hash functions to digital signatures and more [34]. Furthermore, allowing public access to transactions stored on the Blockchain renders it transparent [34]. Besides, Blockchain transactions are time-stamped, which facilitates their traceability [34]. Finally, Blockchain features a notion of programmable agreements that are self-executable when a set of predefined conditions are satisfied, and they are known as smart contracts. These smart contracts help eliminate the requirement for a trusted third party [35,36].
Since 2008, Blockchain has attracted growing attention from both academia and industry, evolving through four major generations that have progressively expanded its capabilities and application domains (see Figure 5).
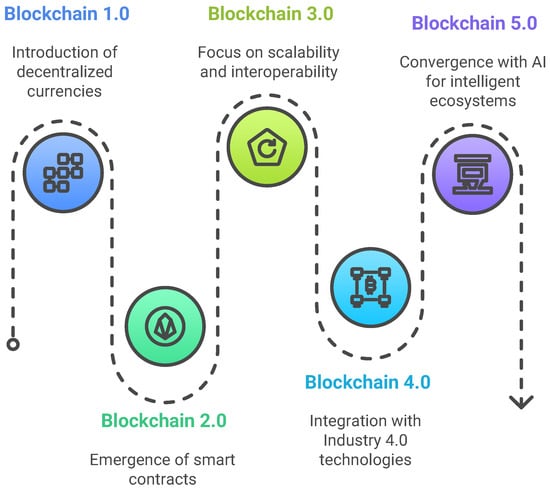
Figure 5.
The Evolution of Blockchain Technology: From Decentralized Currencies to Intelligent Ecosystems.
The first generation, known as Blockchain 1.0, focused primarily on decentralized digital currencies, with Bitcoin offering a peer-to-peer electronic cash system secured through Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus [37]. Early studies [33,38,39,40] explored the underlying cryptographic primitives, distributed consensus, and immutability features that made blockchain a revolutionary financial infrastructure. The second generation, Blockchain 2.0, emerged with Ethereum’s launch in 2015 [41], introducing smart contracts and self-executing code embedded in the blockchain, which enabled decentralized applications (DApps) and opened the door to novel use cases beyond finance, including healthcare [42,43,44], supply chains [45,46], and automated governance systems [47,48]. These smart contracts were extensively analyzed for their potential to automate trust and reduce transactional friction in complex multi-stakeholder environments [49,50]. Blockchain 3.0 addressed critical limitations related to scalability, interoperability, and energy consumption. Platforms like Cardano, Polkadot, and Cosmos introduced energy-efficient consensus mechanisms such as Proof-of-Stake (PoS), sharding, and cross-chain interoperability protocols, which significantly enhanced throughput and adaptability [51,52]. This evolution facilitated blockchain’s penetration into broader sectors, including digital identity verification, secure healthcare data exchange, and transparent logistics management [53,54,55]. More recently, Blockchain 4.0 has emerged [56], aiming to align the technology with the principles of Industry 4.0 by integrating it with AI, the IoT, and big data analytics to enable intelligent, automated, and secure digital ecosystems [57,58,59,60]. Studies have shown that in this context, blockchain serves as a backbone for smart manufacturing, digital twins, predictive maintenance, and secure multi-agent IoT coordination [61,62,63], while also supporting privacy-preserving real-time data sharing in domains like healthcare and urban infrastructure.
Despite the vast body of work detailing blockchain’s technical underpinnings and sector-specific applications, ongoing research continues to explore its evolving role as a trusted infrastructure for decentralized autonomy, interoperability, and intelligent decision making across emerging digital economies. As a demonstration of this trajectory, Blockchain 5.0, exemplified by architectures like Doctrina, enables native on-chain AI execution, decentralized AI training, and autonomous decision making [45,64]. This convergence addresses critical gaps in AI dependency management and computational efficiency, positioning blockchain as a foundational layer for intelligent ecosystems in healthcare, energy, and Society 5.0.
4. The Adoption of IoT in FSCM
FSC chain refers to the processes that describe how food from a farm ends up on our tables. These processes include production, processing, distribution, consumption, and disposal [2]. Figure 6 depicts the movement of food and money in a simple “From Farm To Fork” model.
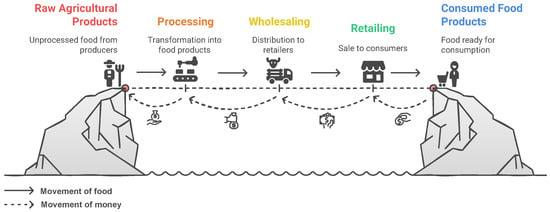
Figure 6.
Movement of food and money in a simple “From Farm To Fork” model.
Managing FSCs presents significant challenges, largely attributable to their inherent characteristics. FSCs are characterized by having multiple collaborating actors, spread out across a wide geographical area, leading to a difficulty in terms of logistics, information sharing, and money transfer. Moreover, they are characterized by the sensitive nature of food products, caused by environmental conditions, and their rapid quality degradation, as well as the dynamic nature of customer demands, and its affectability to social, economic, and natural factors from outside the supply chain.
All these aforementioned features lead to the loss of the equivalent of 1 billion meals every day, while 783 million people suffer from hunger, according to the UN’s Food Waste Index Report 2024 [65]. The report states that this loss is evaluated to be worth 1 trillion USD, and that it is affecting our environment by generating 10% of the global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Consequently, different actors, including governments, private organizations, and intergovernmental organizations, are more committed than ever to finding innovative solutions to tackle this global challenge.
Considerable efforts are directed towards exploring new information and communication technologies (ICT). ICT through its capability of internal (processes) and external (suppliers and customers) integration has been and continues to be an essential enabler for the FSCM [1]. Older FSCM systems used primarily RFID for product tracking, but to monitor the products and their ambient environments, some sort of sensing capabilities are now needed [22].
The primary role of IoT in the FSCM is to track, trace, monitor, and provide business values [19]. RFID offers tracking capabilities and WSN offers sensing capabilities; together, they are used for numerous applications, from monitoring livestock grazing behaviors and monitoring real-time temperature conditions, to tracking containers inside warehouses or on the back of a truck along the road [22]. The adoption of IoT means the use of a huge number of things (sensor, actuators, tracking devices, etc.) to manage the FSC, which means that a huge amount of data will be generated, Cloud computing can be used to handle the coming data from WSNs, and sometimes other layers (Fog and edge) are added to minimize the delay between information capture and decision making.
As mentioned before, the majority of food products are perishables, i.e., they are sensitive to temperature changes, such as meat, fruits, etc., which makes their transportation and distribution a critical stage in the FSCM process [22]. It requires end-to-end monitoring of the product’s quality parameters. Numerous sensor technologies have been developed for this purpose, including electrical, optical, thermal, and chemical sensors. Another promising application of IoT in FSCM is the use of active and intelligent packaging. Active packaging consists of incorporating active agents into packaging materials and works by absorbing food-derived chemicals or releasing active agents into the surrounding environment to extend the produce’s shelf life. Thus, intelligent packaging refers to a package that incorporates materials that can monitor the food quality [1]. IoT technologies can be adopted at all the stages of FSCM, with applications even for the retailing spaces management, such as loyalty card systems, On-Shelf Availability systems, real-time pricing mechanisms, smart carts, etc. [22].
In spite of the numerous advantages IoT has to offer in terms of product monitoring and traceability, it cannot cope with the FSC challenges related to security and privacy. For instance, the lack of trust between the various FSC stakeholders, the data privacy and integrity, and the single point of failure problem that centralized systems face. To tackle these challenges, researchers investigated the integration of IoT with other technologies. Blockchain as a distributed and cryptographically secure database seems to have a great potential to help IoT deal with these security and privacy-related challenges [21].
5. The Integration of Blockchain with IoT in FSCM
Blockchain is a transformative technology for addressing trust-related challenges [21]. It supports businesses through its decentralization, its enhanced security and transparency, bridging the gaps of trust between business partners, along with its increased efficiency, through process automation thanks to its smart contracts [66]. In recent years, this distributed ledger technology has been applied to various industries and research areas, including, finance, healthcare, government, education, transportation, manufacturing, supply chain, etc.
The integration of blockchain with emerging technologies demonstrates its transformative potential. In this section, we will discuss how Blockchain is being integrated with IoT to ensure sustainable, transparent, and efficient FSCs.
5.1. Application Categories
This subsection presents a thorough investigation into the deployment of Blockchain technology to enhance efficiency and ensure the integrity of FSCs. The study identifies and categorizes Blockchain use cases into three distinct categories: provenance and traceability, data management, and efficiency improvement.
5.1.1. Provenance and Traceability
Research has been conducted to discuss the integration of Blockchain and IoT to manage FSCs. The most common use of Blockchain and IoT in FSCs is to ensure an end-to-end product monitoring and traceability, with the aim to avoid food being either wasted or defrauded.
Building upon foundational work in secure tracking mechanisms for perishable food products, Sathiya et al. [67] established important principles for maintaining data security without compromising traceability. This groundwork enabled Yele and Litoriya [68] to advance the field by developing a comprehensive blockchain-based traceability system that empowers customers to track food origins within dining establishments, encompassing both ingredient sourcing and processing stages. However, the system’s validation was constrained by simulation testing with merely 15 nodes and the absence of pilot studies in operational restaurant environments. Moreover, the observed performance degradation with increasing node counts contradicts the claimed scalability advantages.
The integration of physical monitoring with blockchain technology has been further explored by Gondal et al. [69], who combined smart containers for real-time strawberry transportation monitoring with blockchain infrastructure to ensure comprehensive supply chain traceability. While this approach provides a robust monitoring framework, the research would benefit from more extensive investigation of blockchain security aspects beyond smart contract considerations.
In alignment with Industry 4.0 principles, Raza et al. [70] developed Agri-4-All, an IoT and blockchain-enabled traceability framework that complies with the Reference Architectural Model Industry 4.0 (RAMI 4.0). Despite demonstrating theoretical alignment with Industry 4.0 standards, the framework’s evaluation was limited to simulated environments using Ganache/Truffle rather than real-world IoT deployments. This limitation leaves claims regarding gas cost reduction and scalability unsubstantiated under large-scale operational conditions.
The dairy sector has seen notable innovation through Khanna et al. [71], who proposed a four-layer blockchain architecture designed to prevent contamination and adulteration in Indian dairy supply chains. Testing was conducted exclusively on Ethereum test networks; however, without validation in actual supply chain environments. This approach raises significant questions about scalability, stakeholder adoption, and real-world performance while failing to address the economic feasibility for small-scale Indian dairy farmers.
Environmental sustainability in food traceability has been addressed by Varavallo et al. [72], who developed a traceability system specifically for Fontina cheese supply chains. Their claims of low energy consumption lack empirical substantiation through comparative analysis. Although Algorand’s Pure Proof of Stake algorithm is theoretically energy-efficient, the study provided no concrete energy consumption metrics or scalability assessments under high transaction volumes.
Livestock supply chain traceability has been advanced by Khan et al. [73] through an IoT and blockchain-enabled food provenance system. The reported performance metrics were derived from simulations and open-source datasets rather than operational supply chains, limiting their practical relevance. Scalability claims involving 800 nodes remain theoretical without field validation, and the critical issue of interoperability with existing legacy systems was not addressed.
In the grain logistics sector, Hong [74] recommended integrating IoT technologies such as RFID with blockchain systems for real-time grain movement and quality data capture. The study suffers from methodological limitations, including unsubstantiated performance claims without comparative baselines and insufficient experimental detail. The proposed innovation provides only a generic system design without significant technical depth.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Iftekhar and Cui [75] developed an IoT–blockchain model for food product tracing that incorporates safety regulation compliance verification. Their three-layer architecture encompasses physical, blockchain, and application layers. However, the system lacks real-world implementation validation, leaving tamper-proofing and transparency claims unverified. Additionally, the on-chain recording of worker health information raises substantial GDPR compliance and ethical concerns.
The poultry and egg sectors have been examined by Bumblauskas et al. [76], who explored establishing traceable egg supply chains using IoT and blockchain technologies for comprehensive farm-to-consumer visibility. The research lacks quantitative blockchain performance analysis and fails to compare the Proof of Elapsed Time consensus algorithm with alternative approaches. Similarly, Majdalawieh et al. [77] addressed poultry supply chain transparency through an integrated IoT–blockchain system designed to enhance traceability and auditability. Their framework supports governmental inspection by providing regulatory agencies with direct access to traceability data. However, the reliance on Proof-of-Work is poorly suited to the permissioned business context, where verified participants make PoW’s distrust mitigation redundant while imposing unnecessary energy and latency costs.
Recent developments demonstrate continued innovation in this domain. Farina et al. [78] introduced a comprehensive end-to-end traceability framework that leverages IoT sensors for heterogeneous agri-food data capture. The system employs AI and analytics tools for insight refinement while utilizing distributed ledger technology for secure stakeholder collaboration. Data spaces facilitate governance and standardization, enabling seamless system integration. However, scalability discussions for complex supply chains involving numerous stakeholders remain limited, and the study lacks analysis of technical and organizational integration barriers.
Adhiwibowo et al. [79] proposed a web-based traceability system that integrates IoT for real-time data acquisition within halal-compliant animal supply chains, employing a dual-blockchain architecture for data integrity. User testing was limited to only 15 participants, and the system’s scalability to real-world supply chains was not demonstrated. The specific blockchain platform utilized was not identified. Guo et al. [80] developed a comprehensive traceability solution combining blockchain immutability with IoT’s real-time capabilities for systematic, accountable food quality assurance. While the study references tamper resistance and privacy protection, it lacks detailed threat modeling or security analysis and provides no mitigation strategies for IoT device spoofing, Sybil attacks, or smart contract vulnerabilities. Privacy protection claims lack specifics regarding cryptographic mechanisms, and integration with legacy systems remains unaddressed.
Lukacs et al. [81] designed a cost-effective integrated digital system for standard agri-food production environments, demonstrated through certified Hungarian sweet potato production. The solution incorporates Near-Infrared Spectroscopy, Computer Vision, RFID, IoT, and blockchain technologies for comprehensive traceability and quality assurance. However, extensive real-world validation is lacking, and the work inadequately addresses challenges arising from IoT data volume and velocity in large-scale supply chains.
Addressing broader structural challenges, Wang et al. [82] identified significant limitations in conventional Human–Cyberphysical Systems, including poor scalability, weak data security, limited interoperability, and supply chain transparency gaps. Their proposed blockchain-enhanced architecture integrates blockchain with IoT, AI, and Federated Learning across three distinct layers: the Physical System Layer for data collection, the Network System Layer for secure storage and AI training, and the Human–Machine Interaction Layer for user interfaces. However, real-world scalability for large agricultural operations remains untested, and the blockchain’s environmental impact in agricultural contexts is not quantified.
Villegas-Ch et al. [83] proposed an architecture that fuses IoT devices with efficient communication protocols including MQTT, CoAP, and LoRa for real-time, immutable data collection while maintaining energy efficiency through lightweight blockchain technologies. Testing was constrained to 10 nodes and 50 sensors, whereas real-world supply chains typically require significantly more devices, leaving scalability beyond this limited configuration unproven.
Finally, Sheriff and Aravindhar [84] introduced an advanced Federated Learning framework for Smart Supply Chain Management, emphasizing decentralized, privacy-preserving AI model training. The solution incorporates Differential Privacy, Secure Multi-Party Computation, and Homomorphic Encryption to ensure participant confidentiality. Quantum-Inspired Deep Reinforcement Learning enhances blockchain performance dynamically, while Lightweight Lattice-Based Cryptographic Hashing provides quantum-resistant, energy-efficient security aligned with NIST’s CRYSTALS-Dilithium standard. However, reported results rely exclusively on synthetic simulations, and variational quantum circuit simulation at scale may exceed classical hardware capacity. The study lacks integration analysis with existing blockchain platforms and formal cryptanalysis of the proposed cryptographic scheme.
5.1.2. Data Management
Alongside the previously mentioned traceability systems, IoT and Blockchain technologies have been extensively leveraged to enhance productivity control and data-driven decision making within FSCs.
In the realm of food quality assessment, Sathiya et al. [67] developed an innovative approach that combines IoT sensor data with Blockchain-secured storage to evaluate food product quality using an Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS). While this integration represents a meaningful advancement in automated quality control, the methodology exhibits several limitations that constrain its practical application. The ANFIS model’s dependence on a restricted set of sensor parameters including temperature, humidity, light, and vibration overlooks essential perishability indicators such as microbial contamination levels and packaging structural integrity. This narrow data foundation compromises the model’s ability to generate reliable, generalizable shelf-life predictions across diverse real-world scenarios. Furthermore, the absence of comprehensive, scenario-diverse datasets undermines the establishment of robust correlations necessary for accurate shelf-life estimation, thereby limiting the approach’s commercial viability.
Sales forecasting represents another significant application domain where IoT–blockchain integration has shown promise. Khan et al. [73] developed a sophisticated hybrid predictive model that leverages IoT-derived Blockchain data to forecast product sales patterns. Their approach incorporates multiple neural network architectures including recurrent neural networks (RNNs), long short-term memory (LSTM), and gated recurrent units (GRUs) with parameter optimization conducted through Genetic Algorithm (GA) techniques to enhance predictive performance. However, the methodology presents several critical shortcomings that limit its effectiveness in specialized supply chain contexts. The reliance on generic grocery datasets renders the model inappropriate for meat supply chains, which possess distinct characteristics and requirements. Additionally, the arbitrary selection of an LSTM-GRU hybrid architecture, coupled with the computationally intensive GA optimization process, lacks theoretical justification and practical validation of its superior performance over simpler alternatives. Most notably, the research fails to assess the model’s impact on key business performance indicators.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) as an analytical cornerstone has further advanced FSC data management capabilities. Farina et al. [78] positioned AI as the central analytical engine within their comprehensive framework, designed to transform diverse sensor-generated data into actionable operational insights. Their system addresses multiple critical functions including operational optimization, regulatory compliance monitoring, fraud detection, and comprehensive supply chain transparency. The framework achieves synergy between AI analytical capabilities and Blockchain data integrity assurance, while incorporating data spaces to facilitate seamless interoperability across diverse systems and stakeholder networks. This creates a robust, scalable traceability ecosystem with applications extending beyond agri-food sectors. However, despite AI’s prominent positioning as a transformative technology, the research suffers from insufficient technical substantiation. The absence of detailed model specifications, quantitative performance metrics, and empirical validation through real-world testing constitutes a fundamental methodological weakness that undermines the framework’s credibility. Similarly, Lukacs et al. [81] implemented AI-driven analysis of IoT and Blockchain-captured data to enable non-destructive sweet potato quality assessment within smart agricultural environments. While this application demonstrates AI’s potential in precision agriculture, the research methodology presents significant limitations. The Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) calibration relies on a constrained sample size of merely 200 specimens with insufficient validation protocols. To establish robust predictive capabilities, the methodology requires extensive sampling across varied seasonal conditions, geographical regions, and cultivar types, which would substantially improve the approach’s reliability and broader applicability.
5.1.3. Efficiency Improvement
The integration of transaction and process automation in FSCs through blockchain-enabled smart contracts represents a fundamental transformation in how food products are managed, tracked, and delivered. These self-executing contracts systematically automate critical operations while reducing manual intervention and enhancing transparency and efficiency throughout supply chain processes.
Recent research demonstrates the versatile applications of smart contracts across various FSC contexts. Gondal et al. [69] implemented smart contracts to manage buyer–consumer interactions by automating product status updates and providing real-time notifications to end-users regarding any changes. However, their approach assumes binary outcomes (e.g., selfcheck_result == 1 or 0), which fail to capture real-world conditions such as partial damage or environmental fluctuations during transit. While payment automation (sendMoney()) triggers fund release upon container arrival, it lacks mechanisms to verify product quality at the receiver’s end, with physical inspection remaining outside the contract logic. Building on this foundation, Chatterjee et al. [85] developed a smart contract-based system enabling distributors, wholesalers, and retailers to synchronize supplier orders, invoices, and shipments while facilitating automatic payment settlements. Nevertheless, their implementation relies on binary checks (e.g., if (Inventory > Quantity)), which inadequately address real-world complexities such as partial shipments, quality deviations, or transit delays. The system lacks provisions for graded conditions, such as applying penalties for temperature excursions, and depends on manual inputs like retailers encrypting item lists, reducing real-time responsiveness.
The agricultural sector has witnessed similar innovations, with Raza et al. [70] demonstrating how smart contracts can autonomously manage data logging, trigger irrigation and pesticide systems, and execute payment transfers without human intervention. However, their implementation employs rigid thresholds (e.g., soil moisture = 70–88%) without adapting to dynamic conditions such as weather variations or crop-specific requirements, where machine-learning-driven thresholds would prove more effective. These systems assume seamless integration of IoT sensor data into smart contracts yet omit oracle mechanisms (e.g., Chainlink) to validate real-world data. Furthermore, they lack safeguards against erroneous or fraudulent sensor inputs, creating vulnerabilities where a single compromised sensor could trigger incorrect irrigation actions.
The dairy industry has particularly benefited from smart contract implementations. Khanna et al. [71] employed these contracts to streamline information exchange among stakeholders, significantly improving coordination and traceability. While IoT sensors are referenced for data collection, the integration between sensor data and smart contract execution remains unclear. Although the system incorporates mechanisms to initiate recalls for contaminated batches, it fails to consider contamination propagation in downstream products, such as cheese or butter produced across multiple batches, and overlooks automated refund processes for end consumers. Complementing this work, Biradar et al. [86] utilized smart contracts to automate consumer order acceptance through social platforms while providing secure access to blockchain-stored traceability data. Despite assertions that smart contracts accept orders, the study lacks technical details on contract logic, triggering conditions, and integration with IoT and data pipelines. While the Gannet Vulture Optimization Algorithm with Deep Maxout Network (GVOA-DMN) model evaluates food quality, its lack of integration with smart contracts limits the system’s capacity for automated actions based on these evaluations.
The integration of IoT devices with smart contracts has further enhanced operational capabilities, as demonstrated by Khan et al. [73], who showed how smart contracts can register IoT devices on blockchain networks and manage their operations autonomously, though technical implementation specifics remain limited. Advanced monitoring and compliance applications represent another critical area of smart contract deployment. Majdalawieh et al. [77] applied smart contracts to log food quality data collected by IoT devices and issue real-time alerts for violations that could result in product spoilage or health risks. However, the system lacks mechanisms to validate sensor data integrity despite its heavy dependence on IoT sensors.
Uyar et al. [87] developed smart contracts that continuously validate environmental thresholds through real-time IoT sensor data, issuing on-chain compliance certificates for product batches, meeting traceability and environmental integrity requirements throughout their lifecycle. While sensor data is digitally signed, the design lacks on-chain validation of sensor calibration status and mechanisms to detect compromised devices. Sheriff and Aravindhar [84] further advanced this approach by using smart contracts to automatically validate product safety thresholds, flag non-compliant products to mitigate contamination risks, and verify product movement and batch delivery status. Although QI-DRL improves contract execution efficiency, it overlooks the inherent bottlenecks of on-chain computation, where dynamic adjustments lead to increased gas fees, particularly during network congestion periods.
Specialized applications have addressed unique supply chain challenges across different sectors. Farina et al. [78] deployed smart contracts to automate cattle ownership transfers, while Guo et al. [80] implemented multiple smart contracts governing relationships between consecutive supply chain actors, incorporating penalty mechanisms for parties violating agreed-upon terms. However, these contracts lacked the complex conditional logic needed to automate broader supply chain processes, including automatic quality checks, compliance enforcement, and payment settlements. The sophistication of smart contract applications is exemplified by Lukacs et al. [81], who used these contracts to enforce data integrity by storing predefined Smart Attribute Definitions (SADs) for key parameters, automating compliance checks, controlling rule modification rights, and enabling traceability inheritance through SubXiD identifiers linking aggregated and individual batches. Despite claims that smart contracts enable “self-executing” compliance checks, technical implementation details remain unspecified.
Beyond operational automation, smart contracts have proven instrumental in securing and streamlining financial transactions across FSCs. For highly perishable goods such as strawberries, Gondal et al. [69] demonstrated how smart contracts can initiate payment disbursements based on real-time environmental conditions during shipment. Within the Indian dairy industry, Khanna et al. [71] illustrated how trustless payments can be enabled by linking them to delivery verification and product quality assurance. The effectiveness of smart contracts in enforcing payment policies and maintaining tamper-proof audit trails in blockchain-based supply chain systems has been further validated through formal modeling approaches [88,89].
While these studies innovatively integrate blockchain and IoT for traceability, their payment automation remains underdeveloped. The smart contract logic is overly simplistic, failing to capture real-world complexities and lacking mechanisms to handle adversarial scenarios. Although the contracts enable refunds to receivers upon violations, they lack protocols to resolve conflicts arising from false violation claims, sensor inaccuracies, or subjective quality disputes. These limitations highlight the need for more sophisticated contract logic that can accommodate the nuanced realities of food supply chain operations.
Table 3 summarizes the different application categories, along with the targeted food products.

Table 3.
IoT–Blockchain-enabled application in FSCs and their targeted products.
5.2. Blockchain Types
Blockchain technology can be classified into various types based on its structure, accessibility, and use cases. The primary classification is based on the accessibility and how permissions are managed, in addition to the structure of the Blockchain itself. Figure 7 outlines the major Blockchain categories.
5.2.1. Permissionless Blockchain
A permissionless Blockchain network operates as a decentralized system of interconnected computers, each maintaining a copy of a shared ledger. These computers adhere to a standardized set of software protocols, enabling all participants within the network to seamlessly read, submit, and validate transactions without prior approval from a central authority [91]. This category is referred to in the literature as public Blockchain. Its public nature, and the anonymity it ensures, make this type the number one option for cryptocurrencies, for instance Bitcoin [92].
This Blockchain type is widely used in FSCM literature [67,69,71,72,77,89,93].
5.2.2. Permissioned Blockchain
As opposed to a permissionless Blockchain, a permissioned Blockchain eliminates the anonymity, by ensuring that network participants’ identities have to be verified and authorized, before accessing transactions data [92,94]. It is generally utilized by entities sharing common business goals, without fully trusting each other. One such case is the supply chain industry [92].
Based on their governance, permissioned Blockchains can be classified into private Blockchains and consortium Blockchains. A private Blockchain is centrally managed by a single entity, whereas a consortium Blockchain is governed by a group of entities working collaboratively [32].
Considering that most of the studied applications did not focus on integrating cryptocurrencies in FSCs, the full decentralization of FSCs was not a high priority. As a matter of fact, researchers gave more attention to improving the Blockchain’s throughput, and seeing how much ensuring the security and governance of public Blockchains costed in terms of time and computing resources, numerous researchers opted to permissioned Blockchains, for the simple reason that FSC stakeholders are known and identifiable, which eliminates the need for time- and resource-consuming security mechanisms. Private Blockchain’s higher throughput and scalability motivated some authors to adopt it, including [73,74,79,87].
However, private Blockchain is better suited for supply chains managed by a single company, since a central authority is needed to set the rules and control the network, whereas in FSCs with multiple collaborating companies and entities, it would be very difficult to delegate all the authority to a single stakeholder. This is where a consortium Blockchain can shine, given that it combines the advantages of private and public Blockchains. A consortium or a federated Blockchain decentralizes the management among a consortium of stakeholders, ensuring more decentralization than a private Blockchain, but only allowing trusted parties to be part of this consortium, resulting in ensured safety and high throughput at the same time. Consequently, its adoption in FSCs is gaining more attention [70,75,80,81,95,96].
Figure 7 shows the Blockchain types from decentralization and identity management perspectives.
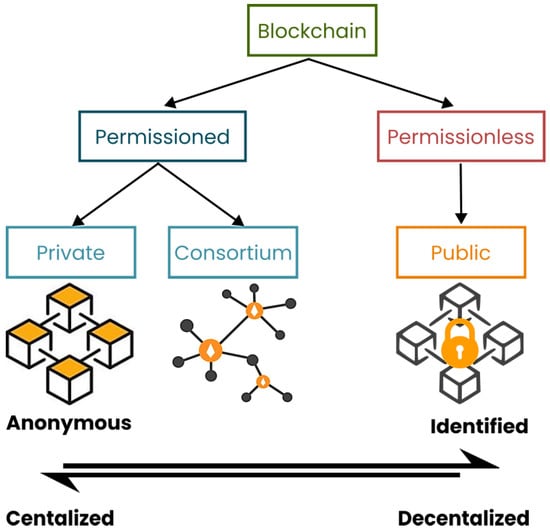
Figure 7.
Blockchain Types [93].
5.3. Blockchain Platforms
Blockchain platforms serve as foundational infrastructures for the creation, deployment, and management of applications built on DLT. By enabling decentralized, secure, and transparent environments for transaction processing and data sharing, these platforms facilitate collaboration among diverse and often geographically dispersed participants.
Unlike early Blockchain systems such as Bitcoin, which were primarily designed for cryptocurrency transactions, modern platforms have evolved to address key limitations, including high energy consumption, limited scalability, and slow transaction speeds. These advancements have broadened their applicability to a wide range of enterprise-grade solutions, particularly within sectors such as supply chain management, finance, and healthcare.
This subsection offers a concise overview of the Blockchain platforms referenced in the reviewed literature, highlighting their distinctive features and relevance to FSC applications.
5.3.1. Ethereum
Ethereum was first introduced by Vitalik Buterin in 2015; it is a decentralized, open-source Blockchain platform designed for the creation and execution of smart contracts and DApps. Recognized as one of the most prominent Blockchain networks, Ethereum ranks second only to Bitcoin in market capitalization [97,98].
At the core of its ecosystem is its native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH), which is used for various purposes within the network, such as paying transaction fees and incentivizing participants. Over time, Ethereum’s architecture and functionalities have undergone significant advancements, providing a robust and versatile infrastructure for developers. Its capabilities extend across various sectors, solidifying its role as a cornerstone of Blockchain innovation [97,98].
The smart contracts and DApps offered by Ethereum made the platform a popular choice for studies that focused on adopting the Blockchain into FSCs. For instance, Chatterjee et al. [85] leveraged Ethereum to develop both a distributed application and smart contracts as part of a Blockchain-based framework aimed at securing smart agriculture operations. Similarly, Gondal et al. [69] utilized Ethereum smart contracts to automate freshness checks for strawberries and to streamline payment processes along the supply chain. In another study, Ramkumar et al. [89] proposed a credit-based payment mechanism in which farmers deposit funds into a Blockchain wallet to purchase seeds without making an upfront payment to seed producers. The producers are compensated only after the farmer’s goods are sold, with any surplus funds returned to the farmer as benefits, thereby creating a trustless, performance-based transaction model. Although Ethereum is primarily used for developing public Blockchains, its versatility allows for the creation of private and consortium-based Blockchain networks as well. This adaptability was demonstrated by Raza et al. [70], who used Ethereum to manage both intra-organizational processes within individual companies and inter-organizational interactions between different entities in the FSC.
5.3.2. Hyperledger Fabric
Hyperledger Fabric, an open-source Blockchain framework developed by the Linux Foundation, is tailored for enterprise-grade applications across diverse industries. Designed for a permissioned network, it restricts access to authorized participants, ensuring secure and controlled interactions. Its modular architecture empowers developers to configure the Blockchain by integrating customizable components, including consensus mechanisms and membership services [99]. With advanced privacy features, Hyperledger Fabric enables selective data sharing, offering robust confidentiality for sensitive information. It employs “chaincode” as its smart contract framework to streamline and automate business processes. Widely adopted in sectors such as supply chain management [100], finance, and healthcare [101], Hyperledger Fabric delivers reliable and efficient Blockchain solutions.
In the context of FSC, Yele and Litoriya [68] used Hyperledger Fabric to develop a permissioned Blockchain-based traceability system that verifies the authenticity of food served at restaurants by tracing it back through all processing stages. Similarly, Hong [74] deployed a private Blockchain built on the Hyperledger Fabric platform to record and manage real-time data related to grain storage conditions. Other studies, such as Balamurugan et al. [102] and Khan et al. [73], have also employed private Blockchains using Hyperledger Fabric to ensure end-to-end traceability and transparency across the FSC.
Beyond private deployments, Hyperledger Fabric has also gained substantial traction as a framework for consortium Blockchains. Its ability to facilitate efficient collaboration among multiple organizations makes it particularly suitable for complex supply chains involving numerous stakeholders. For example, several reviewed studies including [75,80,81,95,96] implemented consortium Blockchain networks based on Hyperledger Fabric to trace food products as they move between FSC actors and to verify their compliance with safety and regulatory standards.
5.3.3. Hyperledger Sawtooth
Hyperledger Sawtooth, another platform within the Hyperledger project, is a versatile and scalable Blockchain framework specifically designed to address challenges related to large-scale integration and performance. Its architecture supports seamless integration with diverse technologies and incorporates quantum-secure communication protocols, ensuring secure and future-proof data exchanges [103]. Sawtooth also enhances smart contract execution, enabling improved performance for complex transactional workflows [104], while maintaining a strong emphasis on data privacy and regulatory compliance [105]. In the context of FSCM, Bumblauskas et al. [76] employed Hyperledger Sawtooth to develop a Blockchain-enabled traceability system for eggs. Their implementation used a permissioned Blockchain architecture, which provided stakeholders with controlled access to sensitive supply chain information, thereby ensuring transparency without compromising privacy or data ownership.
5.3.4. Hyperledger Besu
Hyperledger Besu provides a robust blockchain solution for modern FSC challenges through its Ethereum-compatible enterprise architecture. The platform creates permissioned networks enabling secure collaboration among stakeholders within controlled environments. The platform’s enterprise-grade features utilize Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) smart contracts to enable comprehensive farm-to-fork traceability through immutable record-keeping of product provenance, ownership transfers, and quality parameters, while automating compliance verification processes. Additionally, the system integrates real-time IoT sensor data to monitor environmental parameters affecting food quality and safety throughout distribution. Research in this domain has demonstrated practical applications including the work of Uyar et al. [87], who proposed blockchain-enabled compliance architectures addressing traceability, compliance certification, and cold chain integrity in frozen food supply chains. These implementations employ private blockchain networks with smart contract systems to automate compliance checking processes, reducing manual oversight and enhancing operational efficiency.
5.3.5. Algorand
Algorand is a Blockchain platform and cryptocurrency protocol designed to achieve an optimal balance between security, scalability, and decentralization [106]. Leveraging its high throughput, low latency, and robust consensus mechanism, Algorand provides a reliable and efficient foundation for a wide range of applications, such as digital payments, smart contracts, and stock settlements [107]. Its architecture is particularly well-suited for sustainable and high-performance Blockchain solutions. In the context of FSC, Varavallo et al. [72] employed Algorand to develop an eco-friendly traceability system aimed at enhancing both sustainability and transparency within the Fontina cheese supply chain. The platform’s efficiency and environmental advantages aligned well with the project’s green objectives, making it an appropriate choice for promoting responsible agri-food production.
5.3.6. EOSIO
EOSIO is a high-performance Blockchain platform designed to support DApps with a focus on scalability, speed, and efficiency. It distinguishes itself through key features such as high throughput, zero transaction fees, and the ability to handle millions of transactions per second [108,109]. These capabilities make EOSIO an attractive choice for applications requiring real-time data processing and minimal operational costs. However, research has highlighted challenges including security vulnerabilities and a high prevalence of bot accounts within its ecosystem [108,110]. In FSCM, Sathiya et al. [67] utilized the EOSIO Blockchain to manage and secure data captured along the supply chain. This data was subsequently used to assess the quality of food products, demonstrating EOSIO’s potential for efficient data handling in agri-food traceability systems.
Table 4 presents the various types, platforms, and consensus algorithms reported in the reviewed literature.

Table 4.
Blockchain types, platforms, and consensus algorithms used in FSCs.
5.4. Development Tools for IoT–Blockchain Integration
The successful implementation of Blockchain–IoT systems in FSCs relies not only on the selection of appropriate platforms but also on the availability of robust and versatile development tools. These tools, ranging from smart contract programming languages and software development kits (SDKs) to simulation environments and middleware, are essential for designing, deploying, and testing practical solutions. As highlighted in the literature, a variety of development ecosystems have evolved around the leading Blockchain platforms discussed in Section 5.3, each offering flexible tool-chains tailored to the unique demands of FSC applications. These tools play a pivotal role in enhancing system compatibility, scalability, and operational robustness in real-world deployments.
For instance, Ethereum stands out as one of the most frequently adopted platforms, largely due to its mature development environment [44]. Smart contracts are typically written in Solidity (https://docs.soliditylang.org/ accessed on 8 August 2025), enabling the codification of business rules, such as triggering conditional payments based on real-time IoT sensor readings [111,112,113]. To support the development lifecycle, frameworks like Truffle (https://trufflesuite.com/ accessed on 8 August 2025), Hardhat (https://hardhat.org/ accessed on 8 August 2025), and Remix IDE (https://remix-project.org/ accessed on 9 August 2025) are widely used for coding, testing, and deploying contracts [114,115,116], while Chainlink (https://docs.chain.link/ accessed on 9 August 2025) oracles serve to securely transmit external IoT data into the blockchain [117]. For front-end integration, Web3.js (https://web3js.readthedocs.io/ accessed on 10 August 2025), a JavaScript library, is commonly employed to connect blockchain backends with user interfaces, thereby enabling stakeholder-facing dashboards that support traceability and decision making [118]. In parallel, Hyperledger Fabric offers a permissioned blockchain framework that is particularly suitable for the complex, multi-stakeholder environments typical of FSCs [119]. It supports smart contracts, referred to as Chaincode (https://hyperledger-fabric.readthedocs.io/en/release-1.3/chaincode.html accessed on 10 August 2025), written in Go or Node.js [120], and provides SDKs in various languages, including Java and Python, which facilitate seamless integration with IoT subsystems. Identity management and access control are handled through Fabric CA (https://hyperledger-fabric-ca.readthedocs.io/ accessed on 11 August 2025), while Hyperledger Caliper (https://hyperledger-caliper.github.io/caliper/ accessed on 11 August 2025) is employed to benchmark performance under realistic workload conditions [121], making Fabric especially valuable in scenarios demanding fine-grained access policies and scalable throughput. Hyperledger Sawtooth similarly targets enterprise use cases, with transaction processors in Python or Rust (and support for Go, JavaScript, Java, C++, Swift) [122]. The platform provides a REST API for interfacing with external systems and IoT gateways [123], while its consensus mechanism, Proof of Elapsed Time or PoET (see Section 5.5.4), leverages trusted execution environments to promote fairness and energy efficiency, an asset in FSC contexts involving time-sensitive, perishable goods [124].
Algorand, by contrast, simplifies contract authoring via PyTeal (https://pyteal.readthedocs.io/ accessed on 11 August 2025), a Python-based language for writing smart contracts [125]. Its Sandbox (https://github.com/algorand/sandbox/ accessed on 11 August 2025) environment allows developers to simulate complete IoT-to-blockchain workflows before deployment, supporting scenarios such as farm-level sensor data ingestion, real-time compliance verification, and finality of transactions. This approach significantly reduces development risks, particularly in use cases related to perishable product tracking and monitoring. For scenarios demanding extreme throughput, EOSIO, enables smart contract development in C++ via the EOSIO Contract Development Toolkit (CDT) (https://github.com/EOSIO/eosio.cdt/ accessed on 11 August 2025). It supports integration with mobile and edge computing environments using EOSJS (https://eos.io/for-developers/build/eosio-sdk-for-java/ accessed on 11 August 2025), a JavaScript SDK, and facilitates system evaluation through Jungle Testnet (https://monitor.jungletestnet.io/ accessed on 11 August 2025), which provides a sandboxed environment to simulate global-scale FSC operations.
Beyond these platform-specific ecosystems, the integration of heterogeneous IoT systems with blockchain networks is further enabled by middleware frameworks and cross-platform development environments. Node-RED (https://flows.nodered.org/node/node-red-contrib-blockchain/ accessed on 12 August 2025), a visual programming tool, is frequently used to design device-level workflows and streamline data transmission from sensors to smart contracts, minimizing the need for platform-specific coding [126,127]. In parallel, The Graph (https://thegraph.com/ accessed on 12 August 2025) protocol supports efficient indexing and querying of both on-chain and off-chain data, which is crucial for advanced analytics such as predicting spoilage rates or monitoring regulatory compliance. Furthermore, tools like ZoKrates (https://zokrates.github.io/ accessed on 12 August 2025) introduce privacy-preserving capabilities via zero-knowledge proofs, enabling secure processing of sensitive data while upholding transparency in blockchain-based FSC systems [128,129].
To better contextualize the breadth of tools and frameworks available for Blockchain–IoT integration in FSCs, Table 5 offers a categorized overview, covering platform-specific, cross-platform, and supporting tools.

Table 5.
Summary of Development Tools for IoT–Blockchain Integration in FSCs.
5.5. Consensus Algorithms
Consensus algorithms are fundamental to distributed systems, allowing participants to agree on a single source of truth. In Blockchain, these algorithms ensure that all members of a Blockchain network validate transactions and maintain the overall state of the ledger. This is crucial for preserving the Blockchain’s integrity and security, especially in decentralized environments where mutual trust among participants is not guaranteed [130].
This section provides an overview of various consensus algorithms discussed in the literature.
5.5.1. Proof of Work
Proof of Work (PoW) is a consensus mechanism used in Blockchain networks, first introduced by Bitcoin and later adopted by other cryptocurrencies like Litecoin and Dogecoin. It ensures transaction validation and network security through a competitive mining process, where participants solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle earns the right to add a new block of transactions to the Blockchain and receives a cryptocurrency as a reward [131,132]. While PoW provides high security and decentralization, it also faces challenges such as high energy consumption and scalability issues [133]. Despite these drawbacks, PoW remains a foundational technology for secure and decentralized Blockchain systems. In the context of food supply chains, Majdalawieh et al. [77] implemented PoW as a consensus mechanism in their Ethereum-based Blockchain to address the issues of visibility and transparency in the poultry supply chain.
5.5.2. Delegated Proof of Stake
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a Blockchain consensus mechanism designed to improve efficiency while maintaining decentralization [134]. By enabling stakeholders to delegate their voting power to a select group of representatives, or delegates, DPoS streamlines transaction validation and block creation processes [134,135]. This approach addresses some limitations of traditional Proof of Stake (PoS), which relies on cryptocurrency holdings to determine validators. This consensus mechanism was employed in [67] for transaction validation and block creation within an EOSIO Blockchain network that is responsible for managing the seafood monitoring data.
5.5.3. Pure Proof of Stake
Pure Proof of Stake (PPoS) is an advanced consensus mechanism that enhances decentralization and security by relying on stakeholders’ voting power rather than physical resources. This method addresses limitations of traditional PoS systems, such as security vulnerabilities and usability issues, while promoting scalability and transaction efficiency [136]. PPoS ensures democratic participation by allowing all stakeholders to engage in network validation through a random, cryptographically secure selection process, thus mitigating centralization risks [136]. Additionally, by eliminating energy-intensive mining, PPoS achieves scalability, environmental sustainability, and resilience against malicious attacks through broad stakeholder consensus. For its energy efficiency, PPoS was implemented by Varavallo et al. [72] to ensure an environmentally friendly Blockchain network for a dairy supply chain.
5.5.4. Proof of Elapsed Time
Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET) is a Blockchain consensus mechanism that ensures fairness, security, and energy efficiency by leveraging trusted execution environments (TEEs) to establish verifiable time intervals and allocate block creation rights randomly [137]. Nodes in a PoET network generate a random wait time, and the node with the shortest wait is selected to validate transactions and create new blocks [138]. This hardware-based randomness and verifiable execution enable PoET to achieve low energy consumption compared to Proof of Work (PoW) while maintaining security and scalability, making it a popular choice for permissioned Blockchain systems like Hyperledger Sawtooth. A permissioned Sawtooth Blockchain that relies on PoET was proposed by Bumblauskas et al. [76] to help manage the egg supply chain.
5.5.5. Proof of Authority
Proof of Authority (PoA) is a blockchain consensus mechanism in which a limited set of preapproved validators (authorities) hold exclusive rights to create new blocks and validate transactions. In contrast to PoW and PoS, the selection of validators in PoA is based on verified identity and established reputation rather than computational capacity or token ownership. This design makes PoA a lightweight consensus mechanism, enabling high scalability and energy efficiency. Such characteristics make it well-suited for scenarios involving large-scale deployments of IoT sensors, such as in the monitoring of FSCs. Two examples of PoA implementation in FSCs are provided by the works of [79,83].
Table 6 provides a comparative analysis of the blockchain platforms found in the literature. Ethereum stands out for its high decentralization and security, bolstered further by its transition to Proof of Stake (PoS) [139,140]. Despite its robust public ecosystem, it continues to face challenges with lower transaction throughput (TPS) and high transaction fees [141]. Hyperledger Fabric, designed for enterprise environments, offers excellent scalability and security within permissioned networks, deliberately reducing decentralization to meet business needs [139,141]. Similarly, Hyperledger Sawtooth emphasizes modularity and energy efficiency, though its security model depends heavily on Intel SGX hardware [142]. EOSIO caters to high-performance applications with very fast and inexpensive transactions but compromises on decentralization due to its limited number of block producers [140,143]. Algorand stands out by achieving a strong balance, offering high TPS, low energy consumption, robust security, and commendable decentralization through its innovative consensus mechanisms and commitment to sustainability [143]. PoA is a lightweight, energy-efficient blockchain consensus mechanism that is well-suited for scalable IoT-based applications [144].

Table 6.
Comparative table of Blockchain Platforms [139,140,141,142,143].
Ultimately, selecting the optimal blockchain platform is a nuanced decision that must be informed by the specific needs, priorities, and objectives of the intended use case. Understanding the inherent trade-offs—between scalability, security, decentralization, and energy efficiency—is essential for leveraging the full potential of these technologies in both public and enterprise domains.
6. Challenges and Open Issues Related to the Adoption of IoT and Blockchain in FSCM
The integration of Blockchain and the IoT presents numerous challenges, particularly within contexts like agriculture and FSCs. These barriers span technological, regulatory, organizational, and security domains, emphasizing the complexity of implementing such advanced systems effectively. This section presents the main challenges mentioned in the studied literature.
6.1. Regulatory and Governance Challenges
The widespread integration of Blockchain and IoT technologies in agriculture and food supply chains (FSCs) remains constrained by the absence of harmonized regulatory frameworks [19,20]. This regulatory uncertainty creates substantial barriers for food business operators, who encounter ambiguous compliance requirements, unclear liability structures, and inconsistent data governance standards that collectively discourage investment in transformative digital infrastructure [21].
Established regulatory models in leading jurisdictions demonstrate the critical role of comprehensive legal frameworks in enabling technological adoption. The European Union’s Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 exemplifies this approach by establishing mandatory traceability requirements across all stages of production, distribution, and processing, while establishing clear legal accountability for food business operators regarding product safety [145]. Complementing this framework, the U.S. Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) fundamentally transformed American food safety regulation by prioritizing preventive controls over reactive measures, mandating risk-based oversight mechanisms, and requiring enhanced supply chain transparency [146]. These regulatory architectures provide robust institutional foundations that naturally accommodate digital technologies for compliance monitoring and traceability enhancement.
Building upon these established models, jurisdictions can implement targeted regulatory solutions to accelerate technology adoption. Technology-neutral regulatory sandboxes offer a pragmatic starting point, enabling controlled experimentation with Blockchain and IoT applications while generating evidence-based insights for policy development [147]. International standardization bodies dedicated to agri-food digital technologies can establish harmonized technical specifications and interoperability protocols, thereby reducing cross-border compliance complexity [148]. Furthermore, phased regulatory implementation—beginning with voluntary frameworks before transitioning to mandatory requirements—facilitates industry adaptation while developing regulatory expertise [149]. Strategic public–private partnerships can leverage industry knowledge to develop sector-specific guidelines that align technological capabilities with food safety objectives [150].
These regulatory approaches create essential institutional pathways for digital technology integration, enabling enhanced compliance monitoring, improved traceability systems, and rapid response capabilities for food safety incidents. Conversely, jurisdictions that lack such comprehensive frameworks continue to experience limited technological adoption and remain exposed to systemic food safety vulnerabilities.
6.2. Knowledge and Awareness Challenges
A significant barrier to the effective adoption of Blockchain and IoT systems is the lack of knowledge and skills among workers. Insufficient competency in both the technical aspects of Blockchain and the domain-specific requirements, such as agriculture or FSCs, hampers the development and implementation of these technologies [20]. Organizations often struggle to find personnel proficient in these areas, while stakeholders’ limited understanding of the benefits and functionalities of Blockchain–IoT systems further impedes adoption [20].
6.3. Scalability and Integration Challenges
Scalability remains a fundamental challenge in integrating Blockchain with IoT technologies for FSCM. The primary constraint stems from blockchain’s inherently lower transaction throughput compared to centralized databases [20], creating bottlenecks when processing high-volume, real-time data streams from IoT sensors used for environmental monitoring and perishable goods tracking. This performance limitation particularly affects time-sensitive applications, potentially compromising system reliability and responsiveness.
Integration complexity presents an additional barrier, as many food supply organizations rely on established enterprise resource planning (ERP) and warehouse management systems (WMSs) that are incompatible with decentralized blockchain architectures. The substantial technical and organizational effort required to retrofit or replace these legacy systems creates operational friction, particularly discouraging adoption among smaller stakeholders with limited digital infrastructure [19,21].
Recent research has identified several promising architectural solutions to address these limitations. Off-chain storage mechanisms enable large IoT data volumes to be stored externally while maintaining key hashes or metadata on-chain for verification, reducing blockchain bloat while preserving data integrity [151]. Layer 2 protocols, including sidechains and state channels, enhance scalability by processing transactions off the main blockchain and committing only final states, effectively decoupling high-throughput data handling from blockchain consensus requirements [152,153].
Hybrid architectures combining public and private blockchains offer additional benefits by balancing decentralization with operational efficiency. These consortium models enable selective data sharing among trusted stakeholders while reducing latency and energy consumption [154]. As these technologies mature alongside edge computing and lightweight consensus algorithms, they will further enhance scalability and facilitate broader deployment across diverse FSCM contexts.
These scalable architectural innovations represent a pathway for Blockchain–IoT integration to evolve from limited pilot programs to robust, industry-wide applications, effectively addressing both performance constraints and legacy system compatibility challenges.
6.4. Data Privacy and Security Challenges
The integration of Blockchain and IoT raises critical concerns regarding data privacy and security. While Blockchain offers enhanced transparency, it often comes at the cost of data privacy, particularly given the vulnerabilities inherent to IoT devices [19,20]. Although advancements in Blockchain platforms enable encrypted transaction records, the need for more robust security measures remains paramount to mitigate risks from various attacks [21]. Striking a balance between transparency and privacy is essential for organizations seeking to adopt these technologies effectively.
6.5. Financial and Resource Challenges
The adoption of Blockchain and IoT technologies is significantly hindered by high initial costs and limited resources [21]. The substantial upfront investment required for technology acquisition, infrastructure development, and workforce training poses a major challenge, particularly for smaller organizations with constrained financial capacity [19]. Additionally, inadequate technological infrastructure and financial support further limit the feasibility of implementing these systems, restricting their broader adoption across industries like FSCs [21].
6.6. Stakeholders’ Awareness and Trust Challenges
The integration of Blockchain and IoT technologies is significantly hindered by trust deficits and stakeholder resistance. Concerns about data misuse and reluctance to share information on Blockchain platforms exacerbate these challenges [19]. Additionally, limited awareness of the benefits and functionalities of these systems contributes to resistance, with organizations often reluctant to transition from existing systems deemed sufficient [20,21]. This resistance delays the integration of innovations that could enhance efficiency and transparency, particularly in sectors like agriculture.
Strategic interventions are essential to overcome the multifaceted challenges hindering the integration of Blockchain and IoT in agriculture and FSCs. Establishing clear regulatory frameworks, upgrading infrastructure, and enhancing workforce competency through targeted training are critical steps toward facilitating adoption. Additionally, fostering stakeholder awareness and addressing privacy and scalability concerns through technological advancements are pivotal for success. These measures collectively have the potential to unlock the transformative capabilities of BLC and IoT, driving efficiency and transparency across various sectors.
7. Future Work
While the integration of IoT and blockchain in the food supply chain has been conceptually validated and technically demonstrated in multiple studies, the path toward large-scale, impactful adoption lies in translating these theoretical and experimental advances into real-world, evidence-driven applications. The way forward should be grounded in practical deployments that reveal not only technological possibilities, but also the socio-economic, regulatory, and environmental realities of operating such systems at scale.
7.1. Interoperability and Standardization
The long-term viability of IoT and blockchain integration in food supply chains depends on systems that can communicate seamlessly across diverse platforms and stakeholders. Current real-world deployments often face fragmented architectures, with devices, data formats, and blockchain frameworks operating in isolation, creating unnecessary complexity and cost [155,156]. Adopting common data models and standardized communication protocols may significantly improve interoperability, enabling more transparent and efficient information flows between actors. Practical evidence demonstrates that shared ontologies and protocol alignment can reduce integration barriers, enhance trust, and support scalability [157,158]. By embedding such standardization into system design from the outset, future solutions can move beyond isolated proofs-of-concept toward truly connected, multi-actor food supply chain ecosystems that are both operationally effective and sustainable.
7.2. Scalability and Performance in Real-World Conditions
As IoT–Blockchain solutions transition from controlled pilots to operational food supply chains, performance and scalability become decisive factors. Indeed, the continuous data streams generated by IoT sensors can strain traditional blockchain consensus mechanisms, leading to latency, high energy consumption, and limited throughput [159]. To address these bottlenecks, future work should prioritize the development of lightweight consensus algorithms [160] and explore hybrid architectures that integrate edge-based IoT–Blockchain systems [161]. In addition, integrating scalable design principles early, future implementations can ensure that blockchain-enabled supply chains remain responsive, cost-efficient, and capable of supporting high-volume, high-frequency transactions under real operational conditions.
7.3. Security and Privacy in Operational Environments
As IoT–blockchain systems gain adoption, they have become increasingly attractive targets for cyberattacks aimed at falsifying provenance data or disrupting monitoring infrastructure. Real-world implementations have demonstrated that integrating privacy-preserving cryptographic techniques, like zero-knowledge proofs or homomorphic encryption, can preserve confidentiality while maintaining the transparency needed for trust and regulatory compliance [128,129]. The challenge for future research lies in ensuring that these advanced security measures are both technically robust and operationally feasible from farm to fork. For this requirement, next-generation solutions must integrate advanced lightweight cryptography [162], decentralized identity [163], and privacy-by-design principles [164]. Advancing along these research avenues will not only resolve existing barriers but also position blockchain as a lasting enabler of transparent, robust, and intelligent FSC.
7.4. Economic Viability and Cost–Benefit Analysis
The large-scale adoption of IoT–blockchain systems in food supply chains will ultimately hinge on their economic viability. While our literature analysis demonstrates technical feasibility, deployment at scale demands rigorous cost–benefit analysis that weighs infrastructure investments, transaction costs, and system maintenance against gains in efficiency, waste reduction, and market trust. Future research should integrate empirical field studies with simulation-based modeling to deliver robust, evidence-driven insights that support strategic decision making in IoT–blockchain adoption. Such evaluations must be both longitudinal and sector-specific, ensuring that financial metrics are assessed alongside social and environmental impacts. This approach is particularly critical for small- and medium-sized enterprises operating under constrained budgets, where investment decisions must balance operational efficiency with long-term sustainability and resilience.
7.5. AI-Driven Solutions
The convergence of AI, blockchain, and IoT offers transformative potential for food supply chains by enabling predictive analytics, automated decision making, and real-time optimization. AI algorithms can leverage blockchain’s immutable data to forecast demand fluctuations, detect anomalies in logistics, and optimize inventory management, thereby reducing waste and improving resilience [165,166]. Smart food supply chain pilots have shown that integrating machine learning with IoT sensor networks enhances early detection of quality degradation and improves cold-chain efficiency [167]. Future research should explore adaptive AI models that not only process real-time data but also exhibit lifelong adaptability by continuously learning from blockchain-verified records, ensuring that decisions remain context-aware, transparent, and scalable across diverse FSC environments.
7.6. Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sustainability in emerging digital supply chain solutions demands a balance between technological innovation and environmental stewardship. This survey demonstrated that the integration of blockchain and IoT within FSC have a potential to enhance transparency, optimize resource utilization, and reduce waste [17], yet these benefits must be critically weighed against the ecological footprint of such technologies. The high energy demand of certain consensus mechanisms and the environmental costs of hardware deployment of blockchain present challenges that require targeted mitigation strategies [168]. For this reason, future research must address the environmental footprint of IoT–blockchain solutions, ensuring that sustainability is embedded as a core design principle rather than treated as an afterthought. This entails prioritizing the development of energy-efficient approaches, such as low-carbon blockchain consensus mechanisms, while leveraging renewable-powered infrastructures and incorporating circular economy principles, thereby ensuring that technological advancements contribute positively to long-term environmental resilience.
7.7. Multi-Stakeholder Real-World Pilots
The transition from experimental prototypes to scalable blockchain–IoT solutions in food supply chains hinges on coordinated, multi-stakeholder engagement. Successful deployments require collaboration between producers, processors, logistics providers, retailers, regulators, and technology vendors to ensure that technical solutions align with operational realities, compliance requirements, and consumer expectations. Evidence from projects such as IBM Food Trust (https://www.ibm.com/blockchain/resources/food-trust/demo/accessed on 13 August 2025) and TE-FOOD (https://te-food.com/accessed on 13 August 2025) shows that industry–government partnerships can accelerate trust-building and interoperability while generating actionable insights from live transaction data. Future work should prioritize cross-border, multi-actor pilots with embedded evaluation frameworks to capture economic, social, and environmental impacts in real time, providing a robust evidence base for large-scale implementation.
8. Conclusions
This survey systematically addressed three critical research questions regarding the adoption of Blockchain and IoT technologies in FSCM. Our analysis of literature from January 2020 to July 2025 reveals a rapidly evolving research landscape focused on three primary application domains: provenance and traceability systems for end-to-end monitoring, data management frameworks driven by real-time sensor inputs for quality control, and automation mechanisms powered by smart contracts, with wide-ranging deployment across livestock, dairy, seafood, and grains demonstrating the versatility of these technologies (RQ1). The advantages of combining Blockchain and IoT offer comprehensive solutions to persistent challenges including enhanced traceability and transparency, improved food safety through real-time monitoring, reduced waste through better supply chain visibility, and streamlined operations via smart contract automation, with their convergence enabling robust, system-wide transformations that enhance supply chain integrity and efficiency beyond what either technology achieves independently (RQ2). However, critical barriers hinder adoption across multiple domains, including regulatory ambiguities and absence of harmonized frameworks, scalability limitations in processing high-volume IoT data, integration complexity with legacy systems, knowledge gaps and workforce competency issues, data privacy and security vulnerabilities, substantial financial constraints particularly for smaller stakeholders, and trust deficits among supply chain participants (RQ3). Consortium and permissioned networks have emerged as preferred blockchain infrastructures, offering pragmatic balance between decentralization and operational efficiency, with platforms like Hyperledger Fabric and Ethereum leading implementation choices. The convergence of IoT and Blockchain technologies holds transformative potential for the global food system, with realizing this potential depending on establishing inclusive, sustainable, and regulatory-aligned frameworks that systematically address these multifaceted challenges, providing the foundation for advancing academic and industrial inquiry toward a transparent, efficient, and resilient food supply network powered by digital innovation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization Y.B., A.-E.B., B.M., B.F., K.B. and H.S.; methodology, Y.B., A.-E.B., B.M. and B.F.; software, Y.B.; validation, Y.B., A.-E.B., B.F. and B.M.; formal analysis, Y.B.; investigation, Y.B.; resources, B.M.; data curation, Y.B.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.B., A.-E.B., B.M., B.F., K.B. and H.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.B., A.-E.B., B.M. and B.F.; visualization, Y.B.; supervision, Y.B., B.M. and B.F.; project administration, Y.B., B.M. and B.F.; funding acquisition, B.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The paper was supported by the “Application Domain-Specific Highly Reliable IT Solutions” project, implemented with the support provided by the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary, financed under the Thematic Excellence Programme TKP2021-NVA-29 (National Challenges Subprogramme) funding scheme.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ben-Daya, M.; Hassini, E.; Bahroun, Z.; Banimfreg, B.H. The role of internet of things in food supply chain quality management: A review. Qual. Manag. J. 2020, 28, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassini, E.; Ben-Daya, M.; Bahroun, Z. Impact of Internet of Things on Food Supply Chains. In Smart and Sustainable Supply Chain and Logistics—Challenges, Methods and Best Practices: Volume 2; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Dergan, T.; Ivanovska, A.; Kocjančič, T.; Iannetta, P.P.; Debeljak, M. ‘Multi-SWOT’ Multi-Stakeholder-Based Sustainability Assessment Methodology: Applied to Improve Slovenian Legume-Based Agri-Food Chains. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez Neyra, J.M.; Cequea, M.M.; Schmitt, V.G.H. Current practices and key challenges associated with the adoption of resilient, circular, and sustainable food supply chain for smallholder farmers to mitigate food loss. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1484933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Stašys, R.; Pellegrini, G. Agri-food supply chain optimization through the SWOT analysis. Vadyb. Moksl. Stud. Verslų Jų Infrastruktūros Plėtrai Moksl. Žurnalas 2018, 40, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, T.; Nunes, F.; Mata, F.; Vaz-Velho, M. A SWOT analysis of organizations in the agri-food chain sector from the Northern region of Portugal using the PESTEL and MEETHS frameworks. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnusdei, L.; Krstić, M.; Miglietta, P.P. Is Digitalization Making Agroindustry More Circular? A SWOT-AHP Analysis. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Industrial Engineering and Automation, South Tyrol, Italy, 22–23 June 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 427–436. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Yi, Y.; Li, C.; Shin, C. Sustainability in Global Agri-Food Supply Chains: Insights from a Comprehensive Literature Review and the ABCDE Framework. Foods 2024, 13, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuizinaitė, J.; Morkūnas, M.; Volkov, A. Assessment of the most appropriate measures for mitigation of risks in the agri-food supply chain. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.; Jha, A.K.; Raut, R.; Kumar, M.; Ghoshal, S. Redesigning short and perishable food supply chains getting insight from the causal analysis of challenges to sustainable development. Br. Food J. 2024, 127, 1620–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Parys, E.; Tran, D.; Sampers, I.; Benezech, T.; Loveniers, P.J.; Devlieghere, F.; De Steur, H.; Gellynck, X.; Schouteten, J.J. Evaluating collaborative scenarios for short food supply chains: A case study on high-level processing technology. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 5591–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro Moura Duarte, A.L.; Picanço Rodrigues, V.; Bonome Message Costa, L. The sustainability challenges of fresh food supply chains: An integrative framework. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakuri, M.; Barzinpour, F. A risk-averse sustainable perishable food supply chain considering production and delivery times with real-world application. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackmann, D.; Mardenli, A. Challenges in Food Supply Chain Management: Findings from Literature Review and Expert Survey. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Dynamics in Logistics, Bremen, Germany, 14–16 February 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 69–91. [Google Scholar]
- Moyo, E.H.; Carstens, S.; Walters, J. Simulation model for a sustainable food supply chain in a developing country: A case study of the banana supply chain in Malawi. Logistics 2024, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Agrawal, S. Challenges and opportunities for agri-fresh food supply chain management in India. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 212, 108161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, G.; Kukreja, V.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Yoon, B. Adaptation of IoT with blockchain in Food Supply Chain Management: An analysis-based review in development, benefits and potential applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Khan, S.; Dsilva, J.; Centobelli, P. Blockchain integrated IOT for Food Supply Chain: A grey based Delphi-DEMATEL approach. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.S.; Singh, A.R.; Raut, R.D.; Mangla, S.K.; Luthra, S.; Kumar, A. Exploring the application of Industry 4.0 technologies in the agricultural food supply chain: A systematic literature review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 169, 108304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Raut, R.D.; Agrawal, N.; Cheikhrouhou, N.; Sharma, M.; Daim, T. Integrated blockchain and internet of things in the food supply chain: Adoption barriers. Technovation 2022, 118, 102589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Huang, X.; Fang, H.; Wang, V.; Hua, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, H.; Yi, D.; Yau, L. Blockchain technology in current agricultural systems: From techniques to applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 143920–143937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukala, R.; Panduru, K.; Shields, A.; Riordan, D.; Doody, P.; Walsh, J. Internet of Things: A review from ‘Farm to Fork’. In Proceedings of the 2016 27th Irish Signals and Systems Conference (ISSC), Londonderry, UK, 21–22 June 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Greengard, S. The Internet of Things; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tran-Dang, H.; Krommenacker, N.; Charpentier, P.; Kim, D.S. The Internet of Things for logistics: Perspectives, application review, and challenges. IETE Tech. Rev. 2022, 39, 93–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.M.; Mallick, P.K. The Internet of Things: Insights into the building blocks, component interactions, and architecture layers. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 132, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.B.; Quamara, M. An overview of Internet of Things (IoT): Architectural aspects, challenges, and protocols. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020, 32, e4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qaseemi, S.A.; Almulhim, H.A.; Almulhim, M.F.; Chaudhry, S.R. IoT Architecture Challenges and Issues: Lack of Standardization. In Proceedings of the 2016 Future Technologies Conference (FTC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–7 December 2016; pp. 731–738. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, Z.; Gharsellaoui, H.; Barhoumi, W. Four-layer Architecture for IoT Security in Fog Network. In Proceedings of the 2023 10th International Conference on Internet of Things: Systems, Management and Security (IOTSMS), San Antonio, TX, USA, 23–25 October 2023; pp. 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, A.; Kaur, S. Internet of things (IoT), applications and challenges: A comprehensive review. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 114, 1687–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabraeil Jamali, M.A.; Bahrami, B.; Heidari, A.; Allahverdizadeh, P.; Norouzi, F. The IoT Landscape. In Towards the Internet of Things: Architectures, Security, and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, I. Mastering Blockchain: Inner Workings of Blockchain, from Cryptography and Decentralized Identities, to DeFi, NFTs and Web3; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, R.; Ghosh, A.; Balas, V.; Elngar, A. Blockchain: Principles and Applications in IoT; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.; Abbas, K.; Li, M.; Kamruzzaman, J. Blockchain technology and application: An overview. PeerJ 2023, 9, e1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devisri, M.; Vetriselvan, V.; Baskar, M.; Mylapalli, M.; Jayabalan, K.; Mouli, S.K.M.K. Blockchain Innovations for Secure Online Transactions. In Strategies for E-Commerce Data Security: Cloud, Blockchain, AI, and Machine Learning; Advances in Web Technologies and Engineering Book Series; IGI Global Scientific Publishing: Hershey, PA, USA, 2024; pp. 523–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbashyn, A. Blockchain technologies in international relations: Functional features and capabilities. Philos. Political Sci. Context Mod. Cult. 2024, 16, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, G.; Tyagi, A.K. Blockchain Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Pradhan, C. Blockchain 1.0 to Blockchain 4.0—The Evolutionary Transformation of Blockchain Technology. In Blockchain Technology: Applications and Challenges; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Luntovskyy, A.; Guetter, D. Cryptographic technology blockchain and its applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Telecommunication Technologies and Radio Electronics, Odessa, Ukraine, 10–14 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 14–33. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Lou, W.; Hou, Y.T. A survey of distributed consensus protocols for blockchain networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 1432–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duy, P.T.; Hien, D.T.T.; Hien, D.H.; Pham, V.H. A Survey on Opportunities and Challenges of Blockchain Technology Adoption for Revolutionary Innovation. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology, Danang, Vietnam, 6–7 December 2018; pp. 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Buterin, V. A Next-Generation Smart Contract and Decentralized Application Platform. In Ethereum White Paper; 2014; Volume 3, 37, pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, J.S.; Deshmukh, J. A review study of the blockchain-based healthcare supply chain. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Open 2022, 6, 100328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasyapa, M.S.; Vanmathi, C. Blockchain integration in healthcare: A comprehensive investigation of use cases, performance issues, and mitigation strategies. Front. Digit. Health 2024, 6, 1359858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Capodici, A.; Rucci, P.; Bianconi, A.; Longo, G.; Ricci, M.; Sanmarchi, F.; Golinelli, D. Blockchain for the healthcare supply chain: A systematic literature review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.M.; Siqin, T. Blockchain in logistics and production from Blockchain 1.0 to Blockchain 5.0: An intra-inter-organizational framework. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2022, 160, 102653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.K.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Tseng, M.L. A literature review of blockchain technology applications in supply chains: A comprehensive analysis of themes, methodologies and industries. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 154, 107133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, D. Automating governance: Blockchain delivered governance for business networks. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2022, 102, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcerzak, A.P.; Nica, E.; Rogalska, E.; Poliak, M.; Klieštik, T.; Sabie, O.M. Blockchain technology and smart contracts in decentralized governance systems. Adm. Sci. 2022, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.M.; Saraniemi, S. Trust in blockchain-enabled exchanges: Future directions in blockchain marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2023, 51, 914–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panisi, F. Blockchain and ’Smart Contracts’: FinTech Innovations to Reduce the Costs of Trust. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Xu, C.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S. Measuring Decentralization in Emerging Public Blockchains. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 30 May–3 June 2022; pp. 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Niss, H.; Owuya, S. Performance and Scalability of Emerging Blockchain Technologies. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2:1703907 (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Agbo, C.C.; Mahmoud, Q.H.; Eklund, J.M. Blockchain technology in healthcare: A systematic review. Healthcare. 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz, M.M.; Telles, R.; Bonilla, S.H. Blockchain and supply chain management integration: A systematic review of the literature. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2020, 25, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyskind, G.; Nathan, O. Decentralizing Privacy: Using Blockchain to Protect Personal Data. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops, San Jose, CA, USA, 21–22 May 2015; pp. 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, J.; Ye, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, J.L.; Liu, Q.; Guo, W.; Cao, W.; Fu, L. Blockchain-secured smart manufacturing in industry 4.0: A survey. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 51, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. Blockchain for Big Data: AI, IoT and Cloud Perspectives; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Salah, K.; Rehman, M.H.U.; Nizamuddin, N.; Al-Fuqaha, A. Blockchain for AI: Review and open research challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 10127–10149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muheidat, F.; Patel, D.; Tammisetty, S.; Tawalbeh, L.A.; Tawalbeh, M. Emerging concepts using blockchain and big data. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 198, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlam, H.F.; Azad, M.A.; Alzahrani, A.G.; Wills, G. A Review of Blockchain in Internet of Things and AI. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2020, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, S.; Hussain, R.; Jurdak, R.; Oracevic, A.; Salah, K.; Hong, C.S.; Matulevičius, R. Blockchain-based digital twins: Research trends, issues, and future challenges. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2022, 54, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingmiao, L.; Fukang, Z. A Blockchain-Based Predictive Maintenance Framework. In Proceedings of the 2025 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Industrial Technology Applications (AIITA), Xi’an, China, 28–30 March 2025; pp. 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, M.M.; Van, D.H.; Khan, S.; Qu, Q.; Kholodov, Y. Ai agents meet blockchain: A survey on secure and scalable collaboration for multi-agents. Future Internet 2025, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulkinbekov, K.; Kim, D.H. Doctrina: Blockchain 5.0 for Artificial Intelligence. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Waste Index Report 2024. Think Eat Save: Tracking Progress to Halve Global Food Waste. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/20.500.11822/45230 (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Bulysheva, L.; Kataev, M.Y. Applications of blockchain in industry 4.0: A review. Inf. Syst. Front. 2022, 26, 1715–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiya, V.; Nagalakshmi, K.; Raju, K.; Lavanya, R. Tracking perishable foods in the supply chain using chain of things technology. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yele, S.; Litoriya, R. Blockchain-based secure dining: Enhancing safety, transparency, and traceability in food consumption environment. Blockchain Res. Appl. 2024, 5, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondal, M.U.A.; Khan, M.A.; Haseeb, A.; Albarakati, H.M.; Shabaz, M. A secure food supply chain solution: Blockchain and IoT-enabled container to enhance the efficiency of shipment for strawberry supply chain. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1294829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, Z.; Haq, I.U.; Muneeb, M. Agri-4-all: A framework for blockchain based agricultural food supply chains in the era of fourth industrial revolution. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 29851–29867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Jain, S.; Burgio, A.; Bolshev, V.; Panchenko, V. Blockchain-enabled supply chain platform for Indian dairy industry: Safety and traceability. Foods 2022, 11, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varavallo, G.; Caragnano, G.; Bertone, F.; Vernetti-Prot, L.; Terzo, O. Traceability platform based on green blockchain: An application case study in dairy supply chain. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.W.; Byun, Y.C.; Park, N. IoT-blockchain enabled optimized provenance system for food industry 4.0 using advanced deep learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y. New model of food supply chain finance based on the internet of things and blockchain. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 7589964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftekhar, A.; Cui, X. Blockchain-based traceability system that ensures food safety measures to protect consumer safety and COVID-19 free supply chains. Foods 2021, 10, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumblauskas, D.; Mann, A.; Dugan, B.; Rittmer, J. A blockchain use case in food distribution: Do you know where your food has been? Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdalawieh, M.; Nizamuddin, N.; Alaraj, M.; Khan, S.; Bani-Hani, A. Blockchain-based solution for secure and transparent food supply chain network. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2021, 14, 3831–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, G.; Kocian, A.; Brunori, G.; Chessa, S.; Lai, M.B.; Nardi, D.; Schifanella, C.; Bonura, S.; Masi, N.; Comella, S.; et al. Interoperable Traceability in Agrifood Supply Chains: Enhancing Transport Systems Through IoT Sensor Data, Blockchain, and DataSpace. Sensors 2025, 25, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhiwibowo, W.; Widayat, W.; Syafei, W.A. Design of dual blockchain-based with point of authority for halal traceability system application on fresh meat-based supply chain. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Chen, Y.; Ren, Q.; Li, D.; Bo, W.; Wang, X. Blockchain-Based Trusted Traceability Scheme for Food Quality and Safety. J. Food Qual. 2025, 2025, 5914078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacs, M.; Toth, F.; Horvath, R.; Solymos, G.; Alpár, B.; Varga, P.; Kertesz, I.; Gillay, Z.; Baranyai, L.; Felfoldi, J.; et al. Advanced digital solutions for food traceability: Enhancing origin, quality, and safety through NIRS, RFID, Blockchain, and IoT. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zeng, H.; Yang, X.; Cui, H.; Yi, X.; Piran, M.J.; Luo, M.; Que, Y. Blockchain-Empowered H-CPS Architecture for Smart Agriculture. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2503102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Govea, J.; Moncayo-Moncayo, P.; Navarro, A.M.; Chavez-Pirca, C. Optimization of the Traceability of Perishable Products through Light Blockchain and IoT in the Food Industry. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 67599–67615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, I.M.M.; Aravindhar, D.J. Towards Quantum-Resilient Food Systems: Federated AI and Lightweight Lattice Hashing for Blockchain-Based Traceability. SN Comput. Sci. 2025, 6, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, K.; Singh, A. A blockchain-enabled security framework for smart agriculture. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 106, 108594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biradar, M.; Sidnal, N.; Rokade, R.; Shiragapur, B. Dairy product quality evaluation using optimization-based deep maxout network with blockchain-driven internet of things. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 2025, 18, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, H.; Papanikolaou, A.; Kapassa, E.; Touloupos, M.; Rizou, S. Blockchain-Enabled Traceability and Certification for Frozen Food Supply Chains: A Conceptual Design. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 12, 101085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, H.; Zafar, N.A.; Alkhammash, E.H.; Hadjouni, M. Blockchain-Based Formal Model for Food Supply Chain Management System Using VDM-SL. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, G.; Kasat, K.; PK, N.M.; Raghu, T.; Chhabra, S. Quality enhanced framework through integration of blockchain with supply chain management. Meas. Sens. 2022, 24, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Manning, L.; Cullen, J.M. Systematic assessment of food traceability information loss: A case study of the Bangladesh export shrimp supply chain. Food Control 2022, 142, 109257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seira, A.; Allen, J.; Watsky, C.; Alley, R. Governance of Permissionless Blockchain Networks. In FEDS Notes; Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, N.; O’Dowd, A.; Novotny, P.; Desrosiers, L.; Ramakrishna, V.; Baset, S.A. Blockchain with Hyperledger Fabric: Build Decentralized Applications Using Hyperledger Fabric 2; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Addou, K.; El Ghoumari, M.; Achkdir, S.; Azzouazi, M. A decentralized model to ensure traceability and sustainability of the food supply chain by combining blockchain, IoT, and machine learning. Math. Model. Comput 2023, 10, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, N.; Beije, A.; Krishnamachari, B. Blockchain and the Supply Chain: Concepts, Strategies and Practical Applications; Kogan Page Publishers: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Cengiz, K.; Tomar, R. An IOT and blockchain approach for food traceability system in agriculture. Scalable Comput. Pract. Exp. 2021, 22, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesanhane, H.; Bezerra, W.R.; Koch, F.; Westphall, C. Distributed AgriFood supply chains. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 2024, 32, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangrulkar, R.; Chavan, P.V. Ethereum Blockchain. In Blockchain Essentials; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2024; pp. 123–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Anand, T. Ethereum Architecture and Overview. In Blockchain and Ethereum Smart Contract Solution Development; Apress eBooks: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2022; pp. 209–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathi, U.; Harshitha, R.; Jayashre; Gummaraju, N. Examining Architectural Aspects of Hyperledger Fabric: A Thorough Review. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Innovations and Challenges in Emerging Technologies (ICICET), Nagpur, India, 7–8 June 2024; 8 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickremasinghe, G.B.; Frost, S.; Rafferty, K.; Sharma, V. Demonstrating a Hyperledger Fabric-based Blockchain with Knowledge Graphs for a Supply Chain Ecosystem. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (ICBC), Dublin, Ireland, 27–31 May 2024; pp. 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, M.; Albogamy, F.R.; Alamri, S.S.; Ghani, I.; Mehboob, B. The Hyperledger fabric as a Blockchain framework preserves the security of electronic health records. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1272787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, S.; Ayyasamy, A.; Joseph, K.S. IoT-Blockchain driven traceability techniques for improved safety measures in food supply chain. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2022, 14, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Wang, L.; Irfan, M.; Westerlund, T. Hyperledger sawtooth based supplychain traceability system for counterfeit drugs. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 190, 110021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piduguralla, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Anjana, P.S.; Peri, S. An Efficient Framework for Execution of Smart Contracts in Hyperledger Sawtooth. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.08452. [Google Scholar]
- Moriggl, P.; Asprion, P.M.; Schneider, B. Blockchain Technologies Towards Data Privacy—Hyperledger Sawtooth as Unit of Analysis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilad, Y.; Hemo, R.; Micali, S.; Vlachos, G.; Zeldovich, N. Algorand: Scaling Byzantine Agreements for Cryptocurrencies. In Proceedings of the SOSP ’17: ACM SIGOPS 26th Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, Shanghai China, 28 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Micali, S. ALGORAND. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.01341. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, Q.; Zheng, W.; Wu, J. Exploring EOSIO via Graph Characterization; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzliach, S.; Sinay, T.; Danilchenko, K.; Daltrophe, H. EOS Blockchain-Based Electronic Voting System. In Proceedings of the 2024 6th Conference on Blockchain Research & Applications for Innovative Networks and Services (BRAINS), Berlin, Germany, 9–11 October 2024; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Tyson, G.; Luo, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Huang, G.; Jiang, X. Characterizing EOSIO Blockchain. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.05369. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.05369 (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Bistarelli, S.; Mazzante, G.; Micheletti, M.; Mostarda, L.; Sestili, D.; Tiezzi, F. Ethereum smart contracts: Analysis and statistics of their source code and opcodes. Internet Things 2020, 11, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, C.; Engel, G.; Greiner, T. Distributed Ledger and Smart Contract Based Approach for IoT Sensor Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Omni-layer Intelligent Systems (COINS), Barcelona, Spain, 31 August–2 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Razzaq, A.; Altamimi, A.B.; Alreshidi, A.; Ghayyur, S.A.K.; Khan, W.; Alsaffar, M. IoT data sharing platform in web 3.0 using blockchain technology. Electronics 2023, 12, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, G.; Singh, H.; Rani, S.; Kataria, A.; Min, H. Smart traceable framework for transportation of transplantable organs using IPFS, iot, and smart contracts. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibba, G.; Destefanis, G.; Neykova, R.; Ortu, M.; Aufiero, S.; Bartolucci, S. Dai: A Dependencies Analyzer and Installer for Solidity Smart Contracts. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering-Companion (SANER-C), Rovaniemi, Finland, 12 March 2024; pp. 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.M. Introduction to Remix IDE. In A Brief Introduction to Web3: Decentralized Web Fundamentals for App Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 89–126. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K. Data Authenticity. In A Comprehensive Guide for Web3 Security: From Technology, Economic and Legal Aspects; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 177–200. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, S.K.; Satapathy, S.C. An Investigation Into Smart Contract Deployment on Ethereum Platform Using Web3. js and Solidity Using Blockchain. In Data Engineering and Intelligent Computing: Proceedings of ICICC 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 549–561. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, R.; Kalra, S.; Attri, V.K. An Approach for Secure Product Traceability in Food Supply Chain Based on Blockchain. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. 2021, 12, 221–233. [Google Scholar]
- Foschini, L.; Gavagna, A.; Martuscelli, G.; Montanari, R. Hyperledger Fabric Blockchain: Chaincode Performance Analysis. In Proceedings of the ICC 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 7–11 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal, R.K.; Kumar, N. Exploring Hyperledger Caliper Benchmarking Tool to Measure the Performance of Blockchain Based Solutions. In Proceedings of the 2024 11th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO), Noida, India, 14–15 March 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Connors, C.; Sarkar, D. Comparative study of blockchain development platforms: Features and applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.01913. [Google Scholar]
- Caro, M.P.; Ali, M.S.; Vecchio, M.; Giaffreda, R. Blockchain-Based Traceability in Agri-Food Supply Chain Management: A Practical Implementation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IoT Vertical and Topical Summit on Agriculture-Tuscany (IOT Tuscany), Tuscany, Italy, 8–9 May 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, K.; Bowman, M.; Mitchell, J.; Amundson, S.; Middleton, D.; Montgomery, C. Sawtooth: An introduction; The Linux Foundation: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Nudin, S.; Labus, A.; Lukovac, P.; Suvajdžić, M. DApp for Food Traceability Based on PyTeal and Algorand. E-Bus. Technol. Conf. Proc. 2023, 3, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Deepa, T.; Saraswathi, N.; Hariprasad, S.; Praveen, K.; Elamurugan, P.; Dinesh, V. Design and implementation of blockchain based peer to peer energy trading platform. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2335, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, N.; Agbu, A.; Oloyede, A.; Essien, E.; Eze, A.; Mhambe, C. Software tool to store IoT device data onto a blockchain. Softw. Impacts 2023, 16, 100511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, J.; Tai, S. Zokrates-Scalable Privacy-Preserving Off-Chain Computations. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings) and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE Smart Data (SmartData), Halifax, NS, Canada, 30 July–3 August 2018; pp. 1084–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Ham, Y.; Ryou, J. Privacy-preserving credential smart contracts using Zokrates. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. (TIIS) 2024, 18, 2417–2430. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, I. Blockchain Consensus. In Blockchain Consensus: An Introduction to Classical, Blockchain, and Quantum Consensus Protocols; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2022; pp. 207–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, A.M.; Harding, D.A. Mastering Bitcoin: Programming the Open Blockchain, 3rd ed.; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, E.A. A Comparative Survey of Consensus Algorithms Based on Proof of Work. In Emerging Technologies in Data Mining and Information Security; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F. Challenges of Proof-of-Useful-Work (PoUW). In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 1st Global Emerging Technology Blockchain Forum: Blockchain & Beyond (iGETblockchain), Irvine, CA, USA, 7–11 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Deng, X.Q.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Lou, X. Delegated Proof of Stake Consensus Mechanism Based on Community Discovery and Credit Incentive. Entropy 2023, 25, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiayias, A.; Koutsoupias, E.; Marmolejo-Cossío, F.; Stouka, A.P. Balancing Participation and Decentralization in Proof-of-Stake Cryptocurrencies. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Algorithmic Game Theory, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 3–6 September 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 333–350. [Google Scholar]
- Doolani, N. Proof-of-Stake for SpartanGold. Master’s Thesis, San Jose State University, San Jose, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayet, Q.; Hennebert, C.; Kieffer, Y.; Beroulle, V. Embedded Elapsed Time Techniques in Trusted Execution Environment for Lightweight Blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain (Blockchain), Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–22 August 2024; Volume 21260, pp. 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayet, Q.; Hennebert, C.; Kieffer, Y.; Beroulle, V. Securing Elapsed Time for Blockchain: Proof of Hardware Time and Some of its Physical Threats. In Proceedings of the 2024 27th Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD), Paris, France, 28–30 August 2024; pp. 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, C.; Sarkar, D. Survey of Prominent Blockchain Development Platforms. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2023, 216, 103650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, S.M. A Comprehensive Study of Blockchain Consensus Protocols. ResearchGate. 2024. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/382447691_A_Study_of_Blockchain_Consensus_Protocols (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Eleyan, A.; Hammoudeh, M.; Alohaly, M. Performance and Scalability Analysis of Ethereum and Hyperledger Fabric. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 67156–67167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kushwaha, D.S. A Survey on Blockchain Architecture and Consensus Mechanism: Design Vulnerability and Security Analysis. Int. J. Cloud Comput. 2024, 13, 485–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloder, A. Comparison of Smart Contract Platforms for Decentralized Applications. TU Wien Repository. 2023. Available online: https://repositum.tuwien.at/bitstream/20.500.12708/188244/1/Voloder%20Ammar%20-%202023%20-%20Comparison%20of%20Smart%20Contract%20Platforms%20for%20Decentralized...pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Xie, J.; Tang, H.; Huang, T.; Yu, F.R.; Xie, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. A survey of blockchain technology applied to smart cities: Research issues and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2794–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 of the European Parliament and of the Council. Establishing the General Principles and Requirements of Food Law and the European Food Safety Authority. 2002. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32002R0178 (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA). Focuses on Preventive Controls and Supply Chain Safety. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2011. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/guidance-regulation-food-and-dietary-supplements/food-safety-modernization-act-fsma (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Goo, J.J.; Heo, J.-Y. The Impact of the Regulatory Sandbox on the Fintech Industry, with a Discussion on the Relation between Regulatory Sandboxes and Open Innovation. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2022, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, L.; Ullah, I.; Kim, D.H. Blockchain-Based Frameworks for Food Traceability: A Systematic Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Qin, R. Blockchain-Powered Parallel FinTech Regulatory Sandbox Based on the ACP Approach. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 52, 3547–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilaris, A.; Fonts, A.; Prenafeta-Boldù, F.X. Assessing blockchain and IoT technologies for agricultural food supply chains in Africa: A feasibility analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T. Blocket: A lightweight privacy-preserving framework for IoT data using Blockchain and off-chain storage. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 96, 731–740. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, W. Layer-2 scaling solutions for Blockchain: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 157899–157921. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, M. Scaling Blockchain for large-scale IoT applications: Current solutions and future directions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Casino, F.; Dasaklis, T.K.; Patsakis, C. A systematic literature review of Blockchain-based applications: Current status, classification and open issues. Telecommun. Syst. 2019, 71, 227–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhizadeh, M.; Saberi, S.; Sarkis, J. Blockchain technology and the sustainable supply chain: Theoretically exploring adoption barriers. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 231, 107831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Iakovou, E.; Shi, W. Blockchain in global supply chains and cross border trade: A critical synthesis of the state-of-the-art, challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 2082–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong You King, D.; Riza, M.A.; Kok Leong, L.; Mohamad, U.H.; Kadir, R.A.; Zulkifli, M.F.; Ahmad, M.N. Blockchain-Enhanced Traceability Framework for Smart Farming with Integrated Ontology-Based Data Standardization. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2024, 14, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzouai, C.; Bouarourou, S.; Zannou, A.; Boulaalam, A.; Nfaoui, E.H. Enhancing IoT Scalability and Interoperability Through Ontology Alignment and FedProx. Future Internet 2025, 17, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, A.M.; Lins, F.A.A.; Rosa, N.S. Survey on integration of consensus mechanisms in IoT-based blockchains. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2023, 29, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, V.; Vaish, A.; Kokila, J. The Need for Lightweight Consensus Algorithms in IoT Environment: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2024 Sixteenth International Conference on Contemporary Computing, Noida, India, 8–10 August 2024; pp. 366–376. [Google Scholar]
- Fotia, L.; Delicato, F.; Fortino, G. Trust in edge-based internet of things architectures: State of the art and research challenges. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, K.S. New Trends in Cryptography: Quantum, Blockchain, Lightweight, Chaotic, and Dna Cryptography. In New Frontiers in Cryptography: Quantum, Blockchain, Lightweight, Chaotic and DNA; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 65–87. [Google Scholar]
- Cocco, L.; Tonelli, R.; Marchesi, M. Blockchain and self sovereign identity to support quality in the food supply chain. Future Internet 2021, 13, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Hazrati Fard, S.M.; Amiri-Zarandi, M.; Dara, R. Protecting farmers’ data privacy and confidentiality: Recommendations and considerations. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 903230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, I.A.; Ansarullah, S.I.; Ahmad, F.; Amir, S.; Sidana, S.; Sinha, A.; Khalid, S.; Yazdani, G. Leveraging artificial intelligence in agribusiness: A structured review of strategic management practices and future prospects. Discov. Sustain. 2025, 6, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, J.; Shoomal, A.; Jahanbakht, M.; Ozay, D. Driving Supply Chain Transformation with IoT and AI Integration: A Dual Approach Using Bibliometric Analysis and Topic Modeling. IoT. 2025, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Thani, M.; Hadid, M.; Padmanabhan, R.; Kerbache, L.; Elomri, A. Smart Food Supply Chain Management: A Bibliometric and Systematic Review. Food Humanit. 2025, 5, 100736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bada, A.O.; Damianou, A.; Angelopoulos, C.M.; Katos, V. Towards a Green Blockchain: A Review of Consensus Mechanisms and Their Energy Consumption. In Proceedings of the 2021 17th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems (DCOSS), Pafos, Cyprus, 14–16 July 2021; pp. 503–511. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).