Abstract
Forgeries exist in many fields. Money, goods, and works of art have been imitated for centuries to deceive and make a profit. In the field of Cultural Heritage, nuclear techniques can be used to study art forgeries. Ion beam analysis (IBA), as well as 14C accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS), are now established techniques, and the purpose of this paper is to report on their capacity to provide information on ancient, as well as modern, forgeries. Two case studies are presented: the production of silver counterfeit coins in the 16th century and the detection of recent forgeries of 20th century paintings. For the counterfeit coins, two silvering processes were identified by IBA: mercury silvering (also called amalgam silvering or fire silvering) and pure silver plating. The discovery of 14 mercury silvered coins is an important finding since there are very few known examples from before the 17th century. In the detection of recent forgeries, among the five paintings examined, 14C dating showed that three of them are definitely fakes, one is most likely a fake, and one remains undetermined. These results were obtained by using the bomb peak calibration curve to date canvas and paint samples.
1. Introduction
Counterfeiting is the fraudulent imitation of a valuable product with the intention to deceive. This illegal practice is found in many fields: forgery of currency or documents, imitation of items such as clothing, pharmaceuticals, automobile and aircraft parts, food, electronics, watches, and works of art. One of the main issues for experts is to identify or to date the material used in producing forgeries, as the appearance is generally close to that of the genuine product. Carried out together with other expertise tools, scientific investigations are, thus, conducted to clarify the authenticity of the product, based on composition and/or age determination.
When dealing with genuine or alleged cultural heritage objects, these investigations have to be as minimally invasive as possible. The most widespread methodology is mainly based on imaging techniques, such as multispectral imaging, X-ray radiography, or microscopy, and on chemical analysis to look for anachronisms or contentious materials [1,2,3,4,5]. In recent decades, the advent of nuclear techniques—derived from low-energy accelerators—for art and archaeological study has paved the way for new methodologies to analyze and authenticate cultural heritage objects [6,7,8,9,10,11,12].
Ion beam analysis (IBA), as well as 14C accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS), are now established techniques [13,14], and the purpose of this paper is to report on their capacity to provide information on ancient and modern forgeries. Two case studies are presented: (1) the production of silver counterfeit coins in the 16th century AD and (2) the detection of modern painting forgeries.
The results obtained here contribute to our knowledge of ancient counterfeiting and modern forgery practices.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Counterfeit Coin Characterization by Ion Beam Analysis
It is relatively rare to find counterfeit coins for many reasons. First, counterfeit coins were not commonly kept as valuables by private individuals in the past and, when preserved, collectors have neglected them. Furthermore, the generally poor quality of the imitations, as well as corrosion, prevent good preservation.
However, the hoard of Preuschdorf, found in 2005, offered the opportunity to explore the production of counterfeit coins in the 16th century [15,16]. Among 7527 coins found, 38 counterfeit coins were identified (Table 1), imitating contemporaneous official issues (mainly Pfennige) produced in the Holy Roman Empire between 1535 and ~1620 (Figure 1). Non-destructive techniques were used to investigate their manufacture: X-ray radiography and Ion beam analysis (IBA) for the coins [16,17,18] and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) for fragments collected during restoration. Particle-induced X-ray emission (PIXE) and Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) were carried out simultaneously using the 3 MeV proton beam of the AGLAE accelerator at the Centre de Recherche et de Restauration des Musées de France (Louvre Palace, Paris, France) [19]. PIXE analysis provided elementary composition (mainly Ag, Cu, Au, Pb, Zn, Hg) and RBS—the depth profile of the major elements. The experiments were conducted with a setup combining two Si (Li) X-ray detectors for PIXE and one surface barrier detector for RBS [20]. PIXE spectra were fitted by GUPIX or GUPIXWIN [21], and RBS spectra were simulated with SIMNRA [22]. Altogether, 140 coins were ion beam analyzed; only results on the counterfeit coins and their official counterparts are reported in this paper.

Table 1.
Counterfeit coins identified in the hoard of Preuschdorf (Alsace, France) found in 2005. The design of the coin imitates that of the official coin (Pfennig) produced by entities having the right to mint coins, such as cities, bishoprics, counties, abbeys, and other small territories.

Figure 1.
Examples of counterfeit coins from the hoard of Preuschdorf (d–f) compared to their official counterparts (a–c). Details of their provenance are given in Table 1. (Photos: Anaïs Vigneron, Archéologie-Alsace).
2.2. Painting Forgery Dating by 14C AMS
14C AMS was applied to the study of alleged 19th–20th century paintings. Impressionist, Pointillist, Expressionist, Abstract, and Contemporary paintings were selected. Four of them were seized by police after the discovery of a workshop, and another one came from a private collection. For confidentiality reasons, details on the alleged artists cannot be disclosed.
Different materials were sampled (Table 2): wood from the stretchers, fibers from the canvases, and paint (Figure 2). Fibers were previously identified as natural fibers under the microscope [12]. The paint sample was analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), showing the presence of BaSO4, ZnO, and CaCO3-containing pigments in an organic binder.

Table 2.
Paintings and materials selected for 14C dating: wood from stretcher (W), fiber from canvas (F), paint (P).

Figure 2.
(Left): samples of wood, canvas, and paint. (Right): details of the paint layer.
For radiocarbon dating, fiber and wood samples were pretreated with acid-base-acid washes, and the paint sample was only pretreated with acid due to its small size. Samples were dried under vacuum at 60 °C and then placed in quartz tubes with excess CuO and Ag. The quartz tubes were sealed under vacuum (5 × 10−6 mbar) and heated at 850 °C for 5 h. CO2 gas was produced and separated from H2O using a dry-ice/alcohol trap (−78 °C) [23]. CO2 samples were then reduced to graphite targets by hydrogen over an iron catalyst. Carbon isotopes were measured with the AMS LMC14/ARTEMIS facility (Saclay, France) [24]. The 14C contents were converted into calendar years with the OxCal calibration program [25], using the Intcal20 atmospheric curve [26] for pre-bomb ages (i.e., before 1950) and the Bomb13 NH1 post-bomb atmospheric curve [27] for the most recent decades (i.e., after 1950).
3. Results
3.1. Counterfeit Coins
The compositions, in silver and copper, of the counterfeit coins and their official counterparts are presented in Figure 3. Two main groups are observed. The official coins contain between 20% and 42% of silver, whereas the counterfeit coins show a low silver content.
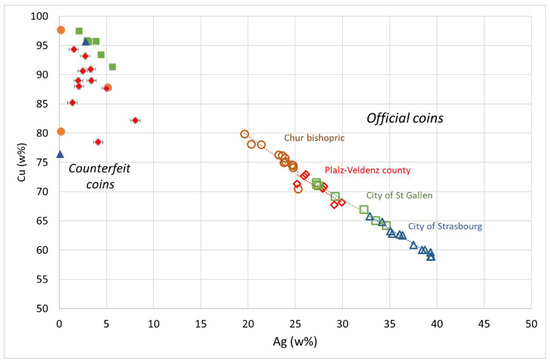
Figure 3.
Silver vs. copper contents (in wt%) for selected coins of the Preuschdorf hoard coming from the cities of Strasbourg and St. Gallen, the county of Pfalz-Veldenz, and the bishopric of Chur. Open symbols correspond to official coins, and filled symbols correspond to counterfeit coins.
For the official coins, two major elements are present: silver and copper. The mean silver concentration for the coins issued by the city of Strasbourg is 37 ± 2%; this high content is in accordance with the official finesses of 375/1000 set by the Imperial minting ordinance (Reichsmünzordnung) of the Holy Roman Empire in 1559 [28]. In contrast, the coins issued by the bishopric of Chur in the Swiss Confederation have a low silver content (23 ± 3%), reflecting a production of poor quality and known to be struck for exportation [29]. The coins produced by the city of St. Gallen and the county of Palatinate (Pfalz-Veldenz) show intermediate silver contents of 30 ± 3% and 27.5 ± 1.8%, respectively.
The counterfeit coins are characterized by their low content in silver (less than 8%) and high content in copper (from 76 to 98 wt%). The values are scattered due to the variable presence of other elements such as mercury, zinc, and tin. Mercury is detected in the counterfeit coins imitating those of the county of Palatinate (Pfalz-Veldenz, (catalogue number 104.F; see Table 1)), in one coin copying that of the city of Strasbourg (151.F), and in another copying that of the bishopric of Chur (188.F). Mercury is clearly correlated to silver (Figure 4), suggesting the presence of an Ag-Hg alloy at the surface of the coin. The mean ratio between silver and mercury is about 1, corresponding to a layer composed of 50% Ag and 50% Hg. However, a large scatter is observed from one coin to another, with ratios from 1.6 to 0.3, corresponding to compositions of ~62% Ag and 38% Hg to 25% Ag and 75% Hg.
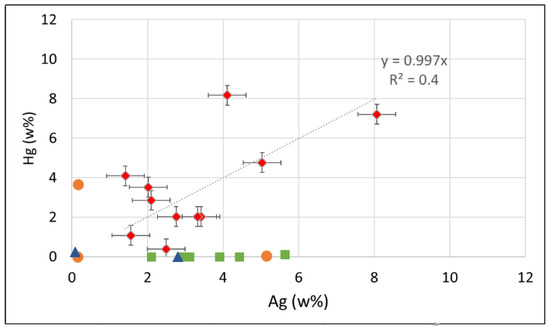
Figure 4.
Silver vs. mercury contents (in wt%) for the counterfeit coins of the Preuschdorf hoard coming from the cities of Strasbourg (blue) and St. Gallen (green), the county of Pfalz-Veldenz (red), and the bishopric of Chur (orange).
The RBS spectrum of a coin containing mercury is presented in Figure 5a. The SIMNRA simulation [22] indicates that silver and mercury are together at the surface of the coin, forming a 1–2 µm thick layer of 50 Hg wt% and 50 Ag wt%. A composition of 27 Hg wt% and 73 Ag wt% was also found for another coin [20]. Both compositions are in agreement with the PIXE results and confirm the presence of a silver-mercury layer at the surface of some counterfeit coins, mostly the imitations from the county of Palatinate (Pfalz-Veldenz, 104.F). For comparison, Figure 5b shows the RBS spectrum of an official coin made of a homogeneous silver-copper alloy.
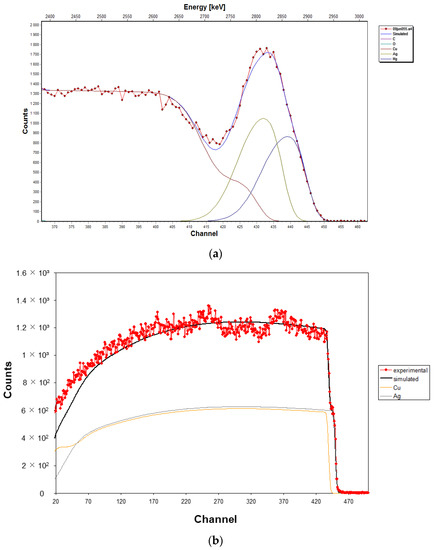
Figure 5.
The 3 MeV proton Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) spectrum of a counterfeit coin (a) and that of an official coin (b). For the counterfeit coin, RBS shows a silver-mercury layer on a copper substrate, whereas for the official coin, RBS shows a homogeneous silver-copper alloy.
None of the other 24 counterfeit coins contain a significant amount of mercury. These are the imitations of the city of St. Gallen (195.F), the bishopric of Speyer (133.F), the bishopric of Mainz (60.F), the county of Stolberg (135.F), the county of Salm (118.F), the two other specimens of the bishopric of Chur (188.F), the other specimen of the city of Strasbourg (151.F), as well as the other identified (160.F, 146.F, 112.F) and unidentified coins. These coins were not well preserved, and observation under the microscope was necessary to interpret the low content in silver (0.2 to 5.6 %). This result is due to a thin layer of pure silver coated at the surface of the coin, and the apparent percentage of silver determined by PIXE is related to the thickness of the silver layer. The cores of these counterfeit coins are composed of copper or brass (copper and zinc).
In summary, two counterfeiting processes were identified by IBA: (a) mercury silvering (also called amalgam silvering or fire silvering) of a copper core for 14 coins, 12 of which come from the county of Palatinate (Pfalz-Veldenz, 104.F), as well as (b) a thin layer of pure silver coated on a brass, bronze, or copper core for 24 coins. The application of pure silver can be achieved by coating a thin silver foil or by electrochemical replacement. The latter process is a plating technique that uses the electro-differential between the solution and the metal to be plated; copper blanks are immersed in a solution containing silver flakes, salt (NaCl), and wine lees (potassium bitartrate, KC4H5O6) [30]. After a few hours, a thin layer of silver is deposited on the substrate [14], and the coins are ready to be struck.
The discovery of 14 mercury silvered coins is an important finding since there are very few known examples from before the 17th century [31,32]. The earliest examples are the forged Iranian dirhem dating from the 9th to 10th centuries [33], four pennies of the 13th century [34], and one coin of the 15th century [35]. The imitation (135.F) of Ludwig II of Stolberg-Königstein (1535–1574) was wrongly attributed to the group of mercury-silvered coins in a previous publication [18]. As a result, the identification of one counterfeit coin (188.F) of Peter II Rascher (1581–1601), the bishop of Chur, and 12 counterfeit coins (104.F) of Johann August of Palatinate-Lützelstein (1598 to 1611), the count of Pfalz-Veldenz, constitutes a significant contribution to our knowledge of ancient counterfeiting practices [36] and the amalgam silvering process.
3.2. Art Forgery Dating
Radiocarbon dating results, obtained for the wooden stretcher of four paintings, are presented in Table 3 and Figure 6.

Table 3.
14C accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) dating results of the wood samples taken from the painting stretchers. Uncalibrated radiocarbon ages are reported in years Before Present (BP), i.e., in years before 1950. Calibrated dates are obtained by calibrating the radiocarbon ages using the Intcal20 atmospheric curve [26] (Figure 7).
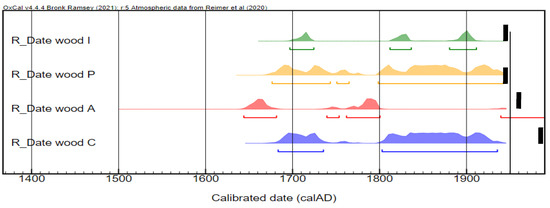
Figure 6.
Radiocarbon calibrated dates (shown in calAD) of the wood samples, taken from the stretchers of the Impressionist (I), Pointillist (P), Abstract (A), and Contemporary (C) paintings. The black bars indicate the death of the alleged artists. The radiocarbon calibrated dates were obtained using the atmospheric calibration curve Intcal20 [26].
All the dates are between the 17th century and 1950, with variable distributions. The ranges are very large due to the shape of the calibration curve for these times (Figure 7). These dates, obtained for the wood, correspond to the time when the trees were still standing and incorporated 14C. To know the time when the trees were cut down, it is necessary to have samples containing sapwood, which is not the case here. As a result, the dated piece of wood can be older than the date of the tree felling (known as the “old wood effect”), making it difficult to estimate the stretcher manufacture. The most recent year recorded by 14C for the stretcher wood is 1911, 1942, 1950, and 1938 for the Impressionist, Pointillist, Abstract, and Contemporary paintings, respectively. These dates are coherent with the lifetime of the alleged artists. However, due to the wide distribution, as well as the old wood effect, which also includes the unknown duration between the felling of the trees and the stretcher manufacture, it is not possible to conclude the date at which the paintings were executed.
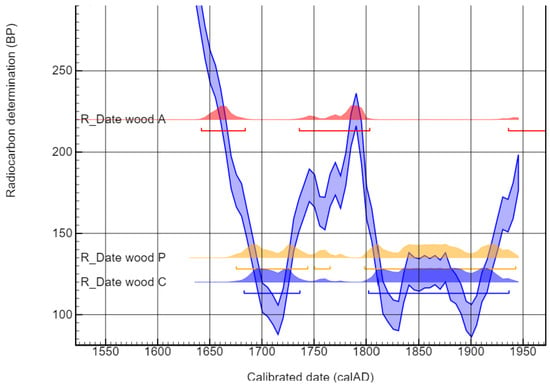
Figure 7.
Calibration of the wood samples taken from the painting stretchers. The blue curve is the atmospheric calibration curve (Intcal20) used to calibrate 14C dates before 1950 [26].
Radiocarbon dating results obtained for the canvas of four paintings and for the paint of one painting are presented in Table 4 and Figure 8.

Table 4.
14C Fraction Modern (F14C) results for the fibers taken from the painting canvases and for a sample of paint taken from the white paint of the Abstract painting. F14C is the unit used for post-bomb samples. Radiocarbon dates were calibrated using the Bomb13 NH1 post-bomb atmospheric curve [27] (Figure 8). See text for details.
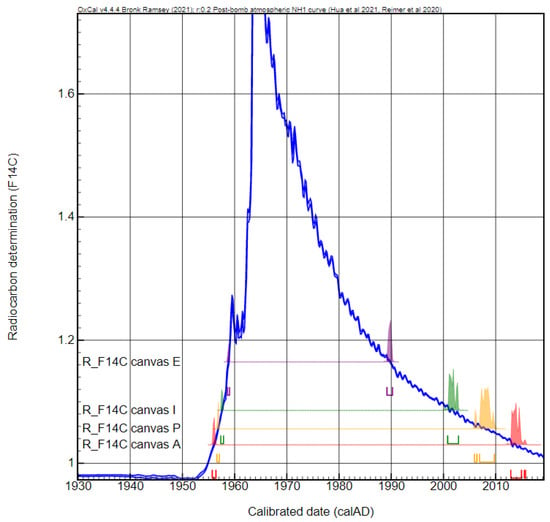
Figure 8.
Calibration of the fiber samples taken from the canvas of the Impressionist, Pointillist, Abstract, and Expressionist paintings. The blue curve is the post-bomb atmospheric calibration curve (Bomb13 NH1) used to calibrate 14C dates after 1950 [25,26,27]. See text for details.
The 14C Fraction Modern (F14C) indicates the proportion of radiocarbon atoms in a sample as compared to samples that were modern in 1950. In the late 1950s and 1960s the 14C concentration in the atmosphere almost doubled due to the atmospheric nuclear weapon tests. Thus, a F14C value higher than 1 indicates “post-bomb” samples. After the atmospheric nuclear test ban treaty in 1963, the 14C content decreased due to its dilution in the atmosphere [37]. This event, including artificial 14C production and decrease, referred to as the “bomb peak”, is used as the calibration curve for radiocarbon dating of recent samples.
The 14C content (F14C) of all the fibers is higher than 1, showing, unambiguously, that the canvas fabrics originate from plants that grew at the time when 14C was in excess in the atmosphere. After calibration, two solutions are determined for each radiocarbon result due to the shape of the calibration curve (Figure 8). The dates, corresponding to the plant harvesting, are the following: 1957 or 2000–2003, 1956–1957 or 2004–2010, 1957–1959 or 1987–1990, and 1955–1956 or 2012–2015 for the Impressionist, Pointillist, Expressionist, and Abstract paintings, respectively. For the first three paintings, both solutions are after the death of the alleged artists in the 1940s-early 1950s. These results demonstrate that these paintings are forgeries performed in the years 1956–1957 or 2000–2010, for the Impressionist and Pointillist specimens, and in the years 1957–1959 or 1987–1990 for the Expressionist one. For the Abstract painting, the interpretation of the results—1955–1956 and 2012–2015—is less straightforward since the alleged artist died in the 70s. The second solution is after the death of the artist, but the first one is 15–20 years earlier. It cannot be excluded that an artist may keep untouched canvases in his/her workshop for one or two decades, even if the typical storage duration is between two and five years [38]. A similar result was obtained for the paint sample (Table 4); however, it is less common to preserve a tube of paint for such a long time. The latter result suggests that the Abstract painting is also a fake. For the Contemporary painting, the canvas dating failed due to the massive presence of glue still embedded in the fibers even after a strong cleaning treatment.
Among the five paintings examined, 14C dating shows that three of them are definitely fake, one is most likely fake, and one remains undetermined.
4. Conclusions
Ion beam analysis (IBA) and 14C accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) are methods of choice to analyze ancient artefacts and works of art since they are minimally invasive. Both techniques can also contribute to the study of counterfeiting and art forgery [39]. In this paper, the metallurgical processes used to produce silver counterfeit coins in the 16th century were studied in detail, revealing the presence of 14 coins silvered with mercury. This discovery is an important finding since there are very few known examples before the 17th century. Five paintings were radiocarbon dated. Using the bomb peak calibration curve, it was unambiguously demonstrated that three paintings, alleged to be of the beginning of the 20th century, are forgeries made after 1956. It is suggested that another painting alleged to be painted in the 1970s could be a more recent forgery.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to restricted access to databases. The IBA archived dataset is managed by the AGLAE group at the Centre de Recherche et de Restauration des Musées de France (Paris, France). The 14C AMS archived dataset is managed by the LMC14 Laboratory (Saclay, France).
Acknowledgments
The author wishes to thank Dominique Robcis (C2RMF), Elise Alloin and Anaïs Vigneron (Archéologie Alsace), Ulrich Klein (numismatist) and the AGLAE group (C2RMF, Paris, France) for their invaluable contribution to the study of the Preuschdorf hoard and her current colleagues of the LMC14 laboratory for the painting sample preparation, 14C measurements and fruitful discussion. Many thanks also to Estelle Itié and Ilenia Cassan for their confidence in the study of one of the paintings presented here. This is LSCE contribution number 7901.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ragai, J. The scientific detection of forgery in paintings. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 2013, 157, 164–175. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/24640239 (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Chaplin, T.D.; Clark, R.J.H. Identification by Raman microscopy of anachronistic pigments on a purported Chagall nude: Conservation consequences. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, A.; Bonizzoni, L. True versus forged in the cultural heritage materials: The role of PXRF analysis. X-Ray Spectrom. 2014, 43, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, A.; Kelman, T.; Murray, P.; Marshall, S.; Stothard, D.J.M.; Eastaugh, N.; Eastaugh, F. Hyperspectral imaging combined with data classification techniques as an aid for artwork authentication. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, C.E.; Dijkema, D.; Rush, K. A discriminating yellow: The detection of an anachronistic organic pigment in two backdated metaphysical paintings by Giorgio de Chirico. Studi Online 2020, 13, 59–68. Available online: https://www.archivioartemetafisica.org/studi-online-anno-vii-n-13-1-gennaio-30-giugno-2020/ (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Biron, I.; Pierrat-Bonnefois, G. La tête égyptienne en verre bleu du musée du Louvre. L’actualité Chim. 2007, 312–313, 47–52. Available online: https://new.societechimiquedefrance.fr/numero/n312-313-octobre-novembre-2007/ (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Calligaro, T.; Coquinot, Y.; Reiche, I.; Castaing, J.; Salomon, J.; Ferrand, G.; Le Fur, Y. Dating study of two rock crystal carvings by surface microtopography and by ion beam analyses of hydrogen. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 94, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedi, M.; Carraresi, L.; Grassi, N.; Migliori, A.; Taccetti, F.; Terrasi, F.; Mandò, P. The Artemidorus papyrus: Solving an ancient puzzle with radiocarbon and ion beam analysis measurements. Radiocarbon 2010, 52, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Caforio, L.; Fedi, M.E.; Mandò, P.A.; Minarelli, F.; Peccenini, E.; Pellicori, V.; Petrucci, F.C.; Schwartzbaum, P.; Taccetti, F. Discovering forgeries of modern art by the 14C Bomb Peak. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2014, 129, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, L.; Hajdas, I.; Ferreira, E.S.B.; Scherrer, N.C.; Zumbühl, S.; Smith, G.D.; Welte, C.; Wacker, L.; Synal, H.-A.; Günther, D. Uncovering modern paint forgeries by radiocarbon dating. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13210–13214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiche, I.; Beck, L.; Caffy, I. New results with regard to the Flora bust controversy: Radiocarbon dating suggests nineteenth century origin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.; Caffy, I.; Mussard, S.; Delqué-Količ, E.; Moreau, C.; Sieudat, M.; Dumoulin, J.-P.; Perron, M.; Thellier, B.; Hain, S.; et al. Detecting recent forgeries of Impressionist and Pointillist paintings with high-precision radiocarbon dating. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 333, 111214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeynes, C.; Palitsin, V.; Kokkoris, M.; Hamilton, A.; Grime, G. On the accuracy of Total-IBA. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2020, 465, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdas, I.; Ascough, P.; Garnett, M.H.; Fallon, S.J.; Pearson, C.L.; Quarta, G.; Spalding, K.L.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yoneda, M. Radiocarbon dating. Nat. Rev. Meth. Primers 2021, 1, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.; Alloin, E.; Klein, U.; Borel, T.; Berthier, C.; Michelin, A. Le trésor de Preuschdorf (Bas-Rhin) XVIIè siècle. Premiers résultats d’une étude pluridisciplinaire. Rev. Numismat. 2010, 166, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.; Alloin, E.; Michelin, A.; Téreygeol, F.; Berthier, C.; Robcis, D.; Borel, T.; Klein, U. Counterfeit coinage of the Holy Roman Empire in the 16th century: Silvering process and archaeometallurgical replications. In Der Anschnitt. Beiheft 26: Archaeometallurgy in Europe III; Hauptmann, A., Modarressi-Tehrani, D., Eds.; Deutschen Bergbau-Museum Bochum: Bochum; Germany, 2015; pp. 97–106. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/14279648 (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Beck, L. Recent trends in IBA for cultural heritage studies. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2014, 332, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.; Alloin, E.; Vigneron, A.; Caffy, I.; Klein, U. Ion beam analysis and AMS dating of the silver coin hoard of Preuschdorf (Alsace; France). Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2017, 406, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calligaro, T.; Pacheco, C. Un accélérateur de particules fait parler les œuvres d’art et les objets archéologiques. Reflets Phys. 2019, 63, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.; Pichon, L.; Moignard, B.; Guillou, T.; Walter, P. IBA techniques: Examples of useful combinations for the characterization of cultural heritage materials. Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 2011, 269, 2999–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L.; Boyd, N.I.; Grassi, N.; Bonnick, P.; Maxwell, J.A. The Guelph PIXE software package IV. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2010, 268, 3356–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M. Improved physics in SIMNRA 7. Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 2014, 332, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumoulin, J.-P.; Comby-Zerbino, C.; Delqué-Količ, E.; Moreau, C.; Caffy, I.; Hain, S.; Perron, M.; Thellier, B.; Setti, V.; Berthier, B.; et al. Status report on sample preparation protocols developed at the LMC14 laboratory, Saclay, France: From sample collection to 14C AMS measurement. Radiocarbon 2017, 59, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, C.; Messager, C.; Berthier, B.; Hain, S.; Thellier, B.; Dumoulin, J.-P.; Caffy, I.; Sieudat, M.; Delqué-Količ, E.; Mussard, S.; et al. ARTEMIS, the 14C AMS facility of the LMC14 National Laboratory: A status report on quality control and microsample procedures. Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 1755–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronk Ramsey, C.; Lee, S. Recent and Planned Developments of the Program OxCal. Radiocarbon 2013, 55, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, P.J.; Austin, W.E.N.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, C.B.; Butzin, M.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. The IntCal20 Northern Hemisphere radiocarbon age calibration curve (0–55 cal kBP). Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 725–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; Turnbull, J.; Santos, G.; Rakowski, A.; Ancapichún, S.; De Pol-Holz, R.; Hammer, S.; Lehman, S.J.; Levin, I.; Miller, J.B.; et al. Atmospheric radiocarbon for the period 1950–2019. Radiocarbon 2021, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, U. L’étude numismatique des monnaies. In Le dépôt monétaire de Preuschdorf: Autopsie d’un Trésor; Cercle d’Histoire et d’Archéologie de l’Alsace du Nord: Soultz-sous-forêts, Val de Moder, France, 2017; pp. 31–55. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, K. Pfennige, Heller, Kupfergeld. Kleingeld im Rheinland vom Spätmittelalter bis ins 19.Jahrhundert; Numis. Gessel. Speyer: Hanhofen, Germany, 2003; pp. 55–67, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Arles, A.; Téreygeol, F. Le procédé de blanchiment dans les ateliers monétaires français au XV-XVIème siècle: Approche archéométrique et expérimentale. Anu. Estud. Mediev. 2011, 41, 699–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anheuser, K. Where is all the amalgam silvering? MRS Online Proceed. Library 1996, 462, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlir, K.; Padilla-Alvarez, R.; Migliori, A.; Karydas, A.G.; Božičević Mihalić, I.; Jakšić, M.; Zamboni, I.; Lehmann, R.; Stelter, M.; Griesser, M.; et al. The mystery of mercury-layers on ancient coins—A multianalytical study on the Sasanian coins under the Reign of Khusro II. Microchem. J. 2016, 125, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachou, C.; McDonnell, J.G.; Janaway, R.C. Experimental investigation of silvering in late Roman coinage. MRS Online Proceed. Library 2001, 712, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Niece, S. Technology of silver-plated coin forgeries. In Metallurgy in Numismatics. Volume 3; Archibald, M.M., Cowell, M.R., Eds.; Royal Numismatic Society: London, UK, 1993; pp. 227–239. [Google Scholar]
- Arles, A.; Téreygeol, F.; Gratuze, B. Two silvering processes used in the French medieval minting. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Archaeometallurgy in Europe, Aquileia, Italy, 17–21 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Deraisme, A.; Beck, L.; Pilon, F.; Barrandon, J.-N. A study of the silvering process of the Gallo-Roman coins forged during the third century AD. Archaeometry 2006, 48, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, I.; Kromer, B.; Hammer, S. Atmospheric Δ14CO2 trend in Western European background air from 2000 to 2012. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2013, 65, 20092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, F.; Eastaugh, N.; Ford, T.; Townsend, J.H. Bomb-pulse radiocarbon dating of modern paintings on canvas. Radiocarbon 2019, 61, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdas, I.; Jull, A.; Huysecom, E.; Mayor, A.; Renold, M.; Synal, H.-A.; Hatté, C.; Hong, W.; Chivall, D.; Beck, L.; et al. Radiocarbon dating and the protection of cultural heritage. Radiocarbon 2019, 61, 1133–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).