Abstract
Crystopal is a mechanically strong yet highly decorative plastic with a translucent and crackled appearance that was produced in the 1960s by the artist and plastics engineer Armand G. Winfield (1919–2009) and his company, Crystopal, Ltd. Many of Winfield’s collected plastic objects are housed within the Syracuse University Libraries, but some lack complete archival descriptions, including plastic compositions. To address this, the non-invasive and non-destructive determination of the polymer identities in Winfield’s artifacts was performed by Raman spectroscopy. Our studies generally begin with the database matching of an artifact spectrum to that of a polymer standard, but when objects known to be fabricated from Crystopal were analyzed, a database of over 100 representative polymers failed to yield the chemical identity of the plastic. However, the Raman spectrum of Crystopal displayed a unique chemical fingerprint that revealed it to be composed of an unsaturated polyester crosslinked with styrene. This Raman spectrum was added to the database and used as reference for the unambiguous identification of Crystopal artifacts, distinguishing them from decorative plastics with similar appearances. The addition of Crystopal to the polymer database provides a pathway toward establishing artifact provenance and preserving objects crafted from this unique and decorative plastic.
1. Introduction
The mid-twentieth century was an era when the use of plastic products became ubiquitous. Plastics were engineered to create almost everything from industrial parts to tableware [1]. While the changeover from natural to plastic materials was considered to be practical and cost-saving, many times, these products were also esthetically pleasing. The physical nature of plastic permits different formulations that achieve a great variety of mechanical and esthetic results. This combination of practical and artistic qualities enabled plastic’s rise into popular culture [2]. Pioneering plastics engineer and artist Armand G. Winfield (1919–2009) is an example of an innovator who advanced the use of plastics in many spheres. During his expansive career, Winfield combined his technical knowledge and artistic skill to formulate specialized plastics and manufacturing techniques to produce a wide assortment of goods, including jewelry, decorative domestic items, and architectural materials. Some highlights of Winfield’s career were designing and directing the construction of 13 pavilions and exhibits for the 1964 New York World’s Fair, consulting for the United Nations to build low-cost durable housing, and developing lightweight fiber-reinforced plastic sets with the Metropolitan Opera in New York City [3,4]. He was also elected as a fellow of the Society of Plastics Engineers in 2000 [5], and his work was collected by the Cooper Hewett Museum Archive [4].
A lesser-known chapter of Winfield’s story took place in the 1960s. It began when he traveled to France to learn and license the recently patented technique for making Crystopal, a decorative plastic with a crackled, translucent appearance and strong mechanical properties [6]. The crackling and pigmentation in the plastic could be altered to change its appearance, including the amount of light scattered by the crackles and the amount of transparency. The different formulations of Crystopal might have been inspired by crackle (ice) glass and uranium glass [7,8,9,10,11]. Winfield was taught to make this decorative plastic directly by Jean Pierre Fisholle, whom Winfield credits [6] as inventing the technique. However, the Crystopal patent [12] names Samuel Guyot as the patent owner. This patent covers the formulation and process for making artistic and decorative objects, including statues.
In January of 1963, Winfield established Crystopal, Ltd., in Hazardville, Connecticut. According to an unnamed spokesperson for Crystopal, Ltd., Winfield’s vision for the company was to custom-make decorative works from plastic [13]. Winfield adapted the original formulation of Crystopal to American manufacturing processes [6] and used Crystopal to produce material samples and decorative domestic articles, many of which are now held by the Special Collections Research Center at the Syracuse University Libraries (SCRC-SUL) [14]. The company also trademarked a product called Crystolume [15,16], which was made into plastic ornaments painted in the style of stained glass. Crystopal Ltd. even produced an 8’ × 4’ mosaic plastic mural for the Hartford Connecticut Chamber of Commerce [13]. Despite the innovative use of plastics, Winfield’s company was a short-lived venture, and Crystopal, Ltd., closed by 1966 [17]. Even so, Winfield and Crystopal are part of the mid-twentieth-century history of plastics in American popular culture.
In addition to being a plastics artist and engineer, Winfield collected plastic art and artifacts, and he archived his many professional documents. Today, collections of his various works and papers are preserved within the Cooper Hewitt Smithsonian Design Museum, the National Museum of American History Archives Center, the University of New Mexico Center for Southwest Research and Special Collections (UNM-CSWR-SC), and the SCRC-SUL. While the SCRC-SUL Plastics Artifacts Collection (PAC) holds the entire known collection of Crystopal objects, UNM-CSWR-SC holds many of Winfield’s papers, including a small file on Crystopal, Ltd. For example, this file contains a magazine article [7] displaying a photograph of a tabletop appearing to be made of Crystopal in the same color combination as Artifact E in this study. These institutions acknowledge the value of Winfield’s career and professional output by collecting and preserving his work and through their commitment to providing access to researchers and curators in the field of cultural heritage.
The Crystopal objects held by SCRC-SUL were obtained from the National Plastics Center and Museum (NPCM) when it closed in 2008. Most of these artifacts were originally donated to NPCM by Winfield, yet some of their archival descriptions are incomplete, and questions remain about these artifacts. In an effort to learn more about their Crystopal holdings, SCRC-SUL began a collaboration with the Syracuse Chemistry of Artifacts Project (SCOAP). The goal of this study is to use Raman spectroscopy (RS) to characterize the polymer content of artifacts lacking archival descriptions of their material identities. RS was chosen because it can noninvasively and nondestructively [18,19,20] obtain a chemical fingerprint for an object that can be used to uncover its composition. This technique uses laser light that is scattered from the surface of an object and does not require sampling of the material. The scattered light is collected by a fiber-optic probe that is held at or near the surface of the object. Furthermore, the technique is portable and relatively quick (<10 min) [18,19,20,21,22]. RS is generally successful when analyzing plastics, and others have described the advantages and disadvantages of RS in more detail [18,19,20,21,22,23,24].
The methodology used in this study was previously described and involved the compilation of the SCOAP library of Raman spectra for 134 reference plastics [25]. Raman spectra of artifacts are compared to the reference spectra using data-matching software to help identify their plastic compositions. In addition to database matching, a visual inspection of the artifact spectra is required prior to making a conclusive positive identification. For example, in our study of mid-twentieth-century plastic purses [25], the population of the SCOAP library was found to be sufficient for unambiguously identifying their plastic contents. However, at the beginning of this Crystopal study, the first artifact analyzed did not positively match any of the database reference plastics. At this point, the need arose for a better understanding of the composition of Crystopal and for adding Crystopal as a new reference material to the library. This inclusion helps enable the identification of authentic pieces of unlabeled Crystopal in both current and future studies.
In addition to examining well-documented Crystopal artifacts, four objects with incomplete archival descriptions originating from Winfield’s personal collection were analyzed. These artifacts have some visual similarities to the documented Crystopal objects, and RS was used to identify their polymer compositions. In part, the interest in the material identities of these pieces in Winfield’s collection was to help uncover the origins of these objects since a close match to the Crystopal reference could link that artifact to Winfield’s time at Crystopal, Ltd.
A further goal of this spectroscopic study was to uncover evidence of formulation variations and product development during Winfield’s tenure at Crystopal, Ltd., since he was known to experiment with plastics to achieve desirable and innovative effects throughout his career [4,5]. Revealing the chemical identity [26,27] of Crystopal also helps to address concerns about the aging and degradation of these plastic artifacts. In this case, the particular concern is the preservation of artifacts having a novel plastic formulation. Raman spectroscopic studies revealing an artifact’s composition aid the process of selecting conservation techniques matched to the requirements of particular polymers. The preservation of Winfield’s collection is critical to the SCRC-SUL’s mission of conserving the historical record of plastics in America and making Crystopal artifacts available to scholars.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raman Instrument and Data Analysis
An overview of the artifact analysis process is provided here; however, detailed descriptions of the experimental and data analysis methodologies are provided in a previous publication [25]. Raman spectra were obtained using a B&W Tek iRaman Plus portable spectrometer (B&W Tek, Plainsboro, NJ, USA), which was equipped with a 785 nm laser, a fiber-optic probe with an 85 µm spot size, and a CCD detector with a spectral range of 65–3400 cm−1 and a resolution of 4.5 cm−1. One-second exposure times were averaged over 225 acquisitions at 50% laser power (approximately 100 mW). BWSpec software (B&W Tek, v. 4.11) was used for instrument control, data acquisition, and baseline correction.
A database of reference spectra was constructed as described previously [25] using the BWID software (B&W Tek, v. 2.03). The same BWID software was used to analyze and match reference spectra to spectra collected from artifacts. This software uses a Savitsky–Golay first-derivative function for data pre-processing and peak correlation analysis. The spectral region of 200–2600 cm−1, a region containing peaks resulting from common functional groups found in plastics, is used for the analysis. All data from this region are available in the Supplementary Information file, Figures S1–S5. The correlations are expressed as a hit quality index (HQI), with a value of 100 meaning exact numerical equality and a value of 0 meaning no correlation between data sets. A score of >90 reveals a positive match.
2.2. Reference Polymers and Artifacts
Reference polymers (134 different samples) used in the SCOAP spectral library were obtained from several sources. The majority of the reference samples were purchased as kits from Scientific Polymer Products Inc., Ontario, NY, USA (Scipoly.com, Polymer Sample Kit #205) and The ResinKit Company, Woonsocket, RI, USA. Additionally, industrial samples obtained from the PAC at SCRC-SUL and donations from the Plastics Pioneers Association were used as reference polymers.
All artifacts analyzed in this study are housed in the SCRC-SUL. Their accession numbers, descriptions, and data from SCRC-SUL records [14] are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Artifact numbers, physical descriptions, and library catalog information.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Two Original Crystopal Objects and the Establishment of a Crystopal Reference
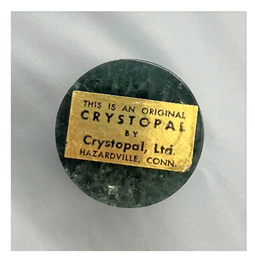
While many of the artifacts from this study are identified as Crystopal in the SCRC-SUL catalog (Table 1), only Artifacts A and B are identified as original pieces of Crystopal with manufacturer-affixed labels (Table 2). Raman spectra of these labeled artifacts were acquired, and the data were analyzed using the BWID software. In both cases, the best match was the styrene/allyl alcohol copolymer (ST/AA) reference, with an HQI of 89.3 for Artifact A and an HQI of 85.6 for Artifact B. This result was surprising since library records [14] identify Crystopal as a reinforced polyester, and this closest-match reference polymer lacks an ester functional group while still having a moderate HQI value. In our previous work [25], an HQI value of >90 was used as a cutoff for the first step in establishing a positive match, with a visual inspection always required before a final determination of the polymer identity is made. The visual inspection of the spectra of Artifacts A and B (Figure 1) reveals that these objects are nearly identical in composition. The artifact spectra show similarities to the ST/AA copolymer reference in that they contain characteristic polystyrene (PST) bands at 1000 cm−1 (ring breathing), 620 cm−1 (in-plane ring deformation), 1455 and 1600 cm−1 (in-plane ring stretching), and aromatic C-H stretching at 3060 cm−1 [28,29,30]. This comparison of the ST/AA copolymer to the Raman spectra of Artifacts A and B reveals that the classic aromatic bands associated with styrene-containing polymers are found in all three spectra and explains the correlation found by the software. However, the artifact spectra have one critical difference from other styrene-containing polymers, a prominent broad peak at 1728 cm−1 that is characteristic of ester carbonyl stretching. The reference ST/AA copolymer spectrum lacks this peak since it does not contain an ester functional group. This precludes assigning the polymer composition of Artifacts A and B as a ST/AA copolymer and also highlights the importance of a careful visual inspection as part of the identification process rather than relying entirely on data-matching algorithms.

Table 2.
Photos of Artifacts A and B.
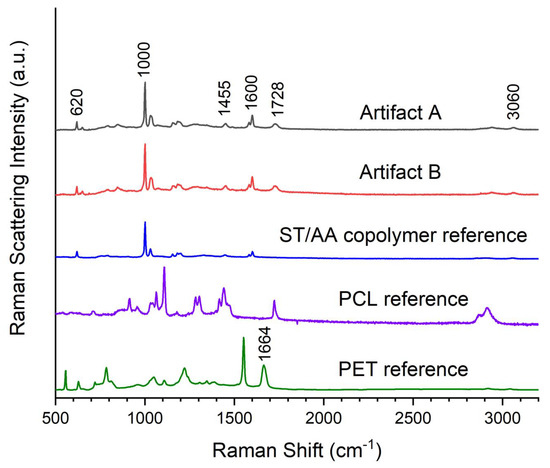
Figure 1.
Comparison of Raman spectra for Artifact A, Artifact B, and references ST/AA, PCL, and PET.
The SCRC-SUL catalog [14] lists the material identity of Crystopal as reinforced polyester, and the artifact spectra do exhibit a characteristic ester carbonyl stretching peak; however, the BWID analysis failed to match the artifact spectra with any polyester standards in our database. These polyesters include polybutylene terephthalate, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyethylene terephthalate glycol-modified, and polycaprolactone (PCL). While none of these references is selected by the BWID analysis as a match, it is useful to make a comparison of two of our polyester references, PET and PCL, to Artifacts A and B (Figure 1). The carbonyl stretching bands in the spectra for Artifacts A and B are at 1728 cm−1 and are similar to that of PCL at 1724 cm−1. Likewise, Koenig’s study [31] of a maleic anhydride-glycol polyester (MA-G) has a carbonyl peak at 1730 cm−1. A higher Raman shift is to be expected for aliphatic esters [29], as illustrated by these results. In contrast, the carbonyl stretching band in the PET spectrum is shifted to 1664 cm−1, typical of aromatic esters. Furthermore, Koenig’s study [31] included the Raman spectrum of the MA-G resin crosslinked (cured) with ST. This spectrum is very similar to the spectra of Artifacts A and B, having both the ester band at 1730 cm−1 and the characteristic PST bands. Ultimately, it can be concluded that the Crystopal artifacts contain aliphatic esters.
One other reference polymer from the SCOAP library related to this study is the styrene-maleic anhydride (ST/MA) copolymer. Since Crystopal contains similar monomers, one might wonder why there was no match with that reference during the BWID analysis. This particular ST/MA copolymer is a vinyl polymer containing anhydride functional groups pendant to the polymer backbone. There are no ester linkages, and thus it lacks an ester carbonyl band. See Figure S1. in the Supplementary Information for more details.
Since Crystopal was patented, the next step in the study was to obtain the original French patent [12] issued in 1958. The patent reveals the formulation of Crystopal to be a combination of two mixtures. The first mixture contains lupersol (an organic peroxide), a polyester resin, and a colorant. The second mixture contains styrene and cobalt naphthenate. The concentration of cobalt naphthenate can be adjusted to control the amount of crackling. These mixtures are reacted in a mold containing glass fibers.
Information from the patent combined with the spectroscopic data leads us to infer that Crystopal is made from an unsaturated, aliphatic polyester resin, providing a double bond along the polymer backbone. Such polyester resins are commonly synthesized by condensation reactions between an unsaturated cyclic anhydride or dicarboxylic acid and a glycol, for example, maleic anhydride and ethylene glycol [31,32,33]. The unsaturated polyester resin is then crosslinked (cured) by addition polymerization with styrene using an organic peroxide initiator and cobalt naphthenate as an accelerator and crackling promotor. This reaction produces the thermoset plastic Crystopal and makes it a glass fiber–reinforced (GFR) unsaturated polyester-styrene (UP/ST) copolymer.
With this understanding of the composition of Crystopal, the Raman spectrum of Artifact A was added to the SCOAP reference library. Artifact B was reanalyzed by the BWID software, and it matched the new reference for Crystopal with an HQI of 99.65. This analysis demonstrates that even visually identical spectra will have some differences in HQI values due in part to the intrinsic noise contained in all spectroscopic measurements. HQI values > 99 indicate extremely high-quality matches between spectra. This result also demonstrates that the pigment differences in the case of Artifacts A and B do not interfere with polymer identification. The BWID match, along with the visual inspection, shows that Artifacts A and B have essentially identical polymer compositions. Since Artifact A was part of Winfield’s personal collection and matches so closely with the other labeled object (Artifact B) and its Raman spectrum contains peaks arising from all of the expected functional groups, it is the best available standard reference for Crystopal.
3.2. Analysis of product Samples and Domestic Items Originating from Winfield’s Personal Collection and Discussion of the HQI Values for Artifacts B–J
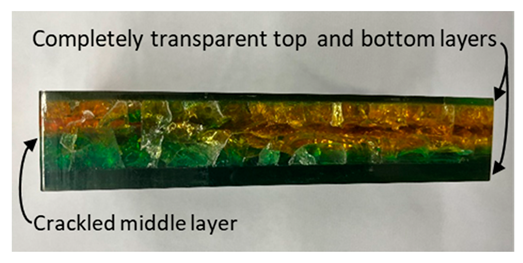
Winfield produced many samples of Crystopal, including Artifacts C, D, and E (Table 3), and Raman spectra were obtained for these artifacts (Figure 2). The spectra for Artifacts C and D were analyzed by the BWID software, and both spectra showed HQI values > 97, matching the Crystopal reference. Visual inspection verifies this analysis since both the typical PST peaks and the ester carbonyl stretch peak are evident. Multiple spectra of Artifact E were taken since this piece is layered with three sections: a completely transparent (lacking any crackling effect) top and bottom and a crackled middle layer. The crackled middle layer is visually typical of Crystopal, while the uncrackled, transparent character of the top and bottom layers does not fit the description from the patent [12] or library description [14]. In all three layers, the Raman spectra match each other by visual inspection and have HQI values > 98, matching the Crystopal reference. These results demonstrate that Winfield was producing items from uncrackled Crystopal in addition to the usual crackled product.

Table 3.
Photos of Artifacts C, D, and E.
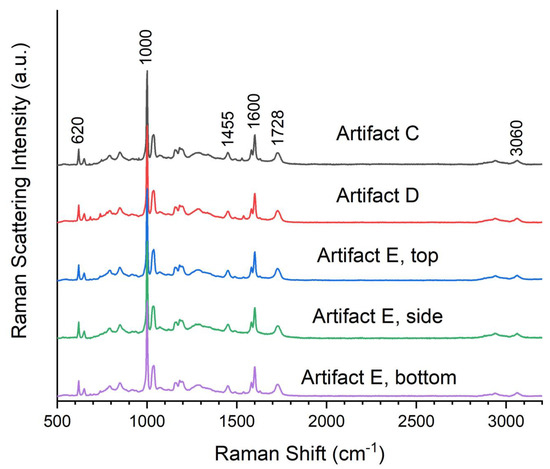
Figure 2.
Raman spectra of Artifacts C, D, and E.
In addition to the sample slabs, Winfield produced decorative items from Crystopal for household use, including candle holders (Artifacts A and F), paperweights (Artifact B), and doorknobs (Artifacts G–J). See Table 2 and Table 4 for photos of these artifacts. Raman spectra of these domestic items were acquired (Figure 3), and BWID analyses for Artifacts F–J were performed. All five decorative artifacts, originally from Winfield’s personal collection, were found to match the Crystopal reference spectrum with HQI values > 95. Visual inspection verified these analyses by identifying the characteristic ester carbonyl stretching peak (1728 cm−1) and characteristic PST peaks (620, 1000, 1455, 1600, 3060 cm−1). The Raman spectrum of Artifact F contains several additional small sharp peaks (685, 740, 777, 817 cm−1) and a 1538 cm−1 peak resulting from heavy pigmentation with phthalocyanine green [34].

Table 4.
Photos of Artifacts F, G, H, I, and J.
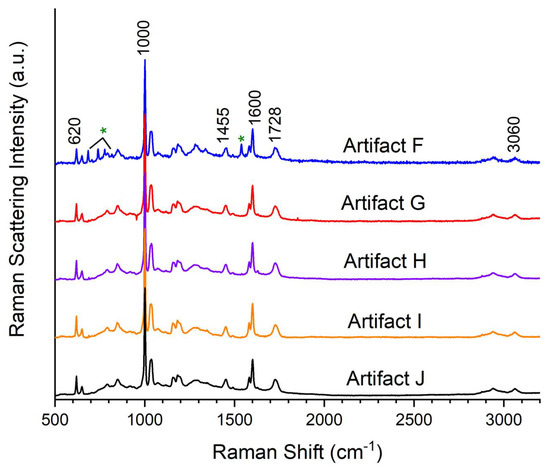
Figure 3.
Raman Spectra of Artifacts F, G, H, I, and J. Peaks marked with “*” originate from phthalocyanine green in Artifact F.
The HQI values for Artifacts B–J show a range of 95–99. Small differences in HQI values are expected because of the heterogeneous nature of Crytopal. Some of this character is due to the varying inclusions of glass fibers and pigments, which can have their own Raman peaks. In some cases, pigments also contribute fluorescence [24] to the spectrum, causing changes to the baseline. Both the additional peaks and fluorescence can act to reduce the HQI value during BWID analysis. Additives to the plastic formulation may not be the whole reason for the range of HQI values. Beginning in the late 1980s, studies of UP/ST copolymers showed that during the addition reaction between the UP resin and ST, microstructures form within the bulk plastic. These microstructures vary in composition and the density of crosslinking and are due to phase separation between the ST and UP as the reaction progresses. When the ST to UP ratio is low, significant amounts of competing intramolecular reactions between double bonds on the UP chain occur, and microgels form, as observed by scanning electron microscopy [35,36,37]. So, the range of HQI values could also be attributed in part to heterogeneous microstructures in the bulk plastic, which cause variations in the Raman spectra. In addition to the heterogeneous morphology of UP/ST copolymers, deviations in HQI could be due to changes in formulation. Winfield was known to experiment with plastic formulations [4,5], and it was shown in this study that he could produce uncrackled Crystopal (Artifact E), which was not described in the Crystopal patent [12]. So, these variations of match quality are to be expected.
3.3. Analysis of Artistic Pieces Originating from Winfield’s Personal Collection and Discussion of the Significance of these Results
The final four objects of this study, Artifacts K–N (Table 5), are artistic pieces donated to the NPCM by Winfield prior to being housed in SCRC-SUL. However, because of incomplete documentation, it is not known if he crafted these pieces or of what they are composed. To aid in uncovering such information, we studied these objects with Raman spectroscopy. Artifact K (Table 5) is a transparent horse bust that is light green with dark green swirls. The plastic lacks the characteristic crackling of the Crystopal Artifacts A–J, yet analysis by BWID shows it has an HQI of 95.17 when compared to the Cystopal reference. Visual inspection of its Raman spectrum (Figure 4) shows characteristic PST and ester carbonyl stretching peaks. The ester carbonyl peak is shifted to 1728 cm−1 as in the spectrum of the Crystopal reference, revealing it contains an aliphatic polyester. Even though Artifact K lacks the characteristic crackling of Crystopal, this study has shown that Winfield was able to produce uncrackled Crystopal in the case of Artifact E, and the Raman spectral analysis identifies Artifact K as Crystopal. Artifact K, however, is the only statue composed of Crystopal, of which we are aware. While it is a unique piece, the Crystopal patent [12] lists the crafting of statues among the uses for this plastic. Thus, this combined information indicates the likelihood that Winfield was involved in its creation.

Table 5.
Photos of artifacts K–N.
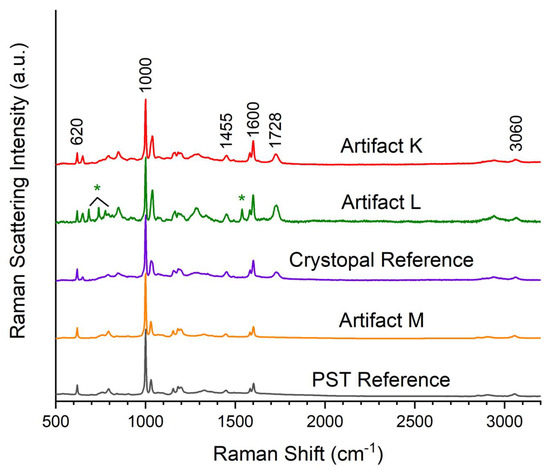
Figure 4.
Raman spectra of Artifacts K–M. Peaks marked with “*” originate from phthalocyanine green in Artifact F.
Artifact L (Table 5) is a green fish-shaped tray with embedded gold glitter and gold paint details. It lacks the characteristic crackling effect and is transparent, although slightly cloudy. There is also a rectangular, white paper label with black printing embedded in the tail of the fish, which is illegible. Artifact L is the only artifact with an embedded label, and the label does not resemble those found on Artifacts A and B. A Raman spectrum of the artifact (Figure 4) was taken, and BWID analysis shows a lack of correlation between Artifact L and the Crystopal reference, with an HQI value of only 80.11. Visual inspection revealed characteristic ester carbonyl stretching and peaks typical of ST-containing plastic. A comparison of the Artifact L and Crystopal reference spectra (with the 1000 cm−1 peaks normalized) reveals Artifact L has relatively higher intensity peaks at 848, 1038, 1163, 1285, and 1730 cm−1. Additionally, there are peaks characteristic of the pigment phthalocyanine green, as in Artifact F. Even though we anticipate heterogeneity among the Crystopal samples, this correlation is too low for a positive match to Crystopal. As shown in our previous paper [25], studies with our instrument and plastics library require an HQI value of >90 for a match, and it is not reasonable to change this protocol since all of the artifacts that were identified by library records as being Crystopal have HQI values of >95. The protocol was even reasonable for the heavily pigmented candle holder, Artifact F. Raman data indicated that Artifact L is made from a UP resin crosslinked with ST, but its polymer composition is not identical to Crystopal. This analysis adds information to the library record about the artifact’s composition but does not aid in establishing a connection to Winfield’s process for making Crystopal.
Artifact M (Table 5) is a colorless, transparent orb with embedded bubbles and lacks the crackled effect typical of Crystopal. BWID analysis of the Raman spectrum of Artifact M (Figure 4) uncovered a very strong correlation to the PST reference with an HQI of 99.12. A visual inspection of the Raman spectrum of Artifact M showed a lack of polyester peaks and confirmed the presence of peaks typical of PST: 620, 1000, 1455, 1600, and 3050 cm−1. While this result proves that Artifact M is not part of Winfield’s Crystopal production, Winfield used many different plastics throughout his career [4,5]. As the identified donor, he could have been involved in creating the piece, but this study cannot confirm it.
Artifact N (Table 5) is a collection of six small bulb-shaped objects, described by the library catalog as paperweights. They are, however, rather small to function as paperweights. The bulbs are decorative in nature and crafted in different colors. Their material appearance is much like Artifacts A–J, having the characteristic crackled effect. BWID analyses of the Raman spectra (Figure 5) of all six bulbs identify these artifacts as Crystopal with HQI values > 98, matching the Crystopal reference. Visual inspection reveals spectral fingerprints of both polyester and PST, verifying these artifacts are Crystopal. This result lends evidence that Artifacts N were crafted by Winfield or Crystopal, Ltd. Data from SCRC-SUL records [14] and a summary of the Raman analyses for Artifacts A–N are listed in Table 6.
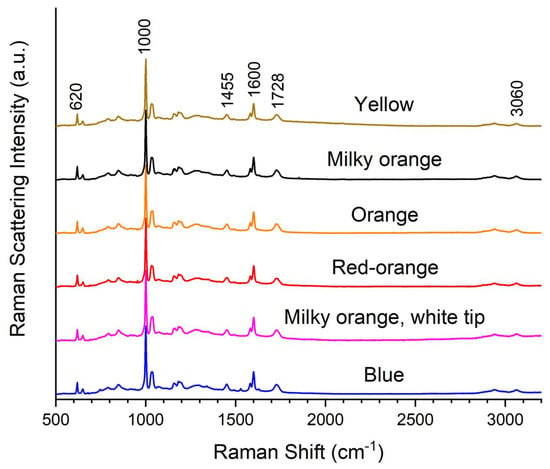
Figure 5.
Raman spectra of Artifacts N consisting of six bulb-shaped objects with varying colors.

Table 6.
Results of Raman analysis and correlation to database standards.
In addition to adding information to library records and helping establish provenance, the analyses of Artifacts A–N provide chemical insight into their needs for preservation. While no studies have been published on the preservation of Crystopal, there have been degradation studies of other GFR UP/ST copolymers. Studies of European art installations [27,38,39,40,41] investigated the degradation and preservation of art made of GFR UP/ST copolymers and showed results from UV exposure, humidity, temperature variations, and aging. GFR UP/ST copolymers, including Crystopal [6], have a reputation for being mechanically strong, yet studies of GRR UP/ST copolymers show they are susceptible to degradation and require conservation. Degradation resulted in physical damage and yellowing of the plastics, with studies showing the need to protect this art from UV light and fluctuations in temperature and humidity. Since Crystopal is a particular type of GFR UP/ST copolymer, it can be inferred that Crystopal requires the same conservation efforts.
4. Conclusions
Raman spectroscopy has provided a non-invasive, non-destructive analytical technique [18,19,20] for revealing the polymer composition of mid-twentieth-century plastic artifacts originating from the personal collection of Armand G. Winfield. Several of these artifacts, including Artifact A, are well-documented to be made of Crystopal, a unique plastic manufactured by Winfield’s company, Crystopal, Ltd. Raman spectroscopic data of Artifact A were combined with information from the 1958 patent to reveal the chemical composition of Crystopal to be a GFR aliphatic UP/ST copolymer. The Raman spectrum of Artifact A produced a unique chemical fingerprint for Crystopal, and it was added as a new reference to the SCOAP library of Raman spectra, allowing for the identification of artifacts made of Crystopal.
Throughout Winfield’s career, he was known to develop a variety of plastic formulations and manufacturing processes [4,5]. We see evidence of such experimentation in these Crystopal artifacts, which exhibit a range of crackling, pigmentation, and translucency. Furthermore, results show that Winfield was able to refine the formulation to achieve a completely transparent product without crackling.
Spectroscopic studies provide insights into the origins of Artfacts K–N. While these artifacts were originally part of Winfield’s personal collection, the source of their fabrication is unknown. Artifact K, the green horse bust, lacks the crackling effect characteristic of Crystopal, yet Raman data yielded a positive match to the Crystopal reference. Although this sculpture is unique to the collection, the strong spectroscopic match combined with the knowledge of Winfield’s ability to produce crackle-free Crystopal yields evidence that the horse bust could have been crafted by Winfield or Crystopal, Ltd. Another positive match to Crystopal was discovered for Artifact N, the small decorative bulbs. Raman spectroscopic data provide evidence that these bulbs were likely crafted by Winfield or Crystopal, Ltd.
In contrast, neither Artifact L (fish tray) nor Artifact M (colorless orb) positively matches the Crystopal reference, and thus, their fabrication cannot be attributed to Winfield or Crystopal, Ltd., by this study. The composition of Artifact L was found to be made of a UP/ST copolymer other than Crystopal, and Artifact M was composed of PST, which was commonly available at the time.
These spectroscopic results, whether identifying the items as composed of Crystopal or not, can be added to the SCRC-SUL’s archival information about artifacts from Winfield’s personal collection. The knowledge of their chemical compositions enhances the research value of these objects locally at SCRC-SUL and as part of the PAC digital collection for remote use. Such additions to the archival information allow researchers to pose further inquiries into these objects’ materiality, origins, creator, and era of manufacture. Uncovering the chemical nature of Crystopal not only gives insight into the provenance of these artifacts but also provides information regarding their specific preservation requirements [26,27]. Since Crystopal belongs to the class of GFR UP/ST copolymers, it requires protection against UV light as well as fluctuations in temperature and humidity. SCRC-SUL is committed to protecting these artifacts and conserving them as a record of mid-twentieth-century cultural history and for future scholarly study.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/heritage6050216/s1, Figure S1: Full spectral range (200–2600 cm−1) used in database matching analysis for Artifact A, Artifact B, polystyrene reference (PST), and styrene/maleic anhydride copolymer reference (ST/MA); Figure S2: Full spectral range (200–2600 cm−1) used in database matching analysis for Artifacts C-E; Figure S3: Full spectral range (200–2600 cm−1) used in database matching analysis for Artifacts F-J; Figure S4: Full spectral range (200–2600 cm−1) used in database matching analysis for Artifacts K-M, the Crystopal reference and PST; Figure S5: Full spectral range (200–2600 cm−1) used in database matching analysis for Artifacts N.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.N.B., C.K.H. and T.M.K.; methodology, M.N.B. and T.M.K.; formal analysis, M.N.B. and T.M.K.; investigation, M.N.B. and T.M.K.; resources, C.K.H. and T.M.K.; data curation, M.N.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.N.B.; writing—review & editing, M.N.B., T.M.K. and C.K.H.; visualization, M.N.B.; supervision, M.N.B. and T.M.K.; project administration, M.N.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no outside funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the article and in the Supplementary Information file.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Elyse M. Kleist for her contributions to the construction of the SCOAP reference plastics library. The authors also thank the University of New Mexico Center for Southwest Research and Special Collections for sharing references [7,16,17].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| GFR | glass fiber–reinforced |
| HQI | hit quality index |
| NPCM | National Plastics Center and Museum |
| PAC | Plastics Artifacts Collection |
| PCL | polycaprolactone |
| PET | polyethylene terephthalate |
| PST | polystyrene |
| SCRC-SUL | Special Collections Research Center at Syracuse University Libraries |
| ST/AA | styrene-acrylic acid copolymer |
| ST/MA | styrene-maleic anhydride copolymer |
| UNM-CSWR-SC | University of New Mexico Center for Southwest Research and Special Collections |
| UP/ST | unsaturated polyester-styrene copolymer |
References
- Meikle, J.L. American Plastic: A Cultural History; Rutgers University Press: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Plastics. Demanded, Desirable, Everywhere. Vogue 1961, 137, 138–143.
- Antosiewicz, F. Winfield collection on display at NPE before entering museum. Plastics News 2003, 15, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Pulkka, W. Curious Creator: [West Side Journal Edition]. Albuquerque J. 2002, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Toner, J.P. Society of plastics engineers honors news fellows. Plast. Eng. 2000, 56, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Winfield, A.G. Casting. In Tool and Manufacturing Engineers Handbook Knowledge Base; Society of Manufacturing Engineers: Southfield, MI, USA, 1998; pp. 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Red and Green Spice for a Christmas Table. House Gard. 1963, 126–131.
- Weitman, S.; Weitman, A. Crackle Glass. Available online: http://www.theglassmuseum.com/crackle.htm (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Features: Unusual Decorations for the House Seen in the Shops. Vogue 1925, 66, 70–71.
- Gudenrath, W. The Techniques of Renaissance Venetian Glassworking: Ice Glass. Available online: https://renvenetian.cmog.org/technique/ice-glass (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Vaseline and Uranium Glass (ca. 1930s). Available online: https://www.orau.org/health-physics-museum/collection/consumer/glass/vaseline-uranium-glass.html (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Guyot, S. Nouveaux objets en matière plastique (statues, vitraux, émaux, formes et analogues) et leurs procédés de fabrication. French Patent FR1161793A, 10 February 1958. [Google Scholar]
- New Form Of Plastic Art Being Produced By Staff Of Company On Abbe Rd. Thompsonville Press 1963, 84, 1.
- The Plastics Collection: About the Collection. Available online: https://plastics.syr.edu/page-about_the_collection.php (accessed on 31 March 2023).
- Crystolume Trademark Announcement. Off. Gaz. US Pat. Off. 1964, 798, 775.
- Crystopal Ltd. Crystolume [Brochure]. Armand G. Winfield Papers, UNM Center for Southwest Research and Special Collections (MSS 538-BC, Box 15, Folder 14); University of New Mexico Libraries: Albuquerque, NM, USA. Available online: https://elibrary.unm.edu/cswr/ (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Sanders, F.M. Correspondence from Fredric M. Sanders to Armand G. Winfield Regarding the Closing of Crystopal, Ltd. In Armand G. Winfield Papers, UNM Center for Southwest Research and Special Collections (MSS 538-BC, Box 15, Folder 14); University of New Mexico Libraries: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Klisińska-Kopacz, A.; Łydżba-Kopczyńska, B.; Czarnecka, M.; Koźlecki, T.; Hoyo Mélendez, J.; Mendys, A.; Kłosowska-Klechowska, A.; Obarzanowski, M.; Frączek, P. Raman spectroscopy as a powerful technique for the identification of polymers used in cast sculptures from museum collections. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2019, 50, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analytical Methods Committee. AMCTB No 67. Raman spectroscopy in cultural heritage: Background paper. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 4844–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousaki, A.; Vandenabeele, P. In situ Raman spectroscopy for cultural heritage studies. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2021, 52, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.L. Infrared and Raman spectroscopy of polymers (Report 134). Rapra Rev. Rep. 2001, 12, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Reggio, D.; Saviello, D.; Lazzari, M.; Iacopino, D. Characterization of contemporary and historical acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)-based objects: Pilot study for handheld Raman analysis in collections. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 242, 118733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousaki, A.; Vandenabeele, P. Chapter 2—Raman and infrared spectroscopy in conservation and restoration. In Spectroscopy, Diffraction and Tomography in Art and Heritage Science; Adriaens, M., Dowsett, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 45–69. [Google Scholar]
- Snively, C.M.; Koenig, J.L. IR and Raman Spectroscopies, Polymer Applications. In Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry, 3rd ed.; Lindon, J.C., Tranter, G.E., Koppenaal, D.W., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Boyden, M.N.; Kleist, E.M.; Asztalos, C.K.; Korter, T.M. Determination of the polymer composition of mid-twentieth century purses by Raman spectroscopy. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashoua, Y. Conservation of Plastics: Materials Science, Degradation and Preservation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- vanOosten, T.B. The Preservation of Plastics. J. Mater. Life Soc. 2004, 16, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, P.C.; Koenig, J.L. A Normal Vibrational Analysis of Isotactic Polystyrene. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 1977, 15, 1885–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, P.J. IR and Raman Spectroscopy Principles and Interpretation; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers, J.M. Spectra-Structure Correlations: Polymer Spectra. In Vibrational Spectroscopy of Polymers: Principles and Practice; Everall, N.J., Chalmers, J.M., Griffiths, P.R., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK; Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 69–112. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig, J.L.; Shih, P.T.K. Structure of unsaturated polyester resins crosslinked with styrene as studied by raman spectroscopy. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-2 Polym. Phys. 1972, 10, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristobal, L.V.; Mendoza, G.A.P. Unsaturated polyesters. Polym. Bull. 1989, 22, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penczek, P.; Czub, P.; Pielichowski, J. Unsaturated polyester resins: Chemistry and technology. In Crosslinking in Materials Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–95. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, K.; Pérez-Alonso, M.; Rodríguez-Laso, M.D.; Fernández, L.A.; Madariaga, J.M. On-line FT-Raman and dispersive Raman spectra database of artists’ materials (e-VISART database). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.M.S.; Zavaglia, C.A.C.; Felisberti, M.I. Unsaturated polyester resins: Influence of the styrene concentration on the miscibility and mechanical properties. Polymer 2000, 41, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.S.; Lee, L.J. Microstructure formation in the cure of unsaturated polyester resins. Polymer 1988, 29, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.P.; Lee, L.J. Free-radical crosslinking copolymerization of styrene/unsaturated polyester resins: 1. Phase separation and microgel formation. Polymer 1993, 34, 4496–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuutinen, U.; Kyllonen, P. Two case studies of unsaturated polyester composite art objects. e-Preservation Sci. 2006, 3, 11–19. Available online: http://www.morana-rtd.com/e-preservationscience/2006/Knuutinen-10-03-2006.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Salvadori, B.; Cantisani, E.; Colombini, M.P.; Tognon, C.G.R. Painted Fiberglass-Reinforced Contemporary Sculpture: Investigating Composite Materials, Techniques and Conservation Using a Multi-Analytical Approach. Appl. Spectrosc. 2016, 70, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, G.; Knuutinen, U.; Laitinen, K.; Spyros, A. Analysis and aging of unsaturated polyester resins in contemporary art installations by NMR spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 3203–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerkens, L.; Stigter, S.; van Oosten, T.; van Keulen, H. Go with the flow: Conservation of a floating sculpture from 1961 made from glass fibre-reinforced polyester resin. In Plastics: Looking at the Future and Learning from the Past; Keneghan, B., Egan, L., Eds.; Archetype: London, UK, 2007; pp. 45–51. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).