Highlights
What are the main findings?
- The first contribution of this study is the proposal of a novel artificial neural network architecture featuring a hybrid design that combines a modified Pi-sigma neural network with simple exponential smoothing.
- The second contribution is the formulation of a novel intuitionistic fuzzy time series forecasting method based on the proposed recurrent neural network.
What is the implication of the main findings?
- The proposed forecasting method demonstrates successful forecasting results across time series data belonging to the stock market and sustainable water resources. This success suggests the establishment of an effective methodology that can be utilized for forecasting time series emerging in other domains.
- The proposed new artificial neural network provides a powerful tool for generating different intuitionistic fuzzy time series forecasting methods.
Abstract
Classical time series methods are widely employed to analyze linear time series with a limited number of observations; however, their effectiveness relies on several strict assumptions. In contrast, artificial neural networks are particularly suitable for forecasting problems due to their data-driven nature and ability to address both linear and nonlinear challenges. Furthermore, recurrent neural networks feed the output back into the network as input, utilizing this feedback mechanism to enrich the information provided to the model. This study proposes a novel recurrent hybrid intuitionistic forecasting method utilizing a modified pi–sigma neural network, principal component analysis (PCA), and simple exponential smoothing (SES). In the proposed framework, lagged time series variables and principal components derived from the membership and non-membership values of an intuitionistic fuzzy clustering method are used as inputs. A modified particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm is employed to train this new hybrid network. By integrating PCA, modified pi–sigma neural networks (MPS-ANNs), and SES within a recurrent hybrid structure, the model simultaneously captures linear and nonlinear dynamics, thereby enhancing forecasting accuracy and stability. The performance of the proposed model is evaluated using diverse financial and environmental datasets, including CMC-Open (I–IV), NYC water consumption, OECD freshwater use, and ROW series. Comparative results indicate that the proposed method achieves superior accuracy and stability compared to other fuzzy-based approaches.
1. Introduction
Traditional time series analysis methods are widely utilized to discern patterns in historical data and predict future outcomes. Among these techniques, simple exponential smoothing (SES) is particularly well-suited for stationary time series devoid of significant trends or seasonality. By assigning exponentially decreasing weights to past observations—thereby placing greater emphasis on recent data—SES renders the model responsive to sudden shifts while effectively mitigating the impact of random fluctuations. The SES method’s key component is the smoothing coefficient, known as the alpha (α) parameter. This value ranges from 0 to 1 and shows how ‘responsive’ the model is. When the alpha value is high, the model focuses more on recent data, while lower alpha values lead to more balanced and smooth predictions. Another technique employed in forecasting is the use of artificial neural networks (ANNs). In contrast to classical time series methodologies, artificial neural networks (ANNs) possess the capability to model both linear and nonlinear relationships effectively. As data-driven, artificial intelligence-based approaches, ANNs are not constrained by the rigid assumption characteristic of traditional methods, allowing them to learn intrinsic patterns directly from the data. Despite the advances in fuzzy and neural forecasting models, existing methods often struggle to balance the linear adaptability of statistical models with the nonlinear learning capacity of neural architectures. In particular, intuitionistic fuzzy time series models lack an efficient mechanism to jointly handle uncertainty, nonlinearity, and temporal feedback. The multi-layer perceptron artificial neural network (MLP-ANN) proposed by [1] is one of the most elementary and pervasive types. It is frequently employed in numerous applications, including regression analysis, classification systems, and time series forecasting. A feedforward artificial neural network consisting of multiple layers is known as an MLP-ANN. An MLP-ANN learns complex relationships in data through hidden layers. Each layer contains many neurons. Another type of artificial neural network, the pi–sigma artificial neural network (PS-ANN) proposed by [2], is a special network through which multiplication and addition operations are combined. Typically, a PS-ANN is two-layered. The first layer calculates the products of various combinations of inputs. The second layer takes the weighted sum of these products. Fewer parameters are required for the PS-ANN method to learn complex relationships, in comparison to the MLP-ANN method. The modified pi–sigma artificial neural networks (MPS-ANNs) proposed by [3] differ from PS-ANNs in that they have adjustable weights and bias values in both the hidden and output layers. As a result, MPS-ANNs have more parameters that can be optimized, which is an advantage. Nevertheless, ref. [3] determined that MPS-YSA generates superior forecasting outcomes in comparison to PS-ANNs. This study proposes a new recurrent-based fuzzy time series forecasting method (Rec-H-IFTS) based on the MPS-ANN. This combines the MPS-ANN with principal component analysis and simple exponential smoothing. In the Rec-H-IFTS method, membership and non-membership values obtained using the fuzzy clustering method are combined into a matrix to which principal component analysis is then applied. The combination of the lags obtained by considering the partial autocorrelation coefficients with the principal component score matrix, obtained as a result of principal component analysis, forms the final inputs for the MPS-ANN. The final forecasts from the proposed method are obtained by combining the exponential smoothing method with the MPS-ANN method. The training of the proposed Rec-H-IFTS method uses a modified particle swarm optimization method. The proposed Rec-H-IFTS model and several alternative fuzzy forecasting methods are applied to both financial (CMC-Open-I–IV) and environmental (NYC, OECD, ROW) time series to evaluate their predictive performance.
This study aims to provide a new recurrent hybrid intuitionistic fuzzy time series (Rec-H-IFTS) method. The research gap lies in the absence of recurrent intuitionistic fuzzy frameworks that integrate data-driven learning with temporal smoothing. The main contributions of this study are as follows: (i) the introduction of a hybrid architecture combining the MPS-ANN and SES to capture both short-term and long-term dependencies; (ii) the use of PCA to compress intuitionistic membership and non-membership matrices, reducing dimensionality while preserving essential variance; and (iii) the development of a modified particle swarm optimization (MPSO) scheme to achieve efficient parameter training.
The following sections make up the rest of this study. The Section 2 presents the MPS-ANN and the exponential smoothing-based feedback hybrid artificial neural network architecture, together. In the Section 3 of the study, the proposed Rec-H-IFTS method is introduced. In the Section 4 of the study, the analysis results for the relevant time series are presented, and these results are then discussed. The Section 5 and Section 6 of the study is a discussion and conclusions.
2. Literature Review
When reviewing the intuitionistic fuzzy time series literature, it is observed that separate contributions are made to the steps of fuzzification, fuzzy relation determination, and defuzzification [4]. In this study, maximum score and minimum accuracy functions were used for intuitionistic fuzzy numbers in the fuzzification process [5]. In this study, the fuzzifying process was performed using the kernel fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. This algorithm assists in the automatic selection of membership and non-membership values for observations in clusters. Other researchers, however, have defined fuzzy sets based on the fragmentation of this set by defining a universal set during the fuzzification stage [6]. In this study, fuzzy relationships were determined using an MLP-ANN in a fuzzy time series method based on universal set decomposition. Ref. [7] presents a new time series data discretization technique for use in universal set decomposition by using fuzzy sets. Ref. [8] presents an approach that creates intuitionistic fuzzy sets using universal set decomposition. The classical decomposition method is used in universal set decomposition. There are studies in the literature showing that universal set intervals are not of equal size. Ref. [9] presents an approach in which intervals can change adaptively in the intuitionistic fuzzy time series method, while the model degree is systematically determined. Ref. [10] used a quantile decomposition approach for partitioning the universe of discourse. Refs. [11,12] used different new methods for partitioning the universal set. In [13], unlike these other methods, particle swarm optimization, an artificial intelligence optimization method, was used in universal set decomposition. However, this study did not include fuzzy sets. In [13], particle swarm optimization was also used as a secondary objective in determining the model degree. Another study [14] determined effective interval lengths using particle swarm optimization. This study also employed a variational weighted approach, resulting in a method that is less affected by outliers. Ref. [14] also presented a method that works with classical fuzzy sets. Another approach in the development of fuzzy time series methods can be said to be the contributions made to the modeling stage, namely the fuzzy relationship determination step. [15] In this study, the fuzzy relationship determination process was performed using a multi-layer sensor, while the use of a feedback model structure was also one of the first contributions in this field. Ref. [16] successfully achieved more effective fuzzy relationship determination using frequency studies. Refs. [17,18] were the first study in the literature to use Bayesian networks for modeling purposes within the fuzzy time series method [19]. In this study, the pi–sigma artificial neural network, a high-order shallow artificial neural network for fuzzy modeling, was utilized. In [20], LSTM was used for the first time as a deep artificial neural network in fuzzy relationship determination [21]. While robust regression methods were used to determine fuzzy relationships in this study, an explainable intuitive fuzzy time series method was introduced for the first time [22]. In this study, a new approach based on pruning membership values was proposed to contribute to both the fuzzification stage and the determination of fuzzy relationships. Ref. [23] presented a new approach based on a multi-layer perceptron that operates using fuzzy sets and ARIMA logic. A method that can be used in modeling linear and nonlinear time series and that addresses a fuzzy time series in a network structure was proposed for the first time in [24]. It can be said that this is the first fuzzy time series method that uses a hybrid approach in fuzzy relationship determination. Ref. [25] presented the first method to use a CNN deep artificial neural network in determining fuzzy relationships. In [26], fuzzy relationship determination was performed using a hybrid approach combining LSTM and SARIMA methods. Refs. [27,28] have taken their place in the literature on other hybrid approaches. Ref. [29] used LSTM and BiLSTM for determining fuzzy relations in a fuzzy time series method. Ref. [30] focused on type-2 fuzzy sets and used butterfly optimization to determine the hyperparameters in the method. Ref. [31] combined a fuzzy time series model with the linear fuzzy information granularity method and used granular computing facilities in a fuzzy time series method. Ref. [32] combined probabilistic fuzzy sets, the adaptive radius clustering technique, and Markov processes and proposed hybrid time series forecasting methods.
Additionally, some other studies have focused on different types of fuzzy sets. Ref. [33] proposed a new time series forecasting method based on q-Runge orthopair fuzzy time series. Ref. [34] is one of the rare studies that deals with the concept of stationarity in fuzzy time series, and [34] proposed a dynamic adjustable non-stationary fuzzy time series method.
3. Recurrent Hybrid Artificial Neural Network Based on Modified Pi–Sigma and Exponential Smoothing
In the analysis of a time series, classical forecasting methods can be used when the time series has linear characteristics, and artificial neural network methods can be used when the time series has nonlinear characteristics. Both classical forecasting methods and artificial neural network methods may be inadequate for analyzing time series with both linear and nonlinear characteristics. Hybrid methods that combine both artificial neural networks and classical forecasting methods are then required. In this study, a new RH-MPS-ANN is proposed. An exponential smoothing mechanism and the MPS-ANN are included in a new architecture. This proposed new artificial neural network has a recurrent network structure with the use of an exponential smoothing structure. The architecture of the RH-MPS-ANN with inputs and hidden-layer nodes is given in Figure 1. The RH-MPS-ANN contains a recurrent connection using the back shift operator, the recurrent input being obtained as .
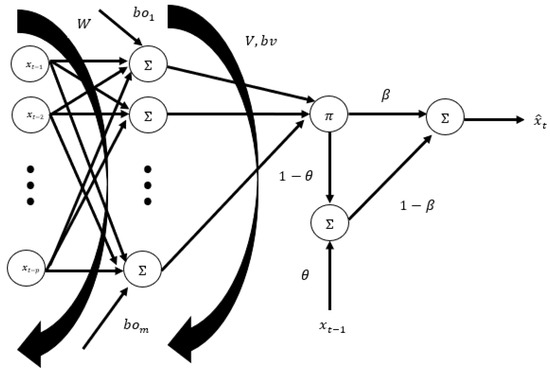
Figure 1.
The architecture of the RH-MPS-ANN.
In the proposed Rec-H-IFTS structure, the exponential smoothing term acts as a temporal stabilizer that moderates rapid changes in the input–output mapping. By incorporating a smoothing factor within the recurrent feedback, the model retains information from previous time steps while attenuating the influence of short-term fluctuations. This mechanism enables the network to capture gradual temporal dependencies more effectively and prevents overreaction to local irregularities, thus improving both the convergence stability and forecasting robustness of the system.
Equations (1) and (2) describe the nonlinear transformation performed in the hidden layer of the MPS-ANN, capturing complex interactions among input variables. The subsequent Equations (5) and (6) introduce an exponential smoothing mechanism into the recurrent loop. This mechanism reduces abrupt variations in output, stabilizes the learning process, and enhances temporal generalization by adaptively weighting recent data points.
The following formulas can be used to compute the output of the RH-MPS-ANN. The outputs of the hidden-layer nodes are obtained by Equations (1) and (2). In Equation (1), is the weight from the input to the hidden-layer unit.
The output of the MPS-ANN is calculated by Equations (3) and (4). In Equation (3), is the weight between the hidden layer and the output of the MP-ANN, and is the bias between the hidden layer and the output of the MPS-ANN. In Equation (4), is the logistic activation function.
The output of the proposed RH-MPS-ANN method is computed by Equations (5) and (6). In Equation (5), is the output of the exponential smoothing, is zero for the first learning sample, and is the exponential smoothing parameter. In Equation (6), is a combination parameter used to calculate the output of the RH-MPS-ANN.
4. The Proposed Method
This study proposes an intuitionistic fuzzy time series method (Rec-H-IFTS) using a hybrid approach of the MPS-ANN, principal component analysis, and simple exponential smoothing. The proposed method incorporates an IFTS method that works with a model with fewer inputs by subjecting data consisting of lagged variables of membership and non-membership values to dimension reduction by principal component analysis. In addition, the partial autocorrelation function is used for the determination of the lagged variables in the IFTS forecasting model. The proposed forecasting method has the ability to strike a balance between SES and the MPS-ANN. It can be transformed into a naive forecasting method or into a pure SES model or MPS-ANN. The algorithm of the proposed method is given in the following, step by step.
Algorithm. The algorithm of the Rec-H-IFTS method.
- Step 1. Determine the model parameters.
- : Minimum and maximum values for the number of intuitionistic fuzzy sets;
- : Minimum and maximum values for the number of hidden-layer units of the MPS-ANN;
- Maximum number of lags;
- Maximum number of iterations;
- Minimum and maximum values for inertia weight;
- Minimum and maximum values for cognitive coefficient;
- Minimum and maximum values for social coefficient;
- Length of training set;
- Length of validation set;
- Length of test set;
- Number of particles;
- Maximum velocity value of particles.
- Step 2. The dataset is block-structured into training, validation, and test sets as given in Equations (7)–(9), respectively.
- Step 3. The transformation given in Equations (10)–(12) is used to normalize the training data.
- Step 4. The partial autocorrelation coefficients , for the time series and the variances of the partial autocorrelation coefficients are calculated for the calculations of confidence intervals by Equations (13)–(15).
- Step 5. The lags corresponding to the partial autocorrelation coefficients outside the limits of are determined. These lags form the elements of the set. The membership function of the set with is given by Equation (16).
- Step 6. Repeat Steps 7–12 for and .
- Step 7. The intuitionistic fuzzy clustering method is used to cluster the observations of the training set . The intuitionistic fuzzy clustering method in [20] is used for clustering. As a result of the clustering, membership and non-membership values of the observations in the time series to each cluster are determined. Membership () and non-membership () matrices are constructed using these values as given in Equations (17) and (18).
- Step 8. Each column of the and matrices is a time series consisting of membership values. The and matrices are created. These matrices consist of the lagged variables of these time series according to the elements of the set. For example, if and , then and are given by Equations (19) and (20).
- Step 9. The and matrices are combined to form a composite matrix, and principal component analysis is applied to this matrix. The score matrix (SM) of the principal components explaining 95% of the variance is obtained. Thus, dimension reduction and steepening operations are performed for the membership and non-membership values. The size of the matrix is from the product of the number of elements of the set and the number of fuzzy sets (n_trn), while the number of columns of the SM is and the number of rows is . In the application of principal component analysis, eigenvalues and eigenvectors are calculated on the variance–covariance matrix of the data matrix . Eigenvalues are obtained from the solution by Equation (21).
In dimensionality reduction, the smallest number that satisfies the inequality given in Equation (22) is determined as . This number is the smallest number of principal components explaining at least 95% of the variance.
- Step 10. From the training data , according to the elements of the set, a lagged variables matrix is created. This matrix and the SM have the same number of rows.
Rationale 1: PCA is used to eliminate redundancy between the membership and non-membership matrices and to improve computational efficiency during training. By retaining components that explain 95% of the variance, the model focuses on the most informative features while reducing the overfitting risk. Rationale 2: The use of the partial autocorrelation function ensures that only statistically significant lags are selected, enabling the model to capture meaningful temporal dependencies.
- Step 11. The input set of the MPS-ANN is obtained by combining the matrix and the SM. The number of inputs of the ANN is . is given by Equation (23).Step 12. The PSO algorithm is used to train the RH-MPS-ANN.
The following steps are used to apply particle swarm optimization to train the RH-MPS-ANN.
- Step 12.1. Initial random velocity and positions are generated by Equations (24) and (25), respectively. What the positions of a particle represent is shown in Figure 2. The initial position and velocity values are generated from a continuous uniform distribution with parameters (0, 1).
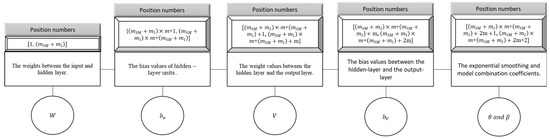 Figure 2. The positions of a particle.
Figure 2. The positions of a particle.
- Step 12.2. The fitness values are calculated for all particles. The root-mean-square error (RMSE) given by Equation (26) is used as the fitness function.is calculated by Equations (27) and (28).
- Step 12.3. Pbest and gbest are generated using the fitness values.
- Step 12.4. The particle swarm optimization parameters are updated by Equations (29)–(34).
The last two positions, corresponding to parameters and , are constrained by Equation (35).
- Step 12.5. The stopping condition is checked by Equation (36). is the fitness function value calculated for gbest in the iteration, and is the counter value used to check for early stopping, with an initial value of zero. If , the algorithm is stopped; otherwise, return to Step 12.4.Step 12.6. The restart counter is checked. This counter is denoted by and has an initial value of zero. The value of the counter is incremented every iteration.
Every 100 iterations, i.e., if , the counter is reset to zero by reproducing the positions and velocities with Equations (24) and (25). Then go back to Step 12.4.
- Step 13. By calculating the forecasts corresponding to data from neural networks trained for and , the error measure given by Equation (38) is calculated for .
- Step 14. The and values that give the lowest value are determined as and .
- Step 15. Steps 7–12 are applied for and and with 30 different random initial value sets by changing the training set as given in Equation (39).
- Step 16. The error measure given by Equation (40) is computed by calculating the forecasts corresponding to the data from the networks trained 30 times for and .
- Step 17. To evaluate the performance of the method, the mean, median, standard deviation, interquartile range, and minimum and maximum statistics of for the error criterion values are calculated.
5. Applications
In this study, five distinct time series were analyzed to evaluate the performance of the proposed forecasting approaches. These were the Coin Market Cap Index opening prices (CMC-OPEN), the total water consumption in New York City (NYC), the per capita water consumption in NYC, the freshwater use in OECD countries, and the freshwater use in ROW (Rest of the World) countries.
The main characteristics of these datasets, such as their time ranges, the numbers of inputs and fuzzy sets, and the lengths of the validation and test subsets, are summarized in Table 1. The temporal behaviors of the financial and environmental time series, including the CMC-Open (I–IV), NYC, OECD, and ROW datasets, are depicted in Figure 3 and Figure 4.

Table 1.
The attributes of the time series.
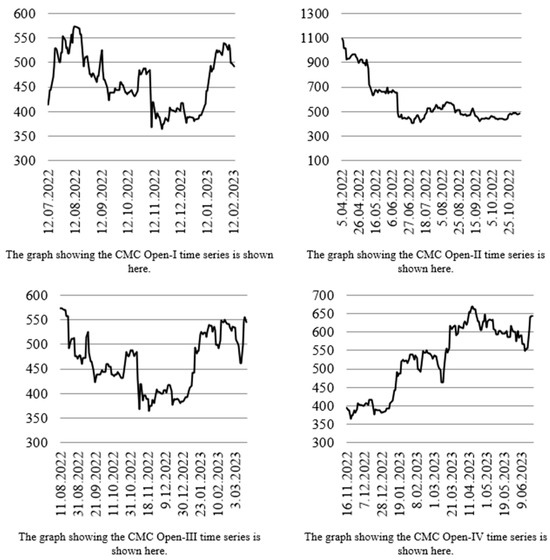
Figure 3.
Time series plots of the CMC-Open-I–IV datasets.
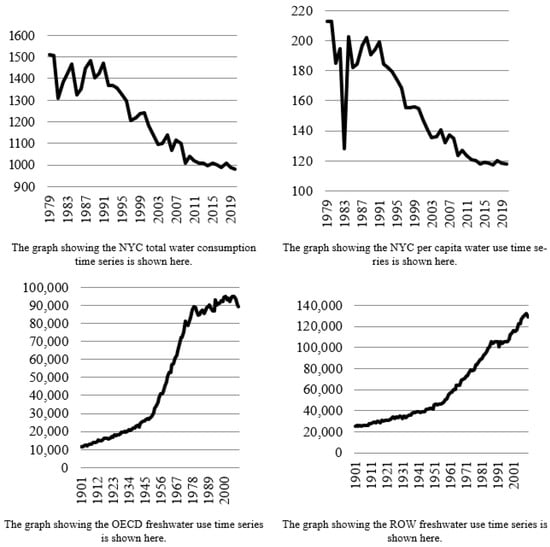
Figure 4.
Time series plots of the NYC, OECD, and ROW water use datasets.
Each time series was also looked at using the methods listed in Table 2, as well as the proposed Rec-H-IFTS method. Also, each way of completing the analysis was performed on its own 30 times with a new random start every time. The mean and standard deviation (SD) statistical results were found for each method.

Table 2.
Analysis methods that are other than those proposed.
Table 3 presents the comparative performance results from the four forecasting methods applied to the CMC-Open-I time series. Among them, the Rec-H-IFTS method achieves the lowest mean error (12.5980) and a very low standard deviation (0.0288), indicating the most stable and accurate performance. In contrast, FTS-N yields the highest mean error and variability, while the traditional FTS method shows moderate performance.

Table 3.
Performance comparison of methods for CMC-Open-I time series.
The results of the CMC-Open-II time series analysis and the corresponding optimal parameter values are summarized in Table 4. SMNM-FTS attains the lowest mean error (10.9298) with zero variance, indicating highly stable performance. FTS shows good accuracy (12.0974). Rec-H-IFTS is stable (Std. Dev. = 0.3944) but less accurate than SMNM-FTS. FTS-N has the highest error and variability.

Table 4.
Performance comparison of methods for CMC-Open-II time series.
As shown in Table 5, the CMC-Open-III series exhibits a performance hierarchy that differs slightly from those for the previous datasets. The SMNM-FTS model again yields the most reliable outcome, producing the lowest mean value (22.7020) and a zero standard deviation, which points to a completely stable estimation process. Although the Rec-H-IFTS approach follows closely with a mean of 23.9341, its minor variability (Std. Dev. = 0.0298) suggests minimal fluctuations in performance.

Table 5.
Performance comparison of methods for CMC-Open-III time series.
Table 6 presents the performance comparison of the four forecasting models for the CMC-Open-IV time series. As shown in the table, all methods produce very similar mean values, implying that this dataset is less sensitive to model structure differences. Among them, Rec-H-IFTS achieves the lowest mean error (21.1510), slightly outperforming the others while maintaining good stability (Std. Dev. = 0.0555). The SMNM-FTS model also performs strongly, with a nearly identical mean (21.5219) and a zero standard deviation, demonstrating perfectly stable behavior. Overall, Table 6 highlights that while all approaches converge toward close accuracy levels, Rec-H-IFTS provides slightly superior and more consistent performance.

Table 6.
Performance comparison of methods for CMC-Open-IV time series.
For the total water consumption series of New York City, Rec-H-IFTS delivers the lowest mean error (0.0137), clearly outperforming the other fuzzy-based models. While FTS, SMNM-FTS, and FTS-N show relatively close mean values (~0.020), their deviations are slightly higher or less stable. This result in Table 7 indicates that the recursive hybrid structure of Rec-H-IFTS can capture temporal dependencies in urban consumption data more effectively than the standard or multiplicative variants.

Table 7.
Performance comparison of methods for NYC total water consumption time series.
In the per capita water use series, Rec-H-IFTS once again provides the most accurate forecasts with a mean error of 0.0146, outperforming FTS-N (0.0169). Table 8 shows that both SMNM-FTS and FTS show higher error levels, indicating lower adaptability to fine-scale variations in individual water usage patterns.

Table 8.
Performance comparison of methods for NYC per capita water use time series.
Within the OECD freshwater use dataset, Rec-H-IFTS once again produces the lowest mean error (0.0181) with modest variance as shown in Table 9. The FTS-N method follows closely (0.0223), maintaining stable but slightly less accurate predictions. By contrast, FTS and SMNM-FTS perform significantly worse, implying that the recursive structure is more capable of handling the gradual and policy-driven variations typical in OECD water use patterns.

Table 9.
OECD freshwater use time series performance comparison for each method.
In the ROW freshwater use series, the FTS model achieves the lowest mean error (0.0144), indicating that for relatively smooth and less nonlinear data, simpler fuzzy structures may offer optimal accuracy as given in Table 10. However, the Rec-H-IFTS method still maintains remarkably stable performance (mean = 0.0219, std. = 0.0001), showing its ability to generate consistent and reliable predictions even when not producing the absolute lowest error. This highlights the model’s general robustness across diverse datasets, performing steadily regardless of variance level or temporal complexity.

Table 10.
ROW freshwater use time series performance comparison for each method.
The comparative performance results presented in Table 3, Table 4, Table 5, Table 6, Table 7, Table 8, Table 9 and Table 10 provide a comprehensive overview of how different forecasting approaches behave across a diverse set of time series, ranging from financial indicators (CMC-Open-I–IV) to environmental and water-related datasets (NYC, OECD, and ROW). Across all datasets, the Rec-H-IFTS (Recursive Hybrid Integrated Fuzzy Time Series) model consistently demonstrates superior accuracy and robustness. It attains the lowest mean error values in most cases (Table 3, Table 4, Table 5, Table 6, Table 7, Table 8 and Table 9), with minimal variance, indicating not only precise predictions but also a stable learning process. Particularly in the CMC-Open-I–III and NYC series, Rec-H-IFTS achieves clear performance dominance.
Figure 5 presents the mean forecasting errors and corresponding standard deviations for all datasets. The Rec-H-IFTS model exhibits the lowest average error across most series while maintaining limited variance, indicating consistent and stable predictive performance. This graphical analysis provides an aggregate visualization of accuracy and serves as an indirect comparison between actual and predicted outcomes.
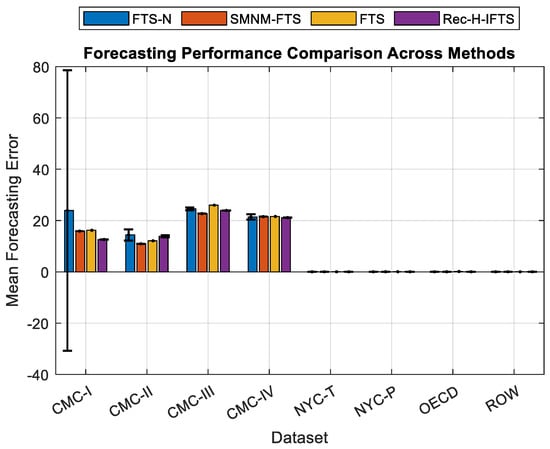
Figure 5.
Forecasting performance comparison across methods.
Finally, a Friedman test was performed to determine whether significant performance differences existed among the four forecasting methods (Rec-H-IFTS, SMNM-FTS, FTS-N, and FTS) across all analyzed datasets. The test indicated a statistically significant difference among the methods (p = 0.0342). Subsequent pairwise comparisons using the Nemenyi post hoc test revealed that the proposed Rec-H-IFTS method achieved significantly lower forecasting errors compared to traditional fuzzy time series approaches (FTS and FTS-N) while maintaining stability comparable to that of SMNM-FTS. Post hoc pairwise comparisons using the Nemenyi test (Figure 6) revealed that the proposed Rec-H-IFTS model significantly outperformed the FTS-N approach (p = 0.0420). Differences between Rec-H-IFTS and the other methods (SMNM-FTS and FTS) were not statistically significant (p > 0.05), although Rec-H-IFTS consistently achieved lower mean ranks across datasets, indicating superior predictive stability.
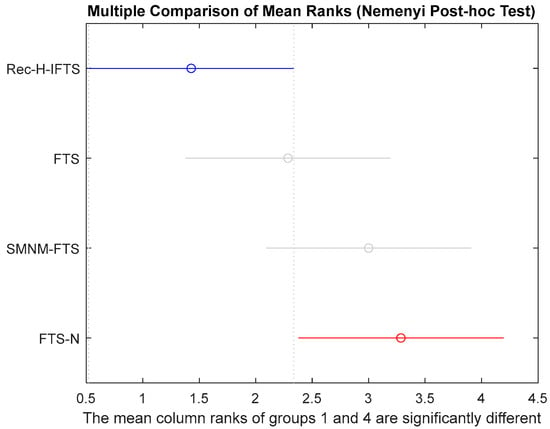
Figure 6.
Multiple comparison of mean ranks (Friedman–Nemenyi test).
6. Conclusions and Discussion
This paper proposed an intuitionistic fuzzy time series method based on a new artificial neural network model, the RH-MPS-ANN. This proposed new RH-MPS-ANN is a hybridization of simple exponential smoothing and the MPS-ANN. In the proposed Rec-H-IFTS method, the input matrix consisting of membership and non-membership values is first subjected to dimension reduction by the PCA method. Rec-H-IFTS uses an MPS-ANN to build the forecasting model, while MPSO is preferred for parameter estimation. Analysis of the results from various stock market time series showed that the proposed Rec-H-IFTS method was successful in forecasting these time series. A Friedman test confirmed statistically significant performance differences among the forecasting methods (p = 0.0342). Post hoc analysis showed that the Rec-H-IFTS model outperformed the FTS-N method (p = 0.0358) and exhibited overall superior forecasting stability. Outliers refer to extreme observations that deviate from the general temporal pattern of the dataset. In Rec-H-IFTS, due to the recurrent feedback mechanism, such anomalies may propagate through time and influence subsequent predictions. The exponential smoothing component mitigates this issue by down-weighting recent abrupt deviations, while the PCA-based input compression further limits their impact on overall variance. Compared to classical fuzzy methods, Rec-H-IFTS exhibits moderate sensitivity to outliers, balancing adaptability and stability.
Future work will explore robust loss functions and pre-filtering strategies to enhance resilience to extreme fluctuations. The framework can also be extended to other forms of uncertainty modeling, such as picture or Pythagorean fuzzy sets, and integrated with deep learning architectures for high-dimensional forecasting tasks.
Author Contributions
T.C.: Methodology, Software, Writing, Conceptualization. E.B.: Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing, Editing. T.A.: Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing, Editing. E.E.: Methodology, Software, Writing, Conceptualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
These data were derived from the following resources available in the public domain: [https://finance.yahoo.com/ (accessed on 10 January 2025)].
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Higher Education Council (YÖK) 100/2000 priority area scholarship. The authors of the article would like to thank Crina Grosan for her English corrections.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Ghosh, J. The pi-sigma network: An efficient higher-order neural network for pattern classification and function approximation. In Proceedings of the IJCNN-91-Seattle International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Seattle, WA, USA, 8–12 July 1991; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Egrioglu, E.; Bas, E. Modified pi sigma artificial neural networks for forecasting. Granul. Comput. 2023, 8, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.S.; Singh, S.R. A score function-based method of forecasting using intuitionistic fuzzy time series. New Math. Nat. Comput. 2018, 14, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, J. An intelligent interval forecasting system based on fuzzy time series and error distribution characteristics for air quality index. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.H.K.; Huarng, K.H. A neural network-based fuzzy time series model to improve forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 3366–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Borah, B. An efficient time series forecasting model based on fuzzy time series. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 2443–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Lei, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, Y. Intuitionistic fuzzy time series forecasting model based on intuitionistic fuzzy reasoning. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5035160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Y. Adaptive partition intuitionistic fuzzy time series forecasting model. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2017, 28, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.S.; Chen, M.Y.; Chang, J.R.; Yu, P.Y. An intuitionistic fuzzy time series model based on new data transformation method. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2021, 14, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, S.; Kumar, S. IFS and SODA based computational method for fuzzy time series forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 209, 118213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, R.M.; Behera, H.S.; Panigrahi, S. A novel high order hesitant fuzzy time series forecasting by using mean aggregated membership value with support vector machine. Inf. Sci. 2023, 626, 494–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, G.; Bisht, D.C. Adaptive hybrid fuzzy time series forecasting technique based on particle swarm optimization. Granul. Comput. 2023, 8, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didugu, G.; Gandhudi, M.; Alphonse, P.J.A.; Gangadharan, G.R. VWFTS-PSO: A novel method for time series forecasting using variational weighted fuzzy time series and particle swarm optimization. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2025, 54, 540–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, C. A new high order fuzzy ARMA time series forecasting method by using neural networks to define fuzzy relations. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 128097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, A.; Bermúdez, J.D.; Vercher, E. Improving stock index forecasts by using a new weighted fuzzy-trend time series method. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 76, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, X. Fuzzy-probabilistic time series forecasting combining Bayesian network and fuzzy time series model. Symmetry 2025, 17, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Chi, M.; Li, Y. Bayesian network based probabilistic weighted high-order fuzzy time series forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egrioglu, E.; Yolcu, U.; Bas, E. Intuitionistic high-order fuzzy time series forecasting method based on pi-sigma artificial neural networks trained by artificial bee colony. Granul. Comput. 2019, 4, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, C.; Egrioglu, E.; Bas, E. A new deep intuitionistic fuzzy time series forecasting method based on long short-term memory. J. Supercomput. 2021, 77, 6178–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, C.; Egrioglu, E.; Bas, E. A new explainable robust high-order intuitionistic fuzzy time-series method. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, M.; Bisht, K.; Negi, S. Computational-based partitioning and Strong α β-cut based novel method for intuitionistic fuzzy time series forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 142, 110336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashe, M.; Bijari, M.; Hejazi, S.R. An extended fuzzy artificial neural networks model for time series forecasting. Iran. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2011, 8, 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Bas, E.; Egrioglu, E.; Aladag, C.H.; Yolcu, U. Fuzzy-time-series network used to forecast linear and nonlinear time series. Appl. Intell. 2015, 43, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaei, H.J.; e Silva, P.C.D.L.; Guimaraes, F.G.; Lee, M.H. Short-term load forecasting by using a combined method of convolutional neural networks and fuzzy time series. Energy 2019, 175, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Yadav, N. A novel hybrid model combining βSARMA and LSTM for time series forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 134, 110019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Hybrid time series interval prediction by granular neural network and ARIMA. Granul. Comput. 2024, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tao, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, H. A hybrid interval-valued time series prediction model incorporating intuitionistic fuzzy cognitive map and fuzzy neural network. J. Forecast. 2025, 44, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y. Combined electricity load-forecasting system based on weighted fuzzy time series and deep neural networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 132, 108375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanja, S.; Das, A. An air quality forecasting method using fuzzy time series with butterfly optimization algorithm. Microsyst. Technol. 2024, 30, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Gong, Z. An interpretable combined forecasting method for stock market based on fuzzy time series model and linear-trend fuzzy information granulation. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 73722–73734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, S.; Kumar, S. PIFS ARC and Markov model based hybrid method for fuzzy time series forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 279, 127510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Chohan, M.S.; Askar, S.; Jabbar, N. q-Rung Orthopair fuzzy time series forecasting technique: Prediction based decision making. AIMS Math. 2024, 9, 5633–5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. A fuzzy time series forecasting model with both accuracy and interpretability is used to forecast wind power. Appl. Energy 2024, 353, 122015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladag, C.H. Using multiplicative neuron model to establish fuzzy logic relationships. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M. Forecasting enrollments based on fuzzy time-series. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1996, 81, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).