Abstract
This study evaluates the sorption behavior of natural zeolite (NZ) and Fe(III)-modified natural zeolite (FeZ) for Ni(II) ions, with the objective of assessing their potential for application in the remediation of nickel-contaminated environments. Optimization of sorption parameters, including pHo, solid/liquid ratio (S/L), contact time, and initial Ni(II) concentration was performed to maximize both the sorption capacity of the zeolites and the removal efficiency of Ni(II) from suspension. The results demonstrated that both pHo and S/L ratio exert a significant influence on Ni(II) sorption onto both zeolites, with a particularly pronounced effect observed for FeZ. Experimental results confirmed that FeZ exhibits a four-to-five times higher sorption capacity for Ni(II) than NZ, which was additionally verified by elemental analysis, SEM-EDS, and elemental mapping of Ni(II)-saturated zeolites. Intraparticle diffusion was identified as the rate-limiting step in the transfer of Ni(II) ions to the active sorption sites. Ion exchange was identified as the main sorption mechanism accompanied by outer-sphere complexation and electrostatic attraction. Leaching tests of Ni(II)-saturated zeolites, conducted in accordance with the standard DIN 38414 S4 method, demonstrated that both zeolites effectively retained Ni(II) within their structures over a wide pH range, 4.11 ≤ pHo ≤ 12.02. These findings indicate the potential applicability of zeolites for remediation of nickel-contaminated environments, with FeZ being particularly promising due to its enhanced sorption capacity for Ni(II) ions.
1. Introduction
Nickel belongs to the group of heavy metals and is ranked as the 24th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, which, for comparison, is twice as abundant as copper [1,2]. The essential function of nickel for human beings is unknown, while it is an essential micronutrient for morphological and physiological functions of plants. Namely, nickel is necessary for the life cycle of plants (photosynthesis, root development, mineral binding, etc.) in small concentrations up to 1.5 μg/g dry weight of the plant, while at higher concentrations, nickel has a phytotoxic effect [1,3,4,5]. It occurs naturally in the form of sulfide, oxide, and silicate minerals, where mineral erosion along with volcanic eruptions and forest fires is the main natural source of nickel emissions in the environment. Unlike natural sources, anthropogenic sources of nickel are a consequence of its wide use, since it is considered one of the most used elements in developed countries due to its unique physical and chemical properties [2,5,6]. Its corrosion resistance (air, water, alkalis) is the main reason for its widespread use in the production of stainless steel and other nickel alloys. In addition, it is used in metallurgy, electroplating, and electroforming; to produce electronic equipment (nickel–cadmium batteries, wires) and nickel-plated products (toilet fittings, belt buckles, zippers, keys, paper clips, eyeglass frames, cheap jewelry); for the production of armaments, aircraft equipment, pigments and dyes, coins, orthodontic braces, catalyst in the chemical and food industry, etc. [1,2,5,7,8]. Its extremely wide application is evidenced by the fact that the world’s annual global nickel production is over 2.7 million tons according to data from 2019 [9]. In contrast, accelerated consumption and disposal of nickel-containing products, mining and smelting activities, industrial activities (metal refining), combustion of fossil fuels (coal, fuel oil, and diesel oil), misuse of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, as well as discharge of wastewater are the main anthropogenic emitters of nickel into the environment. Hence, nickel concentrations are found in all parts of the environment (air, water, soil) [1,4,5]. Annual emissions of nickel into the environment are estimated to range from 150,000 to 180,000 tons, originating from both natural and anthropogenic sources [1,10]. Nickel is emitted into the atmosphere primarily in the form of gaseous compounds (oxides, sulfides, silicates), and less frequently as nickel metal vapor. Average nickel concentrations in unpolluted air are usually low, around 6–20 ng/m3, reaching values of up to 170 ng/m3 in air polluted by anthropogenic sources [6,7,10]. Uncontaminated water typically contains about 0.1 to 0.5 μg Ni/L. On the other hand, nickel concentrations in contaminated water bodies are significantly higher and are estimated to be up to 0.2 mg/L, which is significantly higher than in uncontaminated ones [6,10,11]. In soil, nickel is naturally present in concentrations of up to 100 mg/kg, while concentrations of up to 53,000 mg Ni/kg of soil can be found near anthropogenic sources. Agricultural soils may contain approximately 3–1000 mg Ni/kg of soil as a result of excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides containing nickel. Consequently, nickel is also found in foods such as nuts and vegetables [1,2,10,12]. Therefore, increased nickel concentrations in the environment result in its accumulation in agricultural crops and water for human consumption. Thus, food and drinking water containing nickel are the main sources of nickel poisoning in humans.
Nickel levels in food generally range from 0.1 to 0.5 mg/kg, including in vegetables, fruits, cereals, nuts, seafood, and many others [2,7]. Since many foods are rich in nickel, nickel deficiency in the human body has not been recorded. Moreover, daily dietary intakes of nickel are estimated to be 25–300 μg, which is three-fold more than the daily requirement [6]. Average nickel concentrations in drinking water range from 3 to 10 µg/L, especially if the water supply network uses nickel pipes. Although harm to human health from consuming drinking water containing nickel is extremely rare, the average daily intake of nickel into the body by drinking 1.5 L of water containing 3–10 µg Ni/L is 4.5–15 µg [2,7,10]. Likewise, nickel is also introduced into the human body through cigarette smoking. It is an interesting fact that a tobacco cigarette contains 1.1–3.1 μg of nickel. Approximately 10–20% of nickel enters the human body from the gaseous phase of tobacco smoke, which contains extremely teratogenic and carcinogenic toxic organometallic tetracarbonyl nickel, Ni(CO)4 [6,13,14]. In addition to gastrointestinal absorption (food, water), nickel can also enter the human body through occupational exposure, such as inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact, causing toxic effects in the respiratory tract and immune system [7,15]. Nickel is deposited in the nasopharyngeal, tracheobronchial, or alveolar regions of the respiratory system. It is absorbed most in the lungs, thyroid and adrenal glands, and less in the brain, kidneys, heart, liver, spleen, and pancreas [6,15]. Skin contact with nickel (e.g., nickel jewelry) causes mostly allergic problems such as allergic and contact dermatitis. Although nickel is excreted through urine and feces, about 1–2% of ingested nickel is permanently deposited in organs such as the lungs, heart, pancreas, diaphragm, and brain [6,13,14]. Namely, the nickel toxicity to human health also depends on the dose and length of exposure. Thus, exposure is classified as acute (1 day), subchronic (10–100 days) and chronic (>100 days). Acute toxicity is manifested by nausea, vomiting, vertigo and irritation. Subchronic toxicity occurs through exposure to higher concentrations of nickel (in the range of 0.07–1.1 mg Ni/m3) over a longer period of time and is manifested by visual dysfunctions. Finally, occupational exposure to nickel causes chronic toxicity; respiratory, cardiovascular, and kidney diseases; lung fibrosis; hematological problems; as well as lung and nose cancer [13,14,16]. Overall, nickel intoxication causes a number of pathological effects in humans (genotoxicity, immunological, endocrine, neurogenic, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal, and dermal effects) and the most dangerous route of exposure is inhalation [10,13]. The mechanisms of toxicity are not fully elucidated; however, mitochondrial dysfunctions and oxidative stress are thought to play a major role in its toxicity [14]. Due to numerous adverse effects on human health, the International Agency for Research on Cancer and the European Chemicals Agency have classified soluble and insoluble nickel compounds as carcinogenic to human health, while metallic nickel and alloys are possibly carcinogenic to humans [17,18].
Nevertheless, the pollution of water with nickel and other heavy metals is an important global problem since almost 11% of the world’s population does not have access to drinking water. Moreover, the World Health Organization estimates that water scarcity could affect up to 4 billion people by 2050. Consequently, industrial processes need to be adapted to the circular economy in order to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially SDG 6, which relates to water and sanitation [19,20].
Since nickel has a clear toxicity, various authorities have established maximum permissible levels of nickel in water systems that would not have a toxic impact on humans and the environment. The acceptable maximum level of nickel in drinking water according to a report by the World Health Organization (WHO) is 0.07 mg/L [21]. Likewise, the Croatian regulation on the health safety of drinking water prescribes an even more rigorous limit of 0.02 mg Ni/L [22]. Industrial processes are the main emitters of nickel by releasing nickel-enriched wastewater into the environment without proper treatment [23]. Nickel concentrations in industrial wastewater range from 3 to 900 mg/L [24]. Such waters are environmentally unacceptable even at very low concentrations since nickel is toxic to human health as previously discussed. Due to this reason, the Croatian standard prescribes a maximum permitted level of nickel in treated wastewater of up to 0.5 mg/L, regardless of whether it is discharged into surface waters or public sewage systems [25].
To be precise, the presence of nickel in treated wastewater is a consequence of its reduced removal affinity by conventional wastewater treatment processes [26]. In particular, various physicochemical methods for nickel removal from wastewater, such as chemical precipitation, coagulation/flocculation, electrocoagulation, electrodialysis, membrane methods (reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration), electrochemical reduction/oxidation, ion exchange, and adsorption were investigated [23,24,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. The main prerequisite for selecting an appropriate treatment depends on the requirements and economic possibilities, and most often includes treatment costs and the residual nickel concentration in the wastewater. Certainly, the goal is to avoid time-consuming processes and those that generate secondary waste [26,27].
Namely, classical methods of nickel removal involve chemical precipitation at pH > 9. The method is quite effective for Ni concentrations >100 mg/L. However, the remaining Ni concentration often does not reach a value below 1 mg/L, which is above the legally prescribed values. Moreover, when nickel is present in low concentrations, this method becomes ineffective since it is limited by the solubility product constant of Ni(OH)2. Apart from the fact that low nickel concentrations remain after treatment, it is necessary to neutralize the effluent before discharge into the environment, as well as to manage, transport, and dispose of the generated sludge, which makes this method economically unviable [23,24,27,29,33].
On the other hand, advanced technologies such as membrane filtration and electrochemical methods are characterized by high nickel removal efficiency. These methods are preferred for capturing nickel from industrial wastewater with the possibility of its reuse, i.e., returning to the process. This model is fully in line with the circular economy, i.e., rejection of the linear economy model [23,30]. Contrarily, membrane and electrochemical methods have limitations. Membrane methods do not use chemicals, but they are quite expensive. In addition to energy consumption and sludge production, membrane prices are high. Contrariwise, electrochemical methods do not require large quantities of chemicals, but they generate sludge and require high energy consumption [27,29,31].
Furthermore, Kruszelnicka et al. [30] presented a literature review on nickel removal methods from industrial wastewater. In addition to membrane and electrochemical methods, they pointed out that in the 21st century, sorption has experienced significant growth, especially with the use of inexpensive sorbents. According to Mohammadtaghi et al. [28], adsorption is already applied in several industrial processes for the nickel removal from wastewater. In this light, sorption processes (adsorption and ion exchange) are welcomed due to their affordability, flexibility, simple implementation and plant design, low cost, minimal energy consumption, and environmental acceptability. Thus, the limitations of treatment processes that use chemicals, generate sludge, and have high energy costs can be overcome by using sorption processes that provide a cleaner, greener, and more economical mode of operation [23,24,27]. This knowledge makes sorption a promising and perspective method and provides the possibility and need for further research to find new efficient and more economically profitable sorbents. The application of sorbents for nickel removal from wastewater has been thoroughly reviewed in several comprehensive studies by Mohammadtaghi et al. [28], Kumar et al. [29], and Nthwane et al. [31]. They observed the use of sorbents of mineral (natural zeolites, clays), organic (organic resins, activated carbon), and biological (agricultural wastes, lignin, biomass) origin. According to these review papers [28,29,31], activated carbon has been widely used and has shown extraordinary sorption efficiency. However, conventional activated carbon is derived from non-renewable resources, and the production cost limits its large-scale application. This was the basis for researchers to find new affordable and at the same time effective sorbents. In order to develop new sorbents, it is necessary to know the shortcomings of those that have already been researched or used [28]. Recently, great efforts have been made with the aim of developing and applying cost-effective materials, especially those of natural origin that meet the principles of green chemistry, i.e., environmental friendliness. Natural zeolites are representatives of the latter group of materials. The most commonly used natural zeolite is clinoptilolite, along with cabazite, heulandite, analcime, phillipsite, erionite, and mordenite [29]. Specifically, natural zeolites are crystalline minerals of volcanic origin composed of [SiO4]4− and [AlO4]5− tetrahedra. The interconnection of tetrahedra through common oxygen atoms results in the formation of a three-dimensional network with channels and voids. The isomorphic replacement of Si with Al during their formation results in structural imperfections, i.e., the creation of a negative charge on each aluminum atom. The negative charge is partially neutralized by hydrated cations of alkali and alkaline earth cations. Since the neutralization of the negative charge is achieved by weak electrostatic attractive forces, non-structural cations can easily be exchanged with cations from the surrounding medium. This property makes natural zeolites cationic ion exchangers [23,37]. However, they have a limited sorption capacity compared to synthetic ones. In order to increase their sorption capacity and competitiveness in terms of efficiency and price compared to commercial sorbents, pre-treatment is required. Pre-treatment improves their physicochemical properties, primarily by increasing the number of active sites, i.e., functional groups available for sorption [26]. Chemical modifications of natural zeolites involve treatment with acids, bases, inorganic salts, and surfactants. Treatment with acids aims to dissolve impurities and increase mesoporosity, as well as decationization of ions and dealumination. Modification with bases causes an increase in negative charge and desilication, while modification with surfactants enables the sorption of anions and organic molecules. Additionally, the modification with solutions of inorganic salts such as NaCl and CaCl2 contributes to the equalization of compensatory cations, i.e., their conversion into homoinoic form [38,39]. It is worth mentioning that nickel released into the environment mainly accumulates in soil, where it is strongly sorbed to Fe, Mn, or Al (oxy-hydro)oxides, and is specifically sorbed or co-precipitated with iron oxyhydroxides [2,40]. Due to this realization, modification of zeolites with iron salts has attracted attention because it results in an environmentally acceptable sorbent since Fe-oxyhydroxides are natural constituents of soil. In addition, modified zeolite remains low-cost compared to commercial ones because it does not require extensive processing. Modification of zeolite with iron salts primarily causes the creation of new active sites and an increase in the overall negative charge, making it a more powerful cationic sorbent. The integration of iron onto the external and internal zeolite surface effectively overcomes the limitations of natural zeolites, thereby enhancing their functionality and extending their applicability in environmental remediation [41].
Over the past few years, several authors have systematically reviewed the application of natural zeolites for nickel removal from water systems [38,39,40,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49]. The primary findings of these studies highlight the potential of natural zeolites as environmentally friendly alternative sorbents, while also emphasizing the necessity of appropriate modifications to enhance their sorption selectivity for nickel ions. For instance, nickel removal on natural zeolites is well established [50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66] in contrast to those on natural zeolite converted to homoionic form [67,68,69,70,71,72,73], thermally activated zeolite [1,74], and especially on Fe-modified natural zeolite [75]. This observation presents an opportunity for a more systematic investigation of the use of Fe(III)-modified natural zeolite as sorbent for nickel immobilization, forming the basis of the present study.
Therefore, the aim of this study is to comparatively assess the influence of key sorption parameters, pH, solid/liquid ratio, contact time, sorbent dosage, and initial metal concentration, and their optimization on nickel sorption capacity and removal efficiency using natural and Fe(III)-modified natural zeolites. Furthermore, the sorption mechanism is elucidated through the application of kinetic and isotherm modeling, complemented by SEM-EDS analysis of nickel-saturated zeolite samples. Finally, leaching experiments conducted on nickel-saturated zeolites will offer insights into their potential applicability for both in situ and ex situ remediation of nickel-contaminated environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zeolite Preparation
The natural zeolite (NZ) sample was sourced from the Zlatokop deposit in Vranjska Banja, Serbia. The material was mechanically comminuted and subsequently sieved to isolate the 0.6–0.8 mm particle size fraction, in accordance with the DIN 66165-2 standard procedure [76]. The selected fraction was thoroughly rinsed with ultrapure water to remove surface impurities and then dried at 60 °C.
Fe(III)-modified natural zeolite (FeZ) was prepared following the method described in a previous study [77]. A mass of 20 g of NZ was initially mixed for 2 h at room temperature with 100 mL of a freshly prepared 1 mol/L solution of Fe(NO3)3·9H2O in an acetate buffer at pH = 3.6. Subsequently, the solution was decanted and stirred for 1 h with 90 mL of 1 mol/L NaOH solution. Then, after decantation, the sample was stirred for 1 h at 50 °C with 50 mL of 4% NaNO3. Finally, the sample was rinsed with ultrapure water until a negative reaction to nitrate ions was observed, dried for 24 h at 40 °C, and stored in a desiccator.
The physicochemical characterization of both NZ and FeZ, including chemical composition, SEM/EDS, XRPD, FTIR, BET surface area, and TG/DTG, was comprehensively reported in a previous study [77]. Concisely, XRPD analysis confirmed that NZ is predominantly composed of clinoptilolite (~80%), with quartz, feldspar, and carbonate minerals present as secondary phases. Upon Fe(III) modification, a slight reduction in crystallinity was observed (XRD), along with broadening of hydroxyl-related absorption bands (FTIR), a modest increase in surface area, a pronounced increase in pore volume (BET), and greater overall mass loss (TG/DTG). Zeta potential measurements across a broad pH range (2–12) indicated that both NZ and FeZ possess a net negative surface charge. In general, over the entire pH range, FeZ has a 1.5-fold more negative zeta potential. The isoelectric point for NZ is reached at pH = 1.84, and for FeZ at pH = 1.00. The modification process was designed to facilitate the binding of Fe3(OH)45+ species, predominant at pH 3.6, to the negatively charged NZ surface. The subsequent addition of NaOH promoted the hydrolysis and hydroxylation of Fe species, leading to the formation of negatively charged Fe oxo and hydroxo complexes, thereby enhancing the overall negative surface charge of the FeZ material [77].
2.2. Batch Sorption Experiments
The salt, Ni(NO3)2·6H2O purchased from Kemika, Croatia, was used to prepare a stock solution with an initial concentration of 15.974 mmol/L. Solutions of lower concentrations were prepared by diluting the stock solution. Ultrapure water was used to prepare all solutions, and a 0.1 or 1 mol/L HNO3 solution was used to adjust the pH. All experiments were performed in an incubator shaker at 25 °C, 230 rpm, and for 24 h. Ni(II) concentrations before and after equilibrium were determined using a Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer, AAS, model PinAAcle 900F, (Perkin Elmer Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). A hollow cathode lamp for Ni with a wavelength of 232 nm and a slit width of 0.2 was used. The combustible gas was a mixture of acetylene and air in a ratio of 1:5, burner angle (0°), and flame speed (1800–2200 °C).
2.2.1. Influence of pH
The influence of pHo on the Ni(II) sorption onto NZ and FeZ was examined in the pHo range 2.47 ≤ pHo ≤ 7.02 and at initial concentrations of 4.266 mmol Ni/L. A mass of 1.0 g of NZ or FeZ was mixed with 100 mL of Ni(II) solution (solid/liquid ratio = 10 g/L). After the equilibrium was established, the equilibrium pHe was measured, as well as the amount of released exchangeable cations (Na, K, Ca and Mg) by ion chromatography (Metrohm 761 Compact IC).
2.2.2. Influence of Solid/Liquid Ratio
The influence of the solid/liquid ratio (S/L) was examined at pHo = 6.14 for NZ and FeZ, and at an initial concentration of 4.266 mmol Ni/L. The specified pHo value was determined as optimal based on the experiment described in Section 2.2.1. Experiments for both zeolites were carried out at S/L = 2–18 g/L (m = 0.2; 0.6; 1.0; 1.4 and 1.8 g). After equilibrium was established, the equilibrium pHe was measured.
2.2.3. Influence of Contact Time
The influence of contact time on the Ni(II) sorption onto NZ and FeZ was carried out at a previously determined optimal pHo = 6.14 and at S/L = 10 g/L based on the conducted experiment described in Section 2.2.2. A mass of 20 g of NZ or FeZ was mixed with 2 L of Ni(II) solution with an initial concentration of 10.620 mmol/L at 550 rpm. Liquid samples were collected at selected time intervals within 24 h, whereby the total volume of the samples not exceeding 5–6% of the total volume of the suspension. The saturated samples, designated as NZNi and FeZNi, were collected, washed several times in ultrapure water, dried at 40 °C, and used for leaching experiments.
2.2.4. Influence of Initial Concentration
The influence of initial Ni(II) concentration on Ni(II) sorption onto NZ and FeZ was tested in the concentration range 0.503–15.974 mmol Ni/L at the previously determined optimal S/L = 10 g/L and pHo = 6.14. A volume of 100 mL of Ni(II) solution, of different initial concentrations, was mixed with 1.0 g of NZ or FeZ. After the equilibrium was established, in addition to measuring the equilibrium pHe, the concentrations of released zeolite cations (Na, K, Ca, and Mg) were also measured by ion chromatography. Saturated samples with the highest initial concentration of 15.974 mmol Ni/L were collected, washed several times in ultrapure water, dried at 40 °C, and labeled as NZNi and FeZNi. Then, the chemical composition of the starting samples, NZ and FeZ, and the saturated samples, NZNi and FeZNi, was determined by classical chemical analysis of aluminosilicates [78]. A comparison of the chemical composition of the initial and saturated samples is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of starting and nickel-saturated zeolites.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) combined with energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDS) of nickel-saturated samples, NZNi and FeZNi, was performed on a JEOL JSM-6610 microscope. On selected surfaces of the analyzed samples, the semi-quantitative chemical composition was determined, and the distribution of elements on the surface was determined by mapping analysis.
2.3. Leaching Experiments
Leaching of Ni(II) from the collected saturated samples (NZNi and FeZNi) took place after conducting the experiment described in Section 2.2.3. Samples were subjected to the standard leaching method, DIN 38414 S4 [79]. Ultrapure water with pH pre-adjusted with 0.1 mol/L HNO3 or 0.1 mol/L KOH in the range of 2.05–12.02 was used as leachant. A mass of 1.0 g of NZNi or FeZNi was mixed with 10 mL of ultrapure water of different pHo for 24 h at 25 rpm and at 25 °C. After 24 h, the equilibrium pHe and the concentration of leached Ni(II) were determined in the filtered suspensions by AAS.
2.4. Calculation of Sorption Parameters
The quantity of Ni(II) sorbed onto zeolites at time t (up to 24 h), denoted as qt (mmol/g), as well as the removal efficiency at time t, denoted as αt (%), were determined using Equations (1) and (2):
Here, co and ct represent the concentrations of Ni(II) at t = 0 and at time t (mmol/L), V is the volume of the solution (L), and m is the mass of the zeolite (g). When t = 24 h, qt and αt represent the equilibrium quantity of Ni(II) sorbed (qe) and equilibrium removal efficiency (αe).
The quantity of Ni(II) leached from the saturated zeolites, qleach (mmol/g), and the percentage of Ni(II) leached, αleach (%), were calculated using Equations (3) and (4):
Here, cleach represents the concentration of Ni(II) leached from the saturated zeolites (mmol/L).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Sorption Parameters
Optimization of sorption parameters (pH, solid/liquid ratio, contact time, and concentration range) is essential to saturate the zeolite as much as possible, as well as to maximize the nickel removal efficiency. Namely, the ultimate goal of any sorption process is to achieve the highest possible removal efficiency. Therefore, in addition to the amount of nickel sorbed on the zeolite, the removal efficiency will primarily be considered during the optimization of the sorption process parameters.
3.1.1. pH Optimization
The pH of the suspension is a crucial factor in the sorption process since it directly influences both the zeolite surface charge and the charge and form of the Ni(II) species. Since it is highly expected to know the Ni(II) speciation in dependence on pH, its distribution is plotted in Figure 1 based on Ni(II) hydrolysis constants, which are represented by Equations (5)–(8) [80].
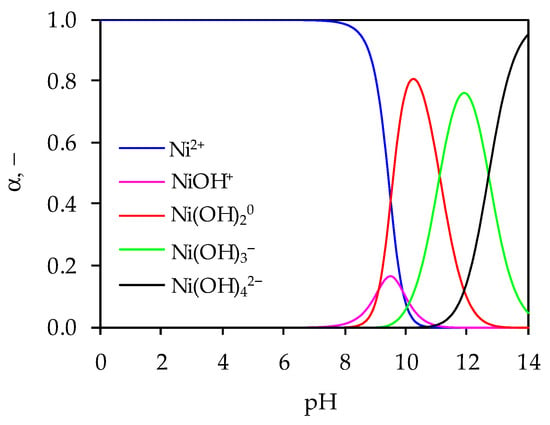
Figure 1.
Ni(II) speciation distribution diagram as a function of pH.
According to Figure 1, Ni(II) exists predominantly in the form of Ni2+ up to pH = 8. Then, with increasing pH, hydroxylated Ni(II) products are formed. Thus, a small fraction of Ni(II) in the form of Ni(OH)+ appears at 8.0 < pH < 10.8, with a maximum distribution of 16% at pH = 9.5. Ni(II) starts to precipitate in the form of hydroxide, Ni(OH)20 in the pH range 8.0–13.5 with a maximum content of 80% at pH = 10.2. At pH > 9.5 Ni(II) exists in the anionic form, Ni(OH)3−, with a maximum content of 76% at pH = 11.9, while the proportion of the anionic form Ni(OH)42− increases continuously above pH = 11.
Accordingly, the sorption process must be carried out under conditions where Ni(II) precipitation is prevented, i.e., below pH = 8. To further confirm the pH at which Ni(II) precipitation occurs (pHppt) depending on the initial Ni(II) concentration, pHppt is calculated according to Equation (9) [81]:
where co[Ni(II)] is the initial Ni(II) concentration and Ksp is the solubility product constant of Ni(OH)2, Ksp = 5.48 × 10−16 [82].
Comparisons of measured pHe values with calculated pHppt for an initial concentration of 4.266 mmol Ni/L as well as Ni(II) removal efficiency on NZ and FeZ as a function of pHo are shown in Figure 2.
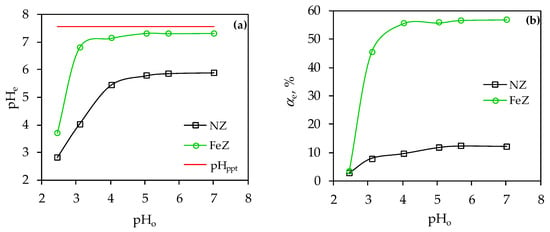
Figure 2.
(a) Comparisons of measured pHe values with calculated pHppt for an initial concentration of 4.266 mmol Ni/L; (b) Ni(II) removal efficiency of NZ and FeZ as a function of different pHo.
Figure 2a primarily indicates that the measured pHe are lower than the calculated pHppt (pHppt = 7.55 for co(Ni) = 4.266 mmol/L) for both zeolite samples and for all pHo, which excludes the possibility of Ni(OH)2 precipitate formation. Additionally, plots of Ni(II) species vs. pH were constructed using Hydra/Medusa software (https://sites.google.com/site/chemdiagr/download, accessed on 19 August 2025), considering the initial Ni(II) concentration and ionic strength of the solution and are shown in Figures S1 and S2 in the Supplementary File. These results further confirmed that Ni(II) precipitation did not occur under the specified experimental conditions. Comparing the results of pHe vs. pHo (Figure 2a) with αe vs. pHo (Figure 2b), the same trend of change in the measured parameters (pHe and αe) is observed. Thus, for NZ, pHe and αe increase up to pHo = 5, while for FeZ up to pHo = 4. After the specified pHo, there is no change in the measured parameters, i.e., a plateau is established. For both samples, the increase in pHe is most pronounced in the highly acidic medium as a consequence of the competition effect of Ni(II) with H+ ions. Since both zeolites have a negative charge in the tested pHo range, especially FeZ due to the modification, the increase in pHe is more pronounced for FeZ as a result of a more pronounced electrostatic attraction. In a slightly acidic medium, at pHo = 5–7 for NZ and pHo = 4–7 for FeZ, the competitive effect is minimal due to the low concentration of H+ ions. However, in this case, the increase in pHe is primarily a consequence of the decrease in Ni(II) concentration in suspension and the shift of the equilibrium reaction of Ni(II) hydrolysis to the left, as shown by Equation (5). In short, the establishment of a plateau in the range 5 < pHo < 7 for NZ and in the range 4 < pHo < 7 for FeZ corresponds to the optimal pH range since the maximum αe is achieved for the observed initial concentration (12% for NZ and 57% for FeZ). The almost five-fold higher efficiency of Ni(II) removal using FeZ justifies the implementation of zeolite modification.
3.1.2. Solid/Liquid Ratio Optimization
The effect of the S/L ratio was evaluated at an initial concentration of 4.266 mmol Ni/L and pHo = 6.14. Figure 3 presents a comparison of pHe with pHppt, along with the removal efficiency, αe, of Ni(II) on NZ and FeZ at various S/L ratios.
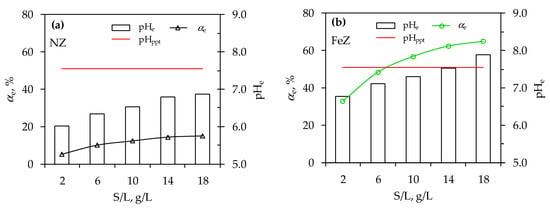
Figure 3.
Comparison of pHe with pHppt and removal efficiency, αe, at various S/L ratios for (a) NZ and (b) FeZ.
From Figure 3 it is clear that the increase in the S/L ratio is accompanied by an increase in αe for both zeolite samples. This is solely due to the greater number of active sites on the zeolites available for Ni(II) sorption since the parameters pHo and the initial concentration of Ni(II) are constant. Conversely, while an increase in the S/L ratio positively influences the removal efficiency, it also leads to an increase in the pHe value, as shown in Figure 3. In the case of NZ, the measured pHe is lower than pHppt at all S/L, while for FeZ up to S/L ≤ 14 g/L. This indicates the appearance of Ni(OH)2 precipitate in the suspension at S/L = 18 g/L for FeZ. Therefore, along with identifying the optimal pHo, it is crucial to determine the optimal S/L ratio to achieve the highest removal efficiency without causing Ni(II) precipitation. This is particularly true for the FeZ sample. Considering the above, the optimal S/L for FeZ is 10 g/L since S/L = 14 g/L is the boundary ratio due to pHe ≈ pHppt. Although the optimal S/L ratio for NZ is 18 g/L, an S/L of 10 g/L for NZ is selected for the purpose of comparing the following experimental results with FeZ. At the optimal S/L = 10, a five-fold higher nickel removal efficiency was obtained on FeZ compared to NZ, i.e., 57% vs. 12%, respectively.
3.1.3. Contact Time Optimization
The amount of Ni(II) sorbed on NZ and FeZ and the removal efficiency as a function of time are shown in Figure 4.
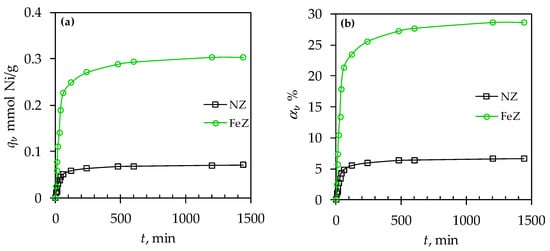
Figure 4.
The amount of sorbed Ni(II) on NZ and FeZ (a) and the removal efficiency (b) as a function of contact time.
The results presented in Figure 4 indicate two-phase Ni(II) sorption onto both NZ and FeZ. The first phase, occurring within 120 min, is marked by a rapid increase in qt and αt, followed by a second phase where qt and αt increase more gradually until equilibrium is achieved. Presence of a two-phase sorption process indicates that the rapid initial sorption is caused by the plentiful accessible surface active sites, while the slower second phase is attributed to the sorption of Ni(II) at less accessible sites within zeolite structure. For both zeolites, the optimal contact time is 600 min, achieving a four-fold higher amount of sorbed Ni(II) on FeZ compared to NZ, i.e., 0.303 mmol/g vs. 0.070 mmol/g (29% vs. 7%), respectively.
Identification of the Kinetic Rate-Controlling Step
Various reaction and diffusion kinetic models are employed to analyze experimental data in order to identify the rate-controlling step, whether it is related to mass transfer, diffusion, or chemical reactions. The most commonly used reaction kinetic models to verify if a chemical reaction is the rate-controlling step are the pseudo-first order (PFO) model (Lagergren), the pseudo-second order (PSO) model (Ho), and the Elovich model. The pseudo-first order non-linear equation is given by the following expression [83,84]:
In this equation, qt represents the amount of Ni(II) sorbed onto the zeolite at time t (mmol/g), k1 is the rate constant of the PFO (1/min), and t is the time (min).
The non-linear form of the pseudo-second order is expressed by Equation (11) [83,84]:
where k2 is the rate constant of the PSO [g/(mmol·min)].
The Elovich model describes the chemical sorption of Ni(II) onto a heterogeneous zeolite surface, and the non-linear form is represented by Equation (12) [84,85]:
where αE represents the initial chemisorption rate [mmol/(g·min)] and βE is associated with the surface coverage (g/mmol).
Since zeolites are porous materials, sorption is frequently restricted by mass transfer to the active sites within the zeolite structure. In well-stirred systems, the rate-controlling step is typically linked to film or intraparticle diffusion, as the resistance to mass transfer from the bulk to the particle surface is negligible. To determine whether film or intraparticle diffusion is the slowest step of sorption process, different diffusion kinetic models can be applied. The rate-limiting step in sorption, whether due to film or intraparticle diffusion, can be determined using the linear equation of the Weber–Morris model, as shown below [86]:
where kWM is the Weber–Morris diffusion constant [mmol/(g∙min1/2)] and I represents the boundary layer thickness (mmol/g).
If I = 0, film diffusion is the sole rate-controlling step; otherwise, both film and intraparticle diffusion contribute to mass transfer. The contribution of film or intraparticle diffusion can be estimated using Equation (14) [86]:
where RC denotes the relative coefficient, expressed as a percentage. Smaller RC values indicate that film diffusion contributes less to the overall mass transfer process.
The Weber–Morris diffusion coefficient, kWM (cm2/min) is calculated using the following equation [86]:
where dp is the zeolite particle diameter (cm).
The two-step sorption kinetics are represented by a double-exponential non-linear model, as shown below [87,88,89]:
Here, B1 and B2 represent the concentrations of the Ni(II) sorbed in the fast and slow steps (mmol/L), while kB1 and kB2 are the rate constants for the fast and slow steps (1/min), respectively.
The total sorption rate, r in [mmol/(g∙min)], is the sum of the fast step, r1, and the slow step, r2 [89,90,91]:
Furthermore, the percentage of Ni(II) sorbed in the fast (RF) and slow (SF) steps can be calculated as follows [87,88,89]:
Vermeulen’s approximation assumes intraparticle diffusion as the rate-controlling step and is given by Equation (20) [90]:
In this equation, DV is the intraparticle diffusion coefficient (cm2/min), and rp refers to the radius of the zeolite particle (cm).
The model parameters were calculated using the mathematical tool MathCad 15. The agreement of the model with the experimental data was determined using the linear and non-linear correlation coefficients, R2 and r2. In addition, two error functions were used, non-linear chi-square test (χ2) and root mean square error (RMSE), as follows [84]:
Figure 5 shows a comparison of the kinetic reaction and diffusion model curves with experimental kinetic data of Ni(II) sorption on NZ and FeZ. The calculated parameters of the kinetic models, along with the indicators of agreement, are presented in Table 2.
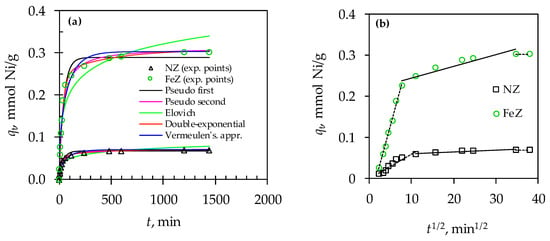
Figure 5.
Comparison of experimental data with: (a) kinetic model curves (pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, Elovich, Vermeulen’s approximation, and double-exponential model), and (b) the Weber–Morris model.

Table 2.
Calculated kinetic model parameters and agreement indicators for Ni(II) sorption on NZ and FeZ.
The agreement with the kinetic reaction models was assessed using the fitting parameters (qexp vs. qm, r2, RMSE, and χ2) presented in Table 2. According to the agreement indicators, the experimental data are aligned with the models in the following order: PSO > PFO > Elovich model. Since the Elovich model shows the highest deviation with the experimental results among the three kinetic reaction models considered, it suggests that chemisorption is not the slowest limiting step in the sorption process. Additionally, comparing the sorption capacity calculated from the model (qm) and the experimentally determined (qexp), the deviation is more pronounced for the PFO model than for the PSO. This suggests that the sorption of Ni(II) on both zeolites is not simply surface sorption, but rather involves more complex interactions, such as chemisorption or diffusion. Considering that chemisorption as a limiting step is ruled out based on the Elovich model’s agreement, it is necessary to fit the experimental data using diffusion kinetic models.
Therefore, the kinetic data for NZ and FeZ were fitted to the Weber–Morris model and plotted as a function of qt vs. t1/2, as shown in Figure 5b. The results demonstrate multicollinearity, suggesting a more complex kinetic mechanism that involves both film and intraparticle diffusion. The first linear section represents rapid sorption, the second indicates slower sorption, and the third reflects the attainment of equilibrium, which is consistent with the results shown in Figure 4a. The parameter values kWM1 > kWM2 and DWM1 > DWM2 confirm that the sorption is faster during the initial phase. Furthermore, these parameters are higher for FeZ compared to NZ, which aligns with the higher amount of Ni(II) sorbed on FeZ and its higher sorption potential. Given that the calculated relative coefficient (RC) is 13% for NZ and 20% for FeZ, it suggests that the contribution of mass transfer via film diffusion is significantly smaller in comparison to intraparticle diffusion.
Vermeulen’s approximation model assumes that intraparticle diffusion is the slowest step in mass transfer. Based on the parameter values presented in Table 2, it can be concluded that intraparticle diffusion is the rate-limiting step for both zeolites. However, to further verify this statement, the experimental results were also analyzed using the double-exponential model.
The calculated correlation indicators for the double-exponential model yielded the most satisfactory results among all the models tested. This supports the two-step sorption of Ni(II) on both zeolites. The first phase, related to mass transfer through the film, is faster (KB1 > KB2) than the second phase, which involves mass transfer via intraparticle diffusion. This aligns with the findings from the Weber–Morris model. Given that B1 > B2 and RF > SF, the majority of Ni(II) was sorbed during the faster first phase on both zeolites. The calculated kinetic parameters (KB1, KB2, B1, and B2) for both sorption phases are higher for FeZ, which is a consequence of the zeolite modification that contributed to an increase in the number of active sites. In summary, Ni(II) sorption on both zeolites occurs through a complex mass transfer mechanism to active sites located on the outer and inner zeolite surface. From a kinetic point of view, intraparticle diffusion is the rate-controlling step of mass transfer.
3.1.4. Concentration Range Optimization
The results of the effect of the initial Ni(II) concentration on the amount of Ni(II) sorbed per gram of NZ and FeZ, as well as the removal efficiency, αe are shown in Figure 6.
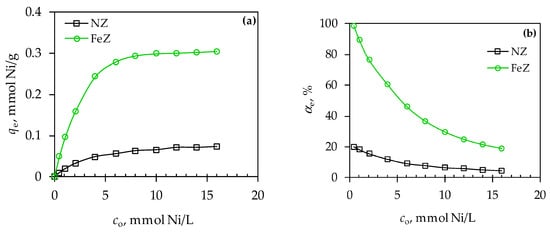
Figure 6.
Effect of initial Ni(II) concentration on: (a) amount of Ni(II) sorbed per gram of NZ and FeZ and (b) Ni(II) removal efficiency.
The amount of sorbed Ni(II) on NZ gradually increases with increasing co up to ≈8 mmol Ni/L, and then a plateau is established. In the case of FeZ, a sudden increase in the amount of sorbed Ni(II) was observed up to co = 6 mmol Ni/L, followed by a gradual increase until a plateau was established. Hence, at co > 8 mmol Ni/L for NZ and 10 mmol Ni/L for FeZ, maximum zeolite saturation is achieved. Further increase in the initial concentration has no effect on the increase in the amount of sorbed Ni(II) since the available sorption sites are completely occupied. Furthermore, from the point of view of Ni(II) removal efficiency, the highest removal efficiency is achieved at the lowest initial concentration, while at concentrations higher than 8 mmol Ni/L for NZ and 10 mmol Ni/L for FeZ, the removal efficiency is minimal. Accordingly, the concentration range for application of NZ is up to co = 8 mmol Ni/L, and FeZ up to co = 10 mmol Ni/L. Additionally, it is noteworthy that FeZ exhibits nearly a fivefold increase in Ni(II) removal efficiency compared to NZ (98.74% vs. 21.20%) at the lowest initial concentration of 0.503 mmol/L (30 mg/L). Moreover, when using FeZ at the aforementioned initial concentration, the residual Ni(II) concentration is reduced to 0.0064 mmol/L (0.37 mg/L), which falls below the regulatory limit of 0.5 mg/L established by Croatian standards [25]. To meet the regulatory limit at higher initial concentrations (co > 0.503 mmol/L), it is necessary to carry out sorption in two or more sequential stages.
To contextualize the present study within the framework of related research, relevant background information from recent investigations is summarized below. Namely, nickel removal using natural zeolites sourced globally has been the focus of numerous scientific investigations. For example, Panayotova [50] determined a maximum sorption capacity of 0.039 mmol Ni/g at pHo = 5 using natural Bulgarian clinoptilolite zeolite. Alvarez-Ayuso et al. [51] determined capacity of natural zeolite clinoptilolite from Pentalofos, Greece in the amount of 0.034 mmol Ni/g. Dal Bosco et al. [52] testified maximum binding capacity of Brazilian natural scolecite zeolite towards nickel to be 0.102 mmol/g at pHo = 6. Sprynskyy et al. [53] reported a sorption capacity of 0.222 mmol Ni/g at pHo = 6.2 for the natural zeolite clinoptilolite from Sokyrnytsya deposit, Ukraine. Argun [54] investigated the uptake of nickel on the natural zeolite clinoptilolite from the deposit in Manisa (Turkey) at pHo = 7 and achieved an ion exchange capacity of 0.060 mmol/g. Al Dwairi et al. [55] applied a mixture of zeolitic tuff (phillipsite and bentonite) originating from Jordan in a ratio of 1:1 and obtained a capacity of 0.560 mmol Ni/g. Salman et al. [56] achieved a capacity of 0.460 mmol Ni/g at pHo = 6 using a mixture of natural phillipsite and chabazite originating from southern Syria. El-Azim et al. [57] have established the capacity of natural zeolite clinoptilolite in the amount of 0.169 mmol Ni/g at pHo = 6. Sokić et al. [58] used natural zeolitic tuff from the Slanci deposit, Serbia for Ni(II) sorption and determined a capacity of 0.044 mmol/g at pHo = 5.1.
Furthermore, several studies have been carried out on natural zeolites converted to the homoionic form. Thus, Al-Haj Ali et al. [67] applied Jordanian phillipsite zeolite tuff converted to the sodium homoionic form and obtained a sorption capacity of 0.341 mmol Ni/g at pHo = 4. Çoruh and Ergun [68] examined the sorption of Ni(II) on natural and Na-conditioned clinoptilolite zeolite from the Manisa-Gördes site in western Anatolia (Turkey) and established a 1.2-fold increase in capacity on the conditioned zeolite in relation to the starting material (0.17 mmol/g vs. and 0.14 mmol/g). Rajić et al. [69] achieved a sorption capacity of 0.180 mmol Ni/g at pHo = 6 using natural zeolite tuff (clinoptilolite) from a Serbian Zlatokop deposit converted into sodium form. Abatal et al. [70] obtained a sorption capacity on clinoptilolite-rich zeolite tuff from Puebla State (Mexico) converted to the Na-homoionic form of 0.005 mmol Ni/g at pHo = 6. Mehdi et al. [71] tested the binding of nickel to the sodium form of Algerian natural zeolite mordenite and achieved a capacity of 0.500 mmol/g at pHo = 5.27. Biblioteca et al. [72] investigated the possibility of using natural and sodium-conditioned zeolite clinoptilolite by simulating conditions in the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, using a Ni(II) solution of 0.034 mmol/L (2 mg/L) at pHo = 4.5, they determined nickel binding of 0.002 mmol/g and 0.003 mmol/g on natural and conditioned zeolite, respectively. Experimental reports indicate that Ni(II) sorption on natural zeolites was carried out at optimal pH, without the possibility of precipitation. In addition, the observed deviations in sorption capacities of zeolites are a consequence of the mineralogical and chemical features of the used zeolites, as well as experimental parameters such as the zeolite–solution contact time, solid/liquid ratio, and initial nickel concentration.
With respect to Fe-modified natural zeolites, the existing literature indicates that only one study has addressed the removal of Ni(II) ions. Namely, Sirotiak et al. [75] used natural zeolite tuff containing clinoptilolite from the Nižný Hrábowec deposit (Slovakia) for the preparation of Fe-modified zeolite. The modification was carried out at 70 °C for 60 h using 1 mol/L Fe(NO3)3 and 5 mol/L KOH solutions. The authors did not define the optimal pH, but they found an increase in nickel sorption capacity by 1.01 times on the modified zeolite compared to the natural one (0.0070 mmol/g vs. 0.0069 mmol/g).
In the current study, the observed maximum amount of sorbed Ni(II) is four times higher on FeZ compared to NZ (0.305 mmol/g vs. 0.073 mmol Ni/g, Figure 6a), which is impressive and justifies the zeolite modification procedure. The increase in the sorption capacity of FeZ is a consequence of the modification that enhanced the zeolite’s negative charge by incorporating Fe species onto the outer and inner surfaces of the zeolite particles, and thus the number of active centers. The resulting negative charge is partly neutralized by the presence of exchangeable alkali and alkaline earth cations, with sodium being the most prevalent. In order to determine the relationship between the amount of sorbed Ni(II) on NZ and FeZ as well as the quantity of released exchangeable ions (Na, K, Ca, and Mg) from the zeolite, the results were compared and presented in Figure 7.
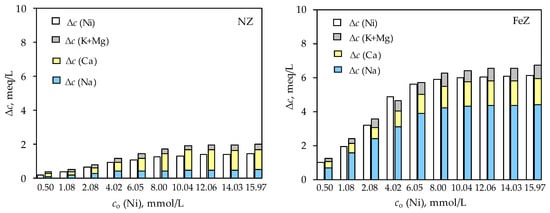
Figure 7.
Relationship between the amount of sorbed Ni(II) and the quantity of released exchangeable ions (Na, K, Ca, and Mg) from the NZ and FeZ as function of different initial Ni(II) concentration.
For both zeolites, in the entire considered concentration range, an almost completely stoichiometric relationship between the amount of sorbed Ni(II) and the released exchangeable cations is observed. This suggests that ion exchange is the dominant Ni(II) sorption mechanism on both zeolites. Calcium is the main exchangeable cation for NZ, while sodium is for FeZ, which is a consequence of the modification procedure. As previously specified, since both zeolites have a negative charge in the pHo range 2–12, the electrostatic attraction between the zeolite and Ni2+ initiates sorption. However, the ion exchange mechanism prevails, which is consistent with the results shown in Figure 7.
To fully understand the mechanism of nickel sorption on zeolites, the elemental quantities for the initial and nickel-saturated zeolites were calculated based on the chemical composition provided in Table 1, and the results are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Element quantity of starting and Ni(II)-saturated zeolites.
The results show that the modification led to a 1.5-fold increase in iron content on FeZ compared to NZ (Table 3). The ratio of Fe increase on the inner and outer surfaces of FeZ corresponds to the ratio of zeta potential change. Specifically, the zeta potential in a wide pH range decreased by an average of 1.5 times on FeZ as a result of the modification. Regarding exchangeable cations, sodium is predominant for FeZ and calcium for NZ. The calcium content decreased slightly for FeZ after modification compared to NZ. According to previous findings, this is a result of the second phase of modification, where sodium replaced calcium, leading to its precipitation on the FeZ surface in an alkaline medium [77]. This is confirmed by the results of almost unchanged amounts of calcium in nickel-saturated FeZ, since calcium is partially available for ion exchange, unlike sodium, due to the aforementioned. The decrease in sodium content in FeZNi and calcium content in NZNi is a result of ion exchange, which is consistent with the findings presented in Figure 7. The nickel content on the FeZNi surface is 4.5 times higher than on the NZNi surface, which is in accordance with previous experimental observations. This implies that the modification affected a significant increase of active sites on the outer surface of the zeolite available for Ni(II) sorption.
To obtain element distribution data on the four selected surfaces of nickel-saturated NZ and FeZ, EDS analysis was performed at a magnification of 35×, as shown in Figure 8. The results of the mass percentages of detected elements on selected surfaces are listed in Table 4 and Table 5.
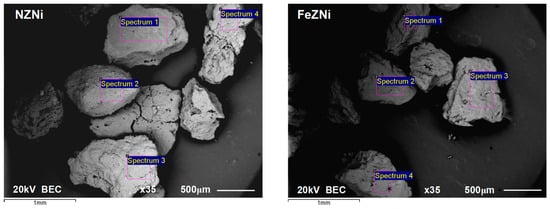
Figure 8.
BSE (backscattered electron) image displaying four marked surfaces (Sp—spectra) on NZNi (left) and FeZNi (right) for EDS analysis.

Table 4.
Semi-quantitative chemical composition (given in wt. %) of the four analyzed surfaces on the NZNi sample shown in Figure 8 (Sp—spectra; analyzed with EDS).

Table 5.
Semi-quantitative chemical composition (given in wt. %) of the four analyzed surfaces on the FeZNi sample shown in Figure 8 (Sp—spectra; analyzed with EDS).
The results of the EDS analysis indicate a very uniform mass percentage of all detected elements on the four analyzed surfaces (spectra, Sp) for both saturated samples. This implies a relatively uniform distribution of active sites on the surface of both samples. The mean nickel mass percentage on the FeZ surface is even six times higher than that on NZ, further confirming the increased sorption capacity of the modified sample. This observation suggests that nickel is more sorbed on the outer surface of the zeolite. Furthermore, for the FeZNi sample, unlike the other detected elements, the mass percentages of iron fluctuate across the four analyzed surfaces. Namely, the slightly higher nickel content detected at Sp 3 and Sp 4 for FeZNi can be associated with a higher iron content. Thus, active Fe-oxyhydroxide centers are responsible for promoting Ni(II) sorption. Regarding the main exchangeable cations, calcium dominates on the NZNi surface, while sodium on FeZNi, which is in accordance with the results of the elemental composition (Table 3).
In order to better understand the distribution of detected elements on the surface of nickel-saturated zeolites, a mapping analysis of the surface of both zeolites was performed after SEM imaging at a magnification of 1000×, and the results are shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10.
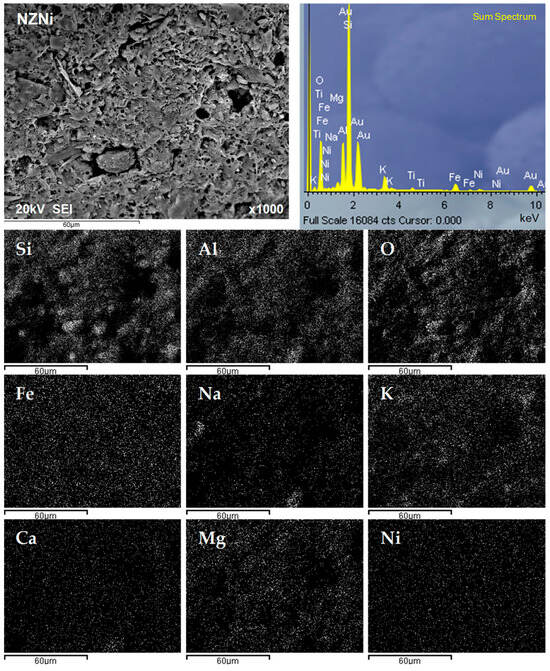
Figure 9.
SEM image and EDS analysis of the NZNi surface, along with the corresponding mapping analysis.
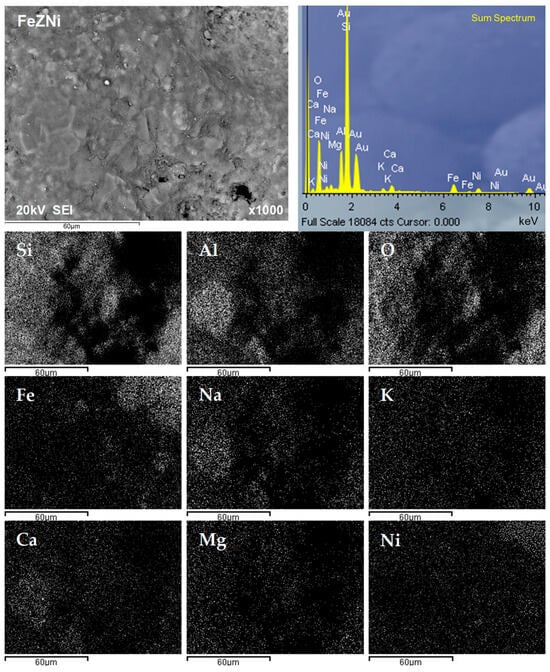
Figure 10.
SEM image and EDS analysis of the FeZNi surface, along with the corresponding mapping analysis.
Figure 9 shows the relationship between the occurrence of Si, Al, and O on the surface of NZNi, since these elements are the main components of the zeolite skeleton. The other detected elements show a fairly even distribution. Similar observations were found for FeZNi regarding the distribution of the main zeolite lattice constituents, Si, Al, and O (Figure 10). However, a more pronounced occurrence of iron is observed in places where the constituent zeolite elements are not present. Moreover, a higher occurrence of nickel was also observed in these locations. This once again proves that the modification of the zeolite surface with Fe species is responsible for the improved nickel sorption.
Ultimately, based on monitoring the concentration of exchangeable cations, elemental composition and EDS analysis, it is concluded that the sorption of Ni(II) on both zeolites is primarily initiated by the electrostatic attraction of the predominantly present Ni2+ to the negatively charged surface of the zeolite. Following the initial electrostatic attraction, outer-sphere complexation of Ni(II) on oxygen-containing surface functional groups occurs, while ion exchange is the primary mechanism governing the overall sorption process. Ion exchange was confirmed by the almost stoichiometric relationship between the amount of sorbed nickel and the released exchangeable cations, as well as the results of EDS analysis. A schematic representation of all possible mechanisms responsible for nickel removal on NZ and FeZ is shown in Figure 11a,b.
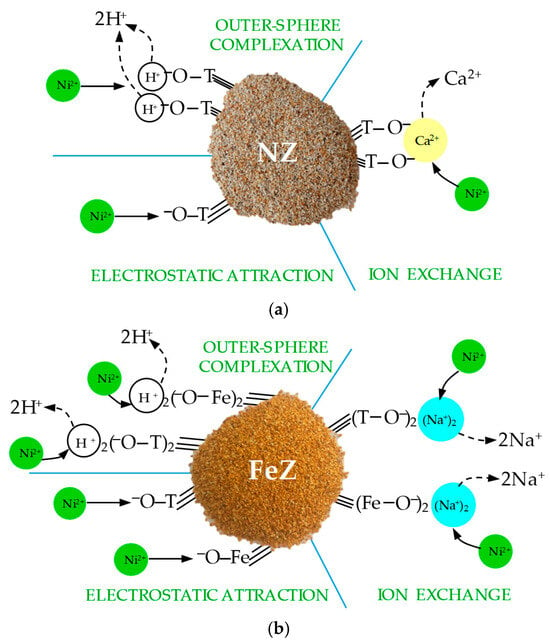
Figure 11.
Schematic representation of the proposed Ni(II) sorption mechanism on (a) NZ and (b) FeZ.
3.2. Leaching Characteristics of Nickel-Saturated Zeolites
The leaching characteristic of nickel-saturated zeolites, NZNi and FeZNi, was examined using the standard DIN 38414 S4 leaching method [79] across a pHo range of 2.05 to 12.02. The percentage of nickel leached from the saturated zeolites is presented in Figure 12.
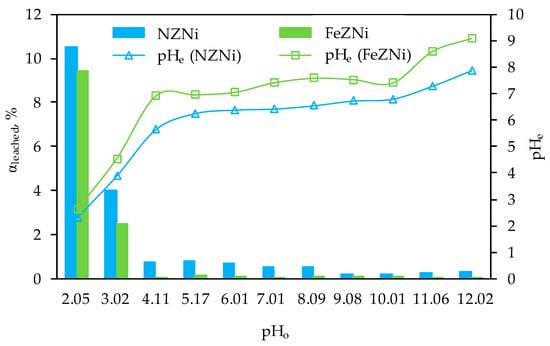
Figure 12.
Percentage of leached nickel from NZNi and FeZNi, and changes in pHe as a function of pHo.
According to the results shown in Figure 12, it can be seen that both zeolites show a neutralization effect of the surrounding medium, which is most pronounced in the range 4.11 < pHo < 11.06 for NZNi, and for FeZNi in the range 4.11 < pHo < 10.01. The neutralizing effect is the result of protonation and deprotonation of silanol (Si–OH) and aluminol (Al–OH) zeolite groups. In an acidic medium, their protonation occurs, causing an increase in the pH of the surrounding medium. On the contrary, in an alkaline medium, their deprotonation occurs, which causes a decrease in the pH value of the surrounding medium. Protonation and deprotonation reactions are shown by Equations (23) and (24) [81,91]:
where T denotes an Si or Al atom.
In addition, zeolite also possesses Brønsted base sites (proton acceptors), i.e., Al–O− groups, and Fe–O− groups in the case of FeZ. The presence of these groups additionally causes an increase in the pH of the surrounding medium in acidic conditions, which is especially pronounced for FeZNi. The protonation reactions of Brønsted base sites are shown by Reactions (25) and (26):
Furthermore, Ni(II) leaching was observed across the entire pHo range tested, whereby more pronounced at pHo ≤ 3.02. Namely, in an extremely acidic medium, leaching is a consequence of the displacement of a high amount of H+ ions with Ni(II). At pHo = 2.05, dealumination of the zeolite cannot be ignored, which is manifested by even more pronounced leaching of Ni(II) as a consequence of partial degradation of the zeolite structure. In the pH range 4.11–8.09, <1% Ni(II) was leached, ranging from 0.5–0.8% from NZNi and 0.07–0.2% from FeZNi. With further increase in pHo ≥ 9.08 for both saturated zeolites, the percentage of leached Ni(II) tends to decrease. Namely, according to the Ni(II) speciation diagram depending on pHo (Figure 1), Ni(II) predominantly exists in the form of precipitate Ni(OH)2o in the pH range 8.0–13.5. This is precisely the reason for the reduced leachability of Ni(II), which is especially evident at more alkaline pH, since the pHo is in the range that satisfies the condition for Ni(II) precipitation. Comparing the results of the percentage of leached Ni(II) from both samples, it is interesting to note a higher percentage of leached Ni(II) from NZNi even though almost five times more Ni(II) was sorbed on FeZ. Thus, the results suggest that, in addition to FeZ having a higher sorption efficiency, it also demonstrates a greater ability to retain Ni(II), making it a more effective sorbent for Ni(II) ions. Finally, the results indicate that at pHo ≥ 4.11, negligible leaching (<1%) of Ni(II) occurs, and FeZ could be used for remediation of nickel-contaminated environments.
4. Conclusions
This study provided a comparative investigation of the optimization and understanding of Ni(II) sorption using natural and Fe(III)-modified natural zeolite. The experimental findings demonstrated the necessity of optimizing sorption parameters to enhance Ni(II) removal efficiency and fully utilize the zeolite sorption capacity. Nickel sorption on both zeolites, particularly on FeZ, is primarily influenced by the suspension pH and the S/L ratio. Under optimized conditions, the most effective pHo range for Ni(II) sorption was 5–7 for NZ and 4–7 for FeZ. The S/L ratio of 10 g/L and the contact time of 600 min were found to be optimal for both zeolites. The upper limit of effective Ni(II) sorption was at co = 8 mmol/L for NZ and co =10 mmol/L for FeZ. The FeZ effectively reduced the Ni(II) concentration to a level compliant with Croatian discharge regulations for both surface water bodies and public sewage systems at co = 0.503 mmol/L. Ni(II) sorption kinetics on both zeolites are governed by a two-step process, with intraparticle diffusion acting as the dominant rate-limiting step and film diffusion playing an insignificant role during the initial sorption stage. A significant enhancement in Ni(II) sorption capacity of FeZ relative to NZ by 4–5 times (0.305 mmol/g vs. 0.073 mmol/g) was confirmed experimentally and substantiated by elemental analysis, SEM/EDS, and mapping analysis of the saturated zeolites. Ni(II) sorption on both zeolites is initiated by electrostatic attraction between Ni2+ ions and the negatively charged zeolite surface, accompanied by outer-sphere complexation, whereas ion exchange identified as the dominant mechanism. Ion exchange was confirmed by the stoichiometric ratio of released zeolite cations and sorbed Ni(II). The quantity of released zeolite cations is higher from FeZ due to the greater number of active Fe-centers available for ion exchange as a result of the modification. Leaching tests conducted on NZNi and FeZNi confirmed the ability to retain Ni(II) within the zeolite structure over a wide pH range, 4.11 ≤ pHo ≤ 12.02. In conclusion, both zeolites are effective in Ni(II) removal, while FeZ shows markedly improved sorption characteristics, indicating its suitability for practical deployment in the in situ and ex situ remediation of nickel-contaminated environments.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cleantechnol7030078/s1, Figure S1: Speciation plot of log [(Ni)II] vs. pH at 4.267 × 10−3 mol Ni/L and an ionic strength of 0.011 mol/L; Figure S2: Plot of Ni(II) species fractions vs. pH at 4.267 × 10−3 mol Ni/L and an ionic strength of 0.011 mol/L.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, investigation, methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, M.U.; experimental analysis, formal analysis, J.D. and S.J.; writing—review and editing, M.U., I.N., J.D., and S.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia (Contract No. 451-03-136/2025-03/200135 and 451-03-136/2025-03/200287).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. The data further supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author, Marin Ugrina, upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AAS | Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer |
| BET | Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller method for surface area determination |
| FeZ | Fe(III)-modified natural zeolite |
| FeZNi | Nickel-saturated Fe(III)-modified natural zeolite |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| NZ | Natural zeolite |
| NZNI | Nickel-saturated natural zeolite |
| PFO | Pseudo-first order kinetic model |
| PSO | Pseudo-second order kinetic model |
| RC | Relative coefficient (%) |
| RF | Proportion of Hg(II) sorbed in rapid step (%) |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| SEM/EDS | Scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| SF | Proportion of Hg(II) sorbed in slow step (%) |
| S/L | Solid/liquid ratio |
| TG/DTG | Thermogravimetry with derivative thermogravimetry |
| XRPD | X-ray powder diffraction |
References
- Shahzad, B.; Tanveer, M.; Rehman, A.; Cheema, S.A.; Fahad, S.; Rehman, S.; Sharma, A. Nickel; whether toxic or essential for plants and environment—A review. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 132, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, W.; Rai, S.; Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Mondal, M.H.; Bhattarai, A.; Saha, B. A comprehensive review on the sources, essentiality and toxicological profile of nickel. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 9139–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.U.; Chattha, M.U.; Khan, I.; Chattha, M.B.; Aamer, M.; Nawaz, M.; Ali, A.; Khan, M.A.U.; Khan, T.A. Nickel toxicity in plants: Reasons, toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and remediation possibilities—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12673–12688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.I.; Ahmad, K.; Ahmad, T.; Zafar, A.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Ashfaq, A.; Akhtar, S.; Mahpara, S.; Mehmood, N.; Ugulu, I. Evaluation of nickel toxicity and potential health implications of agriculturally diversely irrigated wheat crop varieties. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Zulfiqar, U.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Radziemska, M.; Haider, F.U.; Holatko, J.; Hammershmiedt, T.; Naveed, M.; Ali, H.; Kintl, A.; et al. Nickel (Ni) phytotoxicity and detoxification mechanisms: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkhaus, E.; Salnikow, K. Nickel essentiality, toxicity, and carcinogenicity. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 42, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cempel, M.; Nikel, G. Nickel: A Review of Its Sources and Environmental Toxicology. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Jigyasu, D.K.; Kumar, A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Shabnam, A.A.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Malyan, S.K.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Kumar Gupta, D.; et al. Nickel in terrestrial biota: Comprehensive review on contamination, toxicity, tolerance and its remediation approaches. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LePan, N. All the World’ s Metals and Minerals in One Visualization. Visual Capitalist, Vancouver, WA, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.visualcapitalist.com/all-the-worlds-metals-and-minerals-in-one-visualization/ (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Duda-Chodak, A.; Błaszczyk, U. The impact of nickel on human health. J. Elementol. 2008, 13, 685–696. [Google Scholar]
- Lock, K.; Van Eeckhout, H.; De Schamphelaere, K.A.C.; Criel, P.; Janssen, C.R. Development of a biotic ligand model (BLM) predicting nickel toxicity to barley (Hordeum vulgare). Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picarelli, A.; Greco, N.; Sciuttini, F.; Marini, C.; Meacci, A. High consumption of Nickel-containing foods and IBS-like disorders: Late events in a gluten-free diet. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.K.; Reddy, R.C.; Bagoji, I.B.; Das, S.; Bagali, S.; Mullur, L.; Khodnapur, J.P.; Biradar, M.S. Primary concept of nickel toxicity—An overview. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Carocci, A.; Lauria, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Catalano, A. Nickel: Human Health and Environmental Toxicology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, S.; Garman, E.; Heim, K.E.; Lyons-Darden, T.; Schlekat, C.E.; Taylor, M.D.; Oller, A.R. Concise Review of Nickel Human Health Toxicology and Ecotoxicology. Inorganics 2019, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Brocato, J.; Laulicht, F.; Costa, M. Mechanisms of nickel carcinogenesis. In Essential and Non-Essential Metals. Molecular and Integrative Toxicology; Mudipalli, A., Zelikoff, J.T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 181–197. [Google Scholar]
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). Classification, Labelling and Packaging. In Table of Harmonized Entries in Annex VI to CLP.; European Chemicals Agency: Helsinki, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Nickel and nickel compounds. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2012; Volume 100C, pp. 169–218. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization; United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). Progress on Sanitation and Drinking Water: 2014 Update; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/112727 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- United Nations. The UN Sustainable Development Goals. United Nations, New York, 2015. Available online: http://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/summit/ (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240045064 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- NN 64/2023, Croatian Regulation on the Health Safety of Drinking Water. 2023. Available online: https://narodne-novine.nn.hr/clanci/sluzbeni/2023_06_64_1057.html (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Kumar, V.; Dwivedi, S.K. A review on accessible techniques for removal of hexavalent Chromium and divalent Nickel from industrial wastewater: Recent research and future outlook. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khobragade, M.U.; Nayak, A.K.; Pal, A. A Review on the Removal Technologies of Nickel(II) Ion from Aqueous Solution. Recent Pat. Eng. 2017, 11, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croatian Regulation on Wastewater Emission Limit Values. Available online: https://narodne-novine.nn.hr/clanci/sluzbeni/2020_03_26_622.html (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Noman, E.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Mohamed, R.M.S.R.; Al-Sahari, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Vo Dai-Viet, N.; Naushad, M. Sustainable approaches for nickel removal from wastewater using bacterial biomass and nanocomposite adsorbents: A review. Chemosphere 2002, 291, 132862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.M.; dos Reis da Costa, J.G.; de Almeida Neto, A.F. Techniques of nickel(II) removal from electroplating industry wastewater: Overview and trends. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Rafatullah, M.; Yuan, J.; Zwain, H.M.; Mojiri, A.; Gholami, Z.; Gholami, F.; Wang, W.; Giwa, A.S.; Yu, Y.; et al. Nickel ion removal from aqueous solutions through the adsorption process: A review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2021, 37, 755–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Balouch, A.; Pathan, A.A.; Abdullah; Jagirani, M.S.; Mahar, A.M.; Zubair, M.; Laghari, B. Remediation of Nickel ion from wastewater by applying various techniques: A review. Acta Chem. Malays. 2019, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszelnicka, I.; Ginter-Kramarczyk, D.; Góra, W.; Staszak, K.; Baraniak, M.; Lota, G.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Removal of nickel(II) from industrial wastewater using selected methods: A review. Chem. Process Eng. 2022, 43, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nthwane, Y.B.; Fouda-Mbanga, B.G.; Thwala, M.; Pillay, K. A comprehensive review of heavy metals (Pb2+, Cd2+, Ni2+) removal from wastewater using low-cost adsorbents and possible revalorisation of spent adsorbents in blood fingerprint application. Environ. Technol. 2025, 46, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Kaur, P. A review on biological sorbents for nickel removal from wastewater. Int. J. Res. Anal. Rev. 2018, 5, 468–472. [Google Scholar]
- Lech, M.; Gala, O.; Helińska, K.; Kołodzińska, K.; Konczak, H.; Mroczyński, Ł.; Siarka, E. Membrane Separation in the Nickel-Contaminated Wastewater Treatment. Waste 2023, 1, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtab, M.A.; Bari, A.; Khan, S.; Ahteshaam, M.; Khan, S.U.; Farooqi, I.H. Nickel (II) removal from real electroplating wastewater in an electrocoagulation reactor: Parametric optimization by response surface methodology. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 90, 2266–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, O.A.; Safwat, S.M.; Matta, M.E. Nickel removal from wastewater using electrocoagulation process with zinc electrodes under various operating conditions: Performance investigation, mechanism exploration, and cost analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 26650–26662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. Npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmanzadegan, F.; Ghaemi, A. A comprehensive review on novel zeolite-based adsorbents for environmental pollutant. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, M.K.; Azhari, S.; Jaya, M.A.B.T. Modified Zeolite as Purification Material in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Sci. Res. J. 2021, 18, 177–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes de Magalhães, L.; Rodrigues da Silva, G.; Clark Peres, A.E. Zeolite Application in Wastewater Treatment. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 4544104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Awual, M.R.; Angove, M.J. A review on nickel(II) adsorption in single and binary component systems and future path. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, X.; Yi, H.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, J.; Yuan, Y. Synthesis, characterization and application of Fe-zeolite: A review. Appl. Cat. A-Gen. 2022, 630, 118467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, N.P.; Shah, P.U.; Shah, N.K. Adsorptive removal of nickel(II) ions from aqueous environment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 179, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charazińska, S.; Burszta-Adamiak, E.; Lochyński, P. Recent trends in Ni(II) sorption from aqueous solutions using natural materials. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2022, 21, 105–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regina, M.Y.; Saraswathy, S.; Kamal, B.; Karthik, V.; Muthukumaran, K. Removal of nickel (II) ions from waste water using low cost adsorbents: A review. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, R.S.; Sreevelan, M.; Saravanan, G.; Wilsha, R.W.; Hemamalini, C.G. Removal of Nickel from Industrial Wastewater Using Natural Adsorbents: A Review. IJSART 2018, 4, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar]
- Tasić, Ž.Z.; Bogdanović, G.D.; Antonijević, M.M. application of natural zeolite in wastewater treatment—A review. J. Min. Metall. Sect. A-Min. 2019, 55, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudaber, S.; Noori, B.; Batur, J. Zeolites as Effective Adsorbents for Heavy Metal Removal in Wastewater Treatment of Kabul City—A Review. IAR J. Eng. Technol. 2023, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sodha, V.; Shahabuddin, S.; Gaur, R.; Ahmad, I.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Sridewi, N. Comprehensive Review on Zeolite-Based Nanocomposites for Treatment of Effluents from Wastewater. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malamis, S.; Katsou, E. A review on zinc and nickel adsorption on natural and modified zeolite, bentonite and vermiculite: Examination of process parameters, kinetics and isotherms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252–253, 428–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panayotova, M. Kinetics and thermodynamics of removal of nickel ions from wastewater by use of natural and modified zeolite. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2001, 10, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Ayuso, E.; Garcıa-Sánchez, A.; Querol, X. Purification of metal electroplating waste waters using zeolites. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4855–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bosco, S.M.; Jimenez, R.S.; Carvalho, W.A. Removal of toxic metals from wastewater by Brazilian natural scolecite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 281, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Buszewski, B.; Terzyk, A.P.; Namieśnik, J. Study of the selection mechanism of heavy metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+) adsorption on clinoptilolite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 304, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argun, M.E. Use of clinoptilolite for the removal of nickel ions from water: Kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dwairi, R.A.; Al-Rawajfeh, A.E. Removal of cobalt and nickel from wastewater by using Jordan low-cost zeolite and bentonite. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2012, 47, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, H.; Shaheen, H.; Abbas, G.; Khalouf, N. Use of Syrian natural zeolite for heavy metals removal from industrial waste water: Factors and mechanism. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 452–461. [Google Scholar]
- El-Azim, H.A.; Mourad, F.A. Removal of Heavy Metals Cd (II), Fe (III) and Ni (II), from Aqueous Solutions by Natural (Clinoptilolite) Zeolites and Application to Industrial Wastewater. Asian J. Environ. Ecol. 2018, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokić, K.; Dikić, J.; Veljović, Ð.; Jelić, I.; Radovanović, D.; Štulović, M.; Jevtić, S. Preparation and Characterization of Hydroxyapatite-Modified Natural Zeolite: Application as Adsorbent for Ni2+ and Cr3+ Ion Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes 2025, 13, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, B.; Açikel, Ü. Intake of divalent copper and nickel onto natural zeolite from aqueous solutions: A study in mono- and dicomponent systems. Turk. J. Chem. 2022, 46, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parades-Aguilar, J.; Reyes-Martínez, V.; Bustamante, G.; Almendáriz-Tapia, F.J.; Martínez-Meza, G.; Vílchez-Vargas, R.; Link, A.; Certucha-Barragán, M.T.; Calderón, K. Removal of nickel(II) from wastewater using a zeolite-packed anaerobic bioreactor: Bacterial diversity and community structure shifts. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abbad, E.A.; Al Dwairi, R.A. Removal of nickel (II) ions from water by Jordan natural zeolite as sorbent material. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.S.; Khosravi, A.; Tavakoli, H.; Esmhosseini, M.; Khezri, S. Natural zeolite for nickel ions removal from aqueous solutions: Optimization and modeling using response surface methodology based on central composite design. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 16898–16906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olad, A.; Ahmadi, S.; Rashidzadeh, A. Removal of Nickel (II) from aqueous solutions with polypyrrole modified clinoptilolite: Kinetic and isotherm studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 7172–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaoba, S.; Orhan, Y.; Akyüz, T. Kinetics and equilibrium studies of heavy metal ions removal by use of natural zeolite. Desalination 2007, 214, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.H.S.; Zhang, X.T.; Adnan, S.N. Application of clinotptilolite in removal of nickel(II) in plating wastewater. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 18, 659–664. [Google Scholar]
- Merrikhpour, H.; Jalali, M. Comparative and competitive adsorption of cadmium, copper, nickel, and lead ions by Iranian natural zeolite. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2013, 15, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haj Ali, A.; El-Bishtawi, R. Removal of Lead and Nickel Ions Using Zeolite Tuff. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1997, 69, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çoruh, S.; Ergun, O.N. Ni2+ removal from aqueous solutions using conditioned clinoptilolites: Kinetic and isotherm studies. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2009, 28, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajic, N.; Stojakovic, D.; Jovanovic, M.; Zabukovec Logar, N.; Mazaj, M.; Kaucic, V. Removal of nickel(II) ions from aqueous solutions using the natural clinoptilolite and preparation of nano-NiO on the exhausted clinoptilolite. App. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatal, M.; Olguin, M.T.; Abdellaoui, Y.; El Bouari, A. Sorption of Cd (II), Ni (II) and Zn (II) on natural, sodium-, and acid-modified clinoptilolite-rich tuff. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2018, 44, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, B.; Belkacemi, H.; Brahmi-Ingrachen, D.; Braham, L.A.; Muhr, L. Study of nickel adsorption on NaCl-modified natural zeolite using response surface methodology and kinetics modelling. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 17, 100757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biblioteca, I.; Sambucci, M.; Valente, M. Zeolite-Clinoptilolite conditioning for improved heavy metals ions removal: A preliminary assessment. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 39649–39656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghazawi, Z.; Qasaimeh, A.; Al-Bataina, B. Investigation of nickel adsorption onto low Jordanian zeolite dose: Efficiency and Langmuir—Freundlich behaviour. J. Water Land Dev. 2021, 50, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuldeyev, E.; Seitzhanova, M.; Tanirbergenova, S.; Tazhu, K.; Doszhanov, E.; Mansurov, Z.; Azat, S.; Nurlybaev, R.; Berndtsson, R. Modifying Natural Zeolites to Improve Heavy Metal Adsorption. Water 2023, 15, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirotiak, M.; Lipovský, M.; Bartošová, A. Sorption kinetics of selected heavy metals adsorption to natural and Fe(III) modified zeolite tuff containing clinoptilolite mineral. Res. Pap. MTF STU 2015, 23, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN 66165-2; Particle Size Analysis-Sieving Analysis-Part 2: Procedure. Deutsches Institut für Normung: Berlin, Germany, 2016.
- Ugrina, M.; Vukojević Medvidović, N.; Daković, A. Characterization and environmental application of iron-modified zeolite from the Zlatokop deposit. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3557–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinovitch, I.; Debrad-Guedon, J.; Louvrier, J. The Analysis of Silicates; Israel Program for Scientific Translations: Jerusalem, Israel, 1966; pp. 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- DIN 38414 S4; German Standard Procedure for Water, Wastewater and Sediment Testing–Sludge and Sediment. Determination of Leachability; Institut für Normung: Berlin, Germany, 1984.
- Barnum, D.W. Hydrolysis of Cations. Formation Constants and Standard Free Energies of Formation of Hydroxy Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1983, 22, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minceva, M.; Fajagar, R.; Markovska, L.; Meshko, V. Comparative study of Zn2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ removal from water solution using natural clinoptilolitic zeolite and commercial granulated activated carbon. Equilibrium and adsorption. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 2117–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J.G. Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, 16th ed.; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 1338. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Gaur, J.P. Chemical reaction- and particle diffusion-based kinetic modeling of metal biosorption by a phormidium sp.-dominated cyanobacterial mat. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elovich, S.Y.; Larinov, O.G. Theory of adsorption from solutions of non-electrolytes on solid (I) equation adsorption from solutions and the analysis of its simplest form, (II) verification of the equation of adsorption isotherm from solutions. Izv. Akad. Nauk. SSSR Otd. Khim. Nauk. 1962, 2, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Apiratikul, R.; Pavasant, P. Sorption of Cu2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ using modified zeolite from coal fly ash. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczak, A.; Keinath, T.M. Kinetics of sorption and desorption of copper(II) and lead(II) on activated carbon. Water Environ. Res. 1993, 65, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiron, N.; Guilet, R.; Deydier, E. Adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) onto a grafted silica: Isotherms and kinetic models. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3079–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, I. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by clinoptilolite: Determination of isotherm and thermodynamic parameters and comparison of kinetics by the Double exponential model and conventional kinetic models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 970–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helferich, F. Ion Exchange; Mc Graw-Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1962; pp. 250–322. [Google Scholar]
- Filippidis, A.; Godelitsas, A.; Charistos, D.; Misaelides, P.; Kassoli-Fournaraki, A. The chemical behavior of natural zeolites in aqueous environments: Interactions between low-silica zeolites and 1 M NaCl solutions of different initial pH-values. Appl. Clay Sci. 1996, 11, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).