Abstract
Ampakines—positive allosteric modulators of AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs)—are drug candidates that have shown substantial promise in pre-clinical models of various neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric diseases. Much of the study of ampakines has focused on how these drugs modulate neuronal AMPARs to achieve certain therapeutic effects. However, astrocytes also express functional AMPARs and their physiology may be sensitive to modulation by ampakines. Herein, we investigate the effects of multiple ampakines on calcium levels in cortical astrocytes. We find that ampakines augment cytosolic calcium elevations in astrocytes to an extent far greater than that achieved by AMPA alone. This effect is amenable to competitive AMPAR blockade. Furthermore, calcium induction is sensitive to phospholipase Cβ antagonism and blockade of inositol triphosphate receptors located on the endoplasmic reticulum. Low-impact ampakines exerted weaker effects on cytosolic calcium levels in astrocytes and higher concentrations were required to observe an effect. Furthermore, high doses of the low-impact ampakine, CX717, were not toxic to cortical astrocytes at high concentrations, which may serve to differentiate low-impact ampakines from classical AMPAR positive modulators like cyclothiazide. As ampakines are further developed for clinical use, it would be prudent to determine the extent to and manner by which they affect astrocytes, as these effects may also underpin their therapeutic utility in CNS pathologies.
1. Introduction
Astrocytes are the most abundant cell type of the mammalian brain [1]. They were previously considered to be important for structural integrity of the mammalian brain and necessary for the upkeep of a functional blood-brain barrier [2]. Mounting data now demonstrate that astrocytes functionally modify synaptic activities of multiple neuronal types [3,4,5] and that they can respond to inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitters such as GABA [6] and glutamate [7,8], respectively. Astrocytes have been shown to respond to glutamate by releasing glutamate via gap junctions (hemichannel), through purinergic receptors [9] and by exocytosing glutamate vesicles and inducing inward currents in nearby neurons, suggesting that they play an active role in synaptic transmission and plasticity [10].
In the CNS, glutamate activates several metabotropic and ionotropic receptors. Specifically with respect to the ionotropic receptors, glutamate activates the kainate, NMDA and AMPA receptors (AMPAR), the latter of which mediates the majority of excitatory synaptic transmission in the CNS [11,12,13]. Available evidence indicates that AMPARs are also crucial for hippocampal plasticity and long-term potentiation (LTP), a process believed to be pivotal for memory encoding [14,15,16,17,18]. AMPAR dysregulation is thought to contribute to several neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders [19,20,21,22,23]. Furthermore, ampakines—positive allosteric modulators of AMPARs—enhance performance in several pre-clinical cognition assays [21,24,25,26] as well as in humans [27]. Ampakines also exhibit therapeutic effects in models of neurodegenerative disease [28,29,30,31] and in brain and spinal trauma [32,33,34,35,36,37].
Ampakines as a drug class are classified as either high-impact or low-impact [13,38]. High-impact ampakines act specifically by binding the AMPAR tetrameric complex and stabilizing the glutamate-bound, open state confirmation, allowing for increased ion flux into the cell and offsetting desensitization [13,38,39,40,41]. Low-impact ampakines are thought to minimally affect receptor desensitization and agonist binding affinity, though they are believed to accelerate channel opening [13,26,38,42]. Recently, we found that high-impact ampakines induce a Gq-coupled inositol triphosphate (IP3) formation, which does not occur in the presence of the agonist alone in cortical neurons [43]. In addition to agonist-induced elevations of cytosolic calcium, a secondary cytosolic calcium elevation results from IP3-mediated endoplasmic reticular (ER) calcium liberation. This effect could be abrogated by pre-treating neuronal cultures with IP3 receptor and phospholipase C antagonists. Furthermore, this secondary mechanism is partially responsible for the ampakine-mediated enhancement of synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices [43].
Given that astrocytes express AMPARs and physiologically respond to glutamate, we sought to interrogate the effects of ampakines on intracellular calcium levels and the mechanism by which ampakines augment AMPA-induced cytosolic calcium elevations. In the current study, we evaluate the manner in which high- and low-impact ampakines affect AMPA-induced calcium elevations in cortical astrocytes and explore the role of endoplasmic reticular calcium stores in mediating the ampakine effect. We also explore whether low-impact ampakines are toxic to cortical astrocytes. The robust effect of ampakines on astrocytes may help to explain the pro-cognitive effects these drugs elicit in vivo, as well as other therapeutically relevant pharmacological effects.
2. Materials and Methods
Animal studies were carried out in compliance with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and using protocols approved by IACUC of UC Irvine (Irvine, CA, USA). We made efforts to reduce animal suffering and the amount of animals used was reduced whenever possible.
2.1. Solution Preparation
Solutions were prepared in DMSO with <0.1% of final volume. CX681 (Figure 1) was synthesized at RespireRx Pharmaceuticals Inc. (Glen Rock, NJ, USA) Controlled salt solution (CSS: 125 mM NaCl, 25 mM glucose, 25 mM HEPES, 5.0 mM KCl, 1.4 mM CaCl2, 0.8 mM Mg2SO4) was added and the drug was dispersed via vortex mixing. Lipohilic drugs such as U73122 were solubilized with a high power sonic probe to ensure drug dispersal.
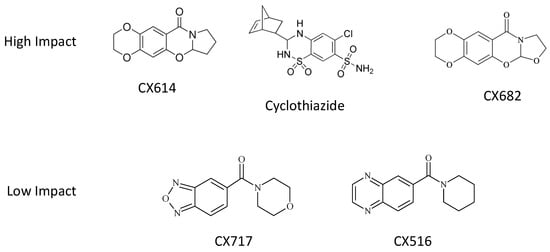
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of high-impact and low-impact ampakines used in this study.
2.2. Astrocyte Cultures
Primary cortical astrocyte cultures were prepared according to standard methods [8,44]. The cortices and hippocampi were dissected from Wistar rats (E15–17). The tissue was vigorously cut into smaller pieces and incubated for 8–10 min with papain (1 mg/mL) in calcium- and magnesium-free HBSS at 37 °C. The cell preparations of dissociated cortices and hippocampi were diluted to 30 mL, and left in an untreated 225 mL tissue culture flask for one hour at 37 °C. During this time astrocytes and oligodendrocytes (but not neurons) adhere to the untreated surface [8,44,45]. After this time, neurons were pelleted and plated in a separate flask for other experiments. DMEM medium containing 10% FBS was added to the astrocyte flask. Cells were incubated overnight at 37 °C. The following day, the astrocyte flask was washed with PBS twice, in order to dislodge residual debris, neurons, and loosely adherent oligodendrocytes. The solution was then replaced with DMEM with 10% FBS and 1% Penn/Strep (Gibco, Waltham, MA, USA).
The fluorimetry experiment setup was described previously [43]. Briefly, cells were counted and plated onto the inner 60 wells of a poly-D/L-lysine coated black-sided 96 well plate (Corning #3603, Corning, NY, USA) in a final volume of 200 μL DMEM per well. To reduce evaporation, the outer wells of the plate were filled with water.
2.3. Calcium Fluorescence Measurements
The protocol for fluorimetry experiments was described previously [43]. On the day of the experiment, the culture media was replaced with 100 μL media containing 2 µM Fluo-4-AM in CSS for 15 min at room temperature. The cells were then incubated with 100 μL fresh CSS for 5 to 10 min. The cells were then incubated with an additional 100 μL of CSS containing ampakine, with or without other investigational drugs. Cultures were then incubated for 30 min prior to initiating studies. Changes in Ca2+cyt were quantified by recording the fluctuation in light emission at 520 nm caused by excitation of the Fluo4-dye via a 485 nm light beam (Fluostar Galaxy fluorimeter, BMG Labs, Cary, NC, USA). Baseline fluorescence values were taken for 15–20 s at 0.1–0.2 s intervals and then studies were imitated by adding 10 μL of 100 μM (s)-AMPA to achieve a final concentration of 5 μM. Changes in fluorescence were then recorded for up to 15 s at 0.1–0.2 s intervals.
2.4. Assessment of CX717 Toxicity in Cortical Astrocytes
Effects of CX717 on astrocyte viability were assessed via XTT viability assay and LDH cell death assay. For each assay, astrocytes were plated onto the inner wells of 96-well plates in DMEM medium and allowed to adhere overnight. On the following day, plates were treated with control solution or with 500 μM CX717 for 48 h. The prior literature suggests that 100 μM cyclothiazide (CTZ) is toxic to cortical astrocytes within 24 h [45], so we hypothesized that 48-h treatment with CX717 should be sufficient to uncover toxic effects. After 48 h of treatment, an XTT assay was performed. PMS electron coupling reagent was made up into a 1.53 mg/mL solution in PBS, and the XTT reagent was prepared as a 1 mg/mL solution in DMEM without serum. PMS solution was mixed with XTT (20 μL PMS solution: 1 mL XTT solution). A total of 25 μL combined solution was added to each well containing 100 μL of media. Plates were incubated for 2 h and read on a microplate reader exc 450 nm with a reference wavelength of 650 nm. Absorbance data were normalized to control-treated cultures. For LDH assay, media from control- or CX717-treated cultures were taken from the 96-well plate and added to new wells of a 96-well plate. Manufacturer’s instructions were followed to prepare the LDH assay reagent. A 2 mg/mL solution of iodonitrotetrazolium was dissolved in PBS. A 36 mg/mL lactate solution (pH 8.5) was prepared in PBS. An enzyme solution (NAD 3 mg/mL, diaphorase 13 units/mL, 0.03% BSA, 1.2% sucrose w/v) in PBS was prepared. The solutions were combined in a 1:1:1 fashion. A total of 50 μL of the combined solution was added to media in the new 96-well plate. Plates were stored in the dark for 30 min and then read on a microplate reader exc 490 nm with a reference wavelength of 650 nm. Absorbance data were normalized to control-treated cultures.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed and plotted using Graphpad Prism (Graphpad, San Diego, CA, USA, https://www.graphpad.com/features) and Microsoft Excel 2022 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). Student’s t-tests were used to compare the two groups. Two-way ANOVAs were used to compare the effects of multiple concentrations over time.
3. Results
In these studies, we utilized two well-characterized, high-impact ampakines: CX614 and CTZ [39]. We also utilized the furan analogue of CX614, CX682 (Figure 1). The low-impact ampakines CX516 and CX717 [21,37,46,47,48] were also utilized as well (Figure 1). We previously showed that, in neurons, AMPA induced a rapid increase in cytosolic calcium levels that reached an asymptote 1–2 s after AMPA addition to the culture medium [43]. In astrocytes, we find that AMPA addition causes a slow rise in calcium levels, which plateaus ~5 s after AMPA addition. With the addition of CX682, CX614 or CTZ, the slope of the calcium elevation increased along with the total fluorescence at the end of the recording period (Figure 2). Two-way ANOVAs were used to evaluate the effects of each ampakine on fluorescence over time. For each ampakine, there was a significant effect of time on fluorescence (p < 0.0001). There was also a significant concentration-dependent increase in fluorescence (p < 0.0001). In addition, there was a significant interaction between time and treatment for the three high-impact ampakines evaluated (p < 0.0001). These preliminary findings demonstrate that neurons and astrocytes respond functionally differently to AMPAR agonists. It is also of interest that, in neurons, saturating concentrations of ampakines augmented AMPA-induced calcium rises by 150–180% [43], whereas, in astrocytes, these ampakines augment AMPA-induced calcium rises in excess of 500% (Figure 2). These data suggest that high-impact ampakines may exert a more robust effect on astrocytes in vivo. These data also suggest that high-impact ampakines can augment AMPA-induced cytosolic calcium elevations in astrocytes at concentrations that modulate neuronal AMPARs [39,49,50,51,52].
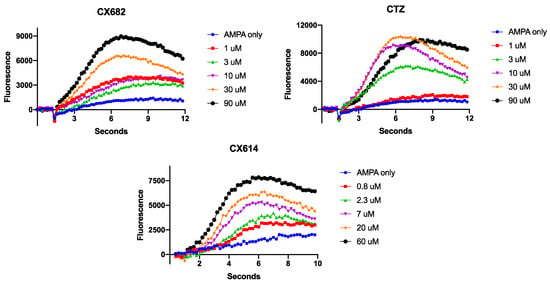
Figure 2.
Representative fluorescence measurements of AMPA-induced cytosolic calcium elevations in cortical astrocytes in the presence of CX682, CTZ or CX614. Graphs are representative of at least three independent experiments.
Further studies with the competitive AMPAR antagonists NBQX and CNQX demonstrate that the ampakine effect is specific to its actions on the AMPARs (Figure 3). NBQX pre-treatment ablates the CX682 effect completely (p < 0.05, t-test). CNQX pre-treatment mitigates the CX682 effect by >80% (p < 0.01, t-test) (Figure 3). Ablation of the ampakines effect with competitive AMPAR antagonists documents that these effects are AMPAR-dependent.
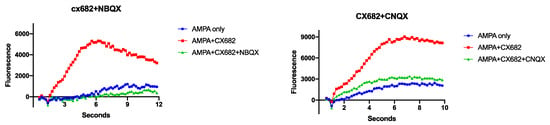
Figure 3.
Competitive AMPAR antagonism ablates CX682 enhancement. Cultures were treated with 10 μM NBQX or 25 μM CNQX prior to AMPA addition. Graphs are representative of 2–3 independent experiments.
In addition to assessing the effects of high-impact ampakines on cortical astrocytes, we were interested in determining whether low-impact ampakines may modulate the effects of AMPA on astrocytes. CX516 is a well-characterized, low-impact ampakine, and we found that CX516 only modestly altered the impact of AMPA on cytosolic calcium. In fact, 800 μM barely affected the slope of the calcium elevation. Slope increases were only observed at concentrations of 2.3 and 7 mM CX516 (Figure 4). In studies utilizing CX717, 100 μM did not alter cytosolic calcium elevations, with 300 μM hardly exhibiting an effect. An amount of 1 mM CX717 did increase the slope of calcium elevation, and both 3 and 9 mM CX717 did not further increase the slope to a greater extent (Figure 4). Two-way ANOVAs revealed for each low-impact ampakine that there was a significant effect of time on fluorescence (p < 0.0001). There was also a significant concentration-dependent increase in fluorescence (p < 0.01). In addition, there was a significant interaction between time and treatment for the two low-impact ampakines evaluated (p < 0.0001). These data highlight that low-impact ampakines may only exhibit a modest effect on astrocytes with very limited potency. In an effort to compare the relative efficacies of high- and low-impact ampakines, the maximum calcium elevation of each ampakine was determined and normalized to the effect of AMPA alone. CX516 and CX717 augmented the AMPA effect by ~3–3.5-fold, whereas the high-impact ampakines produced effects of much higher magnitude, between 5.5 and 8.5-fold at much lower concentrations (p < 0.05, t-test).
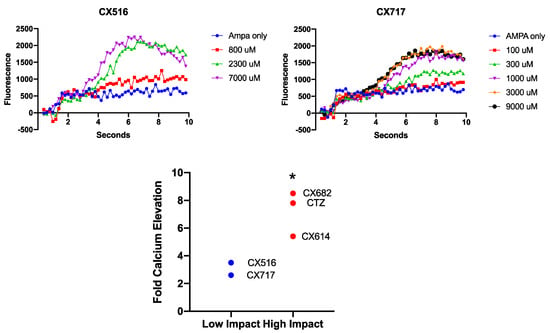
Figure 4.
Effects of low-impact ampakines CX516 and CX717 on AMPA-induced calcium elevations in astrocytes. Graphs are representative of 2–3 independent experiments. Effects of low- and high-impact ampakines on AMPA-induced calcium elevation are listed and compared via student’s t-test. * p < 0.05 between high- and low-impact ampakines assessed in this study.
The prior literature shows that CTZ and kainate, the non-desensitizing AMPAR agonist, are both rapidly toxic to cortical astrocytes at the concentrations required to modulate AMPARs [45]. This toxicity is readily observed 16–24 h after treatment in culture. CX717 at 150 μM fully reverses propofol-induced respiratory depression [53]. A quantity of 150 μM CX717 also strongly reverses respiratory depression produced by ethanol and pentobarbital [48]. Therefore, we sought to determine whether CX717 at higher concentrations would exert toxic effects on astrocytes. In order to assess this possibility, we treated astrocytes with 500 μM CX717 for 48 h, after which time we assessed viability using two different assays. The XTT viability assay demonstrated that 500 μM CX717 increased astrocyte viability by 1% (p = 0.88, t-test, Figure 5A). A quantity of 500 μM CX717 did not affect LDH release (p = 0.99, t-test, Figure 5B), suggesting that 500μM CX717 did not induce astrocyte cell death. This result may serve as another differentiating factor for low-impact and high-impact ampakines. This finding also correlates with our prior work demonstrating that, in flash-frozen brains, high doses of CX717 does not markedly affect astrocytes in vivo [42].
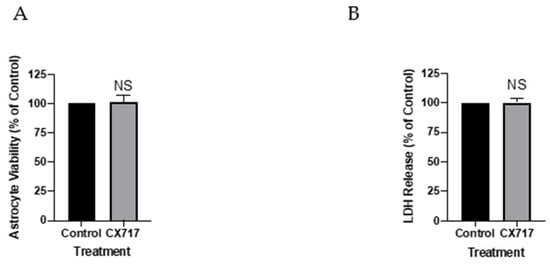
Figure 5.
Effects of CX717 on cortical astrocyte viability. (A) Effects of 500 μM on cortical astrocyte viability using the XTT assay. (B) Effects of 500 μM CX717 on LDH release in astrocytes. Bars represent the mean ± SEM from 3–4 independent experiments. NS, Not significant, Student’s t-test.
In accordance with our prior work [43], we sought to determine whether high-impact ampakines could induce a Gq-protein IP3-dependent ER calcium release in astrocytes. To do this, we pre-treated cultures with 10 µM U73122, which inhibits phospholipase Cβ (PLCβ) from cleaving PIP2 into IP3 and inducing ER calcium release. In the same pathway, we also pre-treated cells with an IP3 receptor blocker—75 µM 2-APB—to inhibit IP3-mediated ER calcium release. In both settings, these drugs completely abolished the ability of CX614 and CX682 to augment AMPA-induced calcium rises (p < 0.01, t-test) (Figure 6), demonstrating a functional ampakine-dependent AMPAR-Gq-protein linkage in astrocytes.
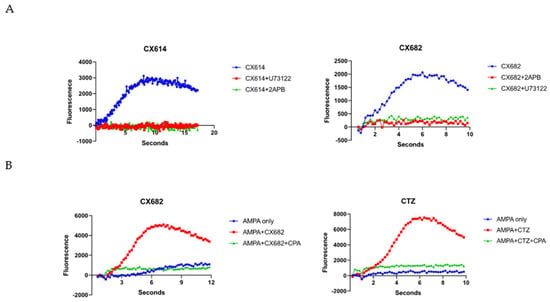
Figure 6.
High-impact ampakine enhancement of calcium elevation is amenable to IP3 receptor antagonism and depletion of ER calcium stores. (A) CX614 and CX682 enhancement is amenable to PLC inhibitor U73122 and IP3 receptor antagonist 2-APB. (B) CX682 and CTZ enhancement is amenable to SERCA ATPase inhibitor CPA. Graphs are representative of at least three independent experiments.
Our subsequent studies sought to further delineate the importance of ER calcium stores in the ampakine-mediated augmentation of AMPA-induced cytosolic calcium rises. We utilized the SERCA ATPase inhibitor cyclopiazonic acid (CPA) (10 µM) to deplete ER calcium stores 30 min prior to AMPA addition. Our data demonstrate that CPA completely ablates the effects of CX682 and CTZ on AMPA-induced calcium elevations (p < 0.01, t-test) (Figure 6). Taken together, these findings in astrocytes suggest that, in the presence of a high-impact ampakine, AMPAR activation induces a Gq-dependent linkage that results in ER calcium liberation (Figure 7), an effect similar to what we have observed in cortical neurons [43].
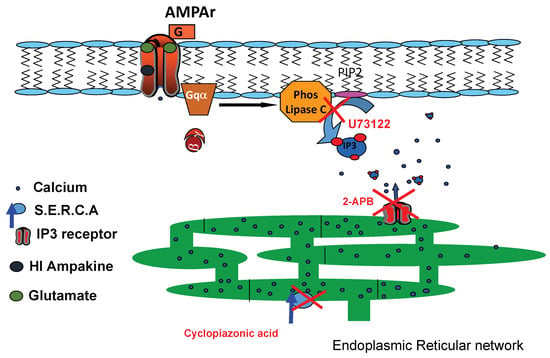
Figure 7.
AMPAR ampakine Gq-protein pathway schematic. In the presence of high-impact ampakines, AMPAR agonist binding initiates Gq-protein activation of PLC to cleave PIP2 into IP3 and DAG. IP3 activates its conjugate receptor on endoplasmic reticulum to liberate ER calcium stores, which governs the majority of ampakine-mediated cytosolic calcium elevations in neurons and astrocytes.
4. Discussion
In the current work, we examined the effects of multiple high- and low-impact ampakines on AMPA-induced calcium elevations in cortical astrocytes. In neurons, high-impact ampakines were shown to augment calcium rises by 150–180% [54], yet, in astrocytes, ampakines augment the AMPA effect by >500% (Figure 2). This may be explained by the fact that AMPA induces a less robust effect alone in astrocytes compared to that seen in cortical neurons [43]. Of note, AMPA induces a slow increase in calcium levels in astrocytes that lasts for up to 5 s (Figure 2), whereas AMPA induces a rapid response in neurons, occurring in <0.5 s. This may be due to astrocytes differentially expressing AMPAR subunits Glur1-4, or to the fact that astrocytes preferentially express different transmembrane AMPAR regulatory proteins (TARPs) [55], which have been shown to profoundly govern AMPAR gating kinetics [56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72]. Prior studies studying high-impact ampakine pharmacology typically utilize one or two high-impact modulators; thus, by including CX682, we attempt to increase the generalizability of the results obtained in these studies.
We expand on our studies by demonstrating the ampakine effect to be AMPAR-dependent, as blocking the enhancement with the AMPAR antagonists NBQX and CNQX (Figure 3) confirms this. In addition, the meaningful modulation by low-impact ampakines was investigated using CX516 and CX717. Very high concentrations of each ampakine were required to observe only modest augmentations of the AMPA effect (Figure 4), demonstrating that the effects of these low-impact ampakines on astrocytes most likely do not explain their therapeutic effects in vivo [21,24,25,26,33,34,47,48,53,73,74,75,76,77]. Furthermore, we identify that concentrations of CX717 well above what is needed to offset respiratory depression by CNS depressants [47,53,78] is not toxic to cortical astrocytes. These findings further highlight the safe nature of low-impact ampakines and suggest that the marked offset of desensitization is not necessary to observe the therapeutic benefits of AMPAR modulation. Furthermore, these findings highlight that the beneficial effects of ampakines can indeed be separated from their neurotoxic effects. The lack of astrocyte toxicity is in stark contrast to the rapid onset of astrocyte toxicity by CTZ in prior studies, at concentrations that are required to modulate AMPARs [45]. The findings of this study also provide further evidence that low-impact ampakines may be exerting their therapeutic effects by modestly amplifying AMPAR activity over serial circuits, such as the respiratory neuraxis, when reversing opiate-induced respiratory depression [26].
We also assessed whether the ampakine-dependent AMPAR-Gq-protein phenomenon we observed in cortical neurons could explain the effects seen in astrocytes. Blockage of PLCβ, which prevents PIP2 conversion to DAG and IP3, and IP3 antagonism abolished the ampakine effect in this assay. Furthermore, depleting ER calcium stores with SERCA ATPase inhibitor CPA ablated CX682′s enhancement effects (Figure 6 and Figure 7). These data demonstrate that the large majority of the calcium entering the cytosol is from the ER. Additionally, the fact that low-impact ampakines such as CX717 and CX516 do not affect cytosolic calcium levels below 1 mM suggests that at lower and more therapeutically relevant concentrations, they may be principally augmenting sodium influx through the AMPAR, as opposed to high-impact ampakines, which affect cytosolic sodium and calcium levels. In fact, whether low-impact ampakines specifically modulate astrocyte AMPARs to a significant extent at therapeutically relevant concentrations remains to be determined.
Our prior work demonstrated that AMPARs, historically considered to be ionotropic glutamate receptors, possess an ampakine-dependent Gq-protein linkage in cortical neurons [43]. The current study demonstrates that this ampakine-dependent linkage (Figure 7) is not limited to one cell type in the mammalian brain, but is prevalent in at least multiple cell types. Astrocytes are now being appreciated for their active role in synaptic transmission and memory encoding [3,4,5], so the fact that ampakines exert a possibly larger effect in these cells than in neurons needs to be considered and further researched for their association with their beneficial effects in multiple neurodegenerative disease models.
Our data coincide with multiple prior reports indicating that AMPAR modulation engenders multiple cellular downstream effects beyond simply augmenting sodium and calcium influx through activated AMPARs. In oligodendrocyte precursor cells, AMPAR activation with agonist alone stimulates IP3 formation [79]. Liu et al. also show that this agonist-alone effect plateaus, but also that treatment with AMPA+CTZ synergistically augments IP3 formation to a level not observed with saturating concentrations of AMPA alone [79]; these findings suggest a possible metabotropic effect unmasked by AMPAR-positive allosteric modulation. In astrocytes, Smith et al. demonstrated that the AMPA+CTZ effect is blocked by the PLC inhibitor U73122, and that AMPA in the presence of CTZ causes a depletion of ER calcium stores [7]. Other reports have indicated that AMPARs couple to G-proteins and exert metabotropic effects in addition to their well characterized ionotropic effects [80,81,82]. Collectively, these findings illustrate the need for future studies to provide additional details as to the separate and interacting roles of neuronal and astrocyte AMPARs, as well as the ionotropic vs. metabotropic influences of ampakines on their therapeutically-beneficial pharmacological actions in CNS disorders.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.P.R., R.C., J.W. and A.L. Methodology, D.P.R. and A.L. Software, D.P.R., Validation, D.P.R. and A.L. Formal analysis D.P.R., Investigation D.P.R., R.C., J.W. and A.L. Resources A.L. Data curation, D.P.R. and A.L. Writing—original draft preparation, D.P.R., R.C., J.W. and A.L. Writing—review and editing, D.P.R., R.C., J.W. and A.L. Visualization, D.P.R., R.C., J.W. and A.L. Supervision, R.C., J.W. and A.L. Project administration, J.W. and A.L. Funding acquisition, A.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding was provided by RespireRx Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by UC Irvine IACUC (protocol #61-05-05B, first approved May 2005).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request made to the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
With respect to the manuscript, Daniel Radin, Arnold Lippa, Jeffrey Witkin, and Rok Cerne all are associated with RespireRx, where A.L. is acting CEO, and D.P.R., R.C. and J.M.W. are non-paid researchers who occasionally conduct studies on these compounds. The company had no role in this study’s design, data gathering, interpretation of the results, and writing of the manuscript. All authors of this study consented to publication.
References
- Brandebura, A.N.; Paumier, A.; Onur, T.S.; Allen, N.J. Astrocyte contribution to dysfunction, risk and progression in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2023, 24, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Profaci, C.P.; Munji, R.N.; Pulido, R.S.; Daneman, R. The blood-brain barrier in health and disease: Important unanswered questions. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopherson, K.S.; Ullian, E.M.; Stokes, C.C.; Mullowney, C.E.; Hell, J.W.; Agah, A.; Lawler, J.; Mosher, D.F.; Bornstein, P.; Barres, B.A. Thrombospondins are astrocyte-secreted proteins that promote CNS synaptogenesis. Cell 2005, 120, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.J.; Bennett, M.L.; Foo, L.C.; Wang, G.X.; Chakraborty, C.; Smith, S.J.; Barres, B.A. Astrocyte glypicans 4 and 6 promote formation of excitatory synapses via GluA1 AMPA receptors. Nature 2012, 486, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Suarez, E.; Liu, T.F.; Kopelevich, A.; Allen, N.J. Astrocyte-Secreted Chordin-like 1 Drives Synapse Maturation and Limits Plasticity by Increasing Synaptic GluA2 AMPA Receptors. Neuron 2018, 100, 1116–1132 e1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Zheng, J.C. Astrocytes: GABAceptive and GABAergic Cells in the Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 892497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.P.; Cunningham, L.A.; Partridge, L.D. Coupling of AMPA receptors with the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in cultured rat astrocytes. Brain Res. 2000, 887, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, L.; Magistretti, P.J. Ampakine CX546 bolsters energetic response of astrocytes: A novel target for cognitive-enhancing drugs acting as alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor modulators. J. Neurochem. 2005, 92, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpura, V.; Scemes, E.; Spray, D.C. Mechanisms of glutamate release from astrocytes: Gap junction “hemichannels”, purinergic receptors and exocytotic release. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Peng, H.; Kang, N.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, J.H.; Stanton, P.K.; Kang, J. Glutamate-induced exocytosis of glutamate from astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24185–24197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collingridge, G.L.; Singer, W. Excitatory amino acid receptors and synaptic plasticity. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1990, 11, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisden, W.; Seeburg, P.H. Mammalian ionotropic glutamate receptors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1993, 3, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, A.C.; Kessler, M. Pharmacology of ampakine modulators: From AMPA receptors to synapses and behavior. Curr. Drug Targets 2007, 8, 583–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, A.C.; Xia, Y.F.; Suzuki, E. Modulation of AMPA receptor kinetics differentially influences synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. Neuroscience 2004, 123, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, G.; Gall, C.M. Ampakines and the threefold path to cognitive enhancement. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.J.; Dix, S. AMPA receptor potentiators as cognitive enhancers. IDrugs Investig. Drugs J. 2007, 10, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, G.; Palmer, L.C.; Gall, C.M. The likelihood of cognitive enhancement. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 99, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, D.P.; Zhong, S.; Purcell, R.; Lippa, A. Acute ampakine treatment ameliorates age-related deficits in long-term potentiation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonomovic, M.D.; Mizukami, K.; Davies, P.; Hamilton, R.; Sheffield, R.; Armstrong, D.M. The loss of GluR2(3) immunoreactivity precedes neurofibrillary tangle formation in the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus of Alzheimer brains. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 56, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirson, G.; Desjardins, P.; Tannenberg, T.; Dodd, P.; Butterworth, R.F. Selective loss of expression of glutamate GluR2/R3 receptor subunits in cerebellar tissue from a patient with olivopontocerebellar atrophy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2002, 17, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porrino, L.J.; Daunais, J.B.; Rogers, G.A.; Hampson, R.E.; Deadwyler, S.A. Facilitation of task performance and removal of the effects of sleep deprivation by an ampakine (CX717) in nonhuman primates. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.; Vissel, B. The essential role of AMPA receptor GluR2 subunit RNA editing in the normal and diseased brain. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Han, H.; Li, H.; Bai, Y.; Wang, W.; Tu, M.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, L.; He, W.; Wu, X.; et al. Long-term potentiation decay and memory loss are mediated by AMPAR endocytosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, R.E.; Rogers, G.; Lynch, G.; Deadwyler, S.A. Facilitative effects of the ampakine CX516 on short-term memory in rats: Correlations with hippocampal neuronal activity. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 2748–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, R.E.; Rogers, G.; Lynch, G.; Deadwyler, S.A. Facilitative effects of the ampakine CX516 on short-term memory in rats: Enhancement of delayed-nonmatch-to-sample performance. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, D.P.; Zhong, S.; Cerne, R.; Shoaib, M.; Witkin, J.M.; Lippa, A. Low-Impact Ampakine CX1739 Exerts Pro-Cognitive Effects and Reverses Opiate-Induced Respiratory Depression in Rodents. Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingvar, M.; Ambros-Ingerson, J.; Davis, M.; Granger, R.; Kessler, M.; Rogers, G.A.; Schehr, R.S.; Lynch, G. Enhancement by an ampakine of memory encoding in humans. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 146, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogier, M.; Wang, H.; Hong, E.; Wang, Q.; Greenberg, M.E.; Katz, D.M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and respiratory function improve after ampakine treatment in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10912–10917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.A.; Rex, C.S.; Palmer, L.; Pandyarajan, V.; Fedulov, V.; Gall, C.M.; Lynch, G. Up-regulating BDNF with an ampakine rescues synaptic plasticity and memory in Huntington’s disease knockin mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4906–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdi, H.; Hamo, L.; Oka, T.; Seegan, A.; Baudry, M. BDNF mediates the neuroprotective effects of positive AMPA receptor modulators against MPP+-induced toxicity in cultured hippocampal and mesencephalic slices. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.A.; Mehta, R.A.; Lauterborn, J.C.; Gall, C.M.; Lynch, G. Brief ampakine treatments slow the progression of Huntington’s disease phenotypes in R6/2 mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 41, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Hao, J.X.; Seiger, A.; Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z. Systemic excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists of the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor and of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor relieve mechanical hypersensitivity after transient spinal cord ischemia in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993, 267, 140–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wollman, L.B.; Streeter, K.A.; Fusco, A.F.; Gonzalez-Rothi, E.J.; Sandhu, M.S.; Greer, J.J.; Fuller, D.D. Ampakines stimulate phrenic motor output after cervical spinal cord injury. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 334, 113465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.; Sunshine, M.D.; Greer, J.J.; Fuller, D.D. Ampakines Stimulate Diaphragm Activity after Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2021, 38, 3467–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkin, J.M.; Radin, D.P.; Rana, S.; Fuller, D.D.; Fusco, A.F.; Demers, J.C.; Pradeep Thakre, P.; Smith, J.L.; Lippa, A.; Cerne, R. AMPA receptors play an important role in the biological consequences of spinal cord injury: Implications for AMPA receptor modulators for therapeutic benefit. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 116302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.; Alom, F.; Martinez, R.C.; Fuller, D.D.; Mickle, A.D. Acute ampakines increase voiding function and coordination in a rat model of SCI. Elife 2024, 12, RP89767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.; Thakre, P.P.; Fuller, D.D. Ampakines increase diaphragm activation following mid-cervical contusion injury in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 376, 114769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, A.C.; Xia, Y.F.; Rogers, G.; Lynch, G.; Kessler, M. Benzamide-type AMPA receptor modulators form two subfamilies with distinct modes of action. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, A.C.; Kessler, M.; Rogers, G.; Lynch, G. Effects of the potent ampakine CX614 on hippocampal and recombinant AMPA receptors: Interactions with cyclothiazide and GYKI 52466. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, M.; Arai, A.C. Use of [3H]fluorowillardiine to study properties of AMPA receptor allosteric modulators. Brain Res. 2006, 1076, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, K.E.; Kessler, M.; Arai, A.C. Modulation of agonist binding to AMPA receptors by 1-(1,4-benzodioxan-6-ylcarbonyl)piperidine (CX546): Differential effects across brain regions and GluA1-4/transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein combinations. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 331, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, R.; Lynch, G.; Gall, C.; Johnson, S.; Sheng, Z.; Stephen, M.R.; Cook, J.; Garman, R.H.; Jortner, B.; Bolon, B.; et al. Brain Vacuolation Resulting From Administration of the Type II Ampakine CX717 Is An Artifact Related to Molecular Structure and Chemical Reaction With Tissue Fixative Agents. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 162, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, D.P.; Zhong, S.; Cerne, R.; Witkin, J.; Lippa, A. High impact AMPAkines induce a Gq-protein coupled endoplasmic calcium release in cortical neurons: A possible mechanism for explaining the toxicity of high impact AMPAkines. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildge, S.; Bohrer, C.; Beck, K.; Schachtrup, C. Isolation and culture of mouse cortical astrocytes. J. Vis. Exp. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.C.; Yamada, K.A.; Bagwe, M.R.; Goldberg, M.P. AMPA receptor activation is rapidly toxic to cortical astrocytes when desensitization is blocked. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertel, B.G.; Felden, L.; Tran, P.V.; Bradshaw, M.H.; Angst, M.S.; Schmidt, H.; Johnson, S.; Greer, J.J.; Geisslinger, G.; Varney, M.A.; et al. Selective antagonism of opioid-induced ventilatory depression by an ampakine molecule in humans without loss of opioid analgesia. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 87, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Ding, X.; Funk, G.D.; Greer, J.J. Ampakine CX717 protects against fentanyl-induced respiratory depression and lethal apnea in rats. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Ding, X.; Greer, J.J. Respiratory depression in rats induced by alcohol and barbiturate and rescue by ampakine CX717. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 113, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partin, K.M.; Fleck, M.W.; Mayer, M.L. AMPA receptor flip/flop mutants affecting deactivation, desensitization, and modulation by cyclothiazide, aniracetam, and thiocyanate. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, M.W.; Bahring, R.; Patneau, D.K.; Mayer, M.L. AMPA receptor heterogeneity in rat hippocampal neurons revealed by differential sensitivity to cyclothiazide. J. Neurophysiol. 1996, 75, 2322–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammes, G.; Swandulla, D.; Spielmanns, P.; Parsons, C.G. Interactions of GYKI 52466 and NBQX with cyclothiazide at AMPA receptors: Experiments with outside-out patches and EPSCs in hippocampal neurones. Neuropharmacology 1998, 37, 1299–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauterborn, J.C.; Lynch, G.; Vanderklish, P.; Arai, A.; Gall, C.M. Positive modulation of AMPA receptors increases neurotrophin expression by hippocampal and cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Lenal, F.; Yang, M.; Ding, X.; Greer, J.J. Coadministration of the AMPAKINE CX717 with propofol reduces respiratory depression and fatal apneas. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasaka, T.; Balasas, T.; Russell, L.J.; Sugimoto, K.J.; Majid, A.; Walewska, R.; Karran, E.L.; Brown, D.G.; Cain, K.; Harder, L.; et al. Five members of the CEBP transcription factor family are targeted by recurrent IGH translocations in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL). Blood 2007, 109, 3451–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molders, A.; Koch, A.; Menke, R.; Klocker, N. Heterogeneity of the astrocytic AMPA-receptor transcriptome. Glia 2018, 66, 2604–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priel, A.; Kolleker, A.; Ayalon, G.; Gillor, M.; Osten, P.; Stern-Bach, Y. Stargazin reduces desensitization and slows deactivation of the AMPA-type glutamate receptors. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouach, N.; Byrd, K.; Petralia, R.S.; Elias, G.M.; Adesnik, H.; Tomita, S.; Karimzadegan, S.; Kealey, C.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. TARP gamma-8 controls hippocampal AMPA receptor number, distribution and synaptic plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Cheng, Y.; Sheng, M.; Walz, T. Three-dimensional structure of an AMPA receptor without associated stargazin/TARP proteins. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, S.; Byrd, R.K.; Rouach, N.; Bellone, C.; Venegas, A.; O’Brien, J.L.; Kim, K.S.; Olsen, O.; Nicoll, R.A.; Bredt, D.S. AMPA receptors and stargazin-like transmembrane AMPA receptor-regulatory proteins mediate hippocampal kainate neurotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18784–18788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; St-Gelais, F.; Zhang, W.; Tomita, S.; Howe, J.R. Two families of TARP isoforms that have distinct effects on the kinetic properties of AMPA receptors and synaptic currents. Neuron 2007, 55, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.S.; Zhou, W.; Milstein, A.D.; Knierman, M.D.; Siuda, E.R.; Dotzlaf, J.E.; Yu, H.; Hale, J.E.; Nisenbaum, E.S.; Nicoll, R.A.; et al. New transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory protein isoform, gamma-7, differentially regulates AMPA receptors. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 4969–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milstein, A.D.; Zhou, W.; Karimzadegan, S.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. TARP subtypes differentially and dose-dependently control synaptic AMPA receptor gating. Neuron 2007, 55, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milstein, A.D.; Nicoll, R.A. Regulation of AMPA receptor gating and pharmacology by TARP auxiliary subunits. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, H.L. The role of transmembrane AMPA receptor regulatory proteins (TARPs) in neurotransmission and receptor trafficking (Review). Mol. Membr. Biol. 2008, 25, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menuz, K.; O’Brien, J.L.; Karmizadegan, S.; Bredt, D.S.; Nicoll, R.A. TARP redundancy is critical for maintaining AMPA receptor function. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 8740–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, E.; Kessler, M.; Arai, A.C. The fast kinetics of AMPA GluR3 receptors is selectively modulated by the TARPs gamma 4 and gamma 8. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 38, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto-Tomita, M.; Zhang, W.; Straub, C.; Cho, C.H.; Kim, K.S.; Howe, J.R.; Tomita, S. Autoinactivation of neuronal AMPA receptors via glutamate-regulated TARP interaction. Neuron 2009, 61, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, D.; Coombs, I.D.; Renzi, M.; Zonouzi, M.; Farrant, M.; Cull-Candy, S.G. Selective regulation of long-form calcium-permeable AMPA receptors by an atypical TARP, gamma-5. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Lu, W.; Milstein, A.D.; Nicoll, R.A. The stoichiometry of AMPA receptors and TARPs varies by neuronal cell type. Neuron 2009, 62, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menuz, K.; Kerchner, G.A.; O’Brien, J.L.; Nicoll, R.A. Critical role for TARPs in early development despite broad functional redundancy. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.S.; Gill, M.B.; Ho, M.T.; Yu, H.; Tu, Y.; Siuda, E.R.; Wang, H.; Qian, Y.W.; Nisenbaum, E.S.; Tomita, S.; et al. Hippocampal AMPA receptor gating controlled by both TARP and cornichon proteins. Neuron 2010, 68, 1082–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.C.; Nicoll, R.A. Stargazin (TARP gamma-2) is required for compartment-specific AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity in cerebellar stellate cells. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 3939–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, J.; Stanley, N.; James, L.M.; Wright, N.; Johnsen, S.; Arbon, E.L.; Dijk, D.J. Acute sleep deprivation: The effects of the AMPAKINE compound CX717 on human cognitive performance, alertness and recovery sleep. J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haw, A.J.; Meyer, L.C.; Greer, J.J.; Fuller, A. Ampakine CX1942 attenuates opioid-induced respiratory depression and corrects the hypoxaemic effects of etorphine in immobilized goats (Capra hircus). Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2016, 43, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radin, D.P.; Johnson, S.; Purcell, R.; Lippa, A.S. Effects of chronic systemic low-impact ampakine treatment on neurotrophin expression in rat brain. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollman, L.B.; Streeter, K.A.; Fuller, D.D. Ampakine pretreatment enables a single brief hypoxic episode to evoke phrenic motor facilitation. J. Neurophysiol. 2020, 123, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakre, P.P.; Sunshine, M.D.; Fuller, D.D. Ampakine pretreatment enables a single hypoxic episode to produce phrenic motor facilitation with no added benefit of additional episodes. J. Neurophysiol. 2021, 126, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorier, A.R.; Funk, G.D.; Greer, J.J. Opiate-induced suppression of rat hypoglossal motoneuron activity and its reversal by ampakine therapy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.N.; Molina-Holgado, E.; Almazan, G. Glutamate-stimulated production of inositol phosphates is mediated by Ca2+ influx in oligodendrocyte progenitors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 338, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Small, D.L.; Stanimirovic, D.B.; Morley, P.; Durkin, J.P. AMPA receptor-mediated regulation of a Gi-protein in cortical neurons. Nature 1997, 389, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, F.; Sterling, P. AMPA receptor activates a G-protein that suppresses a cGMP-gated current. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 2954–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, P.; Fagni, L.; Torrens, Y.; Alcaraz, G.; Couraud, F.; Bockaert, J.; Glowinski, J.; Premont, J. AMPA receptor activation induces association of G-beta protein with the alpha subunit of the sodium channel in neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 14, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).