Abstract
Plant-based seafood analogs are gaining increasing popularity as replacements for traditional fish and other seafood products due to environmental (stock depletion, pollution, and bycatch issues) and health (bioaccumulated toxins, norovirus, and allergies) concerns associated with them. Several companies have launched plant-based fish products, but the market still lacks alternatives to shellfish and other sea delicacies. In this study, a plant-based sea foie gras (monkfish liver product) analog was developed using duckweed RuBisCO protein and omega-3-rich flaxseed oil to form emulsion gels. These gels consisted of a high concentration of flaxseed oil droplets dispersed within a gelled RuBisCO protein network. It was hypothesized that the high disperse phase volume fraction of the oil droplets and the heat-set gelation properties of the RuBisCO proteins would enable us to create emulsion gels that mimicked the properties of sea foie gras. A natural pigment (β-carotene) was incorporated into the oil phase of the emulsions to mimic the red-orange color of conventional sea foie gras. The structural, textural, and optical properties of real and plant-based sea foie gras analogs were characterized using scanning electron microscopy, confocal microscopy, dynamic shear rheology, texture profile analysis, and colorimetry. Emulsion gels prepared using 40% flaxseed oil and 10% RuBisCO proteins produced plant-based products that closely simulated the texture and color of the real products. Rheological analysis suggested that the oil droplets acted as active fillers within the protein gels. Our results suggest that emulsion gels may be used to create more sustainable and healthier plant-based seafood products.
1. Introduction
The food production practices currently employed by the food and agricultural industry are believed to be promoting climate change and environmental degradation, as well as diet-related health problems [1,2]. Many of the problems have been linked with the utilization of the products of terrestrial animals, such as the meat, milk, and eggs obtained from cows, pigs, and poultry. However, the utilization of marine animals as a source of foods, such as fish and shellfish, has also been linked to environmental and health issues [3,4]. Overfishing and climate change are depleting existing fish stocks [5]. Indeed, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations has reported that 90% of the species caught through wild fisheries are either overfished or fished at their maximal capacity [6]. Furthermore, bottom trawling for fish is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions [7]. There are also some health concerns linked to the consumption of certain kinds of fish and shellfish. Many seafood products are polluted with high levels of mercury and other toxic heavy metals [8,9]. Moreover, many seafood products promote allergies in a significant fraction of the population [10,11].
As a potential solution to these issues, the food industry is attempting to develop sustainable and healthy plant-based alternatives to meat and seafood products [12,13,14]. These products are usually assembled from sustainable plant-derived ingredients, such as proteins, polysaccharides, phospholipids, and phytochemicals (such as pigments and preservatives). The composition, structure, and properties of these plant-based products are carefully designed to mimic the desirable quality attributes and nutritional profiles of the animal or seafood products they are designed to replace.
Considerable research has been carried out to simulate the properties of the muscle and adipose tissues of terrestrial animals, such as those in chicken, pork, or beef [15,16]. In this study, we focused on creating a plant-based seafood analog designed to mimic the sensory and nutritional profile of a fatty seafood product, sea foie gras. This product has a semi-solid texture and a bright oily orange appearance (Figure 1). It is considered to be a delicacy in many Asian countries and is created from the liver of the monkfish (Lophius litulon). Monkfish liver is rich in polyunsaturated fats (PUFAs), such as eicosatetraenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), gadoleic acid, and oleic acid, which have been reported to exhibit multiple health benefits when consumed at sufficiently high levels as part of the human diet [17]. Moreover, monkfish liver contains several bioactive peptides that are reported to exhibit antioxidant activity and various health benefits [18]. Compositionally, sea foie gras contains about 40% fat and 10% protein [19]. Structurally, the fat is dispersed as large adipose cells throughout a gelled protein network. We hypothesized that plant-based sea foie gras analogs could be produced by mimicking the composition and structure of the real products.
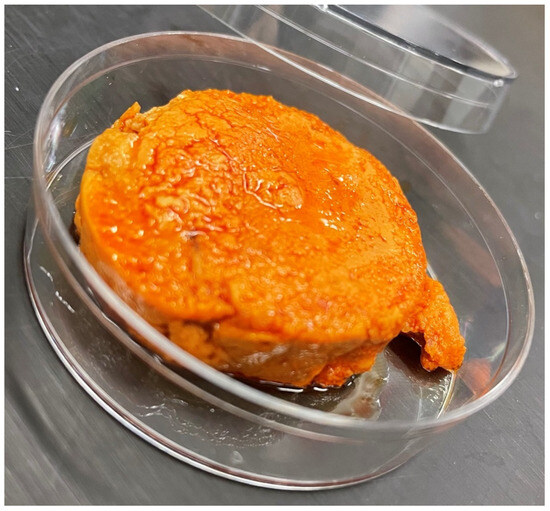

Figure 1.
Photograph of a commercial sea foie gras product.
For this reason, concentrated oil-in-water gelled emulsions were used as a template to formulate the sea foie gras analogs. This type of emulsion gel can be produced by creating a protein-stabilized oil-in-water emulsion with excess protein in the aqueous phase and then promoting aggregation of the protein molecules [20,21]. In this study, the plant-based product contained 40% flaxseed oil droplets and 10% plant proteins to simulate the omega-3-rich fat cells and protein matrix in real sea foie gras [19]. RuBisCO protein extracted from duckweed was selected as a model plant-derived protein because of its good solubility, emulsifying, and gelling properties [22,23,24]. Flaxseed oil was selected as a model plant-derived oil because it contains high levels of omega-3 fatty acids (alpha-linolenic acid, C18:3), as well as omega-6 fatty acids (linoleic acid, C18:2) [25]. However, alpha-linolenic acid is reported to have fewer beneficial physiological effects than the EPA and DHA found in seafood [26]. Emulsion gels were prepared using a series of processing steps. First, fluid O/W emulsions were prepared by homogenizing flaxseed oil and an aqueous solution containing RuBisCo protein together using a high shear mixer or microfluidizer. Second, these emulsions were gelled by heating them above the thermal denaturation temperature of the proteins. Finally, a natural pigment (β-carotene) was incorporated into the gels to imitate the orange-red pigmentation of real sea foie gras (Figure 1). The physicochemical properties of the emulsion gels formed using this process were then compared to those of real sea foie gras, including their optical, textural, and structural properties.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
A RuBisCO protein isolate (P060121) extracted from duckweed was kindly supplied by Plantible Foods (San Diego, CA, USA). The flaxseed oil (Virgin Flaxseed Oil, International Collection, Brighton, UK) was purchased from a local grocery store. The flaxseed oil bottle was immediately wrapped with aluminum foil to avoid any light penetration and stored at room temperature inside a dark cabinet. β-carotene (Type 1, synthetic, powder, C9750-10G) was supplied by the Sigma Aldrich Company (St. Louis, MO, USA). The sea foie gras (Prepared Ankimo, Cooked Monkfish Live, frozen, 5 oz per piece, 4 pieces per pack) was purchased from Intershell Seafood (Gloucester, MA, USA). HNa2O4P, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and hydrochloric acid (HCl) were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). A 10 mM, pH 7.0 phosphate buffer solution (PBS) was prepared by dissolving 2.84 g sodium phosphate dibasic (HNa2O4P) in 2000 mL of deionized water and adjusting the pH to 7.0.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Emulsion Preparation
Coarse oil-in-water emulsions were prepared by blending an aqueous protein solution (1% w/v RuBisCO protein, 10 mM pH 7.0 PBS) and flaxseed oil using a high-shear mixer for 2 min. Prior to use, the protein solution was hydrated overnight in a refrigerator (4 °C) with continuous stirring at 300 rpm to fully dissolve the proteins. The emulsions were prepared using flaxseed oil concentrations of 10%, 20%, and 40% w/w to examine the impact of oil content on their formation and properties. After formation, the coarse emulsions were passed through a microfluidizer (Microfluidics, Newton, MA, USA) at 12,000 psi for 8 passes to obtain fine emulsions. The prepared emulsions were stored in a refrigerator (4 °C) immediately after preparation and then used within a day of preparation.
2.2.2. Emulsion Gel Preparation
The emulsion gels were prepared by heating fluid oil-in-water emulsions containing excess protein in the aqueous phase above the thermal denaturation temperature of the proteins. Initially, additional RuBisCO protein was added to the fluid emulsions containing 1% RuBisCO protein and 40% flaxseed oil to reach a final concentration of 10% w/v, and then, the resulting mixtures were stirred overnight to dissolve the proteins (300 rpm, 4 °C). Then, 5 mL of the resulting emulsions were transferred to 10 mL beakers, which were then heated in a water bath set at either 60 or 70 °C for either 30 or 60 min. These temperatures were selected based on the reported heat-gelling properties of RuBisCO protein [22]. The resulting heat-induced emulsion gels were then immediately cooled in an ice bath to stop further heat-denaturation and stored at 4 °C until analyzed.
In addition to the heating parameters, the effects of droplet size and colorant addition on emulsion gel formation were investigated. The effect of droplet size was examined by preparing coarse (blending) and fine (blending and microfluidization) emulsions containing 10% RuBisCO protein and 40% flaxseed oil and then heating them at 60 °C for 30 min. The effect of colorant addition was examined by adding a natural pigment (0.2% w/w β-carotene in flaxseed oil) to the emulsion gels containing 10% RuBisCO protein and 40% flaxseed oil at different stages during the preparation to establish the most suitable method of including the pigment:
- Method 1 (fine emulsion + free oil): An oil-in-water emulsion containing 10% RuBisCO protein and 20% flaxseed oil fine emulsion was prepared, and then, colored flaxseed oil was added just before heating to achieve a final flaxseed oil content of 40% w/w.
- Method 2 (coarse emulsion): An oil-in-water emulsion containing 40% w/w colored flaxseed oil and 10% RuBisCO solution was prepared by blending for 2 min using a high-shear mixer.
All the colored emulsions were heat-gelled at 60 °C for 30 min by placing the contains holding them within a temperature-controlled water bath and then immediately cooled in an ice bath prior to being stored at 4 °C. All the samples were prepared in triplicate.
2.2.3. Emulsion Droplet Characterization
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) was used to characterize the mean droplet diameter, polydispersity index (PDI), and droplet size distribution of the fine emulsions. After storing the emulsions in a refrigerator (4 °C) overnight, the samples were analyzed using a commercial DLS instrument (Zetasizer Pro, Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK). The average diameter of the droplets in the coarse emulsions was estimated from the confocal microscopy images (see next section) by counting the number of droplets in different particle size categories. The electrical characteristics of the emulsion droplets (ζ-potential) were determined using the electrophoresis component of the same instrument (Zetasizer Pro, Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK) according to a method described previously [27]. The mean droplet diameter, polydispersity index, and ζ-potential of each sample were measured twice, and the average values were calculated.
2.2.4. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
The microstructure of the fluid and gelled emulsions was monitored using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) with fluorescent staining. For fluid emulsions, the oil phase was stained by adding 20 μL of Nile Red (1 mg/mL in ethanol) to 400 μL of an emulsion-PBS (10 mM, pH 7.0) mixture (1:1 v/v) prior to analysis. For emulsion gels and sea foie gras, the samples were frozen (−20 °C) overnight and then the frozen samples were cut into thin slices (18 μm) using a cryostat operating at −20 °C (Jung CM1800, Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany). A glass slide (IHC, FLEX, Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) was then immediately pressed on to the sample to adhere it. The samples on the slides were then air-dried, followed by a staining step using an auto-stainer XL platform (ST5010, Leica Biosystems, Nußloch, Germany). The progressive Haematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) method was used to prepare the samples for observation. This involved water rinsing, dehydrating with 100% alcohol, clearing in xylene, and permanently sealing with DPX (a mixture of distyrene, plasticizer, and xylene) before covering with a coverslip (CV5030, Leica Biosystems, Germany) [28].
The prepared sample slides were viewed using a CLSM instrument (Nikon d-Eclipse C1 80i, Nikon, Melville, NY, USA) with a 40× objective lens and 10× eyepiece lens. The sample slides were prepared in duplicate for emulsion fluids, emulsion gels, and sea foie gras. Information about the average diameter of the oil droplets in the coarse emulsions was obtained from the confocal microscopy images by counting the number of droplets in different size categories (<5, 5–10, 10–25, and 25–50 μm) using a total of 362 droplets from 3 photographic images.
2.2.5. Dynamic Shear Rheology Analysis
The rheological properties of fluid emulsions, emulsion gels, and sea foie gras were characterized using a dynamic shear rheometer (Kinexus, Malvern, Worcestershire, UK) with a plate/plate geometry using a gap size of 1.0 mm. The complex shear modulus (G*) and phase angle (δ) were measured as a function of temperature using a heating–cooling cycle. In some studies, the complex shear modulus was represented as the storage (G′) and loss (G″) modulus. The temperature was increased from 25 to 90 °C at a rate of 5 °C min−1; then, samples were held at 90 °C for 30 min, and then, they were cooled back to 25 °C at the same rate. A frequency of 1 Hz and strain of 0.01% was used in these measurements. The temperature of the system was controlled by an environmental controller and passive heat exchanger. The rheological properties of the samples were also characterized by carrying out strain (0–100%) and frequency (0–100 Hz) sweeps at 25 °C. For the strain sweep measurements, a constant frequency of 1 Hz was used, whereas for the frequency sweep measurements, a constant strain of 0.01% was used. The storage modulus of each sample was calculated by fitting the experimental frequency sweep data to a power law model and analyzing with Bohlin’s equation (Equation (1)) [29]:
Equation (1). Power Law Model (1a) and Bohlin’s Equation (1b)
Here, G′ is the storage modulus (Pa), ω is the frequency (rad/s), and A (Pa) and z are Bohlin’s parameters.
2.2.6. Texture Profile Analysis
The emulsion gels and sea foie gras samples were prepared in uniform cylindrical pieces with a diameter of 2 cm and a height of 1 cm. The textural attributes of the samples were then determined using a texture analyzer (TA.XT2, Stable Micro System, Surrey, UK) with a flat-ended cylinder probe (25 mm diameter). A double-compression test (strain height = 50%) was performed on all samples to obtain force–time curves. The instrument software then calculated the texture profile analysis (TPA) parameters of the samples from these curves, including hardness, cohesion, springiness, and chewiness. The principles behind the calculation of the TPA parameters were described in detail elsewhere [30]. These measurements were performed in triplicate for each sample type.
2.2.7. Color Analysis
The color coordinates of the various samples were quantified using a colorimeter (ColorFlez EZ, HunterLab, Reston, VA, USA). The CIE L*, a*, b* values were measured in triplicate for each sample, and the average was calculated. The L*, a*, and b* values are representative of lightness, redness/greenness, and blueness/yellowness, respectively.
2.2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy
The cylindrical emulsion gels and sea foie gras were prepared, frozen at −20 °C, and then, thin slices were cut from their surfaces. These samples were then dehydrated in a freeze-dryer (Genesis Pilot Lyophilizer, SP Scientific, Stone Ridge, NY, USA) for 5 days and then sputter-coated with gold. The samples were then visualized using a scanning electron microscope (FEI Magellan 400, FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA), operated at an accelerating voltage of 5 kV under low vacuum conditions.
2.2.9. Statistical Analysis
The emulsion gel and sea foie gras samples were prepared in triplicate, and all the quantitative data obtained (TPA and L*a*b* values) were reported as averages and standard deviations. Statistically significant differences between the emulsion gel and sea foie gras samples were determined by conducting a one-way ANOVA (p < 0.05) across one parameter and using a Fisher’s LSD test for difference within one parameter.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Emulsions
Fluid flaxseed oil-in-water emulsions were prepared, and then, their droplet characteristics were measured. These emulsions contained 10, 20, or 40% w/w flaxseed oil and 1% w/v RuBisCO protein. The highest flaxseed oil concentration was based on the fact that monkfish liver contains around 40% fat [19]. The mean particle diameters, polydispersity indices, and particle size distributions of the emulsions were measured and reported (Table 1, Figure 2). The mean droplet diameter of the emulsions increased appreciably when the oil content was increased from 20 to 40% w/w. This effect can be attributed to the fact that the protein-to-oil ratio decreased as the oil content increased, so there was less protein available to adsorb to the oil droplet surfaces and prevent droplet coalescence during homogenization [31,32]. As expected, the oil droplets in the 40% oil-in-water emulsions prepared using high shear mixing were much larger than those in the emulsions prepared using microfluidization, as seen in the light scattering data (Table 1) and confocal microscopy images (Figure 2C,E). This effect can be attributed to the fact that microfluidization generates much stronger disruptive forces than high shear mixing [31]. The size of the oil droplets in the confocal microscopy images of the coarse emulsions were much larger than those determined using dynamic light scattering. This is probably because the oil droplets in the coarse emulsions were too large to detect using this kind of particle sizing technology, which relies on the movement of particles due to Brownian motion. For this reason, the mean droplet diameter was also calculated by measuring the droplet dimensions in the confocal microscopy images. Interestingly, when the 40% fine emulsion was heated at 80 °C for 30 min, there was not much change in the mean particle diameter or microscopy images, which suggests that they were resistant to heat-induced droplet aggregation.

Table 1.
Impact of fat content, heating, and microfluidization on mean particle diameter (nm), polydispersity index, and ζ-potential (mV) of flaxseed oil-in-water emulsions containing 1% RuBisCO protein. All measurements were acquired using dynamic light scattering/zeta-potential analysis, except the mean diameter of the coarse emulsions, which was obtained from analysis of the confocal microscopy images.
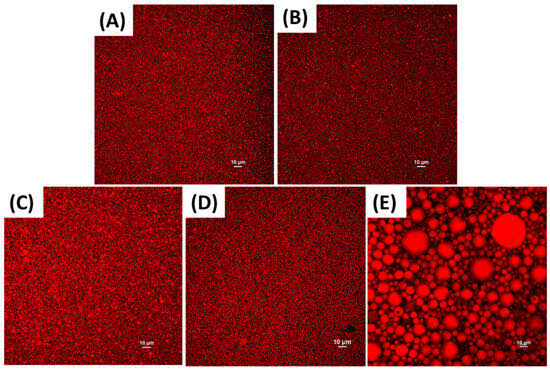
Figure 2.
Impact of fat content, heating, and homogenization on confocal fluorescence microscopy images of flaxseed oil-in-water emulsions containing 1% RuBisCO protein observed at 400× magnification: (A): 10% oil, (B): 20% oil, (C): 40% oil (unheated), (D): 40% oil (heated), (E): 40% oil (blended). Except for the emulsions blended with a high shear mixer (E), all other emulsions were micro-fluidized.
The polydispersity index (PDI) provides an indication of the uniformity of the particle size distribution of colloidal systems. Typically, PDI values below 0.30 are an indication of a relatively narrow particle size distribution in emulsions. In this study, all the PDI values were below 0.3 (Table 1), which suggests that the particle size distribution was relatively narrow. The ζ-potential measurements showed that all the emulsions contained strongly negatively charged droplets, regardless of fat content, heating, or microfluidization, which is because the neutral pH used was well above the isoelectric point of the adsorbed proteins. This high negative charge may account for their resistance to aggregation during heating because there would be a strong electrostatic repulsion between them.
3.2. Rheological Analysis
3.2.1. Thermal Gelation Properties
The thermal gelation properties of the samples were characterized by measuring the change in complex shear modulus and phase angle when they were heated and cooled under controlled conditions. Four samples were analyzed: (i) 10% RuBisCO protein solutions (no oil) (10%R); (ii) 10% RuBisCO protein solutions containing 40% flaxseed oil in the form of fine emulsions (10%R-40%O-FE); (iii) 10% RuBisCO protein solutions containing 40% flaxseed oil in the form of coarse emulsions (10%R-40%O-CE); and (iv) real sea foie gras.
Initially, we characterized the thermal gelation behavior of RuBisCO protein solutions with and without oil droplets. The change in complex shear modulus (G*) and phase angle (δ) with temperature were measured (Figure 3). Prior to heating, the complex shear modulus of the pure protein solutions was relatively low, and the phase angle was relatively high, which can be attributed to their predominantly fluid-like characteristics. During heating, the complex shear modulus remained low, and the phase angle remained high, until the temperature exceeded about 60 °C, after which there was a steep increase in the complex shear modulus and decrease in the phase angle. From 70 to 90 °C, the increase in the complex shear modulus with temperature was more modest, which suggests that the majority of proteins had already participated in the formation of a gel network. The complex shear modulus continued to increase when the samples were held at 90 °C and then when they were cooled back to 25 °C. Overall, these effects can be attributed to the unfolding of the globular RuBisCO proteins when they were heated above their thermal denaturation temperature, which increased their surface hydrophobicity and promoted their aggregation. As a result, a 3D network of crosslinked protein molecules was formed that extended throughout the entire system, which resulted in elastic properties. The gel strength continued to increase during heating and holding at 90 °C because more protein molecules unfolded and became incorporated into this 3D gel network. The gel strength then increased when the samples were cooled due to strengthening of the hydrogen bonds between the protein molecules in the gel network.
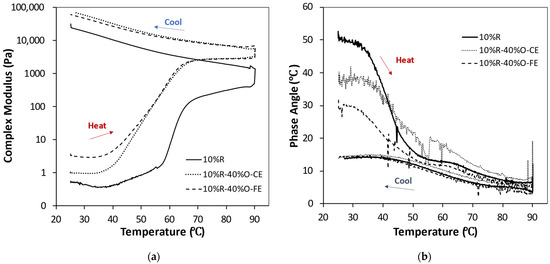
Figure 3.
Change in dynamic shear rheology of RuBisCO protein solutions (10%) in the absence and presence of flaxseed oil (40%) as either fine (10%R-40%O-FE) or coarse (10%R-40%O-CE) emulsions measured at a frequency of 1 Hz: (a) complex shear modulus (G*); (b) phase angle (δ).
The impact of initial droplet size (fine or coarse) on the thermal gelation behavior of flaxseed oil-in-water emulsions containing the same fat (40%) and protein (10%) contents is shown in Figure 3. In general, the rheological properties of these systems followed a similar trend to the pure protein solutions, with the complex shear modulus being relatively low before heating, rising steeply when they were heated above a particular temperature, and then increasing further when they were cooled. Again, this thermal behavior can largely be attributed to the unfolding and aggregation of the protein molecules. However, the presence of the oil droplets did have an appreciable impact on the thermal behavior of the mixed systems. At low temperatures, the presence of the oil droplets increased the complex shear modulus and decreased the phase angle of the protein solutions, with the smaller droplets having a bigger impact than the larger ones. This effect can mainly be attributed to the ability of the oil droplets to alter the flow properties of the solutions. It is well known that adding droplets to a solution increases its viscosity because the fluid has to flow around the oil droplets, which increases their velocity, leading to more frictional losses and energy dissipation [30]. The presence of the oil droplets also changed the temperature where the steep increase in gel strength and decrease in phase angle during heating occurred (Figure 3). Both the small and large droplets led to a decrease in the gelation temperature, which suggests that the proteins were able to form a 3D network at a lower temperature in the presence of the oil droplets. It is possible that protein molecules adsorbed to the oil droplet surfaces unfolded during heating, which caused the oil droplets to aggregate with each other and form a 3D network that increased the gel strength [20]. Both types of oil droplets increased the complex shear modulus and decreased the phase angle of the samples after heating, which is to be expected because incorporating active fillers into polymer networks increases their gel strength [20,21]. An active filler is a particle that is attracted to the polymers in the gel network and so the particles form part of the network. In our study, the active fillers were protein-coated oil droplets, whereas the polymers were proteins, and so they would be expected to be attracted to each other when the proteins unfold during heating and their surfaces become more hydrophobic. The final gel strength was fairly similar for both the small and large oil droplets (Figure 3). The theoretical models and experimental studies of the impact of active fillers on the rheology of polymer gels have shown that the complex shear modulus increases after active fillers are added and may or may not increase as the droplet size decreases, depending on the system [20,33,34].
We then compared the thermal rheological behavior of the plant-based sea foie gras (PB-SFG) with the real sea foie gras (Figure 4). The sample containing 10% RuBisCO and 40% oil (coarse emulsion) was used as a model PB-SFG since it was compositionally and structurally the most similar to real sea foie gras (see later). Unlike the PB-SFG, which went from being a soft gel before heating (low G*, high δ) to a firm gel after heating (high G*, low δ), the real sea foie gras was a firm gel before and after heating (high G*, low δ). For the real sea foie gras, there was a slight decrease in G* during heating from 25 to 90 °C, a progressive increase during holding at 90 °C, and then a slight increase during cooling from 90 to 25 °C. This kind of behavior was mainly attributed to the weakening of hydrogen bonding at higher temperatures, as well as some evaporation of water during the holding period at 90 °C. The commercial sea foie gras was already heated prior to sale, and therefore, the proteins it contained would already be expected to be thermally denatured. As a result, there was not a major increase in gel strength during heating. In contrast, the RuBisCO proteins in the PB-SFG were in a native state prior to heating and underwent unfolding, aggregation, and network formation during heating, leading to a pronounced increase in gel strength. However, the change in G* with temperature during cooling was very similar to that observed for real sea foie gras. One would expect that the PB-SFG would behave like real sea foie gras if it was heated a second time because the proteins would then be denatured.
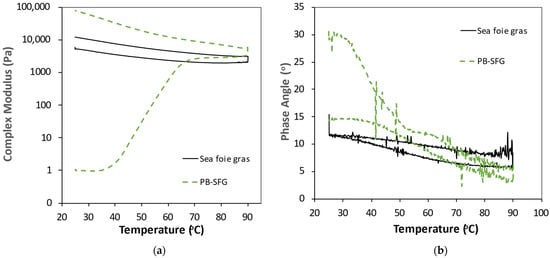
Figure 4.
Change in dynamic shear rheology of real sea foie gras and plant-based sea foie gras (PB-SFG: 10% RuBisCO protein, 40% flaxseed oil, coarse emulsion) (frequency = 1 Hz): (a) complex shear modulus (G*); (b) phase angle (δ).
3.2.2. Strain and Frequency Sweep Analysis
The changes in the complex shear modulus with applied strain and frequency were then measured to provide additional information about the rheological characteristics of the samples. In these experiments, the behavior of the real sea foie gras was again compared to that of the plant-based sea foie gras containing the coarse emulsion (10% RuBisCO, 40% flaxseed oil). Initially, the PB-SFG samples were gelled by heating them at 60 °C for 30 min. The dynamic shear rheology measurements were then carried out at a fixed temperature (25 °C).
Initially, an amplitude strain sweep was performed to identify the linear viscoelastic range (LVR) of the real and plant-based sea foie gras samples at a fixed frequency (1 Hz). The change in storage modulus was measured as the strain was increased (Figure 5). For both samples, the storage modulus remained relatively constant up to approximately 5% strain and then decreased appreciably, which suggests that there was some damage to the structure at higher strains. These results indicate that the plant-based version of the sea foie gras behaved quite similarly to the real version.
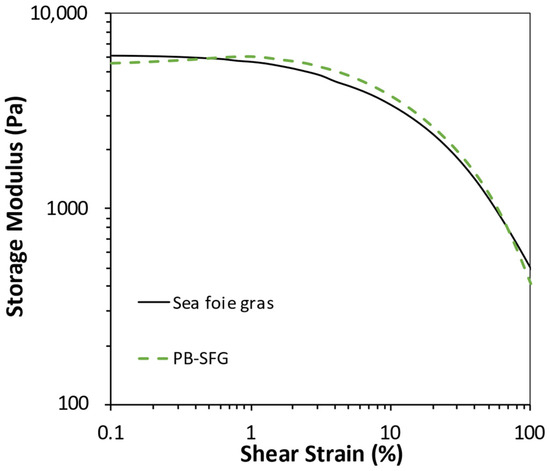
Figure 5.
Comparison of the change in complex shear modulus with increasing applied strain for real sea foie gras and plant-based sea foie gras (PB-SFG: 10% RuBisCO protein, 40% flaxseed oil, coarse emulsion) measured at 25 °C and 1 Hz.
Additional information about the dynamic rheology of the samples was obtained by measuring the frequency dependence of storage modulus at a fixed strain (1%), which was within the linear viscoelastic region (LVR) determined by the strain sweep (Figure 5). The storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G″) were measured as a function of increasing frequency (Figure 6). Again, the real and plant-based sea foie gras exhibited very similar frequency-dependent rheological properties. In both cases, the storage modulus was greater than the loss modulus (G′ > G″) across the entire frequency range, which indicated that the samples were predominantly elastic-like [35]. The storage modulus increased with increasing frequency for both samples, which suggests that they became more rigid at higher frequencies. This is mainly because the molecules in the gel network have less time to rearrange themselves during a cycle of the applied stress at higher frequencies; consequently, they are more resistant to deformation. Again, these results indicate that plant-based seafood can be produced that has similar rheological properties to a real seafood product.
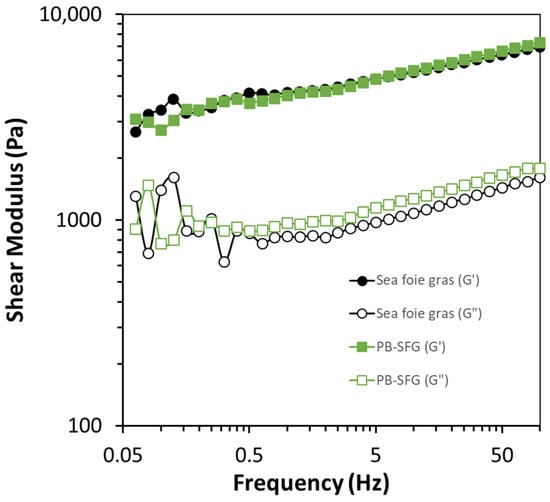
Figure 6.
Comparison of the change in storage and loss modulus (G′ and G″) with increasing frequency for real sea foie gras and plant-based sea foie gras (PB-SFG: 10% RuBisCO protein, 40% flaxseed oil, coarse emulsion) measured at 25 °C and 1% strain.
Furthermore, the complexity and magnitude of the gel network of the real and plant-based sea foie gras were analyzed with Bohlin’s model [29]. As the linearity of both frequency sweeps over storage modulus (G′) was verified by the linear-fitting and their regression coefficients (R2), the Bohlin parameters z and A were determined from the gradients and y-intercepts, respectively (Table 2). According to Bohlin’s theory, the z parameter represents the extensiveness of the network structures in the gel, whereas the A parameter represents the level of magnitude of the network structure in the gel [29]. Although the two z values were relatively similar, real sea foie gras was slightly higher, suggesting a more extensive and complex network compared to the plant-based counterpart. The A value, on the other hand, was significantly higher for the plant-based sea foie gras. This indicates a formation of much stronger molecular interactions in the gel network of plant-based sea foie gras.

Table 2.
Bohlin’s parameters for real sea foie gras and plant-based sea foie gras (PB-SFG: 10% RuBisCO protein, 40% flaxseed oil, coarse emulsion). These parameters were calculated by fitting the Bohlin equation to the average G′ versus frequency curve calculated from three measurements (n = 3).
3.3. Textural Characteristics of Real and Plant-Based Sea Foie Gras
The rheological experiments used to characterize the samples in the previous experiments utilized small shear deformations that did not damage the samples. In practice, seafood products experience large compression deformations, e.g., during cutting or mastication. For this reason, we compared the large deformation behavior of real and plant-based sea foie gras samples. In particular, we examined the impact of processing and formulation conditions on their textural properties. In addition, we measured and compared the appearance and color of the real and plant-based sea foie gras.
3.3.1. Impact of Heating Conditions
The impact of heating time and temperature on the textural properties of the plant-based sea foie gras were tested (Figure 7). As expected, the hardness of the plant-based products increased with increasing heating time and temperature, which can be attributed to the fact that a greater fraction of the globular RuBisCO proteins had unfolded and aggregated with each other, thereby leading to a stronger gel network. Consequently, it may be possible to modulate the textural attributes of the plant-based sea foie gras by controlling the thermal processing conditions. It should be noted, however, that the real sea foie gras was softer than either of the plant-based ones. Consequently, it may be advantageous to reduce the protein concentration in the plant-based products to decrease their hardness and more closely match that of the real sea foie gras.
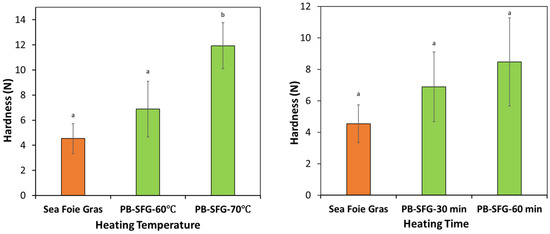
Figure 7.
Impact of heating conditions on the hardness of real and plant-based sea foie gras (PB-SFG) products. The PB-SFG consisted of 10% protein, 40% flaxseed oil (fine emulsion): Left—effect of heating temperature (at a fixed heating time of 30 min); Right—effect of heating time (at a fixed temperature of 60 °C). The lower-case letters above bars indicate statistical similarities of respective measurements.
3.3.2. Impact of Droplet Size
We also examined the impact of oil droplet size on the textural properties of the plant-based sea foie gras (Figure 8). These samples were prepared by heating for 30 min at 60 °C. Interestingly, the plant-based samples containing the smaller oil droplets had a higher hardness than the real sea foie gras, whereas the ones containing the larger oil droplets had a lower hardness. Previous studies have also shown that smaller droplets are more effective at increasing the strength of protein gels than larger ones, when they behave as active fillers [33,34]. This effect may be because the smaller protein-coated oil droplets interacted with the protein molecules in the surrounding biopolymer network, thereby strengthening it. In contrast, the larger oil droplets may be too large to fit into the pores within the surrounding biopolymer network, and so, they disrupted the network and weakened the gels.
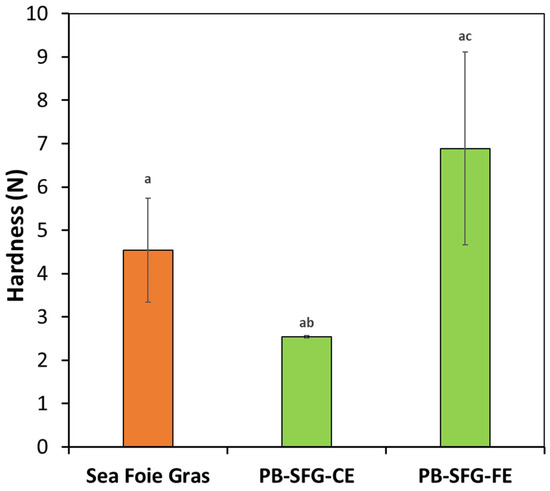
Figure 8.
Impact of droplet size on the hardness of real and plant-based sea foie gras (PB-SFG) products. The PB-SFG consisted of 10% protein and 40% flaxseed oil and either fine or coarse emulsions (prepared by heating for 30 min at 60 °C). The lower-case letters above bars indicate statistical similarities of respective measurements.
3.4. Matching the Appearance of Sea Foie Gras
Real sea foie gras has a distinct orange-yellow color, whereas the RuBisCO emulsion gels had a beige color (Figure 9). Moreover, there was evidence of some free oil on the surface of the real sea foie gras but not on the surface of the emulsion gels.
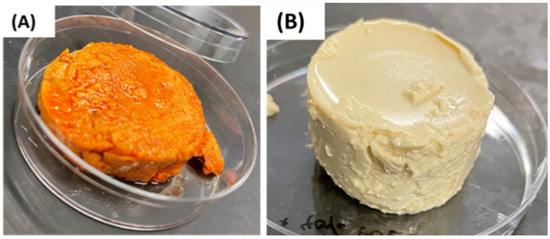
Figure 9.
Comparison of the overall appearance of real sea foie gras (A) and a RuBisCO emulsion gel (B).
For this reason, we examined methods for creating plant-based sea foie gras that had a more similar color to the real product. This was achieved by mixing an orange-yellow pigment that can be obtained from natural plant-based sources (β-carotene) with the oil phase. Moreover, to create products with visible free oil on their surfaces, we examined the effects of incorporating the oil entirely in an emulsified form (40% coarse emulsion) or as a mixture of emulsified and free oil (20% coarse emulsion and 20% bulk oil). These results showed that the presence of the carotenoids gave the emulsion gels an orange-yellow appearance that was closer to that of the real sea foie gras than the original products. However, when all of the oil was incorporated in an emulsified form, the emulsion gels had a more yellowish color than the real sea foie gras. In addition, there was no evidence of free oil on their surfaces. In contrast, when the oil was incorporated as a mixture of emulsified and free oil, both the overall color and the presence of free surface oil was more similar to the real sea foie gras. The instrumental tristimulus coordinates (L*a*b* values) also showed that the color of the plant-based products could be somewhat matched to those of the real ones (Figure 10D). In particular, the L* (lightness) and a* (redness) values were not statistically different, but the b* (yellowness) values of the plant-based products were considerably greater than those of the real products. These results suggest that it is possible to match the overall appearance of the seafood products using plant-based ingredients, such as proteins, oils, and pigments. However, more work is still required to precisely match their optical properties. This might be achieved by incorporating other kinds of natural pigments into the plant-based sea foie gras products.
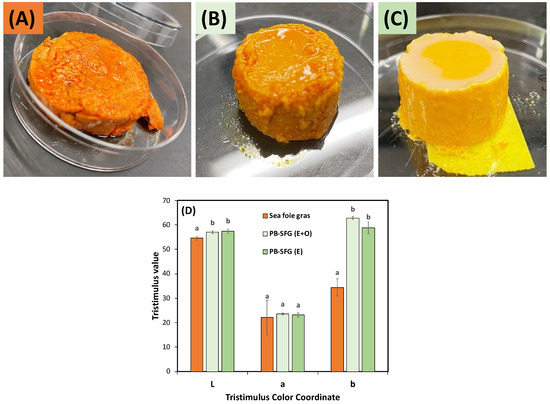
Figure 10.
Comparison of the overall appearance of real sea foie gras (A) with plant-based sea foie gras containing a mixture of emulsified and free oil (B) or all emulsified oil (C). The tristimulus color coordinates of the same samples are shown in (D), respectively. The plant-based products contained a total amount of 40% oil. The lower case-letters above bars indicate statistical similarities of respective measurements.
We also examined the textural attributes of the real and plant-based sea foie gras samples containing the colored oil incorporated in different ways (Figure 11). A texture profile analysis was used to determine the hardness, cohesion, springiness, and chewiness of the different samples. These results indicate that the real and plant-based seafood products had fairly similar textural attributes, but there were some important differences. For instance, the real sea foie gras tended to be harder, more cohesive, chewier, and less springy than the plant-based versions. In future, it may be possible to reformulate the plant-based products to match the textural attributes of the real ones more closely, e.g., by using different types and concentrations of plant proteins or by incorporating other additives such as polysaccharides.
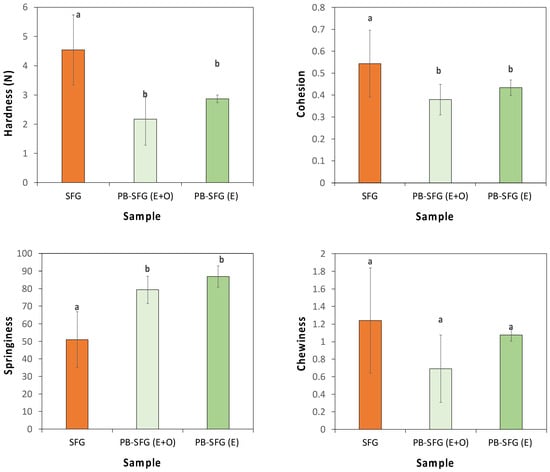
Figure 11.
Comparison of the texture profiles (hardness, cohesion, springiness, chewiness) of real sea foie gras (SFG) with plant-based sea foie gras containing a mixture of emulsified and free oil (PB-SFG (E + O)) or all emulsified oil (PB-SFG (E + O)). Both plant-based products contained a total amount of 40% oil. The lower-case letters above bars indicate statistical similarities of respective measurements.
3.5. Microstructure Analysis
Finally, the microstructure of the real sea foie gras was compared to that of a plant-based version using scanning electron microscopy and confocal fluorescence microscopy (Figure 12). The oil phase in the fluorescence microscopy images was stained red using an oil-soluble dye (Nile red). There were some differences and similarities in the microstructures of the real and plant-based sea foie gras. The real product appeared to have a more fibrous structure than the plant-based ones in the scanning electron microscopy images. However, the confocal microscopy images showed that both samples contained fat droplets dispersed throughout the products, with some regions where there was little fat, which was presumably dominated by protein-rich regions.
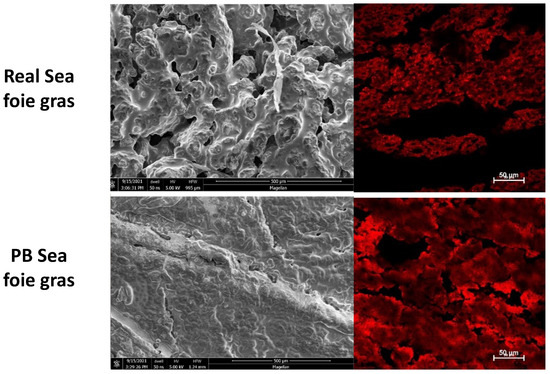
Figure 12.
Scanning electron microscopy and confocal fluorescence images of the emulsion gels. The emulsion gels were unstained and contained 10% protein and 40% flaxseed oil fine emulsions.
4. Conclusions
Sea foie gras is a traditional delicacy in some Asian countries, and is produced from monkfish liver. There is increasing concern about the environmental damage being caused by overfishing, as well as health issues associated with allergies and bioaccumulated toxins in these fish products. Consequently, there is interest in identifying sustainable alternatives to traditional seafood products. In this study, we demonstrated that a plant-based sea foie gras fortified with omega-3 fatty acids could be produced from sustainable protein and lipid sources (duckweed and flaxseed). These seafood analogs were produced using emulsion gel technology by producing concentrated oil-in-water emulsions containing globular proteins in the aqueous phase, which were then gelled by heating the proteins above their thermal denaturation temperature. This led to the formation of gels that could be designed to have textural attributes somewhat similar to that of real sea foie gras. Moreover, the distinct orange-yellow color and oily appearance of sea foie gras could be mimicked by incorporating a natural pigment (β-carotene) that can be isolated from plants in a mixture of emulsified and free form. In the future, it would be useful to test the in vitro bioaccessibility and in vivo bioavailability of the proteins, carotenoids, and omega-3 fatty acids in these plant-based seafood products. It would also be useful to compare their sensory properties with those of real sea foie gras using sensory studies. It should also be noted that flaxseed oil was used as a source of omega-3 fatty acids in this study. Flaxseed mainly contains alpha-linoleic acid (AHA), which is nutritionally different from the omega-3 fatty acids found in fish (DHA and EPA). This difference could be overcome by using algal oil rather than flaxseed oil, as they are also rich sources of DHA and EPA.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K. and D.J.M.; methodology, K.K. and D.J.M.; investigation, K.K.; resources, D.J.M.; data curation, K.K., Z.Z. and D.J.M.; writing—original draft preparation, K.K.; writing—review and editing, D.J.M.; visualization, K.K. and D.J.M.; supervision, Z.Z. and D.J.M.; project administration, D.J.M.; funding acquisition, D.J.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, USDA, Massachusetts Agricultural Experiment Station (MAS00559) and USDA, AFRI (2020-03921 and 2022-09185) grants, as well as the Good Food Institute.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
This material was partly based upon work supported by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, USDA, Massachusetts Agricultural Experiment Station (MAS00559) and USDA, AFRI (2020-03921 and 2022-09185) grants, as well as the Good Food Institute.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Poore, J.; Nemecek, T. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science 2018, 360, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W.; Rockstrom, J.; Loken, B.; Springmann, M.; Lang, T.; Vermeulen, S.; Garnett, T.; Tilman, D.; DeClerck, F.; Wood, A.; et al. Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT-Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. Lancet 2019, 393, 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.; Cao, L.; Gelcich, S.; Cisneros-Mata, M.A.; Free, C.M.; Froehlich, H.E.; Golden, C.D.; Ishimura, G.; Maier, J.; Macadam-Somer, I.; et al. The future of food from the sea. Nature 2020, 588, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Impacts of Climate Change on Fisheries and Aquaculture: Synthesis of Current Knowledge, Adaptation and Mitigation Options; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sumaila, U.R.; Tai, T.C. End Overfishing and Increase the Resilience of the Ocean to Climate Change. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in Action; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.H.; Ferrer, E.M.; Hunt, C.A.; Bleeker, K.; Villasante, S. Exploring Changes in Fishery Emissions and Organic Carbon Impacts Associated With a Recovering Stock. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 788339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiocchetti, G.; Jadan-Piedra, C.; Velez, D.; Devesa, V. Metal(loid) contamination in seafood products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3715–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinadasa, B.; Jayasinghe, G.; Pohl, P.; Fowler, S.W. Mitigating the impact of mercury contaminants in fish and other seafood-A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.B. Seafood allergy: Occurrence, mechanisms and measures. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Johnston, E.B.; Nugraha, R.; Le, T.T.K.; Kalic, T.; McLean, T.R.; Kamath, S.D.; Lopata, A.L. Seafood allergy: A comprehensive review of fish and shellfish allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 28–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazir, M.; Livney, Y.D. Plant-Based Seafood Analogs. Molecules 2021, 26, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekkers, B.L.; Boom, R.M.; van der Goot, A.J. Structuring processes for meat analogues. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 81, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Grossmann, L. A brief review of the science behind the design of healthy and sustainable plant-based foods. Npj Sci. Food 2021, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakopoulou, K.; Keppler, J.K.; van der Goot, A.J. Functionality of Ingredients and Additives in Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Foods 2021, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattice, K.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Evaluating the use of zein in structuring plant-based products. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2020, 3, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera-Oviedo, J.; Yara-Varon, E.; Torres, M.; Canela-Garayoa, R.; Balcells, M. Sustainable Synthesis of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ethyl Esters from Monkfish Liver Oil. Catalysts 2021, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Regenstein, J.; Su, X.R. In vitro and in vivo anti-oxidation and anti-fatigue effect of monkfish liver hydrolysate. Food Biosci. 2017, 18, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-C.; Lou, Y.-J.; Xiong, G.-T.; Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Lou, Y. Composition analysis and evaluation of Goosefish liver nutrition. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2017, 38, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Emulsion gels: The structuring of soft solids with protein-stabilized oil droplets. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjami, T.; Madadlou, A. An overview on preparation of emulsion-filled gels and emulsion particulate gels. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.H.; Nieuwland, M.; de Jong, G.A.H. Characterization of Heat-Set Gels from RuBisCO in Comparison to Those from Other Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10783–10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, E.; Agyei, D.; Njoku, E.N.; Udenigwe, C.C. Plant RuBisCo: An Underutilized Protein for Food Applications. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2018, 95, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.B.; Lee, P.W.; Martens, T.D.; McClements, D.J. Comparison of Emulsifying Properties of Plant and Animal Proteins in Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Whey, Soy, and RuBisCo Proteins. Food Biophys. 2022, 17, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouame, K.; Bora, A.F.M.; Li, X.D.; Sun, Y.; Liu, L. Novel trends and opportunities for microencapsulation of flaxseed oil in foods: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, S.; Sandhu, K.S.; Siroha, A.K.; Dhull, S.B. Omega 3-metabolism, absorption, bioavailability and health benefits-A review. Pharmanutrition 2019, 10, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.T.; Yu, K.; Cheng, C.; Peng, D.F.; Yu, X.; Chen, H.J.; Chen, Y.S.; McClements, D.J.; Deng, Q.C. Effect of sesamol on the physical and chemical stability of plant-based flaxseed oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by proteins or phospholipids. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 2090–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, G.W.; Frost, J.K.; Miller, K.A. A new formula for a half-oxidized hematoxylin solution that neither overstains nor requires differentiation. Acta Cytol. 1974, 18, 300–301. [Google Scholar]
- Bohlin, L. A theory of flow as a cooperative phenomenon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 74, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practice, and Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hakansson, A. Emulsion Formation by Homogenization: Current Understanding and Future Perspectives. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.; Assadpoor, E.; He, Y.H.; Bhandari, B. Re-coalescence of emulsion droplets during high-energy emulsification. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E.; Chen, J.S. Heat-set whey protein emulsion gels: Role of active and inactive filler particles. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 1999, 20, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Monahan, F.J.; Kinsella, J.E. Effect of emulsion droplets on the rheology of whey-protein isolate gels. J. Texture Stud. 1993, 24, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.A. Rheology of Fluid, Semisolid, and Solid Foods: Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; Springer Science: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).