Abstract
Background: The posterior labyrinth is particularly vulnerable to ischemic injury. Vertigo can occasionally be the only presenting symptom of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Acute Bilateral Vestibular Neuropathy (ABVN) is an extremely rare condition, with only three cases previously reported in the literature. Its exact pathophysiological mechanisms remain unclear. Case Presentation: We present the case of a 76-year-old male who presented to the emergency department (ED) with vertigo and severe postural unsteadiness. Subsequently, a silent AMI was diagnosed, prompting cardiac stenting. Vestibular function assessments over the following eight months confirmed the diagnosis of ABVN. A cycle of vestibular rehabilitation yielded limited objective benefit, although the patient reported subjective improvement as measured by the Dizziness Handicap Inventory (DHI). Discussion and Conclusions: This case suggests a potential association between peripheral vestibular dysfunction and acute hemodynamic impairment due to myocardial infarction. Notably, it represents the first reported case of ABVN following a silent AMI, presenting solely with vestibular symptoms.
1. Introduction
Dizziness is exhibited by approximately 2.1 to 3.6% of patients presenting to the Emergency Department (ED) [1]. Given its high prevalence, a comprehensive clinical history and focused bedside assessment are essential to promptly identify or exclude high-risk conditions [2]. Vertigo may be a presenting symptom in up to 8% of patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), often described as faintness or dizziness [3]. In 2006, Newman-Toker and Camargo described a patient with vertigo, fainting, and dizziness associated with episodes of transient asystole, coining the term “cardiogenic vertigo”. According to diagnostic speculation, this may be caused by a sudden cardiac pump failure with hemodynamic impairment, systemic hypotension, and local labyrinthine ischemia [4], similar to what is known to occur in the brain during transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) [5].
1.1. Acute Vestibular Syndrome (AVS)
Acute Vestibular Syndrome (AVS) is a clinical condition generally characterized by sudden onset of severe vertigo lasting from seconds to hours, spontaneous nystagmus, postural unsteadiness, nausea, and vomiting [6]. Differentiating between peripheral and central causes is critical, as central etiologies (e.g., cerebellar hemorrhage or infarction) can pose an immediate life-threatening risk and require urgent intervention [1,7]. When hearing is spared, AVS is most commonly attributed to vestibular neuritis (VN) [8,9]. VN is classically considered inflammatory and of viral origin [9], although increasing evidence suggests that a substantial number of cases may instead have a vascular etiology [10]. When inflammatory, VN may involve the entire vestibular nerve or be limited to either the superior or inferior branch, with the superior branch most commonly affected [11].
1.2. Vascular Supply of Labyrinth
The inner ear has a terminal arterial circulation. The labyrinthine artery, originating from the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA), divides into two branches: the anterior vestibular artery (AVA) and the common cochlear artery. The common cochlear artery further gives rise to the posterior vestibular artery (PVA) that extends towards the posterior labyrinth. The area supplied by the anterior vestibular artery (AVA) includes the anterior and lateral semicircular canal (ASC, LSC), the utricle, and the superior portion of the saccule. The inferior portion of the saccule and the posterior semicircular canals (PSC) are supplied by the PVA. When VN is caused by ischemic damage, the area supplied by AVA is more commonly affected [10]. Inflammatory VN isolated to the superior branch of the vestibular nerve involves the same areas as ischemic VN originating from the AVA, making it difficult to distinguish between these two potential causes [10,12]. The use of instrumental tests like vHIT [13] and VEMPs [14] permits topographic localization of the vestibular lesion in VN [9].
1.3. Bilateral Vestibular Neuropathy and Similar Previous Reports
Vestibular neuritis commonly manifests unilaterally; bilateral sequential occurrence is observed in a mere 1.9% of cases, termed bilateral sequential vestibular neuritis (BSVN) [15]. BSVN generally presents with the appearance of sudden vertigo and could be associated with oscillopsia and ataxia; usually the patient reports previous VN in the contralateral ear. Acute bilateral vestibular neuropathy (ABVN) can be caused by iatrogenic damage through the administration of ototoxic drugs such as gentamicin [16]. In the absence of iatrogenic causes, the onset of ABVN has been described in only three cases in the literature, all with a presumed viral etiology [17,18,19]. In 2018, Yacovino et al. documented the first non-iatrogenic case in a patient who developed vertigo, severe gait ataxia, and oscillopsia one week after an upper respiratory tract infection. Instrumental testing showed bilateral superior vestibular involvement [17]. In 2019, Ichijo et al. described a second case in a patient with dizziness, oscillopsia, and gait unsteadiness following a febrile illness. Evaluation revealed bilateral involvement of both superior and inferior branches of the vestibular nerves bilaterally [18]. In 2022, Lee et al. reported a third case in association with COVID-19. Although vestibular testing was incomplete, bilateral deficits were confirmed [19]. In this article, we report and discuss the case of a patient affected by ABVN during AMI, which, to the best of our knowledge, represents the first reported in the literature.
2. Case Report
A 76-year-old man (weight 80 kg, height 176 cm) presented to the ED of the Sant’Antonio Hospital, University Hospital of Padua, with vertigo and severe postural unsteadiness that had persisted for approximately two days, worsening with positional changes. The night before admission, he experienced a fall caused by marked unsteadiness, resulting in occipital head trauma without loss of consciousness. He denied headache, abdominal pain, dyspnea, palpitations, diaphoresis, or auditory symptoms at the time of evaluation. He was a heavy smoker (120 pack-years), with well-controlled hypertension treated with ramipril 5 mg/day and had a known allergy to iodine. His family history was negative for cardiovascular disease, and no other cardiovascular risk factors were reported. The patient had not received ototoxic medications prior to symptom onset. His medical history included high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer under 8-year follow-up, previously treated with Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) therapy, and prior transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). A brain CT scan showed hypodense lacunae in the periventricular white matter and nucleocapsular region, consistent with chronic small vessel disease. No hemorrhagic lesions were noted. Neurologic examination revealed an alert and cooperative patient, oriented to time and space, without motor or sensory deficits. Deep tendon reflexes were preserved, with no signs of rigidity. He was able to sit unaided with good trunk control. Otoscopy was unremarkable, with clear external auditory canals and bilaterally opaque tympanic membranes. Bedside vestibular assessment showed a low amplitude, spontaneous, unidirectional right beating horizontal nystagmus with weak signs of apogeotropic reinforcement with the patient lying on his left side using Frenzel goggles. Clinical Head Impulse Test (cHIT) showed bilateral corrective saccades. The patient exhibited a tendency to fall without specific directionality on the Romberg test. The Unterberger test was not performed. The therapy was initiated with intravenous administration of 4 mg betamethasone and intramuscular administration of 25 mg levosulpiride. Cardiological evaluation in the ED revealed the patient to be asymptomatic from a cardiac standpoint (no angina, dyspnea, palpitations, or syncope). Electrocardiography (ECG) showed signs of extensive anterior necrosis with subepicardial ischemia. Blood pressure was 150/80 mmHg, and heart rate was 75 bpm. Contrast-enhanced transthoracic echocardiography (Figure 1) revealed akinesia of the entire cardiac apex, mild left ventricular dysfunction, and normal right ventricular motion. No intracavitary thrombi were detected. Blood tests showed elevated troponin I levels: 49 ng/L at admission and 41 ng/L four hours later.
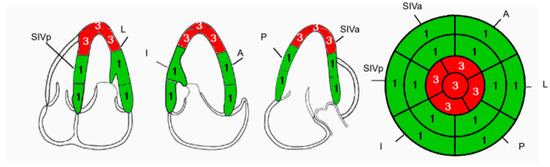
Figure 1.
The figure is a schematic representation of contrast-enhanced cardiac ultrasound. It shows akinesia of the cardiac apex and mild dilation of the left ventricle, while the right ventricle appears normal. No gross intraventricular thrombotic formations were found in the left ventricle. SIVa: Anterior interventricular septum; SIVp: posterior interventricular septum; I: inferior cardiac wall; P: posterior cardiac wall; L: lateral cardiac wall; A: anterior cardiac wall; 1: normokinesis; 3: akinesia. Green: the normokinetic myocardial areas; Red: the akinetic areas.
The patient was transferred to the Cardiac Care Unit (CCU) with a diagnosis of anterior acute myocardial infarction (AMI) for initiation of dual antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapy and for clinical and instrumental monitoring. During the 7-day hospitalization, daily laboratory testing and troponin monitoring showed a downward trend. The N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) reached 1723 ng/L. A coronary stent was placed in the left main artery. At discharge, medical therapy included the following: acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) 100 mg daily, ticagrelor 90 mg twice daily, ramipril 2.5 mg twice daily, rosuvastatin/ezetimibe 20/10 mg daily, and omeprazole 20 mg daily. This clinical case occurred between September 2023 and May 2024, during a period when non-urgent services in the Italian national health system—such as advanced vestibular testing—were still subject to delays due to pandemic-related restrictions. One month after discharge from the CCU, the patient underwent brain and brainstem MRI, as well as intracranial MR angiography, which revealed a small recent ischemic lesion in the right nucleocapsular region. On contrast-enhanced MRI, the labyrinth appeared within normal limits bilaterally, with no macroscopic evidence of ischemic lesions. The patient was referred to our institution, a regional referral center for vertigo, for vestibular assessment. Testing included pure-tone audiometry, videonystagmography (VNG) with bithermal caloric testing (ICS Chartr 200® Otometrics), cervical and ocular air-conducted Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (cVEMPs, oVEMPs—Interacoustics Eclipse and OtoAccess® Database), and video Head Impulse Test (vHIT—Interacoustics VisualEyes™ EyeSeeCam with Head Impulse Paradigm (HIMP) and Suppression Head Impulse Paradigm (SHIMP) protocols), which were repeated at 3 and 6 months. Pure-tone audiometry revealed a mild bilateral sensorineural hearing loss limited to the high frequencies and slightly more pronounced on the left side. The hearing loss was pre-existing and unchanged compared with previous audiometric examinations. Initial vestibular testing was performed 68 days after symptom onset. VNG showed no spontaneous or positional nystagmus, but there were abnormalities in smooth pursuit gain and accuracy. Canal paresis was defined as a ≥25% interaural difference, and asymmetry was calculated using Jongkees’ formula. An asymmetry value ≤ 30% was considered within normal limits for VEMP interpretation, along with the identifiability of P–N and N–P peaks. The bithermal caloric test showed marked bilateral hyporeflexia. cVEMPs were absent on the right and normal on the left; oVEMPs were bilaterally absent (Figure 2).
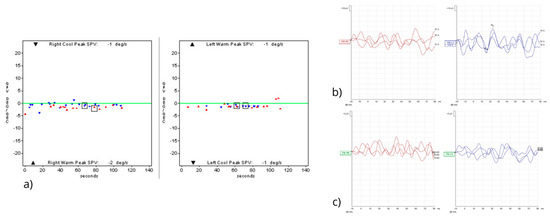
Figure 2.
(a) Bithermal caloric testing revealing complete bilateral vestibular paralysis. (b) cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (cVEMPs) are absent on the right, while the P-N complex is recognizable on the left. (c) ocular Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (oVEMPs) are absent bilaterally.
Mean VOR gain (eye velocity/head velocity) is reported for each semicircular canal. Normal gain values are defined as >0.8 for the lateral canals and >0.7 for the vertical canals. Bilateral severe impulsive deficit of lateral and anterior semicircular canals (LSC and ASC) with bilateral overt saccades was evident, and the posterior semicircular canals (PSC) appeared spared bilaterally in the vHIT (Figure 3). The analysis of SHIMP traces on vHIT did not reveal the presence of compensatory saccades.
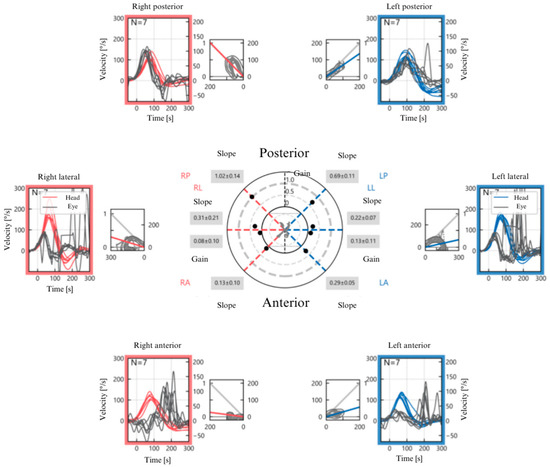
Figure 3.
The figure shows the compact display of vHIT performed on all six semicircular canals. Starting from the top left and proceeding clockwise, it reports the right posterior semicircular canal (PSC) with a Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex (VOR) gain of 1.02 ± 0.14 (n.v. ≥ 0.70), the left PSC with a VOR gain of 0.69 ± 0.11 (n.v. ≥ 0.70), the left lateral semicircular canal (LSC) with a VOR gain of 0.13 ± 0.11 (n.v. ≥ 0.80), the left anterior semicircular canal (ASC) with a VOR gain of 0.29 ± 0.05 (n.v. ≥ 0.80), the right ASC with a VOR gain of 0.13 ± 0.10 (n.v. ≥ 0.80), and finally the right LSC with a VOR gain of 0.08 ± 0.10 (n.v. ≥ 0.80). The examination reveals severe impulse deficit with overt and scattered saccades in bilateral LSC and ASC, while the right PSC appears spared and the left PSC shows mild impairment.
A diagnosis of acute bilateral superior branch vestibular neuropathy in the context of AMI was established. The Dizziness Handicap Inventory (DHI) score was 70. The patient completed a vestibular rehabilitation program. At 8-month follow-up, he reported persistent but improved gait unsteadiness. Instrumental testing showed stability of findings (vHIT, caloric test, cVEMPs, oVEMPs). Computerized posturography (NeuroCom Balance Manager®, Natus Medical Incorporated, San Carlos, CA, USA) before and after rehabilitation revealed abnormal center of gravity (CoG) oscillations during static and dynamic conditions, with modest post-treatment improvement. Subjectively, the patient reported improved quality of life, with a DHI score of 25 at the final evaluation.
3. Discussion
3.1. Rarity of the Condition and Pathophysiological Hypotheses
ABVN is an exceptionally rare condition, with only three non-iatrogenic cases reported in the literature to date [17,18,19]. In the present case, ABVN involving the superior branches of both vestibular nerves occurred during the course of an AMI. The relationship between acute cardiovascular events and peripheral vestibular dysfunction has been documented, although the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms remain poorly understood. Vertigo may be a manifestation of primary cardiovascular disease [4]. In our case, the patient experienced an anterior AMI that presented exclusively with vertigo and severe unsteadiness. The peripheral vestibular system is vascularized by the AVA, which supplies the utricle, LSC, ASC, and the superior portion of the saccule, and by the PVA, which supplies the inferior portion of the saccule and the PSC [10]. In our patient, thromboembolic events were ruled out by both transthoracic echocardiography and MR angiography. The vestibular damage was likely non-occlusive and ischemic in nature, comparable to what is observed during TIAs of the brain [5]. We hypothesize that a transient reduction in cardiac output during the AMI may have caused bilateral interruption of AVA perfusion, sufficient to induce irreversible ischemic injury. The small ischemic lesion observed on brain MRI in the right nucleocapsular region further supports the hypothesis of widespread ischemic involvement affecting both central and peripheral structures.
3.2. Clinical Features and Differential Diagnosis
The clinical presentation—acute onset of prolonged rotational vertigo worsened by head movements, combined with postural unsteadiness and associated vegetative symptoms (nausea and pallor, etc.)—is consistent with VN [9]. In viral VN, the superior branch of the vestibular nerve is typically more susceptible, likely due to anatomical and neurotropic factors [11]. In vascular VN, the reason for this preferential vulnerability remains unclear. The first description of vascular-induced peripheral vertigo was by Lindsay and Hemenway, who proposed that thromboembolic events predominantly affect the superior vestibular nerve branch [20]. In our case, although no thromboembolic occlusion was demonstrated, the area perfused by the AVA showed the most significant dysfunction. When bilateral vestibular dysfunction is identified, BSVN should be considered as a differential diagnosis [15]. Bilateral vestibular dysfunction is more commonly associated with ototoxicity, autoimmune disease, or bilateral Ménière’s disease [16]. However, our patient had no prior episodes suggestive of vestibular neuritis. Our patient reported no previous episodes suggestive of vestibular neuritis in his medical history, which represents a first subjective element raising the suspicion of ABVN. The interpretation of the vHIT traces reasonably supports a recent bilateral vestibular deficit, as the recordings show bilaterally and symmetrically overt saccades that are clearly scattered, in contrast to what would be expected in long-standing deficits, such as sequential bilateral neuritis, which would instead be characterized by gathered and/or covert saccades. Another instrumental finding corroborating the diagnosis of ABVN is the absence of saccades in SHIMP, which are typically observed in long-standing compensated vestibular deficits, a condition that in this case can therefore be excluded. Based on the clinical history and the instrumental findings from the vHIT, a diagnosis of ABVN was established [21].
3.3. Follow-Up, Outcome, and Comparison with the Literature
Persistent bilateral vestibular dysfunction due to ABVN can evolve into bilateral vestibulopathy (BVP), as occurred in our case. According to the Bárány Society, BVP is a chronic condition caused by bilateral vestibular hypofunction (BVH), characterized by unsteadiness, oscillopsia, and gait ataxia [22]. Instrumental assessment enabled accurate topographic localization of the vestibular damage, primarily involving AVA-supplied structures. Our patient demonstrated severe bilateral deficits in the LSCs and ASCs (detected via vHIT) and preservation of both PSCs. cVEMPs were absent on the right and preserved on the left, indicating a right-sided saccular deficit. Finally, a bilateral absence of oVEMPs was observed, suggesting a possible bilateral utricular dysfunction. However, this finding is only partially reliable, as the patient in the present case was 76 years old at the time of assessment, and the reliability of air-conducted oVEMPs is known to decrease with aging [23]. A dissociation between PSC and saccular dysfunction (identified via vHIT and cVEMPs, respectively) has been described in the literature [21]. One explanation involves a branch of the AVA supplying part of the saccule or a possible contribution from the so-called Oort’s anastomosis, which may conduct saccular afferents via the superior vestibular nerve. Based on these findings, we hypothesize that the AVA-supplied structures (utricle, LSCs, and ASCs) are particularly vulnerable to ischemic injury due to their end-arterial vascularization. The right-sided saccular dysfunction may be explained by the dual supply of the saccule from both AVA and PVA. This case underlines the importance of evaluating all ten vestibular end-organs to localize dysfunction accurately. Future anatomical and clinical studies are needed to validate the proposed vascular hypothesis for ABVN. Recovery following VN is variable; approximately 50% of patients report symptom resolution within one year [11]. In the first reported case of ABVN, the patient was asymptomatic at one year but still experienced oscillopsia with rapid head movements. The DHI score improved from 64 to 48, and partial recovery of oVEMPs was noted [17]. In the second case, the patient could walk unaided at one year, with a still-positive Romberg sign. cVEMPs became detectable, but oVEMPs remained absent. The vHIT showed global improvement, and the patient reported dizziness during daily activities, but no DHI score was reported [18]. In the third case, no follow-up vestibular testing was performed. However, a 5-month telephone interview revealed complete resolution of vertigo and gait disturbances [19]. The key data from the literature articles reporting cases of ABVN are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary table of data from case reports in the literature concerning patients with ABVN.
In our patient, instrumental, clinical, and quality of life follow-ups were conducted 8 months after the acute event. Clinically, the patient still exhibited gait unsteadiness. No improvements were observed in the vHIT, VEMPs, or bithermal caloric test. A modest improvement was noted in the CP. Additionally, a significant improvement in quality of life was indicated by the DHI score, which decreased from 70 to 25. The improvement in quality of life experienced by our patient demonstrates that, several months after the onset of ABVN, the general conditions of patients tend to improve. Future studies could help determine etiopathogenesis, the correct diagnostic workup, as well as the most appropriate therapy and prognosis of ABVN.
4. Conclusions
This case report represents the first documented instance of ABVN occurring in the setting of an AMI. The sequence of clinical events highlights a potential susceptibility of the peripheral vestibular system to sudden hemodynamic impairment. These findings underscore the importance of considering underlying cardiac pathology in the differential diagnosis of acute vertigo in the ED. Moreover, the present report supports the hypothesis that the etiopathogenesis of non-iatrogenic ABVN may be vascular in nature, rather than exclusively viral, as previously suggested in the limited literature.
This article is a revised and expanded version of a poster entitled “Neuropatia vestibolare bilaterale acuta in seguito ad infarto del miocardio: un case report” which was presented at the 111th National Congress of the Italian Society of Otolaryngology (S.I.O.), held at the Padova Fair from 28 to 31 May 2025 [24].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.C. and E.B.; methodology, F.C. and E.B.; software, P.M., B.B. and E.B.; validation, F.C. and E.P.; formal analysis, F.C., P.M. and B.B.; investigation, F.C., E.B., E.P., B.B. and P.M.; data curation, E.B., B.B. and P.M.; writing—original draft preparation, F.C. and E.B.; writing—review and editing, F.C., E.B. and E.P.; visualization, F.C. and E.P.; supervision, F.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, as the description of a single clinical case within routine clinical practice does not require a protocol approved by the Ethics Committee, in accordance with the internal regulations of the University Hospital of Padua.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ABVN | Acute Bilateral Vestibular Neuropathy |
| AICA | Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery |
| AMI | Acute Myocardial Infarction |
| ASA | Acetylsalicylic Acid |
| ASC | Anterior Semicircular Canal |
| AVA | Anterior Vestibular Artery |
| AVS | Acute Vestibular Syndrome |
| BCG | Bacillus Calmette–Guerin |
| BSVN | Bilateral Sequential Vestibular Neuritis |
| BVH | Bilateral Vestibular Hypofunction |
| BVP | Bilateral Vestibulopathy |
| CCU | Cardiac Care Unit |
| CP | Computerized Posturography |
| CoG | Center of Gravity |
| DHI | Dizziness Handicap Inventory |
| ED | Emergency Department |
| HIMP | Head Impulse Paradigm |
| LSC | Lateral Semicircular Canal |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NT-ProBNP | N-terminal prohormone of Brain Natriuretic Peptide |
| PSC | Posterior Semicircular Canal |
| PVA | Posterior Vestibular Artery |
| SHIMP | Suppression Head Impulse Paradigm |
| TIA | Transient Ischemic Attack |
| TURP | Transurethral Resection of the Prostate |
| VEMPs | Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials |
| VN | Vestibular Neuritis |
| cVEMPs | cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials |
| oVEMPs | ocular Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials |
| vHIT | video Head Impulse Test |
References
- Edlow, J.A.; Carpenter, C.; Akhter, M.; Khoujah, D.; Marcolini, E.; Meurer, W.J.; Morrill, D.; Naples, J.G.; Ohle, R.; Omron, R.; et al. Guidelines for Reasonable and Appropriate Care in the Emergency Department 3 (GRACE-3): Acute Dizziness and Vertigo in the Emergency Department. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2023, 30, 442–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, I.; Kim, J.-S. Approach to Dizziness in the Emergency Department. Clin. Exp. Emerg. Med. 2015, 2, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ängerud, K.H.; Ericsson, M.; Brännström, M.; Sederholm Lawesson, S.; Strömberg, A.; Thylén, I. Symptoms of Acute Myocardial Infarction as Described in Calls to Tele-Nurses and in Questionnaires. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2023, 38, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman-Toker, D.E.; Camargo, C.A. ’Cardiogenic Vertigo’—True Vertigo as the Presenting Manifestation of Primary Cardiac Disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2006, 2, 167–172, quiz 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Garcia, J.; Gomez, C.R.; Schneck, M.J.; Biller, J. Recent Advances in the Management of Transient Ischemic Attacks. Fac. Rev. 2022, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciotti, P.M.; Anzivino, R.; Galli, J.; Franceschi, F.; Conti, G.; Simeoni, B.; Covino, M. Clinical Evolution of Acute Vestibular Syndrome: Longitudinal Retrospective Analysis of Epidemiological Data and Prognostic Factors for Recovery. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlow, J.A.; Gurley, K.L.; Newman-Toker, D.E. A New Diagnostic Approach to the Adult Patient with Acute Dizziness. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 54, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strupp, M.; Bisdorff, A.; Furman, J.; Hornibrook, J.; Jahn, K.; Maire, R.; Newman-Toker, D.; Magnusson, M. Acute Unilateral Vestibulopathy/Vestibular Neuritis: Diagnostic Criteria. J. Vestib. Res. 2022, 32, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, C.H.; Na, H.G.; Choi, Y.S. Current Diagnosis and Treatment of Vestibular Neuritis: A Narrative Review. J. Yeungnam Med. Sci. 2022, 39, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, J.; Vlaminck, S.; Seiça, R.; Acke, F.; Miguéis, A. Vascular Mechanisms in Acute Unilateral Peripheral Vestibulopathy: A Systematic Review. ACTA Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2021, 41, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.L.; McGarvie, L.A.; Reid, N.; Young, A.S.; Halmagyi, G.M.; Welgampola, M.S. Vestibular Neuritis Affects Both Superior and Inferior Vestibular Nerves. Neurology 2016, 87, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-A.; Yi, H.-A.; Lee, H. Recent Advances in Cerebellar Ischemic Stroke Syndromes Causing Vertigo and Hearing Loss. Cerebellum 2016, 15, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzari, L.; Princi, A.A.; De Angelis, S.; Tramontano, M. Clinical Value of the Video Head Impulse Test in Patients with Vestibular Neuritis: A Systematic Review. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 4155–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpa, A.; Gioacchini, F.M.; Cassandro, E.; Tulli, M.; Ralli, M.; Re, M.; Cassandro, C. Clinical Application of cVEMPs and oVEMPs in Patients Affected by Ménière’s Disease, Vestibular Neuritis and Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Systematic Review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2019, 39, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comacchio, F.; Mion, M.; Armato, E.; Castellucci, A. Sequential Vestibular Neuritis: Report of Four Cases and Literature Review. J. Audiol. Otol. 2021, 25, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-U.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-S. Bilateral Vestibular Dysfunction. Semin. Neurol. 2020, 40, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacovino, D.A.; Finlay, J.B.; Urbina Jaimes, V.N.; Verdecchia, D.H.; Schubert, M.C. Acute Bilateral Superior Branch Vestibular Neuropathy. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichijo, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Fujimoto, C.; Uranaka, T.; Kikkawa, Y.S.; Sugasawa, K.; Yamasoba, T.; Iwasaki, S. Acute Bilateral Vestibulopathy with Simultaneous Involvement of Both Superior and Inferior Vestibular Nerves. Auris Nasus Larynx 2020, 47, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-U.; Kim, T.; Lee, E.-S. Acute Bilateral Vestibulopathy Associated With COVID-19. J. Clin. Neurol. 2022, 18, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martellucci, S.; Malara, P.; Pagliuca, G.; Castellucci, A. Lindsay-Hemenway Syndrome Involving the Horizontal Semicircular Canal: Some Considerations Upon Residual Canal Afferents in BPPV Secondary to an Ipsilateral Acute Unilateral Vestibulopathy. Otol. Neurotol. 2025, 46, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacovino, D.A.; Zanotti, E.; Cherchi, M. The Spectrum of Acute Vestibular Neuropathy through Modern Vestibular Testing: A Descriptive Analysis. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2021, 6, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strupp, M.; Kim, J.-S.; Murofushi, T.; Straumann, D.; Jen, J.C.; Rosengren, S.M.; Della Santina, C.C.; Kingma, H. Bilateral Vestibulopathy: Diagnostic Criteria Consensus Document of the Classification Committee of the Bárány Society. J. Vestib. Res. 2017, 27, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Bhat, J.S.; Sequeira, N.M.; Bhojwani, K.M. Ageing Effect on Air-Conducted Ocular Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential. Audiol. Res. 2015, 5, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comacchio, F.; Biancoli, E.; Poletto, E.; Bellemo, B.; Magnavita, P. Scientific Poster: “Neuropatia Vestibolare Bilaterale Acuta in Seguito ad Infarto del Miocardio: Un Case Report”. In Proceedings of the 111th National Congress of the Italian Society of Otorhinolaryngology (S.I.O.), Padova, Italy, 28–31 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).