Abstract
The recent rise in radiographic and photographic technology in the examination and interpretation of works of art—which has accompanied the digitization of artistic creativity in the contemporary world—has greatly enhanced the power of the naked eye to view and understand the masterpieces of the past. Through modern ‘digital telescopes’ a new breed of art scientists has emerged to both enhance and challenge traditional art scholarship. In this paper, I will first review some of the major projects in this new field of informational aesthetics and provide examples, from the impressive discoveries of Maurizio Seracini and Pascal Cotte, to the magnificent photographic examination of the Ghent Altarpiece by Van der Snickt and his team at the National Gallery of Art in Washington. Secondly, I will present the results of my own three-year exploration of Leonardo da Vinci’s extant paintings and drawings using photographic magnification, leading to the identification of recurrent autographic images and motifs only visible through the lens of a digital camera. Finally, I will discuss the implications of these studies in the philosophy of photography, the world of art and the future of digital humanism.
1. Introduction—The Restricted Gaze of the Real-World Viewer
What is the relationship between information and the creation, understanding and evaluation of the phenomenon we call art? For many centuries, observers of works of fine art have been allowed limited information about the works themselves. For the common man, the viewing of masterpieces has been restricted by the rulers of society—the kings aristocrats, oligarchs and Church officials—to gazing from a distance. The beholder’s role in the aesthetic experience has historically been to accept the values given to a work by the experts of the art world. Masterpieces were once hidden from the common gaze in monasteries, church recesses and the private collections of the wealthy, or displayed at a respectable distance in galleries and exhibitions. With the emergence of the Internet and the high-quality digital versions of artworks in online collections, which can be downloaded, magnified and explored by everybody, art scholarship is becoming more of an evidence-based science than an anecdotal game based on subjective opinion.
2. The Pioneers of Art Science and Digital Aesthetics
In recent decades, we have witnessed the emergence of high-powered radiographic and photographic technologies for the examination and diagnosis of artworks, such as those developed by Pascal Cotte in his Lumière (L.A.M.) projects (for example, the digital restoration of the Mona Lisa, and his multispectral analyses of The Lady with the Ermine and La Bella Principessa) [1,2]; by Maurizio Seracini in his wonderful radiographic examinations of The Adoration of the Magi and the Battle of Anghiari [3]; the terahertz imaging (THz) work on Goya’s 1771 Sacrifice of Vesta by Cristina Seco-Martorell and her colleagues in Barcelona [4]; and the magnificent project from the University of Antwerp and the NGA using macro X-ray fluorescence (MA-XRF) imaging on the Ghent Altarpiece [5]. Since the 1980s—which saw the Camera Lucida (La Chambre Claire) by Roland Barthes, in which he explored the ‘spectrum’ or the beholder’s share of the viewer of photographs, and Vilem Flusser’s Towards a Philosophy of Photography [6,7], which examined the apparatus of the ‘black box’ and its role in digital humanization—there have been several contributors to this new field. Hans Belting’s marvelous explorations of the iconic image throughout history [8] as well as the growth of digital aesthetics [9,10] and metaphotography [11], have provided us with a framework for understanding a world that is dominated by a constant tsunami of invading photographic and cinematic messages, delivered via the ubiquitous media and social networks of our age.
3. The Rise of Digital Art and NFTs
With the emergence of the Internet and the high-quality digital versions of masterpieces in online collections—which can be downloaded, magnified and explored by everybody—art scholarship is becoming more of an evidence-based science than an anecdotal game based on subjective opinion and professional credence.
In the art world itself, aesthetic GIFs and JPEGs are selling for extraordinary prices. Beeple’s digital collage, Everydays: The First 5000 Days, sold recently at Christie’s for USD 69 million as an NFT (Non-Fungible Token). Art has literally become a currency in the Digital Age. Masterpieces are now merely electronic collectibles.
4. Digital Archaeology—Uncovering the Hidden Worlds of Leonardo da Vinci
A genuine Leonardo leaps out at the viewer by virtue of the sheer excellence and enchantment of the painting. Its entrancing quality entices you into hidden worlds scarcely visible to the naked eye. Only with the recent emergence of radiographic technologies are we able to fully see and explore the incredible complexity of his oeuvre. In a forthcoming publication, The Hidden Worlds of Leonardo da Vinci, I have developed an evidence-based protocol (LISA or Leonardo Iconographic Scale of Authentication) based on macrophotographic analyses of his extant paintings, drawings and codices. These observations reveal the presence of dates, a recurring monogram (two lion heads joined by a V-shaped line) and a camouflaged autograph. If verified over time by the art community these features will greatly help art historians and scholars to better place Leonardo’s works in their biographical and historical contexts. They would offer us a chronological guide, his personal Baedeker, leading us through the magnificent landscapes and personages of his world.
Is it possible that we have, so far, merely scratched the surface of his creative genius? (see Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 below).
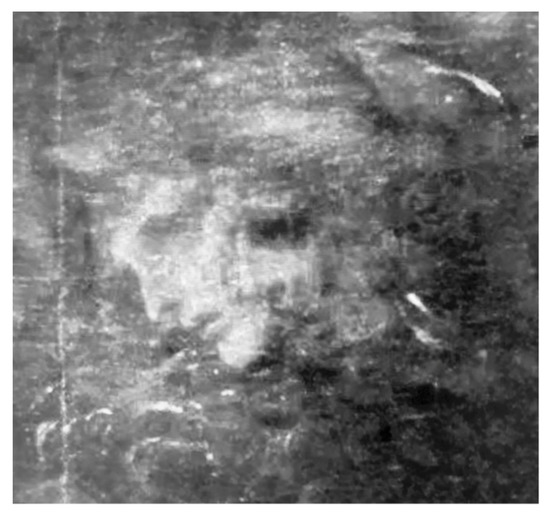
Figure 1.
The hidden image of Dante wearing his laurel wreath and young Leonardo as Virgil emerging from the Dark Wood of the Inferno in the background of The Adoration of the Magi. The shadow over Dante’s eye becomes the cave entrance to the City of Woe and its damned inhabitants. Behind them is the Beast. In green cyphers the disguised date 1482 can be discerned.
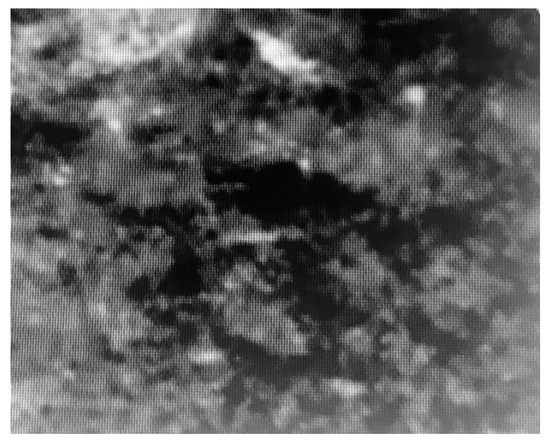
Figure 2.
The date 1482 below the portrait of Dante in Leonardo’s Adoration of the Magi.

Figure 3.
In the background landscape of the Mona Lisa, these giant hands appear to rescue the citizens of Florence in the great flood of 1333, which killed over 3000 people. However, looking more closely, we discover that the hands belong to some infernal Moloch who is about to devour the survivors. Floating corpses and skeletons and the top of the submerged Torre d’Arnolfo are visible in the water below the hands.
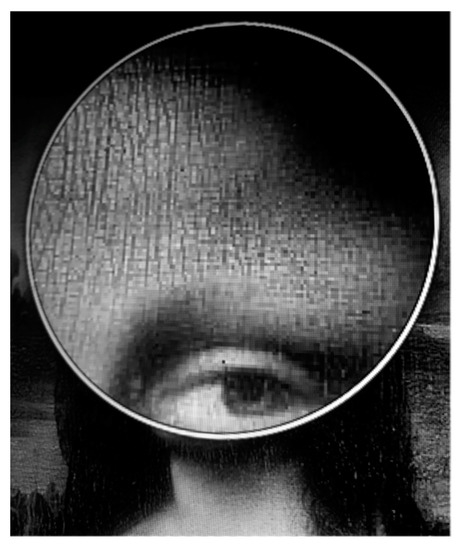

Figure 4.
Close up of Mona Lisa’s forehead.
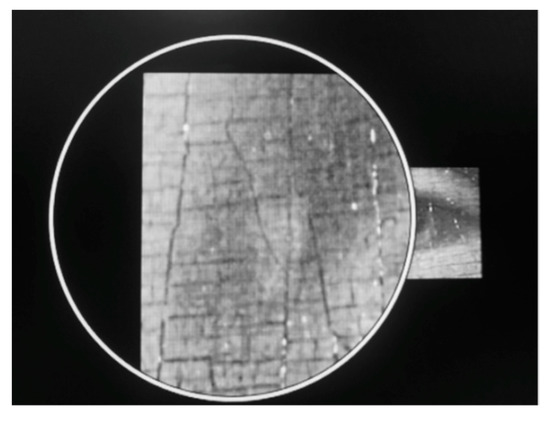
Figure 5.
Mona Lisa’s beauty spot under the magnifying glass.
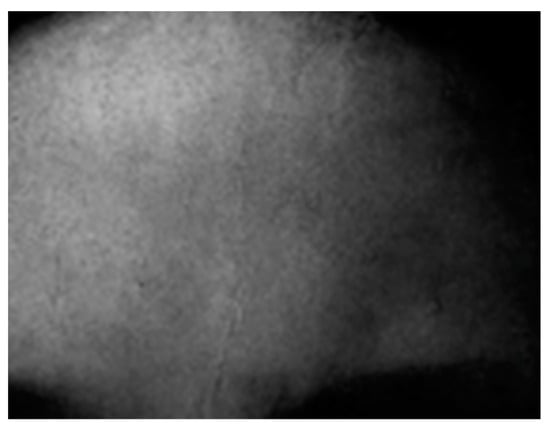
Figure 6.
The date 1489 is visible across the forehead of the controversial Salvator Mundi.
After five hundred years, Mona Lisa finally reveals her age. With the aid of macrophotography the year 1498 can be seen across her forehead. If the Mona Lisa is dated 1498 and painted by Leonardo in Milan, can the original sitter really be Lisa Gherardini?
This autographic marker might indicate that the work is a genuine Leonardo. The recurring hidden monogram with two lion heads joined by a V-shaped line is also present.
5. Conclusions
Digital Aesthetics represents a bold new chapter in the Philosophy of Information, and the exciting investigations and projects in the art world that I have adumbrated here are being matched by the increasing presence of Digital Art, as well as the emerging theoretical and philosophical discussions around the nature and role of photography in society. Information, as Einstein once said about imagination, can take us everywhere—even into the undiscovered corners of Renaissance art.
Since the birth of PI in the 1990s, we have witnessed many fruitful forks in the road, from Floridi’s info-computationalism, to Capurro’s Informational Intercultural Ethics and Wu’s multi-faceted Information Society. My summary of the fledgling study of Informational Aesthetics may open another pathway for us.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Cotte, P. Lumière on the Lady with an Ermine. Unprecedented Discoveries; Vinci Editions: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cotte, P. Lumière on the Mona Lisa: Hidden Portraits; Vinci Editions: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guidi, G.; Atzeni, C.; Seracini, M.; Lazari, S. Painting Survey by 3D Optical Scanning-the case of Adoration of the Magi by Leonardo da Vinci. Stud. Conversat. 2004, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Seco, C.; López, V.; Arauz, G.; Redo, A.; Palacios, J.; Tejada, J. Goya’s Artwork Imaging with Terahertz Waves. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1305.3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Snickt, G.; Dooley, K.A.; Sanyov, J. Dual mode standoff imaging spectroscopy documents the painting process of the Lamb of God in the Ghent Altarpiece by J. and H. Van Eyck. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flusser, V. Towards a Philosophy of Photography; Reaktion Books: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Truscot Smith, C. “The Lens is to Blame”: Three Remarks on Black Boxes, Digital Humanities, and The Necessities of Vilém Flusser’s “New Humanism”. Flusser Stud. Multiling. J. Cult. Media Theory 2014, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Belting, H. Art History after Modernism; Chicago Books: Chicago IL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Capurro, R. Homo Digitalis. Beiträge zur Ontologie, Anthropologie und Ethik der digitalen Technik; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fazi, B. Digital aesthetics: The discrete and the continuous. Theory Cult. Soc. 2019, 36, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, D. Introduction to Meta-Photography: A Self-Reflexive and Self-Critical Mirror for Photography in Digital Culture. Master’s Thesis, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).