Abstract
The present study was conducted to test for in vivo Brine Shrimp Lethality Assay (BSLA) of the Aqueous and ethanolic extracts Annona reticulate Linn. and Allium sativumand correlate cytotoxicity results with known pharmacological activities of the plants. Cytotoxicity was evaluated in terms of LC50 (lethality concentration). Ten nauplii were added into three replicates of each concentration of the plant extract. After 24 h the surviving brine shrimp larvae were counted and LC50 was assessed. Results showed that the presence of alkaloids, tannins, and flavonoids could be accounted for its cytotoxic properties. In the other hand, studies have shown that the leaf extracts of Alcoholic and aqueous extract of Annona reticulata and bulbs of Allium sativum extracts exhibited cumulative activity when they were combined and compared. Thus, the results on the leaf extracts of Alcoholic and aqueous extract of Annona reticulata and bulbs of Allium sativum exhibited increase in activity support its use in traditional medicine.
1. Introduction
The crushed leaves of A. reticulata are used as poultice on boils, ulcers and abscesses and leaf decoction is used as vermifuge. The tree is not especially attractive. It is erect, with a rounded or spreading crown and trunk 10 to 14 in (25–35 cm) thick. Height ranges from 15 to 35 ft (4.5–10 m). The ill-smelling leaves are deciduous, alternate, oblong or narrow-lanceolate, 4 to 8 in (10–20 cm) long, 3/4 to 2 in (2–5 cm) wide, with conspicuous veins.
Free radicals have been accused of initiating many serious diseases [1,2,3]. These free radicals drive oxidative stress and transform the pathophysiological condition of the patient by acting on immune system. It has been known that phenolic and flavonoid compounds of the plant extracts are responsible for antioxidant and antibacterial effects [4,5,6].
Taking all the above concerns into account, we conducted this study to find out more about A. reticulata leaves. We studied the antioxidant effects with presence of such phytochemical constituents as equivalent to standards in different extracts, the cytotoxic effect, and hence antitumor effect.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
The leaves of A. reticulata and Allium sativum (bulbs) were collected from regions of Karjat Dist-Raigad, Maharashtra, India in December 2018. Plant materials were authenticated at “The Blatter Herbarium”—St. Xavier’s College, Mumbai.
After identification and authentication of the plant, leaves of the plant were collected for the experimental process. The leaves were shade dried, made into coarse powder and the powdered material was initially defatted with petroleum ether and then subjected to cold maceration process for 72-h using 1:1 mixture of methanol and water as solvent to prepare hydro-alcoholic extract of Annona reticulata leave (percentage yield 20.5% w/w with respect to dried powder). The extract was filtered and concentrated by rotary evaporator. For the preparation of different fractions method was used [7,8,9].
The sun dried and powdered leaves (76 g) of A. reticulata were successively extracted in a Soxhlet extractor at elevated temperature using 200 mL of distilled n-hexane (40–60) °C which was followed by petroleum ether, methanol, and chloroform. All extracts were filtered individually through filter paper and poured on petri dishes to evaporate the liquid solvents from the extract to get dry extracts. The dry crude extracts were weighed and stored in air-tight container with necessary markings for identification and kept in a refrigerator for future investigations.
2.2. Brine Shrimp Lethality Bioassay
The extracts, fractions and pure isolated compounds were routinely evaluated in a test for lethality to brine shrimp larvae. Toxicities of compounds were tested at 1, 10, 100 and 1000 ppm in 10 mL sea-water solutions with 1% DMSO (v/v). Ten, nauplii were used in each test and survivors counted after 24 h. Three replications were used for each concentration. The blank control is conducted with Distilled water. The lethal concentration for 50% mortality after 24 h of exposure, the chronic LC50 was determined using the probit method, as the measure of toxicity of the extract or fractions. LC50 values greater than 1000 ppm for plant extracts were considered inactive.
The brine shrimp lethality assay (BSLA) is a simple and inexpensive bioassay used for testing the efficacy of phytochemical present in the plant extracts. The present study determined that the extent of lethality was directly proportional to the concentration of the extract. After 24 h of observation all the shrimp were survived in the control. Even though, maximum mortalities were observed upto a concentration of 1000 μg/mL and least mortality at 1 μg/mL concentrations. It was observed that in higher concentration of treatment extracts, the shrimps were start dying only after 8 h and after 24 h all the shrimps died. The lethality concentration (LC50) was calculated by using probit analysis (Table 1). The LC50 (median lethal concentration) values were calculated by using the regression line obtained by plotting the concentration against the death percentage on a probit scale.
2.3. Significance of Brine Shrimp Lethality Assay of the Plant
The evolution of the toxic action of plant extracts is indispensable to consider a treatment safe; it enables the definition of the intrinsic toxicity of the plant, and the effects of acute overdose [10], a cheap and general bioassay that appears capable of detecting a spectrum of bioactivity present in crude extract is the brine shrimp lethality test. The lethality of the test sample in a simple zoological organism like the brine shrimp (Artemia salina) has been utilised by many researchers and has proven to be a useful tool in screening various chemical compounds found in various bioactivities. In this study, it was observed combined aqueous and alcoholic fractions of Annona reticulate and Allium sativum extract exhibited the highest brine shrimp cytotoxic activity.
The combined aqueous and alcoholic fractions of leaves of Annona reticulate and bulbs extracts of Allium sativum exhibited a concentration-dependent cytotoxic activity in brine shrimp and is considered containing active or potent components, brine shrimp lethality assay is inadequate in determining the mechanism of action of the bioactive substances in the plant, but it is useful in providing a preliminary screen that can be supported by a more specific bioassay, once the active compound has been isolated [11,12,13,14].

Table 1.
% Mortality of shrimp nauplii after treating with Alcoholic and aqueous extract of Annona reticulate and Allium sativum.
Table 1.
% Mortality of shrimp nauplii after treating with Alcoholic and aqueous extract of Annona reticulate and Allium sativum.
| Plant Methanolic Extracts | Concentration (ppm or μg/mL) | Number of Surviving Nauplii (after 24 h) | Total Number of Nauplii Survivors | % Mortality | LC50 (μg/mL) | Graph | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | ||||||
| Control (Distilled water) | 1 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 29 | 96% | 372.846 | Figure 1 |
| 10 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 29 | 96% | |||
| 100 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 28 | 93% | |||
| 1000 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 100% | |||
| Standard (Vincristine sulphate) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | 0.00 | ----- |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | |||
| 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | |||
| 1000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | |||
| Annona reticulata (Alcoholic) | 1 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 0% | 24.162 | Figure 2 |
| 10 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 22 | 73% | |||
| 100 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 27% | |||
| 1000 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3.3% | |||
| Annona reticulata (Aqueous) | 1 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 0% | 18.923 | Figure 3 |
| 10 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 20 | 66.6% | |||
| 100 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 33.3% | |||
| 1000 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3.3% | |||
| Allium sativum (Alcoholic) | 1 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 19 | 37% | 10.840 | Figure 4 |
| 10 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 11 | 63% | |||
| 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | |||
| 1000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | |||
| Allium sativum (Aqueous) | 1 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 21 | 70% | 8.180 | Figure 5 |
| 10 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 13.3% | |||
| 100 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 6.6% | |||
| 1000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | |||
| Annona reticulate and Allium sativum (1:1) Alcoholic extracts | 1 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 12 | 40% | 129.257 | Figure 6 |
| 10 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 17 | 56.6% | |||
| 100 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 13.3% | |||
| 1000 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0.03% | |||
| Annona reticulate and Allium sativum (1:1) Aqueous extracts | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 12 | 40 | 93.482 | Figure 7 |
| 10 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 14 | 46.6 | |||
| 100 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 16.6% | |||
| 1000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100% | |||
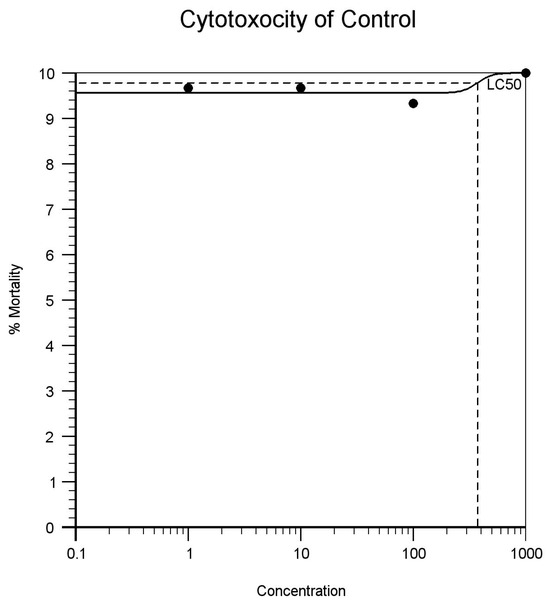
Figure 1.
Cytotoxicity of Control.
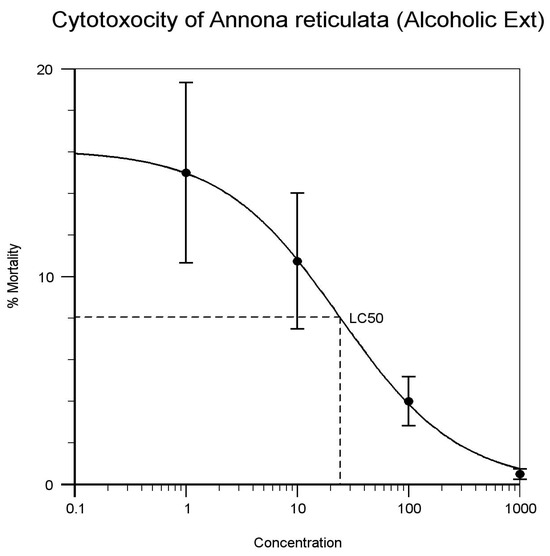
Figure 2.
Cytotoxicity of Annona reticulata. (Alcoholic Extract).
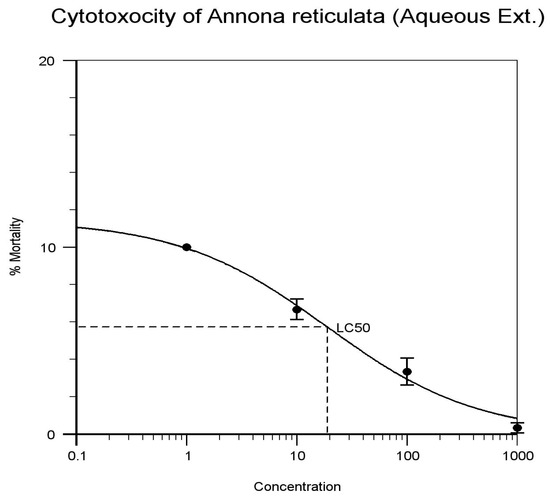
Figure 3.
Annona reticulata. (Aqueous Extract).
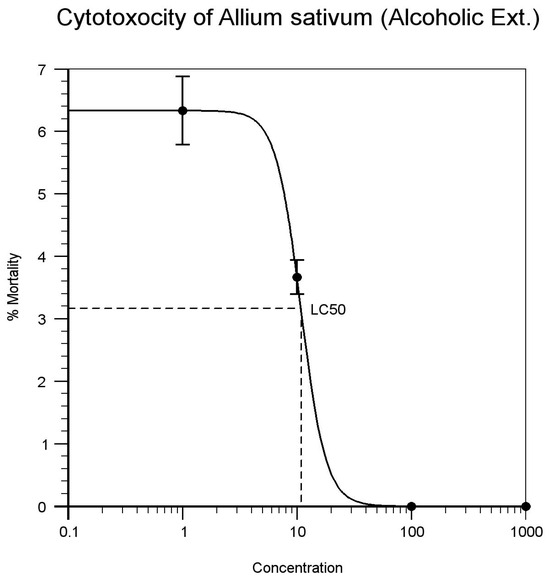
Figure 4.
Allium sativum. (Alcoholic extract).
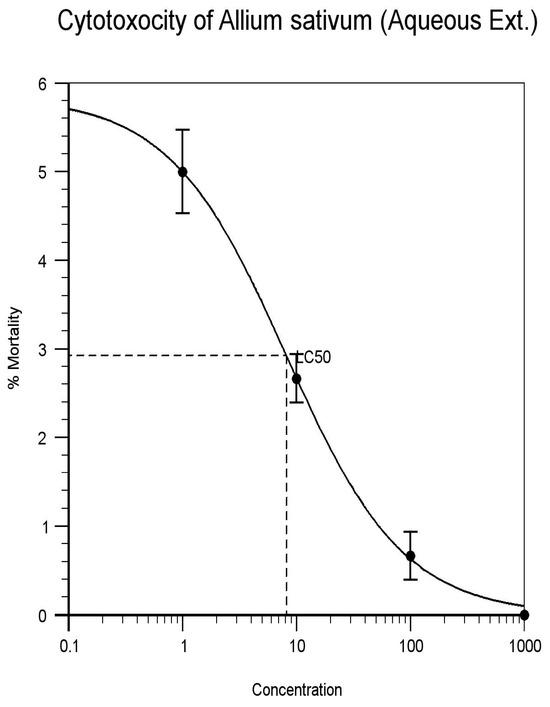
Figure 5.
Allium sativum. (Aqueous extract).
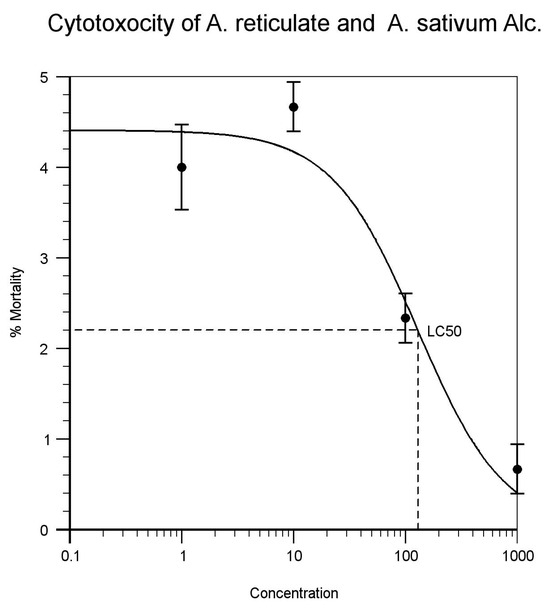
Figure 6.
Annona reticulate and Allium sativum (1:1). Alcoholic extracts.
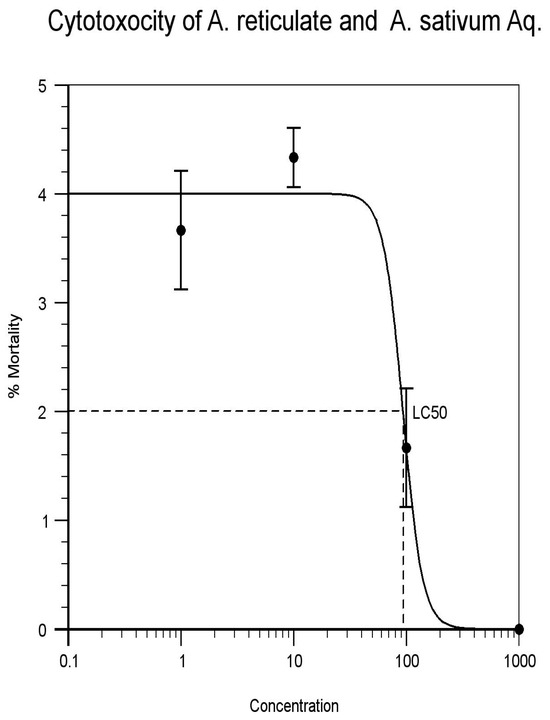
Figure 7.
Annona reticulate and Allium sativum (1:1). Aqueous extracts.
3. Result and Discussion
The result on the lethality of Alcoholic and aqueous extract of Annona reticulate on brine shrimps is in agreement with other studies where its LC50 values are 24.162 μg/mL and 18.923 μg/mL (as indicated in Figure 2 and Figure 3). Alcoholic and aqueous extract bulbs of Allium sativum recorded LC50 values of 10.840 and 8.180 mg/mL (as indicated in Figure 4 and Figure 5) against brine shrimps. The presence of alkaloids, tannins, and flavonoids could be accounted for its cytotoxic properties. In the other hand, studies have shown that the leaf extracts of Alcoholic and aqueous extract of Annona reticulata and bulbs of Allium sativum extracts exhibited cumulative activity when they were combined and compared. Thus, the leaf extracts of Alcoholic and aqueous extract of Annona reticulata and bulbs of Allium sativum exhibited increase in activity support its use in traditional medicine.
4. Conclusions
The leaf extracts of Alcoholic and aqueous extract of Annona reticulata and bulbs of Allium sativum exhibited cytotoxic activity against the brine shrimp and considered as containing active or potent components. This is because their LC50 values are less than 1000 ppm or μg/mL. Annona reticulate and Allium sativum (1:1) Alcoholic extracts shows LC50 values 129.257 μg/mL and Annona reticulate and allium sativum (1:1) Aqueous extracts shows LC50 values 93.482 μg/mL (as indicated in Figure 6 and Figure 7). The Alcoholic and aqueous extract of Annona reticulata and bulbs of Allium sativum when combined in (1:1) proportions, the higher LC50 values shows better cytotoxocity than single extracts. The ethnopharmacological activities of these plant species are due to the different bioactive compounds present in these plants. Although, BSLA is inadequate in determining the mechanism of action of the bioactive substances in the plant, it is very useful by providing a preliminary screen that can be supported by a more specific bioassay, once the active compound has been isolated. Thus, some useful drugs of therapeutic importance may develop out of the research work.
Acknowledgments
The present research work was thankful to Mohan kale, Principal, Bharat Tekade, HOD, Pharmacy Department and Amol Chadekar, HOD of the Pharmacology Department KGRDCP & RI, Karjat.
References
- Malorni, W.; Rivabene, R.; Lucia, B.M.; Ferrara, R.; Mazzone, A.M.; Cauda, R.; Paganelli, R. The role of oxidative imbalance in progression to AIDS effect of the thiol supplier N-acetyl cysteine. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1998, 14, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, A.; Meunier, B. Is alkylation the main mechanism of action of the antimalarial drug artemisinin? Chem. Soc. Rev. Artic. 1998, 27, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, PM. The need for new therapeutic agents: What is in the pipeline? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da-Silva, J.F.M.; De-Souza, M.C.; Matta, S.R.; De-Andrade, M.R.; Vidal, F.V.N. Correlation analysis between phenolic levels of Brazilianpropolisextracts and their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhenic, L.; Skerget, M.; Knez, Z. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of guarana seed extracts. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.A.; Oliveira, I.; Sousa, A.; Valentao, P.; Andrade, P.B. Walnut (Juglansregia L.) leaves: Phenolic compounds, antibacterial activity and antioxidant potential of different cultivars. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2287–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout Soumya, P.; Kar Durga, M.; Mohapatra Santosh, B.; Swain Sharada, P. Anti-hyperglycemic effect Annona reticulata L. Leaves on experimental diabetic rat model. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, S.P.; Kar, D.M. Identification of chemical compounds present in different fractions of Annona reticulata L. Leaf by using GC-MS. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1786–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rout, S.P.; Kar, D.M.; Maharana, L. Anti-Hyperglycemic Effect of different fractions of Annona Reticulata leaf. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 9, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padjama, R.; Arun, P.C.; Prashanth, D.; Deepak, M.; Amit, A.; Anajna, M. Brine shrimp lethality bioassay of Indian medicinal plants. Fitoterapia 2002, 73, 508–510. [Google Scholar]
- Abhilasha, S.; Kuntal, K. Analysis of phytochemical constituents and pharmacological properties of Abrus precatorius L. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2013, 4, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Adelowotan, O.; Aibinu, I.; Aednipekun, E.; Odugbemi, T. The in vitro antimicrobial activity of Abrus Precatorius (L) fabaceae extract on some clinical pathogens. Niger. Postgrad. Med. J. 2008, 15, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashith Kekuda, T.R.; Vinayaka, K.S.; Soumya, K.V.; Ashwini, S.K.; Kiran, R. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of methanolic extract of Abrus pulchellus wall and Abrus precatorius Linn-a comparative study. Int. J. Toxicol. Pharm. Res. 2010, 2, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Adedapo, A.A.; Omoloye, O.A.; Ohore, O.G. Studies on the toxicity of an aqueous extract of the leaves of Abrus precatorius in rats. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2007, 74, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).