Alkali-activated slag (AAS) based materials is one the alternative cementitious binders enabling to reduce CO2 footprint of concrete. In general, AAS concretes have good mechanical properties and excellent durability but suffer from very high drying shrinkage, which can be up to six times higher than observed in Portland cement based concretes. In this study, shrinkage and creep coefficient of alkali-activated high-MgO slag concretes were modelled using ACI-209R-92, GL2000 and CEB MC90-99 models. The predicted data were compared with actual measured values for laboratory cured high-MgO AAS concrete activated with 10 wt.% sodium silicate (Mix SS10), 10 wt.% sodium carbonate (Mix SC10) and a combination of both (Mix SC5+SS5). The results showed that the measured shrinkage values of SC-activated slag concrete were two times higher than predicted by the ACI 209R model, and about three times higher when SS- and (SC+SS) were used as alkali activators. The GL2000 model showed a relatively good prediction of the creep coefficient of SS-activated slag concrete, Figure 1. However, in the case of concretes activated with the (SC+SS) and SC the actual measured values were three to four times higher. The shrinkage of AAS concrete was strongly affected by curing conditions, activator type and dosage, chemical composition and fineness of the precursor. The study showed that existing models should be modified to account for all parameters specific for alkali activated systems.
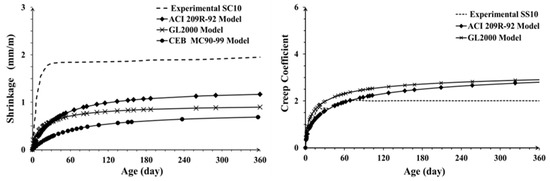
Figure 1.
The predicted shrinkage of mix SC10 (left) and the predicted creep coefficient of mix SS10 (right).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).