Despite the large strength of the coherent effects of particle deflection and radiation in crystals, all their applications are essentially limited by the incoherent scattering process. Though the difference of the latter from the scattering process in amorphous media was, in fact, envisaged by both the x-ray diffraction and coherent bremsstrahlung theories, the relational effect of multiple scattering reduction in crystals is scarcely known, has not been clearly observed, despite some attempts, and is usually missed in interpretation of the abundant experimental data. At the same time, this effect is presently important for the problems of particle deflection by long crystals, for both channeling and crystal undulator radiation, etc., and needs to be implemented in theory.
Since multiple scattering reduction arises in crystals due to correlations of particle collisions with the strings or plane atoms, it can be observed at any high energy in the wide angular regions. At the same time, this effect can be clearly observed only under the rear conditions of any coherent scattering effect complete suppression. To reveal the latter, we applied the quantum Born approximation theory, being also equivalent to the classical one in straight trajectory approximation, and found a particular conditions of 1 GeV particle incidence at the angles of 2 degree and 3 mrad with respect to the ‹001› axis and (110) plane of Si crystal, respectively, making possible to observe the multiple scattering reduction under the complete absence of coherent scattering, as Figure 1 illustrates.
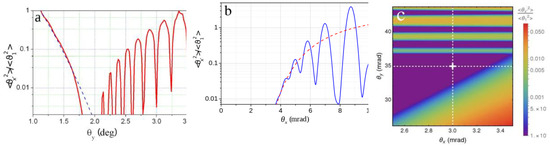
Figure 1.
Dependence of multiple scattering mean square angle on in incidence angle θy w.r.t. the Si ‹001› axis at θx = 3 mrad (a); on that of θx w.r.t. the Si (110) plane at θy = 34.9 mrad (2є) (b) and on both θx and θy (c), in units of ‹θ12›, corresponding to the maximum incoherent scattering reduction.
To treat the effect of multiple scattering reduction in general case, one has to abandon Born approximation, preserving at the same time a quantum treatment of the particle scattering by separate crystal atoms. Applying the Wigner function approach, we introduced accordingly some new quantum incoherent particle scattering treatment, applicable on a classical trajectory [1].
Reference
- Tikhomirov, V.V. Quantum features of high energy particle incoherent scattering in crystals. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 2019, 22, 054501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).