Abstract
We report the presence of an asymmetry that arises when considering the performances of quantum communication channels whose outputs are connected via a rigid, distance-preserving, yet not completely-positive, transformation. From a classical perspective these transmission lines should exhibit the same communication efficiency which is lost in the quantum setting.
1. Introduction
Quantum information theory often relies on harnessing effects which are counterintuitive with respect to the classical intuition to produce technological applications. One such effect arises when trying to communicate a chosen direction to a distant party. Indeed it turns out that, if we encode the directional information on the state of two quantum spin systems, such direction can be more efficiently estimated when using antiparallel spins rather than parallel ones [1]. The presence of similar asymmetries was recently reported in Ref. [2] in the broader context of classical communication on noisy quantum channels [3] by introducing the notion of reciprocal quantum maps. A reciprocal pair of quantum channels are two communication lines and acting on the same system which admit a rigid, distance-preserving, yet not completely-positive transformation that allows one to reproduce the outcome of the first from the corresponding outcome of the second, i.e.,
the symbol “∘” representing super-operator composition. From a classical perspective these transmission lines should exhibit the same communication efficiency as the relative distance between different output states are exactly the same for the two mappings. This is no longer the case in the quantum setting where explicit asymmetric behaviours can be found. In the following we report a special instance of this effect that one can observe when analyzing the case of depolarizing channels [4].
2. Results
A depolarizing quantum channel is a completely-positive transformation which, acting on a quantum system S of dimension d, transforms its density matrices into the output states
with a real parameter that characterizes the level of noise introduced by the map, and with I being the identity operator on the Hilbert space of S [4]. Complete-positivity forces to only take values in the interval , the lower threshold being the negative quantity
This set of maps have been extensively studied. In particular their associated classical and entanglement assisted capacities [3] have been explicitly computed, resulting in the following analytical expressions [4]:
with being the minimum von Neumann entropy attainable at the output of the channel, i.e., the quantity
As also evident from Figure 1, the functions (4) and (5) exhibit a non-symmetric behaviour with respect to sign inversion of noise parameter in the domain where this is allowed, i.e., for . In particular given we have
with the only exception of for which Equation (8) still holds but (7) is replaced with an identity (the function being even in the domain ).
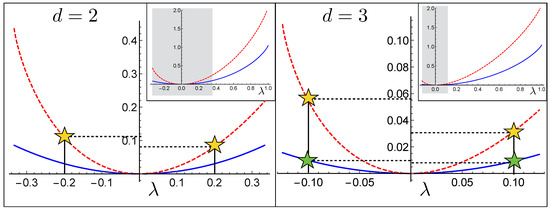
Figure 1.
Plots of the classical capacity of Equation (4) and entanglement assisted classical capacity of Equation (5) as a function of the noise parameter belonging to the interval of interest , for (left panel) and (right panel). Notice the asymmetric behaviour of and (the classical capacity instead is symmetric). The insets show the capacity for the full range of . All the curves have being rescaled by .
It turns out that this is exactly the kind of example we are looking for. Indeed given , the channels and represent an instance of reciprocal pairs, connected as in Equation (1) via the linear transformation
with representing the identity channel, i.e., . Equation (9) is not completely positive, but as required by our definition, it acts as a rigid transformation which preserve the relative distance between states, i.e.,
for all and , and for all suitable norm (e.g., the trace-class norm).
References
- Gisin, N.; Popescu, S. Spin Flips and Quantum Information for Antiparallel Spins. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, M.; Giovannetti, V. Asymmetric information capacities of reciprocal pairs of quantum channels. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 052318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holevo, A.S. Quantum Systems, Channels, Information: A Mathematical Introduction; De Gruyter Studies in Mathematical Physics; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- King, C. The capacity of the quantum depolarizing channel. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2003, 49, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).