Abstract
Eelgrass (Zostera marina) loss occurs worldwide due to increasing water temperatures and decreasing water quality. In the U.S., widgeongrass (Ruppia maritima), a more heat-tolerant seagrass species, is replacing eelgrass in certain areas. Seagrasses enhance sediment denitrification, which helps to mitigate excess nitrogen in coastal systems. Widgeongrass and eelgrass have different characteristics, which may affect sediment nitrogen cycling. We compared net N2 fluxes from vegetated areas (eelgrass and widgeongrass beds, using intact cores that included sediment and plants) and adjacent unvegetated areas from the York River, in the lower Chesapeake Bay during the spring and summer of one year. We found that seagrass biomass, sediment organic matter, and NH4+ fluxes were significantly higher in eelgrass beds than in widgeongrass beds. Eelgrass was also net denitrifying during both seasons, while widgeongrass was only net denitrifying in the summer. Despite differences in the spring, the seagrass beds had a similar rate of N2 production in the summer and both had higher denitrification rates than unvegetated sediments. Both species are important ecosystem components that can help to mitigate eutrophication in coastal areas. However, as the relative composition of these species continues to change, differences in sediment nitrogen cycling may affect regional denitrification capacity.
1. Introduction
Climate change has modified estuarine and marine ecosystems, particularly in the distribution patterns of various species [1,2,3]. In some instances, these shifts or losses have been accompanied by emergence of other, more opportunistic species with a higher tolerance for changing conditions [4,5]. Worldwide, seagrass distribution and abundance have been affected by these changing conditions [6,7]. Temperature changes and declining water quality have led to a loss of some seagrass species and replacement by others [7,8,9,10]. Seagrass species differ in morphology, physiology, shoot density, and seasonality [11,12]. These traits influence carbon storage, sediment trapping, and habitat quality [13,14,15]. Given the different traits, it is likely that changes or shifts in species will influence the ecosystem services and functions provided by seagrasses.
The seagrass Zostera marina (eelgrass) is a dominant primary producer and key foundation species in the north Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, Mediterranean Ocean, and Black Sea [11]. Eelgrass beds provide valuable ecosystem services such as water quality improvement and habitat for fishes and crustaceans [16,17]. Despite its ecological and economic importance, eelgrass has been virtually eradicated in several areas along the east coast of the U.S. [18,19]. In the lower Chesapeake Bay area, eelgrass has declined by 64% during the last three decades, due to reduced light availability and physiological stress [10,20]. This is particularly troubling because Chesapeake Bay is close to the southern limits for the optimum temperature range of eelgrass, making its populations less likely to recover, even if robust management actions are taken to improve water quality [10].
With expected changes in light and temperature in the Chesapeake Bay region, eelgrass may be replaced by widgeongrass (Ruppia maritima) in certain areas [9,18,20,21]. Widgeongrass and eelgrass co-occur but their physiologies differ; widgeongrass is more tolerant of higher temperature conditions than eelgrass [22], but may also require more light [23]. In the Chesapeake Bay, eelgrass is typically larger than widgeongrass, with a taller canopy, deeper roots, and greater above- and below-ground biomass [13,24]. Additionally, in this region, eelgrass typically reaches its greatest growth rates and biomass in the spring (May–June), while widgeongrass growth and biomass are highest in the summer (August–September) [23]. These physical and seasonal differences suggest that the two seagrasses may not provide the same ecosystem functions or services. For example, widgeongrass can be less valuable for fauna than eelgrass [15,25]. Yet, knowledge of how other services vary between these two species remains unknown.
Seagrass beds provide an important ecosystem service by effectively processing and removing nitrogen through denitrification [26,27,28]. Denitrification involves the microbial conversion of bioavailable nitrogen (as nitrate) into N2 gas. Denitrification can occur when nitrate (the terminal electron acceptor) is available and when there is an ample supply of carbon. Since facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denitrification, oxygen conditions should be low. Denitrification is vital in mitigating excess nutrients in coastal areas like the Chesapeake Bay, where eutrophication is a concern, because it effectively removes nitrogen from the bioavailable pool. Numerous studies have demonstrated higher denitrification rates in seagrass sediments than in unvegetated sediments [29,30,31,32], including via eelgrass restoration efforts [16]. Denitrification rates in seagrass habitats are often driven by high rates of respiration, which increase the supply of ammonium (NH4+) for coupled nitrification–denitrification processes [33]. Additionally, seagrasses enhance denitrification by trapping organic material [34]. The accumulation of organic material on the sediments and subsequent decomposition modifies redox gradients and creates conditions favorable for denitrification. This deposition of organic material, including seagrass biomass, mediates changes that can also influence sediment oxygen demand and the flux of dissolved inorganic nitrogen back to the water column through decomposition [27].
While seagrass beds have been recognized as ‘hotspots’ for denitrification [35]; additional nitrogen processing occurs in seagrass beds. For instance, seagrass assimilates ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3−), limiting the N available for use by fast-growing algae, until seagrass tissue degrades [36]. Ammonium is the preferred source of inorganic N for these plants and, during the day, it is rapidly consumed [37,38]. This N uptake can occur through roots or leaves [36] and can vary seasonally and by species [39]. N-fixation can also supply N to meet nutritional requirements during growth [40]. In some regions, N-fixation can account for 5 to 12% of seagrasses’ annual N requirements [41,42]. Given the importance of N-fixation for seagrasses, it is unsurprising that N-fixation can be higher than denitrification in seagrasses, affecting whether seagrasses are a source or sink of N [43].
A variety of abiotic and biotic factors may shape whether seagrass meadows are net denitrifying or net nitrogen fixing. The differences in physical structure between seagrass species could modify resource availability to the sediment microbial community, affecting sediment N cycling. For instance, sediment denitrification could be enhanced by radial oxygen loss from seagrass roots, which increases the anoxic and oxic interfaces where coupled nitrification–denitrification occurs [44,45]. Eelgrass has a more complex root structure than widgeongrass, which may lead to more coupled nitrification–denitrification. Additionally, eelgrass has greater above-ground biomass, which may trap more fine material [13,38] and increase the supply of organic matter to the sediment microbial community. Widgeongrass is also more ephemeral than eelgrass and its presence is highly variable from year to year [38]. Due to these differences, widgeongrass and eelgrass likely have unique effects on sediment nitrogen cycling, and a shift in species distribution or dominance could, therefore, have ecosystem-level consequences.
We investigated the effects that eelgrass and widgeongrass have on sediment nitrogen cycling processes. We compared net N2 fluxes, sediment oxygen demand, and dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN; NH4+ + NOx) fluxes in vegetated sediments (collected from widgeongrass and eelgrass beds) to unvegetated sediments in the lower Chesapeake Bay. We hypothesized that eelgrass sediments would exhibit higher rates of denitrification than widgeongrass sediments, due to their deeper root structure, which may increase the amount of oxic and anoxic interfaces, and their greater above-ground biomass, which may trap more fine material and enhance the supply of organic matter to the sediment microbial community. We also expected eelgrass sediments to have more organic matter, which would also cause an increase in ammonium flux due to decomposition. We expected that both eelgrass and widgeongrass sediments would have higher rates of nitrogen cycling processes (nutrient and gas fluxes) compared to the unvegetated sediment. By examining net N2 fluxes from the different seagrass species in the spring and summer, we assessed whether widgeongrass can provide similar denitrification services to eelgrass. Given that eelgrass biomass is decreasing in the lower Chesapeake Bay region, these findings have implications for future management activities related to water quality and habitat restoration in the region.
2. Methods
Study site—The seagrass meadows located at Goodwin Island (37°13′1″ N, 76°23′19″ W) near the mouth of the York River, a tributary of the Chesapeake Bay, were selected for this study. Goodwin Island is located within the Chesapeake Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve, where Ruppia maritima (widgeongrass) and Zostera marina (eelgrass) populations have been monitored since 2004 [18]. The two seagrasses typically exhibit a zonation pattern, in which widgeongrass occupies the shallower areas nearshore and eelgrass occurs in deeper depths up to 75 cm, while both co-occur at intermediate depths [18]. Unvegetated areas also exist throughout seagrass meadows within this region. For this study, we selected seagrass and unvegetated areas that were a minimum of 300 m apart and at similar depths.
Field Sampling—To encompass the conditions found during each species’ seasonal growing periods, nitrogen cycling measurements were conducted during the spring (27 May) and summer (2 September) of 2014. Intact sediment cores were collected for continuous flow incubations. Acrylic cores (10 cm deep × 7 cm diameter) of intact water, seagrass plants, and sediments were haphazardly taken within monospecific stands of each seagrass species and in adjacent unvegetated areas. We collected three cores from each location in May and four cores in September. Approximately 170 L of seawater from the site were collected for use in the continuous flow incubations. Water column temperature, dissolved oxygen, and salinity at the time of core collection were measured with a handheld YSI 6600 (YSI Corporation, Yellow Springs, OH, USA). Samples were also collected for dissolved nutrients (described below).
Sediment Core Incubation—Intact vegetated and unvegetated cores and incubation seawater were transported, immediately after collection, to an environmental chamber at the Virginia Institute of Marine Science, Gloucester Point, Virginia, USA, which was set to the recorded in situ temperature (26.5 °C in spring and 27.1 °C in summer) at the sampling site for each sampling day. The cores were submerged in aerated site water in the chamber and were allowed to remain undisturbed overnight. The following morning, each core was sealed with a gas-tight lid equipped with an inflow and outflow port [27]. Unfiltered, aerated water was passed over the cores at a flow rate of 2–3 mL per minute for 18 h to establish steady-state. After that initial incubation period, samples were collected three times over the next 24 h. Dark conditions were maintained throughout the experiment, because preliminary experiments showed that photosynthesis-mediated bubble production at light levels representative of the study system would interfere with dissolved gas measurements [46]. The short-term dark incubations, with aerated water, were sufficient for plant metabolism and to prevent senescence. There are limitations to conducting incubations with photosynthetic organisms under dark conditions and we consider this limitation in the interpretation of the results.
Samples for DIN (dissolved inorganic nitrogen) species (NOx and NH4+) and dissolved gasses (O2, N2, and Ar) were collected in triplicate from each core’s outflow and an inflow line, which flowed directly to sample vials, three times after an initial 18 h acclimation. Water samples for dissolved gases were collected into 12 mL Labco Exetainer vials by slowly filling each from the bottom and allowing the sample to overflow by several volumes. Samples were preserved with 100 µL of saturated ZnCl2 solution and stored submerged in water below collection temperature until analysis for dissolved gasses on a membrane inlet mass spectrometer (MIMS) [47]. Concentrations of dissolved gasses (N2 and O2) from triplicate samples were determined using the ratio with dissolved Ar [47]. Water samples (25 mL) from the inflow and outline lines were collected for NOx and NH4+ analysis. Samples were immediately filtered through a 0.45 µm Whatman polyethersulfone (PES) filter and were frozen until analysis. The filtrate was analyzed with a Lachat Quick-Chem 8000 (Lachat Instruments, Milwaukee, WI, USA) automated ion analyzer. The detection limits for NOx and NH4+ were 0.20 and 0.36 μM, respectively.
At the end of the experiment, the upper 2 cm of sediment (measured from the sediment–water interface) from within each core was extruded from the core barrel. The sediment was dried and combusted for sediment organic matter (SOM) via loss on ignition [48]. We sampled the upper 2 cm of sediment to capture the surface sediments, which have reactive organic matter and abundant bacteria, but also reflect environmental conditions [49]. Seagrass material within each core was removed, lightly rinsed, separated into above- and below-ground material, and was dried in a 65 °C drying oven until a constant weight was reached. Plant biomass was scaled to grams dry weight (g DW) per m2.
Calculations—Fluxes for dissolved gases and nutrients were calculated as follows:
where [i_outflow] and [i_inflow] are the concentrations (µM) of dissolved constituents leaving and entering the core, respectively; F is the peristaltic pump flow rate (2–3 mL min−1); and A is the surface area of the core (m2). A positive flux indicates production to the water column, while a negative flux indicates demand from the water column [50]. This method does not distinguish between microbial and plant metabolism since roots and rhizomes were included in the core. This technique determines the net N2 flux such that a positive N2 flux indicates denitrification in excess of nitrogen fixation (net denitrification) and a negative flux indicates nitrogen fixation in excess of denitrification (net nitrogen fixation). This method does not discern between the sources of N2; therefore, net denitrification refers to production from both heterotrophic metabolism, anammox, and any other N2-producing processes occurring in excess of nitrogen fixation. Sediment oxygen demand was determined from the O2 fluxes. A negative O2 flux was considered a demand and was expressed as a positive value. The mean of successive flux measurements from each core was used to prevent pseudo-replication associated with sampling the same core over time.
J = ([i_outflow] − [i_inflow]) × F/A
Note that the core samples taken (plants and sediment, unvegetated included sediment only) are referred to as “habitats”, or individually as “eelgrass”, “widgeongrass”, or “unvegetated sediment” throughout this article.
Statistical Analysis—A two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to examine the effects of date (spring or summer) and habitat (eelgrass, widgeongrass, or unvegetated sediment) on nitrogen (NH4+, NOx, and N2) fluxes, oxygen demand, and organic matter. When the date-by-habitat interaction was insignificant, the main effect of habitat was considered and Tukey’s HSD post hoc tests were used to compare between habitats. When the habitat-by-date interaction was significant, a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey HSD post hoc test was used to compare differences between the habitats within a season. For all tests, data were log-transformed, when necessary, to meet the normality and homogeneity assumptions of ANOVA. All analyses were considered significant at the p < 0.05 level and all error estimates are reported as standard error. Statistical analyses were performed in R 4.3.3 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing 2024).
3. Results
Water characteristics and biomass—Discrete samples taken at the sampling site showed lower water temperature (26.5 °C compared to 27.1 °C) and salinity (15.8 compared to 19.3) in the spring compared to the summer (Table 1).

Table 1.
Conditions of site water used for the continuous flow incubations for each sampling event. Mean and standard error (n = 2) are included for dissolved oxygen (DO), NOx, and NH4+.
The eelgrass biomass was approximately three times greater in the spring and two times greater in the summer than that of widgeongrass. The widgeongrass biomass was relatively consistent between the spring and summer, whereas eelgrass biomass decreased by approximately half (Table 2). Above-ground biomass was not different between habitats (F1,10 = 3.12, p = 0.11) or seasons (F1,10 = 0.277, p = 0.610); the interaction was also not significant (F1,10 = 0.92, p = 0.36). Below-ground biomass was significantly higher for eelgrass than widgeongrass (F1,10 = 31.09, p < 0.001), but the interaction was not significant (F1,10 = 0.83, p = 0.38). Total biomass was not statistically different between seasons (F1,10 = 2.23, p = 0.16). However, eelgrass total biomass was significantly greater than widgeongrass biomass (F1,10 = 11.49, p = 0.001).

Table 2.
Mean and standard error of above-ground (AG), below-ground (BG), and total biomass (DW = dry weight), as well as sediment organic matter (SOM) percentage. Note there is no biomass for the unvegetated habitat. Sample size (n) indicates the number of cores used for the calculations.
Sediment characteristics—Sediment organic matter (SOM; Table 2) and sediment oxy gen demand (SOD; Table 3) were highest in eelgrass sediment and lowest in unvegetated sediment. SOD had a significant interaction between date and habitat (F2,15 = 11.025, p = 0.001). Eelgrass SOD was significantly greater than unvegetated sediment in both spring and summer (Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.02, p < 0.001, respectively), but widgeongrass SOD was only significantly higher than unvegetated sediment in the summer (Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.002). For eelgrass, SOD was significantly greater during the summer than the spring (p < 0.001). There was no significant interaction for SOM between date and habitat (F2,15 = 3.124, p = 0.29); eelgrass had significantly more SOM compared to widgeongrass (Tukey’s HSD, p < 0.001), which has significantly more SOM compared to unvegetated sediment (Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.003).

Table 3.
Mean and standard error of NOx, NH4+, and O2 fluxes. Oxygen fluxes are presented as sediment oxygen demand and are expressed as a positive flux to reflect the demand.
Nitrogen biogeochemistry—Eelgrass was net denitrifying (positive net N2 flux) during both spring and summer, while widgeongrass and unvegetated sediment switched from net N-fixing to net denitrifying from the spring to the summer (indicated by the change from a negative N2 flux to a positive N2 flux, Figure 1A). There was a significant interaction between habitat and season for N2 flux (F2,15 = 4.226, p = 0.035). Though eelgrass N2 production was significantly higher than that of unvegetated sediment (Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.032), and marginally higher that of widgeongrass (Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.093) during the spring, it was not different from widgeongrass sediments during the summer, when widgeongrass also had net positive N2 fluxes. During the summer, N2 production from both eelgrass and widgeongrass was significantly higher compared to unvegetated sediment (Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.002 for eelgrass, p = 0.001 for widgeongrass).
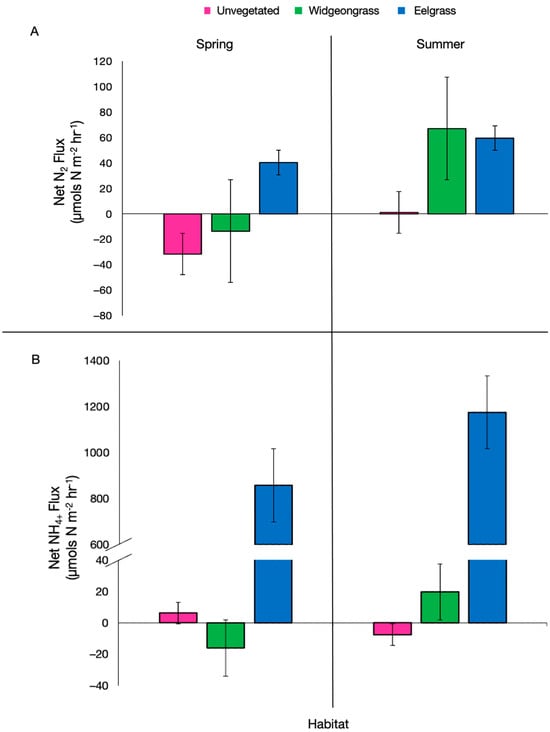
Figure 1.
(A) Net nitrogen gas (N2) and (B) net ammonium (NH4+) fluxes from unvegetated (bare), widgeongrass, and eelgrass vegetated sediment during the spring and summer sampling events, mean ± standard error.
NH4+ constituted the majority of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (NH4+, NOx) flux (70%, Table 2) and significance tests using only NH4+ versus DIN did not change these results, therefore we chose to focus on net NH4+ fluxes. The net NOx flux was not statistically different between seasons (F1,15 = 0.986, p = 0.33) or habitats (F1,15 = 1.25, p = 0.31) and there was weak evidence of an interaction (F1,15 = 2.66, p = 0.10). The net NH4+ flux was not statistically different between seasons (F1,15 = 0.101, p = 0.75); however, there was a significant effect of habitat (F2,15 = 3.871, p = 0.04). Eelgrass sediments produced significantly more NH4+ than that of either unvegetated (Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.04) or widgeongrass (Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.04, Figure 1B). Widgeongrass had a net negative NH4+ flux in the spring (indicating demand) but switched to NH4+ production in the summer. The production of NH4+ indicates more N recycling back to the water column during the dark experimental conditions here, which, in light conditions, the seagrass may have used.
4. Discussion
Though eelgrass has historically been abundant in the lower Chesapeake Bay, decreasing water clarity and warming temperatures have led to a steep decline in its populations, allowing for proliferation of widgeongrass in some areas that eelgrass previously occupied [9,10]. Given that these two seagrass species have differing characteristics, we aimed to understand how this shift could affect seagrass ecosystem services, specifically nitrogen removal. Our study revealed seasonal variation in denitrification (net N2 production) among the two seagrass species, as well as species differences in dissolved inorganic nitrogen fluxes. During the summer sampling, denitrification rates were similar in eelgrass and widgeongrass sediments, but in the spring, eelgrass was net denitrifying, while widgeongrass was nitrogen fixing. Consistent denitrification rates in eelgrass sediments across seasons suggest its potential for continuous N2 production, though the absence of winter or fall measurements limits our ability to determine annual denitrification rates. At a minimum, during certain times of the year, eelgrass loss and potential replacement with widgeongrass could result in a decline in seagrass-mediated nitrogen removal.
Like previous research findings, our study found that nearby seagrass vegetation increases organic matter and, consequently, denitrification in sediments [26,28,31,51]. Lower denitrification rates in the unvegetated sediments compared to the two vegetated sediment types suggest the importance of labile carbon for denitrification. Seagrasses are able to trap organic material in their canopies and deposit carbon (photosynthate) into the sediment via root exudates. Mineralization of the organic material produces ammonium, which, coupled with the oxygenated microzones in the roots, leads to increased nitrification. Although the incubation was conducted under dark conditions, plants are still able to transport oxygen to the sediments and maintain meristematic O2 levels [52,53]. The additional nitrate, labile carbon in the exudates, oxygen microzones in the sediment, and organic matter trapped by biomass could increase denitrification, relative to unvegetated areas. The unvegetated areas in our study had the lowest amount of organic matter of the three habitats, likely because of a lack of structure to trap particulate organic matter and no roots to decompose and release photosynthate.
The amount of vegetation is also likely to be important to organic matter availability. Seagrass canopies can trap particles, allowing for allochthonous material to accumulate [54]. They also add organic matter directly to sediments as seagrass biomass, although some of this material is likely exported out of the meadow [55,56]. Within each season sampled, eelgrass had 2–3 times the biomass and almost twice the sediment organic matter of widgeongrass. The greater organic matter and biomass associated with eelgrass may also explain the higher ammonium fluxes associated with the mineralization of this material. Because NH4+ is the preferred form of inorganic nitrogen for seagrasses, it would likely be rapidly consumed during light conditions [38]. Studies have shown that average water column DIN levels are lower in meadows of these seagrass communities than in shallow unvegetated areas [38,57,58], likely associated with uptake by seagrasses.
Although eelgrass consistently produced N2 during both seasons, widgeongrass was net denitrifying only in the summer and was a source of new nitrogen via nitrogen fixation in the spring. This could be because eelgrass beds remain established over the winter and still persist, come the spring [59], compared to widgeongrass, which typically loses much of its biomass over the winter [18,21]. In Chesapeake Bay, eelgrass can survive during cold, low-light winter months and experiences increased growth and biomass in the spring, peaks in early summer, and declines in the fall. In contrast, widgeongrass tends to die off in winter, have sparse coverage in the spring, and growth and biomass peak in the summer [18,21]. Seagrass bed stability and the presence of the more persistent species could be sustaining denitrification because of the consistent supply of resources to the sediment microbial community. This finding is consistent with findings from Florida, where carbon storage was higher with stable, persistent meadows [14].
Unlike eelgrass, widgeongrass shifted from nitrogen fixation in the spring to denitrification in the summer. This transition from net nitrogen-fixing to net denitrifying may be associated with the growing season, where the seagrass utilizes available nitrogen to support growth. A similar study showed mixed-species seagrass meadows in North Carolina, USA had net negative N2 fluxes in the spring growing season, followed by net denitrification in the summer [27], while a study in Shinnecock Bay, New York, USA also found the co-occurrence of denitrification and nitrogen fixation in eelgrass meadows [31]. We observed net nitrogen fixation and the associated uptake of ammonium for widgeongrass during the spring growing season. This shift is consistent with other studies including those from dwarf eelgrass (Zostera noltii) and have shown that plants not only depend on internal reserves and nitrogen fixation for nitrogen requirements, but also support denitrification [29]. Our results are in line with the literature that suggests that as seagrass is growing, additional nitrogen might be needed to meet its demands, resulting in the observed nitrogen fixation [29,60,61].
The similarity in summer net denitrification rates between the two species was unexpected, considering the smaller form (lower biomass) of widgeongrass and the lower amount of organic matter in its sediment (Table 2). We expected the nitrogen cycling responses to be related to density, which has been observed in other seagrass systems [62,63]. One possible explanation is the variation in sediment oxygen conditions. Jovanovic et al. [52] found higher oxygen loss per biomass unit in widgeongrass roots compared to eelgrass roots. This increased oxygenation of the sediments may provide fuel for coupled nitrification–denitrification processes. Alternatively, widgeongrass sediments might be more aerobic due to their larger grain size. A prior study, also conducted at Goodwin Island in the Chesapeake Bay, indicated that sediments in widgeongrass beds were coarser than sediments in nearby eelgrass beds, potentially because of the shorter canopy [13]. Coarse-grained sediments with higher oxygen penetration depths may exhibit higher nitrification rates, and an associated increase in nitrate availability will fuel denitrification. Sediment type and oxygen conditions can be key drivers for denitrification [64].
Net N2 fluxes, whether indicative of nitrogen fixation or dentification, were lower in our study compared to other studies. Studies associated with seagrasses in temperate regions report nitrogen fixation rates less than 20 μmol N m−2 h−1 [65] or up to 500 μmol N m−2 h−1 [66]. Net denitrification rates for temperate, tropical, and subtropical seagrass species on the US east coast and Gulf of Mexico can range from 50 to 500 μmol N m−2 h−1 [27,32]. Our highest net nitrogen fixation rates were around 20 μmol N m−2 h−1, while our highest net denitrification rates were around 60 μmol N m−2 h−1. The variation and large range in rates is due, in part, to the variety of methods used to measure these processes. In addition to the methods for measuring denitrification, our experimental approach may have affected rates. Our incubations were in the dark and contained seagrass biomass. These conditions may have suppressed nitrogen fixation, since higher nitrogen fixation rates can occur under illuminated conditions [41,60]. Dark conditions limit photosynthesis, and prolonged low light or dark conditions, excessively high temperatures, and other factors [53] can reduce oxygenated zones without the rhizosphere and access to exudates, which can change resources to the microbial community, leading to lower rates. However, our temporary dark conditions provided good comparative estimates of the steady-state fluxes associated with the seagrasses, as well as the sediment microbial community, but may not capture rates under highly stressed conditions. The dark incubations were used to prevent bubbles in the light that interfere with gas measurements. Studies have demonstrated that under high photosynthesis in the light, excess oxygen is produced through photosynthesis and is released into the water column [52,53]. In the dark, provided the water is well oxygenated (which was the case here), meristematic oxygen levels and those in the rhizosphere are not significantly reduced, as the oxygen diffuses from the overlying water through the plant, where some of it is used for respiration, and then diffuses out into the rhizosphere. This oxygen uptake would be captured in our oxygen demand.
Overall, eelgrass habitats exhibited the greatest biomass and the highest organic matter percentages, N2 fluxes, sediment oxygen demand, and NH4+ fluxes of the three habitats. This combination of results suggests that organic matter lability may be highest in eelgrass cores [33]. There are unique features of eelgrass (extensive root system, vast canopy, and the habitat it provides for other organisms) that help to supply the sediments with carbon and nitrogen that can support nitrogen cycling processes like denitrification. As a result, there may be a greater sediment oxygen demand in eelgrass beds. This demand can be associated with the plant metabolism and the processing of the organic matter, producing more NH4+, as a result of this decomposition [58].
N2 and NH4+ fluxes were both higher during the summer than in spring in all habitats, which could be a result of the buildup of organic matter on the surface and photosynthate and decomposing root material within sediments throughout the season [38,67]. These changes in organic matter sources would impact quality and may not be reflected in our SOM measurements, which are a measure of quantity. Previous studies have documented differences in decomposition rates between seagrasses species [67]. Only the eelgrass sediment cores produced a large net flux of NH4+ over the sampling period, yet the production rates were similar, although on the higher side, to other studies looking at eelgrass or turtlegrass [31,32]. While ammonium production is linked to organic matter loading, the increase could have been a result of high temperatures, root decomposition, and subsequent organic matter release. Seagrass meadows are associated with high rates of remineralization and ammonium production [58,68]. Long-term organic matter storage and reduced conditions may exist in the sediment, which would increase nitrogen recycling. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) has been observed in seagrass meadows globally [69] and in eelgrass meadows in Chesapeake Bay [28]. It is possible that with the high organic matter, reduced conditions (as indicated by the large SOD), and low supply of nitrate, DNRA was occurring and contributing to the NH4+ production in the eelgrass cores.
Our hypothesis that widgeongrass and eelgrass areas would exhibit higher net N2 fluxes than the unvegetated areas during both seasons was supported. Unvegetated areas had the lowest amount of organic matter of the three habitats, likely a function of no structure to trap particulate organic matter and no roots to decompose and release photosynthate, all factors that may limit nitrogen cycling [58,65]. Additionally, research shows fewer bioturbating animals live in unvegetated sediment compared to adjacent sediment [70] and, because bioturbation can both enhance denitrification [71] and heighten NH4+ flux when the animals die, this could also contribute to the low NH4+ and near-zero N2 fluxes seen in the unvegetated areas.
5. Conclusions
The finding that different seagrass species have differential effects on sediment nitrogen cycling, especially net denitrification rates, has important implications for the management and restoration of temperate coastal ecosystems. Widgeongrass, with its smaller form and quicker vegetative growth, may be adapted to rebound after stressful water quality or temperature events and may be more suited to survive in degraded conditions compared to eelgrass [9,18]. However, its effects on important aspects of nitrogen cycling differ from the eelgrass species it may replace in these important shallow water environments. As seagrass beds in Chesapeake Bay change in abundance and composition from climate and other anthropogenic changes, it is important to identify how these changes may trickle down to affect ecosystem functions and services [9]. The loss of a stable, persistent species and replacement by a more ephemeral and variable species may affect the nitrogen removal capacity of the ecosystem. Continuing to study how one seagrass species compares to another, in terms of ecosystem functions such as nitrogen removal, will help guide the direction of seagrass restoration and recovery efforts and water quality restoration efforts both locally and beyond.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.F. and A.R.S.; methodology, E.F., A.R.S. and K.A.M.; formal analysis, E.F., investigation, E.F., A.R.S. and K.A.M.; resources, A.R.S., L.K.R. and K.A.M.; data curation, E.F. and A.R.S.; writing—original draft preparation, E.F.; writing—review and editing, A.R.S., L.K.R. and K.A.M.; visualization, E.F.; supervision, A.R.S., L.K.R. and K.A.M.; project administration, A.R.S.; funding acquisition, A.R.S. and K.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the David H. Smith Conservation Research Postdoctoral Fellowship to A.R.S., funding from the Chesapeake Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve in Virginia, and from the Virginia Institute of Marine Science, School of Marine Science, College of William and Mary.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Erin Shields and Hunter Walker for field and laboratory assistance. Conversations with B.K. Song, A. Murphy, I. Anderson, A. Johnson, and J. Lefcheck greatly improved this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Poloczanska, E.S.; Burrows, M.T.; Brown, C.J.; García Molinos, J.C.; Halpern, B.S.; Ehoegh-Guldberg, O.; Kappel, C.V.; Moore, P.J.; Richardson, A.J.; Schoeman, D.S.; et al. Responses of Marine Organisms to Climate Change across Oceans. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinsky, M.L.; Selden, R.L.; Kitchel, Z.J. Climate-Driven Shifts in Marine Species Ranges: Scaling from Organisms to Communities. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2019, 12, 153–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.A.; Jarvis, J.C. Estuarine Seagrass and Climate Change. In Climate Change and Estuaries; Kennish, H., Paerl, J.C., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, Fl, USA, 2024; pp. 401–430. [Google Scholar]
- Vergés, A.; Steinberg, P.D.; Hay, M.E.; Poore, A.G.B.; Campbell, A.H.; Ballesteros, E.; Heck, K.L.; Booth, D.J.; Coleman, M.A.; Feary, D.A.; et al. The Tropicalization of Temperate Marine Ecosystems: Climate-Mediated Changes in Herbivory and Community Phase Shifts. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20140846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernberg, T.; Bennett, S.; Babcock, R.C.; de Bettignies, T.; Cure, K.; Depczynski, M.; Dufois, F.; Fromont, J.; Fulton, C.J.; Hovey, R.K.; et al. Climate-driven regime shift of a temperate marine ecosystem. Science 2016, 353, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, J.A.; Burkholder, D.A.; Heithaus, M.R.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Fraser, M.W.; Statton, J.; Kendrick, G.A. Extreme temperatures, foundation species, and abrupt ecosystem change: An example from an iconic seagrass ecosystem. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyndes, G.A.; Heck, K.L.; Vergés, A.; Harvey, E.S.; Kendrick, G.A.; Lavery, P.S.; McMahon, K.; Orth, R.J.; Pearce, A.; Vanderklift, M.; et al. Accelerating Tropicalization and the Transformation of Temperate Seagrass Meadows. BioScience 2016, 66, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waycott, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Olyarnik, S.; Calladine, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Hughes, A.R.; et al. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12377–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, M.J.S.; Patrick, C.J.; Orth, R.J.; Wilcox, D.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Gurbisz, C.; Hannam, M.P.; Landry, J.B.; Moore, K.A.; Murphy, R.R.; et al. Rise of Ruppia in Chesapeake Bay: Climate Change–Driven Turnover of Foundation Species Creates New Threats and Management Opportunities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2220678120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefcheck, J.S.; Wilcox, D.J.; Murphy, R.R.; Marion, S.R.; Orth, R.J. Multiple stressors threaten the imperiled coastal foundation species eelgrass (Zostera marina) in Chesapeake Bay, USA. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 3474–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.; Carruthers, T.; Dennison, W.; Waycott, M. Global seagrass distribution and diversity: A bioregional model. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 350, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilminster, K.; McMahon, K.; Waycott, M.; Kendrick, G.A.; Scanes, P.; McKenzie, L.; O’Brien, K.R.; Lyons, M.; Ferguson, A.; Maxwell, P.; et al. Unravelling complexity in seagrass systems for management: Australia as a microcosm. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 534, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, E.; Moore, K. Canopy Functions of R. maritima and Z. marina in the Chesapeake Bay. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 97–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijak, A.L.; Reynolds, L.K.; Smyth, A.R. Seagrass meadow stability and composition influence carbon storage. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 4419–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Duffy, J. Foundation species identity and trophic complexity affect experimental seagrass communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 556, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, L.R.; McGlathery, K.J.; Oreska, M.P.J. Seagrass restoration reestablishes the coastal nitrogen filter through enhanced burial. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Heck, K.L. Structural Components of Eelgrass (Zostera marina) Meadows in the Lower Chesapeake Bay: Fishes. Estuaries 1980, 3, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.A.; Shields, E.C.; Parrish, D.B. Impacts of Varying Estuarine Temperature and Light Conditions on Zostera marina (Eelgrass) and its Interactions with Ruppia maritima (Widgeongrass). Estuaries Coasts 2013, 37, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bologna, P.A.; Gibbons-Ohr, S.; Downes-Gastrich, M. Recovery of eelgrass (Zostera marina) after a major disturbance event in Little Egg Harbor, New Jersey, USA. Bull. N.J. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, J.; Lefcheck, J.; Orth, R. Warming temperatures alter the relative abundance and distribution of two co-occurring foundational seagrasses in Chesapeake Bay, USA. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 599, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, E.C.; Parrish, D.; Moore, K. Short-Term Temperature Stress Results in Seagrass Community Shift in a Temperate Estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.S.; Webb, K.L.; Penhale, P.A. Photosynthetic temperature acclimation in two coexisting seagrasses, Zostera marina L. and Ruppia maritima L. Aquat. Bot. 1986, 24, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.T.; Burdick, D.M.; Kaldy, J.E.; Iii, J.E.K. Mesocosm experiments quantify the effects of eutrophication on eelgrass, Zostera marina. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Moore, K.A. Distribution of Zostera marina L. and Ruppia maritima L. sensu lato along depth gradients in the lower Chesapeake Bay, U.S.A. Aquat. Bot. 1988, 32, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Calderon, J.; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R.; Rodríguez-Baron, J.M.; Carrión-Cortez, J.; Torre, J.; Meling-López, A.; Hinojosa-Arango, G.; Hernández-Carmona, G.; García-Hernández, J. Outstanding appearance of Ruppia maritima along Baja California Sur, México and its influence in trophic networks. Mar. Biodivers. 2010, 40, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, B.D.; Maher, D.; Oakes, J.M.; Erler, D.V.; Glasby, T.M. Differences in benthic metabolism, nutrient fluxes, and denitrification in Caulerpa taxifolia communities compared to uninvaded bare sediment and seagrass (Zostera capricorni) habitats. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2011, 56, 1737–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, A.R.; Thompson, S.P.; Siporin, K.N.; Gardner, W.S.; McCarthy, M.J.; Piehler, M.F. Assessing Nitrogen Dynamics Throughout the Estuarine Landscape. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 36, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, L.R.; McGlathery, K.J. Restoration enhances denitrification and DNRA in subsurface sediments of Zostera marina seagrass meadows. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 602, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, D.T.; Bartoli, M.; Nizzoli, D.; Castaldelli, G.; Riou, S.A.; Viaroli, P. Denitrification, nitrogen fixation, community primary productivity and inorganic-N and oxygen fluxes in an intertidal Zostera noltii meadow. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 208, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, B.; Ferguson, A. Comparison of carbon production and decomposition, benthic nutrient fluxes and denitrification in seagrass, phytoplankton, benthic microalgae- and macroalgae-dominated warm-temperate Australian lagoons. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 229, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnoch, C.B.; Hoellein, T.J.; Furman, B.T.; Peterson, B.J. Eelgrass meadows, Zostera marina (L.), facilitate the ecosystem service of nitrogen removal during simulated nutrient pulses in Shinnecock Bay, New York, USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.K.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Gardner, W.S.; Niewinski, D.N.; Gao, J.; Mutchler, T.R. Relative Contributions of DNRA and Denitrification to Nitrate Reduction in Thalassia testudinum Seagrass Beds in Coastal Florida (USA). Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, B.D.; Maher, D.T.; Sanders, C. The contribution of denitrification and burial to the nitrogen budgets of three geo-morphically distinct Australian estuaries: Importance of seagrass habitats. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 1144–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, B.D.; Maher, D.T.; Squire, P. Quantity and quality of organic matter (detritus) drives N2 effluxes (net denitrification) across seasons, benthic habitats, and estuaries. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2013, 27, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcias-Bonet, N.; Fusi, M.; Ali, M.; Shaw, D.R.; Saikaly, P.E.; Daffonchio, D.; Duarte, C.M. High denitrification and anaerobic ammonium oxidation contributes to net nitrogen loss in a seagrass ecosystem in the central Red Sea. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 7333–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchette, B.W.; Burkholder, J.M. Review of nitrogen and phosphorus metabolism in seagrasses. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 250, 133–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Lee, K.-S.; Rez, M.P.; Mateo, M.A.; Alcoverro, T. Nutrient Dynamics in Seagrass Ecosystems in Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 227–254. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, K.A. Influence of Seagrasses on Water Quality in Shallow Regions of the Lower Chesapeake Bay. J. Coast. Res. 2004, 10045, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, E.; Herbeck, L.S.; Viana, I.G.; Jennerjahn, T.C. Meadow trophic status regulates the nitrogen filter function of tropical seagrasses in seasonally eutrophic coastal waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2023, 68, 1906–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.; McGlathery, K. Nitrogen fixation in restored eelgrass meadows. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 448, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, D.; Bourguès, S.; de Wit, R.; Auby, I. Effect of plant photosynthesis, carbon sources and ammonium availability on nitrogen fixation rates in the rhizosphere of Zostera noltii. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1997, 12, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlathery, K.; Risgaard-Petersen, N.; Christensen, P. Temporal and spatial variation in nitrogen fixation activity in the eelgrass Zostera marina rhizosphere. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 168, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, B.D.; Connell, S.D.; Uthicke, S.; Muehllehner, N.; Fabricius, K.E.; Hall-Spencer, J.M. Future Seagrass Beds: Can Increased Productivity Lead to Increased Carbon Storage? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 73, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic, Z.; Pedersen, M.; Larsen, M.; Kristensen, E. Glud Rhizosphere O2 dynamics in young Zostera marina and Ruppia maritima. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 518, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, O.I.; Gribsholt, B.; Kristensen, E.; Revsbech, N.P. Microscale distribution of oxygen and nitrate in sediment in-habited by Nereis diversicolor: Spatial patterns and estimated reaction rates. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 34, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, B.D.; Rysgaard, S.; Dalsgaard, T.; Christensen, P.B. Comparison of isotope pairing and N2: Ar methods for measuring sediment-denitrification-assumptions, modifications, and implications. Estuaries 2002, 25, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kana, T.M.; Darkangelo, C.; Hunt, M.D.; Oldham, J.B. Membrane inlet mass spectrometer for rapid high-precision de-termination of N2, O2, and Ar in environmental water samples. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 4166–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erftemeijer, P.L.; Koch, E.W. Sediment geology methods for seagrass habitat. In Global seagrass research methods; Short, F.T., Coles, R.G., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 345–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Trevathan-Tackett, S.M.; Skilbeck, C.G.; Sanderman, J.; Curlevski, N.; Jacobsen, G.; Seymour, J.R. Losses and recovery of organic carbon from a seagrass ecosystem following disturbance. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20151537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrentyev, P.J.; Gardner, W.S.; Yang, L. Effects of the zebra mussel on nitrogen dynamics and the microbial community at the sediment-water interface. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 21, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, W.; Yang, J. Denitrification in the rhizosphere of the two seagrasses Thalassia hemprichii (Ehrenb.) Aschers and Halodule uninervis (Forsk.) Aschers. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1997, 218, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, K.; Borum, J.; Hasler-Sheetal, H.; Shields, E.; Sand-Jensen, K.; Moore, K. High Temperatures Cause Reduced Growth, Plant Death and Metabolic Changes in Eelgrass Zostera Marina. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 604, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, T.M.; Borum, J.; Pedersen, O. Meristematic oxygen variability in eelgrass (Zostera marina). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, M.; Asplund, M.E.; Deyanova, D.; Franco, J.N.; Koliji, A.; Infantes, E.; Perry, D.; Björk, M.; Gullström, M. High Seasonal Variability in Sediment Carbon Stocks of Cold-Temperate Seagrass Meadows. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haviland, K.A.; Howarth, R.W.; Marino, R.; Hayn, M. Variation in sediment and seagrass characteristics reflect multiple stressors along a nitrogen-enrichment gradient in a New England lagoon. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2022, 67, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, H.; Beggins, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Holmer, M.; Marbà, N.; Middelburg, J.J. Seagrass sediments as a global carbon sink: Isotopic constraints. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24, 6696–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Cintra-Buenrostro, C.E.; Fierro-Cabo, A. Decomposition and nitrogen dynamics of turtle grass (Thalassia testudinum) in a subtropical estuarine system. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 25, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, S.; Benner, R. Nutrient cycling in the water column of a subtropical seagrass meadow. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 188, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Moore, K.A. Seasonal and year-to-year variations in the growth of Zostera marina L. (eelgrass) in the lower Chesapeake Bay. Aquat. Bot. 1986, 24, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, D.T. Nitrogen fixation in seagrass meadows: Regulation, plant-bacteria interactions and significance to primary productivity. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 3, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, P.; Evrard, V.; Woodland, R. Factors controlling nitrogen fixation in temperate seagrass beds. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 525, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Nielsen, S. Sediment sulfur dynamics related to biomass- density patterns in Zostera marina (eelgrass) beds. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 146, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, B.R.; Zeller, M.A.; Lopes, C.; Smyth, A.R.; Böttcher, M.E.; Osburn, C.L.; Zimmerman, T.; Profrock, D.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Thomas, H. Calcification-driven CO2 emissions exceed “Blue Carbon” sequestration in a carbonate seagrass meadow. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabj1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, P.L.M.; Kessler, A.J.; Eyre, B.D. Does denitrification occur within porous carbonate sand grains? Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 4061–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.G.; Warry, F.Y.; Cook, P.L.M. The balance between nitrogen fixation and denitrification on vegetated and non-vegetated intertidal sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 2058–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, L.; McGlathery, K. High rates of N fixation in seagrass sediments measured via a direct 30N2 push-pull method. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 616, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenworthy, W.; Thayer, G. Production and Decomposition of the Roots and Rhizomes of Seagrasses, Zostera Marina and Thalassia Testudinum, in Temperate and Subtropical Marine Ecosystems. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1984, 35, 364–379. [Google Scholar]
- Kenworthy, W.J.; Zieman, J.C.; Thayer, G.W. Evidence for the influence of seagrasses on the benthic nitrogen cycle in a coastal plain estuary near Beaufort, North Carolina (USA). Oecologia 1982, 54, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salk, K.R.; Erler, D.V.; Eyre, B.D.; Carlson-Perret, N.; Ostrom, N.E. Unexpectedly high degree of anammox and DNRA in seagrass sediments: Description and application of a revised isotope pairing technique. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 211, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Heck, K.L.; van Montfrans, J. Faunal communities in seagrass beds: A review of the influence of plant structure and prey characteristics on predator-prey relationships. Estuaries 1984, 7, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysgaard, S.; Christensen, P.; Nielsen, L. Seasonal variation in nitrification and denitrification in estuarine sediment colonized by benthic microalgae and bioturbating infauna. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 126, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).