Abstract
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is one of the main greenhouse gases and its emissions from vegetable production systems have brought a sustainability challenge. The objective of this study was to evaluate the potential of reducing N2O emissions from silt loam soil by mixing nitrogen (N)-rich broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica) residue with wheat straw or water-washed wheat straw. An experiment was conducted in randomized complete block design with five treatments; unamended or control (BS), wheat straw (+S), broccoli residue (+CR), broccoli residue and wheat straw (+CR+S) and broccoli residue and washed wheat straw (+CR+Sw) and was replicated four times. The +CR and +S were added at the rate of 3.5 kg and 2.0 kg fresh matter m−2 and their mixtures, +CR+S and +CR+Sw, were incorporated in 3.5 kg of silt loam soil at 60% water-filled pore space (WFPS) and packed in soil microcosms. Nitrous oxide emissions were measured once a day during the 14-day of study period. Daily fluxes of N2O were found to be reduced on +CR+W and +CR+Sw when compared to single-amended +CR treatment. Similarly, N2O fluxes on +CR+Sw (2772 µg N m−2 h−1) were significantly lower than +CR+S (3606 µg N m−2 h−1) soon after the amendment but did not vary significantly thereafter. Moreover, the amendment mixture, +CR+S and +Cr+Sw, resulted in lower net N2O emissions by 73.3% and 74.2%, respectively, relative to +CR treatment. While the results clearly suggest that the +CR+S or +CR+Sw reduced N2O emissions, it necessitated further studies, possibly by increasing the frequency of sampling to clarify if washed wheat straw would further mitigate N2O emissions from the vegetable production system.
1. Introduction
Nitrous oxide is the third most important contributor of the current radiative forcing (after CO2 and CH4) [1]. Apart from being a potent greenhouse gas, it is also one of the most important ozone-depleting substances in the stratosphere [2]. Out of an annual estimated figure of 6.3 Tg N2O-N emissions from agricultural land use [3], direct emissions from agricultural soils contribute a one-third share, i.e., 2.1 Tg N2O-N y−1, and crop residue-specific emissions accounted for 0.4 Tg N2O-N y−1 [4], but it has so far been neglected from the management perspective [5].
All vegetable crops, particularly cole crops, are harvested before they attain physiological maturity; they need a considerable amount of nitrogenous fertilizer even at the time of harvest [6]. The recommended minimum soil mineral nitrogen (SMN) in vegetable production at harvest is 40 kg N ha−1 above the expected N uptake by vegetables [6], clearly promoting SMN content after harvest [7]. An additional source of SMN in the vegetable cropping system is the easily mineralizable N content in its residue biomass, owing to its typically low C/N ratio [8]. Enhanced SMN has climate relevance as it triggers soil microbial processes of nitrification and denitrification, leading to N2O emissions as their intermediate product [9]. While nitrification is most likely at ≤60% WFPS [10], the probability of denitrification will be more at higher amounts of easily available organic C inputs [11], as the denitrifiers consume O2 with subsequent CO2 release in the process of C substrate utilization [12]. Whatever the process and the reason, sustainable management techniques in vegetable cropping systems are needed to reduce gaseous N loss into the atmosphere and to maintain a closed N cycle within the system.
Michell et al. [13] reported a reduction in N leaching and denitrification by delayed incorporation (at the end of winter) of autumn harvested crop residue. Conversely, de Ruijter et al. [14] conducted a similar study using leek residue, but still found substantial N loss. Additionally, loss of N from undisturbed residues through other modes, for example via ammonia volatilization, could be high [15]. Introduction of catch crops after the harvest of the main crop is another frequently used option to reduce N loss but may not work for vegetable crops that are harvested in late autumn (for example, cole crops). Maximum N uptake from catch crops with subsequent N loss reduction in winter occurs only when they are sown in summer [16], and the efficiency of catch crops drastically reduces when sown later than September [17].
Similarly, few researchers [5,18,19] have documented lower N mineralization rates and consequently N2O emissions by amending crop residues with high C/N ratios. However, C/N ratio alone is not an accurate indicator that determines immobilization and/or mineralization potential of the residue as it does not state how microbes utilize different C and N forms [20]. Moreover, Seiz et al. [21] noticed a rapid increment of N2O fluxes soon after the wheat straw amendment despite a high C/N ratio, which might be attributed to the presence of readily available C fractions of straw and their utilization by the denitrifers [22]. Furthermore, an earlier study by Reinertsen et al. [23] reported that intermediately available C is also metabolized simultaneously with readily available C-compounds of straw, and cold-water washing of straw only removes readily available plant fractions.
The objective of the current study is to compare N2O emissions from broccoli single applications to those from the mixture of broccoli residue and wheat straw or (hot water) washed wheat straw. We assumed that washing straw with hot water would leach out both liable and intermediately liable C fractions of straw. We hypothesized that the combined residue amendment would reduce N2O emissions when compared to broccoli residue-only application and the amendment mixture of broccoli residue and hot-water washed straw would further intensify N immobilization.
2. Results
2.1. Nitrous Oxide Emissions
Nitrous oxide fluxes varied widely among the treatments and they changed over time in the 14-day study period (Figure 1). While treatments +CR, +CR+S and +CR+Sw showed higher emissions for the first few sampling days after crop residue amendment, N2O fluxes on soil microcosms with BS and +S treatments were close to zero throughout the experimental period. Nitrous oxide fluxes on +CR treatment reached a peak (12,479 µg N m−2 h−1) on the first day and plummeted after the second day of the amendment, but surprisingly a little peak reappeared after the 11th day. Nitrous oxide fluxes were lower in +CR+S and +CR+Sw than in the +CR treatment. Peak N2O fluxes in +CR+S (3606 µg N m−2 h−1) and +CR+Sw (2772 µg N m−2 h−1) occurred soon after amendment and then gradually decreased over time. Treatment +CR+S maintained higher fluxes than +CR+Sw until the second day of the amendment, but there was no coherent increment of fluxes afterward.
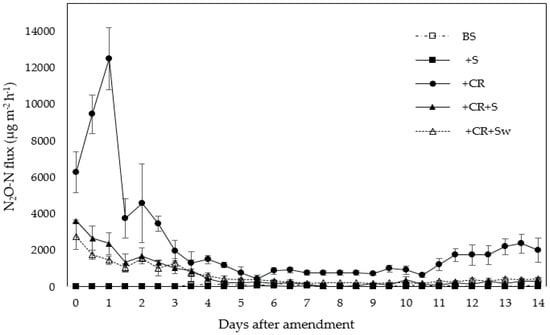
Figure 1.
Daily N2O flux (mean ± SE; n = 4) from soil microcosms with different treatments: BS = unamended soil, +S = wheat straw, +CR = broccoli crop residue, +CR+S = broccoli straw and +CR+Sw = broccoli washed straw.
Nitrous oxide fluxes significantly reduced under +CR+S and +CR+Sw treatments when compared to the broccoli single amendment until the fifth day of soil incubation (Table 1), which followed a sudden drop of N2O fluxes in +CR treatment. There were no significant differences among the treatments in most of the sampling days afterward. Lower N2O flux rate on +CR+Sw was evident until the third day when compared to +CR+S with significantly lower fluxes on the first sampling day. Daily N2O fluxes were statistically lower in BS and +S than in other treatments.

Table 1.
Nitrous oxide fluxes from soil microcosms on different days following the broccoli residue and wheat straw amendments.
Cumulative N2O emissions during the incubation period (14 days) were significantly higher (7.7 kg N ha−1) in the broccoli residue-amended soil (Figure 2). Mixing broccoli residue with straw (+CR+S) or hot water-washed straw (+CR+Sw) significantly lowered emissions when compared to +CR, however there was no significant difference among them. Moreover, the reduction potential of wheat straw and washed wheat straw (relative to broccoli single amendment) was 73.3% and 74.2%, respectively (Table 2).
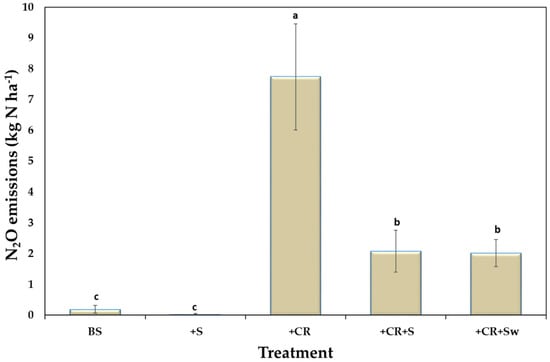
Figure 2.
Cumulative N2O emissions (mean ± SE; n = 4) from soil microcosms with different treatments: BS = unamended or control, +S = wheat straw, +CR = broccoli residue, +CR+S = broccoli residue and wheat straw, +CR+Sw = broccoli residue and washed wheat straw. Means with different letters across treatments are significantly different at p < 0.05.

Table 2.
Cumulative N2O emissions and calculated immobilization potential of wheat straw used in the microcosm throughout the experimental period.
2.2. Carbon Dioxide Emissions
The magnitude of average CO2 flux over the entire experimental period was in the order of +CR+S > +CR+Sw > +CR > +S > BS (Figure 3). While the peak CO2 fluxes on +CR+S (5114 mg CO2-C m−2 h−1), +CR+Sw (3247 mg CO2-C m−2 h−1) and +CR (3597 mg CO2-C m−2 h−1) occurred on the third day, CO2 fluxes on BS (117 mg CO2-C m−2 h−1) and +S (895 mg CO2-C m−2 h−1) attained a slight noticeable peak only on the eighth day of amendment. In contrast to +CR+S and +CR+Sw where the elevated CO2 fluxes noticeably decreased over time with distinct small intermediate peaks in between, CO2 peaks on +CR plummeted sharply after the fifth day of amendment with no intermediate peaks after.
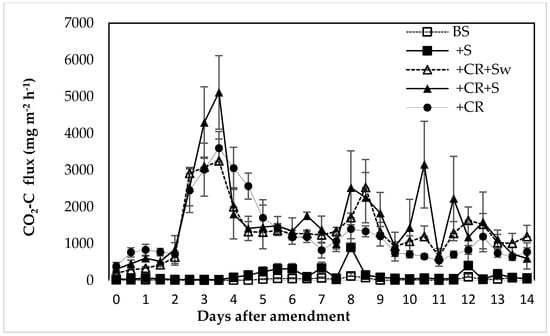
Figure 3.
Daily CO2-C flux (mean ± SE; n = 4) from soil microcosms with different treatments: BS = unamended soil, +S = wheat straw, +CR = broccoli crop residue, +CR+S = broccoli straw and +CR+Sw = broccoli washed straw.
3. Discussion
3.1. Effect of Broccoli Residue on N2O Emissions
A high but ephemeral flux peak of nitrous oxide that occurred soon after the broccoli residue single amendment was obvious and consistent with the N2O emissions pattern of previous similar incubation studies [24,25]. The cumulative N2O emissions of 7.7 kg N ha−1 from broccoli residue corresponds to 3.0% of added (broccoli) residue N, which is in line with the emission factor (EF) value (>1.5%) for N rich vegetable crop residues suggested by Veltholf et al. [26] but is higher than the default value (1.25% of residue N) set by the Intergovernmental Panel of Climate Change (IPPC). Thus, our results on EF gives a guideline for IPPC methodology to devise more residue-specific emission factors. Surprisingly little N2O peaks appeared in the later stage of soil incubation and may be the result of slow but successive increase in moisture content inside soil microcosms due to high water holding capacity of silt loam soil that impedes complete percolation, leading to high denitrification rates. According to Groffman and Tiedje [27], the presence of a large proportion of micropores in fine textured soil may cause greater water retention, thus despite continuously running percolation systems, WFPS might have reached between 60% to above 70%, favoring denitrification [28,29] until the final stage of the incubation study.
3.2. Effect of Straw Addition to Soil
Wheat straw, as a sole application (+S) or in combination with broccoli residue (+CR+S or +CR+Sw), decreased daily N2O fluxes as well as net flux when compared to +CR treatment. Calculated immobilization potential of wheat straw (73.3%) was higher than what Chevas et al. [30] (60%) obtained, however that was a short-term incubation study (50 h) which might have failed to realize full immobilization potential of the straw. Nevertheless, the immobilization potential of the immobilizers has been found to be higher during laboratory incubation because of the incorporation of finely chopped and thoroughly mixed residue particles (crop residue and immobilizer) that allow better contact with immobilizing microorganisms which leads to enhanced immobilization potential of the immobilizer rather than the real field condition [31]. The decrease in N2O emissions might be attributed to a high C/N ratio of wheat straw, due to soil microbes assimilating/immobilizing mineralizable N into their biomass and making it temporarily available [32]. According to Parton et al. [32], net immobilization takes place when decomposing material has a low N content, as decomposers seek more N from other substrates, such as broccoli residue N in this case. Thus, in +CR+S and +CR+Sw, the N content of broccoli residue might have been utilized by microbes to decompose straw which otherwise could have been lost through denitrification or other processes. Furthermore, high lignin content (43.9%) in wheat straw [33] could also be responsible for reduced N2O emissions in the straw-amended soil [34]. A negative relationship between lignin content and the mineralization rate has been well-documented in several past research studies [35,36,37]. A possible reason for the retardation of N mineralization is the production of low molecular weight polyphenol following lignin degradation, which has tendency to combine with organic N compounds to form a resistant complex [38].
Nitrous oxide flux from +CR+Sw was significantly lower than +CR+S only on the first sampling day or 24 h after incubation and showed a general lower trend of emissions for the next two sampling days. This indicated that washing steps might have intensified the immobilization potential of wheat straw in the early stages of the incubation study by removing hot water-leachable C and N from the straw surface, as soil microbes might have assimilated more N mineralized from broccoli residue and from inherent SMN. However, +CR+Sw treatment did not lower cumulative N2O emission significantly when compared to +CR+S treatment. To truly understand the fate of washed straw on reducing N2O emissions in early stages of decomposition and its role on maximizing overall N immobilization, a short-term incubation trial with more frequent sampling, as previously suggested by Chaves et al. [30], would be needed to clearly elucidate the potential of washed straw on reducing N2O emissions in the early stages of incubation.
3.3. Effect of Residue Application on CO2 Emissions
Carbon dioxide emissions peaked within the first few days of crop residue amendment. Elevated CO2 indicated that heterotrophic denitrification was a source of N2O emissions in this study. During microbial degradation of plant residue, soil microbes consume O2 and respire CO2, thereby creating an anoxic environment in the soil system favorable for denitrification [39]. The overall decomposition of residue-amended soil followed a biphasic model used by several researchers [40,41,42]. This model assumes rapid decomposition of an easily degradable fraction followed by the start of the slow decomposition phase [43]. Initially high CO2 peak on +CR, +CR+S and +CR+Sw treatments (but not in +S) would confirm a large amount of easily available C pool on +CR [44]. While the decline in CO2 emissions without any intermediate peaks on +CR could be related to substrate exhaustion, small intermediate CO2 peaks on +CR+S, +CR+Sw and +S which occurred throughout the incubation period could be related to successive decomposition of compounds that were previously resistant to decomposition. Residue fraction such as fats, waxes, resins and oils are utilized once readily soluble fractions including sugars, starch, proteins and organic acids are used up [20,45]. Additionally, the slow nature of the microorganism [46] involved in the later stage could be the cause for a lower maxima of CO2 evolution and the time lag between two maxima.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Soil
The soil used in this study was silt loam (haplic luvisol derived from periglacial loess) and collected from Heidfeldhof, an experimental farm of the University of Hohenheim, Germany (48°43′00″ N latitude and 9°11′40″ E). The stone-free topsoil contained 2% clay, 68% silt and 30% sand with an initial pH (10−2 M CaCl2) of 6.5.
4.2. Broccoli Residue and Straw Preparation
Shredded broccoli residues were dried and cracked into small pieces before application. Wheat straw (chopped into 2–3 cm length) was immersed in hot (70 °C) distilled water and shaken vigorously, then the leachate was drained. A similar process was repeated for seven times, preserving the leachate sample each time for laboratory analysis. The final leachate contained <32 mg C L−1 and <1 mg N L−1, which represents 6% less C and 71% less N than the first leachate sample. Chemical constituents of broccoli crop residue and wheat straw used as amendment materials are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Chemical constituents of crop residue used in this incubation study.
4.3. Soil Microcosm and Experiment Set-Up
The soil microcosm system comprised a cylindrical Plexiglas core (inner diameter = 13 cm, height = 20 cm), a thick broad bottom plate with central hole to provide outlet of percolate water and a Plexiglas lid with an irrigation nozzle on the top and fittings for inlet and outlet for gas exchange on the opposite side (Figure 4). Circular rubber seals were installed in between the bottom plate, the Plexiglas lid connected three parts and the screw running through made the system airtight.
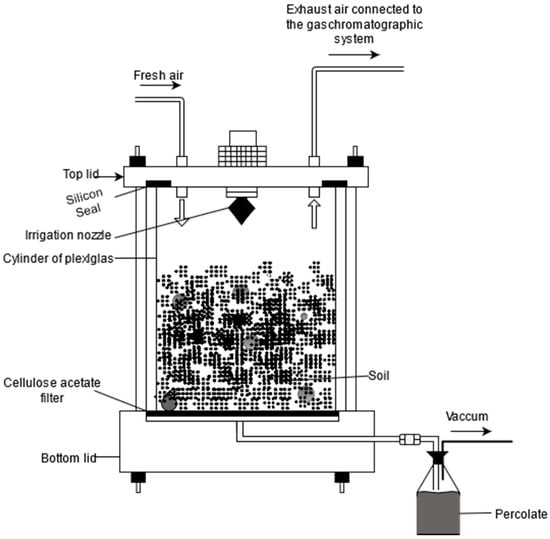
Figure 4.
Individual Microcosm Design Used in this Experiment.
During packing of soil into microcosms, the surface of the bottom plate was covered with cellulose acetate filter paper (pore size 0.45 µm, Sartorius, Göttingen, Germany) that separated the percolate water from the soil system. Individual microcosms were packed up to 15 cm with 2703 g soil and irrigated to adjust to 60% WFPS with a bulk density of 1.2 g cm−3. Soil microcosms were incubated in the climate chamber at a constant temperature of 20 °C. Each microcosm was irrigated at 25 mL per day through an irrigation nozzle connected to a pressure cylinder filled with irrigation solution (0.01 M CaCl2). The partial pressure of 10 kPa maintained at the bottom ensured continuous percolation. The microcosms system was flushed with ambient air supply on the headspace at a flow rate of 15 mL min−1 for the whole experimental period. The flow rate was adjusted by a high precision digital flow meter (Thermo Scientific, Langenselbold, Germany).
Soil microcosms were pre-incubated to stabilize their respiration and gas fluxes while feeding them with irrigation solution until soil nitrate contents reached comparable low levels. A quick test was performed to estimate nitrate content of percolate every two days by using a reflectometer Nitracheck (Hermann Wolf Ltd., Wuppertal, Germany). After a quick test revealed the removal of a considerable amount of nitrate from the soil, microcosms were fertigated with 0.01 M CaCl2 and 4.1 mg (NH4)2NO3 L−1 solution. This soil nitrate content represents a typical N amount (50 kg N ha−1) after broccoli crop harvest.
4.4. Experimental Design
The experiment was carried out as a randomized complete block design with five treatments and four replications in July/August 2015. The treatments used were unamended or control (BS), wheat straw (+S), broccoli residue (+CR), broccoli residue and wheat straw (+CR+S) and broccoli residue and washed wheat straw (+CR+Sw). The schematic diagram of the experimental design is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the experimental design. The numbers 1–5 represent treatment as 1 = unamended or control (BS), 2 = wheat straw (+S), 3 = broccoli residue (+CR), 4 = broccoli residue and wheat straw (+CR+S) and 5 = broccoli residue and washed wheat straw (+CR+Sw). All treatments were replicated four times.
During the residue amendments into the microcosms, soil was scooped out from the microcosm up to a depth of 7 cm and mixed with respective treatments. Broccoli residue and wheat straw were incorporated at 3.5 kg fresh matter m−2 and 2 kg fresh matter m−2, respectively. The mixture was sieved (4 mm) to maintain soil aggregation and it was finally placed back in the climate chamber and incubated for 14 days with respected tube fittings.
4.5. Gas Measurement
Gas samples from the microcosms were obtained every 12 h by inserting a vial (ambient pressure) to the respective outlet tubing system, which was fed by the headspace gas. Glass vials (22.4 mL) equipped with crimp lock and isobutyl plugs were used for all gas samplings. Gas samples thus collected from individual microcosms were analyzed for their N2O and CO2 concentration using gas chromatography (GC 456 greenhouse gas analyzer, Bruker Daltonic) with a 63Ni electron capture detector. Raw gas flux measurements thus obtained from gas chromatograph were expressed in g m−2 h−1 with following equation:
where,
gas = greenhouse gases i.e., N2O or CO2
K(N2O) = Conversion factor N2O with value 1.25 N2O-N L−1
K(CO2) = Conversion factor of CO2 with value 0.536 CO2-C L−1
T = Temperature [K]
Gas = Gas concentration of inlet air (ppm for CO2 and ppb for N2O)
S = air velocity [L h−1]
A = area [m2]
4.6. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using SAS (SAS 9.4). The N2O emissions data were, respectively, y = sqrt(y + 1) and y = log(y + 1), transformed (back-transformed at the end) to achieve normal distribution for statistical analysis. Statistical significance was evaluated at p < 0.05 unless otherwise stated. Percentage reduction in cumulative emissions from +CR+S and +CR+Sw treatments relative to emissions in broccoli was calculated by subtracting cumulative N2O emissions of broccoli from +CR+S and +CR+Sw treatments, respectively, and dividing this by N2O emissions from the +CR treatment. Similarly, N2O emission factor (EF) was calculated according to Velthof et al. [26]:
5. Conclusions
In the current study, +CR amendment showed higher N2O emissions than the other treatments, and the effect of simultaneous incorporation of broccoli residue with wheat straw or washed wheat straw on reducing N2O emissions relative to broccoli residue single amendment was also clear. When compared to +CR treatment, N2O emission in +CR+S and +CR+Sw was reduced by 73.3% and 74.2%, respectively. However, the effect of washed wheat straw with broccoli residue mixture amendment on reducing N2O fluxes (when compared to broccoli residue and unwashed straw) was evident only for the first few sampling days and the trend was rather elusive. Therefore, future field studies in vegetable production should also focus on the effect of N2O reduction through straw application over the long-term, as well as on environmental hazards through the release of the transient immobilized mineral N.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.R. and P.S.; methodology, R.R. and P.S.; software, R.B.; validation, P.S., R.R. and D.P.; formal analysis, R.B. and D.P.; investigation, R.B.; resources, T.M.; data curation, P.S and R.B.; writing—original draft preparation, R.B. and D.P.; writing—review and editing, R.B., D.P., P.S., R.R. and T.M.; visualization, D.P.; supervision, R.R. and P.S.; project administration, T.M.; funding acquisition, T.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Bed Prakash Bhatta for English editing services.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Not applicable.
References
- Forster, P.; Ramaswamy, V.; Artaxo, P.; Berntsen, T.; Betts, R.; Fahey, D.W.; Nganga, J. Changes in atmospheric constituents and in radiative forcing. In Climate Change 2007; The Physical Science Basis. 2007. Chapter 2; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rodhe, H. A Comparison of the Contribution of Various Gases to the Greenhouse Effect. Science 1990, 248, 1217–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES) for the IPCC: Kanagawa, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mosier, A.; Duxbury, J.; Freney, J.; Heinemeyer, O.; Minami, K. Assessing and Mitigating N2O Emissions from Agricultural Soils. Clim. Chang. 1998, 40, 7–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggs, E.; Rees, R.; Smith, K.; Vinten, A. Nitrous oxide emission from soils after incorporating crop residues. Soil Use Manag. 2006, 16, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, C.; Fink, M.; Laber, H.; Maync, A.; Paschold, P.; Scharpf, H.C.; Schlaghecken, J.; Strohmeyer, K.; Weier, U.; Zeigler, J. Dungung im Freilandgemusebau (in German). In Schriftenreihe des Leibniz-Instituts fur Gemuse-und Zierpflanzenbau (IGZ), 3rd ed.; Fink, M., Ed.; Leibniz Institute for Vegetable and Ornamental Plant Cultivation: Grossbeeren, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Everaarts, A.P. General and quantitative aspects of nitrogen fertilizer use in the cultivation of Brassica vegetables. In Workshop on Ecological Aspects of Vegetable Fertilization in Integrated Crop Production in the Field; ISHS: Einsiedeln, Switzerland, 1992; pp. 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Pfab, H.; Palmer, I.; Buegger, F.; Fiedler, S.; Müller, T.; Ruser, R. Influence of a nitrification inhibitor and of placed N-fertilization on N2O fluxes from a vegetable cropped loamy soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 150, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiba, U.; Smith, K. The control of nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural and natural soils. Chemosphere Glob. Chang. Sci. 2000, 2, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbie, K.E.; Smith, K.A. Nitrous oxide emission factors for agricultural soils in Great Britain: The impact of soil water-filled pore space and other controlling variables. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, E.G.; Trevors, J.T.; Paul, J.W. Carbon Sources for Bacterial Denitrification. In Advances in Soil Science 12; Metzler, J.B., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 1989; pp. 113–142. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hu, F.; Shi, W. Plant material addition affects soil nitrous oxide production differently between aerobic and oxygen-limited conditions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 64, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.D.J.; Harrison, R.; Russell, K.J.; Webb, J. The effect of crop residue incorporation date on soil inorganic nitrogen, nitrate leaching and nitrogen mineralization. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 32, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruijter, F.; Berge, H.T.; Smit, A. The fate of nitrogen from crop residues of broccoli, leek and sugar beet. Acta Hortic. 2010, 852, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruijter, F.J.; Huijsmans, J.F.M.; Rutgers, B. Ammonia volatilization from crop residues and frozen green ma-nure crops. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3362–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, I.K.; Hansen, E.M. Cover crop growth and impact on N leaching as affected by pre- and postharvest sowing and time of incorporation. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 30, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, J.N. Effect of catch crops on the content of soil mineral nitrogen before and after winter leaching. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 1992, 155, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, M.S.; Walters, D.T.; Doran, J.W.; Francis, D.D.; Mosier, A.R. Crop Residue Type and Placement Effects on Denitrification and Mineralization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, W.; Vaughan, S.M.; Dalal, R.C.; Menzies, N.W. Crop residues and fertilizer nitrogen influence resi-due decomposition and nitrous oxide emission from a Vertisol. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, J.F.; Papendick, R.I.; Oschwald, W. Factors Affecting the Decomposition of Crop Residues by Microorganisms. Anim. Manure 2015, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiz, P.; Guzman-Bustamante, I.; Schulz, R.; Müller, T.; Ruser, R. Effect of crop residue removal and straw addi-tion on nitrous oxide emissions from a horticulturally used soil in South Germany. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, B.; De Neve, S.; Boeckx, P.; Van Cleemput, O.; Hofman, G. Manipulating Nitrogen Release from Nitrogen-Rich Crop Residues using Organic Wastes under Field Conditions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinertsen, S.; Elliott, L.; Cochran, V.; Campbell, G. Role of available carbon and nitrogen in determining the rate of wheat straw decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1984, 16, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, S.M.; Dalal, R.C.; Harper, S.M.; Menzies, N.W. Effect of fresh green waste and green waste compost on mineral nitrogen, nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide from a Vertisol. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zou, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X. Nitrous oxide emissions as influenced by amendment of plant residues with different C: N ratios. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthof, G.L.; Kuikman, P.J.; Oenema, O. Nitrous oxide emission from soils amended with crop residues. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 62, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffman, P.M.; Tiedje, J.M. Denitrification in north temperate forest soils: Relationships between denitrification and environmental factors at the landscape scale. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1989, 21, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbie, K.E.; Smith, K.A. The effects of temperature, water-filled pore space and land use on N2O emissions from an imperfectly drained gleysol. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2001, 52, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruser, R.; Flessa, H.; Russow, R.; A Schmidt, G.; Buegger, F.; Munch, J. Emission of N2O, N2 and CO2 from soil fertilized with nitrate: Effect of compaction, soil moisture and rewetting. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, B.; De Neve, S.; Cabrera, M.D.C.L.; Boeckx, P.; Van Cleemput, O.; Hofman, G. The effect of mixing organ-ic biological waste materials and high-N crop residues on the short-time N2O emission from horticultural soil in model experiments. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2005, 41, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bending, G.D.; Turner, M.K. Turner Interaction of biochemical quality and particle size of crop residues and its effect on the microbial biomass and nitrogen dynamics following incorporation into soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1999, 29, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parton, W.; Silver, W.L.; Burke, I.C.; Grassens, L.; Harmon, M.E.; Currie, W.S.; King, J.Y.; Adair, E.C.; Brandt, L.A.; Hart, S.C.; et al. Global-Scale Similarities in Nitrogen Release Patterns During Long-Term Decomposition. Science 2007, 315, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Wine, R.H. Determination of Lignin and Cellulose in Acid-Detergent Fiber with Permanganate. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 1968, 51, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, C.; Sanchez, P. Nitrogen release from the leaves of some tropical legumes as affected by their lignin and polyphenolic contents. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1991, 23, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlauwe, B.; Nwoke, O.C.; Sanginga, N.; Merckx, R. Impact of residue quality on the C and N mineralization of leaf and root residues of three agroforestry species. Plant Soil 1996, 183, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahn, C.R.; Lillywhite, R.D. A study of the quality factors affecting the short-term decomposition of field vegetable residues. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Liu, J.; Peng, B.; Gao, D.; Wang, C.; Dai, W.; Jiang, P.; Bai, E. Nitrogen, lignin, C/N as important regulators of gross nitrogen release and immobilization during litter decomposition in a temperate forest ecosystem. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 440, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bending, G.D.; Read, D.J. Nitrogen mobilization from protein-polyphenol complex by ericoid and ectomycorrhi-zal fungi. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1996, 28, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olk, D.C.; Cassman, K.G.; Randall, E.W.; Kinchesh, P.; Sanger, L.J.; Anderson, J.M. Changes in chemical properties of organic matter with intensified rice cropping in tropical lowland soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajwa, H.A.; Tabatabai, M.A. Decomposition of different organic materials in soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1994, 18, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.S. Studies on the decomposition of plant material in soil. v. the effects of plant cover and soil type on the loss of carbon from14c labelled ryegrass decomposing under field conditions. J. Soil Sci. 1977, 28, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, J.T.; Clark, M.D.; Sigua, G.C. Estimating Net Nitrogen Mineralization from Carbon Dioxide Evolution. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboneka, S.; Sabbe, W.E.; Mauromoustakos, A. Carbon decomposition kinetics and nitrogen mineralization from corn, soybean, and wheat residues. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1997, 28, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Jiménez, E. Nitrogen availability from a mature urban compost determined by the 15N isotope dilution method. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reber, H.; Schara, A. Degradation sequences in wheat straw extracts inoculated with soil suspensions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1971, 3, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.; Ekbohm, G. Litter mass-loss rates and decomposition patterns in some needle and leaf litter types. Long-term decomposition in a Scots pine forest. VII. Can. J. Bot. 1991, 69, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).