Abstract
Today’s rapid growth of elderly populations and aging problems coupled with the prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and other health related issues have affected many aspects of society. This has led to high demands for a more robust healthcare monitoring, diagnosing and treatments facilities. In particular to Sleep Medicine, sleep has a key role to play in both physical and mental health. The quality and duration of sleep have a direct and significant impact on people’s learning, memory, metabolism, weight, safety, mood, cardio-vascular health, diseases, and immune system function. The gold-standard for OSA diagnosis is the overnight sleep monitoring system using polysomnography (PSG). However, despite the quality and reliability of the PSG system, it is not well suited for long-term continuous usage due to limited mobility as well as causing possible irritation, distress, and discomfort to patients during the monitoring process. These limitations have led to stronger demands for non-contact sleep monitoring systems. The aim of this paper is to provide a comprehensive review of the current state of non-contact Doppler radar sleep monitoring technology and provide an outline of current challenges and make recommendations on future research directions to practically realize and commercialize the technology for everyday usage.
Keywords:
sleep monitoring; patient monitoring; non-contact monitoring; vital signs monitoring; health monitoring; obstructive sleep apnea; sleep; sensors; Doppler radar; non-contact vital signs; respiration; cardiac activity; pressure; Tidal volume; sleep wake pattern; apnea-hypopnea index; Cheyne-Stokes respiration; computer vision; machine learning; body orientations; body movements 1. Introduction
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common and potentially lethal sleep disorder affecting at least 4% of adult males and 2% of adult females world-wide [1]. Statistics published in 2013 reported that the prevalence of OSA had increased between 10–17% for adult males and 3–9% for adult females in the United States of America (USA) [2].
OSA is the cessation of airflow due to the collapse of the upper airway during sleep and can occur at any age from infancy to old age. Statistics have shown that the male to female ratio is about 2:1 and probably affects prepubertal males and females at equal rate [3]. Evidence has indicated that OSA is associated with ischemic heart disease, increased prevalence of stroke, coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation (AF), chronic heart failure (CHF), and cardiac sudden death [4]. In addition, OSA may also be associated with increase cholesterol, hypertension [5], type 2 diabetes [6,7], and cancer mortality [8]. OSA can also lead to oxygen desaturations, oxidative stress, blood pressure, heart rate changes, and interrupted sleep [9,10].
The gold-standard for OSA diagnosis is the overnight sleep monitoring system using polysomnography (PSG), which records the electric potentials of the brain, heart, eye movement, muscle activity, respiratory effort, airflow, oxygen saturation, and leg movements throughout the night [11]. Despite the quality and reliability of the PSG system, it is not well suited for long-term continuous monitoring usage [12] due to limited mobility as well as causing possible irritation, distress, and discomfort to patients during the monitoring process [13]. These limitations have led to stronger demands for non-contact sleep monitoring systems.
Non-contact biosensor such as microwave Doppler radar for physiological vital signs monitoring was discovered in the 1970s. Literature has been published regarding non-contact assessments of respiratory and heart rates. However, the tendencies of reported achievements are based on “stationary” and “direct-facing” subject measurements, which is not an ideal scenario for the complexity of sleep environment.
As documented in literature, the issue with getting an accurate reading from a non-contact monitoring device is due to background clutter, phase-nulling or null point, DC offsets, motion artefacts and electromagnetic interferences [13]. In addition, for continuous sleep monitoring in particular, the challenges are in the complexity of the sleep environment, noises associated with the unpredictability of body movements, body orientations, changes in sleeping posture, multi-subjects cancellation, undesired harmonics, and intermodulation [14,15].
There have also been numerous reviews, comparison studies [16,17,18,19], and smart systems designs [20,21] regarding unobtrusive [22], nonintrusive [23], and non-contact physiological vital signs monitoring for sleep monitoring. However, a comprehensive review of the non-contact Doppler radar for health monitoring for OSA diagnosis has been limited. This is the primary motivation of this review paper.
The aim of this paper is to provide a comprehensive review on the current state of non-contact Doppler radar for sleep monitoring technology. This includes a review of the system theoretical fundamentals, signal processing methodologies, techniques, achievements and challenges. In addition, this paper also discusses potential future research directions, as well as, potential applications of this technology in the daily life.
The topic used for the literature search is “sleep monitoring using non-contact Doppler radar.” The searching of relevant literature ranges across multiple databases and online journals; including the University of Technology, Sydney (UTS, Ultimo NSW 2007, Australia) databases, PubMed, ScienceDirect, IEEE Xplore, and many more. The inclusions and/or exclusions of certain articles are based on its relevance to the field of non-contact Doppler radar physiological vital signs estimations and sleep indices predictions.
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the topologies and architectures of the non-contact Doppler radar systems. Section 3 describes the fundamentals principles of the non-contact Doppler radar systems. Section 4 outlines the sources of noises associated with the non-contact Doppler radar systems. Section 5 describes the signal processing techniques, whilst Section 6 categories the techniques of non-contact Doppler radar physiological vital signs estimations and sleep monitoring. Section 7 provides a brief outline of the ultra-wide band (UWB) Doppler radar systems and its usage in the vital signs estimations. Section 8 outlines current challenges and makes recommendations for future research directions. Finally, Section 9 concludes the work presented in this paper.
2. Non-Contact Doppler Radar Architecture
2.1. Heterodyne versus Homodyne Topology
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing of two frequencies. These new frequencies are called “Heterodynes.” Heterodyne transceiver usually contains a separate local oscillator (LO) oscillating at the radar’s operating frequency (RF) to radiate and transmit signal (Tx). The received signal (Rx) is filtered by a band-pass filter (BPF) and mixed with another separate LO oscillating at different frequency compared to the RF. This means that the mixed signal is modulated on a non-zero intermediate frequency (IF) rather than being converted directly to baseband. The mixed signal is also filtered by another BPF, followed by a low noise amplifier (LNA), and demodulated directly or mixed down to baseband before demodulation [13,18,24]. An illustration of the heterodyne transceiver topology is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Heterodyne transceiver topology.
The advantage of heterodyne topology is that different received frequencies can be converted to the same IF prior to the amplification or filtering processes and the IF is also at a considerably lower frequency than the RF. However, a major disadvantage of heterodyne topology is the high number of circuitry components and passives [13,18,24].
Homodyne is often referred to as direct-conversion receiver (DCR), synchrodyne, or zero-IF receiver. The received signal is mixed with a LO at the RF, i.e., the same frequency as its carrier, which converts the signal to baseband. The baseband signal is filtered using baseband BPF and is amplified using baseband LNA prior to baseband demodulator process or digitizer [13,18,24]. An illustration of the homodyne transceiver topology is given in Figure 2.
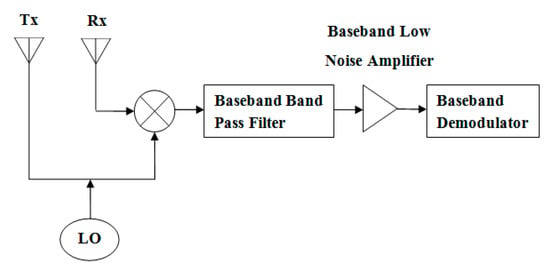
Figure 2.
Homodyne transceiver topology.
The advantage of homodyne topology is the simplification of the basic circuit complexity. However, a major disadvantage of homodyne topology is the amount of DC offsets introduced by the system, which can cause saturation for digitizer process [13,18,24].
2.2. Continuous-Wave versus Pulsed-Wave Architecture
The continuous-wave (CW) radar system continuously transmits and receives narrow bandwidth signal. CW radar consists of a signal source that can be used for both transmitting and receiving. Either heterodyne or homodyne topology can be used in CW radar system. However, homodyne topology is more commonly used in CW. This radar system has the advantages of simplicity, potential of minimal spread in the transmitted spectrum, and unambiguously measure velocity of targets. In addition, CW radar simplifies the filters at each stage of the receiver, and the signal processing is seemingly straightforward if velocity or displacement information is targeted. However, a disadvantage of the CW radar system is the inability to separate reflections temporally, causing DC offsets and low-frequency noises to be introduced in the received signal [25].
A pulsed-wave (PW) radar system requires a switch to pulse the transmitting and receiving signals and has a wider bandwidth. The advantage of PW radar is its ability to instantaneously measure target range, temporally separate transmitter leakages, and strong short-range echoes from the weaker echoes of long-range targets. However, a disadvantage of the PW radar system is the ambiguity in both range and velocity measurements. In non-contact physiological vital signs monitoring, the target is typically at the same or shorter range than the nearest clutter; therefore, the PW radar advantage is limited to the elimination of leakage. Since range measurements does not aid in physiological motions monitoring, the increased complexity of PW radar over CW radar does not result in a commensurate increase in benefits [25].
2.3. Single versus Quadrature Architecture
The Doppler radar transceivers can be built based on a single-channel or a quadrature design. The performance of single-channel is known to be sensitive to the position of the targets and, in the worst case of null-point, produced virtually no phase-modulated signal for the estimation of physiological motions. The quadrature transceiver is mainly used to mitigate the null-point issue in single-channel transceiver by selecting the better of the quadrature, i.e., I-channel (in-phase) or Q-channel (90° out-of-phases) for optimum signal demodulation [13,24,26]. The illustrations of the single-channel and quadrature designs are shown in Figure 3a,b.

Figure 3.
(a) Single-channel architecture; (b) Quadrature architecture.
3. Non-Contact Doppler Radar Principle
Doppler radar for physiological vital signs monitoring was discovered in the 1970s. The use of Doppler radar was demonstrated for detection of respiratory rate in 1975 and heart rate in 1979. Since the 1980s, the use of pulsed-wave (PW), continuous-wave (CW), frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW), Linear-Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave (LFMCW), and ultra-wide band (UWB) radars have also been explored for physiological sensing [25,27,28,29,30,31].
The basic principle of Doppler radar is to transmit a microwave signal towards a target. The transmitted frequency of the microwave signal is usually within the unlicensed, not unregulated Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) radio bands, e.g., 5.8 GHz, 10 GHz, or 24 GHz. The phase-modulated of the backscattered signal is then measured to estimate the periodic motions between the target and the source of transmission. This technology utilized the principle known as the “Doppler Effect.”
The Doppler Effect occurs when there is a shift in the frequency of the signal, either the transmitted or echo signal, due to relative motion between the transmitter and the receiver. In other words, when the target has a time-varying position with a net zero velocity, the echo signal is phase-modulated proportionally to the target variation [27,32,33].
In a general case, the Doppler shift in frequency can be expressed as
The time-varying phase shift proportional to the displacement can be expressed as
The transmitting (T(t)) and received signal (R(t)) can be represented as
In the case of physiological vital signs monitoring, the target object is usually the subject’s chest or abdominal region. The echo signal is then demodulated in the receiver to obtain information regarding the subject’s chest or abdominal movements. Typically, the movements contain information for both respiratory and heart rates [27,32,33]. It has also been reported that abdominal movements cause stronger Doppler shift due to higher amplitude and deeper displacement compared to chest movements [32].
The demodulated baseband quadrature outputs I and Q channels are generally expressed as
where ‘VI’ & ‘VQ’ are the DC offsets of the channels and ‘AI’ & ‘AQ’ are the amplitude gain constants of the channels. ‘θ0’ is the initial constant phase-shift of the system in radian. ‘λ’ is the wave length, which equal the speed of light ‘c’ divided by the radar operating frequency in Hertz. ‘d0’ is the initial distant between the radar and the subject’s chest or abdomen in meter. ‘ϕ’ is the phase noise of the system oscillation in radian. ‘x(t)’ is the function of respiratory that causes changes in the chest displacement in meter. ‘y(t)’ is the function of heart that causes changes in the chest displacement in meter.
Typically, Doppler radar is designed for measuring velocity of moving targets and therefore the scope of its applications are more restricted. However, it is not limited to respiratory and/or cardiac activity monitoring in a single subject [34]. The information for both respiratory and heart rates can be extracted from the phase-modulated by the time varying physiological periodic movement of the chest-wall. Nevertheless, such physiological motions are elastic, deformable with clothing which can create significant noise issue and adversely affecting the sensitivity of the system [32]. An illustration of the non-contact Doppler radar setup in a sleep laboratory or at home is shown in Figure 4.
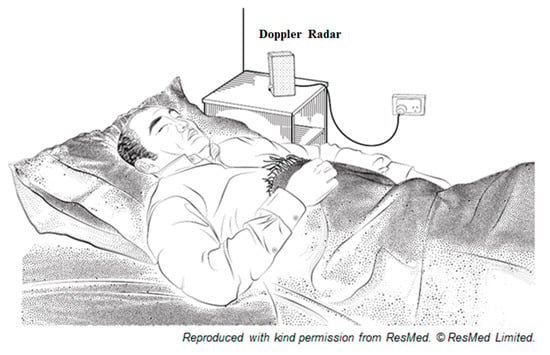
Figure 4.
Non-contact Doppler radar setup in a sleep laboratory or at home.
The physiological parameters and sleep indices which have been demonstrated feasible in estimation and/or prediction using non-contact Doppler radar is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Feasible parameters that can be estimated using non-contact Doppler radar.
The application of Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) radars, utilizing the “Doppler Effect” principle for sensing physiological vital signs, has also been reported in the literature. Researches in the field of UWB radars mainly focus on through-wall life-signs detection targeting respiratory and heart rates. The most challenging task is the registration of respiration activity of an unconscious person. The other focus is aimed at sensing some key physiological bio-markers of astronauts during intra-vehicular and extra-vehicular activities [52,53].
4. Sources of Noise in Non-Contact Doppler Radar
4.1. Clutter and DC Offset
In a radar system, clutters are generally echoes from all objects other than the target. Clutter detected at the receiver is commonly in the form of a single-tone component of the same frequency as the local oscillator (LO), however, with a different phase offset. The constant phase-shift is the function of the surface reflectivity and the size of the stationary portion of the target. When clutters are mixed with the LO, it will result in a DC offset in the baseband signal, and it is therefore difficult to separate in the frequency domain. If there is a significant DC component present at the signal output, the output is no longer linearly proportional to the displacement [54,55]. As a result, DC offset can saturate and desensitize the receiver in conventional CW radar system, and this is a critical issue [56].
4.2. Phase-Nulling or Null-Point
In a Doppler radar system, the most important limitation in measuring periodic motions such as respiratory and heart rates, is the presence of phase-nulling or null-point. The null-point occur when the received signal is either in-phase or 180° out-of-phases compared to the local oscillator [33]. The null-point occurs with the target’s distance every quarter of the radar transmitted signal wave-length (λ/4), and in the worst case produced virtually no phase-modulated signal for the estimation of physiological motions [26,33,56].
4.3. Others Sources of Noise
Besides clutters, other issues such as DC offsets, phase-nulling contributions, motions artefacts and electromagnetic interferences are also posing as challenges to the signal processing of Doppler radar signals [13,57]. Another major challenge in sleep monitoring application is the noise associated with unpredictable body movements, body orientations, changes in sleeping posture, multi-subjects cancellation, undesired harmonics and intermodulation [14,15,39].
5. Non-Contact Doppler Radar Signal Processing
It has been decades since the first observation of non-contact Doppler radar in measuring physiological motions such as respiratory and heart rates. However, to date, a complete understanding of the mechanism and causes of the observed modulations, frequencies penetrations and body electromagnetic radiation absorptions are not yet fully achieved.
There has been a number of attempts either in the form of experimental or simulation to investigate the contributions of blood perfusion, internal body organ movements, body surface movement, and black-body radiation (due to temperature variations) to the phase-modulated of the received signal [58]. However, the most dominating theory on the cause of observed modulations is still believed to be the small periodic movements of the chest wall (due to respiratory and heart motions) resulting in a small phase changes in the received signal.
Single and multiple Doppler radar systems have also been explored for physiological vital signs estimations. Advances in hardware circuitry design, antenna exploratory, signal processing techniques, and classification algorithms have also been explored. However, the main challenges in using Doppler radar systems for physiological measurement is still the analysis and processing of the received signal data [59].
5.1. Clutter and DC Offset Cancellation
Earlier work on the Doppler radar system used a single antenna with a circulator to isolate the transmitting and receiving paths [60], however a major disadvantage in using a circular was self-mixing, which translate to DC offsets on the output signal [55]. Dual-antennas with separated transmit and receive paths have also been explored with the advantage of reduced DC offsets [26,61].
Low-pass filters, high-pass filters, notch filters, and complex digital signal processing algorithms have also been reported for noise filtering and DC offsets elimination [26,27,33,61,62,63]. The reported filters are types of Sallen-Key [61,64,65,66], Elliptic [62,67], Butterworth, and RC passive [33,55,59,68] filters. Phase and Self-Injection-Locked (PSIL) oscillator with dual-tuning voltage-controlled oscillator has also been reported to achieve high signal-to-noise ratio [56]. Filtering at signal processing level, including Finite Impulse Response (FIR) with Kaiser window [36,61,69], Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) [29], and Savitzky-Golay Polynomial Least Squares (SG) [32] filters have also been proposed.
Other phase-modulation methods have also been proposed to address DC offset. These include using arctangent demodulation technique with DC offset calibrated through empty-room measurements [55] or at predetermined displacement range and periodic motions measurements [70]. However, these methods may not be valid because the DC offset value depends on the surface reflectivity, the size of the stationary portion of the target, and cannot be calibrated other than the subject under test [55]. Complex signal demodulation method using Bessel’s functions has also been explored to remove DC offset; however, it is still affected by the even order harmonics that are present in the baseband signal [71].
5.2. Phase-Nulling Cancellation
The main limitation in Doppler radar measurement of periodic motions is the presence of phase-nulling or null-point. The most prevailing solution is the quadrature (I/Q) architecture, where at least one of the outputs I/Q is not at null-point. Channel selection is then required to select the most optimum channel for processing at any given point in time [27,32,56]. However, I/Q output channels are not always in quadrature because of the inherent amplitude and phase imbalance due to imperfect system components [70]. The contribution of extra flicker noise caused by the mixers also contribute to the degradation of the detection accuracy [56].
The arctangent demodulation method combines the in-phase and quadrature (i.e., ±90° out-of-phases) baseband signals into a single channel to eliminate null-point. The equation that governs the extraction of angle/phase from I and Q channels is provided in (9), where Фr(t) is the demodulated Doppler angle/phase in radians.
The successful arctangent demodulation depends on the correction of channel imbalances and the removal of undesired DC offsets [72]. Channel imbalances can be corrected by using Gram-Schmidt procedure [72], however complex calibrations on the DC offsets is required for accurate demodulation [27,56].
Self-Injection-Locked (PSIL) oscillator with dual-tuning, voltage-controlled oscillator and single-channel receiver topology, using path-diversity transmission (where one path is 90° out-of-phases) has also been proposed to address the null-point issue. The proposed path-diversity, which is the periodic switching, to ensure at least one path is at optimal point while other experienced a null-point. The reported advantage of path-diversity transmission is the reduced average transmitted power. In other words, PSIL with path-diversity is more similar to the pulsed-wave radar topology [56].
Other several radar topologies have also been explored to overcome the phase-nulling issue. Topologies such as phase-diversity using phase-shifted two-channel receiver, two-channel receiver with displaced antennas, single-channel receiver with variable phase-shifter, and frequency-diversity (e.g., double sideband) transmission (to ensure at least one of the sidebands is not at null-point) have also been reported [33].
A “Relative Demodulation” technique has also been proposed to address the phase-nulling and DC offsets issues in quadrature (I/Q) architecture demodulation. This technique pivoted from conventional displacement and/or phase-shift analysis to introduce derivatives analysis. The relative demodulation technique provides real-time DC offsets, clutters, and null-points automatic elimination. The technique also approximates the instantaneous derivatives of the subject’s chest periodic motions with the separation of the instantaneous subject’s respiratory and heart periodic displacements [40]. The relative demodulation equation that governs the extraction of the chest motions velocity (v(t)) is given in (10) and (11).
Where: ‘AI’ and ‘AQ’ are the amplitude gain constants of I and Q channels.
5.3. Multi-Targets and Motions Artefacts Cancellation
Even through the literature that reported to have addressed noises associated with Doppler radar for physiological measurements in a single-subject, the focus on addressing multi-targets cancellation methodologies have rather been limited.
One of the limitations of a non-contact Doppler radar system when measuring physiological vital signs is its sensitivity to non-physiological motions of the subject, such as any background motions, body movements, body orientations, and multi-targets motions. These types of interferences once occurred at the same frequency band as that of the physiological motion is extremely difficult to remove using simple filtering techniques. The consequence is the degradation of accuracy in the estimation of the physiological vital signs.
In an attempt to address the multi-targets cancellation problem, a technique referred to as Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test (GLRT), based on a model of the heartbeat was proposed to firstly distinguish between the presence of 2, 1, or 0 subjects using a single-antenna Doppler radar system. Using multiple antennas will also result in detection of up to 2N-1 subjects. The use of a single antenna method is based on the subject’s heartbeat signature in the frequency domain, and the use of the multiple antennas method is based on the angle of signal arrival. The results demonstrated the theoretical concept; however, accuracy and reliability were not consistent when this method was applied [73].
Multiple transceivers system has been reported to cancel the noise caused by random body movements. Additionally, the use of differential front-end Doppler radar operating at two different frequencies, with dual helical antennas, has also been reported to improve the performance in cancelling motion artefacts [74].
An alternative approach to quantify the physical characteristics of the subjects (such as orientations, body size, body mass index, sleeping positions, body responses to illuminating waves) have also been explored through the vital signs cross section approach [54,75]. This approach considers the similarity between the conventional radar cross section—which is affected by target geometry—to the orientations and material composition. Regardless of the motions of the respiratory rate or heart rate, the vital sign cross section remains unchanged. This is the key in relation to human cardiopulmonary activity and can be used to distinguish the front and side torso of the measuring subject. The indicated body position can also be linked to the use of multi-targets cancellation and random body movements.
Arctangent demodulation and complex signal demodulation method using Bessel’s functions and dual-radar systems have also been reported to address the random body movements and DC offsets issues. The complex signal demodulation is simpler in implementation, robust in DC offsets elimination, and is more favorable for random body movement cancellation. However, the arctangent demodulation has the advantage of eliminating the harmonic and intermodulation interference at high frequencies using high gain antennas. The common challenge faced by these methods is the present of even order harmonics in the baseband signal [13,71,76].
Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD) has been noted in the literature as an effective method in analyzing non-stationary and non-linear signals. Its application for non-contact Doppler radar system in separating and removing motions artefacts has also been proposed. As documented in the literature, EMD is used for breaking down the radar signal output into its Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs). The removal of the motions artefacts interferences is achieved by selecting the proper IMFs. However, the proposed EMD application has its limitation in handling the interferences that occur at frequencies very close to the heart rate. EMD is also limited in removing interferences of the same type from the background objects [77].
A separation of mixed respiratory signals between two individuals, using dual-radar system and applying Blind Source Separation (BSS) signal processing technique, has also been proposed. The method was confirmed using simulated and experimental results, however, the sample data was deemed to be too low to provide convincing evidence of the reported accuracy and reliability [78].
Chen et al. proposed a separation of mixed respiratory signals between two individuals using dual-radar system and Blind Source Separation (BSS). The method was validated against simulated and experimental results; however, the sample data was too low to provide convincing evidence regarding the accuracy and reliability of the method. [78].
Cyclostationary approach for body movement cancellation using Doppler radar system has also been proposed. Cyclostationary theory is believed to be one of the most suitable methods for analyzing signals that have a cyclic pattern of statistical properties. The advantage of this approach is the robustness of cyclostationary processing in an environment with high noise and interferences. Numerical results have demonstrated that the vital signs can be extracted as cyclic frequencies, independent of signal to noise ratio (SNR) and without any filtering or phase unwrapping. Experimental results also illustrate that when applying cyclostationary theory to a complex radar signal, the respiratory and heart rates can be accurately estimated in an environment with high noise volume, long ranges, and weak signals. This includes high body movement artefacts without the need of phase unwrapping or demodulation [79].
A frequency domain signal processing method has been reported to extract both respiratory and heart rates for single and multiple subjects [80]. For a single-subject, the signal processing method utilized a digital FIR filter with Kaiser Window functions to achieve relatively smooth pass-band amplitude response and to increase the stop-band attenuation. For two-subjects, two-radars are used with natural gradient Blind Source Separation (BSS) algorithm to separate the mixed signals in real-time. The average respiratory rate error percentage ranges between 4.25–6.6% and the heart rate is approximately around 6.25%. The paper noted that the respiratory and heart rates can be successfully extracted from a single subject, and mixed signals can be separated with two subjects. However, the number of population samples is too low to effectively conclude the robustness, accuracy or reliability of the method.
6. Categories of Non-Contact Doppler Radar Signal Processing Techniques
To-date, signal processing techniques being investigated and reported in literature for non-contact Doppler radar can be categorized into the following four categories:
- Time-Frequency Analysis: this methodology uses time-series and frequency domain as the basis of signals analysis.
- Numerical Analysis: this methodology uses numerical techniques such as statistical, transformation and complex frequency as the basis of signals analysis.
- Classification & Training: this methodology utilizes machine learning methodologies and algorithms as the basis of signals analysis and predictions.
- Other Methodologies: these methodologies utilize experimental and mathematical modeling as the basis of signals analysis and estimations.
The subsequent sub-sections provide details on each of the identified categories.
6.1. Time-Frequency Analysis
Numerous works have been explored using the time-domain autocorrelation with peak detection, autocorrelation output with Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) [26,61] and statistical analysis [27,32,63] to detect both respiratory and heart rate peaks. Time-domain peak detection method with the addition of smoothing methods, such as the Newton relation, have also been reported in the literature to achieve the detection of the variability of peaks interval, revealing information such as heart rate variability for diagnosis and prognosis [27,41,81].
Frequency-domain analysis applying FFT or alternative Chirp Z-Transform (CZT) [33] with or without Fourier Spectral Subtraction (FSS) [82], have been proposed to identify the highest peak on the frequency-domain at a specific bandwidth targeting respiratory or heart rate. The highest peak at the frequency detected correlates to the rate of the targeted physiological measurement such as respiratory or heart rates. The ranges of the reported filter bandwidth frequencies for respiratory rate are from 0.1–0.5 Hz which is equivalent to 6–30 breaths per minute. The heart rate frequencies are from 0.8–2.0 Hz which is equivalent to 48–120 beats per minute [13,26,32,39,40,59,61,63,65,69].
Another time-frequency domain analysis that have been proposed is the application of Gabor transform, which is basically a Short Time Fourier Transform (STFT) component selection and Gabor expansion, to identify patterns in the time-frequency domain and to extract vital signs such as respiratory and heart rates. This approach differs from the conventional approach of phase observation in the baseband signal. The experimental results noted an accuracy of less than three beats per minute error in measuring heart rate with motion artefacts. However, identifying a best fit pattern for the vital signs in time-frequency domain, especially for respiratory, still poses a difficult challenge for this approach [83].
Additionally, it has also been reported in literature that since there is a large difference in respiratory and heartbeat induced displacements, simultaneous measures of the respiratory and heart rates will require a large dynamic range to cover the substantial difference in signal levels. The higher order harmonics of respiratory rate near the heart rate may appear and can cause error in the heart rate measurement. Complex signal demodulation without the need for DC offset calibration in the frequency-domain has also been proposed to eliminate the harmonics interference problem. Experimental results have demonstrated that when the harmonics of the respiration signal is strong, the proposed harmonics cancellation method can reduce the average error from 15.9% to 3.2% [84].
Studies have reported some commendable achievements, such as error of less than 0.5 breath per minute for respiratory rate and one beat per minute for heart rate [26,27,61]. In addition, the achieved accuracy of Doppler radar in measuring physiological parameters, such as respiratory rate is 92% [39], heart rate is 88% [39,59,81] to 91% [40], and with the addition of harmonics interference, the average error can be reduced further to 3.2% [84]. However, conventional FFT may not always be able to reliably separate the rich sinusoidal components due to smearing and leakage problems, particularly from the limited data samples [74]. Also, the number of samples under study is often too low to conclusively verify and validate the accuracy, reliability, and robustness of the proposed methods.
6.2. Numerical Analysis
There are a number of discretized numerical signal processing algorithms which have been reported for physiological vital signs estimations [85]. The first and simplest approach reported is the Mean of Signals (MEAN) method, with the assumption of phase changes varying between 0–2π uniformly and the offset is stable in a single window. The second approach is the Least Squares (LS) method, where the offset is fixed in small duration and the selected data samples fitted on a circle (the circle is plotted on Lissajous curve). The third is the Hough Transformation (HOUGH) method, applicable for data samples that distributed inhomogeneously, for example, when the target has no motion and caused biased estimation. The fourth approach is the Particle Filter (PF) method, a kind of Bayesian Filter, with features of robust estimation of the state and less restriction on the filter design. The fifth approach is the Direct Phase Estimation, based on Vector Difference (DIFF) method to estimate the phase changes by calculating the angle differences in which the estimation of offsets is not required. The experimental results have demonstrated that the phase estimation based on LS method, is the most preferable approach for respiratory measurements and with respect to accuracy and calculation time.
The Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) approach for both respiratory and heart rates estimation has also been proposed [86]. The proposed EKF is a non-linear extension of the earlier proposed conventional Kalman Filter (KF). The EKF algorithm is based on defining a state space model of the quadrature I/Q signals in combination with EKF to simultaneously estimate the respiratory and heart rates using unified statistically approach. The experimental results illustrate an acceptable level of accuracy with an error of approximately 1.7 beats per minute for heart rate. However, there is still a lack of dynamic modeling for other sources of noise and the comparison against other current methodologies and techniques [72].
The use of Wavelet Transform (WT) [87], Wavelet Filter [88], Wavelet Packet Decomposition (WPD) [39], Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), and Complex Wavelet Transform (CWT) with Morlet mother wavelet [29] have also been proposed in literature for respiratory and heart rate estimations. The advantage of Wavelet analysis over conventional methods, such as FFT, is that Wavelet is designed to operate on non-stationary signals and retains time and frequency information, providing good frequency resolution at lower frequencies. The experimental results demonstrate that the wavelet frequency has an absence of harmonics, which is an advantage over the conventional FFT. Harmonics in conventional FFT can cause difficulty in detecting heart rates when the third and fourth harmonics of respiratory rate overlaps with the heart rate [87].
Another approach reported in literature is the parametric and cyclic optimization approach referred to as the RELAX algorithm. RELAX is a spectral estimation and it is computationally efficient in comparison to many other spectral estimation algorithms. However, it is still more computationally demanding than the conventional Periodogram. Both theoretical and experimental results have demonstrated success in mitigating the effects of smearing and leakage problems of the conventional Periodogram. The smearing and leakage problems are often due to limited data length of both respiratory and heart rates [89].
Lomb-Scargle Periodogram has also been reported in literature for respiratory rate estimation. An application of the Lomb-Scargle Periodogram as signal processing technique to identify respiratory rate in sleeping subjects has also been reported. In using Lomb-Scargle Periodogram, the corrupted signals, which are often caused by intermittent movements or motion artefacts, can be excluded by treating those portions as missing data segments. Results have demonstrated that the Lomb-Scargle Periodogram has been successfully used on evenly sampled data, with periods of missing data, to achieve an average error of less than 0.4 breath per minute and standard deviation of 0.3 breath per minute for respiratory rate estimation [90].
6.3. Classification and Training
Support Vector Machine (SVM) has been explored for the detection of aspiration and apnea events for those subjects in lying position [91]. The calculation of the SVM utilized the training sets of three portions and one test data portion with the assumption of near ideal low-disturbance environment. However, the results do not support the accuracy and reliability of the machine.
Sleep stages classification algorithm based on bodily movements and the variability of the respiratory changes has been proposed for the sleep/wake pattern recognition. Recognizing the long-noted characteristic of respiratory rate appears to be steadier in both frequency and amplitude during the rapid-eye-movement (REM) stage compared to the wakefulness stage. The body movements also change between sleep stages, with the proposed algorithm demonstrating an accuracy level of 69% for the awake state and 88% for the sleep stages. In general, good performance results have been demonstrated for this classification method in recognizing the five standard sleep stages (Stages I-IV and REM) [12] (sleep stages that are prior to AASM classification in 2007).
Additionally, a linear discriminants classifier based on bio-motions has also been proposed for sleep/wake pattern recognition. This method applies initial training sets of six recordings to train the linear discriminants classifier in classifying sleep/wake states in sleeping subjects. The experimental results reported an overall per-subject accuracy of 78% [46].
Linear discriminants classifier-based detection algorithms using feature extraction, vector transformation and pattern recognition techniques have also been proposed to recognize Cheyne-Stokes respiration (CSR) and apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) events. The detection of CSR & AHI via non-contact Doppler radar is relatively new and very few attempts have been made. The experiments demonstrated promising result with correlation co-efficient of 0.87 with %CSR > 5.0 and 0.8 with AHI > 15.0. However tested samples were too low and require a larger study cohort to confirm the diagnostic value [48,49].
6.4. Other Methodologies
The other methodologies category includes the DC reconstruction and calibration techniques that are proposed to extract the tidal volume measurement from the non-contact Doppler radar signal [44]. Based on experiments, the paper indicates that there is a linear relationship between lung volume and chest-wall displacement during unobstructed breathing. The relationship is then used to detect and estimate the lung volume or tidal volume measurement based on the output of the non-contact Doppler radar signal. The proposed DC reconstruction employs the integration of the AC-coupled signal and the calibration of the signal amplitude as a ratio against the spirometer sensors. The experimental results reported an average mean difference of 38.9 mL in seated subjects and 23.5 mL in supine subjects.
A pulmonary ventilation mathematical model and algorithm that defines the relationship between the intrapulmonary pressure and the chest displacement has also been proposed [43]. The mathematical model and algorithm estimate the tidal volume from the non-contact Doppler radar I/Q signals from a set of 24 chronic heart failure (CHF) patients with median sleep duration of 7.76 h. The tidal volume estimation median accuracy achieved is 83.13%, with a median error of 57.32 milliliters.
These works have demonstrated a potential application of non-contact continuous monitoring of intrapulmonary pressure and tidal volume during sleep in the home.
7. Ultra-Wide Band Doppler Radar
A simple architecture of ultra-wide band (UWB) system, as proposed in [52], requires only one antenna and a rather simple signal processing algorithms in frequency-domain (FFT analysis) to extract respiratory motions and to compensate for the body movements. The results demonstrated feasibility of concept. However, it is not suitable for real-life applications. The reason for the unsuitability is due to its unrealistic hypothesis that respiration frequency is to be constant during body movement.
An alternative signal processing method for UWB radar using 2-D FFT and time–frequency analysis method S-Transform (ST) to detect and identify the subject’s respiratory motions under strong clutter with high SNR has also been reported. Even though the results are promising, limitations such as using experimental data and low-sample population with stationary standing subjects, has only resulted in demonstration of feasibility of the method [92].
Dual-pair sensors impulse UWB radar to track a single subject’s respiratory motions has also been proposed. The signal processing technique is the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) based method, where the respiratory rate of the subject is estimated from the backscattered signals from the dual-pair receiver antennas. The results showed the estimated respiratory rate can be successfully extracted with an accuracy of 81% [93].
Another proposed detection algorithm, with three stages finite impulse response (FIR) filters in the fast-time domain and linear trend subtraction (LTS) algorithm, is also used for clutter suppression. The respiratory rate is estimated using improved harmogram matrix threshold-based detection method. Analysis of the results have shown that approximately 1.5 dB improvement of SNR and signal to clutter and noise (SNCR) in comparison with the algorithm proposed by Xu et al. [94].
Impulse UWB radar for both respiratory and heart rates detection for non-line-of-sight (NLOS) has also been reported. The proposed signal processing technique is derived from the Developed Adaptive Line Enhancer (DALE) technique. This technique processes the signals in discrete form with DALE FIR filter and the respiratory and heart rates are estimated by finding the maximum peak. The results demonstrates that both respiratory and heart rates can be extracted using UWB, with the target subject located at non-line-of-sight, however, clutter, motions, and non-stationary complex scenarios still posed as a challenge [95].
A measurement method based on MUltiple SIgnal Classification (MUSIC) algorithm for through-wall life-signs detection has also been proposed. This method analyses the phase modulation, spatial smoothing de-correlation strategy that applied to the traditional algorithm for MUSIC, mandated to single out the spectral components of the received phase signal. The results indicate the feasibility of the algorithm. However, performance is an area that will require further improvement [96].
Another signal processing methodology has been proposed to estimate sleep apnea detection and respiratory rate from a single-subject measurement [97]. The signal processing incorporates the suppressing of clutter, body movement and body orientation detection. The signal processing uses digitalized frequency domain technique with the estimation of respiratory rate determined from Lomb Periodogram algorithm. The removal of quasi-static clutter to enhance the breathing signal detection is achieved using a moving averaging filter. Body movements are removed using a threshold method, and motion is detected using the time delay that maximizes the received signal after a clutter removing algorithm is applied. The apnea periods are detected after the clutter removal is defined by the cessation of respiratory efforts. The results indicate that respiratory rates and apnea event detection can be successfully extracted. However, a major challenge for the practical application of night breathing monitoring system is the noise signal produced by the body motion, where it is difficult to estimate the breathing rate during motion periods.
8. Challenges and Future Research Directions
Prior to identifying the challenges and future research directions, it is important to provide an overview of the current achievements of sleep monitoring using non-contact Doppler radar. The current achievements are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Sleep monitoring using non-contact Doppler radar achievements.
There are numerous published examples in the literature regarding non-contact assessments of respiratory and heart rates, however limited attempts have been made for non-contact assessment of heart rate variability. It is also important to emphasize the tendencies of reported achievements on non-contact physiological vital signs estimations, to be based on “stationary” and “direct-facing” subject measurements, which is not an ideal scenario for sleep monitoring. There has also been recognition that the assessment of non-contact heart rate and heart rate variability, with “non-stationary” and “non-direct facing” subject poses a greater challenge in the signal processing of non-contact Doppler radar system [14,15]. In conjunction with continuous improvements on accuracy of non-contact physiological vital signs estimations, there are two important areas in the non-contact sleep monitoring space that future researches may want to consider:
- First, it is recommended that future research be broadened to include non-contact assessment of heart rate and heart rate variability, as well as, targeting sleep monitoring with “non-stationary” and “non-direct facing” subject measurements. Additionally, pulse pressure, intrapulmonary pressure, tidal volume, minute ventilation, air flow, oxygen saturation, and Cheyne-Stokes respirations estimations are also encouraged to be explored extensively. The future achievements in these areas will significantly contribute to the screening, diagnosing and monitoring of cardiovascular comorbidity in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) patients. This will also lead to new opportunities and market potentials towards Cardiology in Sleep Disordered Breathing (SDB).
- Second, it is recommended that future research be broadened to include the complexity of sleep environment, such as noises associated with unpredictable body movements, body orientations, changes in sleeping posture, multi-subjects cancellation, undesired harmonics, and intermodulation. The future achievements in these areas will significantly contribute to the practical realization and commercialization of non-contact sleep monitoring and diagnosing technology.
With the increasing prevalence of OSA and its comorbidities, particularly cardiovascular comorbidity, there are substantial market potentials for the realization of non-contact continuous sleep monitoring technology. The most current prevailing market potential is the non-contact remote monitoring and screening of OSA at home. The applications of non-contact Doppler radar for sleep monitoring can widely be utilized in homes, hospitals, primary care sectors, nursing home facilities and sleep laboratories.
9. Conclusions
In this article, a comprehensive review of the non-contact Doppler radar technology for monitoring different physiological parameters during sleep was provided. The presented information, covering most aspects of the current research field, can be used as foundational knowledge. Along with the challenges identified, the recommended future research directions can help facilitate the practical realization and commercialization of the technology, especially for obstructive sleep apnea screening and monitoring which can be used in everyday life.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.P.T. and A.A.A.-J.; Methodology, V.P.T.; Formal Analysis, V.P.T.; Investigation, V.P.T.; Resources, V.P.T., A.A.A.-J., and S.M.S.I.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, V.P.T.; Writing—Review and Editing, V.P.T., A.A.A.-J., and S.M.S.I.; Supervision, A.A.A.-J.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of the Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship and Collaboration Enhancement Scheme 2016 grant (No. 22905) of Edith Cowan University (ECU).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Young, T.; Palta, M.; Dempsey, J.; Skatrud, J.; Webber, S.; Badr, S. The Occurrence of Sleep-Disordered Breathing Among Middle-Aged Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Barnet, J.H.; Palta, M.; Hagen, E.W.; Hla, K.M. Increased Prevalence of Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International Classification of Sleep Disorders, Revised: Diagnostic and Coding Manual; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Chicago, IL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, R.S.T.; Bradley, T.D. Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 2147–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, R.P.; Drager, L.F.; Gonzaga, C.C.; Sousa, M.G.; De Paula, L.K.G.; Amaro, A.C.S.; Amodeo, C.; Bortolotto, L.A.; Krieger, E.M.; Bradley, T.D.; et al. Obstructive Sleep Apnea: The Most Common Secondary Cause of Hypertension Associated With Resistant Hypertension. Hypertension 2011, 58, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronsohn, R.S.; Whitmore, H.; Cauter, E.V.; Tasali, E. Impact of Untreated Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Glucose Control in Type 2 Diabetes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 181, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seicean, S.; Strohl, K.P.; Seicean, A.; Gibby, C.; Marwick, T.H. Sleep Disordered Breathing as a Risk of Cardiac Events in Subjects With Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Exercise Echocardiographic Findings. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 111, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, F.J.; Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Finn, L.; Hla, K.M.; Farré, R. Sleep-disordered Breathing and Cancer Mortality: Results from the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, T.; Skatrud, J.; Peppard, P.E. Risk Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 291, 2013–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.J.; Jain, V.; Park, A.-M.; Day, R.M. Oxidative stress and oxidant signaling in obstructive sleep apnea and associated cardiovascular diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 40, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attarian, H.P.; Sabri, A.N. When to suspect obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Symptoms may be subtle, but treatment is straightforward. Postgrad. Med. 2002, 111, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazal, P.D.; O’Hare, E.; Fox, N.; Heneghan, C. Assessment of Sleep/Wake Patterns Using a Non-Contact Biomotion Sensor. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual International IEEE EMBS Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–24 August 2008; pp. 514–517. [Google Scholar]
- Lie, D.Y.C.; Ichapurapu, R.; Jain, S.; Lopez, J.; Banister, R.E.; Nguyen, T.; Griswold, J. A 2.4 GHz Non-Contact Biosensor System for Continuous Monitoring of Vital-Signs. In Telemedicine Techniques and Applications; Graschew, G., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 211–238. [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa, M.; Ueki, K.; Tojima, H.; Matsui, T. Noncontact Screening System with Two Microwave Radars for the Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 2052–2055. [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Kubota, M.; Kurita, A.; Matsui, T. An overnight vital signs monitoring system for elderly people using dual microwave radars. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference 2011, Melbourne, Australia, 5–8 December 2011; pp. 590–593. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Kong, L.; Foroughian, F.; Wang, H.; Theilmann, P.; Fathy, A.E. Comparison Study of Noncontact Vital Signs Detection Using a Doppler Stepped-Frequency Continuous-Wave Radar and Camera-Based Imaging Photoplethysmography. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 3519–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, H.O.; Khushaba, R.N.; Zaffaroni, A.; Colefax, M.; Farrugia, S.; Schindhelm, K.; Teschler, H.; Weinreich, G.; Grueger, H.; Neddermann, M.; et al. Development and validation of a novel non-contact monitor of nocturnal respiration for identifying sleep-disordered breathing in patients with heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2016, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, J.-H.; Kao, J.-C.; Huang, T.-W. Review on Microwave/Millimeter-wave Systems for Vital Sign Detection. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Topical Conference on Wireless Sensors and Sensor Networks (WiSNet), Newport Beach, CA, USA, 19–23 January 2014; pp. 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.; Lie, D.Y.C.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Mayeda, J.C.; Lie, P.E.; Lopez, J.; Banister, R.E. Non-Contact Sensor for Long-Term Continuous Vital Signs Monitoring: A Review on Intelligent Phased-Array Doppler Sensor Design. Sensors 2017, 17, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-T.; Prasad, M.; Chung, C.-H.; Puthal, D.; El-Sayed, H.; Sankar, S.; Wang, Y.-K.; Singh, J.; Sangaiah, A.K. IoT-Based Wireless Polysomnography Intelligent System for Sleep Monitoring. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacchirema, D.C.; Sarabia-Jacome, D.; Palau, C.E.; Esteve, M. A Smart System for Sleep Monitoring by Integrating IoT With Big Data Analytics. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 35988–36001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, G.; Lina, J.-M.; Carrier, J.; Kaddoum, G. Unobtrusive Sleep Monitoring Using Cardiac, Breathing and Movements Activities: An Exhaustive Review. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 45129–45152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, I.; Seet, E.; Biswas, J.; Abdulrazak, B.; Mokhtari, M. Nonintrusive Vital Signs Monitoring for Sleep Apnea Patients: A Preliminary Study. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 2506–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lubecke, V.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lin, J. A Review on Recent Advances in Doppler Radar Sensors for Noncontact Healthcare Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 2046–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalise, L. Non Contact Heart Monitoring. In Advances in Electrocardiograms—Methods and Analysis; Millis, R., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 81–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ichapurapu, R.; Jain, S.; Kakade, M.U.; Lie, D.Y.C.; Banister, R.E. A 2.4 GHz Non-Contact Biosensor System for Continuous Vital-Signs Monitoring on a Single PCB. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th International Conference, Changsha, China, 20–23 October 2009; pp. 925–928. [Google Scholar]
- Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.; Mostafanezhad, I.; Park, B.-K.; Massagram, W.; Jokanovic, B. Doppler Radar Architectures and Signal Processing for Heart Rate Extraction. Mikrotalasna Rev. 2009, 15, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Avagyan, H.; Hakhoumian, A.; Hayrapetyan, H.; Pogosyan, N.; Zakaryan, T. Portable Non-Contact Microwave Doppler Radar for Respiration and Heartbeat Sensing. Am. J. Phys. 2012, 5, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Postolache, O.A.; Girão, P.S.; Postolache, G. Comparative analysis of two systems for unobtrusive heart signal acquisition and characterization. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 7021–7024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Munoz-Ferreras, J.-M.; Gu, C.; Li, C.; Gomez-Garcia, R. Linear-Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave Radar for Vital-Sign Monitoring. In Proceedings of the Wireless Sensors and Sensor Networks (WiSNet), Newport Beach, CA, USA, 19–23 January 2014; pp. 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Fathy, A.E. CW and Pulse–Doppler Radar Processing Based on FPGA for Human Sensing Applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3097–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Pathirana, P.N.; Caelli, T.; Li, S. Further Applications of Doppler Radar for Non-contact Respiratory Assessment. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 3833–3836. [Google Scholar]
- Girbau, D.; Lázaro, A.; Ramos, Á.; Villarino, R. Remote Sensing of Vital Signs Using a Doppler Radar and Diversity to Overcome Null Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostov, K.; Liptsen, E.; Boutchko, R. Medical applications of shortwave FM radar: Remote monitoring of cardiac and respiratory motion. Med. Phys. 2010, 37, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shouldice, R.B.; Heneghan, C.; Petres, G.; Zaffaroni, A.; Boyle, P.; McNicholas, W.T.; Chazal, P.D. Real Time Breathing Rate Estimation from a Non Contact Biosensor. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August –4 September 2010; pp. 630–633. [Google Scholar]
- Vasu, V.; Heneghan, C.; Sezer, S.; Arumugam, T. Contact-free Estimation of Respiration Rates during Sleep. In Proceedings of the 22nd IET Irish Signals and Systems Conference, Dublin, Ireland, 23–24 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ballal, T.; Shouldice, R.B.; Heneghan, C.; Zhu, A. Breathing Rate Estimation from a Non-Contact Biosensor Using an Adaptive IIR Notch Filter. In Proceedings of the Biomedical Wireless Technologies, Networks, and Sensing Systems (BioWireleSS 2012), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 15–18 January 2012; pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Baboli, M.; Gao, X.; Yavari, E.; Padasdao, B.; Soll, B.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V. Considerations for Integration of a Physiological Radar Monitoring System with Gold Standard Clinical Sleep Monitoring Systems. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 2120–2123. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, V.P.; Al-Jumaily, A.A. Non-Contact Dual Pulse Doppler System based Respiratory and Heart Rates Estimation for CHF Patients. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 4202–4205. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, V.P.; Al-Jumaily, A.A. Non-Contact Dual Pulse Doppler System Based Real-Time Relative Demodulation and Respiratory & Heart Rates Estimations for Chronic Heart Failure Patients. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 76, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Obeid, D.; Zaharia, G.; Sadek, S.; El Zein, G. Microwave Doppler Radar for Heartbeat Detection Vs Electrocardiogram. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2012, 54, 2610–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Lubecke, V.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Pulse Pressure Monitoring Through Non-Contact Cardiac Motion Detection Using 2.45 GHz Microwave Doppler Radar. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 4336–4339. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, V.P.; Al-Jumaily, A.A. Non-Contact Real-Time Estimation of Intrapulmonary Pressure and Tidal Volume for Chronic Heart Failure Patients. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Orlando, FL, USA, 18 October 2016; pp. 3564–3567. [Google Scholar]
- Massagram, W.; Hafner, N.; Lubecke, V.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Tidal Volume Measurement through Non-Contact Doppler Radar with DC Reconstruction. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3397–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Pathirana, P.N.; Steinfort, C.L.; Caelli, T. Non-Contact Measurement of Respiratory Function and Deduction of Tidal Volume. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 594–597. [Google Scholar]
- Chazal, P.D.; Fox, N.; O’Hare, E.; Heneghan, C.; Zaffaroni, A.; Boyle, P.; Smith, S.; O’Connell, C.; McNicholas, W.T. Sleep⁄wake measurement using a non-contact biomotion sensor. J. Sleep Res. 2011, 20, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaffaroni, A.; Chazal, P.D.; Heneghan, C.; Boyle, P.; Ronayne, P.; McNicholas, W.T. SleepMinder: An Innovative Contact-Free Device for the Estimation of the Apnoea-Hypopnoea Index. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–6 September 2009; pp. 7091–7094. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, H.O.; Khushaba, R.; Bateman, P.; Farrugia, S.; Schindhelm, K.; Simonds, A.K.; Cowie, M.R. A Novel Non-Contact Device That Identifies and Categorises Sleep Disordered Breathing in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Heart 2013, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Savage, H.O.; Khushaba, R.; Bateman, P.; Farrugia, S.; Schindhelm, K.; Simonds, A.K.; Cowie, M.R. Cheyne Stokes respiration in patients with heart failure detected by a novel non-contact monitor of nocturnal respiration. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2013, 12, S1. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Pal, R.; Li, C. Non-contact Multi-Radar Smart Probing of Body Orientation based on Micro-Doppler Signatures. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2014, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.P.; Al-Jumaily, A.A. Non-Contact Doppler Radar Based Prediction of Nocturnal Body Orientations Using Deep Neural Network for Chronic Heart Failure Patients. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical and Computing Technologies and Applications (ICECTA), Ras Al Khaimah, UAE, 21–23 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Baldi, M.; Appignani, F.; Zanaj, B.; Chiaraluce, F. Body Movement Compensation in UWB Radars for Respiration Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE First AESS European Conference on Satellite Telecommunications (ESTEL), Rome, Italy, 2–5 October 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, J.; Helbig, M.; Herrmann, R.; Kmec, M.; Schilling, K.; Zaikov, E. Remote vital sign detection for rescue, security, and medical care by ultra-wideband pseudo-noise radar. Ad Hoc Netw. 2012, 13, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriazi, J.E.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V. Considerations in Measuring Vital Signs Cross Section with Doppler Radar. In Proceedings of the Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS 2011), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 16–19 January 2011; pp. 426–429. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.-K.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.M. Arctangent Demodulation With DC Offset Compensation in Quadrature Doppler Radar Receiver Systems. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2007, 55, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-H.; Jau, J.-K.; Li, C.-J.; Horng, T.-S.; Hsu, P. Phase- and Self-Injection-Locked Radar for Detecting Vital Signs with Efficient Elimination of DC Offsets and Null Points. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, M.; Leonhardt, S. Non-Contact Monitoring of Heart and Lung Activity by Magnetic Induction Measurement. Acta Polytech. 2008, 48, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Aardal, Ø.; Paichard, Y.; Brovoll, S.; Berger, T.; Lande, T.S.; Hamran, S.-E. Physical Working Principles of Medical Radar. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, V.; Fox, N.; Brabetz, T.; Wren, M.; Heneghan, C.; Sezer, S. Detection of Cardiac Activity using a 5.8 GHz Radio Frequency Sensor. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–6 September 2009; pp. 4682–4686. [Google Scholar]
- Droitcour, A.D.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.M.; Lin, J.; Kovacs, G.T.A. Range Correlation and I/Q Performance Benefits in Single-Chip Silicon Doppler Radars for Noncontact Cardiopulmonary Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2004, 52, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichapurapu, R.; Jain, S.; John, G.; Monday, T.; Lie, D.Y.C.; Banister, R.; Griswold, J. A 2.4GHz Non-Contact Biosensor System for Continuous Vital-Signs Monitoring. In Proceedings of the Wireless and Microwave Technology Conference, Clearwater, FL, USA, 20–21 April 2009; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, R.; Han, J. Low-Cost Differential Front-End for Doppler Radar Vital Sign Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2009; pp. 1325–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.; Yang, F.; Tian, Y.; Jing, X.; Wang, J. Contact-free Measurement of Heart Rate Variability via a Microwave Sensor. Sensors 2009, 9, 9572–9581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, V.; Boothby, A.; Hwang, R.; Nguyen, T.; Lopez, J.; Lie, D.Y.C. Antenna Evaluation of a Non-Contact Vital Signs Sensor for Continuous Heart and Respiration Rate Monitoring. In Proceedings of the Biomedical Wireless Technologies, Networks, and Sensing Systems (BioWireleSS 2012), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 15–18 January 2012; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Kim, J.-G.; Hong, S. A Compact Ka-Band Doppler Radar Sensor for Remote Human Vital Signal Detection. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2012, 12, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boothby, A.; Das, V.; Lopez, J.; Tsay, J.; Nguyen, T.; Banister, R.E.; Lie, D.Y.C. Accurate and Continuous Non-Contact Vital Signs Monitoring Using Phased Array Antennas in a Clutter-Free Anechoic Chamber. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 2862–2865. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, R.R.; Kulkarni, S. Wearable Doppler radar with integrated antenna for patient vital sign monitoring. In Proceedings of the Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS 2010), New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–14 January 2010; pp. 276–279. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, M.A.; Sinnappa, M.; Azman, H.; Abidin Abd Aziz, M.Z.; Ismail, M.M.; Hussein, M.N.; Sulaiman, H.A.; Misran, M.H.; Meor Said, M.A.; Ramlee, R.A.; et al. 5.8 GHz Microwave Doppler Radar for Heartbeat Detection. In Proceedings of the 23th Conference Radioelektronika, Pardubice, Czech Republic, 16–17 April 2013; pp. 367–370. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.-J.; Hong, Y.-P.; Jang, B.-J.; Yook, J.-G. Comparative Study of 2.4 GHz and 10 GHz Vital Signal Sensing Doppler Radars. In Proceedings of the 40th European Microwave Conference, Paris, France, 28–30 September 2010; pp. 501–504. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Singh, A.; Yavari, E.; Lubecke, V.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Non-contact Displacement Estimation Using Doppler Radar. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 1602–1605. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Lin, J. Complex Signal Demodulation and Random Body Movement Cancellation Techniques for Non-contact Vital Sign Detection. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–20 June 2008; pp. 567–570. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.S.; Kim, K.-D. Extended Kalman Filter for Rate Estimation in Doppler Radar Cardiopulmonary Monitoring System. Int. J. Bio-Sci. Bio-Technol. 2012, 4, 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, J.; Høst-Madsen, A.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V. Detection of Multiple Heartbeats Using Doppler Radar. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing, Toulouse, France, 14–19 May 2006; pp. 1160–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Lin, J. Recent Advances in Doppler Radar Sensors for Pervasive Healthcare Monitoring. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference 2010, Yokohama, Japan, 7–10 December 2010; pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kiriazi, J.E.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.M. Radar Cross Section of Human Cardiopulmonary Activity for Recumbent Subject. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–6 September 2009; pp. 4808–4811. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Lin, J. Random Body Movement Cancellation in Doppler Radar Vital Sign Detection. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2008, 56, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafanezhad, I.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V.; Mandic, D.P. Application of Empirical Mode Decomposition in Removing Fidgeting Interference in Doppler Radar Life Signs Monitoring Devices. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–6 September 2009; pp. 340–343. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tan, H.; Hu, B.; Li, Y. Doppler Radar Based Non-Contact Multi-Person Respiration Signals Separation. In Proceedings of the IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI 2012), Hong Kong and Shenzhen, China, 2–7 January 2012; pp. 799–802. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi, S.; Ghorbani, A.; Amindavar, H.; Li, C. Cyclostationary approach to Doppler radar heart and respiration rates monitoring with body motion cancelation using Radar Doppler System. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 13, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; He, T.; Hu, B.; Li, Y. Non-contact physiological signal detection using continuous wave Doppler radar. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 993–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Obeid, D.; Sadek, S.; Zaharia, G.; El Zein, G. Doppler Radar for Heartbeat Rate and Heart Rate Variability Extraction. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on E-Health and Bioengineering, Iaşi, Romania, 24–26 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yavari, E.; Padasdao, B.; Lubecke, V.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Packet Radar Spectrum Recovery for Physiological Signals. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 1760–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Birsan, N.; Munteanu, D.-P.; Iubu, G.; Niculescu, T. Time-Frequency Analysis in Doppler Radar for Noncontact Cardiopulmonary Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on E-Health and Bioengineering—EHB 2011, Iaşi, Romania, 24–26 November 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, J.; Lin, J. Respiration Harmonics Cancellation for Accurate Heart Rate Measurement in Non-contact Vital Sign Detection. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (IMS), Seattle, WA, USA, 2–7 June 2013; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi, H.; Kubo, H.; Mori, T.; Sato, T.; Sanada, H. Signal Phase Estimation for Measurement of Respiration Waveform Using a Microwave Doppler Sensor. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 6740–6743. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.S.; Jang, B.-J.; Kim, K.-D. A New Digital Signal Processor for Doppler Radar Cardiopulmonary Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (ICECE 2008), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 20–22 December 2008; pp. 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, A.; Shiraz, H.G. Doppler Radar Vital Signs Monitoring using Wavelet Transform. In Proceedings of the 2010 Loughborough Antennas & Propagation Conference, Loughborough, UK, 8–9 November 2010; pp. 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Real-time remote vital sign detection using a portable Doppler sensor system. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS), Queenstown, New Zealand, 18–20 February 2014; pp. 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Ling, J.; Li, J.; Lin, J. Accurate Doppler Radar Noncontact Vital Sign Detection Using the RELAX Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 687–695. [Google Scholar]
- Vasu, V.; Fox, N.; Heneghan, C.; Sezer, S. Using the Lomb Periodogram for Non-Contact Estimation of Respiration Rates. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 2407–2410. [Google Scholar]
- Inui, S.; Okusa, K.; Maeno, K.; Kanakura, T. Recognizing Aspiration Presence using Model Parameter Classification from Microwave Doppler Signals. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science (WCECS 2012), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–26 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, J.; Liu, F. Through-Wall Detection of Human Being’s Movement by UWB Radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijsure, Y.; Tay, W.P.; Gunawan, E.; Wen, F.; Yang, Z.; Guan, Y.L.; Chua, A.P. An Impulse Radio Ultrawideband System for Contactless Noninvasive Respiratory Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Qiao, D.; Li, Y.; Dai, H. A Novel Through-Wall Respiration Detection Algorithm Using UWB Radar. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 1013–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.Z.; Li, Z.; Lv, H.; Lu, G.H.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, X.J.; Li, S.; Wang, J.Q. A new method for non-line-of-sight vital sign monitoring based on developed adaptive line enhancer using low centre frequency UWB radar. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2013, 133, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascione, M.; Buonanno, A.; D’Urso, M.; Angrisani, L.; LoMoriello, R.S. A New Measurement Method Based on Music Algorithm for Through-the-Wall Detection of Life Signs. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, A.; Girbau, D.; Villarino, R. Techniques for Clutter Suppression in the Presence of Body Movements during the Detection of Respiratory Activity through UWB Radars. Sensors 2014, 14, 2595–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).