Abstract
Trout fishing is one of the primary recreational activities in the southern Appalachians, with large amounts of fish stocked on a regular basis. However, very little is known regarding the fate of hatchery reared carcasses not captured by anglers, representing a likely important ecological resource to local communities. We tested the efficacy of underwater video to characterize short term decomposition and consumption by aquatic scavengers of native brook and non-native rainbow trout, Salvelinus fontinalis and Oncorhychus mykiss. This study took place on the Cherokee Qualla Boundary in North Carolina, a location with one of the highest riverine stocked trout densities in the eastern United States. During May 2017, 10 waterproof cameras were deployed for 1-hour intervals on each carcass twice daily for a period of 5 days. We observed that 75.3% of recorded video contained river chub, Nocomis micropogon, with only 24.7% visited by crayfish, with a maximum of 9 and a mean of 1.93 for N. micropogon. Half of the carcasses were removed within 2 days. Based on natural history evidence and some trail cameras, we believe that otters were removing carcasses. Otters showed no preference for either trout species. Underwater video allowed us to characterize initial decomposition within stream diurnal scavengers in a short period using a visual, non-destructive low-cost method. Future studies should monitor large mammalian scavengers to further elucidate the role of fish stocking on aquatic communities.
1. Introduction
Animal remains are important components in food webs of North American rivers [1]. Scavenging ecology has recently become recognized as an important ecosystem process in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems [2,3]. Marine ecosystem scavengers have become increasingly identified using baited remove underwater video (BRUV) as a non-invasive method to observe fish assemblages [4,5,6]. However, the role of scavenger communities in streams has received limited attention [7,8] when compared to marine ecosystems. Therefore, there exists a paucity of information on riverine scavenging communities.
Salmonid carcasses are ideal to assess the role of scavenging in streams, as they provide a source for nutrient cycling [9] and direct resources for many taxa. Carcasses of salmon may be consumed by a wide range of scavengers including birds, mammals, and invertebrates [10,11]. Moreover, carcasses in riparian zones have recently been documented to support a diverse community of scavengers [12]. Presently, the Eastern Band of Cherokee Indian stocks approximately a ton of fish a week with their ultimate fate unknown. Subsequently, very little is known regarding potential trout carcass scavengers in Appalachian stream ecosystems.
Action cameras, such as GoPro™ cameras, have become increasingly utilized for video recording and documentation of species diversity [6,13,14], as baited remote underwater videos BRUV [8], to measure fish [15], and to record fish behavior [16], due to their portability, low-cost, and high quality video. Species identification of fish assemblages with camera systems can even provide similar identification compared to net-based catch methods [17]. The use of BRUVs has increased for measuring fish diversity in freshwater habitats [7,18]. However, to our knowledge, there is no study which has assessed the potential for differential use of native over non-native species of trout by scavengers in Appalachian stream ecosystems using action cameras.
Therefore, in the following study, we seek to (1) assess the efficacy of action cameras to study scavenging and decomposition of native and non-native trout carcasses and (2) report on riverine scavenging communities which might affect trout decomposition.
2. Results and Discussion
We used waterproof cameras to record a total of 77 events (45 Brook and 32 Rainbow trout) over 5 days. Video events represented 10 morning and 10 afternoon events each day of the experiment, with the exception of 9 each morning and afternoon event on day four, and only 9 morning video events recorded on day five. Due to the loss of carcasses, the sample size for daily camera recordings shifted toward the end of the experiment and were as follows for brook (B) and rainbow trout (R), Day 1 = 5B, 5R; Day 2 = 10B, 10R; Day 3 = 12B, 8R; Day 4 = 12B, 6R; and Day 5 = 6B, 3R. These represented 39 afternoon events (22 brook and 17 rainbow) and 38 morning events (23 brook and 15 rainbow).
In total, we detected primarily River chub, Nocomis micropogon (Cyprinidae) most frequently and crayfish sp. (Decapoda) across all sites on both types of carcasses (Table 1). Max N across all carcass types for N. micropogon and crayfish was 9 and 1 respectively, with a max N mean of 1.93 for N. micropogon and never varying for carcasses visited by crayfish. Max N for N. micropogon was 9 and 7, with means of 2.08 and 1.65 for brook and rainbow trout, respectively (Table 1). However, N. micropogon scavenging visits to carcasses (Figure 1a) were similar for both brook and rainbow trout video events (28 afternoons and 30 mornings) while crayfish (Figure 1b) were observed more frequently on afternoon video events (12 afternoons and 7 mornings) but were not statistically significant. In general, carcasses were scavenged near the tail, eye, operculum, vent, and even within the abdominal cavity in some cases.

Table 1.
Summary of scavenging events observed on brook and rainbow trout showing the maximum number of scavenging fish observed at any one time (Max N); frequency of video events with Nocomis micropogon (river chub) scavenging; and frequency of videos with crayfish observed scavenging. Percentages calculated from 77 total video events (45 Brook and 32 Rainbow trout) across 5 days.
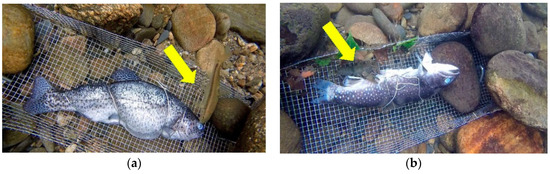
Figure 1.
Images captured during hour-long GoPro™ video events showing (a) Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) scavenged by Nocomis micropogon and (b) Brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) carcass visited by crayfish. Scavenger species are indicated by a yellow arrow.
We found salmonid carcasses were scavenged relatively quickly, i.e., the same day we deployed 20 carcasses, we lost 20% of carcasses. Within 24 h, we lost 35% of carcasses. Within 2 days we lost 50% of carcasses. Lastly, 60% of carcasses were removed completely during the short term video study by day 5. This is consistent with our model which predicted that we likely lost 20% of our carcasses within 4 h (15,000 s; Figure 2). Across the video experiments, brook and rainbow trout mass changed at a similar rate with brook trout losing on average 6.56 g per day, with rainbow trout losing on average 10.78 g per day. By the end of the 5-day experiment, we noted most carcasses were colonized by fungi and bacteria as noted in other studies in decomposition [19,20]. We found no significant difference for the survival analysis (persistence) of rainbow versus brook trout carcasses, p = 0.742, Z = 0.3295, indicating that fish species were taken at a similar rate over time (Figure 2).
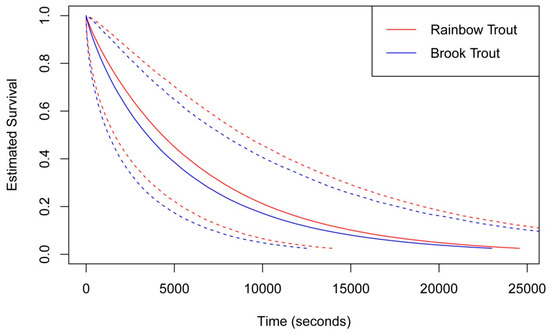
Figure 2.
Survival analysis curve showing the fate of brown (Salvelinus fontinalis) and rainbow trout (Oncorhychus mykiss) carcasses over the course of the experiment. Rainbow trout estimated survival (persistence of carcass) is shown in red and Brook trout is shown in blue. Dotted lines indicate standard errors around the fit line for the estimated survival of species.
During our experiment, the following environmental averages were recorded: over-all mean water temperature (16.59 °C ± 1.693), dissolved oxygen (9.27 mg/L ± 0.524), turbidity (3.067 FNU, ± 1.875), discharge (412.144 cub.ft./s ± 39.571), pH (6.931 ± 0.298), nitrite (0.2 mg/L ± 0.032), and specific conductivity (23.437 μS /cm ± 1.31).
We recommend future research combines underwater cameras with trail cameras. Furthermore, the carcass tray should be placed close enough to shore to allow the detection of a variety of potential scavenging species which may use trout carcasses as a resource. In addition, future work could investigate seasonal differences, distance of carcass to shore, and the effect of water movement on carcass decomposition. Hypothetically, these considerations could significantly alter what species scavenge and feed on a carcass if near the shore or seasonal temperatures influencing decay rates and overall scavenger activity or diversity. However, since 50% of the carcasses were taken within 48 h of deployment, we do not believe carcasses had sufficient time to break apart or drift far. Other studies have found the decay of carcass to vary from ~50 days [21] to as little as ~11 days [20]. Therefore, it appears both rainbow and brook trout are likely scavenged in this ecosystem during the late spring soon after they die by a combination of local scavengers, most likely river otters, which we documented in our same tray deployment sites with trail cameras following our short-term experiment. Moreover, otters are the only animal in this area able to remove fish from this depth and flow with delicate precision, leaving empty, almost pristinely cleaned experimental fish trays as we observed in this study.
Other studies using trail cameras have found birds to be dominant predators of live hatchery released salmonids [22] with eagles, ravens, and gulls utilizing salmonid carcasses [23]. Trail camera evidence provided indirect observation that river otters are a dominant scavenger likely responsible for the removal of several carcasses during our experiment. We also observed a tray lodged into a hole, which is a standard otter behavior. In our study, we found it likely that otters removed carcasses very quickly. It is unknown to what extent trout allows local otter populations to grow, as they were virtually extinct and subsequently reintroduced into western North Carolina in 1990–1995 [24]. However, this cascading effect of population growth could have impacts on other native species that otters are known to prey upon, such as the locally at-risk species eastern hellbenders (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis) or sicklefin redhorse (Moxostoma sp.). Both brook and rainbow trout clearly provide valuable subsidies for otters, fish, and invertebrates. As such, high levels of trout stocking could influence Appalachian ecosystem processes. Therefore, future research should focus on furthering the ecological connections between otters and other species, as well as examining how historical otter populations may have impacted native fish. Additional research could compare the differences between both scavenging and detrital components of salmonid-dominated Appalachian and Pacific Northwest ecosystems, as salmon-derived nutrients of Appalachian ecosystems are less studied.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental Design
This experiment took place in the Oconaluftee River located in Swain County, North Carolina. We obtained brook (Salvelinus fontinalis) and rainbow (Oncorhynchus mykiss) trout from the Cherokee hatchery located in the Big Cove community of Cherokee North Carolina during April 2017. We obtained full grown fish within 2 hours of natural death and initially froze them into individual plastic storage containers at −20 °C for ~15 days upon which we transferred the fish to a −80 °C frost-free freezer until they were used in the experiment in May 2017. We used fish of equivalent sizes based on initial mass (Mean = 233 g ± 42). On the day of deployment (8 May 2017), fish were slowly thawed on ice at ~4 °C inside a 51 L cooler on the day of the experiment.
To measure fish decomposition and consumption, we placed brook (N = 10) and rainbow (N = 10) trout into separate scavenging trays that we weighed once a day from 8–17 May 2017. We made trays from galvanized wire with 0.5 cm2 mesh and shaped them into ~40 × 15× 5 cm with zip ties to secure edges. The carcass trays weighed 91 g ± 6 g. The mesh allowed the tray to rest on the substrate and suppress vegetation around the carcass bait, ensuring they were not hidden from potential scavengers, and to retain fish tissue. To prevent fish from drifting away in the current, we staked the tray down with two 17.5 cm galvanized nails and fish were secured to trays with a 0.1-cm gauge wire. Trays were left with the top open to allow most organisms access to the carcass. To ensure that scavenging animals independently sampled trays, we spaced trays between shallow riffle waters and an average of 65 m (SD ± 24 m) when spaced within deeper stretches of water (Figure 3).
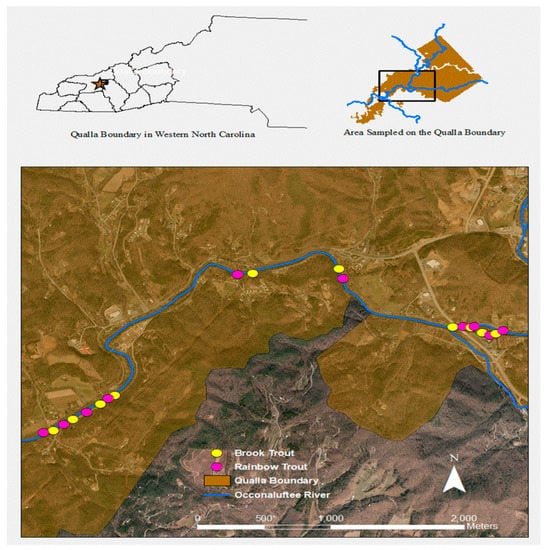
Figure 3.
Site map showing deployment locations of carcasses on the Oconaluftee River on the Cherokee Qualla, western North Carolina.
To identify what organisms scavenged brook and rainbow trout carcasses diurnally, we observed the 20 trays from 8–12 May 2017 up to twice a day (randomly selecting either afternoon or morning time frames) using an underwater video camera (GoPro™ Hero; model HWBL1; San Mateo, CA, USA). Waterproof cameras contain a CMOS optical sensor and were set to record in 1080 p at 30 frames per second on 32 GB microSD cards and set to the proper date and time before being deployed. In order to reduce disturbance, we attached cameras to a 2-m pole and extended it above the tray for 30 s to ensure proper attachment. We used a total deployment of 10 cameras at any one time (afternoon or morning time frames) to monitor carcasses by recording 1-hour videos, hereafter referred to as “events”; then retrieved cameras; backed up video; charged batteries; and prepared cameras for redeployment. Individual cameras were labeled to ensure proper deployment on appropriate brook or rainbow trout carcass trays. For each camera deployment during the experiment, we standardized the sample size for both trout species (Five cameras on brook and five cameras on rainbow) when the field conditions and availability of carcasses permitted. To further determine if carcasses were taken nocturnally for survivorship curve analysis, we visited each deployed carcass nightly using an additional GoPro™ waterproof camera attached to a dive light to illuminate the carcass tray. During these nocturnal visits, we placed cameras carefully on carcasses and ensured the field of view encompassed an area of approximately 0.6 m to either side and above the tray, and 2–3 m behind the tray (depending on water clarity) for a period of ~15 s. In addition, immediately following the experiment, we deployed Reconyx trail cameras at three of our carcass locations to ascertain the effect of mammalian communities which may have scavenged our carcasses. To inform survivorship analysis (presence of carcasses) and decomposition rates, we weighed and monitored carcasses until 5 days after video recording, 17 May 2017.
We extracted abiotic data stored from the online United States Geologic Survey stream gauge station (USGS Hydrological Unit 06010203), which is located at the middle point of our experimental transect (Latitude 35°27′41″, Longitude 83°21′13″ NAD83). Abiotic data included measurements of water temperature, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, discharge, pH, nitrite, and specific conductivity, all collected at 15-min intervals.
3.2. Data Analysis
Data collected from the underwater videos (recorded 8 to 12 May 2017) were analyzed for the species observed (to lowest taxonomic level when possible) and grouped into either Nocomis micropogon fish (Cyprinidae) or crayfish (Decapoda) for ease of video analysis. Videos were reviewed in VLC media player (version 3.0.4; VideoLAN, Paris, France). We recorded the maximum number of fish or crayfish which were actively scavenging a carcass (Max N) for each experimental video trial deployment [18,25,26]. Calculation of Max N was performed by both authors after 10% of videos were reviewed and authors achieved over 90% agreement. We conducted a survival analysis using an interval censored method in R because we only knew the fate of the trout up to a point. The estimates are from a range of data where the predicted fate is based on the last time the carcass was observed present and accounts for when it is missing (right and left censored). We fit our data using a parametric proportional odds model with a gamma distribution using icenReg (v1.3.5) in the program R [27].
4. Conclusions
In summary, few opportunistic aquatic scavengers visit recently deceased trout carcasses, as we observed using underwater cameras (mostly Nocomis micropogon or crayfish). Nonetheless, most of our trout carcasses were scavenged by aquatic mammals (otters). However, the use of action cameras appears to be an effective way to document aquatic scavenging communities and trout decomposition, albeit with some constraints (length of battery life and thus video, diurnal monitoring). Longer term studies could also compare the frequency of visits across time for each type of scavenger observed in streams across decomposition, possibly using underwater cameras with a longer battery life. Further studies should utilize emerging underwater technologies in addition to increased camera trapping of riparian communities to assess the fate of native and non-native trout species in Appalachian streams.
Author Contributions
C.H. and S.U. were responsible for conceptualization, methodology, validation, data curation, and writing.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
Field work was conducted under Cherokee permitting. The Eastern Band of Cherokee provided materials needed for this research. We thank EBCI Hatchery for providing fish for this experiment. We thank Candice Moreau, Dallas Bradley, and Nick Reed for field assistance. We also thank Josh Parris for ArcMap work and field assistance. All authors have read, revised, and approved of the final version of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, no competing or financial interest. No one other than the two authors had any role in the design of the study, interpretation of results, or writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish results.
References
- Wenger, S.J.; Subalusky, A.L.; Freeman, M.C. The missing dead: The lost role of animal remains in nutrient cycling in North American rivers. Food Webs 2019, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVault, T.L.; Rhodes, O.E., Jr.; Shivik, J.A. Scavenging by vertebrates: Behavioral, ecological, and evolutionary perspectives on an important energy transfer pathway in terrestrial ecosystems. Oikos 2003, 102, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inger, R.; Cox, D.T.C.; Per, E.; Norton, B.A.; Gaston, K.L. Ecological role of vertebrate scavengers in urban ecosystems in the UK. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 7015–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, T.J.; Babcock, R.C. A baited underwater video system for the determination of relative density of carnivorous reef fish. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2000, 51, 75–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.; Harvey, E.S.; Anderson, M.J.; Kendrick, G.A. A comparison of temperate reef fish assemblages recorded by three underwater stereo-video techniques. Mar. Biol. 2005, 148, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmarsh, S.K.; Fairweather, P.G.; Huveneers, C. What is Big BRUVver up to? Methods and uses of baited underwater video. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2017, 27, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.J.; Duncan, A.G.; Buckle, D.J.; Novak, P.A.; Fulton, C.J. Efficacy of remote underwater video cameras for monitoring tropical wetland fishes. Hydrobiologica 2018, 807, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, K.; Reis-Filho, J.A.; Harvey, E.; Giarrizzo, T. Baited remote underwater video a promising nondestructive tool to assess fish assemblages in clearwater Amazonian rivers: Testing the effect of bait and habitat type. Hydrobiologica 2017, 784, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richey, J.E.; Perkins, M.A.; Goldman, C.R. Effects of Kokanee Salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) decomposition on the ecology of a subalpine stream. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1975, 32, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.E.; Scheuerell, M.D.; Moore, J.W.; Gende, S.M.; Francs, T.B.; Palen, W.J. Pacific salmon and the ecology of coastal ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 1, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, M.D.; Reimchen, T.E. Consumption and distribution of salmon (Oncorhynchus spp.) nutrients and energy by terrestrial flies. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlighting, P.E.; Love, C.N.; Webster, S.C.; Beasley, J.C. Efficiency and composition of vertebrate scavengers at the land-water interface in the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone. Food Webs 2019, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kiggins, R.S.; Knott, N.A.; Davis, A.R. Miniature baited remote underwater video (mini-BRUV) reveals the response of cryptic fishes to seagrass cover. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2018, 101, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, E.M.A.; Morris, R.L.; Coleman, R.A.; Fiqueria, W.F.; Steinberg, P.D.; Johnston, E.L.; Bishop, M.J. Increasing microhabitat complexity on seawalls can reduce fish predation on native oysters. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letessier, T.B.; Juhel, J.; Vigliola, L.; Meeuwig, J.J. Low-cost small action cameras in stereo generates accurate underwater measurements of fish. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2015, 466, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Garcon, J.; Leis, J.; Newman, S.; Harvey, E. Presettlement schooling behavior of a priacanthid, the purtplespotted bigeye Priacanthus tayenus (Priacanthidae: Teleostei). Environ. Biol. Fish. 2014, 97, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egg, L.; Pander, J.; Mueller, M.; Geist, J. Comparison of sonar-, camera-, and net-based methods in detecting riverine fish-movement patterns. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2018, 69, 1905–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, B.C.; Fulton, C.J.; Cousins, S.; Donaldson, J.A.; Kennard, M.J.; Meynecke, J.; Schaffer, J. Filming and snorkeling as visual techniques to survey fauna in difficult to access tropical rainforest streams. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2015, 66, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.H.; Sedell, J.R. Detritus processing by macroinvertebrates in stream ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1979, 24, 351–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidami, S.; Amyot, M. Fish decomposition in boreal lakes and biogeochemical implications. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minshall, G.W.; Hitchcock, E.; Barnes, J.R. Decomposition of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) carcasses in a forest stream ecosystem inhabitated only by nonanadromous fish populations. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1991, 48, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, L.; Squires, T.; Araki, H. Experimental evaluation of predation of stocked masu salmon by riparian wildlife: Effects of prey size and predator behaviors. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2017, 69, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, T.; Wheat, R.E.; Allen, J.M.; Wilmers, C.C. Differential us of salmon by vertebrate consumers: Implications for conservation. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spelman, L.H. North American river otter (Lutra canadensis) translocation in North Carolina 1989–1996. In Proceedings of the Combined Meeting, Chester Zoo, UK, 21–24 May 1998; Zwart, P., Ed.; European Association of Zoo and Wildlife Veterinarians: Courtland, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Cappo, M.; Speare, P.; De’ath, G. Comparison of baited remote underwater video stations (BRUVS) and prawn trawls for assessments of fish biodiversity in inter-reefal areas of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 302, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladstone, W.; Lindfield, S.; Coleman, M.; Kelaher, B. Optimisation of baited remote underwater video sampling designs for estuarine fish assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 429, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson-Bergman, C. IdenReg: Regression models for interval censored data in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 81, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).