Compound Heterozygosity for a Novel Frameshift Variant Causing Fatal Infantile Liver Failure and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation of POLG c.3286C>T Variant
Abstract
1. Introduction
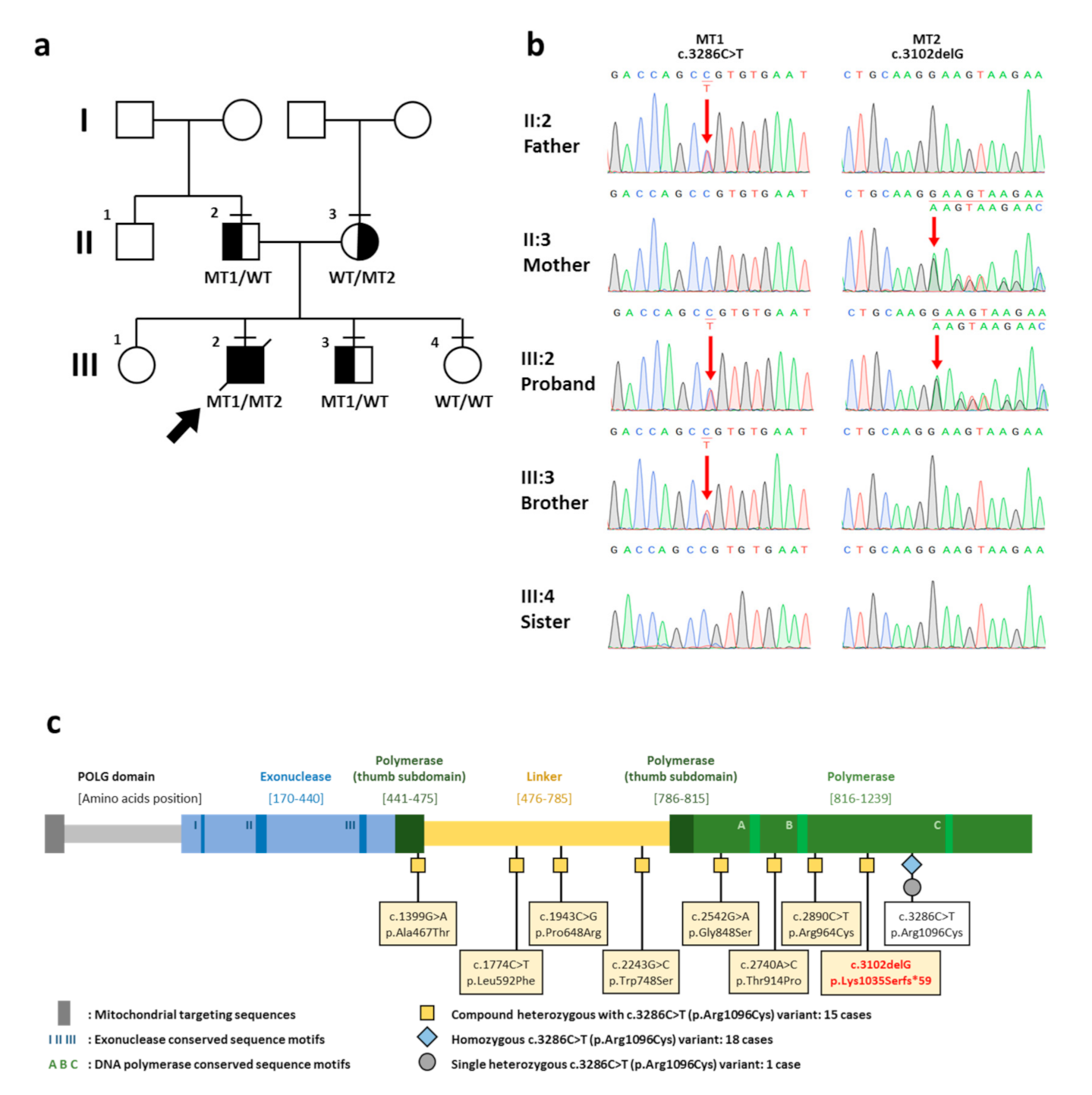
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, L.J.; Naviaux, R.K.; Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Zhang, Q.; Schmitt, E.S.; Truong, C.; Milone, M.; Cohen, B.H.; Wical, B.; Ganesh, J.; et al. Molecular and clinical genetics of mitochondrial diseases due to POLG mutations. Hum. Mut. 2008, 29, E150–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Copeland, W.C. POLG-related disorders and their neurological manifestations. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, J.; Saneto, R.; Copeland, W. Clinical and molecular Features of POLG-related mitochondrial disease. Csh Perspect Biol. 2013, 5, a011395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Wang, J.; Lee, N.C.; Milone, M.; Halberg, M.C.; Schmitt, E.S.; Craigen, W.J.; Zhang, W.; Wong, L.J. Mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma mutations: An ever expanding molecular and clinical spectrum. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 48, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowwarote, N.; Theerapanon, T.; Osathanon, T.; Pavasant, P.; Porntaveetus, T.; Shotelersuk, V. Amelogenesis imperfecta: A novel FAM83H mutation and characteristics of periodontal ligament cells. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemwong, N.; Phokaew, C.; Srichomthong, C.; Tongkobpetch, S.; Srilanchakon, K.; Supornsilchai, V.; Suphapeetiporn, K.; Porntaveetus, T.; Shotelersuk, V. A patient with combined pituitary hormone deficiency and osteogenesis imperfecta associated with mutations in LHX4 and COL1A2. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 21, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, S.; Carmody, L.; Vasilevsky, N.; Jacobsen, J.O.B.; Danis, D.; Gourdine, J.-P.; Gargano, M.; Harris, N.L.; Matentzoglu, N.; McMurry, J.A.; et al. Expansion of the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) knowledge base and resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D1018–D1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenson, P.D.; Mort, M.; Ball, E.V.; Shaw, K.; Phillips, A.; Cooper, D.N. The Human Gene Mutation Database: Building a comprehensive mutation repository for clinical and molecular genetics, diagnostic testing and personalized genomic medicine. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, K.; FathAllah, W.; Ahmed, E. Gender variability in presentation with Alpers’ syndrome: A report of eight patients from the UAE. J. Inherit. Metab Dis. 2011, 34, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, N.; O’Rourke, A.; Smith, C.; Adams, S.; Gowda, V.; Zeviani, M.; Brown, G.; Fratter, C.; Poulton, J. Depletion of mitochondrial DNA in fibroblast cultures from patients with POLG1 mutations is a consequence of catalytic mutations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 2496–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijarnia-Mahay, S.; Mohan, N.; Goyal, D.; Verma, I. Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome causing liver failure. Indian Pediatr. 2014, 51, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.D.; Schoeler, S.; Sitarz, K.S.; Horvath, R.; Hallmann, K.; Pyle, A.; Yu-Wai-Man, P.; Taylor, R.W.; Samuels, D.C.; Kunz, W.S.; et al. POLG mutations cause decreased mitochondrial DNA repopulation rates following induced depletion in human fibroblasts. Biochim. Biophys Acta. 2011, 1812, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, A.; Rahman, S.; Fratter, C.; Ng, J.; Meyer, E.; Carr, L.J.; Champion, M.; Clarke, A.; Gissen, P.; Hemingway, C.; et al. Spectrum of movement disorders and neurotransmitter abnormalities in paediatric POLG disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kentab, A. Alpers–Huttenlocher syndrome presenting with epilepsia partialis continua. JNSK 2019, 9, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, R.; Hudson, G.; Ferrari, G.; Futterer, N.; Ahola, S.; Lamantea, E.; Prokisch, H.; Lochmuller, H.; McFarland, R.; Ramesh, V.; et al. Phenotypic spectrum associated with mutations of the mitochondrial polymerase gamma gene. Brain 2006, 129, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kovel, C.G.; Brilstra, E.H.; van Kempen, M.J.; Van’t Slot, R.; Nijman, I.J.; Afawi, Z.; De Jonghe, P.; Djemie, T.; Guerrini, R.; Hardies, K.; et al. Targeted sequencing of 351 candidate genes for epileptic encephalopathy in a large cohort of patients. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2016, 4, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lax, N.Z.; Whittaker, R.G.; Hepplewhite, P.D.; Reeve, A.K.; Blakely, E.L.; Jaros, E.; Ince, P.G.; Taylor, R.W.; Fawcett, P.R.W.; Turnbull, D.M. Sensory neuronopathy in patients harbouring recessive polymerase γ mutations. Brain 2012, 135, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.G.; Devine, H.E.; Gorman, G.S.; Schaefer, A.M.; Horvath, R.; Ng, Y.; Nesbitt, V.; Lax, N.Z.; McFarland, R.; Cunningham, M.O.; et al. Epilepsy in adults with mitochondrial disease: A cohort study. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 78, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heighton, J.; Brady, L.; Sadikovic, B.; Bulman, D.; Tarnopolsky, M. Genotypes of chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia in a large adult-onset cohort. Mitochondrion 2019, 49, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu-Wai-Man, C.; Smith, F.E.; Firbank, M.J.; Guthrie, G.; Guthrie, S.; Gorman, G.S.; Taylor, R.W.; Turnbull, D.M.; Griffiths, P.G.; Blamire, A.M.; et al. Extraocular muscle atrophy and central nervous system involvement in chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, B.; Naini, A.B.; Copeland, W.C.; Lu, J.; Dimauro, S.; Hirano, M. A novel POLG gene mutation in a patient with SANDO. J. Exp. Integr. Med. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masingue, M.; Adanyeguh, I.; Tchikviladzé, M.; Maisonobe, T.; Jardel, C.; Galanaud, D.; Mochel, F. Quantitative neuroimaging biomarkers in a series of 20 adult patients with POLG mutations. Mitochondrion 2019, 45, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostino, A.; Valletta, L.; Chinnery, P.; Ferrari, G.; Carrara, F.; Taylor, R.; Schaefer, A.; Turnbull, D.; Tiranti, V.; Zeviani, M. Mutations of ANT1, Twinkle, and POLG1 in sporadic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). Neurology 2003, 60, 1354–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouzier, C.; Chaussenot, A.; Serre, V.; Fragaki, K.; Bannwarth, S.; Ait-El-Mkadem, S.; Attarian, S.; Kaphan, E.; Cano, A.; Delmont, E.; et al. Quantitative multiplex PCR of short fluorescent fragments for the detection of large intragenic POLG rearrangements in a large French cohort. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, A.G.; Troedson, C.; Wilson, M.; Procopis, P.G.; Li, F.Y.; Brundage, E.K.; Yamazaki, T.; Thorburn, D.R.; Wong, L.J. Application of oligonucleotide array CGH in the detection of a large intragenic deletion in POLG associated with Alpers Syndrome. Mitochondrion 2011, 11, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurminen, A.; Farnum, G.A.; Kaguni, L.S. Pathogenicity in POLG syndromes: DNA polymerase gamma pathogenicity prediction server and database. BBA Clin. 2017, 7, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, B.H.; Chinnery, P.F.; Copeland, W.C. POLG-related disorders. In GeneReviews; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J., Mirzaa, G., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, J.N.; Leung, M.C.; Rooney, J.P.; Sendoel, A.; Hengartner, M.O.; Kisby, G.E.; Bess, A.S. Mitochondria as a target of environmental toxicants. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 134, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.S.; Longley, M.J.; Naviaux, R.K.; Copeland, W.C. Mono-allelic POLG expression resulting from nonsense-mediated decay and alternative splicing in a patient with Alpers syndrome. DNA Repair (Amst) 2005, 4, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Age of Onset | Age at Report | Age at Death | Nationality | Genotype | Clinical Manifestations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Other Variant | Expected Amino Acid Change of the Other Variant | Exon | Domain | Liver Failure | Seizure | Other Signs and Symptoms | Reference | |||||
| Homozygous variant | ||||||||||||
| 1. | birth | 4 y | NA | United Arab Emirates | NA | NA | NA | NA | - | + | subtle neurodevelopmental problem, develop left-sided weakness | Mohamed et al., 2011 [10] |
| 2. | 6 w | 4 m | 11 m | United Arab Emirates | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | Alpers syndrome, hepatomegaly, abnormal liver function, mid hypotonia | Mohamed et al., 2011 [10] |
| 3. | 4 m | 6 m | NA | United Arab Emirates | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | Alpers syndrome, severe hypotonia, modulate liver involvement | Mohamed et al., 2011 [10] |
| 4. | 4 m | 6 m | NA | United Arab Emirates | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | + | Alpers syndrome, severe neurological disease, chronically elevated liver enzymes | Mohamed et al., 2011 [10] |
| 5. | 5 m | 5 m | NA | United Arab Emirates | NA | NA | NA | NA | - | + | hypotonia, lethargy, moderate developmental delay | Mohamed et al., 2011 [10] |
| 6. | 5 m | 11 m | NA | United Arab Emirates | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | + | - | Mohamed et al., 2011 [10] |
| 7. | 5 m | 5 m | 15 m | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | + | Alpers syndrome, non-specific encephalopathy and blindness, severe coagulopathy, hypoglycemia, epilepsy, hepatopathy | Ashley et al., 2008 [11] |
| 8. | 8 m | 8 m | 18 m | Afghanistan | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | + | altered sensorium, hypotonia, mild hepatomegaly | Bijarnia-Mahay et al., 2014 [12] |
| 9. | 9 m | 9 m | NA | Arab states | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | dementia, encephalopathy | Tang et al., 2011 [4] |
| 10. | <12 m | 3 y | NA | United Arab Emirates | NA | NA | NA | NA | - | + | hypotonia, refractory epilepsia partialis continua, severe neurological disability | Mohamed et al., 2011 [10] |
| 11. | 12 m | 12 m | NA | Arab states | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | + | - | Tang et al., 2011 [4] |
| 12. | 12 m | 12 m | NA | NA | NA a | NA a | NA | NA | NA | + | Alpers syndrome, dementia | Wong et al., 2008 [1] |
| 13. | NA | 12 m | NA | Arab states | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | Alpers syndrome, multifocal therapy-refractory epilepsy, hippocampal sclerosis, COX-negative fibers, reduced mtDNA copy number, mtDNA deletions. | Stewart et al., 2010 [13] |
| 14. | 13 m | 13 m | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Choreoathetosis; myoclonus (epileptic and non-epileptic); intermittent, myoclonic jerks sometimes in sleep, worsened by illness; abnormal neurotransmitters | Papandreou et al., 2018 [14] |
| 15. | 14 m | 14 m | NA | Saudi arabia | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | + | Alpers syndrome, epilepsia partialis continua (EPC), hypotonia | Kentab, 2019 [15] |
| 16. | 24 m | 24 m | NA | Arab states | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | developmental delay, elevated transaminases, lactic acidosis | Tang et al., 2011 [4] |
| 17. | 24 m | 9 y | NA | NA | NA a | NA a | NA | NA | + | NA | encephalopathy, myoclonus achalasia | Horvath et al., 2006 [16] |
| 18. | NA | NA | NA | European | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | + | Leigh syndrome | De Kovel et al., 2016 [17] |
| Compound Heterozygous Variant with Frameshift Variant | ||||||||||||
| 19. | 4 m | 4 m | 4 m | Thai | c.3102delG | p.Lys1035Serfs*59 | 19 | P | + | - | developmental delay, hepatic failure | This study |
| 20. | 5 m | 5 m | 11 m | NA | c.2542G>A | p.Gly848Ser | 16 | P | + | NA | encephalopathy, hypotonia | Stumpf et al., 2013 [3] |
| 21. | <12 m | <12 m | 14 m | NA | c.2740A>C | p.Thr914Pro | 18 | P | + | NA | Alpers syndrome, hypotonia, myoclonic epilepsy, respiratory insufficiency, hepatopathy, choreoathetosis, ataxia, ataxic nystagmus | Ashley et al., 2008 [11] |
| 22. | 24 m | 24 m | NA | Arab states | c.2542G>A | p.Gly848Ser | 16 | P | + | NA | developmental delay, hypotonia, dementia/encephalopathy, exercise intolerance, muscle weakness, easy fatigability, ptosis, gastrointestinal reflux, delayed gastric emptying, cyclic vomiting, elevated transaminases, lactic acidosis, short statue, failure to thrive | Tang et al., 2011 [4] |
| 23. | 17 y | 42 y | NA | England | c.1399G>A | p.Ala467Thr | 7 | L | NA | NA | chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia, ptosis, peripheral neuropathy, sensory and motor neuronopathy, distal and proximal neurogenic change | Lax et al., 2012 [18] |
| 24. | 25 y | 49 y | NA | England | c.2243G>C | p.Trp748Ser | 13 | L | NA | NA | chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia, ptosis, peripheral neuropathy, epilepsy, severe sensory and moderate motor neuronopathy | Lax et al., 2012 [18] |
| 25. | 26 y | 45 y | NA | European | c.1399G>A | p.Ala467Thr | 7 | L | NA | + | myoclonic seizures, epilepsy | Whittaker et al., 2015 [19] |
| 26. | 26 y | 55 y | NA | European | c.2243G>C | p.Trp748Ser | 13 | L | NA | + | myoclonic and tonic-clonic seizures, epilepsy, multifocal epileptiform abnormalities | Whittaker et al., 2015 [19] |
| 27. | 40 y | 61 y | NA | NA | c.2890C>T | p.Arg964Cys | 18 | P | NA | NA | chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia, ptosis | Heighton et al., 2019 [20] |
| 28. | 42 y | 42 y | NA | NA | c.1399G>A | p.Ala467Thr | 7 | L | NA | NA | severe ptosis, myopathy, cerebella dysfunction, peripheral neuropathy | Yu-Wai-Man et al., 2013 [21] |
| 29. | 48 y | 48 y | NA | NA | c.1774C>T | p.Leu592Pheb | 10 | L | NA | NA | sensory ataxic neuropathy, dysarthria, ophthalmoplegia, dysphagia | Kurt et al., 2012 [22] |
| 30. | 49 y | 55 y | NA | NA | c.1943C>G | p.Pro648Arg | 10 | L | NA | NA | sensory ataxic neuropathy, dysarthria, ophthalmoparesis | Masingue et al., 2019 [23] |
| 31. | 53 y | 55 y | NA | NA | c.1943C>G | p.Pro648Arg | 10 | L | NA | NA | progressive external ophthalmoplegia, myopathy | Horvath et al., 2006 [16] |
| 32. | 54 y | 54 y | NA | NA | c.2243G>C | p.Trp748Ser | 13 | L | NA | NA | ataxia, epilepsy, peripheral neuropathy, cognitive impairment | Yu-Wai-Man et al., 2013 [21] |
| 33. | NA | NA | NA | NA | c.2243G>C | p.Trp748Ser | 13 | L | NA | NA | mitochondrial recessive ataxia syndrome | Masingue et al., 2019 [23] |
| Single heterozygous variant | ||||||||||||
| 34. | 23 y | 23 y | NA | Italian | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | sporadic progressive external ophthalmoplegia | Agostino et al., 2003 [24] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sriwattanapong, K.; Rojnueangnit, K.; Theerapanon, T.; Srichomthong, C.; Porntaveetus, T.; Shotelersuk, V. Compound Heterozygosity for a Novel Frameshift Variant Causing Fatal Infantile Liver Failure and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation of POLG c.3286C>T Variant. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2021, 7, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7010009
Sriwattanapong K, Rojnueangnit K, Theerapanon T, Srichomthong C, Porntaveetus T, Shotelersuk V. Compound Heterozygosity for a Novel Frameshift Variant Causing Fatal Infantile Liver Failure and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation of POLG c.3286C>T Variant. International Journal of Neonatal Screening. 2021; 7(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleSriwattanapong, Kanokwan, Kitiwan Rojnueangnit, Thanakorn Theerapanon, Chalurmpon Srichomthong, Thantrira Porntaveetus, and Vorasuk Shotelersuk. 2021. "Compound Heterozygosity for a Novel Frameshift Variant Causing Fatal Infantile Liver Failure and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation of POLG c.3286C>T Variant" International Journal of Neonatal Screening 7, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7010009
APA StyleSriwattanapong, K., Rojnueangnit, K., Theerapanon, T., Srichomthong, C., Porntaveetus, T., & Shotelersuk, V. (2021). Compound Heterozygosity for a Novel Frameshift Variant Causing Fatal Infantile Liver Failure and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation of POLG c.3286C>T Variant. International Journal of Neonatal Screening, 7(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijns7010009






