Abstract
The incidence of congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is increasing in different areas around the world. Potential causes include changes in population ethnic composition, environmental factors, changing screening program methodology and lowering of TSH cutoff levels. The incidence of CH in different regions of Macedonia has not been evaluated before. A total of 251,008 newborns from all eight regions in the country have been screened between 2002 and 2015, by measurement of the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from blood spots, sampled 48–72 h after birth, using the DELFIA assay. Overall CH incidence confirmed at birth was 1/1976. The highest CH incidence was observed in the Vardar region (1/970), while the Eastern region had the lowest incidence (1/4202; p = 0.021). In the other regions, the following CH incidence was detected: Northeastern 1/1459, Pelagonia 1/1627, Polog 1/1444, Skopje 1/2430, Southwestern 1/3226, and Southeastern 1/1843. Interestingly, in the Vardar region, 4.44% of the screened newborns had a TSH concentration > 5 mIU/L, as an indicator of regional iodine deficiency, compared to the Eastern region where 1.66% of newborns had a TSH > 5 mIU/L. The higher CH incidence in some of the regions may be due to increasing exposure to environmental toxic agents and/or deficient iodine intake. Further research into the potential environmental determinants of increased CH risk is warranted.
1. Introduction
Congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is a clinical condition caused by decreased production or inadequate action of thyroid hormones, resulting in a reduction of metabolic processes and impaired neurodevelopment. The disorder is classified as primary when the origin of the defect is in the gland itself, or secondary when the hypothalamic-pituitary axis is affected [1,2]. According to the world-wide data obtained from neonatal thyroid screening programs, the incidence of primary CH is approximately 1:3000 to 1:4000. However, despite similarity in the risk factors for CH in different countries such as female gender, birth defects, twins, preterm deliveries, geographic location, ethnicity, iodine deficiency, etc., the currently reported CH incidence varies widely worldwide [1,2,3]. In the USA, the incidence of CH among white newborns (1:1815) is higher than among black infants (1:1902), while Hispanic and Asian infants have the highest incidence (1:1559 and 1:1016, respectively) [4]. Changes in the ethnic composition of the population by the increasing migration of some ethnic groups with a high risk for CH and high fertility rate may have contributed to the rise of CH incidence [4]. The differences in CH incidence have mostly been attributed to the change of screening procedures, and the reduction of cutoff levels [5,6]. The incidence is higher in preterm infants (1:1396) than in full-term infants (1:1843), and infants from older mothers had a higher incidence (1:1328) than those from younger mothers (1:1703) [7]. Some studies reported a seasonality in the CH incidence, suggesting that environmental factors may play a role in the variation of CH incidence [8,9]. However, differences of CH incidence are more likely due to iodine deficiency or to the type of screening method than to ethnic affiliation [10].
The Republic of Macedonia is a country in the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe with a total of 25,713 km2 area. It is divided into eight statistical regions (Eastern, Northeastern, Pelagonia, Polog, Skopje, Southeastern, Southwestern, and Vardar) [11].
The aim of this retrospective study (2002–2015) was to assess CH incidence in different regions of Macedonia as well as its correlation with the percent of neonates with TSH concentrations above 5 mIU/L whole blood on screening, as an indicator of iodine deficiency in the population.
2. Materials and Methods
Neonatal thyroid screening in Macedonia is carried out by one screening center using one screening strategy, and covers over 95% of the total neonatal population (approximately 24,000 births per year). It has been mandatory since 2007. A total of 251,008 (96.72%) newborns delivered in birth centers from all statistical regions in the country (Eastern, Northeastern, Pelagonia, Polog, Skopje, Southwestern, Southeastern, and Vardar regions) were screened between April 2002 and December 2015. Using the DELFIA assay, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) was measured in the whole blood collected on filter paper from Schleicher and Schuell Inc., Keene, NH, USA (Whatman 903) by heel prick, 48–72 h after birth [12]. A cutoff value of 15 mIU/L was used for the whole blood TSH until 2010, and 10 mIU/L was used as a cutoff thereafter. The clinical evaluation and biochemical analysis for the diagnosis of CH, adopted by all of the Macedonia regions, were described previously [13,14]. Permanent CH was diagnosed for neonates with persistent deficiency of thyroid hormone that requires life-long treatment. In cases where thyroid hormone levels reverted back to normal after discontinuation of the treatment, neonates were classified as babies with transient CH [7].
Using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (version 20.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), statistical analysis was performed. Descriptive analysis was performed on the obtained TSH values. The comparison of proportions was performed with Pearson χ2, and statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
The Local Ethics Committee and Human Research Ethics Committee of University Pediatric Clinic, Skopje, approved the study. The authors declare that all investigations were performed according the rules of the Declaration of Helsinki of 1975. Formal consent was not required for the retrospective study.
3. Results
A 14-year retrospective population-based study showed an overall CH incidence confirmed at birth of 1/1976. Some variations in the CH incidence among different regions of the country were detected. The highest CH incidence of 1/970 was detected in the Vardar region, while the lowest CH incidence of 1/4202 was observed in the Eastern region (Figure 1). The difference was statistically significant (p = 0.021; x2 = 5.33). Additionally, there was a significant difference between the CH incidence in Vardar and the Southwestern region (1/3226), (p = 0.052; x2 = 3.77). There was no statistically significant difference in CH incidence among the rest of the regions (Table 1).
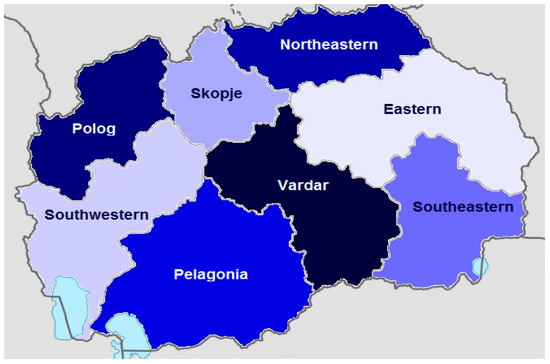
Figure 1.
Regional variation in the CH incidence (brightest color corresponds with the lowest CH prevalence).

Table 1.
Regional variation in CH incidence and percentage of newborns with whole blood TSH > 5 mIU/L, between 2002 and 2015.
Interestingly, in the Vardar region, we found 4.44% of the screened newborns with whole blood TSH concentration above 5 mIU/L, compared to the Eastern region where 1.66% of newborns had TSH > 5 mIU/L (Table 1). Moreover, we found a high percentages of cases with transient CH, including 33.3% in the Vardar region, 40% in the Southwestern, and 20% in the Polog region, as regions with more than 3% of the neonates with TSH > 5 mIU/L (Table 1). On the other hand, percentages of cases with transient CH in the rest of the regions were 18% in Skopje, 12.5% in Southeastern, 10.5% Pelagonia, and 0% in both Eastern and Northeastern regions. In these regions, the percentage of neonates with THS > 5 mI/L was below 3% (Table 1).
4. Discussion
The incidence of CH and the percentage of neonates with a whole blood TSH concentration >5 mIU/L (as an indicator for the iodine intake in the population) per region have not been separately evaluated before in the Republic of Macedonia. Between 2002 and 2015, overall CH incidence confirmed at birth was 1/1976. This is higher than the incidence of primary CH reported for neighboring Serbia (1:3728) [15], and some of the other countries in the region, such as Montenegro (1/2397) [16], Slovenia (1/2323) [17], and Croatia (1/4127) [18]. There were variations in the CH incidence among different regions of the country. CH incidence in the Vardar region was more than four-fold higher than the incidence in the Eastern region, the region with the lowest incidence in the country. Additionally, it was more than three-fold higher than the incidence in the Southwestern region, and two-fold higher than the overall CH incidence in the country, although without statistical significance. It is well known that the incidence of CH varies among ethnic groups. For instance, CH is less prevalent among African Americans compared to Hispanics (1:10,000 vs. 1:2700) [4,19]. The Republic of Macedonia is a multi-ethnic country. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians of Slavic origin (64.2%).Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks (3.9%), Roma (2.7%), Serbs (1.8%), and others (2.2%) [11]. In the Vardar region, with 7.4% of the total population of the country, Macedonians (89%) are the largest ethnic group followed by Albanians (3.3%), Turks (2%), Bosniaks (1.9%), Roma (0.8%), and others (3%). A similar ethnic composition is present in the Eastern region, with 8.6% of the total population of the country, and Macedonians forming the majority group (92.4%) followed by Roma (3.8%), Turks (1.5%) and others (2.2%) [11]. Although we found a significant increase in CH incidence in the Roma population as a whole [13], it is unlikely that this can contribute to the regional differences since the Roma population is small and scattered across the entire country. Taking this into account, factors other than ethnicity are involved in different CH incidences in different regions in Macedonia. Higher incidence of CH due to cases with transient hypothyroidism as a consequence of a lower cutoff point for TSH levels has been reported [20,21]. We found a high percentage of cases with transient CH in the Vardar region (33.3%) compared with none in the Eastern region. This may be due to iodine deficiency, although Macedonia as a whole is no longer recognized as an iodine-deficient area [22]. However, some regions might still belong to iodine-deficient areas [23]. This is in accordance with our finding that 4.44% of the screened newborns in the Vardar region had a TSH concentration above 5 mIU/L whole blood, as an indicator of iodine deficiency, in comparison with the Eastern region where only 1.66% of newborns had TSH>5 mIU/L. Possible mild iodine deficiency in the Vardar region has been described previously [23]. Iodine intake at the population level is a major determinant of thyroid function, and decreasing intake is reflected in increasing neonatal TSH levels [24,25]. Another factor in the variation of the number of CH cases may be exposure to other environmental factors such as chemical agents toxic to the thyroid gland, e.g., dioxin and polychlorinated biphenyl [26]. For instance, the 30-year-old smelting factory for zinc and lead situated in the center of the town of Veles, Vardar region, is one of the environmental hot spots in Macedonia [27]. Moreover, a ferronickel smelter plant located in the surrounding area of the town of Kavadarci, as the largest Macedonian and European ferro-nickel producer for many years, is the reason for natural and anthropogenic enrichment with heavy metals in the Vardar region [28,29,30]. Additionally, there is a distribution of high concentrations of arsenic, antimony, and thallium in topsoil and subsoil in the Kavadarci region, probably as a consequence of natural erosion from Allchar mine deposits on Kožuf Mountain [31]. We speculate that the location of one mine deposit and two smelter plants in the Vardar region, out of a total of four smelter plants within the entire territory of the country, might be associated with the highest incidence of CH found in this region. On the other hand, infections or seasonally varying dietary factors might have environmental effects on CH incidence in different geographical areas. A number of previous studies have reported seasonal variation in CH incidence in different geographical areas including Finland [32], the West Midlands of England [33], and Japan [8]. In contrast, seasonality in CH incidence has not been observed in the Netherlands [34], Canada [35], Saudi Arabia [36], or the Northwest of England [37]. No significant seasonality in the incidence of CH was observed in our study (unpublished data). Finally, the use of TSH assays with different test methodologies has been shown to influence the incidence of CH [19]. This cannot be an explanation for different CH incidence in the regions of Macedonia, because all newborns in the study regions were screened in a single center using one screening strategy. However, environmental determinants of genetic mutations and epigenetic factors cannot be ruled out.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we have observed a significant regional difference in CH incidence in Macedonia. The reasons for the increasing CH incidence in some of the regions are unclear. Iodine insufficiency and the lowering of TSH cutoff level might contribute. Further research is required to elucidate potential environmental determinants of increased CH risk.
Author Contributions
All authors have contributed to the critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. Violeta Anastasovska carried out the thyroid screening in the country, and contributed to the retrospective evaluation of the data, idea and concept of the manuscript and well as the designing, writing, and editing of the manuscript. Mirjana Kocova was instrumental in the design, composition, editing, and final approval of the manuscript, she diagnosed, treated, classified, and followed babies and children with congenital hypothyroidism. Elena Sukarova-Angelovska contributed to diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of the patients with congenital hypothyroidism. Milica Pesevska and ElizabetaTaseva carried out the thyroid screening in the country and contributed to searching the literature.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rapaport, R.; Simpser, T. Update on some aspects of neonatal thyroid disease. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2010, 2, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- LaFranchi, S. Congenital hypothyroidism: Etiologies, diagnosis, and management. Thyroid 1999, 9, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, D.A.; Dussault, J.H.; Foley, T.P., Jr.; Klein, A.H.; LaFranchi, S.; Larsen, P.R.; Mitchell, M.L.; Murphey, M.H.; Walfish, P.G. Screening for congenital hypothyroidism: Results of screening one million North American infants. J. Pediatr. 1979, 94, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.B.; Pass, K.A. Increase in congenital hypothyroidism in New York State and in the United States. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2007, 91, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, G.; LaFranchi, S. Screening for congenital hypothyroidism: A worldwide view of strategies. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbetta, C.; Weber, G.; Cortinovis, F.; Calebiro, D.; Passoni, A.; Vigone, M.C.; Beck-Peccoz, P.; Chiumello, G.; Persani, L. A 7-year experience with low blood TSH cutoff levels for neonatal screening reveals an unsuspected frequency of congenital hypothyroidism (CH). Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 71, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, M.V.; LaFranchi, S.H. Congenital hypothyroidism. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamizo, M.; Toyabe, S.; Asami, T.; Akazawa, K. Seasonality in the incidence of congenital hypothyroidism in Japan. J. Pediatr. Child Health 2005, 41, 390–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.H.; Kato, T.; Harada, S.; Inomata, H.; Saito, T.; Aoki, K. Seasonality in the incidence of congenital hypothyroidism in Japan: Gender-specific patterns and correlation with temperature. Thyroid 2007, 17, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klett, M. Epidemiology of congenital hypothyroidism. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 1997, 105, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- General and Regional Statistics. State Statistical Office of the Republic of Macedonia. Available online: http://www.stat.gov.mk (accessed on 31 August 2010).
- Kocova, M.; Anastasovska, V.; Sukarova-Angelovska, E.; Tanaskoska, M.; Taseva, E. Clinical practice: Experience with newbornscreening for congenital hypothyroidism in the Republic of Macedonia—A multiethnic country. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 174, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasovska, V.; Kocova, M. Ethnicity and incidence of congenital hypothyroidism in the capital of Macedonia. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 30, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdraveska, N.; Anastasovska, V.; Kocova, M. Frequency of thyroid status monitoring in the first year of life and predictors for more frequent monitoring ininfants with congenital hypothyroidism. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 29, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrovic, K.; Vukovic, R.; Milenkovic, T.; Todorovic, S.; Radivojcevic, J.; Zdravkovic, D. Changes in the incidence and etiology of congenital hypothyroidism detected during 30 years of a screening program in central Serbia. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2016, 175, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samardžić, M.; Gligorović-Barhanović, N.; Popović, N.; Popović-Samardžić, M. Newborn screening program for congenital Hypothyroidism in Montenegro. Paediatr. Today 2013, 9, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmon, A.; Grošelj, U.; ŽerjavTanšek, M.; Biček, A.; Oblak, A.; Zupančič, M.; Kržišnik, C.; RepičLampret, B.; Murko, S.; Hojker, S.; Battelino, T. Newborn screening in Slovenia. Zdr. Varst. 2015, 54, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarnavka, V. Neonatal screening. Pediatr. Croat. 2004, 48, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, H.E.; Moore, C.A.; Fernhoff, P.M.; Brown, A.L.; Khoury, M.J. Population study of congenital hypothyroidism and associated birth defects, Atlanta, 1979–1992. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1997, 71, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, J.S.; Lin, M.; Grosse, S.D.; Hintonn, C.F.; Drummond-Borg, M.; Borgfeld, L.; Sullivan, K.M. The impact of transient hypothyroidism on the increasing rate of congenital hypothyroidism in the United States. Pediatrics 2010, 125, S54–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetzberg, V.; Mei, J.; Therrell, B.L. Effect of laboratory practices on the incidence rate of congenital hypothyroidism. Pediatrics 2010, 125, S48–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanfilski, B.; Bogdanova, V.; Vaskova, O.; Miceva-Ristevska, S.; Loparska, S.; Kuzmanovska, S. Macedonia begins to monitor IDD in pregnant and lactating women along with school-age children. IDD Newsl. 2009, 33, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasovska, V.; Kocova, M. Newborn screening for thyroid-stimulating hormone as an indicator for assessment of iodine status in the Republic of Macedonia. J. Med. Biochem. 2016, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delange, F. Screening for congenital hypothyroidism used as an indicator of the degree of iodine deficiency and of its control. Thyroid 1998, 8, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delange, F. Neonatal thyroid screening as a monitoring tool for the control of iodine deficiency. Acta Paediatr. 1999, 88, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.M.; Green, M.L.; DePinto, J.V.; Hornbuckle, K.C. Results from the Lake Michigan Mass Balance study: Concentrations and fluxes of atmospheric polychlorinated biphenyls and trans-nonachlor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafilov, T.; Šajn, R.; Pančevski, Z.; Boev, B.; Frontasyeva, M.V.; Strelkova, L.P. Heavy metal contamination of topsoils around a lead and zinc smelter in the Republic of Macedonia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 896–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bačeva, K.; Stafilov, T.; Šajn, R.; Tănăselia, C.; Ilić Popov, S. Distribution of chemical elements in attic dust in the vicinity of a ferronickel smelter plant. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2011, 20, 2306–2314. [Google Scholar]
- Stafilov, T.; Šajn, R.; Boev, B.; Cvetković, J.; Mukaetov, D.; Andreevski, M.; Lepitkova, S. Distribution of some elements in surface soil over the Kavadarci region, Republic of Macedonia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 1515–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bačeva, K.; Stafilov, T.; Šajn, R.; Tănăselia, C. Moss biomonitoring of air pollution with heavy metals in the vicinity of a ferronickel smelter plant. J. Environ. Sci. Health ATox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2012, 47, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafilov, T.; Šajn, R.; Alijagić, J. Distribution of Arsenic, Antimony, and Thallium in Soil in Kavadarci and its Surroundings, Republic of Macedonia. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2013, 22, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, M.; Mäenpää, J.; Pikkrainen, J.; Pitkänen, L.; Perheentupa, J. Aetiology of congenital hypothyroidism in Finland. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1989, 78, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.K.; Hutchesson, A.C.J.; Kirk, J.M. Congenital hypothyroidism, seasonality and consanguinity in the West Midlands, England. Acta Paediatr. 1999, 88, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijneveld, S.A.; Verkerk, P.H. No evidence for seasonality of congenital hypothyroidism in The Netherlands. Acta Paediatr. 1993, 82, 212–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deladoëy, J.; Bélanger, N.; Van Vliet, G. Random variability in congenital hypothyroidism from thyroid dysgenesis over 16 years in Québec. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3158–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, G.; Sobki, S.H.; Othman, J.M. Screening for congenital hypothyroidism. Saudi Med. J. 2002, 23, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, M.; Addison, G.M.; Price, D.A. Congenital hypothyroidism: Increased incidence in Asian families. Arch. Dis. Child. 1988, 63, 790–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).