Abstract
The rising amount of electronic waste (e-waste) presents serious threats to the environment and public health. Addressing this challenge necessitates a focus on improving the e-waste recycling rate, which is facilitated by consumers’ spontaneous participation. This paper explores the factors influencing young consumers’ e-waste recycling behavior (EWRB) from a developing country’s perspective. Though existing literature has addressed various factors affecting EWRB, the role of individuals’ pro-environmental goals (PEG) remains underexplored. This paper provides an integrated theoretical model that incorporates PEG alongside factors drawn from the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), Norm Activation Model (NAM), and Behavioral Reasoning Theory (BRT). Data were collected through a survey and analyzed using structural equation modeling. The results reveal that young consumers’ intentions toward EWRB are significantly influenced by economic benefits, perceived behavioral control, moral norms, and PEG, while economic benefits emerge as the most influential factor. However, the impact of attitude and subjective norm on intention was found to be insignificant. Results indicate that despite having positive intentions, young consumers were often deterred from recycling e-waste due to perceived risks, indicating a negative moderating effect of perceived risk on the intention–behavior relationship. Conversely, PEG positively moderates the impact of intention on EWRB, reducing the intention–behavior gap. This paper contributes to the literature by enhancing our understanding of how PEG interacts with other factors affecting EWRB. Practically, the findings offer valuable recommendations for policymakers and practitioners aiming to promote EWRB among young consumers, particularly in Bangladesh.
1. Introduction
The global amount of electronic waste (e-waste) is rapidly increasing due to irresponsible consumption patterns. In 2022, 62 million tons of e-waste were generated worldwide, and this figure is projected to increase by 32%, reaching 82 million tons by 2030 [1]. Despite this, only about 22% of the total e-waste produced was recycled, a figure that is expected to decline to 20% by 2030 if current trends continue [1]. The low recycling rate of e-waste in 2022 resulted in an estimated loss of USD 62 billion worth of raw materials [1]. However, if nations collaborate to raise the e-waste recycling rate to 60% by 2030, an additional USD 38 billion worth of materials could be recovered [1]. Urgent action is therefore required from countries to enhance the global e-waste recycling rate.
Bangladesh, located in South Asia, produced approximately 367 million kilograms of e-waste in 2022, a figure projected to rise to 2.5 million tons by 2030 and 4.6 million tons by 2035, reflecting an annual growth rate of 20% [2]. Based on these statistics, e-waste generation in Bangladesh is expected to increase more than tenfold over the next decade, contributing 3% of total global e-waste by 2030. A study reported that, during the fiscal year 2021–2022, municipal solid waste in Bangladesh comprised approximately 19% food waste, 16% plastic, 10% textiles, and 19% paper [3]. Furthermore, the same report highlighted that e-waste accounted for around 2.3% of the total municipal solid waste generated in Bangladesh during the fiscal year 2020–2021 [3]. Despite the sheer percentage of e-waste being low compared to other types of waste, Bangladesh can potentially make an annual business from e-waste worth USD 221 million [4]. However, the e-waste recycling rate in Bangladesh, currently around 15%, falls below the global average, suggesting that a substantial portion of e-waste ends up in landfills [4]. A study estimated that proper recycling could recover materials from mobile phones and computers worth USD 1 billion per year by 2030 in Bangladesh [4]. Figure 1 provides an overview of e-waste in Bangladesh. One of the main reasons for the low e-waste recycling rate is consumers’ reluctance to engage in recycling practices, which impedes the implementation of the concept of a circular economy [5]. Consequently, authorities in Bangladesh must develop a clear understanding of how to promote e-waste recycling behavior (EWRB) at the consumer level, which will be addressed in this research.
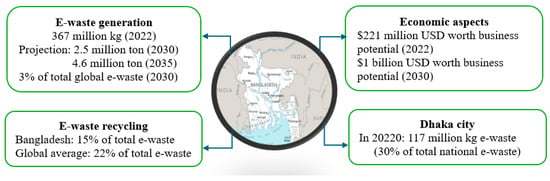
Figure 1.
Overview of e-waste in Bangladesh.
Several research tried to identify the factors impacting consumers’ EWRB, adopting from behavioral science theories, such as the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), Norm Activation Model (NAM), Behavioral Reasoning Theory (BRT), Theory of Interpersonal Behavior (TIB), and Value Belief Norm, etc. [6,7]. Scholars posit diverse viewpoints to explain consumers’ waste management and recycling behavior. One viewpoint considers pro-environmental behavior as a result of systematic thinking, which could be explained by the TPB [8,9]. Another viewpoint emphasizes the altruistic factors to explain the considered pro-environmental behavior, as addressed in NAM theory [8,9]. Other scholars considered the importance of noncognitive factors like our habit of waste management behavior, as addressed in TIB [10,11]. Researchers argued that recycling behavior is too complex to be explained by one theory [9]. Hence, researchers tried to develop an integrated model by combining factors from multiple theories (see Table 1) that could provide a comprehensive understanding of consumers’ EWRB [12,13,14].
Despite scholars’ efforts to identify factors impacting consumers’ EWRB, the existing literature reveals a lack of studies focused on predicting the EWRB of young consumers in developing countries’ perspectives [10,15], highlighting a notable research gap. Scholars underscored that an individual’s pro-environmental behavior, such as recycling, is impacted by cultural aspects and demographic factors, such as gender and age [16]. Given that a significant portion of electronic products are used by young consumers, it is essential to understand the factors that motivate this demographic to adopt EWRB. In Bangladesh, e-waste recycling is affected due to a lack of proper collection systems and infrastructures [4]. Additionally, according to Hofstede’s cultural dimensions, the country exhibits a high power distance and is characterized by collectivism, restraint, risk aversion, and short-term orientation [17]. Literature suggests that a society with high power distance and short-term orientation shows less pro-environmental behavior [16]. Furthermore, in a collectivist, restrained, and risk-averted society that shows less pro-environmental behavior, it is difficult to adopt pro-environmental behavior [16]. Given such odds, it is important for practitioners to understand how to motivate young consumers in Bangladesh to posit a sustainable EWRB. However, empirical studies that provide a comprehensive understanding of EWRB for young consumers in Bangladesh are limited.
Another research gap identified in the literature is the lack of exploration of the impact of pro-environmental goals (PEG) on EWRB. Recently, Ajzen and Kruglanski (2019) proposed the Theory of Reasoned Goal Pursuit (TRGP), which emphasizes the significance of individuals’ goals in fostering sustainable behavior [18]. The latest studies by Concari et al. (2023) and Islam et al. (2024) also underscored the importance of PEG in sustaining pro-environmental behavior among consumers [19,20]. However, a review of the literature reveals that PEG has rarely been considered as a factor predicting EWRB, which represents another research gap. Consequently, further research is needed to enhance our understanding of how PEG interacts with other factors influencing consumers’ EWRB.
To address the identified research gaps, this paper pursues two objectives. The first is to identify the factors influencing young consumers’ e-waste recycling behavior (EWRB) from a developing country’s perspective. The second is to explore the role of individuals’ pro-environmental goals in shaping their EWRB. To achieve these objectives, the study synthesizes relevant literature to identify key factors and conducts an empirical investigation using data collected from young consumers residing in Dhaka City, located in Bangladesh.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Summary of Literature on E-Waste Recycling Behavior and Research Gaps
A summary of the articles that identified factors from multiple theories to predict the EWRB is presented in Table 1. Referring to Table 1, TPB is widely adopted, followed by NAM theory, to predict EWRB. Puzzo and Prati (2024) conducted a meta-analysis, identifying 14 factors that are widely used to predict EWRB [6]. While the majority of the empirical studies have been conducted in developing countries, research focusing on young consumers is very limited. Aboelmaged (2021) identified EWRB for young consumers in the UAE [10]. Zhang et al. (2019) collected data from university students in China to predict their EWRB [21]. However, empirical studies focusing on understanding the EWRB for young consumers in developing countries context, such as India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Vietnam, etc., are limited.
Notable research gaps were identified after reviewing the literature. Firstly, research related to adopting TRGP in the EWRB context is yet to be carried out. Secondly, research related to addressing PEG as a construct for the EWRB context is scant, delimiting our understanding of how PEG impacts EWRB. Thirdly, while several empirical studies were conducted in developing countries, research related to identifying the impact of the factors on young consumers’ EWRB in developing countries context is limited. These research gaps will be addressed in this paper.

Table 1.
Summary of key literature related to E-waste recycling behavior.
Table 1.
Summary of key literature related to E-waste recycling behavior.
| Author (Year) | Country | Theories Considered * | Variables Considered ** | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPB | NAM | TIB | BRT | ||||
| Prabhu and Majhi (2024) | India | √ | √ | √ | ATT, SN, MN, INT, SR, AC, HB, WTP, CR, EB, PLR, RP | [13] | |
| Kumar (2019) | India, China | √ | √ | ATT, SN, PBC, SR, AC, INT | [15] | ||
| Vijayan et al. (2023) | India | √ | √ | ATT, SN, PBC, HB, INT, EWRB, CN | [14] | ||
| Aboelmaged (2021) | UAE | √ | √ | ATT, SN, PBC, HB, INT | [10] | ||
| Waheed et al. (2023) | UAE | √ | √ | √ | ATT, SN, PBC, INT, EWRB, AC, CR, CN | [22] | |
| Sabbir et al. (2023) | Bangladesh | √ | √ | √ | ATT, SN, PBC, INT, EWRB, EB, HB | [23] | |
| Mohamad et al. (2022) | Malaysia | √ | √ | ATT, SN, PBC, MN, AC, INT, EWRB | [12] | ||
| Xu et al. (2017) | China | √ | √ | √ | ATT, SN, PBC, PLR, CN, AC, HB, INT | [24] | |
| Wang et al. (2018) | China | √ | √ | AC, SR, MN, ATT, SN, PBC, IP, INT | [25] | ||
| Koshta et al. (2022) | India | √ | √ | ATT, INT, SN, PBC, WTP, AC | [26] | ||
| Muthukumari et al. (2024) | South Korea | √ | √ | √ | ATT, INT, PBC, SN, AC, MN, CN, IP | [27] | |
| Pham et al. (2023) | Vietnam | √ | √ | √ | ATT, INT, SN, PBC, MN, HB, WTP | [28] | |
| Sari et al. (2021) | Indonesia | √ | √ | √ | √ | ATT, INT, SN, PBC, AC, EB, CN | [29] |
| Ramzan et al. (2019) | China | √ | √ | ATT, SN, PBC, INT, PR, PB | [30] | ||
| Laeequddin et al. (2022) | India | √ | AC, SN, INT, PBC, PLR | [31] | |||
| Ben Yahya et al. (2023) | UAE | √ | √ | ATT, SN, PBC, INT, PR, EB | [32] | ||
| Sabbir et al. (2023) | Bangladesh | √ | √ | ATT, SN, INT, PBC, AC, PLR | [33] | ||
| Zhang et al. (2019) | China | √ | √ | ATT, SN, PBC, INT, CN | [21] | ||
* (√) indicates consideration of the theory. ** Codes for variables: Awareness of Consequences (AC), Sense Responsibility (SR), Moral Norm (MN), Attitude (ATT), Subjective Norm (SN), Perceived Behavioral Control (PBC), Information Publicity (IP), Intention (INT), Convenience (CN), Habit (HB), Cost of recycling (CR), Economic benefit (EB), willingness to pay (WTP), Policy, Law and Regulation (PLR), Perceived risks (RP).
2.2. Factors Impacting E-Waste Recycling Behavior and Hypotheses Development
Referring to Table 1, a wide range of the literature tried to predict the EWRB of consumers using factors addressed in theories, such as TPB, NAM, TIB, and BRT. These theories can be used to predict behavior regardless of their demographic aspects, such as gender and age. For instance, Kumar (2019) used TPB and NAM theories to predict the EWRB of young consumers in India and China [15]. Aboelmaged (2021) used TPB and TIB theories to predict EWRB for young consumers in the UAE [10]. Li et al. (2023) used TPB and BRT theories to predict young consumers’ EWRB in China [34]. Hence, considering the suitability of these theories to predict the EWRB, this paper tried to identify the factors impacting EWRB for the given context from TPB, NAM, BRT, and TRGP theories at the outset.
2.2.1. Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB)
According to the TPB (first proposed by Ajzen (1991)), intention is the main precursor of our behavior, which is further impacted by factors- attitude, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control (PBC) [35]. Attitude refers to our positive and negative perception of a certain action [1]. Subjective norm indicates our perception of others’ thoughts and reactions to a certain behavior [36]. PBC could be viewed as the degree of convenience or comfort to perform the action. PBC could be viewed as the availability of a facility to perform recycling e-waste at a convenient location, information and availability about exchanging offers for end-of-life electronics items, knowledge about where and how to recycle e-waste, etc. [36].
TPB says that our attitude, subjective norm, and PBC impact forming intention, which ultimately leads to the intended action [35]. Several research reported a significant impact of attitude, subjective norm, and PBC in forming the intention of EWRB [15,22,33]. For instance, Kumar (2019) identified a significant impact of attitude, subjective norm, and PBC on the intention of EWRB of young consumers in India and China [15]. Despite the impact of these factors on intention as addressed in TPB, few research reported an insignificant impact of attitude, subjective norm, and PBC in forming the intention of EWRB, and criticized TPB [10,12]. For instance, Aboelmaged (2021) identified an insignificant impact of a subjective norm and PBC on young consumers’ intention of EWRB in UAE [10]. However, considering the gravity of the well-established TPB model and empirical evidence from the literature, the following hypotheses could be postulated.
H1.
Attitude significantly impacts the intention of EWRB.
H2.
Subjective norm significantly impacts the intention of EWRB.
H3.
Perceived behavioral control significantly impacts the intention of EWRB.
H4.
Intention significantly impacts EWRB.
2.2.2. Norm Activation Model (NAM)
NAM theory, which was first introduced by Schwartz (1977) underscores the importance of altruistic factors in forming the intention of a certain behavior [37]. According to NAM theory, moral norm (MN) is the main precursor of our intention, which is further impacted by our awareness of consequence (AC) and sense of responsibility (SR) [37]. For recycling behavior, AC could be viewed as an individual’s eco-awareness related to the harmful impact of the increased amount of waste on climate and nature [38]. MN could be perceived as our obligation to perform or abstain from certain actions out of morality [38]. Scholars addressed that many people perform pro-environmental behavior due to strong MN, rather than thinking of cost–benefit analysis. Several research underscored the importance of MN in pro-environmental behavior, especially EWRB [12,13,27]. As NAM theory suggests, MN is impacted by AC and SR which was further validated by numerous research in the recycling context [9,38]. Mohamad et al. (2022) reported a significant impact of MN on the intention of EWRB for consumers in Malaysia [12]. Wang et al. (2018) identified a significant impact of AC and SR on MN that further impacts the intention of EWRB for consumers in China [25]. Therefore, based on NAM theory and empirical support from the literature, the following hypotheses could be delineated.
H5.
Awareness of consequences significantly impacts moral norm.
H6.
Sense of responsibility significantly impacts moral norm.
H7.
Moral norm significantly impacts the intention of EWRB.
2.2.3. Behavioral Reasoning Theory (BRT)
BRT suggests that an individual’s action depends on their assessment of perceived benefits and perceived risks associated with the action [39]. Several research highlighted that consumers’ perceived economic benefit associated with exchanging end-of-life electronics, or obtaining incentives by recycling e-waste impacts their intention to EWRB [13,33]. Sabbir et al. (2023) identified a significant impact of economic benefits on Bangladeshi consumers’ intention to exchange end-of-life electronics products [33].
On the other hand, in the e-waste recycling context, scholars emphasized the importance of associated risks such as personal data security issues [13,40]. Due to fear that personal data might be stolen or misused, consumers refrain from recycling their electronic items, such as laptops, mobile phones, and smart watches, despite having the intention to do so [13,40]. Similarly, having an emotion towards personal electronics products, or perceiving not achieving sufficient economic value, people refrain from recycling e-waste. Hence, scholars considered perceived risks (PR) associated with recycling e-waste as an important factor determining consumers’ EWRB [41,42]. The latest study by Chang et al. (2022) reported a significant moderating impact of PR on the intention-to-behavior relationship in the e-waste recycling context [43]. Therefore, this research postulates the following hypotheses.
H8.
Economic benefit significantly impacts the intention of EWRB.
H9.
Perceived risk significantly negatively moderates the impact of the intention on EWRB.
2.2.4. Impact of the Pro-Environmental Goal on EWRB
Referring to the Goal Framing Theory (GFT), our behavior is impacted by different types of goals, such as gain goal, hedonic goal and normative goal [44]. Scholars highlighted the significance of normative type goal in pro-environmental behavior [44,45]. An individual’s pro-environmental goal (PEG), such as a lifetime goal to serve the environment, marine life, or wildlife could be considered a normative type goal [45,46]. The latest research highlighted the significance of normative goal (i.e., PEG) in EWRB [47].
Recently, Ajzen and Krunglaski (2019) proposed the Theory of Reasoned Goal Pursuit (TRGP), highlighting the importance of goals that drive people to pursue a certain behavior day after day [18]. The latest study by Concari et al. (2023) and Islam et al. (2024) tested the TRGP in household waste recycling and plastic waste reduction behavior, respectively, suggesting the significance of PEG to form the intention of pro-environmental behavior [19,20]. Hence, it could be understood that people with PEG would posit their actions linked to reducing e-waste so that their PEG could be achieved. Therefore, this research suggests PEG as a precursor of the intention of EWRB, proposing the following hypothesis.
H10.
Pro-environmental goal significantly impacts the intention of EWRB.
One of the strengths of TRGP is that it can provide a better explanation of sustaining certain behaviors [18]. TRGP considers the goal as a precursor of intention that motivates people to perform the behavior to achieve their goal, reducing the intention–behavior gap [20,48]. For instance, despite having an intention people may refrain from recycling due to lack of convenient locations nearby. Despite this odd, people may drive a long distance to perform recycling because it could lead them to achieve their PEG (i.e., normative goal) [49]. Several research highlighted the importance of normative goal for reducing the intention–behavior gap [50,51]. Orbell (2004) and Prestwich et al. (2008) suggested that chasing a goal enhances their intention to actualize the behavior [50,51]. Weiber et al. (2015) suggested that fostering normative goals could reduce the intention–behavior gap by enhancing motivation and commitment toward intended action [48]. Hence, PEG could be considered as a factor that can moderate the impact of intention to behavior, reducing the intention–behavior gap. Therefore, this research proposes the following hypothesis.
H11.
Pro-environmental goal significantly positively moderates the impact of intention on EWRB.
Figure 2 provides an overview of the hypotheses that will be tested in this research.
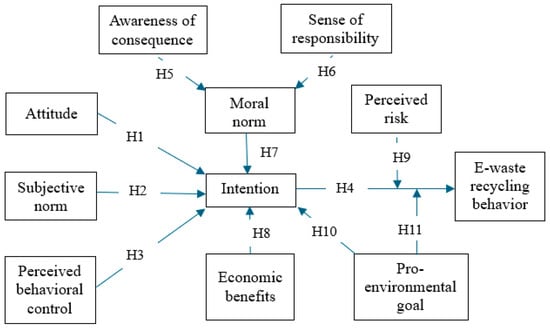
Figure 2.
Overview of hypotheses.
3. Methodology
An empirical study was conducted in Dhaka City. Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh, is home to more than 20 million people, accounting for 11% of the country’s total population [52]. In 2022, Dhaka generated 117 million kilograms of e-waste [53], which constitutes over 30% of the nation’s total e-waste. Therefore, considering the fact that a significant portion of e-waste is generated from the city itself, data were collected from young consumers residing in Dhaka city.
A survey was conducted on 348 university students aged between 18 and 30 years who reside in Dhaka. Kumar (2019) conducted a study to compare the EWRB of young consumers in India and China, where data were collected from consumers aged between 20 and 29 years [15]. Islam et al. (2024) conducted a study to examine young consumers’ plastic waste recycling behavior and data were collected from consumers aged 18 to 30 years [20]. Hence, the selection of the population in the age group of 18 to 30 years is supported by literature.
Respondents were selected randomly from multiple universities. Among the respondents, 57% were male, and the rest were female. Regarding the age distribution, 80% were between 20 and 25 years and the rest were between 26 and 30 years old. The survey was conducted using a paper-based self-guided questionnaire, and during the data collection time, multiple researchers were present for clarification. The items of each construct were developed from the literature. Table 2 provides a list of items for the constructs and their respective codes. The items presented in Table 2 were used to develop the questionnaire using a 5-point Likert scale, where “1” represents “fully disagree” and “5” represents “fully agree”. The questionnaire was reviewed by all researchers. Before surveying, a pilot study was conducted among 30 students to remove ambiguity in the questionnaire.

Table 2.
Constructs and items.
Regarding the minimum sample size, using the G*Power (version 3.1.9.6) software [54], where considering the effect size: 0.15, significance criterion: 0.05, and power: 0.95, the minimum sample size appears to be 178. Additionally, considering the sample-to-variable ratio of 20:1, as per recommendation of Hair et al. (2019) [55], the minimum sample size appears to be 220 for 11 variables used in this study. Furthermore, considering the fact that the population aged between 18 and 30 years in Dhaka city is approximately 28% of its 20 million people [56]. Considering the 95% confidence level and 5% margin of error, the sample size appears to be 310. Therefore, the sample size of 348 satisfies the criteria of minimum sample size for further analysis that would provide an adequate estimation of the population. Data were analyzed using the partial least square-based structural equation modeling technique (PLS-SEM). SPSS (version 28) and Smart PLS (version 3) software were used for data analysis.
4. Result
First, the reliability and validity of the measurement model was checked. Table 3 provides the factor loadings of each item, found above 0.70, suggested by Hair et al. (2018). Referring to Table 4, the Cronbach’s Alpha and Composite Reliability (CR) score for each variable were found above 0.7, and the Average Variance Extracted (AVE) value for each variable was above the threshold value of 0.5, as recommended by Hair et al. (2018) [55].

Table 3.
Factor loadings of all items.

Table 4.
Reliability and validity of measurement model.
The VIF values of ATT1 and ATT2 were found to be 3.332 and 3.613, respectively, and all other items were found below three, which indicates the absence of collinearity among the items. The Fornell–Larcker Criterion [57] of discriminant validity analysis reveals that the square root of AVE for the diagonal elements (representing inter-construct correlation) is higher than the off-diagonal elements (see Table 5). Additionally, the Heterotrait–Monotrait ratios [HTMT] were checked, and the highest correlation value was found to be 0.878, which falls within the permissible threshold of 0.90 [58]. Therefore, the measurement model provided adequate reliability and validity to conduct the hypotheses testing.

Table 5.
Fornell–Larcker Criterion.
The hypotheses were tested considering the bootstrapping of 2000 samples. The result of hypotheses testing is presented in Table 6. All the hypotheses, except H1 and H2, were accepted having a p-value less than 0.05 and a t-value greater than 1.96. The result shows that 54.7% variation in EWRB (R2 = 0.547) could be explained by the theoretical model. EWRB is significantly impacted by consumers’ intentions, supporting hypothesis H4. The intention (R2 = 0.361), which is the main determinant of EWRB, result shows a 36.1% variation in it by its predictors. Among different determinants, PBC, MN, PEG, and EB have a significant direct impact on the INT, supporting hypotheses- H3, H7, H8, and H10. However, the impact of ATT and SN were found to have an insignificant impact on INT, not supporting hypotheses H1 and H2.

Table 6.
Result of hypotheses testing.
Regarding the formation of MN, it was found that AC and SR significantly impact MN, supporting hypotheses H5 and H6. The result also shows that PR significantly moderates the relationship of INT to EWRB negatively, supporting hypothesis H10. Regarding the moderating role of PEG, results suggest that PEG significantly positively moderates the impact of INT on EWRB, supporting hypothesis H11.
5. Discussion
Based on the result, the impact of ATT and SN on INT was found to be insignificant, contradicting the TPB. However, several research reported similar findings for the EWRB context, suggesting an insignificant impact of ATT on INT [12], and SN on INT [10,12,13,29]. Referring to the concept of the attitude–behavior gap [59], despite having a positive attitude, people show reluctance to act pro-environmentally, which was found in this study. Regarding the impact of SN, in Bangladesh waste management system is very poor, including sorting at home, disposing, and recycling properly [33]. Hence, there is a lack of social pressure to conduct recycling. Researchers addressed similar issues in other developing countries, such as Malaysia, India, and Indonesia, and identified the lack of impact of SN on EWRB [12,13,29]. Therefore, this study is in line with earlier research suggesting an insignificant impact of ATT and SN on young consumers EWRB. However, this scenario is not only limited to developing countries. The study of Aboelmaged (2021) in UAE reported an insignificant impact of SN on INT of EWRB [10]. Therefore, further study is required to generalize our understanding of the impact of SN on EWRB for different economic, cultural, and geographic contexts.
Regarding external factors, this research identified a significant impact of PBC and EB on INT, suggesting the importance of proper facilities, information availability, and attractive offers when exchanging end-of-life electronics items boosting young consumers’ intention to perform EWRB. These contradict the findings of earlier studies that reported an insignificant impact of PBC on INT [10,13] and EB on INT [29] in the e-waste recycling context. However, an earlier study by Sabbir et al. (2022) identified a significant impact of PBC and EB for exchanging end-of-life electronics products for Bangladeshi consumers [33]. Therefore, this study is in line with their findings, suggesting a significant impact of external factors, especially PBC and EB, on young consumers’ EWRB.
Regarding the internal factors, the result identified a significant impact of MN and PEG on the INT of EWRB. NAM theory suggests that MN is a precursor of intention, which is significantly impacted by EA and SR [37]. This research identified similar relationships, supporting hypotheses H5, H6, and H7, in line with the NAM theory. Several research underscored MN as the strongest precursor of the intention of pro-environmental behavior [12,38,60]. However, in this research, comparing the β-value, the impact of MN (H7: MN → INT, β: 0.135) was found to have a less significant impact on the intention of EWRB compared to EB (H8: EB → INT, β: 0.220) and PBC (H3: PBC → INT, β: 0.221). The PEG exerts more impact on INT compared to MN (H10: PEG → INT, β: 0.145). Therefore, comparing the β-value, it was found that EB exerts the strongest impact on INT, followed by PBC, PEG, and MN. Hence, the findings indicate that the external factors (i.e., EB and PBC) exert more impact on the INT of EWRB compared to intrinsic factors (i.e., MN and PEG) for young consumers. This finding is not unexpected because e-waste or end-of-life electronics products carry an economic value, and consumers tend to keep it hoping to receive the desired price. While scholars posit a viewpoint that pro-environmental behavior is impacted by altruistic factors addressed in NAM theory, this research does not deny the view considering the significant impact of MN and PEG on INT of EWRB. However, this research suggests that the availability and convenience of receiving economic value exerts a dominant impact on consumers’ EWRB, rather than intrinsic factors like moral norms and PEG.
The result also suggests that despite having an intention, young consumers EWRB is impacted by the PR, such as feeling insecure about personal data misuse, perception of obtaining less value by selling or exchanging and having some emotional attachment to personal electronics gadgets. Due to these sorts of PR, consumers are reluctant to recycle their e-waste. This finding is in line with the previous study by Chang et al. (2022), suggesting PR negatively moderates the INT to EWRB relationship [43]. Therefore, PR could be viewed as a factor augmenting the intention–behavior gap, supporting earlier research having similar findings [43].
One of the novelties of this research is exploring the impact of PEG on EWRB. Synthesizing literature, this paper hypothesized PEG as a precursor of intention, which is supported by empirical study. Additionally, this research signifies another crucial role of PEG regarding its positive moderating impact on the INT to EWRB relationship, indicating its influence on reducing the intention–behavior gap. Recently, Ajzen and Krunglaski (2019) proposed TRGP modifying TPB, highlighting the importance of individual goals on consumers’ stainable pro-environmental behavior [18]. Ajzen and Krunglaski (2019) argued that chasing the active goal would motivate a person to actualize the intended action [18], which is in line with other scholars suggesting the influence of an individual’s goal in reducing the intention–behavior gap [48,50,51]. While numerous studies emphasized the impact of moral norm and eco-awareness on intention [12,13,27], their intention is less likely to actualize due to the intention–behavior gap, which is a challenge for practitioners to resolve. This study suggests that consumers’ PEG could be a factor in addressing this challenge, reducing the intention–behavior gap.
How PEG reduces the intention–behavior gap in the EWRB context could be explained in several ways. One of the plausible reasons could be that not fulfilling the intended action would cause them to feel guilty. Consequently, people can challenge themselves to fulfill their goals despite a lack of convenience or having perceived risks on data security issues. Another reason could be PEG forms pro-environmental habits among consumers. When PEG forms within individuals, they try to exert pro-environment behavior in all aspects of their lifestyle, stimulating a pro-environmental habit. The study by Sabbir reported that consumers’ pro-environmental habit, such as recycling different types of waste, like paper and plastic, exert a direct significant impact on their EWRB [33]. Therefore, practitioners require fostering PEG among young consumers to promote EWRB.
To summarize the discussions, it could be understood that factors addressed in TPB, such as ATT and SN, show insignificant impacts on INT, which is supported by earlier research. On the other hand, hypotheses developed based on NAM, BRT, and TRGP theories were supported. It was found that external factors like PBC and EB and internal factors like MN and PEG thrive as the main motivating factors to drive young consumers’ intention of EWRB. As addressed before, from a cultural perspective, Bangladesh has a collective society with a restrictive, short-term oriented, and uncertainty avoidance mindset. Due to the absence of social norm for following pro-environmental behavior, it is difficult to implement a sustainable EWRB among mass consumers as people show reluctance to adopt new ideas and change their regular lifestyle. As the data were collected from educated university students, it was found that SN has an insignificant impact on their EWRB. It was not unexpected because the young generation in the country is gradually developing an indulgence mindset. Therefore, the impact of MN and PEG was found to be significant on young consumers of EWRB. Additionally, while the PR broadens the intention–behavior gap, their PEG significantly moderates the impact of intention on EWRB, reducing the intention–behavior gap.
6. Conclusions, Implication, and Future Research Direction
6.1. Conclusions
One of the objectives of this paper is to identify the factors impacting young consumers’ EWRB in a developing country context. Synthesizing literature, several factors were identified as presented in Figure 2. The empirical study shows their EWRB is significantly impacted by their intention, which is further impacted by economic benefit, perceived behavioral control, moral norm, and a pro-environmental goal. Among these factors, economic benefit exerts the strongest impact on the intention of EWRB. However, the perceived risks hinder consumers’ intention of EWRB to actualize suggesting a negative moderating impact. Another objective of this paper was to explore the impact of pro-environmental goal on EWRB. The result shows that apart from a direct impact on intention, PEG also significantly moderates the impact of intention on EWRB, reducing the intention–behavior gap.
6.2. Theoretical Contributions
This paper has two distinct theoretical contributions. Firstly, while reviewing the literature, it was found that literature considering an individual’s PEG as a construct predicting EWRB is limited. This research provides empirical evidence that PEG significantly impacts the intention of EWRB and reduces the intention–behavior gap, thereby augmenting our understanding of how it impacts EWRB.
Secondly, this paper addresses a significant research gap concerning the limited understanding of young consumers’ EWRB in developing countries. Although prior research has attempted to identify the factors influencing young consumers’ EWRB, inconsistencies in findings underscore the need for further investigation to generalize knowledge in this area. This study provides additional empirical evidence regarding the factors that significantly impact young consumers’ EWRB in a developing country’s context having a collective, restrictive, short-term oriented, and risk avoidance culture. Therefore, the findings provide further insight on how to develop a sustainable EWRB among young consumers in a developing country’s context with such cultural aspects.
6.3. Practical Implications and Suggestions for Policymakers
This research tried to develop a body of knowledge for practitioners and policymakers to form effective strategies to enhance the E-waste recycling rate. It was found that young consumers’ EWRB depends on their intention, which is significantly impacted by their moral norm, pro-environmental goal, PBC, and associated economic benefits. Therefore, authorities need to ensure adequate facilities to dispose of e-waste. Additionally, proper regulations need to be imposed so that electronics companies provide favorable offers for exchanging end-of-life electronics products.
In parallel, the result suggests moral norms as one of the significant determinants of intention, which is impacted by eco-awareness and a sense of responsibility. Hence, necessary measures need to be taken to enhance youngsters’ eco-awareness and corresponding responsibilities to boost their moral norm to perform pro-environmental behavior in their daily lives. Additionally, PEG was found to be a significant precursor of intention, which also impacts reducing the intention–behavior gap. Therefore, proper measures need to be taken to form PEG among youngsters so that their intrinsic motivation to pursue PEG thrives and they can constantly perform EWRB.
Finally, it was found that despite having positive intentions, perceived security risks, such as the misuse of personal information, hinder young consumers from performing intended EWRB. Hence, authorities need to take proper action plans to enhance security issues throughout recycling operations.
It is expected that the proper implementation of the suggested action plans would enhance the e-waste recycling rate in Bangladesh and reduce landfill waste. Though the research was conducted in a Bangladeshi context, the findings were supported by earlier empirical studies from developing countries. Hence, it is expected that the suggested action plans would assist in improving the e-waste recycling rate in other developing countries as well, especially those having the same cultural traits and poor infrastructure in managing waste.
6.4. Limitation and Future Research Direction
This research posits several limitations. Firstly, data were collected from university students, who are highly educated and tend to have higher eco-awareness. This delimits our understanding of the factors that influence less educated young consumers’ EWRB. Hence, further research could be carried out covering young populations from diverse educational backgrounds and economic statuses. Additionally, data were collected only from residents of Dhaka city. Collecting data from diverse locations would have provided further validation of the findings from the country’s perspective. Secondly, this research only focused on identifying the motivating factors of young consumers’ EWRB, delimiting our understanding of the impact of these factors on diverse age groups. Hence, a comparative study could be carried out among diverse age groups.
Thirdly, this research did not identify the EWRB for any specific types of electronic products. Hence, further empirical studies could be conducted using the theoretical model for different types of e-waste to augment our understanding of the impact of the factors on consumers’ EWRB based on different types of electronics products. Fourthly, this research conducted an empirical study in Bangladesh that delimits the generalization of the findings. Hence, testing the theoretical model by collecting data from other developing countries would improve the generalization of the findings. Finally, this research did not consider emotional factors like affection or anticipation of guilt, and other factors addressed in Table 1. Incorporating such factors in the theoretical model would provide a further comprehensive understanding of EWRB.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H.I.; Methodology, M.H.I. and B.B.; Software, M.H.I.; Validation, B.B. and M.M.O.I.; Formal analysis, M.H.I., M.R.H. and S.Z.H.; Investigation, M.T.I.; Data curation, S.Z.H.; Writing—original draft, M.H.I., M.R.H. and S.Z.H.; Writing—review & editing, M.H.I., M.T.I., M.R.H., S.Z.H., B.B., M.M.O.I. and M.F.H.; Visualization, B.B. and M.F.H.; Project administration, M.T.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- UNITAR. Global E-Waste Monitor 2024. Geneva/Bonn. 2024. Available online: https://ewastemonitor.info/the-global-e-waste-monitor-2024/ (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- DoE. Assessment of Generation of E-Waste, Its Impacts on Environment and Resource Recovery Potential in Bangladesh. Dhaka. 2019. Available online: https://doe.portal.gov.bd/site/page/976b9daa-b0eb-42bf-bc85-d17a8f13b424/- (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Ministry of Planning—Bangladesh. MUNICIPAL WASTE MANAGEMENT (MWM) SURVEY 2022. Dhaka. 2023. Available online: http://nsds.bbs.gov.bd/en/posts/101/Municipal%20Waste%20Management%20(MWM)%20Survey%202022 (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Roy, H.; Islam, M.S.; Haque, S.; Riyad, M.H. Electronic waste management scenario in Bangladesh: Policies, recommendations, and case study at Dhaka and Chittagong for a sustainable solution. Sustain. Technol. Entrep. 2022, 1, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Huda, N.; Baumber, A.; Shumon, R.; Zaman, A.; Ali, F.; Hossain, R.; Sahajwalla, V. A global review of consumer behavior towards e-waste and implications for the circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzzo, G.; Prati, G. Psychological correlates of e-waste recycling intentions and behaviors: A meta-analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 204, 107462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, J.L.; Steg, L.; van der Werff, E.; Ünal, A.B. A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. J. Environ. Psychol. 2019, 64, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phulwani, P.R.; Kumar, D.; Goyal, P. A Systematic Literature Review and Bibliometric Analysis of Recycling Behavior. J. Glob. Mark. 2020, 33, 354–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, J.Z. Predicting Recycling Behavior in New York State: An integrated model. Environ. Manag. 2022, 70, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelmaged, M. E-waste recycling behaviour: An integration of recycling habits into the theory of planned behaviour. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 124182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Islam, M.H.; Kamal, M.A. Role of Habit in Household Waste Recycling Behavior: Evidence from an Emerging Country. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2024, 19, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.S.; Thoo, A.C.; Huam, H.T. The Determinants of Consumers’ E-Waste Recycling Behavior through the Lens of Extended Theory of Planned Behavior. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, N.S.; Majhi, R. An empirical investigation to understand mobile phone users’ behavioural intention to give their end-of-life mobile phones for formal recycling. Waste Manag. 2024, 177, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, R.V.; Krishnan, M.M.; Parayitam, S.; Duraisami, S.P.A.; Saravanaselvan, N.R. Exploring e-waste recycling behaviour intention among the households: Evidence from India. Clean. Mater. 2023, 7, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. Exploring young adults’ e-waste recycling behaviour using an extended theory of planned behaviour model: A cross-cultural study. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.; Qiao, L.; Xu, T.; Gan, X.; Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Qiao, Y.; Hou, J. Promoting sustainable development: The impact of differences in cultural values on residents’ pro-environmental behaviors. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 1539–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, H.; Zheng, A.; Chico, E.; Gonseauz, B. Cultural Differenes Among Canada, Japan, Thailand & Bangladesh Based on Hofstede’s Six Cultural Dimensions; Institute for Global Business Research: Nashville, TN, USA, 2018; pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ajzen, I.; Kruglanski, A.W. Reasoned Action in the Service of Goal Pursuit. Psychol. Rev. 2019, 126, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concari, A.; Kok, G.; Martens, P.; Brink, N. Investigating the Role of Goals and Motivation on Waste Separation Behavior Through the Lens of the Theory of Reasoned Goal Pursuit. Environ. Manag. 2023, 72, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.H.; Anam, M.Z.; Islam, M.T.; Sabbir, M.M. Exploring the impact of goals and motivation on young consumers’ sustainable plastic management behavior using the Theory of Reasoned Goal Pursuit. Clean. Waste Syst. 2024, 8, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qu, J.; Sheng, H.; Yang, J.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Z. Urban mining potentials of university: In-use and hibernating stocks of personal electronics and students’ disposal behaviors. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 143, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, K.A.; Singh, A.; Siddiqua, A.; El Gamal, M.; Laeequddin, M. E-Waste Recycling Behavior in the United Arab Emirates: Investigating the Roles of Environmental Consciousness, Cost, and Infrastructure Support. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbir, M.M.; Khan, T.T.; Das, A.; Akter, S.; Hossain, M.A. Understanding the determinants of consumers’ reverse exchange intention as an approach to e-waste recycling: A developing country perspective. Asia-Pac. J. Bus. Adm. 2023, 15, 411–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ling, M.; Lu, Y.; Shen, M. Understanding household waste separation behaviour: Testing the roles of moral, past experience, and perceived policy effectiveness within the theory of planned behaviour. Sustainability 2017, 9, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, B. How does information publicity influence residents’ behaviour intentions around e-waste recycling? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshta, N.; Patra, S.; Singh, S.P. Sharing economic responsibility: Assessing end user’s willingness to support E-waste reverse logistics for circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 130057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumari, W.A.C.S.; Ahn, J.; Kim, M. Impact of information publicity on Korean residents’ E-waste recycling intentions: Applying the norm activation model and theory of planned behavior. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.T.; Lam, T.P.M.; Le Dang, H.; Pham, N.T. Consumers’ willingness to pay an environmental fee for e-waste recycling in Vietnam: Integrating the theory of planned behaviour and the norm activation model. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 2900–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, D.P.; Masruroh, N.A.; Asih, A.M.S. Consumer Intention to Participate in E-Waste Collection Programs: A Study of Smartphone Waste in Indonesia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, S.; Liu, C.; Munir, H.; Xu, Y. Assessing young consumers’ awareness and participation in sustainable e-waste management practices: A survey study in Northwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 20003–20013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laeequddin, M.; Abdul, W.K.; Sahay, V.; Tiwari, A.K. Factors That Influence the Safe Disposal Behavior of E-Waste by Electronics Consumers. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, T.B.; Jamal, N.M.; Sundarakani, B.; Omain, S.Z. The Effects of Data Security and Perceived Benefits on Mobile Phone Recycling Behaviour and the Recycling Intention Mediation Role. Recycling 2023, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbir, M.M.; Taufique, K.M.R.; Nomi, M. Consumers’ reverse exchange behavior and e-waste recycling to promote sustainable post-consumption behavior. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2023, 35, 2484–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Jiao, J.; Yang, R.; Zha, J. Do recycling channels affect young consumers’ choices for formal power battery recycling? J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, F.; Daud, D.; Weng-Wai, C.; Jiram, W.R.A. Waste separation at source behaviour among Malaysian households: The Theory of Planned Behaviour with moral norm. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.H. Normative Influences on Altruism. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 1977, 10, 221–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.T.; Huang, M.H.; Cheng, B.Y.; Chiu, R.J.; Chiang, Y.T.; Hsu, C.W.; Ng, E. Applying a comprehensive action determination model to examine the recycling behavior of taipei city residents. Sustainability 2021, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westaby, J.D. Behavioral reasoning theory: Identifying new linkages underlying intentions and behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2005, 98, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ran, W.; Jiang, S.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Z. Understanding consumers’ behavior intention of recycling mobile phone through formal channels in China: The effect of privacy concern. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 5, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, A.; Malodia, S.; Awan, U.; Sakashita, M.; Kaur, P. Extended valence theory perspective on consumers’ e-waste recycling intentions in Japan. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, A.; Koshta, N.; Goyal, R.K.; Sakashita, M.; Almotairi, M. Behavioral reasoning theory (BRT) perspectives on E-waste recycling and management. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-S.; Yue, Z.; Qureshi, M.; Rasheed, M.I.; Wu, S.; Peng, M.Y.-P. Residents’ waste mobile recycling planned behavior model: The role of environmental concern and risk perception. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2023, 18, 6388–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenberg, S.; Steg, L. Normative, Gain and Hedonic Goal Frames Guiding Environmental Behavior. J. Soc. Issues 2007, 63, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steg, L.; Lindenberg, S.; Keizer, K. Intrinsic Motivation, Norms and Environmental Behaviour: The Dynamics of Overarching Goals. Int. Rev. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2016, 9, 179–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steg, L.; Bolderdijk, J.W.; Keizer, K.; Perlaviciute, G. An Integrated Framework for Encouraging Pro-environmental Behaviour: The role of values, situational factors and goals. J. Environ. Psychol. 2014, 38, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzzo, G.; Prati, G. Unraveling the influence of convenience situational factors on e-waste recycling behaviors: A goal-framing theory approach. Sustain. Dev. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieber, F.; Thürmer, J.L.; Gollwitzer, P.M. Promoting the translation of intentions into action by implementation intentions: Behavioral effects and physiological correlates. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 140516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onel, N.; Mukherjee, A. Why do consumers recycle? A holistic perspective encompassing moral considerations, affective responses, and self-interest motives. Psychol. Mark. 2017, 34, 956–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestwich, A.; Perugini, M.; Hurling, R. Goal desires moderate intention—Behaviour relations. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 2008, 47, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbell, S. Intention–behavior relations: A self-regulation perspective. In Contemporary Perspectives on the Psychology of Attitudes; Psychology Press: Hove, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- World Population Review. Dhaka Population. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/world-cities/dhaka-population (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- Easin, E.I.; Tabassum, N.; Islam, A.; Hossain, M.A. Quantitative Analysis of E-Waste in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2022), Khulna, Bangladesh, 10–12 February 2022; pp. 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.; Black, W.; Babin, B.; Anderson, R. Multivariate Data Analysis, 8th ed.; Cengage Learning: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. Population & Housing Census 2022. 2022. Available online: https://sid.portal.gov.bd/site/page/7b8589b9-d534-46e4-bc3b-7f43905aadf0/Population-and-Housing-Census (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error: Algebra and Statistics. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElHaffar, G.; Durif, F.; Dubé, L. Towards closing the attitude-intention-behavior gap in green consumption: A narrative review of the literature and an overview of future research directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 122556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lai, K.H.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z. From intention to action: How do personal attitudes, facilities accessibility, and government stimulus matter for household waste sorting? J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).