Abstract
The GLK gene family is of great significance in regulating chloroplast development and participating in chlorophyll synthesis. However, the mechanism of GLK involvement in Citrus chlorophyll synthesis remains unclear. In this study, bioinformatics methods were used to analyze the gene structure, protein evolution, chromosome distribution, promoter elements and expression profile of GLK gene family in Citrus. Overall, 27 CsGLK TFs were identified from Citrus genome and divided into three subgroups according to the conserved domains. All members were distributed on nine chromosomes. The tandem replication events (ka/ks < 1) indicated that CsGLK TFs underwent a purification selection evolutionary process. The intron variation might be a vital configuration for the evolution of CsGLK genes. The expression pattern of CsGLKs showed that family members had higher expression levels in different tissues and at different growth stages and could actively respond to dark stress. CsGLK TFs of the same group had similar structures, but their expression patterns were quite different, indicating that they may have different functions and not be redundant. Correlation analysis showed that CsGLK2, CsGLK9, CsGLK10, CsGLK11, CsGLK20 and CsGLK24 were significantly positive correlations with Chl a and Chl b contents. In addition, CsGLK2, CsGLK5, CsGLK10, CsGLK11, CsGLK12, CsGLK15, CsGLK20 and CsGLK24 were significantly positive related to Mg-Proto IX, Proto IX and Pchl.
1. Introduction
Golden2-like (GLK) protein is an important transcription factor in the GARP superfamily [1,2,3]. In this family, GLK genes are monophyletic, but the gene replication occurs independently in monocots and eudicots [4]. Most GLK genes have a Myb-DNA-binding domain (DBD) and C-terminal domain (GCT-box) [5]. In addition, some members of subgroups have conserved MYB-CC-LHEQLE domains [6,7]. The DBD sequence, which exists in green algae and terrestrial plants, is highly conserved among GARP superfamily members [8], while the GCT box is only found in terrestrial plants and has specificity for the GLK gene [9].
It is found that GLK family members are essential for chloroplast formation and development [10,11,12,13]. GLK regulates the chloroplast development of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), peach (Prunus persica L.cv LuYou Tao1) and Arabidopsis thaliana [10,11,14,15,16], and it coordinates the expression of photosynthetic genes in the nucleus to adapt to different environments and developmental conditions [17]. The overexpression of GLK in Arabidopsis leads to the biogenesis and photosynthesis of chloroplasts in non-photosynthetic organs (root and fruit) [18]. Moreover, GLK genes promote the production of plant chloroplasts and optimize photosynthesis under different biotic and abiotic environmental stress conditions [12,19,20].
Meanwhile, the overexpression of GLK gene in peach and tomato can increase plastid number and pigment content [21,22]. Analysis of phenotypic and transcriptome data for leaves in diploid and triploid E. urophylla revealed a positive correlation between EgrGLK genes and chlorophyll synthesis [23]. Studies have shown that GLK is involved in the regulation of multiple chlorophyll synthase activities [24], such as δ-Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALAD, catalyzing the synthase of ALA), protoporphyrinogen deaminase (PGBD, catalyzing the synthase of PBG), protoporphyrinogen oxidase (PROTOX, catalyzing the synthase of protoporphyrinogen IX), magnesium chelatase (MGCH, catalyzing the synthase of protoporphyrinogen IX), magnesium protoporphyrin ester cyclase (MPECYC, catalyzing the synthase of protoporphylide), protochlorophyll oxidoreductase (POR, catalyzing Chl a and Chl b synthesis), etc. [21]. Through transient in vivo induction of Arabidopsis, GLK1 and GLK2 transcripts and ChIP analysis of anti-GLK1 antibodies, the key genes of chlorophyll biosynthesis were determined [17].
Previous studies have shown that, although GLK1 and GLK2 have the same function, they have different regulatory pathways and tissue-specific characteristics in various organs [7]. In corn, ZmGLK1 and ZmGLK2 are a pair of homologous genes with basically the same function, which are expressed in mesophyll cells and vascular bundle sheath cells, respectively [25]. GLK1 is mainly expressed in leaf tissue and GLK2 is mainly expressed in fruit [26]. In tomato, SlGLK2 is only expressed in the fruit and affects the content of sugar and carotenoids by regulating chloroplast development [13,27]. In addition, some studies have found that the KNOTTED1-LIKE HOMEOBOX (KNOX) gene acts downstream of SlGLK2 and only affects the chloroplast development in tomato fruit, but does not affect leaf tissue [28].
GLK gene has an important impact on chloroplast development, chlorophyll synthesis, leaf growth and development. Identifying members of GLK family and finding out members that respond positively during growth and under dark stress are of great significance for improving photosynthetic capacity and fruit quality. Sweet orange, which is also a very appropriate research model of woody plant, accounts for more than 60% of the yield of Citrus, being both rich in nutrients and economic value. In this work, we performed a comprehensive examination of the GLK gene in Citrus, including genome-wide identification, phylogenetic classification, gene structure, chromosomal position, replication events, collinearity and expression levels in various tissues, growth stages and dark stress.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
On the 3rd, 7th, 11th, 18th, 25th and 32nd days after the summer shoot sprouting, the sweet orange leaves were collected and named D3, D7, D11, D18, D25 and D23, respectively. At the same time, after 11 days of shoot pulling, the plants were put into the incubator for dark treatment, and the control group (LT) grew under 16 h light (200 μmol·m−2·s−1)/8 h dark conditions. Take samples (DK1, DK2, DK3) on the first, second and fourth days after dark treatment. The 5 plants were treated for each treatment, with 3 repetitions.
2.2. Identification and Physicochemical Properties Analysis of CsGLKs
The GLK protein sequences of Arabidopsis thaliana were downloaded from Plant TFDB V5.0 (http://planttfdb.gao-lab.org/index.php, accessed on 15 April 2022), and the hidden Markov model (HMM) was constructed by HMMER 3.0 (http://hmmer.org/, accessed on 17 April 2022) software. The GLK family protein sequences (http://citrus.hzau.edu.cn/index.php, version2, accessed on 17 April 2022) were searched by HMMER 3.0 software. The CD Search website [29] was used to examine the domains of all candidate GLK proteins in Citrus. Finally, the complete sequence of Myb DBD was retained and renamed CsGLK1~27.
2.3. Structural and Phylogenetic Analysis of CsGLKs
The conserved motifs of Citrus GLK family members were analyzed by MEME (https://meme-suite.org/, accessed on 16 April 2022). TBtools was used to extract and visualize gene structures. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by neighbor-joining (NJ) method with 1000 bootstrap replicates after aligning multiple protein sequences of Arabidopsis, rice and Citrus using ClustalW.
2.4. Chromosomal Locations, Duplication Events and Collinearity among CsGLKs
Information on the chromosomal position image of the CsGLK genes was obtained based on the gff3 file of Citrus Pan-genome to Breeding Database (http://citrus.hzau.edu.cn/index.php, accessed on 20 April 2022). Gene duplication of CsGLKs was detected using MC Scan X. TBtools software was used for the collinearity analysis.
2.5. Measurement of Chlorophyll Precursor
The contents of ALA, PBG, Mg-ProtoIX ME, Proto IX, Mg-Proto IX, Pchl and POR were measured by Elisa test kits (ZhenKe, Shanghai). The method to determine chlorophyll content referred to Moran and Porath [30]. The determination of chlorophyll a (Chl a) and chlorophyll b (Chl b) was performed the following method: add 5 mL of 95% ethanol (V:V) and 5 mL of 80% acetone solution to 0.5 g leaves, then extract in dark for 24 h, until the leaves turn white. The absorbance values of the extract at 665 nm and 649 nm are then measured in the dark.
Chl a = (12.7 × OD663 − 2.69 × OD645) × V/W
Chl b = (22.9 × OD645 − 4.68 × OD663) × V/W
T-Chl = (20.0 × OD645 + 8.02 × OD663) × V/W
2.6. Analysis of GLK Expression Pattern in Citrus
Based on the transcription data, the expression profiles of CsGLKs in different tissues (pericarp, pulp, leaf, root) were studied. The expression level was expressed as Log2 (FPKM + 1).
The expression patterns of GLK family members in different periods and under dark stress were analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR. Primer 3.0 was used to design specific primers. M5 HiPer Plant RNeasy Complex Mini Kit (Mei5bio, Beijing, China) was used to extract and purify RNA. After detecting RNA concentration and integrity, the 2X M5 HiPer SYBR Premium Estaq was used for fluorescence quantification. The primer sequences were listed in Table S1. The relative gene expression values were calculated by the 2−∆∆Ct method. In order to compare the expression amount between different periods and members synchronously, CsGLK7, with the lowest expression in D3, was used to normalize all members. The experiment included 3 biological replicates and technical replicates. TBtools was used for visualization.
2.7. Data Analysis
The significance analysis was performed using SPSS 20.0 software using one-way ANOVA or Tukey test (p < 0.05). The correlation analysis was conducted by Origin2021.
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Physicochemical Properties of CsGLKs
According to the predictions made by Plant TFDB database, 105 CsGLKs were preliminarily identified. Then, combining local blast with hmmer 3.0, 27 CsGLK TFs were finally obtained and divided into three groups (I to III), and their basic physicochemical properties were predicted and analyzed (Table 1, Table S2). Amino acid length (number of aa) of CsGLKs protein was 236 to 664, molecular weight (MolWt) ranged from 26941.09 to 73051.88, the isoelectric point (pI) range was 5.1–10.45, the range of instability coefficient (II) was 27.25 to 70.30 and the hydrophobicity index (GRAVY) ranged from −0.1057 to −0.579.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of CsGLKs.
3.2. Structural and Phylogenetic Analysis of CsGLKs
In order to investigate the evolutionary relationships of the GLK family, a NJ phylogenetic tree was constructed by the aligned amino acid sequences from C. sinensis, Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa. According to the phylogeny and motif analysis, the GLK family was divided into three groups. Group I was the largest group, containing 20 members. By contrast, Group II and III contained only three and four genes, respectively (Figure 1).
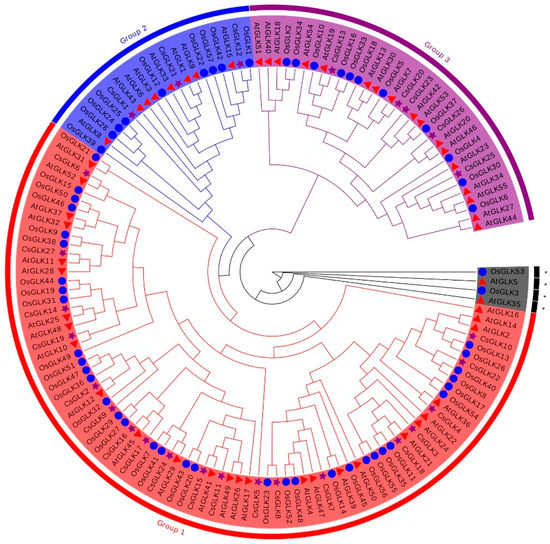
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of Citrus sinensis, Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa GLKs. Circles of different colors represented different subgroups. ☆ represented citrus, ○ represented maize and △ represented Arabidopsis. * referred to proteins that were not clustered. The tree was constructed from amino sequences using MEGA-X software by the neighbor-joining program with 1000 bootstrap replicates. Clades with different colors represent diverse subgroup.
The phylogenetic relationship was also proved by the motif analysis of 27 GLK genes in Citrus. The conserved motifs of 27 CsGLKs genes were analyzed. A total of 20 motifs (Figure 2B) were detected. The MEME website was used for motif alignment of two major domains (MEME-1) SHAQKYF (myb-like DNA-binding domain) and (MEME-2) Myb-CC-LHEQLE. It was found that the positions and types of amino acids in the two domains were conservative in all members (Figure 2E). The motif sequence was shown in Table S3. Through the CD search tool of NCBI, five motifs were functionally annotated and defined as Myb DNA-binding domain, Myb-CC-LHEQLE, Myb-CC-LHEQLE superfamily, Alfin and Response_reg. Myb DBD, which acts as a transcriptional activator to bind to the I-box located in the C-terminal DNA-binding domain in plants and yeasts [31,32], was highly conserved in CsGLKs and contains a SHAQKYF structure. In addition to two conserved binding domains, Group I and Group III contained exclusive motifs, which may represent the function diversity and specificity among members of each group. Group I had a Myb-CC-LHEQLE domain, which had a highly conserved LHEQLE sequence. The domain seems to respond to various abiotic stresses, such as phosphate starvation signals [6,33]. Group III contained the Response_Reg domain, a response-regulated receiving domain that receives signals from sensors in bacterial two-component systems [34].
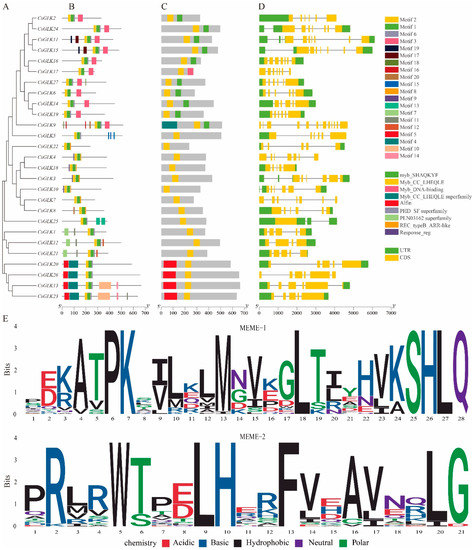
Figure 2.
(A) Protein phylogeny, (B) conserved motif, (C) conserved domain, (D) gene structure and (E) conserved domain sequence. The scale bar at the bottom was used to estimate the sizes of protein structure and gene structure.
In the analysis of gene structure, different intron regions were found in CsGLK genes (the number ranged from 3 to 12). Generally, CsGLKs clustered in the same group showed similar exon number and intron length, such as the members of Group II and Group III (Figure 2C). However, the members of Group I differ greatly in gene structure, with a maximum of 12 introns (CsGLK9) and a minimum of 2 (CsGLK25). The variation of introns might be one of the critical factors leading to the functional diversity during evolution.
In order to further determined the similarity between Citrus GLK domains, 27 CsGLKs domain sequences were compared with DNAMAN 8 (Figure 3). The results showed that Myb DBD in CsGLKs contained an HLH structure, and its two regions were particularly conserved. The initial sequence PELHRR of the first helix always contained 14 amino acids, and the second helix contained the initial NI/VASHLQ motif. In many transcriptional regulators, the HLH domain bound to DNA and mediated dimerization [35,36].

Figure 3.
Multiple sequence alignment of the CsGLKs conserved domain. The same sequence was shown in black shadow.
3.3. CsGLKs Chromosomal Location, Collinearity Analysis and Gene Replication
In total, 27 CsGLKs were distributed on each chromosome. The number of CsGLKs on chromosomes 4 and 7 were the largest, and there was only one GLK gene on chromosome 1 (Figure 4). The uneven distribution of CsGLKs was similar to that of maize [37].
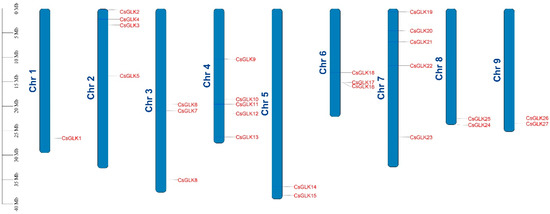
Figure 4.
Chromosomal distribution of GLK genes in Citrus. The scale represents 40 Mb chromosomal distance.
To further inferred the evolutionary mechanism of Citrus CsGLKs, the collinearity was constructed. There were 19 homologous genes between Citrus and Arabidopsis (Table S4) and 11 homologous genes between Citrus and rice (Table S5). 6 CsGLKs were collinear with both Arabidopsis and rice, indicating that these 6 CsGLKs may have existed before the differentiation of monocotyledons and dicotyledons, and the number of direct homologous pairs of CsGLK-OsGLK was less than that of CsGLK-AtGLK. These results showed that the differentiation between rice and dicotyledons occurred before the differentiation of Citrus and Arabidopsis.
CsGLKs replication events in Citrus genome were estimated by collinearity analysis. It was found that only one gene tandem replication event occurred in the evolution process, including two genes (CsGLK16 and CsGLK17), located in Chr6 (Figure 5A). The ka/ks value of the collinear pair was less than 1 (Table S6), indicating that CsGLKs underwent a purification selected evolution process.
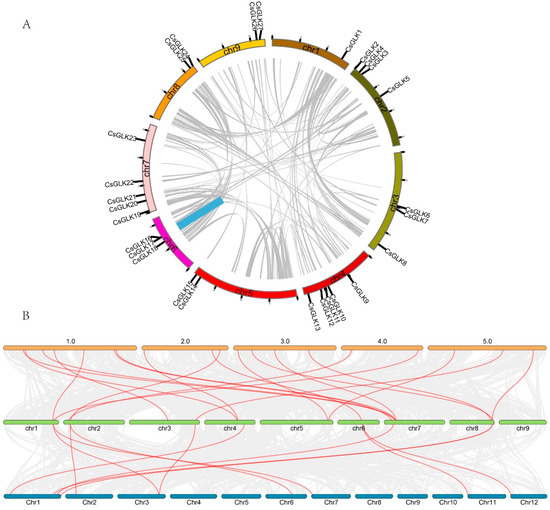
Figure 5.
Collinearity analysis of CsGLK. (A) GLK gene replication event. The grey line represented all autosomes in the Citrus genome, and the blue line represented CsGLK gene replication events. (B) The homologous gene pairs between sweet orange and Arabidopsis and sweet orange and rice. The yellow chromosome represented Arabidopsis, the blue chromosome represented rice and the green chromosome represented Citrus. Red lines indicated homologous gene pairs.
3.4. Analysis of GLK Expression Pattern
In order to detect the transcription of GLKs gene of Citrus, the transcriptome data were analyzed. The 27 CsGLKs expression profiles of four tissues were mapped into heat maps and clustered with similar expression patterns (Figure 6A). The GLK family is divided into three subfamilies (S1–S3) according to the expression pattern. S2 and S3 contained 8 and 7 genes, respectively. The expression of these 15 genes was higher than that of the other 12 genes, and most of them belong to the Group1 of GLK. The tissue expression of S1 subfamily was unbalanced, the expression of CsGLK17 was higher in peel, that of CsGLK18 in root is higher, CsGLK1 was highly expressed in pulp and CsGLK27 was highly expressed in leaves. 7 genes (CsGLK2, CsGLK8, CsGLK9, CsGLK11, CsGLK15, CsGLK20, CsGLK27) in leaves, 9 genes (CsGLK2, CsGLK8, CsGLK9, CsGLK11, CsGLK13, CsGLK15, CsGLK18, CsGLK20, CsGLK21) in root and 9 genes (CsGLK2, CsGLK6, CsGLK9, CsGLK11, CsGLK15, CsGLK16, CsGLK19, CsGLK20, CsGLK21) in pulp, 8 genes (CsGLK2, CsGLK6, CsGLK7, CsGLK9, CsGLK11, CsGLK15, CsGLK16, CsGLK25) presented high expression levels (Log2 (FPKM + 1) > 4). Among them, CsGLK2, CsGLK9, CsGLK11 and CsGLK15 were highly expressed in the four tissues. The members with high tissue specific expression were CsGLK7 and CsGLK25 (in peel), CsGLK6 and CsGLK19 (in pulp), CsGLK13 and CsGLK18 (in root) and CsGLK8 and CsGLK27 (in leaf).
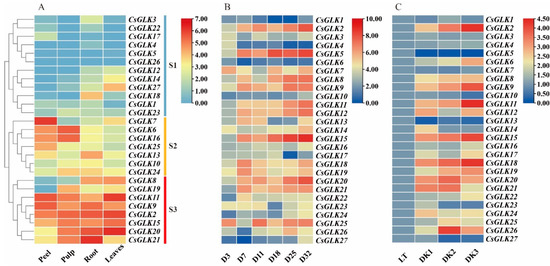
Figure 6.
(A) Expression of CsGLKs in different tissues. (B) Expression of CsGLKs in different growth stages. (C) Expression of CsGLKs under dark stress. Color gradient from red to blue indicates that expression values change from high to low.
The qRT-PCR results showed that many members of the GLK family showed high expression levels during the growth process (Figure 6B), such as CsGLK2, CsGLK5, CsGLK8, CsGLK9, CsGLK12, CsGLK15, CsGLK18, CsGLK20, etc. Conversely, there were some genes with low expression, such as CsGLK1, CsGLK4, CsGLK6, CsGLK10, CsGLK17, CsGLK24, CsGLK27, etc. The expression of CsGLK1, CsGLK3, CsGLK4, CsGLK7, CsGLK10, CsGLK13, CsGLK23 and CsGLK27 remained low throughout the growth period (Figure 6C). The expression of some members fluctuated in different growth periods, such as CsGLK8, CsGLK11, CsGLK12 and CsGLK25, which were lower in the early growth stage, and then increased in the late growth stage. In dark environment, the expressions of CsGLK2, CsGLK9, CsGLK11, CsGLK15, CsGLK18, CsGLK19 and CsGLK24 were significantly increased, indicating that these genes may be the positive regulators of dark stress (p < 0.05, Table S7). The expression levels of CsGLK5 and CsGLK13 were significantly decreased (p < 0.05, Table S7). Genes highly expressed during leaf growth and under dark stress included CsGLK2, CsGLK9, CsGLK15, CsGLK18 and CsGLK20. They may be the key members to optimize photosynthesis, promote chlorophyll synthesis and chloroplast development under abiotic stress.
3.5. Chlorophyll Precursor Content
During leaf growth, ALA, POR, Chl a, Chl b and T-Chl showed an overall upward trend; Mg ProtoIX ME, ChlM and UROD first increased and then decreased; Glu-tRNAs activity reached the maximum on the 11th day; and the changes in other periods were not significant (Figure 7). The expression of GLK members during the growth period also showed a fluctuation. To further study the relationship between chlorophyll precursors and GLK members, the correlation analysis was conducted.
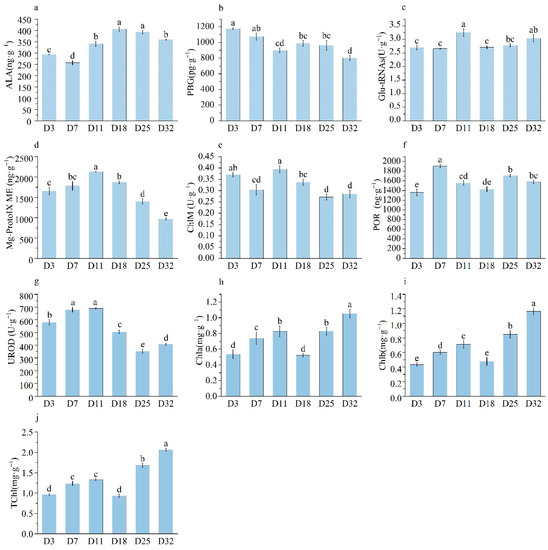
Figure 7.
Chlorophyll precursor and chlorophyll content of different sampling time.
3.6. Correlation Analysis
CsGLK5, CsGLK8, CsGLK9, CsGLK11, CsGLK15, CsGLK16, CsGLK18, CsGLK20, CsGLK25 and CsGLK26 were positively correlated with the contents of Proto IX, Mg Proto IX and Pchl (Figure 8). CsGLK2, CsGLK9, CsGLK10, CsGLK11, CsGLK20 and CsGLK24 were significantly positive correlations with Chl a and Chl b contents. CsGLK2, CsGLK5, CsGLK10, CsGLK11, CsGLK12, CsGLK15, CsGLK20 and CsGLK24 are positively significantly related to Mg-Proto IX, Proto IX and Pchl. By contrast, CsGLK1, CsGLK2, CsGLK10, CsGLK1, CsGLK12, CsGLK14, CsGLK16 and CsGLK20 had a negative correlation with ALA and PBG. All members had little significant correlation with the activities of ChlM and Glu-tRNAs (Table S8).
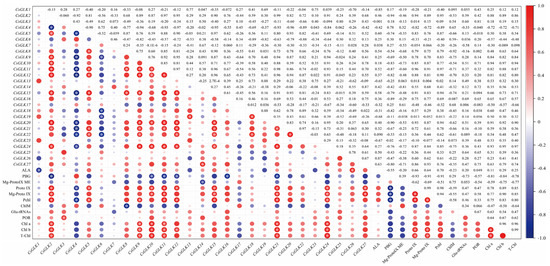
Figure 8.
Correlation analysis. Color and size changes represented the degree of correlation. The larger the circular area and the darker the color, the stronger the correlation, and vice versa. Red represented negative correlations and blue represents positive correlations. * in the circular area means significant correlation (p ≤ 0.05).
4. Discussion
The HLH region and GCT box in GLK TFs family were highly conserved [10]. Two conserved helix structures of HLH were identified in this study. Multiple sequence alignment showed that the second helix region (VK/VASHLQ) among CsGLK genes was highly conserved, while many variants of CsGLK genes were observed in the first helix, but L and H were relatively conserved. This indicated that the first helix might be the decisive factor for the functional differentiation and diversity of CsGLKs. Functional diversity caused by sequence variation also appeared in maize [37].
Polygenic families are usually derived from gene replication, and amplification mechanisms include fragment/tandem repeat, reverse transcription transposition and genome polyploidy [38,39]. In this study, we found that only one gene replication event (CsGLK16, CsGLK17) occurred in sweet orange, indicating that the main way of evolution of GLK family members may not be gene replication. Intron loss and insertion often occur, which may be of great significance to gene evolution. The number of introns in eukaryotes has been greatly reduced in the process of evolution, while the increasing frequency is low [40]. In addition, the analysis of rice fragment replication events show that loss of introns more than acquisition [41]. In this study, the distribution of introns in CsGLK gene had great variability, ranging from 2 to 12 (Table 1). Therefore, it was inferred that the variation of introns was the main structure of CsGLK gene evolution since its origin. The variation of gene structure was not only manifested in the number of introns, but also in the length of exons, which suggests that the changes of transcription length (extension or termination) affected the gene structure and acquisition or loss of domain, thereby changing the function of protein.
When gene replication occurs, each duplicated gene has two different possibilities: (1) a copy mostly keeps stable and maintains the original feature by negative selection or (2) the remaining copies are not selected and became pseudogenes [42]. The expression of CsGLK1, CsGLK4, CsGLK6, CsGLK10, CsGLK17 and CsGLK27 was very low or not expressed in all tissues and growth period, indicating they may be a pseudogene or a silent paralog. It seems that mutations in the regulatory regions, up/downstream and coding region (exon site) might affect the expression and function of the new members of GLK gene family under evolution events [43,44].
The GLK gene is essential for chloroplast development in plants [11]. However, the expression levels of CsGLK2, CsGLK20 and CsGLK21 were very high in roots. In the study of tissue-specific expression of maize GLK gene, it was found that ZmGLK2, ZmGLK9, ZmGLK28, ZmGLK35 and ZmGLK44 were also relatively high in roots [37]. These genes may be involved in stress response.
Research shows that GLK induced upregulation in three main steps: (1) the formation of diethylene protochlorophyllide, (2) the formation of chlorophyll a and (3) the formation of chlorophyll b [17]. In this study, CsGLK8, CsGLK11, CsGLK15 and CsGLK22 were significantly positive correlations with Chl a and Chl b contents. In addition, CsGLK2, CsGLK9 and CsGLK18 are also significantly related to ALA, Mg-ProtoIX ME, Mg-Proto IX and Proto IX. Meanwhile, these genes were also highly expressed at different stages and dark. They may adapt to different environments by increasing the content of the above precursors.
5. Conclusions
In general, 27 CsGLKs were identified in the sweet orange genome and divided into three groups according to gene structure, motif composition and phylogenetic analysis. Before the differentiation of monocotyledons and dicotyledons, the GLK transcription factor family already existed. The variation of introns suggested that it might be a main configuration for the evolution of CsGLKs. The CsGLKs were unevenly distributed across all nine chromosomes. There was only one pair of tandem duplicated CsGLK genes. The expression of GLK family members was variable, with different expressions at different growth stages and tissues, and could actively respond to dark stress. CsGLKs of the same group had a similar structure, but their expression patterns were quite different. They might have different functions but not be redundant. This means that the primary and secondary metabolic pathways during plant development are a very complex system. Therefore, the specific functions of CsGLKs need to be further verified, and it is great significance to reveal the homologous sequences in each branch.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae8111076/s1, Table S1: Primers of CsGLKs; Table S2: Motif sequences; Table S3: Physicochemical properties of CsGLK TFs in Citrus; Table S4: Collinear pair gene of At-Cs; Table S5: Collinear pair gene of Os-Cs; Table S6: Ka/Ks values of CsGLK collinearity pairs; Table S7: Expression of CsGLKs; Table S8: Correlation analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.W.; Data curation, Y.G., Q.L., L.L. (Ling Li), H.M., L.L. (Ling Liao), X.W., H.D. and M.Z.; Writing—original draft, B.X. and Y.G.; Visualization, B.X., Y.G., Q.L., L.L. (Ling Li) and H.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Key R & D Program of China (2021YFD1600802-02), and the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province, China (2021ZHCG0084).
Data Availability Statement
All the data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and Supplementary File.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- La Marca, M.; Beffy, P.; Pugliese, A.; Longo, V. Fermented Wheat Powder Induces the Antioxidant and Detoxifying System in Primary Rat Hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.; Martin, G.; Reuber, L.; Jiang, C.; Keddie, J.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Samaha, R.R.; et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; You, S.; Kong, W.; Tang, Q.; Bai, W.; Cai, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, C.; et al. A GARP transcription factor anther dehiscence defected 1 (OsADD1) regulates rice anther dehiscence. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 101, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumura, Y.; Moylan, E.C.; Langdale, J.A. A Conserved Transcription Factor Mediates Nuclear Control of Organelle Biogenesis in Anciently Diverged Land Plants. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1894–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Bioinformatics Analysis of Tomato G2 Like Transcription Factor Family and Identification of Stress Resistance Related Genes; Northeast Agricultural University: Harbin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, M.; Zhang, B.; Gu, G.; Yuan, J.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Xie, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of the G2-Like Transcription Factor Genes and Their Expression in Different Senescence Stages of Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Shuang, J.; Li, Z.; Xiao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wei, Y.; Hu, S.; Wan, S.; Peng, R. Identification of the Golden-2-like transcription factors gene family in Gossypium hirsutum. Peerj 2021, 9, e12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoda, K.; Imamura, A.; Katoh, E.; Hatta, T.; Tachiki, M.; Yamada, H.; Mizuno, T.; Yamazaki, T. Molecular structure of the GARP family of plant Myb-related DNA binding motifs of the Arabidopsis response regulators. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2015–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Garcia, A.; Yasumura, Y.; Langdale, J.A. Specialization of the Golden2-like regulatory pathway during land plant evolution. New Phytol. 2009, 183, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, L.; Cribb, L.; Martin, D.J.; Langdale, J.A. The maize golden2 gene defines a novel class of transcriptional regulators in plants. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1231–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitter, D.W.; Martin, D.J.; Copley, M.J.; Scotland, R.W.; Langdale, J.A. GLK gene pairs regulate chloroplast development in diverse plant species. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2002, 31, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, M.T.; Moylan, E.C.; Langdale, J.A. GLK transcription factors regulate chloroplast development in a cell-autonomous manner. Plant J. 2008, 56, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, A.L.T.; Nguyen, C.V.; Hill, T.; Cheng, K.L.; Figueroa-Balderas, R.; Aktas, H.; Ashrafi, H.; Pons, C.; Fernandez-Munoz, R.; Vicente, A.; et al. Uniform ripening Encodes a Golden 2-like Transcription Factor Regulating Tomato Fruit Chloroplast Development. Science 2012, 336, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, M.T.; Langdale, J.A. The making of a chloroplast. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 2861–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, D.; Ji, Q.; Jing, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, R. Transposase-Derived Proteins FHY3/FAR1 Interact with PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR1 to Regulate Chlorophyll Biosynthesis by Modulating HEMB1 during Deetiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1984–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, L.N.; Rossini, L.; Langdale, C. GOLDEN 2: A Novel Transcriptional Regulator of Cellular Differentiation in the Maize Leaf. Plant Cell Online 1998, 10, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, M.T.; Wang, P.; Korkaric, M.; Capper, R.G.; Saunders, N.J.; Langdale, J.A. GLK Transcription Factors Coordinate Expression of the Photosynthetic Apparatus in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1109–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Sasaki, D.; Noguchi, K.; Fujinuma, D.; Komatsu, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Sato, M.; Toyooka, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Niyogi, K.K.; et al. Photosynthesis of Root Chloroplasts Developed in Arabidopsis Lines Overexpressing GOLDEN2-LIKE Transcription Factors. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Guo, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, H. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of G2-Like Transcription Factor Genes in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Molecules 2022, 27, 5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, I.; Wu, X.; Yu, Q.; Ge, L. Comprehensive Genomic Analysis of G2-like Transcription Factor Genes and Their Role in Development and Abiotic Stresses in Arabidopsis. Diversity 2022, 14, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Wen, B.; Yang, C.; Xiao, W.; Fu, X.; Li, D.; Chen, X.; Gao, D.; et al. Transcriptomic and functional analyses reveal that PpGLK1 REGULATES CHLOROPLAST DEVELOPMENT IN PEACH (Prunus persica). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Bradley, G.; Pyke, K.; Ball, G.; Lu, C.; Fray, R.; Marshall, A.; Jayasuta, S.; Baxter, C.; van Wijk, R.; et al. Network Inference Analysis Identifies an APRR2-Like Gene Linked to Pigment Accumulation in Tomato and Pepper Fruits. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xiong, T.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, B.; Chen, H.; Kang, X.; Yang, J. Genome-wide characterization and analysis of Golden 2-Like transcription factors related to leaf chlorophyll synthesis in diploid and triploid Eucalyptus urophylla. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 952877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampomah Dwamena, C.; Thrimawithana, A.H.; Dejnoprat, S.; Lewis, D.; Espley, R.V.; Allan, A.C. A kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) R2R3-MYB transcription factor modulates chlorophyll and carotenoid accumulation. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-M.; Liu, W.-Y.; Shih, A.C.-C.; Shen, M.-N.; Lu, C.-H.; Lu, M.-Y.J.; Yang, H.-W.; Wang, T.-Y.; Chen, S.C.C.; Chen, S.M.; et al. Characterizing Regulatory and Functional Differentiation between Maize Mesophyll and Bundle Sheath Cells by Transcriptomic Analysis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ji, M.; Wen, B.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Gao, D.; Li, L. GOLDEN 2-LIKE Transcription Factors of Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.V.; Vrebalov, J.T.; Gapper, N.E.; Zheng, Y.; Zhong, S.; Fei, Z.; Giovannoni, J.J. Tomato GOLDEN2-LIKE Transcription Factors Reveal Molecular Gradients That Function during Fruit Development and Ripening. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadakuduti, S.S.; Holdsworth, W.L.; Klein, C.L.; Barry, C.S. KNOX genes influence a gradient of fruit chloroplast development through regulation of GOLDEN2-LIKE expression in tomato. Plant J. 2014, 78, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, W.; Xiang, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Gao, L.; Zhang, W. Genome-Wide Characterization of GRAS Family and Their Potential Roles in Cold Tolerance of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, R.; Porath, D. Chlorophyll determination in intact tissues using n,n-dimethylformamide. Plant Physiol. 1980, 65, 478–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.; Meier, I.; Wienand, U. The tomato I-box binding factor LeMYBI is a member of a novel class of myb-like proteins. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 1999, 20, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, J.-f.; Zhao, H.-y.; Sun, X.-y.; Wu, T.-r.; Pei, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.-f.; Yang, H.-h.; et al. Genome-wide identification of Tomato Golden 2-Like transcription factors and abiotic stress related members screening. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, V.; Linhares, F.; Solano, R.; Martín, A.C.; Iglesias, J.; Leyva, A.; Paz-Ares, J. A conserved MYB transcription factor involved in phosphate starvation signaling both in vascular plants and in unicellular algae. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2122–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pao, G.M.; Saier, M.H., Jr. Response regulators of bacterial signal transduction systems: Selective domain shuffling during evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, M.E.; Murre, C. Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins: Regulators of Transcription in Eucaryotic Organisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Gu, S.; Yu, J.; Liang, G.; Yan, C.; Xu, C. Genomewide comparative phylogenetic and molecular evolutionary analysis of tubby-like protein family in Arabidopsis, rice, and poplar. Genomics 2008, 92, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xu, Y.; Han, G.; Zhou, L.; Ali, A.; Zhu, S.; Li, X. Molecular Evolution and Genetic Variation of G2-Like Transcription Factor Genes in Maize. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Evolution by gene duplication: An update. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passardi, F.; Longet, D.; Penel, C.; Dunand, C. The class III peroxidase multigenic family in rice and its evolution in land plants. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1879–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogozin, I.B.; Carmel, L.; Csuros, M.; Koonin, E.V. Origin and evolution of spliceosomal introns. Biol. Direct 2012, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhu, W.; Silva, J.C.; Gu, X.; Buell, C.R. Intron gain and loss in segmentally duplicated genes in rice. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, V.E.; Pickett, F.B. Splitting pairs: The diverging fates of duplicated genes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, S.; Heidari, P.; Amouei, H.; Filiz, E.; Poczai, P. Investigation and Computational Analysis of the Sulfotransferase (SOT) Gene Family in Potato (Solanum tuberosum): Insights into Sulfur Adjustment for Proper Development and Stimuli Responses. Plants 2021, 10, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, P.; Abdullah; Faraji, S.; Poczai, P. Magnesium transporter Gene Family: Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization in Theobroma cacao, Corchorus capsularis, and Gossypium hirsutum of Family Malvaceae. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).