Abstract
This study evaluated the effective pollination period (EPP) in four European plum (Prunus domestica L.) cultivars (‘Mallard’, ‘Edda’, ‘Jubileum’, and ‘Reeves’) during two years (2018–2019) under the environmental conditions in western Norway. The pollination of plum cultivars was carried out one, three, five, seven, and nine days after anthesis (DAA) with a pollen mix of two compatible cultivars (‘Victoria’ and ‘Opal’). Initial, middle-season, and final fruit set was recorded after one month and two months after pollination and just before the harvest, respectively. On average from both years cultivar ‘Jubileum’ had the highest fruit set when pollinated one, three, five, seven, and nine DAA (33.23%, 30.83%, 8.47%, 3.08%, and 1.15%, respectively), which was more than two folds higher fruit set than in the other studied cultivars. Cultivar ‘Jubileum’ showed significantly reduced fruit set between pollination on five and nine DAA, while cultivars ‘Mallard’, ‘Edda’, and ‘Reeves’ had markedly reduced fruit set if pollinated three to five DAA, implying that the EPP in ‘Jubileum’ was five days while in the rest it was three days. Variation of weather conditions during the flowering period in both years did not have a major effect on the receptivity of stigmas in the studied plum cultivars, which means that the existing differences in the length of EPP is maternal-genotype dependent.
1. Introduction
There are two important species of plum in commercial horticulture, namely European plum and prunes (Prunus domestica L.) and the Asian or Japanese plums (Prunus salicina). Both belong to the Rosaceae family and have been cultivated for at least 2000–4000 years.
The European plum is a very important temperate zone fruit species, but can be grown both in a cooler climate and in sub-tropical conditions. The P. salicina plums are mostly grown in China and P. domestica in southern Europe. However, P. domestica is well adapted to cooler climate such as northern Europe. The world plum production is 2.7 million ha and, with 12.6 million t. China is the leading country (>7 million tons on >2.1 million ha) followed by Romania (>692,000 tons, >65,000 ha) and Serbia with >558,000 tons on >72,000 ha [1]. Regardless of the wide geographic distribution of plum cultivars over various climate zones in each area only specific cultivars can be grown [2]. Independent of countries, the plum production is mainly destined for fresh consumption, drying, preserves, and brandy making.
Commercial fruit production in Norway is located in the fjord districts of the southwestern part and around lakes at eastern part of the country at latitude around 60° north. This represents the world’s northern border of commercial fruit production. The climate, where the temperate fruits are grown, is closely linked with the Gulf Stream which flows from southern latitudes northeastward of the Norway coast. The warm sea and the atmosphere moderate the climate of Norway and northern Europe, making it more temperate. In such a climate, plum flowering is delayed with almost no risk for spring frost. Besides, cool climate influences the reduced pest and disease problems [3]. Plum production in Norway is low in an international perspective (covering 430 ha and giving <2500 t of fruits), but has been increasing in the last decade.
In plums, as in other Prunus species, flowers have one pistil made of only one carpel with two ovules. In order to have profitable production with marketable accepted plum fruits, pollination and fertilization of at least one of them are ultimate prerequisite since Prunus species are unable to bear fruit parthenocarpically [4]. According to Wertheim [5] in dependence of the plum cultivar, fruit set from 0–4% is considered as low, 5–9% as moderate, 10–24% as good and >25% as very good. Szabo and Nyeki [6] and Meland and Maas [7] have stated that fruit set from 5 to 15% is necessary to have high yields and fruits preferred by the fresh fruit market. But, when too many fruits are set, problems with branch breakage, low fruit size, and low quality can occur. Excessive fruit numbers often reduce the numbers and quality of flowers in the following season, which may lead to the establishment of a biennial pattern of cropping [7].
Reproductive biology plays an extremely important role in achieving high yields. However, evaluation of the reproductive potential of a certain genotype is hard to perceive since flower morphology and all processes within the flower is either genetic or environmental dependent (or under the influence of their interaction) [8]. Fruit yield is strongly determined by the fruit set, which is the result of a series of physiological events, such as overlapping of flowering period, pollen transfer, pollen germination, pollen–pistil interaction, pollen tube growth, synchrony between pollen tube arrival to the ovule and embryo sac maturation, ovule longevity and fertilization of an ovule, and successful early embryo development [9]. A poor fruit set in some plum cultivars may occur due to genetic predispositions which are mostly addressed to irregularities and/or early degenerations of some embryo sac’s cells [10]. To make things more difficult, pollination of plums is impaired by the full/partial auto-incompatibility [Gametophytic Self-Incompatibility system (GSI)] which prevents selfing and promotes outcrossing. Fruit set is also affected by factors as climatic conditions (prevailing temperature, wind, air humidity and rainfall at flowering), together with biennialism and some management factors such as crop loads, nutrients, irrigation, flower quality, beehives management, type of training systems, and leaf to fruit ratio [11,12,13]. Not only honeybees (Apis dorsata, A. mellifera, A cerana and A. florea) are important for plum pollination, but also representatives of Osmia sp., Xylocopa sp., Andrena sp., Megachile sp., Musca sp., Syrphus sp. and others contribute to fruit production [14]. Furthermore, the effects of climate change such as earlier flowering and more variable and extreme weather conditions are influencing the final fruit set.
Frequent apple and pear production problems led Williams [15] to introduce the term ‘effective pollination period’ (EPP) in fruit production and science, which was defined as the period when a flower keeps its capability to give a fruit. In other words, EPP is the difference between ovule longevity and the number of days which are needed for pollen tube to reach the egg cell and accomplish the fertilization. Practically, the longer the effective pollination period is, the higher is the chance for successful fertilization and fruit development. This period is conditioned by stigmatic receptivity, pollen tube kinetics and ovule longevity [16]. In ideal circumstances if a flower is pollinated just after opening (or within two to four days after flower opening) with compatible pollen grains, fertilization will occur. However, any kind of disruption, such as delay in stigma maturation, slow growing pollen tubes, and/or abnormalities during ovule development can limit EPP. The first method that was applied for assessing EPP was ‘indirect method’, which required the determination of stigmatic receptivity, pollen tube growth rate, and ovule longevity based of microscopic observations. Later the ‘direct method’ was used for the sequential pollination and the evaluation of the final fruit set [15].
The length of the EPP can vary due to the flower quality, flower position within the inflorescence, and also due to certain cultural practices such as chemical treatments [16]. In diploid cultivars, the egg apparatus is ‘mature’ and ready to be fertilized during flower opening, but in triploid cultivars the maturation is delayed until two to three days after anthesis, which results in extended ovule longevity and a longer EPP [17]. Besides, other abiotic factors, in most cases temperature, can speed up or slow down the span of EPP [16].
The profitability of plum growing is strongly affected by fruit set, and the pollination must happen in the right moment in order to have satisfactory yields. EPP has been proved to have great impact on post-fertilization fruit drop, and it plays a significant role in year-to-year cropping variability, which taken together influences yields. Thus, the aim of this study was to determine the effective pollination period in four plum cultivars grown in a Nordic climate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
The effective pollination period was determined in ‘Mallard’ (old English plum cultivar), ‘Edda’ (‘Czar’ × ‘Pêche’), ‘Jubileum’ (‘Giant’ × ‘Yakima’), and ‘Reeves’ (‘Prune Peche’ open pollinated, Canadian plum cultivar). Since all studied cultivars belong to the Prunus domestica L., they are all hexaploids (2n = 6x = 48) [18]. The study was conducted in an experimental plum orchard at the Njøs Fruit and Berry Centre, Leikanger (at latitude 61°10′43.2″ N, longitude 6°51′34.3″ E), at the Sognefjord, western Norway during two consecutive years (2018–2019).
The trees were planted in 2012 and all cultivars were grafted on the rootstock St. Julien A. The tree row orientation was South-North in a Southern slope; trees trained as slender spindle trees and limited 2.5 m height. Orchard floor management consisted of grass in the inter-rows and a 1-m wide vegetation- free strip in the intra-row spaces (wowed plastic). The trees were irrigated by drip irrigation when water deficits occurred.
2.2. Air Temperature and Precipitation
West Norway, especially the fjord areas have a cool, maritime, Nordic climate which is under the influence of the Gulf Stream. Summers are cool and winters are mild. Leikanger, where the experiment was conducted, is located in the county of Vestland, along the Sognefjord, West Norway. Average annual air temperature is 7.3 °C (during spring 4–11 °C), annual rainfall is 1063 mm (with May being driest with 15 rainy days) and an average annual humidity percentage of 78.0%. Average monthly hours of sunshine are the highest in May (~175 h) and the mean monthly wind speed over the year is 3 m/s. Unfavorable environmental conditions, especially cold temperatures, fog and rain can often occur during spring. For the purpose of this study daily temperatures (average, max and min) and precipitation (mm) were recorded during flowering period of plum cultivars (https://lmt.nibio.no/station/35/, accessed 20 December 2021) and presented on Figure 1 and Figure 2.
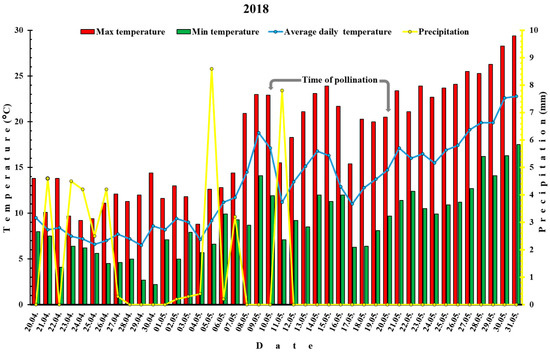
Figure 1.
Temperatures (min, max and average) and precipitation before and after pollination of plum cultivars in 2018.
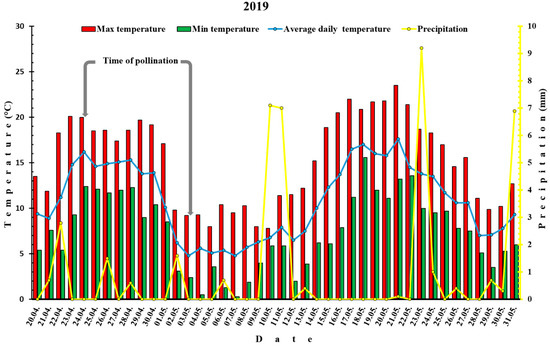
Figure 2.
Temperatures (min, max and average) and precipitation before and after pollination of plum cultivars in 2019.
2.3. Flowering, Pollen Collection and Pollen Germination In Vitro
Flowering stages for studied plum cultivars were recorded according to the BBCH scale [19]. The beginning of flowering (BBCH stage 61) was the date when 10% of flowers were open, full bloom (BBCH stage 65) was determined when 50% of flowers were open, while end of flowering was noticed when the majority of petals were fallen (BBCH stage 67). Determination of flowering in all plum cultivars studied herein was carried out on five trees per cultivar.
Pollen was gathered in two consecutive years (2018 and 2019). A mixture of the freshly gathered pollen of the two plum cultivars (‘Victoria’ and ‘Opal’), being fully compatible as proved by Meland et al. [20], were used as pollinizers in both years and for all four tested cultivars. Pollen sampling and in vitro pollen germination was carried out according to Fotirić Akšić et al. [21]. Pollen gathering was carried out from four trees per pollinizer by collecting flowers from all around the canopy.
2.4. Emasculation and Pollination
In order to determine effective pollination period, the pollination was carried out one, three, five, seven, and nine days after anthesis (DAA). Tents for isolation were placed over the trees in the ‘balloon’ phase (BBCH stage 59). Emasculation for studying effective pollination period were carried out in cultivars ‘Edda’, ‘Mallard’, ‘Reeves’, and ‘Jubileum’. Flowers in the balloon stage were emasculated by removing the whole perianth. About 20 flowers per 5 replicates were emasculated per each cultivar and per each term of pollination. Every branch was labeled with date of emasculation, replication and planned pollination day. The hand pollination of emasculated flowers was carried out first by dipping a finger into the mixture of two-plum-cultivars pollen and then by touching the exposed stigma two times. Pollination was considered successfully carried out when yellowness was observed on the stigma. At pollination, the number of pollinated flowers was counted, and the number of pollinated flowers was written on the labels. If an open, un-emasculated flower appeared, it was eliminated immediately. The tents were removed one week after the last pollination.
2.5. Fruit Set
The percentage of initial (IFS), middle-season (MFS), and final fruit set (FFS) was counted one month, two months after pollination and just before the harvest, respectively, in both years. Fruit set (IFS, MFS and FFS) was calculated as follows: IFS/MFS/FFS = (number of developing fruitlets/total number of flowers) × 100.
Harvesting time of cultivar ‘Edda’ was carried out on 27 July, for ‘Jubileum’ 12 August, for ‘Mallard’ 14 August and for ‘Reeves’ 16 August in 2018. In the next year (2019) cultivar ‘Edda’ was picked on 7 August, ‘Jubileum’ on 30 August, ‘Mallard’ on 19 August, and ‘Reeves’ on 16 August.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The data obtained for fruit set were statistically analyzed using Fisher’s model of two-factor analyses of variance (ANOVA). The significances of the individual differences for the investigated factors were determined using the least significant difference (LSD 0.05 = 95% confidence). Statistical analyses were conducted using STATISTICA for Windows 6.0 (StatSoft Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Meteorological Data
The weather conditions during the two-year experiment differed significantly. Average maximal and minimal temperatures in 2018 were 24.8 °C and 13 °C, respectively, while in 2019 it was 10.3 °C and 3.2 °C. The average vegetation temperature (from April to September) was 13.6 °C in 2018 in contrast to 12.9 °C in 2019. Much larger discrepancy between ecological factors between two years was noticed in the 10-days after flowering period. In this period in 2018, the mean average daily temperatures were 18.5 °C compared to 2019, where average daily temperatures were 6.5 °C (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
Regarding precipitation, in 2018 (Figure 1), only one spring shower occurred during pollination (7.8 mm/day) with no rain ten days afterwards. In 2019 (Figure 2), three short rainfalls took place during the pollination (1.5 mm/day; 0.6 mm/day and 1.6 mm/day) and three in a 10-days-after-pollination period (0.7 mm/day; 7.1 mm/day and 0.4 mm/day).
3.2. Flowering and In Vitro Pollen Germination
In 2018, all plum cultivars were flowering in May (Figure 3), while in 2019 it was two weeks earlier (in April). The sequence of the cultivar’s flowering was the same in both years. A period from full flowering (BBCH stage 65) till petal fall (BBCH stage 67) for all studied cultivars and both years lasted six to seven days [22].
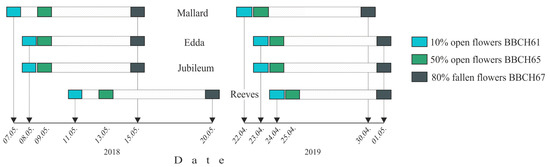
Figure 3.
Flowering periods of plum cultivars in 2018 and 2019.
In both years, cultivars ‘Victoria’ and ‘Opal’, whose pollen was mixed and used for testing effective pollination period of ‘Mallard’, ‘Jubileum’, ‘Edda’ and ‘Reeves’, flowered in the same interval. Pollen germination rates of cultivar ‘Victoria’ in both years were very high (91.2% in 2018, and 72.3% in 2019), while cultivar ‘Opal’ had a bit lower pollen germination rate in 2018 (22.4%), but a quite high in 2019 (54.1%) [22].
3.3. Fruit Set and Effective Pollination Period
The average fruit set in all four plum cultivars in this study was significantly higher in 2018 compared to 2019 when flowers were pollinated one, three, five, and nine DAA, while it was statistically lower in seven DAA (Table 1). The cultivar ‘Jubileum’ showed the highest fruit set in both experimental years in one, three, five, seven, and nine DAA (33.23%, 30.83%, 8.47%, 3.08%, and 1.15%, respectively). On one, three, five, and seven DAA, ‘Reeves’ had the lowest fruit set (16.72%, 11.88%, 4.0% and 0.5%, respectively). Cultivars ‘Reeves’ and ‘Mallard’ didn’t set any fruits when pollinated at nine DAA. All studied cultivars showed very low fruit set, from 0.5% (‘Reeves’) to 3.08%, (‘Jubileum’) when pollinated at seven DAA, and from 0% (‘Mallard’ and ‘Reeves’) to 0.15% (‘Jubileum’) when pollinated at nine DAA.

Table 1.
Average fruit set ± standard deviations of five replications in four plum cultivars for 2018 and 2019 in different treatments.
In the first year of the study, cultivars ‘Mallard’, ’Edda’, and ‘Reeves’ presented the maximum of IFS, MFS, and FFS on the one DAA (Figure 4). For the cultivar ‘Jubileum’ the maximum of IFS, MFS, and FFS was on the three DAA, and significantly higher from the results obtained for fruit set on the one DAA. In 2019, behavior of the plum cultivars ‘Mallard’ and ‘Reeves’ was similar. The situation with ‘Edda’ was a bit different, which maximum IFS and MFS were three DAA, while FFS was on the one DAA. Also, ‘Jubileum’ changed, and its IFS, MFS, and FFS was the highest on the 1 DAA.

Figure 4.
Initial (IFS), middle-season (MFS) and final fruit set (FFS) of four plum cultivars during 2018 and 2019 (different small letters in the same column denote a significant difference between the cultivars according to LSD test, p < 0.05).
The evaluation of the EPP in 2018 using sequential pollination showed that plum cultivars ‘Mallard’, ‘Edda’, and ‘Reeves’ achieved maximum FFS when pollinated in 1 DAA (10%, 8%, and 6.4%, respectively), and significantly lower but still satisfactory FFS (>5%) in 3 DAA (6.2%, 5.6%, and 5%, respectively). The cultivar ‘Jubileum’ had the highest FFS in three DAA (39.93%), while in one DAA (37.80%) and five DAA (11.6%), the results were significantly lower but still considerable valuable for a plum cultivar. In the second year, all studied cultivars had the highest FFS in one DAA, but satisfactory fruit set in three DAA, while only cultivar ‘Jubileum’ had ably fruit set >5% even in five DAA (5.33%). From all of this can be estimated that the EPP for ‘Mallard’, ‘Edda’, and ‘Reeves’ is three days, while in ‘Jubileum’, which gives acceptable yields in five DAA, is five days (Figure 5).
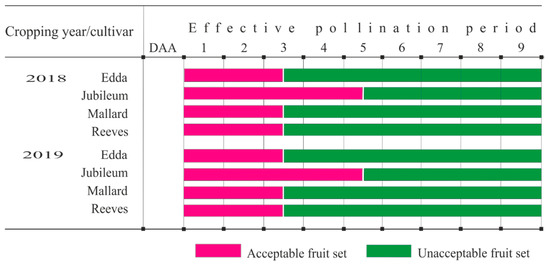
Figure 5.
The duration of the EPP in four studied plum cultivars during 2018–2019.
4. Discussion
4.1. Flowering
Awareness of flowering time of plum cultivars is fundamental for a proper choice of cultivar combination that provides successful pollination and fertilization for acceptable fruit set [11]. Thus, in case that plum cultivar(s) bloom too early with short flowering period, and without overlapping with other cultivars, those should be avoided due to the poor fruit set [23]. The length of the flowering period in plums is both genetically inherited and a result of the influence of the climatic conditions. Most European plum genotypes have simultaneous flowering periods, providing an adequate overlap for effective cross-pollination among them [24]. Corresponding to Koskela et al. [11], overlapping is considered too short if the difference between the dates of full bloom is six days or more. The duration of flowering in the studied plum cultivars was seven to nine days in 2018 and seven to eight days in 2019, which is in accordance to Szabo and Nyeki [6] who stated that the length of blooming in Prunus domestica is from six to eleven days. According to those authors, temperatures before flowering are not as important as those after anthesis, so there is negative correlation between the mean temperatures and the blooming period. The overlapping of flowering in the studied cultivars with pollen donors (‘Victoria’ and ‘Opal’) in the climatic conditions of western Norway has been already proved by Meland et al. [20] and Cerović et al. [22].
4.2. Effective Pollination Period
In fruit trees, the EPP varies a lot and depends on species and cultivars, nutritive state of the tree, crop load, chemical treatments and alternate bearing [12]. The duration of the EPP is influenced by many factors which include pollen tube growth, stigmatic receptivity and ovule longevity period. Low fruit set and EPP in some Prunus species has been related to unfavorable environmental conditions of the localities and seasons such as low and or high temperatures before and after flowering, winds, and drought [16,25,26,27]. The time required for pollen tubes to grow from stigma to the base of styles, and later enter to the micropila and carry out fertilization, decreases with increasing day/night temperature from 13/2 to 24/7 °C [28]. At excess temperatures, the number of pollen tubes that reach the base of the style can decline [29]. Also, manipulation with the flowers (mostly emasculation) can shorten EPP since damage the flowers can cause flower and/or fruitlet drops due to premature degeneration of ovules [30,31,32].
The duration of the EPP in fruits varies and can be from one day, as found in pear cultivar ‘Doyenné du Comice’ [15] up to 12 days in peach cultivar ‘Earlihale’ [32] and some olive cultivars [33]. EPP has been studied in many temperate and subtropical fruit species, such as apple [30,34], pear [35], japanese quince [36], peach [37], apricot [38], sweet cherry [39], sour cherry [21], almond [40], olive [41], red currant [42], rabbiteye blueberry [43], kiwi [13,44], mango [45], avocado [46], and some citruses [47].
The EPP in ‘Mallard’, ‘Edda’, and ‘Reeves’ lasted for three days, whereas, in ‘Jubileum’ was longer and lasted five days. No matter that the environmental conditions during sequential pollination of plum cultivars were different, the life span of egg cells in the studied four plum cultivars were constant and maternal-genotype dependent. Similar findings were found by Guerra et al. [48] for some Japanese plum cultivars, which had a stable response to factors that caused ovule degeneration. Our results coincide with Keulemans and van Laer [49] who proved that EPP in plum cultivars ‘Monsieur Hatif’ and ‘Bleue de Belgique’, with thresholds of 10% fruit set, was six and three days, respectively.
4.3. Fruit Set
Fruit set depends on many factors (climate, source of pollinators, pollination, pollen tube growth, ovule longevity, compatibility between the cultivars, overlapping of the flowering periods, and others) but pollen germination is one of the main prerequisites to have high yields [50]. Since fruit trees of the Rosaceae depend on cross-pollination and, therefore, commercial orchards need to contain at least two cross-compatible cultivars with synchronous flowering, we picked two compatible cultivars as pollinizers [51]. Both cultivars that were used as-pollinizers showed satisfactory pollen germination which is consistent with the values obtained for the pollen germination in vitro for numerous plum cultivars that ranged from 12.96 to 71.6% [52,53,54].
Kron and Husband [55] reported that an increased number of pollen donors might promote seed set and reduce seed abortion. Since most research studies evaluated a single pollen donor at a time, a pollen mixture of two compatible cultivars was applied for EPP determination in this study. Besides that, a long time ago Keulemans and Van Lear [49] claimed that cultivars ‘Opal’ and ‘Victoria’ show good pollen germination and fast growth of pollen tubes (even at low temperatures).
For the family Rosaceae, Janssen et al. (2008) [56] and Bonghi et al. (2011) [57] proved that reproductive biology (flower buds’ production and decline, flowering time, synchrony between pollen tube arrival to the ovule and embryo sac maturation, syngamy, and successful early embryo development) and fruit set are determined by genes however, external environmental factors play important role too. In numerous fruit species and/or cultivars, stigma is receptive during anthesis. Unfortunately, however, the life span of the receptivity differs between species, and if it is too short it can jeopardize the fruit set [47]. Besides, abiotic factors (temperature, rainfall, wind, and drought) and nutritive stage of the flower can influence fruit set too [22,58].
In both years of the experiment values of IFS were much higher than the values of MFS and FFS (Figure 4), which implies that the physiological fruit drop happened before counting MFS. In 2018 this happened before 10 July and in 2019 before 25th June. In all studied plum cultivars, FFS was ~five-folds lower than IFS. This is expected since FFS is affected by the management factors such as crop loads, nutrients, irrigation, type of training system, and many more. Similar results were obtained by Đorđević et al. [24] for ‘Pozna Plava’, ‘Čačanska najbolja’ and ‘Presenta’, where FFS compared to IFS was two- to five-folds lower.
Comparing the average of IFS in both years, it can be concluded that the cultivar ‘Jubileum’ had the highest fruit set both in all terms of pollination, and averagely for all treatments (2.2 fold higher than ‘Edda’, 1.8 folds higher than ‘Mallard’ and ~2.75 folds higher than ‘Reeves’). High fruitfulness of this cultivar that is widely grown in Norway was already proved by Meland and Birken [59], who claimed that it initiates too many flowers and set too many fruits. The highest fruit set was determined on one DAA (‘Edda’, ‘Mallard’ and ‘Reeves’) and three DAA (‘Jubileum’) with a progressive decrease thereafter. It is very important that the stigmas are receptive at or shortly after flower opening since the first flowers are inclined to give fruits of the best size and quality [11].
By calculating just FFS, averagely for both years, cultivar ‘Jubileum’ gave the highest values of fruit set in all treatments, 13.3% fruit set when pollinated in one DAA, 11.6% in three DAA, 7.25% in five DAA, 1.2% in seven DAA and 0.7% in nine DAA. This goes in the line with the findings of Sanzol and Herrero [16] who found that in some fruit species/cultivars, good correlations have been found between the percentages of fruit set following delayed pollination and ovule development, pollen tube growth, and stigma receptivity. The rest of the studied cultivars had a maximum fruit set of one DAA. The very low fruit set in seven DAA (0.5 to 3.08%) and in nine DAA (0 to 0.15%) implies that either the egg cell was not receptive or the style and transmitting tissue inside was not able to support pollen tube growth.
The discrepancy in the fruit set between the cultivars, besides stemming from a genetic component, could be due to the temperature differences during the blooming time and in the period after pollination. In 2018, ‘Mallard’ bloomed four days before ‘Reeves’ and, in 2019, it bloomed two days earlier. In both gap-periods, temperature maximums were over 20 °C. Generally, high temperatures can alter the soluble carbohydrate content in the pistil, which decreases the pollen tube growth along the style or ovule fertility and reduces in fruit set [60]. In post pollination periods in 2018, temperatures were over 20 °C, while in 2019 the daily maximum did not reach 10 °C. According to Weinbaum [61] temperatures below 10 °C can cause a loosening of the contact between the pollen grain and tube membrane.
4.4. Correlation between Effective Pollination Period and Fruit Set
To evaluate the correlation between fruit set and EPP, the pattern of average fruit set on sequential pollination was plotted against the pattern of EPP. EPP was positively and significantly correlated with each pollination time but the highest coefficient of correlation was between EPP and one DAA (r = 0.83, p = 0.011). This correlation also decreased with the delay in pollination time. These results indicated that the length of EPP depend the most on fruit set immediately after flower opening (with ‘Jubileum’ as an exception where delayed pollination gave acceptable results too). The reason of such a short EPP in ‘Mallard’, ‘Edda’, and ‘Reeves’ could be due to the degeneration and low viability of the reproductive organs. A tendency towards early ovule degeneration, both in pre-fertilized and post-fertilized stages, may negatively affect fertilization and fruit set. A short life span of plum ovules has been already reported in plums [17]. Egea and Burgos [62] and Kodad and Socias i Company [63] defined a term ‘style receptivity period’ or ‘style suitability period’ which can also limit EPP. In case of delayed pollination, maybe egg cells in the studied plum cultivars were still viable but stigma senescence prevented pollen germination and fertilization of the ovule. Short EPP that was provoked by early stigma degradation was previously determined in sweet cherry [64], apricot [65], pear [35], and almond [63].
Unfavorable weather conditions at blooming time are known to have a detrimental effect on fruit set by reducing the germination of pollen on the stigma and its growth down the style into the ovary and minimize insect activity. Prolonged EPP of the ‘Jubileum’ is extremely important for the west Norwegian and/or similar climatic condition, especially in the changing weather during springs (with often showers, north winds, high humidity, and low temperatures), when fertilization and fruit set can be endangered. Under this kind of weather five-days-long EPP of ‘Jubileum’ can give an opportunity to this cultivar to ‘wait for better days’ and set acceptable fruit set and secure satisfactory yield.
5. Conclusions
Stigma receptivity in studied plum cultivars was adequate during anthesis, and plum flowers were able to produce optimum fruit set when pollinated at the beginning of flowering. As the flowers were aging, the fruit set was markedly reduced, especially from three to five DAA, in ‘Mallard’, ‘Edda’, and ‘Reeves’ and from five to seven DAA, in ‘Jubileum’, so it can be concluded that EPP in these cultivars was three and five days, respectively. Since this study was conducted in the west of Norway, the results can be used for different locations with similar climatic conditions.
These finding have practical implications in plum production. It is relevant to know until which day the pollination has to be carried out in certain cultivars in order to secure satisfactory yields. Regarding future breeding work, only cultivars (in this case ‘Jubileum’) that show long EPP should be used as parents for creating new plum cultivars to obtain genotype which will have high ovule longevity and/or stigma receptivity. Only this kind of genotypes can ensure regular and high yields (especially in the changing environmental climate such as west Norway).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.F.A., R.C. and M.M.; methodology, M.F.A., R.C. and M.M.; formal analysis, M.F.A., R.C. and S.H.H.; investigation, M.F.A., R.C., S.H.H. and M.M.; data curation, M.F.A. and R.C.; writing—original draft preparation, M.F.A. and R.C.; writing—review and editing, M.F.A., R.C., S.H.H. and M.M.; supervision, M.M.; project administration, M.M.; funding acquisition M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by The Research Council of Norway (project No. 269227).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are presented in this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Kurab Røen, Njøs Fruit and Berry Centre, Leikanger, Norway for technical support during the field trials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- FAOStat. 2019. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- Sharma, D.D.; Kumar, M.; Singh, N.; Shylla, B. Plant growth and fruiting behavior of newly introduced plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.) cultivars under mid-hills conditions of Himachal Pradesh. Pharm. Innov. J. 2018, 7, 408–413. [Google Scholar]
- Redalen, G. Plum growing in Norway at 60° N. Acta Hortic. 2002, 577, 385–389. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, W.; Neümuller, M. Plum breeding. In Breeding Plantation Tree Crops: Temperate Species; Jain, S.M., Priyadarshan, P.M., Eds.; Springer Science: Stuttgart, Germany, 2009; pp. 161–231. [Google Scholar]
- Wertheim, S.J. Chemical thinning of deciduous fruit trees. Acta Hortic. 1998, 463, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, Z.; Nyéki, J. Floral biology and fertility in peaches (Review article). Int. J. Hortic. Sci. 2000, 6, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meland, M.; Maas, F.M. Regulation of fruiting in plum production. In Proceedings of the 6th Conference „Innovation in Fruit Growing”, Belgrade, Serbia, 2 February 2017; Faculty of Agriculture: Belgrade, Serbia, 2017; pp. 51–67. [Google Scholar]
- Fotirić Akšić, M.; Rakonjac, V.; Nikolić, D.; Zec, G. Reproductive biology traits affecting productivity of sour cherry. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2013, 48, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Herrero, M. Male and female synchrony and the regulation of mating in flowering plants. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 358, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ðorđević, M.; Cerović, R.; Radičević, S.; Nikolić, D.; Milošević, N.; Glišić, I.; Marić, S.; Lukić, M. Pollen Tube Growth and Embryo Sac Development in ‘Pozna Plava’ Plum Cultivar Related to Fruit Set. Erwerbs-Obstbau 2019, 61, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskela, E.; Kemp, H.; van Dieren, M.C.A. Flowering and Pollination Studies with European Plum (Prunus domestica L.) Cultivars. Acta Hortic. 2010, 874, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotirić Akšić, M.; Rakonjac, V.; Nikolić, D.; Čolić, S.; Milatović, D.; Ličina, V.; Rahović, D. Effective pollination period in ‘Oblačinska’ sour cherry clones. Genetika 2014, 46, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheshlaghi, E.A. Effective pollination period and its influence on fruit characteristics of Hayward’ kiwifruit. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2019, 33, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- Abrol, D.P.; Sharma, D.; Monobrullah, M. Abundance and diversity of pollinating insects visiting peach and plum flowers and their impact on fruit production. J. Res. SKUAST J. 2005, 4, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.R. Pollination studies in fruit trees. II. The effective pollination period for some apple and pear varieties. Rep. Long Ashton Res. Stn. 1965, 1966, 136–138. [Google Scholar]
- Sanzol, J.; Herrero, M. The effective pollination period in fruit trees. Scientia Hortic. 2001, 90, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerović, R.; Ružić, Đ.; Mićić, N. Viability of plum ovules at different temperatures. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2000, 137, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhebentyayeva, T.; Shankar, V.; Scorza, R.; Callahan, A.; Ravelonandro, M.; Castro, S.; DeJong, T.; Saski, C.A.; Dardick, C. Genetic characterization of worldwide Prunus domestica (plum) germplasm using sequence-based genotyping. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, U. Growth Stages of Mono- and Dicotyledonous Plants: BBCH Monograph, 2nd ed.; Federal Biological Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry: Berlin, Germany; Brunswick, Germany, 2001; pp. 1–158. [Google Scholar]
- Meland, M.; Frøynes, O.; Fotiric Akšić, M.; Pojskić, N.; Kalamujić Stroil, B.; Lašić, L.; Gaši, F. Identifying Pollen Donors and Success Rate of Individual Pollinizers in European Plum (Prunus domestica L.) Using Microsatellite Markers. Agronomy 2020, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotirić Akšić, M.; Cerović, R.; Rakonjac, V.; Bakić, I.; Čolić, S.; Meland, M. Vitality and in vitro pollen germination in ‘Oblačinska’ sour cherry clones. Genetika 2017, 49, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerović, R.; Fotirić Akšić, M.; Đorđević, M.; Meland, M. The effects of pollinizers on pollen tube growth and fruit set of European plum (Prunus domestica L.) in a Nordic climate. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 288, 110390. [Google Scholar]
- Ohata, K.; Togano, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Uchida, Y.; Kurahashi, T.; Itamura, H. Selection of Prune (Prunus domestica L.) Cultivars Suitable for the East Asian Temperate Monsoon Climate: Ripening Characteristics and Fruit Qualities of Certain Prunes in a Warm Southwest Region of Japan. Hortic. J. 2017, 86, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đorđević, M.; Radičević, S.; Cerović, R.; Milošević, N.; Mitrović, M. Initial and final fruit set in plum cultivar ‘Pozna Plava’ as affected by different types of pollination. Acta Hortic. 2012, 968, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, J.; Herrero, M. The onset of fruiting in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). J. Appl. Bot. 2002, 76, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hedhly, A.; Hormaza, J.I.; Herrero, H. Warm temperatures at bloom reduce fruit set in sweet cherry. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2007, 81, 158–164. [Google Scholar]
- Hedhly, A.; Hormaza, J.I.; Herrero, M. Flower emasculation accelerates ovule degeneration and reduces fruit set in sweet cherry. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 119, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, K.; Yuan, R.C.; Combs, L.; Byers, R.; Mcferson, J.; Schmidt, T. Effects of temperature and the combination of liquid lime sulfur and fish oil on pollen germination, pollen tube growth, and fruit set in apples. Hortic. Sci. 2009, 44, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irenaeus, T.K.S.; Mitra, S.K. Understanding the pollen and ovule characters and fruit set of fruit crops in relation to temperature and genotype—A review. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual 2014, 87, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Prieto, V.M.; Rascón-Chu, A.; Romo-Chacón, A.; Berlanga-Reyes, D.I.; Orozco-Avitia, J.A.; Gardea-Béjar, A.A.; Parra-Quezada, R.; Sánchez-Chávez, E. Effective pollination period in ‘Red Chief’ and ‘Golden Delicious’ apples (Malus domestica Borkh). Span. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 7, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.E.; Wünsch, A.; López-Corrales, M.; Rodrigo, J. Flower emasculation as the cause for lack of fruit set in Japanese plum crosses. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 135, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, T.K. The pollen receptivity period and its relation to fruit setting in the stone fruits. Fruit Var. J. 1980, 34, 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, J.; Pinillos, V.; Polito, V.S. Effective pollination period for ‘Manzanillo’ and ‘Picual’ olive trees. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, S.; Serra, S.; Musacchi, S. Effective Pollination Period and Parentage Effect on Pollen Tube Growth in Apple. Plants 2021, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanzol, J.; Rallo, P.; Herrero, M. Asynchronous development of stigmatic receptivity in the pear (Pyrus communis; Rosaceae) flower. Am. J. Bot. 2003, 90, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmane, E.; Rumpunen, K. Pollination, pollen tube growth and fertilization in Chaenomeles japonica (Japanese quince). Sci. Hortic. 2002, 94, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, S.F.; Hajilou, J.; Nahandi, F.Z. Pollen germination and pistil performance in several Iranian peach cultivars. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 1, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Nejatian, M.; Arzani, K. Determination of self-incompatibility and effective pollination period in four local Iranian apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) cultivars. Iran. Int. J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2004, 5, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Hedhly, A.; Hormaza, J.I.; Herrero, M. The effect of temperature on stigmatic receptivity in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodad, O.; Oukabli, A.; Mamouni, A.; Lahlou, M.; Socias i Company, R. Flowering and pollination time affect fruit set of foreign almond cultivars in Morocco. Acta Hortic. 2011, 912, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selak, G.V.; Cuevas, J.; Ban, S.G.; Pinillos, V.; Dumicic, G.; Perica, S. The effect of temperature on the duration of the effective pollination period in ‘Oblica’ olive (Olea europaea) cultivar. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2014, 164, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromp, J.; Visser, K.A.; Dijkstra, J. Fruit set and the effective pollination period in red currant as affected by nitrogen fertilization and exposure to red light. J. Hortic. Sci. 1994, 69, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevis, P.A.; Nesmith, D.S.; Wetzstein, H.Y. Flower age affects fruit set and stigmatic receptivity in rabbiteye blueberry. Hortic. Sci. 2006, 41, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferradás, Y.; López, M.; Rey, M.; Victoria González, M. Programmed cell death in kiwifruit stigmatic arms and its relationship to the effective pollination period and the progamic phase. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dag, A.; Eisenstein, D.; Gazit, S. Effect of temperature regime on pollen and the effective pollination of ‘Kent’ mango in Israel. Sci. Hortic. 2000, 86, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, M.L.; Hormaza, J.I. Avocado Pollination and Fruit Set—A Perspective from Spain. Calif. Avocado Soc. Yearb. 2009, 92, 113–135. [Google Scholar]
- Mesejo, C.; Martínez-Fuentes, A.; Reig, C.; Agustí, M. The effective pollination period in ‘Clemenules’ mandarin, ‘Owari’ Satsuma mandarin and ‘Valencia’ sweet orange. Plant Sci. 2007, 173, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, M.E.; Wünsch, A.; López-Corrales, M.; Rodrigo, J. Lack of Fruit Set Caused by Ovule Degeneration in Japanese Plum. J. Amer. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2011, 136, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keulemans, J.; Van Laer, H. Effective pollination period of plums: The influence of temperature on pollen germination and pollen tube growth. In Manipulation of Fruiting; Wright, C.J., Ed.; Butterworths: London, UK, 1989; pp. 159–171. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolić, D.T.; Rakonjac, V.S.; Fotirić-Akšić, M. The effect of pollenizer on the fruit set of plum cultivar Čačanska najbolja. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 57, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldway, M.; Stern, R.; Zisovich, A.; Raz, A.; Sapir, G.; Schnieder, D.; Nyska, R. The self-incompatibility fertilization system in Rosaceae: Agricultural and genetic aspects. Acta Hortic. 2012, 967, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, Y. In vitro pollen germination in stone fruit tree of Rosaceae family. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 6021–6026. [Google Scholar]
- Đorđević, M.; Cerović, R.; Radičević, S.; Nikolić, D.; Marić, S.; Milosević, N.; Glišić, I.S. Influence of pollination mode on fruit set in plum (Prunus domestica). Acta Hortic. 2016, 1139, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glišić, I.; Cerović, R.; Milošević, N.; Đorđević, M.; Radičević, S. Initial and final fruit set in some plum (Prunus domestica L.) hybrids under different pollination types. Genetika 2012, 44, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kron, P.; Husband, B.C. The effects of pollen diversity on plant reproduction: Insights from apple. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2006, 19, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, B.J.; Thodey, K.; Schaffer, R.J.; Alba, R.; Balakrishnan, L.; Bishop, R.; Bowen, J.H.; Crowhurst, R.N.; Gleave, A.P.; Ledger, S.; et al. Global gene expression analysis of apple fruit development from the floral bud to ripe fruit. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonghi, C.; Trainotti, L.; Botton, A.; Tadiello, A.; Rasori, A.; Ziliotto, F.; Zaffalon, V.; Casadoro, G.; Ramina, A. A microarray approach to identify genes involved in seed-pericarp cross-talk and development in peach. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyomora, A.M.S.; Brown, P.H.; Pinney, K.; Polito, V.S. Foliar application of boron to almond trees affects pollen quality. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2000, 125, 265270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meland, M.; Birken, E. Ethephon as a Blossom and Fruitlet Thinner Affects Crop Load, Fruit Weight and Fruit Quality of the European Plum Cultivar ‘Jubileum’. Acta Hortic. 2010, 884, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, J.L.; Oosterhuis, D.M.; Loka, D.A.; Kawakami, E.M. High temperature limits in vivo pollen tube growth rates by altering diurnal carbohydrate balance in field-grown Gossypium hirsutum pistils. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbaum, S.A.; Parfitt, D.E.; Polito, V.S. Differential cold sensitivity of pollen grain germination in two Prunus species. Euphytica 1984, 33, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea, J.; Burgos, L. Effective pollination period as related to stigma receptivity in apricot. Sci. Hortic. 1992, 52, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kodad, O.; Socias i Company, R. Effect of pollination time on fruit set in an autogamous almond cultivar. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Prieto, V.M.; Vasilakakis, M.D.; Lombard, P.B. Factors controlling fruit-set of Napoleon sweet cherry in Western Oregon. HortScience 1985, 20, 913. [Google Scholar]
- Burgos, L.; Egea, J.; Dicenta, F. Effective pollination period in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) varieties. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1991, 119, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).