Documentation of Commonly Used Ethnoveterinary Medicines from Wild Plants of the High Mountains in Shimla District, Himachal Pradesh, India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
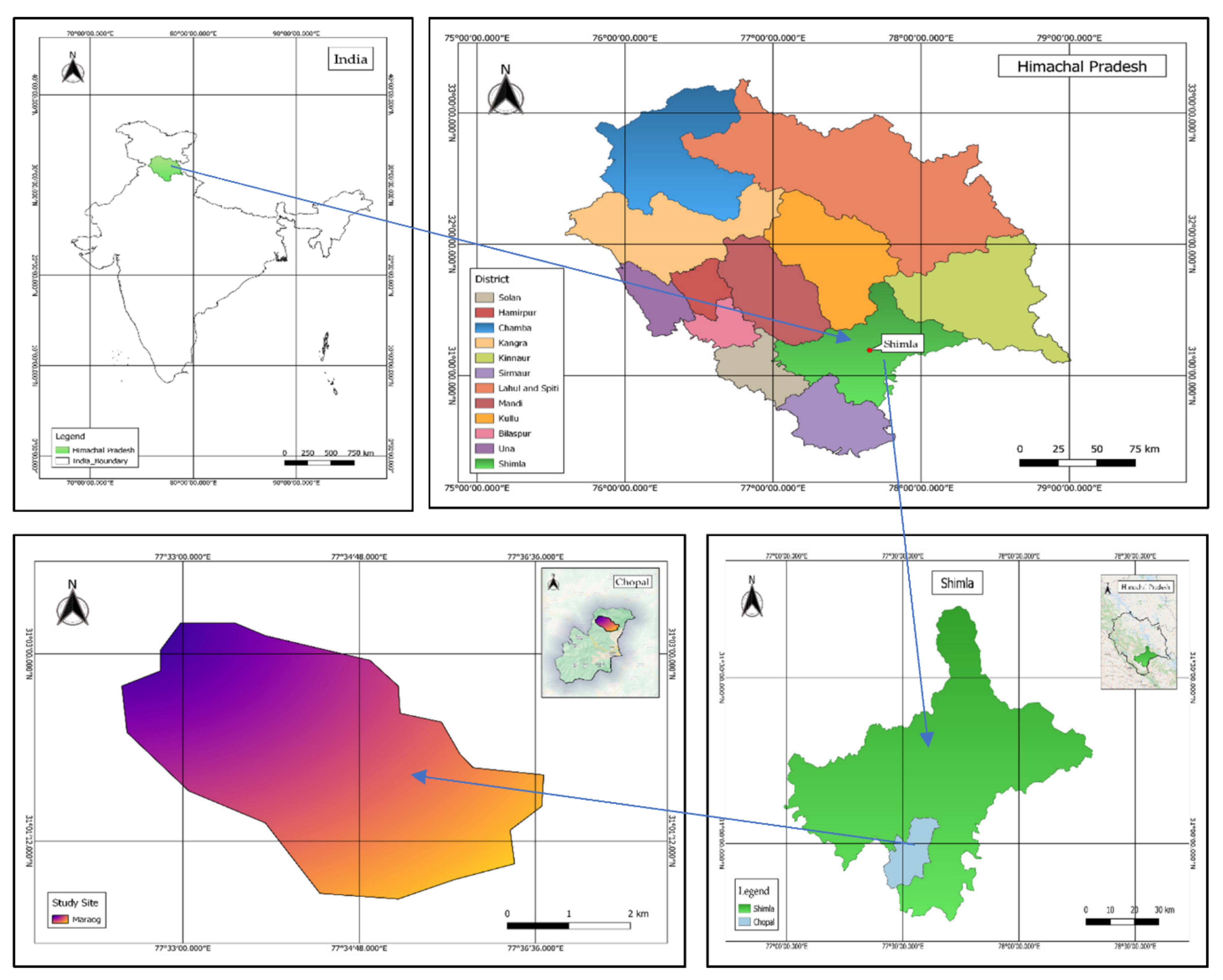
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Sampling Informants
2.3. Ethnoveterinary Data Collection and Ethical Considerations
Questionnaire for Conducting the Ethnoveterinary Study
2.4. Data Analysis
Use Value
3. Results
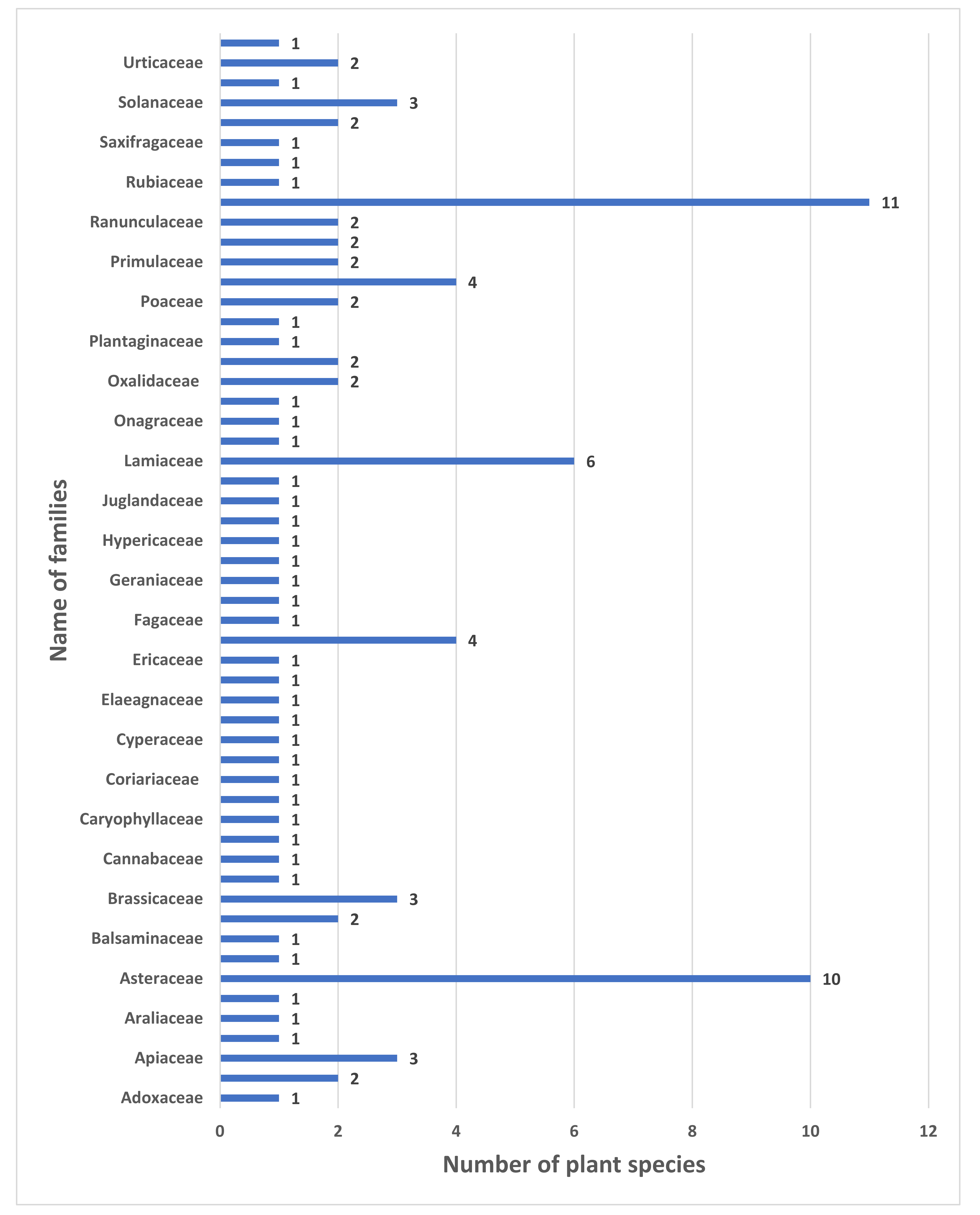
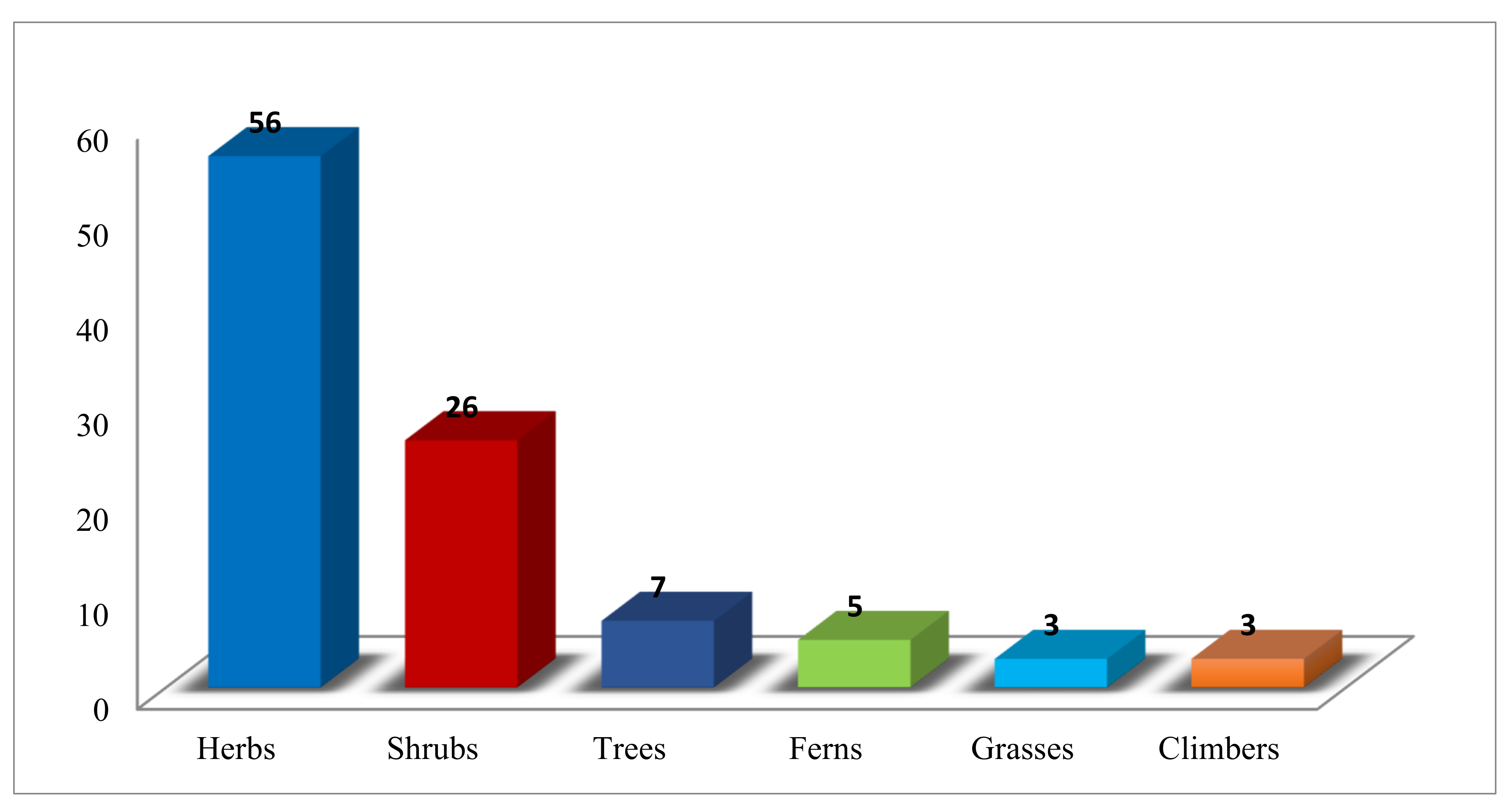
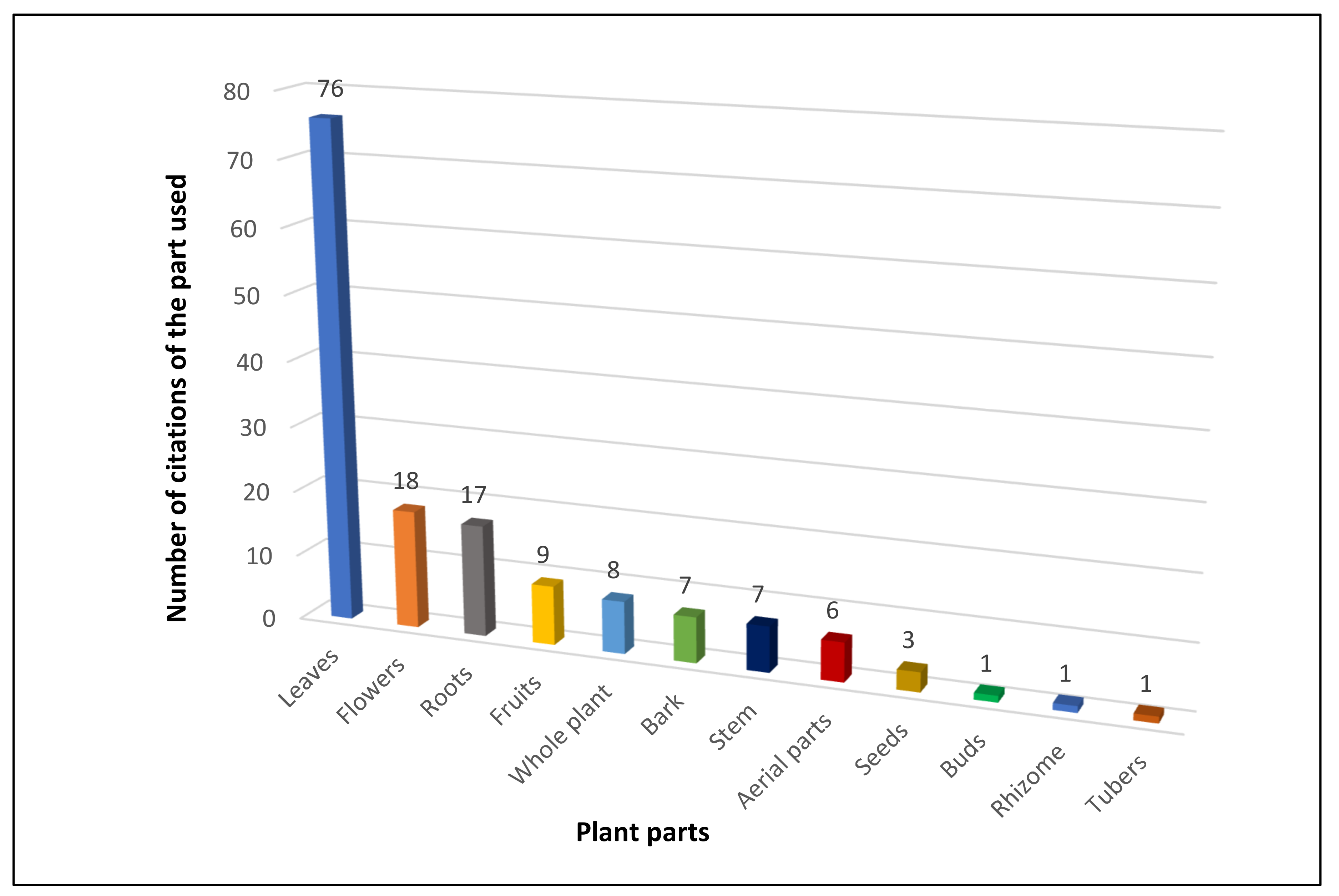
3.1. Ethnoveterinary Plants Reported by the Informants
3.2. Use Value of Medicinal Plants
4. Discussion
4.1. Ethnoveterinary Prospective of Wild Plants
4.2. Prospects of Using Wild Plant Species in Horticulture
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barboza, R.R.; De MS Souto, W.; Da S Mourão, J. The use of zootherapeutics in folk veterinary medicine in the district of Cubati, Paraíba State, Brazil. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2007, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGaw, L.J.; Famuyide, I.M.; Khunoana, E.T.; Aremu, A.O. Ethnoveterinary botanical medicine in South Africa: A review of research from the last decade (2009 to 2019). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 257, 112864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, A.M.; Panyadee, P.; Inta, A.; Huffman, M.A. Asian elephant self-medication as a source of ethnoveterinary knowledge among Karen mahouts in northern Thailand. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Hoste, H.; Custódio, L. A systematic review on the ethnoveterinary uses of mediterranean salt-tolerant plants: Exploring its potential use as fodder, nutraceuticals or phytotherapeutics in ruminant production. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 267, 113464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Health Organization General Guidelines for Methodologies on Research and Evaluation of Traditional Medicine; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dhiman, N.; Shivani, Y.S.T.; Kumar, S. Diversity of ethnomedicinal plants in Churdhar Wildlife Sanctuary of district Sirmour of Himachal Pradesh, India. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 9, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Tangjang, S.; Namsa, N.D.; Aran, C.; Litin, A. An ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants in the Eastern Himalayan zone of Arunachal Pradesh, India. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, R.M. Monograph of Schisandra (Schisandraceae); American Society of Plant Taxonomists: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V. Diversity of Plant and Soil Nematodes in Uttarakhand, India. In Pests of Forest Importance & Their Management; Tyagi, B.K., Veer, V., Prakash, S., Eds.; Scientific Publishers: Jodhpur, India, 2008; p. 251. [Google Scholar]
- Mekhemar, M.; Geib, M.; Kumar, M.; Radha, S.P.; Hassan, Y.; Dörfer, C. Salvadora persica: Nature’s Gift for Periodontal Health. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Changan, S.; Tomar, M.; Prajapati, U.; Saurabh, V.; Hasan, M.; Sasi, M.; Maheshwari, C.; Singh, S.; Dhumal, S.; et al. Custard apple (Annona squamosal L.) leaves: Nutritional composition, phytochemical profile, and health-promoting biological activities. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, Z.A.; Kumar, N. Akash Ethnobotanical Study of Some Threatened Plants in District Baramulla, Kashmir, Jammu and Kashmir, India. Int. J. Curr. Res. Biosci. Plant Biol. 2016, 3, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.K.; Dey, A. A validated and densitometric HPTLC method for the simultaneous quantification of reserpine and ajmalicine in Rauvolfia serpentina and Rauvolfia tetraphylla. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2016, 26, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, S.P.; Puri, S. Assessment of wild medicinal plant used by migratory shepherds in alpine area of Rakchham-Chitkul Wildlife Sanctuary of district Kinnaur in Himachal Pradesh. Plant Arch. 2019, 19, 418–429. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Punia, S.; Grasso, S.; Arrutia, F.; Choudhary, J.; Singh, S.; Verma, P.; Mahapatra, A.; Patil, S.; et al. Cottonseed: A sustainable contributor to global protein requirements. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, S.P.; Chauhan, P.; Puri, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Pundir, A. A study of wild medicinal plants used in Nargu Wildlife Sanctuary of district Mandi in Himachal Pradesh, India. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 11, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.P.; Prakash, S.; Bhatia, R.; Negi, M.; Singh, J.; Bishnoi, M.; Kondepudi, K.K. Generation of structurally diverse pectin oligosaccharides having prebiotic attributes. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 105988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikhuri, R.K.; Semwal, R.L.; Singh, A.; Nautiyal, M.C. Wild fruits as a contribution to sustainable rural development: A case study from the Garhwal Himalaya. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 1994, 1, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Dasgupta, S.; Jhaldiyal, V.; Chauhan, D.; Todaria, N. Diversity pattern of vegetation in and around proposed Kotlibhel hydroelectric project along the Alaknanda River in Garhwal Himalaya (India). iForest Biogeosci. For. 2011, 4, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteiro, M.V.; Bevilaqua, C.M.; Palha, M.D.; Braga, R.R.; Schwanke, K.; Rodrigues, S.T.; Lameira, O.A. Ethnoveterinary knowledge of the inhabitants of Marajó Island, Eastern Amazonia, Brazil. Acta Amaz. 2011, 41, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, S.P.; Pundir, A. Survey of wild medicinal plants used by migratory shepherds in Summer Hill of District Shimla in Himachal Pradesh. Bio Bull. 2019, 5, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Mathias, E. Ethnoveterinary medicine in the era of evidence-based medicine: Mumbo-jumbo, or a valuable resource? Vet. J. 2006, 173, 241–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, R.A.; Monteiro, M.V.B.; Monteiro, F.; Rodrigues, S.T.; Soares, M.L.; Silva, J.C.R.; Palha, M.D.D.C.; Biondi, G.F.; Rahal, S.; Tourinho, M.M. Ethnoveterinary knowledge and practices at Colares island, Pará state, eastern Amazon, Brazil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 144, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khattak, N.S.; Nouroz, F.; Rahman, I.U.; Noreen, S. Ethnoveterinary uses of medicinal plants of district Karak, Pakistan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 171, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.A.; Vallejo, J.R. The use of domestic animals and their derivative products in contemporary Spanish ethnoveterinary medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 271, 113900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, P.R.; Mukerji, B. Role of indigenous drugs in veterinary medicine in India. Indian Vet. J. 1958, 1, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Mazars, G. Traditional veterinary medicine in India. Rev. Sci. Tech. 1994, 13, 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Assefa, A.; Bahiru, A. Ethnoveterinary botanical survey of medicinal plants in Abergelle, Sekota and Lalibela districts of Amhara region, Northern Ethiopia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 213, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Singh, J.; Sharma, D. Traditional wisdom to treat the most common ailments in Chopal region of Shimla district, Himachal Pradesh, India. Plant Arch. 2018, 18, 2759–2769. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.K. Ethnobotany. Interdiscip. Sci. Rev. 1986, 11, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namsa, N.D.; Tag, H.; Mandal, M.; Kalita, P.; Das, A. An ethnobotanical study of traditional anti-inflammatory plants used by the Lohit community of Arunachal Pradesh, India. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 125, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, O.; Gentry, A.H. The useful plants of Tambopata, Peru: I. Statistical hypotheses tests with a new quantitative technique. Econ. Bot. 1993, 47, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossato, S.C.; Leitao-Filho, H.; Gegossi, A. Ethnobotany of Caicaras of the Atlantic Forest coast (Brazil). Econ. Bot. 1999, 53, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, U.P.; Lucena, R.F.; Monteiro, J.M.; Florentino, A.T.; Cecília de Fátima, C.B.R. Evaluating Two Quantitative Ethnobotanical Techniques. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2006, 4, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yabesh, J.M.; Prabhu, S.; Vijayakumar, S. An ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used by traditional healers in silent valley of Kerala, India. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 774–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, V.A.; Andrade, L.D.; De Albuquerque, U.P. Revising the cultural significance index: The case of the Fulni-ô in northeastern Brazil. Field Methods 2006, 18, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.S.; Abdelrasool, F.E.; Elsheikh, E.A.; Ahmed, L.A.; Mahmoud, A.L.; Yagi, S.M. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants in the Blue Nile State, South-eastern Sudan. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 4287–4297. [Google Scholar]
- Radha, S.P.; Puri, S.; Pundir, A. Review on Ethnomedicinal Plant: Trillium govanianum Wall. Ex, D. Don. Int. J. Theor. Appl. Sci. 2019, 11, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lans, C. Possible similarities between the folk medicine historically used by First Nations and American Indians in North America and the ethnoveterinary knowledge currently used in British Columbia, Canada. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 192, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stucki, K.; Dal Cero, M.; Vogl, C.R.; Ivemeyer, S.; Meier, B.; Maeschli, A.; Hamburger, M.; Walkenhorst, M. Ethnoveterinary contemporary knowledge of farmers in pre-alpine and alpine regions of the Swiss cantons of Bern and Lucerne compared to ancient and recent literature–is there a tradition? J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 234, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-EL-Sooud, K. Ethnoveterinary perspectives and promising future. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2018, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, M.S.; Pljevljakušić, D.S.; Nikolić, B.M.; Miladinović, D.L.; Djokić, M.M.; Rakonjac, L.B.; Jovanović, V.P.S. Ethnoveterinary knowledge in Pirot County (Serbia). S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 137, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.A.; Amich, F.; Postigo-Mota, S.; Vallejo, J.R. The use of wild vertebrates in contemporary Spanish ethnoveterinary medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 191, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miara, M.D.; Bendif, H.; Ouabed, A.; Rebbas, K.; Hammou, M.A.; Amirat, M.; Greene, A.; Teixidor-Toneu, I. Ethnoveterinary remedies used in the Algerian steppe: Exploring the relationship with traditional human herbal medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 244, 112164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radha, S.P.; Puri, S.; Kumar, V. Phytochemical screening of medicinal plants used by tribal migratory shepherds in Western Himalaya. Ann. Biol. 2019, 35, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Radha, S.P.; Kumar, M.; Puri, S.; Pundir, A.; Bangar, S.P.; Changan, S.; Choudhary, P.; Parameswari, E.; Alhariri, A.; Samota, M.K.; et al. Evaluation of nutritional, phytochemical, and mineral composition of selected medicinal plants for therapeutic uses from Cold Desert of Western Himalaya. Plants 2021, 10, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoroge, G.N.; Bussmann, R.W. Herbal usage and informant consensus in ethnoveterinary management of cattle diseases among the Kikuyus (Central Kenya). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 108, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grade, J.T.; Tabuti, J.R.; Van Damme, P. Ethnoveterinary knowledge in pastoral Karamoja, Uganda. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 273–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilshad, S.M.; Iqbal, Z.; Muhammad, G.; Iqbal, A.; Ahmed, N. An inventory of the ethnoveterinary practices for reproductive disorders in cattle and buffaloes, Sargodha district of Pakistan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, S.P.; Pundir, A. Survey of ethnomedicinal plants used by migratory shepherds in Shimla district of Himachal Pradesh. Plant Arch. 2019, 19, 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- Radha, S.P.; Puri, S. Study of wild medicinal plants used by tribal migratory shepherds in hills of Shimla District, Himachal Pradesh. Plant Arch. 2019, 19, 785–790. [Google Scholar]
- Alawa, J.; Jokthan, G.; Akut, K. Ethnoveterinary medical practice for ruminants in the subhumid zone of northern Nigeria. Prev. Veter. Med. 2002, 54, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabuti, J.R.; Dhillion, S.S.; Lye, K.A. Ethnoveterinary medicines for cattle (Bos indicus) in Bulamogi county, Uganda: Plant species and mode of use. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 88, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, S.P.; Janjua, S.; Srivastava, S.; Negi, V. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used in Shikari Devi Wildlife Sanctuary of Himachal Pradesh, India. Med. Plants 2020, 12, 666–673. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Prakash, S.; Radha, S.P.; Kumari, N.; Pundir, A.; Punia, S.; Saurabh, V.; Choudhary, P.; Changan, S.; Dhumal, S.; et al. Beneficial role of antioxidant secondary metabolites from medicinal plants in maintaining oral health. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Saurabh, V.; Sasi, M.; Punia, S.; Potkule, J.; Maheshwari, C.; Changan, S.; Radha, S.P.; Bhushan, B.; et al. Delineating the inherent functional descriptors and biofunctionalities of pectic polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Potkule, J.; Patil, S.; Mageshwaran, V.; Radha, S.P.; Satankar, V.; Berwal, M.K.; Mahapatra, A.; Saxena, S.; Ashtaputre, N.; et al. Evaluation of detoxified cottonseed protein isolate for application as food supplement. Toxin Rev. 2021, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerwein, M.; Shimomura, K. Degradation of 17α-O-methylyohimbine in Amsonia elliptica roots. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 1449–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabhosseini, A.; Huisman, W.; Van Boxtel, A.; Müller, J. Long-term effects of drying conditions on the essential oil and color of tarragon leaves during storage. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, I.; Topcu, A.; Duran, A.; Turan, S.; Ozturk, B. Effect of hot air drying and sun drying on color values and β-carotene content of apricot (Prunus armenica L.). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, S.P.; Puri, S. Phytochemical analysis of ethanolic extracts of leaves of some selected medicinal plants used by tribal community of Sangla Valley, District Kinnaur, Himachal Pradesh. Plant Arch. 2019, 19, 397–403. [Google Scholar]
- Jagtap, S.; Deokule, S.; Bhosle, S. Some unique ethnomedicinal uses of plants used by the Korku tribe of Amravati district of Maharashtra, India. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 107, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendruscolo, G.S.; Mentz, L.A. Study of the concordance of the citations of use and importance of the species and families used as medicinal by the community of the Ponta Grossa neighborhood, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil. Acta Bot. Bras. 2006, 20, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Snafi, A.E. The chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Chenopodium album—An overview. Int. J. Pharmacol. Screen. Methods 2015, 5, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Shakil, S.S.; Gowan, M.; Hughes, K.; Azam, M.N.; Ahmed, M.N. A narrative review of the ethnomedicinal usage of Cannabis sativa Linnaeus as traditional phytomedicine by folk medicine practitioners of Bangladesh. J. Cannabis Res. 2021, 3, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Snafi, A.E. Chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Cynodon dactylon—A Review. IOSR J. Pharm. (IOSRPHR) 2016, 6, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.M.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Zafar, M.; Khan, H.; Muhammad, N.; Sultana, S. Medicinal plants used for the treatment of jaundice and hepatitis based on socio-economic documentation. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Snafi, A.E. The chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Capsella bursa-pastoris—A review. Int. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 5, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Snafi, A.E. The pharmacology of Equisetum arvense—A review. IOSR J. Pharm. (IOSRPHR) 2017, 7, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Lal, B. Ethnomedicines used against four common ailments by the tribal communities of Lahaul-Spiti in western Himalaya. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 115, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Ruby, K.M.; Shori, A.; Dwivedi, J. Solanum nigrum with dynamic therapeutic role: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2012, 15, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Girish, C.; Pradhan, S. Indian herbal medicines in the treatment of liver diseases: Problems and promises. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 26, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giday, M.; Teklehaymanot, T.; Animut, A.; Mekonnen, Y. Medicinal plants of the Shinasha, Agew-awi and Amhara peoples in northwest Ethiopia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 110, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthu, C.; Ayyanar, M.; Raja, N.; Ignacimuthu, S. Medicinal plants used by traditional healers in Kancheepuram District of Tamil Nadu, India. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2006, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nesello, L.A.; Beleza, M.L.; Mariot, M.; Mariano, L.N.; De Souza, P.; Campos, A.; Cechinel-Filho, V.; Andrade, S.F.; Da Silva, L.M. Gastroprotective value of berries: Evidences from methanolic extracts of Morus nigra and Rubus niveus fruits. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 7089697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahimi Madiseh, M.; Heidarian, E.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Biochemical components of Berberis lycium fruit and its effects on lipid profile in diabetic rats. J. HerbMed Pharmacol. 2014, 3, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, P.S.; Bisht, S.; Ahmed, S. Traditional and ethnobotanical uses of medicinal trees in district Tehri Garhwal (Western Himalayas). Int. J. Ayurvedic Herb. Med. 2017, 7, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Dhupper, R.; Sharma, S. Survey of ethnomedicinal plants used by indigenous people of Nerwa range, Chopal forest division, Himachal Pradesh, India. Med. Plants Int. J. Phytomed. Relat. Ind. 2020, 12, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklani, S.; Chandra, S.; Badoni, P.P.; Dogra, S. Antimicrobial activity, nutritional profile and phytochemical screening of wild edible fruit of Rubus ellipticus. Int. J. Med. Aromat. Plants 2012, 2, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Shigaeva, J.; Darr, D. On the socio-economic importance of natural and planted walnut (Juglans regia L.) forests in the Silk Road countries: A systematic review. For. Policy Econ. 2020, 118, 102233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yan, F.; Chen, F. Main physical chemistry characteristics and fatty acid composition of three plant oils and their bio-diesel fuels. Guangxi Zhiwu/Guihaia 2007, 27, 448–452. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z. Advances in Research of the Prinsepia utilis Royle In China. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2011, 2011, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Maikhuri, R.K.; Singh, A.; Semwal, R.L. Prinsepia utilis Royle: A wild, edible oil shrub of the higher Himalayas. Plant Genet. Resour. Newslett. 1994, 98, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Singani, A.A.S.; Ahmadi, P. Manure Application and Cannabis Cultivation Influence on Speciation of Lead and Cadmium by Selective Sequential Extraction. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2012, 21, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudeta, K.; Julka, J.; Kumar, A.; Bhagat, A.; Kumari, A. Vermiwash: An agent of disease and pest control in soil, a review. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ali, A.S.; Ali, S.A. Green nanotechnology a boon in silver nanoparticle (AgNPs) synthesis-certain aspects of AgNPs biomedical applications and an outline of its toxicological impacts—A mini review. Eur. J. Pharm. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 261–273. [Google Scholar]
- Negi, P.S.; Subramani, S.P. Wild edible plant genetic resources for sustainable food security and livelihood of Kinnaur district, Himachal Pradesh, India. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2015, 6, 657–668. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, G.; Duggal, S. Ethnomedicinal diversity of aromatic plants in foot hill regions of Himachal Pradesh, India. Int. J. Theor. Appl. Sci. 2019, 11, 18–39. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, J.T. Cultivating and Preserving American Wild Flowers, 1890–1965; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shigeta, M. Folk in-situ conservation of ensete [Ensete ventricosum (Welw.) EE Cheesman]: Toward the interpretation of indigenous agricultural science of the Ari, Sowthwestern Ethiopia. Afr. Study Monogr. 1990, 10, 93–107. [Google Scholar]
| Sr. No. | Age Groups | No. of Informants | ||||
| 1. | 25–36 | 18 (10, Male and 8 Female) | ||||
| 2. | 37–46 | 25 (15 Male and 10 Female) | ||||
| 3. | 47–56 | 37 (21 Male and 16 Female) | ||||
| 4. | 57–66 | 10 (7 Male and 3 Male) | ||||
| 5. | 67–80 | 6 (4 Male and 2 Female) | ||||
| Literacy Among Informants: | Age Groups | |||||
| 25–36 | 37–46 | 47–56 | 57–66 | 67–80 | ||
| 1. | Never attended school | 0 | 0 | 3 (2 Male, 1 Female) | 5 (3 Male, 2 Female) | 5 (4 Male, 1 Female) |
| 2. | Attended school up to primary level (1–5 class) | 0 | 5 (2 Male, 3 Female) | 2 (1 Male, 1 Female) | 1 (1 Male) | 1 (1 Male) |
| 3. | Attended school up to middle level (6–8) | 0 | 5 (3 Male, 2 Female) | 6 (4 Male, 2 Female) | 3 (2 Male, 1 Female) | 0 |
| 4. | Attended school up to metric level (9–10 class) | 18 (10 Male, 9 Female) | 15 (9 Male, 6 Female) | 26 (15 Male, 11 Female) | 1 (1 Male) | 0 |
| Botanical Name | Actual Morphology of Ethnomedicinal Plant | Family | Common Name | Voucher No. | Habit | Parts Used | Disease Treated | Mode | Ailment Treated and Citations | Use-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abies pindrow (Royle ex D. Don) Royle |  | Pinaceae | Tonss | SUBMS/BOT-4184 | Tree | Leaves | Udder infection | Topical | Leaf paste is applied on udder of cow to treat clotting of milk (66). | 0.68 |
| Adiantum venustum D. Don |  | Pteridaceae | Jamna | SUBMS/BOT-4185 | Fern | Leaves | Skin disease | Topical | Paste of plant part is applied on chronic tumors for rapid healing (57). | 0.59 |
| Ajuga parviflora Benth. |  | Lamiaceae | Neel kanthi | SUBMS/BOT-4186 | Herb | Aerial part | Sores, Wounds | Topical | Fine powder of aerial parts with few drops of edible oil is applied on skin of cattle to treat sores, wounds (69). | 0.71 |
| Amaranthus, blitum L. |  | Amaranthaceae | Sukhichalayi | SUBMS/BOT-4187 | Herb | Leaves | Diarrhea, Dysentery, Skin infection | Oral, Topical | Fresh leaves are used to cure diarrhea and dysentery. Paste of leaves is useful in curing skin infection (48). | 0.50 |
| Androsace sarmentosa Wall. |  | Primulaceae | Phoolru | SUBMS/BOT-4188 | Herb | Leaves | Skin infections | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves is applied on skin infections (45). | 0.46 |
| Artemisia vestita Wall. Ex Besser |  | Asteraceae | Chamber | SUBMS/BOT-4189 | Herb | Leaves, Flowers | Wounds | Topical | Paste of leaves or flowers is used to treat wounds (54). | 0.56 |
| Aruncus dioicus (Walter)Fernald |  | Rosaceae | Pothee | SUBMS/BOT-4190 | Herb | Roots | Internal bleeding, Stomach pains, Diarrhea | Oral | Roots along with warm water is used to stop bleeding after birth Paste of fresh roots cures stomachache and diarrhea (56). | 0.58 |
| Asplenium dalhousiae Hook. |  | Aspleniaceae | Nanwein | SUBMS/BOT-4191 | Fern | Whole plant | Skin infection | Topical | Whole plant is used to treat bacterial skin infections (48). | 0.50 |
| Berberis lycium Royle |  | Berberidaceae | Kashmal | SUBMS/BOT-4192 | Shrub | Leaves, Roots, Stem Bark, | Tonic, Bone fractures, Wounds, Stomach infection, Skin infections | Topical, Oral | The paste of root bark is externally applied on wounds and on bone fracture. Decoction of root and stem barks are used against stomach infection (61). | 0.63 |
| Berberis aristata DC. |  | Berberidaceae | Chatra | SUBMS/BOT-4193 | Shrub | Leaves | Mouth infections, Itching, Eye infections | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves cure mouth and skin infections. Juice extract from fresh leaves is affective against eye infection (59). | 0.61 |
| Bergenia ciliata (Haw.) Sternb. |  | Saxifragaceae | Daclambu | SUBMS/BOT-4194 | Herb | Leaves, Roots | Wound healing | Topical | Paste of leaves/ root is applied on wound. Wood ash is also used for wound healing (55). | 0.57 |
| Bromus hordeaceus L. |  | Poaceae | Jawi | SUBMS/BOT-4195 | Grass | Whole plant | Fodder | Oral | Plant is used as fodder for livestock as rich in nutritional content (50). | 0.52 |
| Buddleja crispa Benth. |  | Scrophulariaceae | Taakla | SUBMS/BOT-4196 | Shrub | Leaves | Cold, Dysentery, Bleeding | Oral, Topical | Fresh leaves are given to animals to cure cold and dysentery. Paste of fresh leaves is used to stop bleeding (47). | 0.48 |
| Cannabis sativa L. |  | Cannabaceae | Bhang | SUBMS/BOT-4197 | Herb | Leaves | Intestinal worms, Stomach pain | Oral | Powdered leaf balls are given to cattle to treat intestinal worms and body pain (76). | 0.79 |
| Capsella bursa-pastoris (L.) Medik. |  | Brassicaceae | Khandwa | SUBMS/BOT-4198 | Herb | Leaves | Wound | Topical | Leaf paste is used to cure wounds (54). | 0.56 |
| Cedrus deodara (Roxb. ex D.Don) G. Don |  | Pinaceae | Devdar | SUBMS/BOT-4199 | Tree | Leaves | Skin infections | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves is applied on skin to cure infections (53). | 0.55 |
| Chenopodium album L. |  | Amaranthaceae | Bathuwa | SUBMS/BOT-4200 | Herb | Whole plant | Skin disorders | Oral | Decoction of whole plant with Solanum surrattense is given orally to cure skin diseases (67). | 0.69 |
| Cirsium arvense (L.) Scop. |  | Asteraceae | Bhenda | SUBMS/BOT-4201 | Herb | Whole plant | Digestion | Oral | Used as feed for ruminants due to high nutritional value (45). | 0.46 |
| Clematis buchananiana DC. |  | Ranunculaceae | Silra | SUBMS/BOT-4202 | Climber | Whole plant | Wound healing | Topical | Plant paste is applied on wounds (56). | 0.58 |
| Clematis vitalba L. |  | Ranunculaceae | Garol | SUBMS/BOT-4203 | Shrub | Leaves | Skin eruptions | Topical | Paste of leaves is applied on skin eruptions in livestock (47). | 0.48 |
| Coriaria nepalensis Wall. |  | Coriariaceae | Gandhla | SUBMS/BOT-4204 | Shrub | Leaves, Fruits | Dysentery | Oral | Fresh leaves and ripened fruits are used to cure dysentery (49). | 0.51 |
| Cotoneaster microphyllus Wall. ex Lindl. |  | Rosaceae | Jampradua | SUBMS/BOT-4205 | Shrub | Leaves | Acute dermatitis | Topical | Leaf paste is used to treat acute dermatitis (51). | 0.53 |
| Curculigo orchioides Gaertn. |  | Hypoxidaceae | Lehsun-phool | SUBMS/BOT-4206 | Herb | Leaves, Flowers | Diarrhea | Oral | Paste of dried leaves and flowers is used to cure diarrhea (46). | 0.47 |
| Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. |  | Poaceae | Droob | SUBMS/BOT-4207 | Grass | Leaves | Eye diseases, Stomach, Skin infections infection, Cold | Topical, Oral | Juice extract of leaves is used to treat eye diseases. Fresh leaves given to cure stomach infection and cold (72). | 0.75 |
| Cyperus cyperoides (L.) Kuntze |  | Cyperaceae | Kadreen | SUBMS/BOT-4208 | Grass | Leaves | Fodder | Oral | It is used as fodder (52). | 0.54 |
| Daphne papyracea Wall. ex G. Don |  | Thymelaeaceae | Baruvaa | SUBMS/BOT-4209 | Shrub | Aerial part | Mange, Stomach pain | Oral, Topical | Paste of aerial part is applied on skin for the treatment of mange. Decoction from aerial part is used to treat stomach pain (44). | 0.45 |
| Datura stramonium L. |  | Solanaceae | Datura | SUBMS/BOT-4210 | Shrub | Leaves | Skin infection | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves is used to get rid of skin parasites (69). | 0.71 |
| Desmodium elegans DC. |  | Fabaceae | Murta | SUBMS/BOT-4237 | Shrub | Leaves | Fodder | Oral | Fresh leaves are used as fodder (43). | 0.44 |
| Deutzia scabra Thunb. |  | Hydrangeaceae | Suniya | SUBMS/BOT-4211 | Shrub | Leaves | Skin infections | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves is useful against skin infections (51). | 0.53 |
| Diplazium esculentum (Retz.) Sw |  | Athyriaceae | Lingar | SUBMS/BOT-4239 | Fern | Leaves | Diarrhea | Oral | Young leaves boiled in water is useful against diarrhea (39). | 0.40 |
| Elaeagnus umbellata Thunb. |  | Elaeagnaceae | Genhi | SUBMS/BOT-4212 | Shrub | Flowers | Reduce inflammation | Topical | Flowers are used to reduce inflammation on affected areas (44). | 0.45 |
| Epilobium hirsutum L. |  | Onagraceae | Dandri | SUBMS/BOT-4213 | Herb | Leaves | Mouth ulcers, Wasp sting | Oral, Topical | Paste of leaves is used to treat mouth ulcers and wasp stings (42). | 0.43 |
| Equisetum arvense L. |  | Equisetaceae | Ramban | SUBMS/BOT-4214 | Herb | Aerial part | Urinary tract infections | Oral, Topical | Plant extract is used to treat urinary tract infections and other health infection (49). | 0.51 |
| Erigeron alpinus L. |  | Asteraceae | Chipru | SUBMS/BOT-4215 | Herb | Leaves | Bleeding | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves is applied on bleeding wound (40). | 0.41 |
| Erigeron bonariensis L. |  | Asteraceae | Kupru | SUBMS/BOT-4216 | Herb | Leaves | Stomach pain, Urinary infection | Oral | Plant is used to treat stomach pain and urinary infection (47). | 0.48 |
| Evolvulus nummularius (L.) L. |  | Convolvulaceae | Ghareu | SUBMS/BOT-4217 | Herb | Leaves | Skin infection | Topical | Paste of fresh as well as dry leaves is applied to cure skin infections caused by parasites (53). | 0.55 |
| Fagopyrum acutatum (Lehm.) Mansf. ex K. Hammer |  | Polygonaceae | Fafri | SUBMS/BOT-4218 | Herb | Leaves | Skin infections | Topical | Paste of leaves is applied on skin infections (45). | 0.46 |
| Foeniculum vulgare Mill. |  | Apiaceae | Sounph | SUBMS/BOT-4219 | Herb | Leaves, Seeds | Poisoning, Cough, Tonic, Skin infection | Oral, Topical | Dried seeds are given to cure poisoning and cough. Seeds with hot water is given to animals after parturition, used as tonic. (59). | 0.61 |
| Fragaria virginiana Mill. |  | Rosaceae | Bhumbal | SUBMS/BOT-4220 | Herb | Roots, Leaves, Fruits | Skin infection, Indigestion | Oral, Topical | Juice of ripened fruit is applied on skin infection. Paste of powdered root and leaves is applied on cuts and wounds (48). | 0.50 |
| Galinsoga quadriradiata Ruiz & Pav. |  | Asteraceae | Sheliya | SUBMS/BOT-4221 | Herb | Leaves | Cuts, Wounds | Topical | Paste of dry as well as fresh leaves is applied on cuts and wounds (47). | 0.48 |
| Gentiana argentea (Royle ex D.Don) Royle ex D.Don |  | Gentianaceae | Bhuin neem | SUBMS/BOT-4222 | Herb | Leaves, Flowers, Roots | Skin infections, Wound, Poisoning | Topical, Oral | Paste of fresh leaves are used to treat skin infections and wounds. Decoction of whole plant is used in the treatment of poisoning (51). | 0.53 |
| Geranium nepalense Sweet |  | Geraniaceae | Bhrago-ro-naush | SUBMS/BOT-4223 | Herb | Leaves | Skin infections | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves is used to cure skin infections (49). | 0.51 |
| Girardinia diversifolia (Link) Friis |  | Urticaceae | Lindu bhaber | SUBMS/BOT-4224 | Shrub | Leaves | Gastric infection | Oral | Fresh leaves boiled with hot water is used for treating gastric infection (47). | 0.48 |
| Goodyera repens (L.) R.Br. |  | Orchidaceae | Kaligatti | SUBMS/BOT-4225 | Herb | Leaves, Roots | Stomach pain | Oral | Powdered leaves and roots are used to treat stomach pain (55). | 0.57 |
| Hedera nepalensis K.Koch |  | Araliaceae | Kanewari | SUBMS/BOT-4226 | Climber | Leaves | Leeches | Topical | Leaf extract is used to remove leeches in sheep (66). | 0.68 |
| Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench |  | Asteraceae | Dhareri | SUBMS/BOT-4227 | Herb | Aerial part | Cough | Oral | Extract obtained from the plant is used to treat cough (48). | 0.5 |
| Heracleum maximum W. Bartram |  | Apiaceae | Patla | SUBMS/BOT-4228 | Herb | Roost | Swellings, Blisters | Topical | Paste prepared from the root is applied on swellings and blisters (43). | 0.44 |
| Hypericum perforatum L. |  | Hypericaceae | Choli phulya | SUBMS/BOT-4229 | Shrub | Aerial part | Relive pain | Oral | Used to relive nerve pain due to puncture wounds (57). | 0.59 |
| Ilex dipyrena Wall. |  | Aquifoliaceae | Khareu | SUBMS/BOT-4230 | Tree | Leaves | Enhance milk production | Oral | Fresh leaves are fed to cattle to enhance the milk secretion and to increase strength (61). | 0.63 |
| Impatiens glandulifera Royle |  | Balsaminaceae | Rdheu | SUBMS/BOT-4231 | Herb | Leaves, Flowers | Poisoning | Oral | Infusion of fresh leaves and flowers is used to cure poisoning occurred from toxic plants (59). | 0.61 |
| Indigofera gerardiana Baker |  | Fabaceae | Kathi | SUBMS/BOT-4232 | Shrub | Bark | Broken bones | Topical | Bark is boiled in milk and a bandage is formed and is used externally to treat broken bones (47). | 0.48 |
| Juglans regia L. |  | Juglandaceae | Akhrot, khodh | SUBMS/BOT-4233 | Tree | Bark | Oral diseases | Topical | Paste of bark is used to cure oral diseases (54). | 0.56 |
| Juncus effusus L. |  | Juncaceae | Kirala | SUBMS/BOT-4234 | Herb | Leaves | Urine infection | Oral | Fresh leaves are given to cure urine infection (48). | 0.5 |
| Juniperus communis L. |  | Cupressaceae | Gala | SUBMS/BOT-4235 | Shrub | Leaves | Intestinal parasites, Snake bite | Oral, Topical | Paste of dried leaves is used treat the worms inside the digestive tract. Paste of dried leaves is used to cure snake bite (42). | 0.43 |
| Lepidium campestre (L.) R.Br. |  | Brassicaceae | Khoru | SUBMS/BOT-4236 | Herb | Leaves, Stem | Skin infection | Topical | Infusion of leaves and stem prepare in hot water is used to treat skin infections (45). | 0.46 |
| Malva verticillata L. |  | Malvaceae | Mikanchi | SUBMS/BOT-4238 | Herb | Leaves | Flatulence | Oral | Infusion of leaves is used for the treatment of flatulence (47). | 0.48 |
| Mentha viridis (L.) L. |  | Lamiaceae | Pahari pudina | SUBMS/BOT-4241 | Herb | Leaves | Stomach infection, Skin infections, Hoof diseases | Oral, Topical | Fresh leaves are given to cure stomach infection. Paste of fresh leaves is beneficial against skin infection and hoof diseases (63). | 0.65 |
| Nicotiana tabacum L. |  | Solanaceae | Tambakhoo | SUBMS/BOT-4240 | Herb | Leaves, Stem | Pain relief | Oral | Decoction of leaves is used to reduce pain (50). | 0.52 |
| Oxalis articulata Savigny |  | Oxalidaceae | Shash | SUBMS/BOT-4242 | Herb | Leaves, Flowers | Poisoning, Cold | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves is used to treat poisoning in animal. Whole plant is given to cure cold (47). | 0.48 |
| Oxalis corniculata L. |  | Oxalidaceae | Shash | SUBMS/BOT-4243 | Shrub | Leaves, Flowers | Snakebites, Cold | Topical, Oral | Paste of fresh leaves is used to treat snakebites. Whole plant is given to cure cold (52). | 0.54 |
| Petridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn |  | Dennstaedtiaceae | Barna | SUBMS/BOT-4244 | Fern | Leaves, Roots | Bone fractures, Pain | Topical, Oral | Paste of leaves is used in binding bone fracture. Decoction of roots is used as pain reliving agent (48). | 0.5 |
| Platanus orientalis L. |  | Platanaceae | Kimti | SUBMS/BOT-4245 | Shrub | Leaves, Bark | Diarrhea, Dysentery, Wounds | Oral, Topical | A decoction of bark is used to cure diarrhea, dysentery. Leaves are used to heal wounds (46). | 0.47 |
| Potentilla indica var. wallichii (Franch. & Sav.) Th.Wolf |  | Rosaceae | Bhumbhal | SUBMS/BOT-4246 | Herb | Leaves, Fruits | Insect bite | Topical | Paste of fresh fruits and leaves is applied on insect bites (40). | 0.41 |
| Potentilla tabernaemontani Asch. |  | Rosaceae | Diyuda | SUBMS/BOT-4247 | Herb | Flowers, Leaves, Roots | Stomach infection, Hoof infection | Oral, Topical | Juice from fresh leaves and flowers is used to cure stomach infection. Paste of powdered root is applied on hoof infections (61). | 0.63 |
| Primula denticulata Sm. |  | Primulaceae | Lattar-phul | SUBMS/BOT-4248 | Herb | Flower | Snake bite | Topical | Flower paste is used to treat snakebites in cattle (54). | 0.56 |
| Prinsepia utilis Royle |  | Rosaceae | Bhekhal | SUBMS/BOT-4249 | Shrub | Fruits | Joint pain | Topical | Oil of fruits is used to relieve from joint pain (45). | 0.46 |
| Pteris cretica var. laeta (Wall. ex Ettingsh.) C. Chr. & Tardieu |  | Pteridaceae | Barne | SUBMS/BOT-4250 | Fern | Leaves | Skin infection, Bleeding | Topical | Paste of green leaves is used to treat skin infection and bleeding (49). | 0.51 |
| Pyrus pashia Buch-Ham. ex D.Don |  | Rosaceae | Kainth | SUBMS/BOT-4251 | Tree | Fruits | Eye infection | Topical | Juice of ripe fruit is used to cure eye infection (49). | 0.51 |
| Quercus floribunda Lindl. ex A.Camus |  | Fagaceae | Moru | SUBMS/BOT-4252 | Tree | Leaves | Skin infection | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves are applied to cure skin infection (46). | 0.47 |
| Rhododendron arboreum Sm. |  | Ericaceae | Buransh | SUBMS/BOT-4253 | Tree | Flowers, Leaves | Snake bite, Diarrhea | Oral | Paste of dried flowers is used against snake bite. Paste of powered leaves is used to cure diarrhea (69). | 0.71 |
| Rosa brunonii Lindl. |  | Rosaceae | Kujja | SUBMS/BOT-4254 | Shrub | Fruits, Leaves | Diarrhea, Lactation | Oral | Ripe fruits are used to cure diarrhea. Fresh leaves are given to increase milk quantity of goats and sheep (43). | 0.44 |
| Rosa sericea Wall. ex Lindl. |  | Rosaceae | Junglee kuja | SUBMS/BOT-4255 | Shrub | Fruits, Leaves | Gastric infection | Oral | Ripe fruits are used to cure gastric infection (39). | 0.40 |
| Rubia cordifolia L. |  | Rubiaceae | Majith | SUBMS/BOT-4256 | Shrub | Stem, Leaves | Hoof diseases, Blisters | Topical | Paste of dried root is used to treat hoof diseases. Paste of fresh leaves is applied on blisters (44). | 0.45 |
| Rubus ellipticus Sm. |  | Rosaceae | Hinser | SUBMS/BOT-4257 | Shrub | Bark, Roots | Urine infection, Gastric troubles | Oral | Juice of the root is used in the diarrhea. The bark from this plant is used to cure urinary infection (41). | 0.42 |
| Rubus niveus Thunb. |  | Rosaceae | Kamrai | SUBMS/BOT-4258 | Shrub | Fruits | Snake bite, Tonic | Oral | Extracts and juices from the fruits is used as an antidote for snake bites and as a tonic during pregnancy (37). | 0.38 |
| Rumex obtusifolius L. |  | Polygonaceae | Kransh | SUBMS/BOT-4259 | Herb | Leaves, Roots | Skin infection, Sores | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves is applied on skin infections. Paste of dried roots is applied on sores (40). | 0.41 |
| Rumex tuberosus L. |  | Polygonaceae | Khatti patti | SUBMS/BOT-4260 | Herb | Leaves | Skin infection | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves is applied on skin infections (37). | 0.38 |
| Rumex hastatus D. Don |  | Polygonaceae | Bhanora | SUBMS/BOT-4261 | Herb | Leaves, Tuber | Wound, Dysentery | Topical, Oral | The extract of leaves of plant is applied on wounds and cuts to check bleeding. The juice of the plant is used in the treatment of dysentery (33). | 0.34 |
| Salix triandra L. |  | Salicaceae | Bhaill | SUBMS/BOT-4262 | Shrub | Bark, Leaves | Fever, Joint pains | Oral, Topical | Powder of leaves is given to cure fever. Paste of bark and leaves is affective against joint pains (36). | 0.37 |
| Salvia lanata Roxb |  | Lamiaceae | Kuku-ro-bath | SUBMS/BOT-4263 | Herb | Leaves | Healing wounds | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves are applied on external wounds (43). | 0.44 |
| Sarcococca saligna Mull.Arg. |  | Buxaceae | Shangal | SUBMS/BOT-4264 | Shrub | Leaves | Fever | Oral | Aqueous extract of leaves is used as antipyretic (41). | 0.42 |
| Scutellaria ovata Hill |  | Lamiaceae | Kathiya | SUBMS/BOT-4265 | Herb | Leaves, Flowers | Respiratory infection, Diarrhea, Nose bleeding | Oral, Topical | Plant extract with hot water is affective against respiratory infection and diarrhea. Paste of leaves is useful for preventing nose bleeding (38). | 0.39 |
| Scutellaria scandens D.Don |  | Lamiaceae | Kadwi | SUBMS/BOT-4266 | Herb | Leaves, Flowers | Skin infection | Topical | Powdered leaves and flowers are applied on skin infections for its cure (48). | 0.50 |
| Selinum wallichianum (DC.) Raizada & H.O. Saxena |  | Apiaceae | Chamber ghass | SUBMS/BOT-4267 | Herb | Roots | Stomachache | Oral | Dried and powdered leaves are used for abdominal diseases (49). | 0.51 |
| Silene vulgaris (Moench) Garcke |  | Caryophyllaceae | Monch | SUBMS/BOT-4268 | Herb | Leaves, Roots | Vomiting, Poisoning, Constipation, Skin infections | Topical, Oral | Decoction of roots is used to treat vomiting, poisoning and constipation. Liquid extract of leaves is used to cure skin infections (42). | 0.43 |
| Solanum nigrum L. |  | Solanaceae | Genhi | SUBMS/BOT-4269 | Herb | Leaves, Flowers, Roots, Fruits | Itching, Oral ulcer, Cough, Urine infection | Topical, Oral | Paste of powdered leaves, fruit, flower is used against itching, oral ulcers. Extracts of roots and flowers are used for curing cough. Decoction obtained from leaves cure urinary troubles (44). | 0.45 |
| Sonchus asper (L.) Hill |  | Asteraceae | Dudhiya | SUBMS/BOT-4270 | Herb | Whole plant, Leaves, Stem | Skin infection | Topical | Freshly prepared plant extract is applied on skin infections (57). | 0.59 |
| Sonchus brachyotus DC. |  | Asteraceae | Sadhi | SUBMS/BOT-4271 | Herb | Bud, Flowers, Leaves, Stem, Roots | Puss in ear, Dermatitis, Ulcers | Topical, Oral | Extract of bud is used against puss formed in the ear. A decoction of the whole plant is used to treat stomach infection, itching, ulcers (36). | 0.37 |
| Sonchus oleraceus (L.) L. |  | Asteraceae | Dudhi | SUBMS/BOT-4272 | Herb | Leaves, Whole plant | Diarrhea, Inflammation Warts | Oral, Topical | Whole plant is given to animals suffering from diarrhea. Latex is applied on the inflammation and warts (48). | 0.5 |
| Stemmacantha rhapontica (L.) Dittrich |  | Asteraceae | Kusumphool | SUBMS/BOT-4273 | Herb | Bark, Leaves | Indigestion | Oral | Extract of bark and roots is used for indigestion (36). | 0.37 |
| Thlaspi arvense L. |  | Brassicaceae | Mahula | SUBMS/BOT-4274 | Herb | Seeds, Whole plant | Inflammation, Fever, Tonic | Topical, Oral | Powdered form of seeds is used to calm down swelling of limbs. Plant juice is used as tonic (47). | 0.48 |
| Thymus linearis Benth. |  | Lamiaceae | Marcha | SUBMS/BOT-4275 | Herb | Flowers, Leaves | Stomach infection, Fever | Oral | Paste of flowers and leaves are used to cure stomach infection. Semi-solid paste of dried plant is given in the form of small balls to cure fever during the winter (50). | 0.52 |
| Trifolium repens L. |  | Fabaceae | Khatti shash | SUBMS/BOT-4276 | Herb | Leaves, Flowers | Skin infection, Cough | Topical, Oral | Paste of fresh leaves used to treat skin infection. Powdered flowers along with leaves are used to cure cough (41). | 0.42 |
| Urtica dioica L. |  | Urticaceae | Kunkshi | SUBMS/BOT-4277 | Herb | Leaves | Diarrhea, Skin infection | Oral | Semifluid paste of leaves with hot water is beneficial against diarrhea. Leaves with other food is given to cattle to get relief in skin diseases during lactation (39). | 0.40 |
| Valeriana jatamansi Jones |  | Caprifoliaceae | Mushki | SUBMS/BOT-4278 | Herb | Leaves, Rhizome | Skin infection, Wound healing, Redness of eyes | Topical | Powdered leaves are used to cure skin infections. Paste of root is applied on wounds for better healing. Rhizomes are used to treat dryness and redness of eyes in the cattle (52). | 0.54 |
| Verbascum thapsus L. |  | Scrophulariaceae | Kukurdara | SUBMS/BOT-4279 | Herb | Leaves, Flowers, Roots | Pain, Warts, Flatulence | Topical, Oral | Decoction leaves is used to treat warts on the skin. Decoction of inflorescence is used to cure flatulence in cattle (42). | 0.43 |
| Veronica persica Poir. |  | Plantaginaceae | Raat ki kali | SUBMS/BOT-4280 | Herb | Leaves | Skin infection, Wound healing | Topical | Paste of fresh leaves used to cure skin disorders and serve as an excellent wound healing remedy (47). | 0.48 |
| Viburnum grandiflorum Wall. ex DC. |  | Adoxaceae | Pothi | SUBMS/BOT-4281 | Shrub | Leaves | Constipation | Oral | A paste of leaves with hot water is affective against constipation (44). | 0.45 |
| Vicia sativa L. |  | Fabaceae | Matari | SUBMS/BOT-4282 | Climber | Seeds, Leaves | Skin infection | Topical | Paste of dry seeds and leaves are used against skin parasites (49). | 0.51 |
| Viola canescens Wall. |  | Violaceae | Banaksha | SUBMS/BOT-4283 | Herb | Leaves, Flowers, Stem, Roots | Dysentery, Cold, Cough, Skin infection | Oral, Topical | Powder of whole plant with hot water is used for dysentery. Decoction of flowers along with fennel is used to cure cold and cough. Paste of fresh leaves and stem is used to treat skin infections (61). | 0.63 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prakash, P.; Radha; Kumar, M.; Pundir, A.; Puri, S.; Prakash, S.; Kumari, N.; Thakur, M.; Rathour, S.; Jamwal, R.; et al. Documentation of Commonly Used Ethnoveterinary Medicines from Wild Plants of the High Mountains in Shimla District, Himachal Pradesh, India. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7100351
Prakash P, Radha, Kumar M, Pundir A, Puri S, Prakash S, Kumari N, Thakur M, Rathour S, Jamwal R, et al. Documentation of Commonly Used Ethnoveterinary Medicines from Wild Plants of the High Mountains in Shimla District, Himachal Pradesh, India. Horticulturae. 2021; 7(10):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7100351
Chicago/Turabian StylePrakash, Pramod, Radha, Manoj Kumar, Ashok Pundir, Sunil Puri, Suraj Prakash, Neeraj Kumari, Mamta Thakur, Sonia Rathour, Radhika Jamwal, and et al. 2021. "Documentation of Commonly Used Ethnoveterinary Medicines from Wild Plants of the High Mountains in Shimla District, Himachal Pradesh, India" Horticulturae 7, no. 10: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7100351
APA StylePrakash, P., Radha, Kumar, M., Pundir, A., Puri, S., Prakash, S., Kumari, N., Thakur, M., Rathour, S., Jamwal, R., Janjua, S., Ali, M., Bangar, S. P., Singh, C., Chandran, D., Rajalingam, S., Senapathy, M., Dhumal, S., Singh, S., ... Abdel-Daim, M. M. (2021). Documentation of Commonly Used Ethnoveterinary Medicines from Wild Plants of the High Mountains in Shimla District, Himachal Pradesh, India. Horticulturae, 7(10), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7100351










