Abstract
Due to the high respiration rate and ethylene production at the cut surface of bamboo (Dendrocalamus latifloxus Munro) shoots after harvesting, browning and lignification at the cut surface reduce their quality and shelf life. Due to the demand of consumers, using physical treatment to inhibit microbial growth and maintain quality has become more and more popular. In this study, bamboo shoots were treated with hot water at 70 °C for 30 s after harvesting and then stored at 1, 3, or 5 °C for 4 weeks to measure the quality change. Our results show that the L* value and h° angle at the cut surface of the bamboo shoots were significantly higher, but the respiration rate was significantly lower when stored at 1 °C compared with those at 3 and 5 °C. In terms of quality, the bamboo shoots showed lower firmness and cutting force values, and no decay was observed at 1 °C. The results from the shelf simulation test with rewarming of the cold-treated bamboo shoots at ambient temperature (25 °C) for 1 day indicated that the L* value and h° angle were significantly higher for the bamboo shoots stored at 1 °C compared with those stored at 3 and 5 °C. Taken together, browning and lignification at the cut surface were effectively inhibited, quality was maintained, and the storage life could be extended to 4 weeks at 1 °C.
1. Introduction
Bamboo (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro) is a perennial monocotyledonous plant which belongs to the Poaceae family and is distributed widely below an altitude of 500 m in Taiwan. It thrives in humid and warm climate conditions, particularly when temperatures range between 20 and 30 °C and there is adequate water supplementation. Tender and young bamboo shoots are considered an important vegetable in Asia because they are rich in proteins, minerals, carbohydrates, and dietary fiber, which are beneficial to human health. The edible part of the bamboo shoot consists of rapidly growing meristematic tissues, but current harvesting methods cause a large cut surface at the bottoms of young shoots. It is a challenge to extend the shelf life of bamboo shoots after harvesting due to the high respiration rate of meristematic tissues and wound-induced ethylene of the cut areas [1]. These intensive physiological changes result in tissue browning and lignification at the cut surface, increase firmness, deteriorate quality, and reduce the shelf life [2,3]. After harvesting, bamboo shoots are typically transported at ambient temperature in Taiwan. However, this practice often results in a limited shelf life of three days in traditional markets or auction markets.
Browning and lignification of bamboo shoots during storage are associated with enzymatic reactions activated by enzymes such as phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL), polyphenol oxidase (PPO), and peroxidase (POD) [2,4,5,6,7]. Lower temperatures can delay the activation process of enzymes related to lignification and browning and slow down the metabolic process of respiration and ethylene production, thus maintaining better postharvest quality and extending the shelf life of bamboo shoots [8]. Moreover, appropriate temperatures not only reduce respiration rates and ethylene production but also inhibit microbial growth. On the contrary, storage under inappropriate low temperatures could induce signs of chilling injury symptoms, such as water-soaked brown flesh [9,10].
Previous studies indicated that postharvest treatments such as modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), hot air, UV-C, gamma irradiation, 1-methylcyclopropene (1-MCP), salicylic acid, and oxalic acid may effectively prevent quality deterioration of bamboo shoots (Phyllostachys praecox f. prevernalis) during storage [9,11,12,13,14,15]. Among these, hot air treatment (heat treatment) is considered to be friendly to human health and the environment. Optimal heat treatment condition might enhance the chilling injury tolerance of horticultural products by maintaining cell membrane integrity, increasing the synthesis of heat shock proteins (HSPs), and activating antioxidant systems [16,17]. Furthermore, heat treatment affected the total phenolic content (TPC) and the PAL, PPO, and POD activities of horticulture crops during storage, thereby delaying browning [13,18,19]. Additionally, the optimal storage temperature for bamboo shoots (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro) has still not been thoroughly investigated. Therefore, the present study aims to explore the effect of hot water treatment followed by low-temperature storage on the activities of browning-related enzymes and the quality of bamboo shoots as well as determine their optimal storage temperature.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
Bamboo shoots (Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro) were harvested in the early morning from a plantation located in the Taiping District of Taichung, Taiwan and then transferred to a laboratory within 3 h. Harvested bamboo shoots with a uniform size (weighing approximately 2 kg) and without blemishes or diseases were sampled for experimentation.
2.2. Treatments and Storage Conditions
The outer layer of a bamboo shoot was first cleaned with tap water and air-dried for 1 h. After a segment of each shoot (approximately 1–2 cm in length) was trimmed off from the base, the shoots were immersed in hot water at 70 °C for 30 s. Each bamboo shoot was then dried immediately and individually sealed in a 0.03 mm LDPE bag, and 10 bags were packaged in 1 box. The boxed bamboo shoots were then subjected to three different storage temperature treatments—1, 3, or 5 °C—for 4 weeks, with each treatment having 5 replicates and each replicate consisting of one box. After the low-temperature treatment, the LDPE bag was removed, and the bamboo shoots were rewarmed at ambient temperature (25 °C) for 1 day to simulate shelf conditions. The shoot color, firmness, cutting force, weight loss, decay ratio, electrolyte leakage, respiration rate, and ethylene production rate were assessed at the second, third, and fourth weeks after storage. Shoot flesh was sampled from the base portion of the bamboo shoot at 5 cm above the shoot base, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −20 °C for measurements of the TPC and enzyme activities.
2.3. Measurement of Color
The color at the cut surface of a bamboo shoot was determined by using a portable spectrophotometer (MiniScan EZ 4000S, HunterLab, Reston, VA, USA) with D65 illuminant. The color was indicated by the L* value (lightness), a* value (redness-greenness), b* value (yellowness-blueness), C* value (chroma), and h° value (hue angle). Three points at the cut surface of each shoot were measured and averaged as one replication, with a total of 5 replications per treatment.
2.4. Determination of Decay Ratio
The decay ratio was evaluated by calculating the percentage of bamboo shoots showing the presence of microbial lesions or mucilage along with an odor at the cut surface according to the following formula:
Decay ratio (%) = (number of bamboo shoots with microbial lesions at the cut surface/total number of bamboo shoots) × 100%
2.5. Measurement of Weight Loss
Weight loss was measured by determining the weight difference between the initial weight of a bamboo shoot before storage and the weight of a bamboo shoot recorded at the sampling date, and the ratio of weight loss was calculated according to the following formula:
Weight loss ratio (%) = [(shoot weight before storage − shoot weight after storage)/shoot weight before storage] × 100%
2.6. Measurement of Texture
The firmness and cutting force of the bamboo shoots were determined by a rheometer (CR-100, Sun Scientific Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) equipped with a round probe 0.5 cm in diameter and a sharp blade, measured at a rate of 100 mm·min−1. Firmness was expressed as an average value of the firmness measured in the middle (about 5 cm above the bottom) and in the bottom portion of each sampling shoot.
To measure the cutting force, a drill with a diameter of 16 mm was used to drill a cylinder flesh sample from the shoot at a position 5 cm above the bottom. The shoot cylinder was placed horizontally on the platform of the rheometer and measured by vertically cutting with a sharp blade. The cutting force was expressed as an average value evaluated at two random sites of the shoot cylinder. Five shoots from each treatment were evaluated.
2.7. Measurement of Electrolyte Leakage
Electrolyte leakage was measured according to the method of Woolf [20] and Luo et al. [9] with some modifications. In brief, each disc (approximately 1 mm thick and 16 mm in diameter) was excised from the bottom of the shoot cylinder as mentioned above, rinsed with deionized water, incubated in 10 mL of 300 mmol/L mannitol, and shaken at 100 rpm for 3 h at ambient temperature. The initial conductivity was monitored at 25 °C with a conductivity meter (Suntex SC-2300, Suntex Instruments Co., Ltd., Taiwan). Then, each sample was frozen at −20 °C for 3 days, thawed, and frozen again at −20 °C to completely disrupt the cells. After the second thawing, the total electrolyte conductivity was monitored by incubating the sample in 10 mL of 300 mmol/L mannitol and shaken at 100 rpm for 3 h at ambient temperature. The electrolyte leakage was expressed as a percentage of the initial conductivity versus the total conductivity.
2.8. Measurements of Respiration Rate and Ethylene Production
To measure the respiration rate, five bamboo shoots from each temperature treatment were placed in a closed chamber (one bamboo shoot per chamber) at 25 °C for 1 h. Then, 1 mL of gas was extracted from the chamber using a plastic syringe and injected into the infrared CO2 analyzer (UNOR 610, Maihak AG, Hamburg, Germany).
For determination of the ethylene production, 1 mL of gas was also extracted from the same chamber mentioned above and then injected into a gas chromatography detector (GC-8A, Shimadzu Scientific Instruments Inc., Columbia, MD, USA).
2.9. Measurement of TPC
The TPC was determined according to the method of Keith et al. [21] with some modifications. Two grams of a bamboo shoot flesh sample was homogenized with 5 mL of 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) and then centrifuged with 20,000× g at 4 °C for 20 min. One mL of the supernatant was mixed with 0.1 mL of Folin–Ciocalteu phenol reagent and 0.2 mL of 20% sodium carbonate. The mixed solution was diluted to a total volume of 10 mL with distilled water and heated in boiling water for 3 min. The TPC was then measured at 660 nm with an Elisa Reader (BMG LABTECH, FLUOstar Omega Ω, Ortenberg, Germany) and expressed as micrograms of caffeic acid equivalents per g FW.
2.10. PAL Activity
The PAL activity was assayed using the method of Zhou et al. [22]. One unit of PAL activity was defined as an increase of 0.001 in OD290 per min per g FW.
2.11. PPO and POD Activities
Two grams of a bamboo shoot flesh sample was homogenized with 5 mL of different buffers to assay the activities of different enzymes. Sodium borate buffer (0.1 M, pH 8.8) containing 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 2 mM EDTA, and 1% (v/v) polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP) was used for PAL analysis, and phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.0) containing 0.25% triton and 1% (v/v) PVPP was used for measurements of both the POD and PPO activities. The mixtures were centrifuged (20,000× g, 4 °C, 20 min), and the supernatants were used to determine the enzymatic activities. All steps were carried out at 4 °C. POD activity was assayed through the method of Johnson and Cunningham [23], and PPO activity was assayed using the method of Lee and Smith [24] with some modifications. The PPO and POD activities were expressed as a change of 0.01 in OD420 and OD490 per min per g FW, respectively.
2.12. Statistical Analysis
The experiments were laid out in a completely randomized design. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed, and means were compared using the least significant difference (LSD) (p < 0.05). The analyses were performed using the statistical software COSTAT 6.4 (CoHort Software, Pacific Grove, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Storage Duration and Temperature on Visual Appearance of Bamboo Shoots
Temperature is the major factor affecting physiological and metabolic processes such as browning in bamboo shoots during storage. Thus, it was critical to study the optimal storage temperature. The L* value of the bamboo shoots significantly declined with the storage duration at 5 °C, while it kept a similar value at 1 °C. Similarly, after 4 weeks of storage, the L* value for the bamboo shoots at 5 °C (84.24) was significantly lower than the L* value for those stored at 1 °C (86.66). In addition, the bamboo shoots at 5 °C showed a higher a* value and lower h° value, but a lower a* value and higher h° value were observed at 1 °C (Table 1). Because there was negative correlation between browning and both the L* and h° values, these results suggest that a storage temperature of 1 °C might effectively slow down the browning process at the cut surface of bamboo shoots.

Table 1.
Effects of storage duration and temperature on color at cut surface of postharvest bamboo shoots stored at 1, 3, and 5 °C for 2 (2W), 3 (3W), and 4 (4W) weeks.
The L* and h° values at the cut surface of the bamboo shoots were significantly lower, but the a* value was higher for those stored at 5 °C compared with those stored at 1 °C after rewarming for one day at 25 °C (Table 2), indicating that the browning was more severe after rewarming for those stored at 5 °C. Moreover, the decay ratio was 10% at 3 °C and 80% at 5 °C after 4 weeks of storage (Figure 1). However, no microbial contamination was observed at the cut surface of the bamboo shoots after 4 weeks of storage at 1 °C and rewarming at 25 °C for 1 day (Figure 1).

Table 2.
Effects of storage duration, temperature, and rewarming on color at cut surface of postharvest bamboo shoots stored at 1, 3, and 5 °C for 2 (2W), 3 (3W), and 4 (4W) weeks and then rewarmed at 25 °C for 1 day (1D).
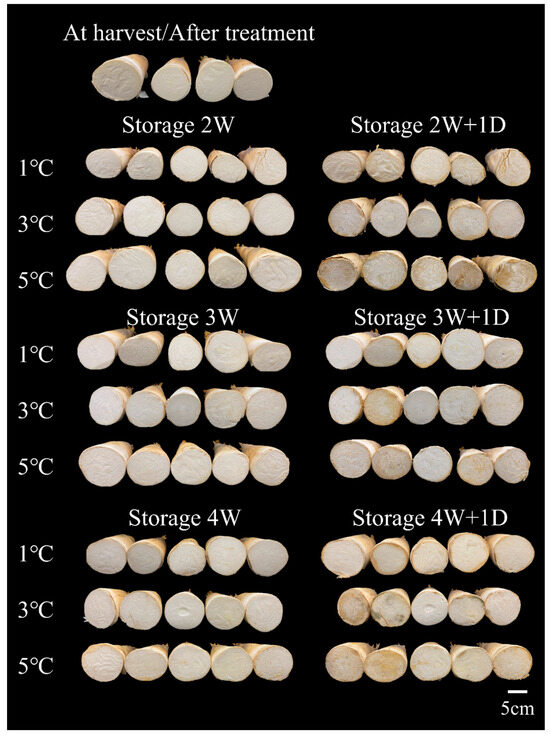
Figure 1.
Effects of storage duration and temperature on appearance of postharvest bamboo shoots. Bamboo shoots were stored at 1, 3, and 5 °C for 2 (2W), 3 (3W) and 4 (4W) weeks and then rewarmed at 25 °C for 1 day (1D).
3.2. Effects of Storage Duration and Temperature on Respiration Rates of Bamboo Shoots
The edible part of bamboo is the tender young shoot with a large wounding area at the base when harvested, and thus the respiration rates were high, with a value of 239.06 mL·CO2 kg−1·h−1 (Figure 2). Low-temperature storage could significantly reduce the metabolic rate and respiration rate of bamboo shoots. In this study, ethylene was not detected during low-temperature storage from 1 to 5 °C. The respiration rate of the bamboo shoots stored at 1 °C decreased gradually throughout the course of storage. After storage for 4 weeks, the respiration rate of those stored at 1 °C was 42.98 CO2 mL·kg−1·h−1, which was significantly lower than the rate of those stored at 5 °C, with a value of 173.89 mL CO2·kg−1·h−1. The respiration rates of the bamboo shoots stored at 5 °C for 2, 3, or 4 weeks were 1.4, 3.4, and 4 times higher than those stored at 1 °C, respectively. Overall, storage at 1 °C might significantly suppress the respiration rate during the storage and shelf-life period (Figure 2).
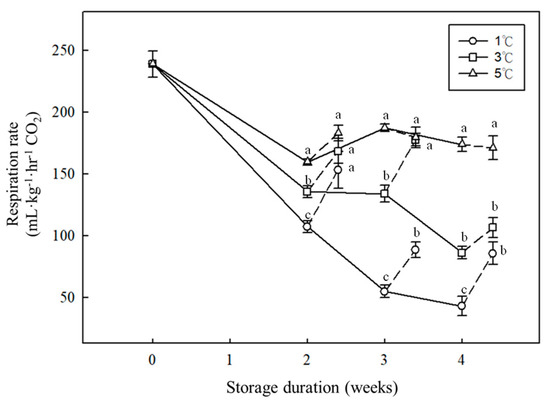
Figure 2.
Effects of storage duration and temperature on respiration rate of postharvest bamboo shoots. Bamboo shoots were stored at 1, 3, or 5 °C for 2, 3, and 4 weeks. Dashed line represents the respiration rate of stored samples after rewarming at 25 °C for 1 day. Vertical bars represent standard error (n = 5). Means between different treatments in the same storage duration with the same letters were not significantly different at p < 0.05 according to LSD test.
3.3. Effects of Storage Duration and Temperature on Firmness and Cutting Force of Bamboo Shoots
Compared with the bamboo shoots stored at 1 °C and 3 °C, those at 5 °C exhibited the highest firmness, with a value of 166.90 N·cm−2 after 2 weeks of storage and 149.88 N·cm−2 after 4 weeks of storage (Figure 3a). Similarly, the bamboo shoots stored at 5 °C exhibited a higher cutting force value throughout the course of storage than those stored at 1 °C and 3 °C. For the bamboo shoots stored at both 1 °C and 3 °C for 4 weeks, the cutting force was similar to that of the fresh shoots (0 weeks), while the cutting force of those stored at 5 °C for 4 weeks was 1.9 times higher than that of the fresh shoots (Figure 3b). Therefore, storage at 1 °C significantly alleviated the increase in firmness and cutting force during storage.
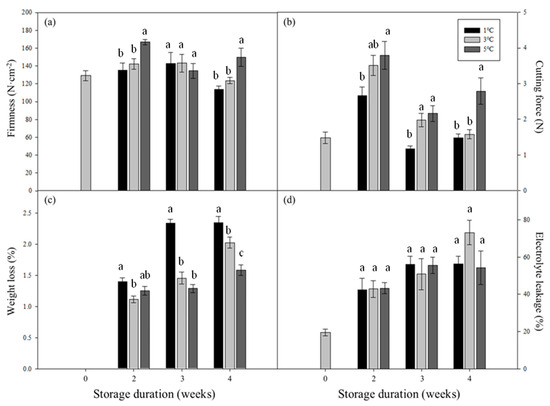
Figure 3.
Effects of storage duration and temperature on firmness (a), cutting force (b), weight loss (c), and electrolyte leakage (d) of postharvest bamboo shoots. Bamboo shoots were stored at 1, 3, and 5 °C for 2, 3 and 4 weeks. Vertical bars represent standard error (n = 5). Means between different treatments in the same storage duration with the same letters were not significantly different at p < 0.05 according to LSD test.
3.4. Effects of Storage Duration and Temperature on Weight Loss and Electrolyte Leakage of Bamboo Shoots
The weight loss of the bamboo shoots increased with the storage duration from 1 to 5 °C. However, there was a negative correlation between weight loss and temperature (1–5 °C). After storage for 4 weeks, the bamboo shoots stored at 1 °C showed significant weight loss (2.34%), followed by those stored at 3 °C (2.03%) and those stored at 5 °C (1.59%) (Figure 3c).
Electrolyte leakage has been considered as an indicator of membrane damage and a qualitative indicator of chilling injury. Our results show that electrolyte leakage increased as the storage duration increased. However, no significant difference was observed during 1–5 °C storage for 2–3 weeks (Figure 3d).
3.5. Effects of Storage Duration and Temperature on TPC and PPO, POD, and PAL Activities of Bamboo Shoots
The TPC and activities of browning-related enzymes were determined under various storage durations and temperatures to understand the effects of the storage duration and temperature on the browning of bamboo shoots at the cut surface. The bamboo shoots stored at 3 °C for 4 weeks exhibited a significantly higher TPC (1030.9 μg·g−1 FW) than other treatments. Furthermore, the storage duration or storage temperature displayed no significant effect on TPC, but their interaction had a significant effect on the TPC (Table 3).

Table 3.
Effects of storage duration and temperature on TPC content and enzymatic activities of POD, PPO, and PAL in postharvest bamboo shoots stored at 1, 3, and 5 °C for 2 (2W), 3 (3W), and 4 (4W) weeks.
The storage duration had significant effects on the PPO and POD activities. After storage for 2 weeks, PPO activity was significantly higher at 5 °C compared with that at 3 °C. In addition, PPO showed significantly higher activity for those shoots stored at 3 °C relative to that for the shoots stored at 5 °C after 3 weeks of storage. After 4 weeks of storage, no significant difference in PPO activity was detected among those shoots stored at 1–5 °C. POD activity increased after storage at 1 °C and 3 °C for 4 weeks, with values of 2328 and 2243 U·g−1 FW, respectively, which were significantly higher than those for the shoots stored at 5 °C (1653 U·g−1 FW) (Table 3).
The storage temperature had significant effects on PAL activity. After storage for 3 weeks, the PAL activity increased from 279.2 U·g−1 FW at 1 °C to 346.8 U·g−1 FW at 5 °C. On the contrary, after storage for 4 weeks, the PAL activity at 1 °C increased to a value of 401.5 U·g−1 FW, which was significantly higher than that for the shoots stored at 5 °C, with a lower value of 206.0 U·g−1 FW (Table 3).
4. Discussion
The primary factor influencing the physiological metabolism of postharvest bamboo shoots is the storage temperature [8]. Finding the optimal storage temperature for bamboo shoots is crucial to maintain quality and extend their shelf life. Although low-temperature storage could inhibit the activities of browning-related enzymes and microbial growth, inappropriate low temperatures may result in chilling injury symptoms and reduce marketability [9,10]. As the bamboo shoot consists of rapidly growing meristematic tissues, harvested bamboo shoots exhibit high metabolic activity and a short shelf life. Moreover, the harvesting method results in a large wound at the bottom, which induces wound ethylene. Therefore, it is critical to slow down the respiration rate of bamboo shoots to prolong their storage duration [15]. Therefore, a temperature of 1 °C is recommended for 4 weeks of storage to maintain a low respiration rate and high quality.
The browning of bamboo shoots shortens their shelf life, and the severity of browning is negatively correlated with the L* and h° values [25,26]. In this study, the bamboo shoots stored at 5 °C showed significantly lower L* and h° values and higher a* and b* values, indicating obvious browning at the cut surface. After one day of rewarming at 25 °C, the browning became even more pronounced (Table 1 and Table 2, Figure 1). Conversely, the bamboo shoots at 1 °C maintained a bright and white cut surface which was not significantly different from those of the freshly harvested ones.
While most vegetables and fruits become tender and turned soft after harvesting, bamboo shoots exhibit a rapid increase in firmness after harvesting due to tissue lignification and lose their commercial value [2,7]. Lignin synthesis starts with the conversion of phenylalanine to cinnamic acid catalyzed by PAL, following a series of enzymatic reactions to form lignin monomers. These monomers are then polymerized into large lignin molecules by POD [27]. Luo et al. [8] showed that low-temperature storage inhibits the activity of lignification-related enzymes such as PAL, cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD), and POD, which in turn delays the accumulation of lignin and cellulose and slows down the increase in firmness. In several studies, there has been a significant positive correlation observed between the contents of lignin and cellulose in postharvest bamboo shoots and their firmness [4,8,12]. Similarly, we analyzed changes in firmness and cutting force to investigate lignification in postharvest bamboo shoots. Our results indicate that the bamboo shoots stored at 1 °C exhibited 24% and 47% reductions in firmness and cutting force, respectively, compared with those shoots stored at 5 °C. Additionally, storing bamboo shoots at 5 °C did not effectively prevent the increase in firmness or cutting force, while storage at 1 °C could maintain a texture and crispness similar to fresh ones (Figure 2 and Figure 3a,b). Our data reveal that both the POD and PAL activities of the bamboo shoots were significantly higher when stored at 1 °C relative to those stored at 5 °C after 4 weeks of storage. However, the PAL activity showed an opposite trend upon 3 weeks of storage (Table 3), suggesting that the process of lignin and cellulose accumulation might take place earlier when stored at 5 °C compared with 1 °C.
Many research findings indicated that browning and lignification of bamboo shoots during storage are related to their associated enzyme activities, such as PAL, PPO, and POD [2,3,4,5,7,9,13,14]. However, our results show that the storage temperature had no significant effect on the TPC or PPO or POD activities (Table 3), which might be attributed to the relatively small temperature differences between 1, 3, and 5 °C. Nonetheless, there were significant differences in the PAL activities among the bamboo shoots stored at 1, 3, and 5 °C for 3 and 4 weeks. Because PAL is a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of phenolic compounds, the browning reaction might have taken place earlier in the bamboo shoots stored at 5 °C for 3 weeks, as indicated by the higher PAL activity at this temperature (Table 3). On the other hand, the bamboo shoots stored at 1 °C for 4 weeks showed a higher PAL activity, indicating that the browning reaction initiated more slowly compared with those stored at 5 °C (Table 3). PAL serves as the most upstream enzyme in the shikimic acid pathway. It converts phenylalanine to cinnamic acid by removing the amino group and leads to the biosynthesis of several secondary metabolites, including lignin, tannins, and flavonoids [27,28]. Based on this, increased PAL activity might also lead to higher levels of precursor compounds for polyphenol biosynthesis. Whether the reaction moves toward polyphenol or lignin biosynthesis depends on its downstream enzyme activities.
Our results show that the POD activity increased as the storage duration increased, and the bamboo shoots stored at 1 °C and 3 °C for 4 weeks had higher POD activity than those stored at 5 °C (Table 3). Furthermore, fewer browning symptoms and lower firmness and lignification at the cut surface were detected in the bamboo shoots stored at 1 °C and 3 °C relative to those stored at 5 °C (Table 1; Figure 3a,b). This might be attributed to activation of the antioxidant system by POD, because POD plays a vital role in scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS). During long-term and cold storage, bamboo shoots may suffer oxidative stress due to the accumulation of ROS, and high POD activity may mitigate oxidative damage.
Low-temperature storage effectively inhibited physiological metabolism and extended the shelf life. However, some research results also indicate that low-temperature storage could lead to increased electrolyte leakage, the incidence of chilling injury, or a higher browning index in postharvest bamboo shoots [3,9,10,12]. In this study, the bamboo shoots stored at 1, 3, and 5 °C did not exhibit significant differences in electrolyte leakage (Figure 3d), and no chilling injury symptoms were observed. Moreover, the bamboo shoots stored at 1 °C still showed significantly lower respiration rates after rewarming at 25 °C for 1 day (Figure 2). Because chilling injury symptoms often appeared and worsened after rewarming, our results indicate that the bamboo shoots stored at 1 °C did not suffer from membrane damage during the rewarming period.
5. Conclusions
Our results suggest that storing bamboo shoots at 1 °C could effectively prevent decay and browning at the cut surface, and this effect may extend to the rewarming period at 25 °C for 1 day. Furthermore, bamboo shoots stored at 1 °C could maintain a low respiration rate and high-quality traits, including a low decay ratio, less browning, and vegetable crispness, because browning-related enzymes and lignification would be effectively inhibited.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision, and writing, H.-L.L.; methodology, writing—original draft, conduction of experiment, and statistical analyses, P.-R.W.; data interpretation, writing, and editing, S.-G.H.; writing, review, and editing, C.-L.C. This paper is a part of the first author’s master thesis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fresh preservation packaging material performance testing (NCHU:111DA220).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge expert advice from Ching-Chang Shiesh in the Department of Horticulture at National Chung Hsing University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Ye, F.; He, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, G. A systematic review on the composition, storage, processing of bamboo shoots: Focusing the nutritional and functional benefits. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 71, 104015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Limwachiranon, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Fu, M.; Luo, Z. Hydrogen peroxide accelerated the lignification process of bamboo shoots by activating the phenylpropanoid pathway and programmed cell death in postharvest storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 153, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, X. Effect of oxalic acid on edible quality of bamboo shoots (Phyllostachys prominens) without sheaths during cold storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 109, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Cai, Z.; Yan, B. Effects of ethylene and 1-methylcyclopropene (1-MCP) on lignification of postharvest bamboo shoot. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, C.; Wu, F.; Cheng, J. Effect of nitric oxide on browning and lignification of peeled bamboo shoots. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2010, 57, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zheng, J.; Huang, C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H.; Sun, Z. Effects of combined aqueous chlorine dioxide and chitosan coatings on microbial growth and quality maintenance of fresh-cut bamboo shoots (Phyllostachys praecox f. prevernalis.) during storage. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Suo, J.; Xuan, L.; Ding, M.; Zhang, H.; Song, L.; Ying, Y. Bamboo shoot-lignification delay by melatonin during low temperature storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 156, 110933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Yan, B. Accumulation of lignin and involvement of enzymes in bamboo shoot during storage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wu, X.; Xie, Y.; Chen, C. Alleviation of chilling injury and browning of postharvest bamboo shoot by salicylic acid treatment. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Luo, Z.; Zeng, F.; Jiang, L.; Tang, K. Effect of brassinolide on energy status and proline metabolism in postharvest bamboo shoot during chilling stress. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 111, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Kong, F.; Wang, Q. Effect of modified atmosphere packaging on the browning and lignification of bamboo shoots. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Yan, B. Use of 1-methylcyclopropene for alleviating chilling injury and lignification of bamboo shoot (Phyllostachys praecox f. prevernalis) during cold storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Feng, S.; Pang, J.; Mao, L.; Shou, H.; Xie, J. Effect of heat treatment on lignification of postharvest bamboo shoots (Phyllostachys praecox f. prevernalis.). Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2182–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Z. Effect of UV-C treatment on modulating antioxidative system and proline metabolism of bamboo shoots subjected to chilling stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Luo, Z.; Xie, J.; Feng, S. Gamma radiation control quality and lignification of bamboo shoots (Phyllostachys praecox f. prevernalis.) stored at low temperature. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2015, 102, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, M.S.; Sevillano, L.; Flores, F.B.; Bodbodak, S. Heat shock proteins as biochemical markers for postharvest chilling stress in fruits and vegetables. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 160, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, M.S.; Bodbodak, S. Postharvest heat treatment for mitigation of chilling injury in fruits and vegetables. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 7, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Alvarez, M.; Salazar-Salas, N.Y.; López-Angulo, G.; Pineda-Hidalgo, K.V.; López-López, M.E.; Vega-García, M.O.; Delgado-Vargas, F.; López-Valenzuela, J.A. Metabolomic changes in mango fruit peel associated with chilling injury tolerance induced by quarantine hot water treatment. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 169, 111299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Salas, N.Y.; Chairez-Vega, D.A.; Vega-Alvarez, M.; González-Nuñez, D.G.; Pineda-Hidalgo, K.V.; Chávez-Ontiveros, J.; Delgado-Vargas, F.; Lopez-Valenzuela, J.A. Proteomic changes in mango fruit peel associated with chilling injury tolerance induced by quarantine hot water treatment. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 186, 111838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, A.B. Reduction of chilling injury in stored ‘Hass’ avocado fruit by 38℃ water treatments. HortScience 1997, 32, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, R.W.; Le Tourneau, D.; Mahlum, D. Quantitative paper-chromatographic determination of phenols. J. Chromatogr. A 1958, 1, 534–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dahler, J.M.; Underhill, S.J.; Wills, R.B. Enzymes associated with blackheart development in pineapple fruit. Food Chem. 2003, 80, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.B.; Cunningham, B.A. Peroxidase activity in healthy and leaf-rust-infected wheat leaves. Phytochemistry 1972, 11, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Smith, N.L. Blanching effect on polyphenol oxidase activity in table beets. J. Food Sci. 1979, 44, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurila, E.; Kervinen, R.; Ahvenainen, R. The inhibition of enzymatic browning in minimally processed vegetables and fruits. Postharvest News Inf. 1998, 9, 53–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tsouvaltzis, P.; Deltsidis, A.; Brecht, J.K. Hot water treatment and pre-processing storage reduce browning development in fresh-cut potato slices. HortScience 2011, 49, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whetten, R.; Sederoff, R. Lignin biosynthesis. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, R.A.; Barros, J. Lignin biosynthesis: Old roads revisited and new roads explored. Open Biol. 2019, 9, 190215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).