Integration of RNA-Seq and Metabolite Analysis Reveals the Key Floral Scent Biosynthetic Genes in Herbaceous Peony
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
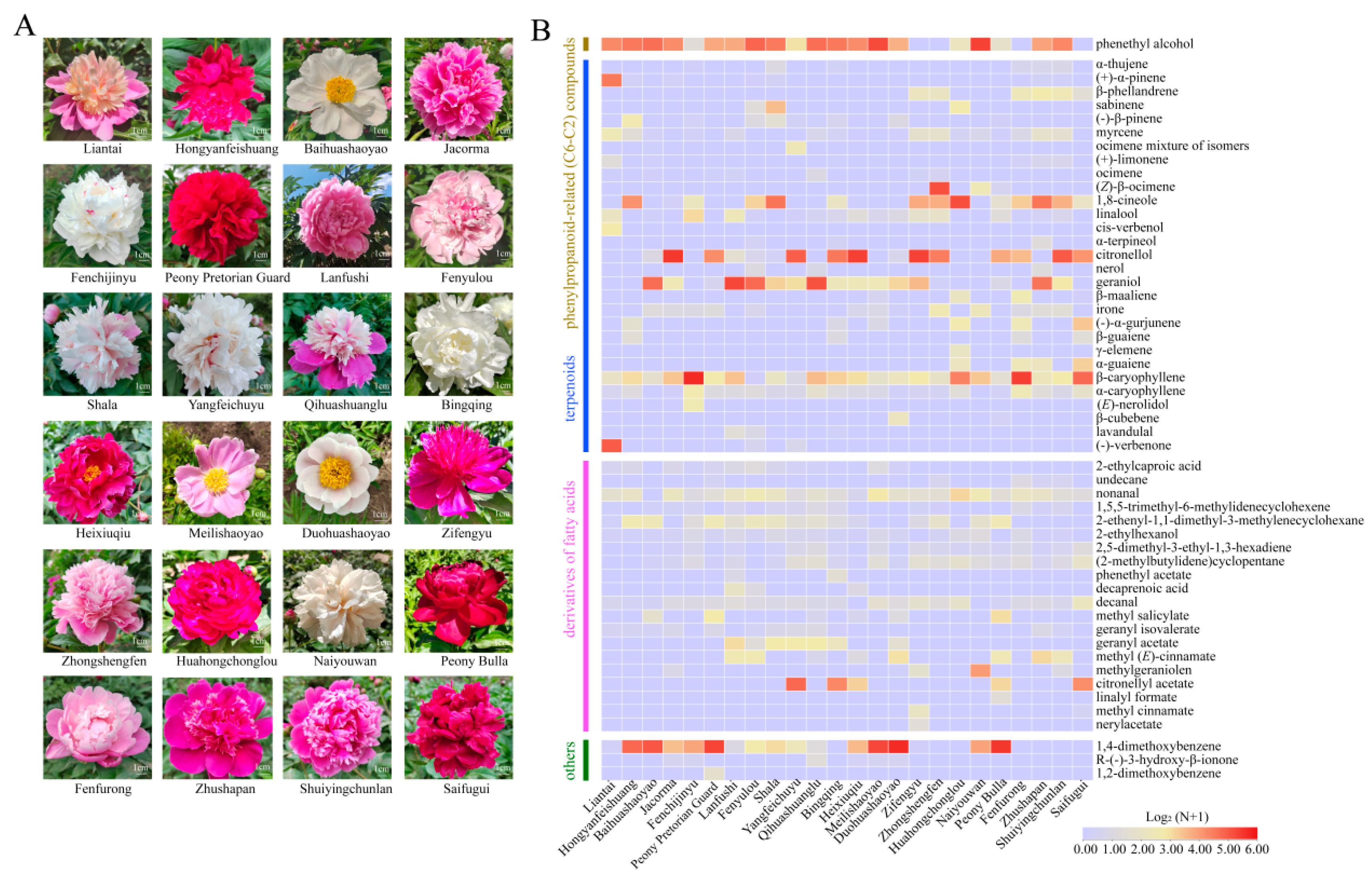
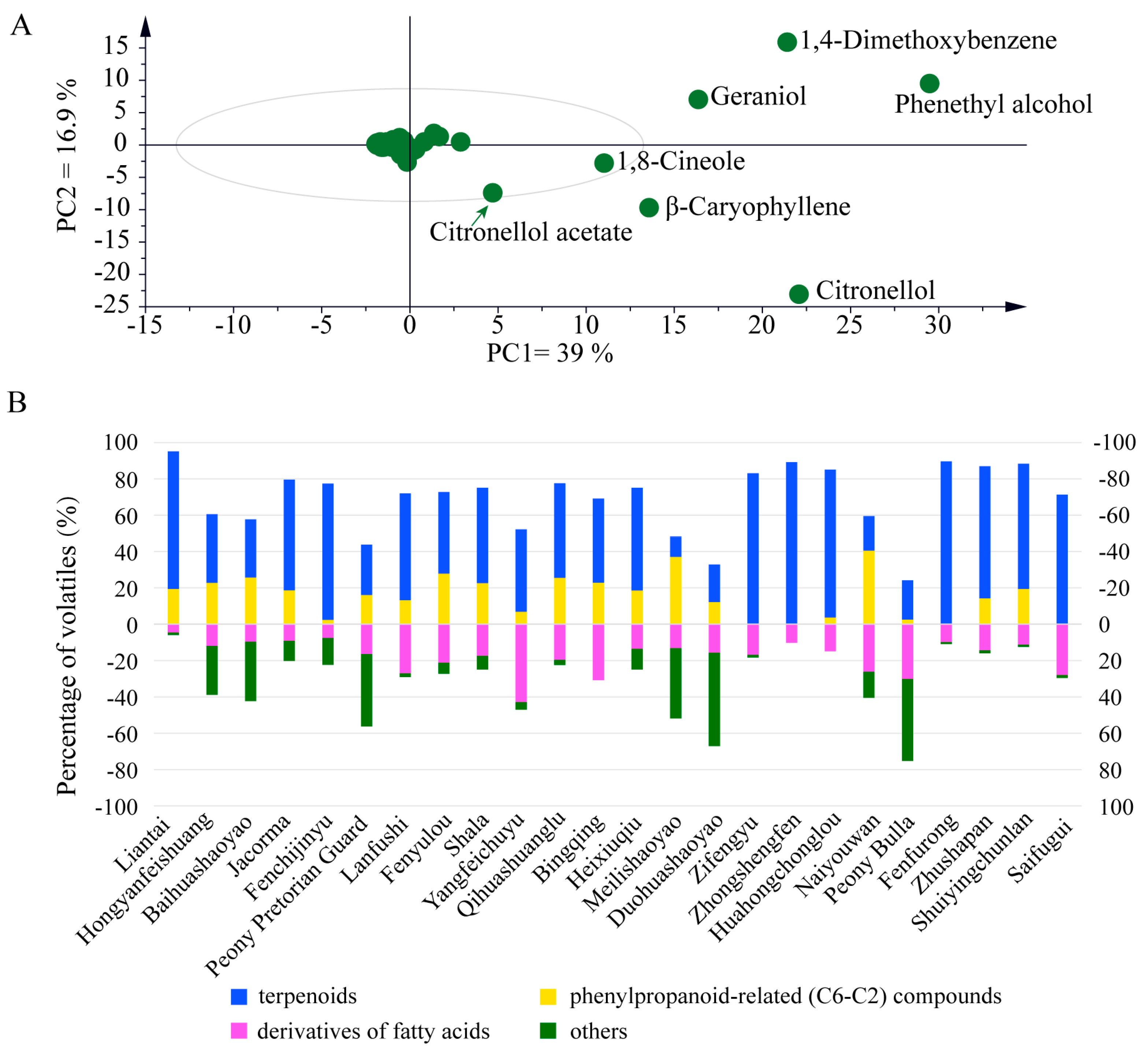
2.1. Cultivar-Specific Volatile Profiles Unveil the Intricate Levels and Blends of Floral Scent in Herbaceous Peony
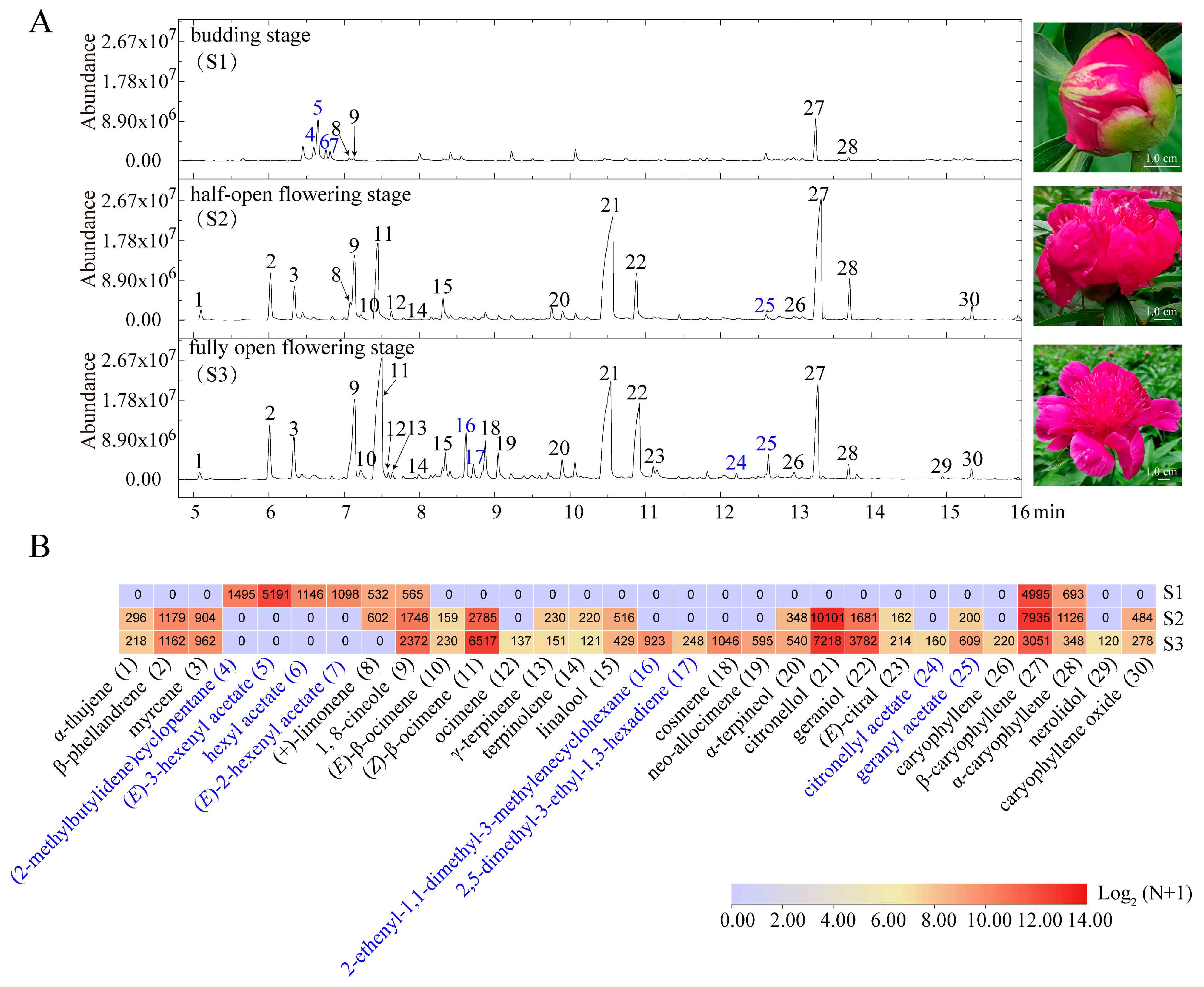
2.2. VOC Emission Profiles Vary across Different Flowering Stages in P. lactiflora cv. Zifengyu
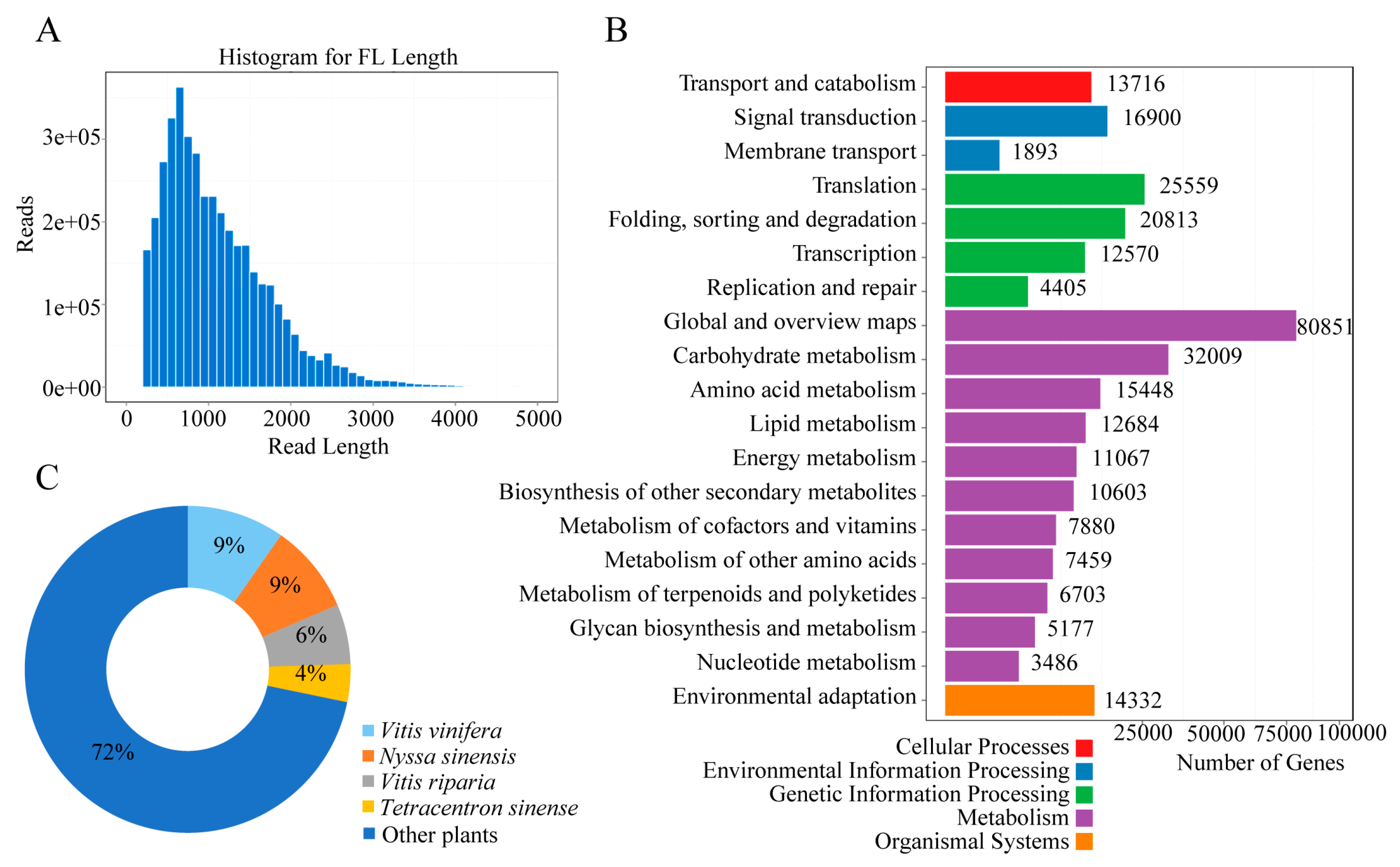
2.3. Transcriptomes Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
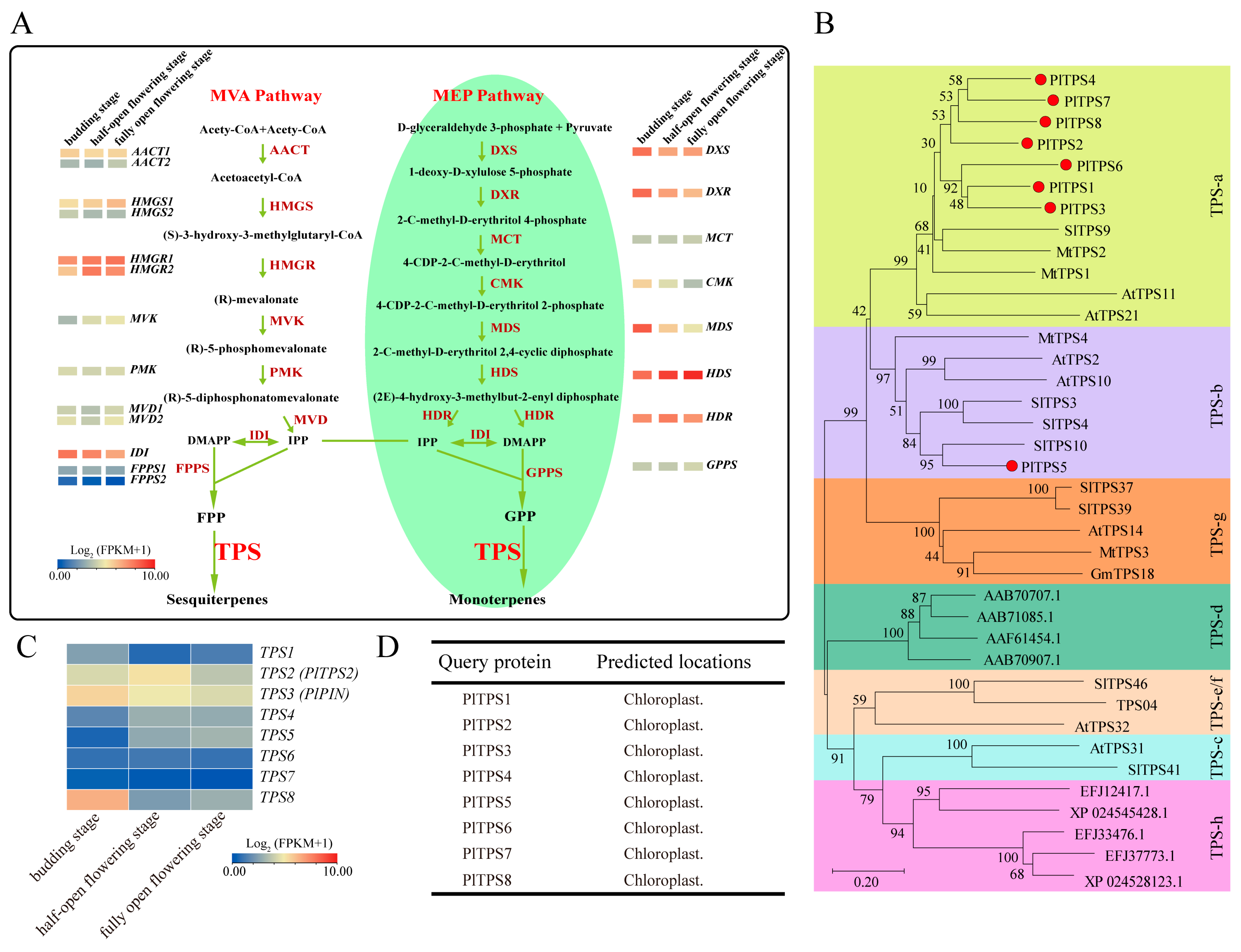
2.4. Screening of Candidate Genes Related to Terpenoid Biosynthetic Pathways
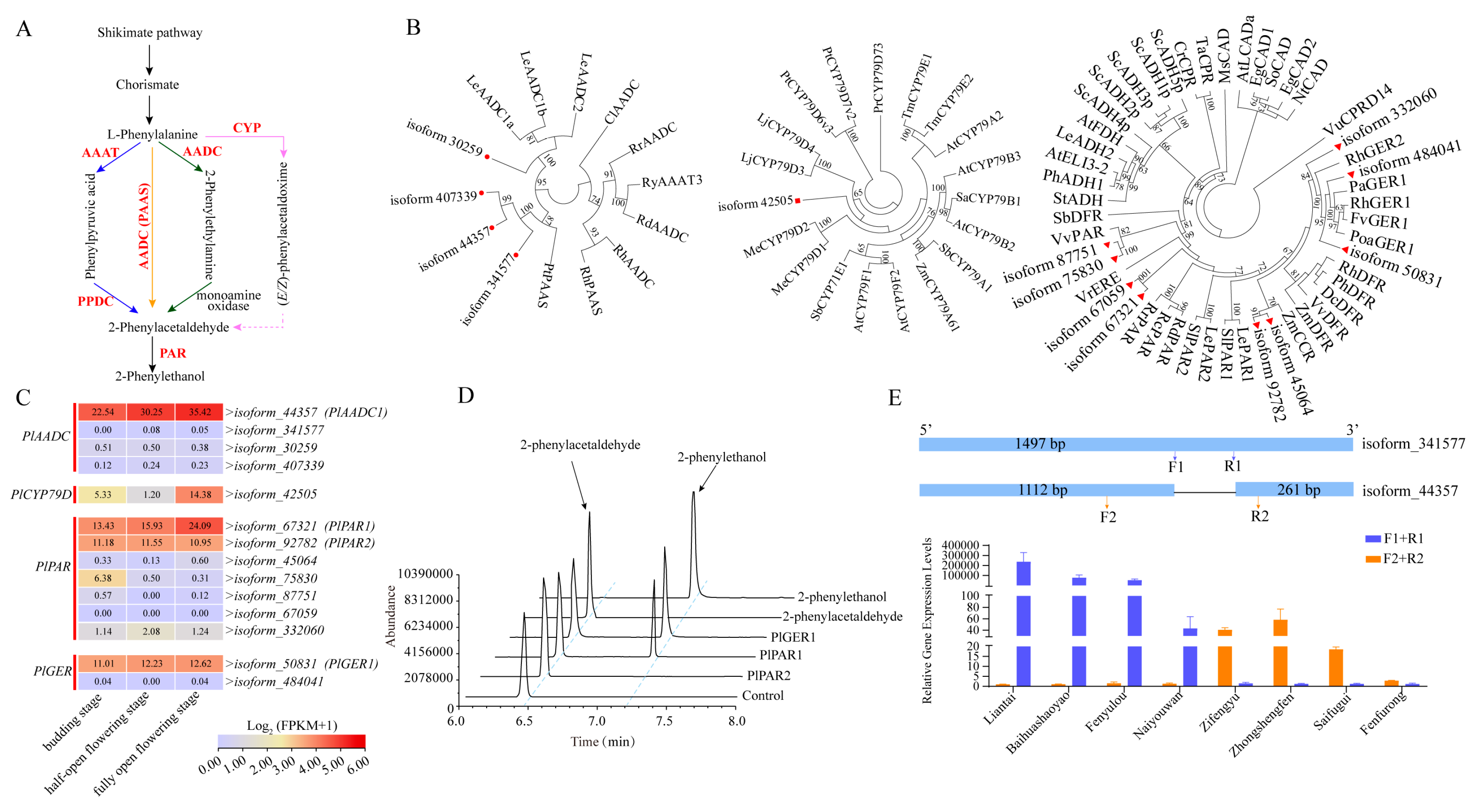
2.5. Screening of Candidate Genes Related to 2-PE Biosynthetic Pathway
3. Discussion
3.1. Terpenoids and 2-PE Represent the Primary Components of Peony, with Monoterpene Content Notably Surpassing That of Sesquiterpene
3.2. P. lactiflora cv. Zifengyu Is a Good Candidate for Extracting or Studying Rhodinol
3.3. 2-PE Diversity in Peonies Might Result from AADC Splice Variants
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
5.2. Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Floral Volatiles in Herbaceous Peonies
5.3. RNA Extraction
5.4. Library Construction, RNA Sequencing, and Data Processing
5.5. Identification and Analysis of Putative Genes Linked to Floral Scent
5.6. RT-qPCR Analysis
5.7. Molecular Cloning and Heterologous Expression of PAR and GER Genes
5.8. In Vitro Assay of PAR and GER from P. lactiflora
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dudareva, N.; Klempien, A.; Muhlemann, J.K.; Kaplan, I. Biosynthesis, function and metabolic engineering of plant volatile organic compounds. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tholl, D. Biosynthesis and biological functions of terpenoids in plants. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2015, 148, 63–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vranová, E.; Coman, D.; Gruissem, W. Network analysis of the MVA and MEP pathways for isoprenoid synthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 665–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, A.; Vaughan, M.; Schmelz, E.; Christensen, S. Biosynthesis and function of terpenoid defense compounds in maize (Zea mays). Planta 2019, 249, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daletos, G.; Katsimpouras, C.; Stephanopoulos, G. Novel strategies and platforms for industrial isoprenoid engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagegowda, D.A.; Gupta, P. Advances in biosynthesis, regulation, and metabolic engineering of plant specialized terpenoids. Plant Sci. 2020, 294, 110457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tholl, D.; Rebholz, Z.; Morozov, A.V.; O’Maille, P.E. Terpene synthases and pathways in animals: Enzymology and structural evolution in the biosynthesis of volatile infochemicals. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 766–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichersky, E.; Raguso, R.A. Why do plants produce so many terpenoid compounds? New Phytol. 2018, 220, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, L.A.; Jeffrey, C.S. Chemically Mediated Multi-trophic Interactions. In Plant-Animal Interactions: Source of Biodiversity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 17–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tetali, S.D. Terpenes and isoprenoids: A wealth of compounds for global use. Planta 2019, 249, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlemann, J.K.; Klempien, A.; Dudareva, N. Floral volatiles: From biosynthesis to function. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 1936–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Dudareva, N. The shikimate pathway and aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildermuth, M.C. Variations on a theme: Synthesis and modification of plant benzoic acids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, M.; Hirata, H.; Sayama, H.; Sekiguchi, K.; Itano, H.; Asai, T.; Dohra, H.; Hara, M.; Watanabe, N. Production of 2-phenylethanol in roses as the dominant floral scent compound from L-phenylalanine by two key enzymes, a PLP-dependent decarboxylase and a phenylacetaldehyde reductase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 2408–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, H.; Ohnishi, T.; Watanabe, N. Biosynthesis of floral scent 2-phenylethanol in rose flowers. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, H.; Ohnishi, T.; Tomida, K.; Ishida, H.; Kanda, M.; Sakai, M.; Yoshimura, J.; Suzuki, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Dohra, H. Seasonal induction of alternative principal pathway for rose flower scent. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieman, D.; Taylor, M.; Schauer, N.; Fernie, A.R.; Hanson, A.D.; Klee, H.J. Tomato aromatic amino acid decarboxylases participate in synthesis of the flavor volatiles 2-phenylethanol and 2-phenylacetaldehyde. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8287–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhandapani, S.; Jin, J.; Sridhar, V.; Chua, N.-H.; Jang, I.-C. CYP79D73 participates in biosynthesis of floral scent compound 2-phenylethanol in Plumeria rubra. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieman, D.M.; Loucas, H.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Clark, D.G.; Klee, H.J. Tomato phenylacetaldehyde reductases catalyze the last step in the synthesis of the aroma volatile 2-phenylethanol. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ul Hassan, M.N.; Zainal, Z.; Ismail, I. Green leaf volatiles: Biosynthesis, biological functions and their applications in biotechnology. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Yuan, M.; Li, B.; Niu, L.; Shi, Q. Transcriptome and volatile compounds profiling analyses provide insights into the molecular mechanism underlying the floral fragrance of tree peony. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 162, 113286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathe, U.; Tissier, A. Cytochrome P450 enzymes: A driving force of plant diterpene diversity. Phytochemistry 2019, 161, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Alseekh, S.; Fernie, A.R.; Luo, J. The structure and function of major plant metabolite modifications. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutanaev, A.; Moses, T.; Zi, J.; Nelson, D.; Mugford, S.; Peters, R.; Osbourn, A. Investigation of terpene diversification across multiple sequenced plant genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E81–E88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christenhusz, M.; Byng, J. The number of known plants species in the world and its annual increase. Phytotaxa 2016, 261, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wei, M.; Shi, M.; Hao, Z.; Tao, J. Identification and comparative profiling of miRNAs in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) with red/yellow bicoloured flowers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Ma, H.; Teixeira da Silva, J.; Yu, X. Pollen morphology of herbaceous peonies (Paeonia lactiflora) with different ploidy levels. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2016, 141, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; da Silva, J.T.; Yu, X. Variation in ploidy and karyological diversity in different herbaceous peony cultivar groups. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2017, 142, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, M.; Li, S.; Chen, Q.; da Silva, J.A.T.; Wang, A.; Yu, X.; Wang, L. Germplasm resources and genetic breeding of Paeonia: A systematic review. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Wang, Q.; da Silva, J.T.; Yu, X. The genetic diversity of Paeonia lactiflora. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 143, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Kimani, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ning, G.; Wang, L. Allelic variation of terpene synthases drives terpene diversity in the wild species of the Freesia genus. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 2419–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Köllner, T.G.; Gershenzon, J.; Chen, F. MTPSLs: New terpene synthases in nonseed plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, N.; Kimani, S.; Li, Y.; Bao, T.; Ning, G.; Li, L.; Liu, B.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. Characterization of terpene synthase variation in flowers of wild Aquilegia species from Northeastern Asia. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhab020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Bao, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Shan, X.; Yan, H.; Kimani, S.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X. The coordinated interaction or regulation between floral pigments and volatile organic compounds. Hortic. Plant J. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Jin, X.; Lan, L.; Yang, B.; Yu, K.; Ni, X.; Li, N. Draft genome of the famous ornamental plant Paeonia suffruticosa. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 4518–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Fan, R.; Ye, X.; Lin, R.; Luo, Y.; Fang, N.; Zhong, H.; Chen, S. The transcriptome of flower development provides insight into floral scent formation in Freesia hybrida. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 86, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, R.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Kong, P.; Lu, K.; Adnan; Liu, M.; Ao, F.; Zhao, C.; et al. The biochemical and molecular investigation of flower color and scent sheds lights on further genetic modification of ornamental traits in Clivia miniate. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Liu, B.; Li, M.; Gao, X.; Fang, Q.; Liu, C.; Ding, H.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. Identification and characterization of terpene synthase genes accounting for volatile terpene emissions in flowers of Freesia × hybrida. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 4249–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Wang, Q.; da Silva, J.A.T.; Yu, X. Identification of floral fragrances and analysis of fragrance patterns in herbaceous peony cultivars. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2018, 143, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Gu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhi, H.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y. Volatile composition and classification of Paeonia lactiflora flower aroma types and identification of the fragrance-related genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Guo, J.; Ma, Y.; Jin, B.; Zhan, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, L. Characterization of a monoterpene synthase from Paeonia lactiflora producing α-pinene as its single product. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Sun, M.; Lv, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, L. Biogenesis of flavor-related linalool is diverged and genetically conserved in tree peony (Paeonia × suffruticosa). Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhac253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, L.; Zeng, Y.; Wei, T.; Zhu, M.; Fang, X.; Yuan, X.; Luo, Y.; Feng, L. Cloning and functional verification of genes related to 2-phenylethanol biosynthesis in Rosa rugosa. Genes 2018, 9, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuyuki, H.; Miyako, I. Parfum of Rose; Nihon Kourido Publisher: Japan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Du, F.; Wang, T.; Fan, J.-M.; Liu, Z.-Z.; Zong, J.-X.; Fan, W.-X.; Han, Y.-H.; Grierson, D. Volatile composition and classification of Lilium flower aroma types and identification, polymorphisms, and alternative splicing of their monoterpene synthase genes. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Yuan, M.; Li, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q. Variation of floral volatiles and fragrance reveals the phylogenetic relationship among nine wild tree peony species. Flavour Fragr. J. 2020, 35, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Jin, R.; Chen, Y.; He, S.; Li, K.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Kong, M.; Dudareva, N. The functional evolution of architecturally different plant geranyl diphosphate synthases from geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 2293–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, F.; Ke, Y.; Yu, R.; Yue, Y.; Amanullah, S.; Jahangir, M.M.; Fan, Y. Volatile terpenoids: Multiple functions, biosynthesis, modulation and manipulation by genetic engineering. Planta 2017, 246, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galen, C.; Kaczorowski, R.; Todd, S.L.; Geib, J.; Raguso, R.A. Dosage-dependent impacts of a floral volatile compound on pollinators, larcenists, and the potential for floral evolution in the alpine skypilot Polemonium viscosum. Am. Nat. 2011, 177, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurr, G.M.; Liu, J.; Pickett, J.A.; Stevenson, P.C. Review of the chemical ecology of homoterpenes in arthropod–plant interactions. Austral Entomol. 2023, 62, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninkuu, V.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J.; Fu, Z.; Yang, T.; Zeng, H. Biochemistry of terpenes and recent advances in plant protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Shao, Y.; Gao, R.; Gao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, L. Functional characterization of a (E)-β-Ocimene synthase gene contributing to the defense against Spodoptera litura. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Miettinen, K.; Goedbloed, M.; Verstappen, F.W.A.; Voster, A.; Jongsma, M.A.; Memelink, J.; van der Krol, S.; Bouwmeester, H.J. Characterization of two geraniol synthases from Valeriana officinalis and Lippia dulcis: Similar activity but difference in subcellular localization. Metab. Eng. 2013, 20, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaliter, O.; Livneh, Y.; Agron, S.; Shafir, S.; Vainstein, A. A whiff of the future: Functions of phenylalanine-derived aroma compounds and advances in their industrial production. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1651–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, B.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Yang, Z.; Ma, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Cloning and characterization of two iridoid synthase homologs from Swertia mussotii. Molecules 2017, 22, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yu, Z.; da Silva, J.A.T.; He, C.; Wang, H.; Si, C.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, D.; Duan, J. Functional characterization of a Dendrobium officinale geraniol synthase DoGES1 involved in floral scent formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnard, J.L.; Roccia, A.; Caissard, J.C.; Vergne, P.; Sun, P.; Romain, H.; Annick, D.; Laurence, H.O.; Frédéric, J.; Florence, N.; et al. Biosynthesis of monoterpene scent compounds in roses. Science 2015, 349, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conart, C.; Saclier, N.; Foucher, F.; Goubert, C.; Rius-Bony, A.; Paramita, S.; Moja, S.; Thouroude, T.; Douady, C.; Sun, P. Evolution of scent genes in roses. In Proceedings of the XXXI International Horticultural Congress (IHC2022): International Symposium on Innovations in Ornamentals: From Breeding to Market, Angers, France, 14–20 August 2022; pp. 361–370. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, M.E.; Bhardwaj, M.; Phillips, M.A. Cytosolic geraniol and citronellol biosynthesis require a Nudix hydrolase in rose-scented geranium (Pelargonium graveolens). Plant J. 2021, 107, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, M.E.; Franks, A.E.; Phillips, M.A. Biosynthesis, natural distribution, and biological activities of acyclic monoterpenes and their derivatives. Phytochem. Rev. 2023, 22, 361–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Bohman, B.; Wong, D.C.; Rodriguez-Delgado, C.; Scaffidi, A.; Flematti, G.R.; Phillips, R.D.; Pichersky, E.; Peakall, R. Complex sexual deception in an orchid is achieved by co-opting two independent biosynthetic pathways for pollinator attraction. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1867–1877.e1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, M.; Kenmoku, H.; Takahashi, H.; Lee, J.-B.; Toyota, M.; Asakawa, Y.; Kurosaki, F.; Taura, F. Characterization of 12-oxophytodienoic acid reductases from rose-scented geranium (Pelargonium graveolens). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1934578X1601101201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, L.; Bihanic, C.; Bony, A.; Gros, F.; Conart, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Casabianca, H.; Schiets, F.; Chietera, G.; Boachon, B. Citronellol biosynthesis in pelargonium is a multistep pathway involving progesterone 5β-reductase and/or iridoid synthase-like enzymes. Plant Physiol. 2024, 194, 1006–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.S.; Hassan, M.; Hussein, Z.A.M.; Ismail, I.; Ho, K.L.; Ng, C.L.; Zainal, Z. Structural and kinetic studies of a novel nerol dehydrogenase from Persicaria minor, a nerol-specific enzyme for citral biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, E.; Karami, A.; Ebrahimie, E. Isolation of 2-phenylethanol biosynthesis related gene and developmental patterns of emission of scent compounds in Persian musk rose (Rosa moschata Herrm.). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 101176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Zhang, X.T.; Yu, Z.G. Analysis of volatiles in Paeonia obovata flowers by HS-SPME-GC-MS. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Guo, X. Preliminary study of aromatic components in herbaceous peonies of ‘Yangfei Chuyu’ and ‘Dafugui’. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2010, 37, 817–822. [Google Scholar]
- Pichersky, E.; Lewinsohn, E. Convergent evolution in plant specialized metabolism. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2011, 62, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.J.; Smith, C.W.; Jiggins, C.D. Alternative splicing as a source of phenotypic diversity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xue, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, X. Cloning and functional characterization of chalcone isomerase genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in Clivia miniata. Ornam. Plant Res. 2021, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-M.; Kobayashi, H.; Sakai, M.; Hirata, H.; Asai, T.; Ohnishi, T.; Baldermann, S.; Watanabe, N. Functional characterization of rose phenylacetaldehyde reductase (PAR), an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the scent compound 2-phenylethanol. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clean Data | Mean Reads (103) | Total Unigenes | Unigenes (Length > 1 kb) | Q30 | Overall Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34.32 Gb | 133.99 | 311,155 | 26,724 | 0.9389 | 44,307 |
| Floral Samples | Total Clean Reads (103) | Clean Read Q20 | Clean Read Q30 | Clean Read Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Budding | 134.3 | 97.91% | 93.41% | 79.63% |
| Half-open | 133.09 | 97.88% | 92.69% | 80.79% |
| Fully open | 134.59 | 98.23% | 93.61% | 70.53% |
| Parameters | Number |
|---|---|
| Total polymerase reads | 1,799,987 |
| Total subreads | 37,444,331 |
| Total reads of insert (ROIs) | 1,625,074 |
| Full-length non-chimeric reads (FLNC) | 4,064,073 |
| Total isoforms | 3,884,048 |
| Isoform sequence length | 1099 |
| Isoform mean quality | 0.99 |
| Total coding DNA sequences (CDSs) | 295,835 |
| Final total number of isoforms | 493,042 |
| Final length of isoforms | 610,095,296 |
| Minimum length of the isoform sequence | 200 |
| Max. length of the isoform sequence | 30,833 |
| Final N50 of the isoform sequence | 1618 |
| Final isoform sequence GC (%) | 41.62% |
| Overall isoform annotation | 408,826 (82.92%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kimani, S.K.; Wang, S.; Xie, J.; Bao, T.; Shan, X.; Li, H.; Adnan; Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Li, Y. Integration of RNA-Seq and Metabolite Analysis Reveals the Key Floral Scent Biosynthetic Genes in Herbaceous Peony. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060617
Kimani SK, Wang S, Xie J, Bao T, Shan X, Li H, Adnan, Wang L, Gao X, Li Y. Integration of RNA-Seq and Metabolite Analysis Reveals the Key Floral Scent Biosynthetic Genes in Herbaceous Peony. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(6):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060617
Chicago/Turabian StyleKimani, Shadrack Kanyonji, Shuxian Wang, Jinyi Xie, Tingting Bao, Xiaotong Shan, Hongjie Li, Adnan, Li Wang, Xiang Gao, and Yueqing Li. 2024. "Integration of RNA-Seq and Metabolite Analysis Reveals the Key Floral Scent Biosynthetic Genes in Herbaceous Peony" Horticulturae 10, no. 6: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060617
APA StyleKimani, S. K., Wang, S., Xie, J., Bao, T., Shan, X., Li, H., Adnan, Wang, L., Gao, X., & Li, Y. (2024). Integration of RNA-Seq and Metabolite Analysis Reveals the Key Floral Scent Biosynthetic Genes in Herbaceous Peony. Horticulturae, 10(6), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10060617





