Abstract
Head and neck cancers (HNC) encompass a broad spectrum of neoplastic disorders characterized by significant morbidity and mortality. While contemporary therapeutic interventions offer promise, challenges persist due to tumor recurrence and metastasis. Central to HNC pathogenesis is the aberration in numerous signaling cascades. Prominently, the Wnt signaling pathway has been critically implicated in the etiology of HNC, as supported by a plethora of research. Equally important, variations in the expression of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have been identified to modulate key cancer phenotypes such as cellular proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, metastatic potential, recurrence, and treatment resistance. This review aims to provide an exhaustive insight into the multifaceted influence of ncRNAs on HNC, with specific emphasis on their interactions with the Wnt/β-catenin (WBC) signaling axis. We further delineate the effect of ncRNAs in either exacerbating or attenuating HNC progression via interference with WBC signaling. An overview of the mechanisms underlying the interplay between ncRNAs and WBC signaling is also presented. In addition, we described the potential of various ncRNAs in enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapeutic and radiotherapeutic modalities. In summary, this assessment posits the potential of ncRNAs as therapeutic agents targeting the WBC signaling pathway in HNC management.
1. Introduction
Head and neck cancers (HNC), encompassing malignancies arising from the oral cavity, oropharynx, nasopharynx, hypopharynx, and larynx, represent a significant global health burden, as underscored by their pronounced prevalence [1]. The high prevalence of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) among HNCs (about 95%) led to the belief that it is a relatively uniform disease when compared to other types of cancers [1]. However, emerging evidence delineates the notable heterogeneity inherent to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), which hinders the accurate prognostication, therapeutic strategy formulation, and, from a molecular perspective, identification of key oncogenic determinants [1,2,3]. Established risk factors for HNC include tobacco consumption, excessive alcohol intake, and infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), with the disease accounting for over about 444,347 mortalities in the year 2020 [4,5,6,7]. Contemporary therapeutic modalities for HNC include concurrent chemoradiation, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgical interventions. Nonetheless, the persistence of suboptimal patient survival rates and adverse sequelae associated with these interventions underlines the therapeutic challenges [5,8,9,10]. Consequently, the elucidation and development of innovative therapeutic targets, as well as compounds with anti-neoplastic, anti-metastatic, and anti-angiogenic properties that interact with salient proteins or signaling pathways pivotal to tumor progression, are of critical significance for cancer therapy [2,11,12,13,14,15,16,17].
One of the core signaling processes responsible for regulating cell proliferation, cell polarity, and cell fate determination in embryonic development and tissue homeostasis is signaling via the Wnt family of secreted glycolipoproteins [18,19,20,21]. Wnt signaling consists of two interconnected and mutually regulated signaling cascades, canonical and non-canonical pathways. Canonical Wnt signaling, or the Wnt/β-catenin (WBC) pathway, is dependent on β-catenin translocation into the nucleus and the subsequent transcription of target genes [22]. Contrarily, the non-canonical pathway operates independently of β-catenin and its affiliated transcription factors, including T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor (TCF/LEF). While the canonical axis predominantly influences cellular proliferation, the non-canonical circuitry primarily oversees cellular polarity and migration [22]. Additionally, the Wnt signaling pathway in humans comprises 19 different Wnt proteins that are evolutionarily conserved cysteine-rich glycoproteins and are integral for the self-renewal process in many mammalian tissues [23,24,25]. Beyond these roles, Wnt signaling extends to encompass hepatic differentiation, pulmonary tissue regeneration and repair, hair follicle renewal, hematopoietic system development, organ aging, and osteoblast maturation [24,25,26,27].
In recent years, the emergence of non-coding RNA (ncRNA) has profoundly expanded our understanding of cellular and molecular biology. Intriguingly, based on Ensemble1 (v76) data, a mere 34% of the human transcriptome encodes proteins, while the residual 66% encompasses non-coding genes. This segment includes entities such as ncRNAs, antisense RNAs, and pseudogenes, among others [28,29,30]. Cumulative research over the past decades has delineated the pivotal role of ncRNAs in modulating transcription across various strata [31]. Hence, these RNAs have emerged as master regulators of gene expression, notwithstanding their non-protein-coding nature. For example, a recent investigation examined the expression patterns of three microRNAs (miRNAs), a prominent subclass of ncRNAs, in laryngeal neuroendocrine carcinoma (LNEC), an infrequent subtype of HNC. The study demonstrated a pronounced downregulation of miR-133b in LNEC patients, positioning it as a tumor suppressor. In contrast, miR-223 and miR-449a manifested oncogenic properties [32]. Considering the clinical challenge posed by metastasis of laryngeal cancer (LC) cells to cervical lymph nodes, targeted therapeutic strategies are imperative. A noteworthy investigation revealed that the ectopic expression of miR-449a curtailed both proliferation and invasiveness of LC cells, concurrently downregulating Notch1 and Notch2, thereby positioning miRNAs as prospective therapeutic markers for nodal metastasis in LC [33]. In light of these findings, this review endeavors to furnish an exhaustive analysis of the interplay between ncRNAs and proteins within signaling cascades, emphasizing their influence on the WBC pathway and its mechanistic ramifications in HNC.
2. Wnt Signaling and Cancer
The components of the WBC signaling pathway were initially elucidated through genetic investigations in Drosophila [34]. In 1982, Nusse and Varmus identified the mouse Wnt1 gene, originally termed Int-1, as a favored integration locus for the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) in the induction of mammary carcinomas [35]. A few years later, scientists unraveled the link between mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene and the progression of hereditary colon cancer, which strongly cemented the close association between Wnt signaling and colorectal cancer [36]. Later, many studies showcased the importance of this pathway in the initiation, development, and progression of different cancers.
The WBC signaling pathway operates through a complex network of interactions and signaling events. At the center of this pathway is β-catenin, a protein that plays a dual role as a core component of the pathway and a transcriptional co-factor [24]. In the absence of Wnt ligands, cytoplasmic β-catenin is constantly targeted for degradation through a series of phosphorylation events orchestrated by the Axin complex, which is comprised of scaffolding protein, Axin, casein kinase 1 (CK1) and glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β), and APC proteins. This intricate process involves the sequential phosphorylation of β-catenin by CK1 and GSK3β, leading to its recognition by the beta-transducin repeat-containing protein (β-TrCP) and subsequent ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation [19]. However, when the Wnt ligand binds to its receptor, the pathway gets activated, and a cascade of events is set in motion. The Wnt ligands interact with a seven-transmembrane receptor, Frizzled (FZD), forming a larger cell surface complex together with lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) 5/6 co-receptors. This complex activates the dishevelled (Dvl) proteins, which recruits the Axin complex to the receptors, leading to the displacement of GSK3β from the Axin complex. Consequently, β-catenin escapes degradation, accumulates in the cytoplasm, and translocates to the nucleus [19]. In the nucleus, β-catenin binds to LEF/TCF transcription factors, displacing co-repressors and recruiting co-activators. This intricate interplay ultimately activates the expression of the Wnt target genes, thereby influencing crucial cellular processes including cell proliferation, survival, and migration [19].
Given the essential roles played by WBC signaling in development and overall well-being, it is no wonder that mutations to the components of this pathway have been linked to several congenital disabilities, cancer development, and other serious diseases [25]. The strong correlation between aberrant WBC signaling and various cancer types is firmly established. This connection is exemplified by mutations affecting key components of the Wnt pathway, encompassing events like the silencing or inactivation of proteins of the Wnt secretory cascade or their co-factors [37,38,39]. Nevertheless, within the WBC signaling pathway, the prevalent mutation implicated in oncogenic progression pertains to alterations in the β-catenin gene [40]. Deregulation in the WBC signaling cascade is observed in the majority of tumorigenesis stages, from tumor development to metastasis and resistance to drugs [41]. Furthermore, modulation of this pathway may perturb cancer immune surveillance, enhancing the evasion of immunotherapies and hindering the effectiveness of immune checkpoint blockers [42,43,44]. Despite the advancements in human genome sequencing technologies and the characterization of the component proteins of major pathways, the role of Wnt signaling in cancer biology is intricate and complex, and its effects are not yet fully understood [45].
3. Wnt Signaling in HNC
The development of HNC consists of sequential alterations to the cellular and molecular pathways in the squamous epithelium, leading to gradual proliferation from pre-malignant lesions to tumors [46]. The WBC signaling pathway is crucial in the development of HNSCC, where the abnormal activation of the WBC signaling pathway has been found to contribute to the malignant transformation of cells, leading to tumor formation. The vital role of elevated WBC signaling in the initiation, development, and progression of HNSCC has been well documented in several studies. For instance, Yang and his colleagues elucidated that introducing a mutated β-catenin gene into HNSCC cells inhibited death receptor-mediated apoptosis and enhanced invasion of these tumor cells [47]. Another study revealed that abnormal accumulation of β-catenin in cytoplasm upregulated MMP-7 and induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), ultimately resulting in the invasion and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells [48]. The accumulated evidence has proven that, apart from invasion, lymph node metastasis (LNM) is a critical prognostic factor of HNSCC [49]. A recent study has proved that the WBC pathway promoted the invasion and LNM of HNSCC by partially activating Slug [50]. These studies demarcated that the dysfunctions of this pathway induced malignant transformation and metastasis of HNSCC; therefore, targeting WBC signaling may be a potential therapeutic approach in the treatment of this cancer.
4. Crosstalk between ncRNAs and WBC Signaling in HNSCC
The 21st century witnessed the discovery of transcripts that do not code for any proteins due to the successful achievements of the Human Genome Project and the subsequent initiative termed ENCODE (The Encyclopedia of DNA Elements project) in 2005 (ENCODE Project Consortium, 2012) [51]. The major classes of regulatory ncRNAs include miRNAs, piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs), and enhancer RNAs (eRNAs), along with housekeeping ncRNAs, including rRNAs, tRNAs, small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), and telomerase RNAs [51]. miRNAs are small transcripts with an average length of 22 nucleotides that usually bind to 3′ UTR of mRNA and regulate its gene expression [52]. About 40% of miRNA genes are present in the intronic regions or within the exons of other genes from which they are transcribed into primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs). Pri-miRNAs are processed by DROSHA into precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs) which are then transported to the cytoplasm by exportin 5 (XPO5). Furthermore, they are cleaved by DICER into small RNA duplexes which are then loaded onto the Argonaute (AGO) protein, which makes the miRNA single-stranded. Hence, the miRNA, along with the AGO and other co-factors, forms the miRNA-RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) which is responsible for binding and inhibiting target mRNAs [53].
lncRNAs are a highly heterogenous group of transcripts that are more than 200 nucleotides in length and do not code for any protein [31,54]. They can be transcribed in the sense or anti-sense direction and they are called long intergenic RNAs (lincRNAs) when transcribed from intergenic regions [31]. Various categories of lncRNAs are transcribed from multiple DNA elements, including enhancers, promoters, and intergenic regions within eukaryotic genomes. Diverse mechanisms contributing to lncRNA biogenesis encompass processes such as RNaseP-mediated cleavage to form mature ends, the generation of snoRNA and the establishment of caps at their extremities through the assembly of protein snoRNP complexes, as well as the formation of circular structures. However, the exact processes involved in the synthesis and regulation of various lncRNAs remain unknown [55]. In contrast to miRNAs, lncRNAs employ a diverse array of mechanisms. They engage in interactions with transcriptional regulatory proteins, as well as bind complementarily to mRNAs or directly to miRNAs. The process by which lncRNAs sequester miRNAs is often referred to as the “sponge effect.” Through this mechanism, lncRNAs modulate the regulatory influence of miRNAs on gene expression (Figure 1) [31].
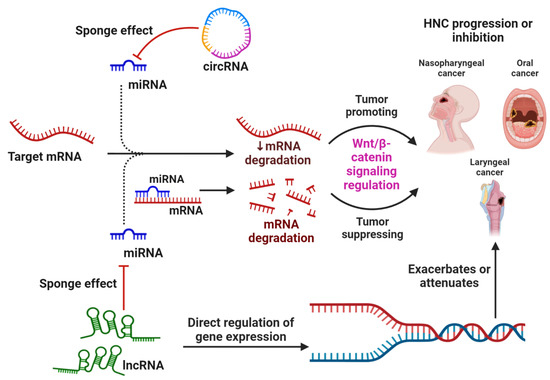
Figure 1.
The general mechanism by which non-coding RNAs, specifically miRNAs, circRNAs, and lncRNAs, regulate the mRNA expression of genes associated with the WBC signaling pathway and thereby resulting in the suppression or progression of HNC types. Apart from directly regulating gene expression, circRNA and lncRNA also act by sponging miRNAs, which prevents their normal function of binding and inhibiting the target mRNA.
Another subclass of ncRNAs is represented by circRNAs, which are ubiquitously distributed in the blood, various bodily fluids, and tissues [56]. circRNAs are produced from pre-mRNA by back-splicing, where a 5′ splice site joins back to a 3′ splice site to form a closed head-to-tail continuous molecule, termed as circRNA [57]. Their inherent circular configuration provides circRNAs a remarkable stability, rendering them resilient to nuclease-mediated degradation [56]. Expression profiles of circRNAs display tissue and cell specificity, and these molecules play pivotal roles in developmental processes, cellular proliferation, innate immunity, neuronal functions, and the pathogenesis of an array of diseases, including malignancies [56].
A growing body of literature has demonstrated the importance of ncRNAs in human malignancies [58,59]. They have been found to act as either oncogenes or tumor suppressors, thereby influencing the development and progression of cancer [59,60]. Moreover, plenty of these ncRNAs can be discharged from cancer cells into bodily fluids, acting as diagnostic and prognostic markers [61]. Several ncRNAs have been found to modulate the proteins in the WBC pathway, which in turn regulates the tumorigenesis, invasion and migration, angiogenesis, and metastasis of HNSCC [62,63]. In addition, the modulation of the WBC pathway by ncRNAs, primarily miRNAs and lncRNAs, affects cancer cell proliferation, resistance to treatments, and poorer prognoses in HNC.
4.1. Interplay between ncRNAs and the WBC Pathway in Modulating Cell Proliferation and Survival
Research indicates that anomalies in Wnt signaling can induce unbridled cellular proliferation, thereby fostering tumor initiation and advancement [19]. Specifically, in HNSCC cells, perturbed Wnt signaling has been linked with augmented cell proliferation and viability, concomitant with diminished apoptosis [64]. Furthermore, various ncRNAs have been found to either manifest oncogenic attributes or function as tumor suppressors through interactions with distinct constituents of the WBC signaling cascade. Such interactions either exacerbate or attenuate the severity of the malignancy, as delineated in Table 1 and Table 2, and presented in Figure 2 [60,65].
A comprehensive body of research exemplifies the involvement of lncRNAs and miRNAs in mediating cell proliferation in HNSCC cells through the modulation of the Wnt signaling pathway (Figure 3). For example, Mao et al. (2022) documented elevated levels of the lncRNA human leucocyte antigen complex group-18 (HCG18) in HNSCC cell lines and tissues. Amplification of HCG18 was found to potentiate HNSCC cell proliferation by interacting with cyclin D1, an integral protein in the Wnt cascade, while its suppression reduced proliferation. Moreover, HCG18-depleted cells exhibited marked downregulation in Axin2, c-Myc, survivin, and β-catenin [62]. Chen and colleagues (2019) illustrated that the activation of lncRNA placenta-specific protein 2 (PLAC2) via H3K27 acetylation induced OSCC cell proliferation, a phenomenon corroborated by the upregulation of cyclin D1 and Ki-67 levels [63]. Concurrently, a series of investigations consistently identified various lncRNAs, namely AC007271.3, MINCR, Taurine upregulated gene 1 (TUG1), and IGF2BP2-AS1, that augmented cell proliferation and viability in OSCC cells [66,67,68]. In a distinct study, Ai et al. (2020) showed that the activation of long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 941 (LINC00941) by EP300 (a histone acetyltransferase) in OSCC cells via H3K27 promoter modification led to increased CAPRIN2 expression through DNA looping, ultimately amplifying the canonical Wnt signaling pathway as evidenced by upregulated MYC, CCND1, SOX9, β-catenin, and p-LRP6 [69].
Furthermore, another study demonstrated that SLCO4A1-AS1 functions as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) binding to miR-7855-p, leading to SETD7 upregulation. This lncRNA also upregulated the WBC pathway proteins, which augmented cell proliferation while inhibiting apoptosis [70]. Further investigations by Lin et al. (2023) and Zhao et al. (2023) revealed that lncRNA WDFY3-AS2 and IGFL2-AS1, respectively, induced cell proliferation in OSCC and tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) cells by influencing the WBC pathway [71,72]. Liang and team identified the role of lncRNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) in enhancing tongue cancer cell proliferation through canonical Wnt signaling modulation [73]. Moreover, studies indicated that miRNAs such as miR-25 and miRNA-215 elevated cell proliferation and colony formation in nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) by enhancing the expression of WBC pathway proteins [74,75]. Lastly, Sun et al. (2019) highlighted that overexpression of the lncRNA urothelial carcinoma associated 1 (UCA1) in LC cells increased β-catenin levels, promoting cell proliferation [76].
Several studies have reported the role of lncRNAs in modulating the WBC signaling pathway and its components by functioning as “miRNA sponges”. For instance, Jin et al. (2020) reported that overexpression of the lncRNA TIRY in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) activated the WBC signaling pathway, promoting the proliferation of OSCC cells. This upregulation was attributed to a sponging mechanism that reduced miR-14 expression [77]. Concurrently, Qiao et al. (2022) reported that lncRNA SNHG17 promoted oral cancer cell proliferation by acting as a decoy and inhibiting miR-384 [78]. In another study, lncRNA AC104041.1 was identified as a sponge for miR-6817-3p, resulting in the increased proliferation of OSCC cells [79]. Li et al. (2019) demonstrated that HCG18 exerted oncogenic effects in NPC cells by functioning as a ceRNA for miR-140, leading to the upregulation of both the WBC and Hedgehog signaling pathways [80]. Additionally, another study elucidated the oncogenic potential of lncRNA CCAT1 in enhancing OSCC cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis by activating the WBC pathway and suppressing miR-181a [81]. Chen et al. (2020) detected a marked upregulation of disheveled-Axin domain containing 1 (DIXDC1) and lncRNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 20 (SNHG20), paired with the targeted suppression of miR-29a in OSCC cells and tissues. This upregulation in SNHG20 promoted cell viability and proliferation while inhibiting apoptosis in OSCC cells, correlating with a poor prognosis for OSCC patients. Interestingly, treating cells with a miR-29a mimic considerably suppressed OSCC cell proliferation by downregulating Wnt-3a and β-catenin proteins. However, introducing DIXDC1 to cells treated with si-SNHG20 and miR-29a mimics intensified these effects, suggesting that SNHG20 facilitates OSCC progression via the miR-29a/DIXDC1/Wnt signaling axis [82]. Cao and Sun (2019) demonstrated that miR-200c enhanced proliferation and cell viability in NPC cells by upregulating canonical Wnt signaling proteins and suppressing the cell fate determinant factor, Dachshund family transcription factor 1 (DACH1) [83]. In another study, Xiong et al. (2020) identified that lncRNA HOTTIP facilitated the proliferation of TSCC cells by targeting miR-124-3p and influencing Wnt signaling [84]. Furthermore, Kang et al. (2020) elucidated that lncRNA SNHG3 augmented cell viability and glycolysis in LSCC cells by modulating the WBC pathway and targeting the miR-340-5p/YAP1 axis [85].
An emerging number of studies have investigated the role of ncRNAs in the suppression of proliferation and survival, and the induction of apoptosis of HNSCC cells by modulating the WBC signaling pathway. For instance, a recent study demonstrated that an siRNA-mediated knockdown of circRNA hsa_circ_0136839 markedly enhanced the cell cycle progression and cell proliferation of NPC cells by upregulating Wnt signaling proteins such as β-catenin and cyclin D1. However, this was significantly reduced by overexpressing this circRNA. Therefore, this study reinforced the notion that the aberrant expression of circRNA results in the development of HNSCC [56]. Additionally, numerous miRNAs, miR-9, miR-638, miR-329, miR-410, and miR-27b, were reported to repress the growth and proliferation of different OSCC cell lines by targeting key proteins involved in canonical Wnt signaling, such as frizzled7 (FZD7), Wnt-7b, phospholipase D1 (PLD1), and CXCR4 [86,87,88,89]. Furthermore, lncRNA LINC00961 suppressed the proliferation of TSCC by downregulating WBC signaling [90]. Furthermore, another study reported that miR-384 induced apoptosis and DNA fragmentation and inhibited the proliferation of LC cells via Wnt signaling. In addition, this study also proved that miR-384 specifically targeted and inhibited the expression of Wnt-induced secreted protein-1 (WISP1) gene [91]. Another study conducted in hypopharyngeal cancer established that miR-338-3p suppressed proliferation by targeted inhibition of metalloproteinase 17 or ADAM17, thereby subsequently downregulating β-catenin and cyclin D1 [92]. Likewise, lncRNA NEF also abolished cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in LC cells by downregulating WBC signaling [93].
Interestingly, a range of natural compounds has demonstrated anticancer properties against diverse cancer types, including HNC [10,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102]. Importantly, a couple of studies have provided critical evidence regarding the potential of natural compounds to inhibit the progression of HNC by modulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. For instance, Xiao and his group showed that curcumin, a compound extracted from turmeric (Curcuma longa) inhibited the proliferation of OSCC cells by upregulating miR-9 and repressing WBC signaling [103]. In addition, another study revealed that isoliquiritigenin, a flavonoid extracted from licorice root (Glycyrrhizae radix), suppressed NPC cell growth and proliferation as well as induced apoptosis by suppressing miR-32 and downregulating canonical Wnt signaling [104]. Therefore, it is imperative to study the effect of natural compounds in modulating the expression of ncRNAs through WBC signaling. Taken together, these studies suggest that ncRNAs are not only involved in regulating gene expression, but they are also able to orchestrate multiple cellular processes such as proliferation, survival, and viability by regulating WBC signaling to ultimately enable or suppress HNSCC progression.
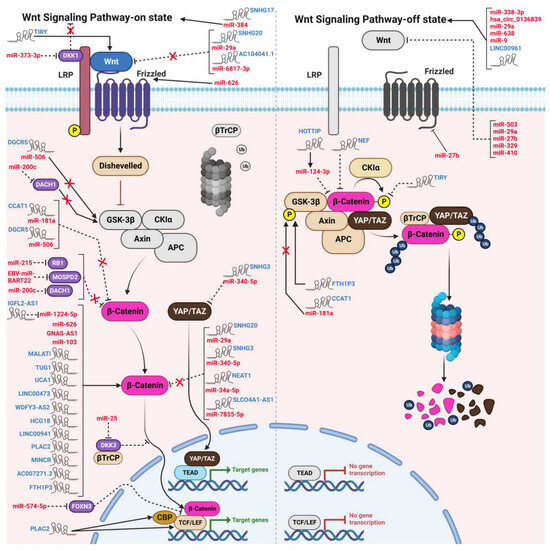
Figure 2.
The modulatory functions of oncogenic and tumor suppressive ncRNAs on the “switch on” and “switch off” states of WBC signaling in HNCs. lncRNAs, circRNAs, and miRNAs bind to and induce or attenuate the expression of various components in the WBC pathway, thereby influencing the development of different types of HNCs. The mechanism of action of the WBC pathway, both in the ON-state and OFF-state, is also depicted in the figure.
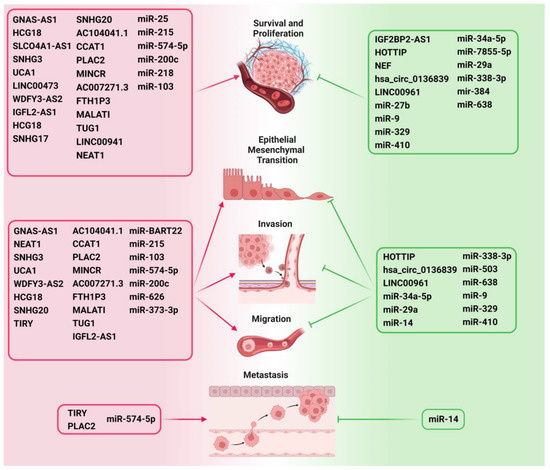
Figure 3.
ncRNAs as critical modulators of various hallmarks of HNC such as survival, proliferation, EMT, invasion, migration, and metastasis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. The ncRNAs that promote the important hallmarks of cancer development and progression are depicted on the left side of the figure and are highlighted in red. The ncRNAs that inhibit cancer progression are depicted on the right side and are highlighted in green.

Table 1.
Wnt signaling modulating oncogenic ncRNAs in HNC.
Table 1.
Wnt signaling modulating oncogenic ncRNAs in HNC.
| ncRNA | Type of Study | Cell Line/Cancer Model | Target | Mechanism/Mode of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasopharyngeal Cancer | |||||
| EBV-miR-BART22 b | In vitro | CNE1, CNE2, SUNE1 (Overexpression) | MOSPD2 | ↑Cell migration, invasion, N-cadherin, vimentin, Snail, β-catenin, EMT ↓E-cadherin, MOSPD2 | [105] |
| EBV-miR-BART22 b | In vitro | C666-1 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑E-cadherin, MOSPD2 ↓Cell invasion, migration, N-cadherin, vimentin, Snail, β-catenin, EMT | [105] |
| EBV-miR-BART22 b | In vivo | Hepatic metastasis BALB/c nude mice model (Overexpression) | - | ↑Cell motility, tumor invasiveness | [105] |
| miR-25 b | In vitro | HONE-1 (miRNA inhibitor) | DKK3 | ↑Apoptosis, DKK3 ↓Colony formation | [74] |
| miR-25 b | In vitro | HONE-1 (Overexpression) | - | ↑TCF4, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 | [74] |
| miR-215 b | In vitro | C666-1 (Overexpression) | RB1 | ↑Cell proliferation, migration, EMT, N-cadherin, vimentin, p-β-catenin ↓RB1, E-cadherin | [75] |
| miR-215 b | In vitro | C666-1 (miRNA inhibitor) | RB1 | ↑RB1, E-cadherin ↓Cell proliferation, migration, p-β-catenin, N-cadherin, vimentin | [75] |
| miR-103 b | In vitro | CNE1, SUNE1 (Overexpression) | TIMP3 | ↑β-catenin, CyclinD1, invasion, migration, proliferation ↓TIMP3 | [106] |
| GNAS-AS1 a | In vitro | SUNE1 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | β-catenin | ↓Cell proliferation, c-Myc, Cyclin D, MMP-2, β-catenin, invasion, migration | [107] |
| miR-574-5p b | In vitro | C666-1 (Overexpression) | FOXN3 | ↑Cell viability, β-catenin, TCF4, invasion, metastasis ↓ FOXN3 | [108] |
| HCG18 a | In vitro | SUNE1, CNE2 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | miR-140 | ↑miR-140, apoptosis, Caspase-3 and 9 ↓Cell growth, migration, invasion, Cyclin D1, β-catenin, c-Myc, Hedgehog signaling | [80] |
| miR-140 b | In vitro | SUNE1, CNE2 (Overexpression) | HCG18 | ↓HCG18, Cyclin D1 | [80] |
| miR-200c b | In vitro | CNE2, SUNE1 (miR-200c-inhibitor) | DACH1 | ↑DACH1 ↓Cell proliferation, colony number, migration, β-catenin, c-Myc, GSK3β, Cyclin D1 | [83] |
| NEAT1 a | In vitro | CNE1, CNE2, SUNE1, SUNE2, 5-8F | miR-34a-5p | ↓miR-34a-5p | [109] |
| NEAT1 a | In vitro | 5-8F (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | miR-34a-5p | ↑ miR-34a-5p, E-cadherin ↓β-catenin, Cyclin D1, and c-Myc, N-cadherin, vimentin, cell proliferation, invasion, migration, EMT | [109] |
| NEAT1 a | In vivo | SCID mouse xenografts (5-8F (shRNA mediated knockdown) xenografts) | miR-34a-5p | ↑ miR-34a-5p, E-cadherin ↓Tumor growth, β-catenin, Cyclin D1, c-Myc, N-cadherin, vimentin | [109] |
| Laryngeal Cancer | |||||
| SLCO4A1-AS1 a | In vitro | SNU46, TU177 (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | miR-7855-5p | ↑miR-7855-5p ↓Cell proliferation, colony formation, β-catenin, Cyclin D1, c-Myc | [70] |
| SNHG3 a | In vitro | TU177, AMC-HN-8 (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑Apoptosis, miR-340-5p, E-cadherin ↓Cell viability, glycolysis, YAP1, β-catenin, c-Myc, Bcl-2 | [85] |
| SNHG3 a | In vivo | BALB/c nude mice xenograft (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑miR-340-5p ↓Tumor volume, weight, YAP1 | [85] |
| UCA1 a | In vitro | AMC-HN-8 (Overexpression) | - | ↑Cell proliferation, invasion, migration, β-catenin ↓ p-GSK3β | [76] |
| UCA1 a | In vitro | AMC-HN-8 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↓Cell proliferation, invasion, migration | [76] |
| DGCR5 a | In vitro | Hep2R | miR-506 | ↑DGCR5, ↓miR-506, CSC-like phenotype | [87] |
| DGCR5 a | In vitro | Hep2R (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | miR-506 | ↑GSK3β, ↓Sox2, Oct4, Nanog, spheroid formation, β-catenin, Cyclin D1 | [87] |
| DGCR5 a | In vitro | Hep2R (siRNA-mediated knockdown and Radiation) | - | ↓Radioresistance | [87] |
| miR-506 b | In vitro | Hep2R (Overexpression) | - | ↓Sox2, Oct4, Nanog, β-catenin, Cyclin D1 | [87] |
| miR-506 b | In vitro | Hep2R (Overexpression and Radiation) | - | ↓Radioresistance | [87] |
| LINC00473 a | In vitro | SCC25, CAL27 (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑Apoptosis, Bax, ↓Cell viability, colony number, Bcl-2, β-catenin, c-Myc | [65] |
| LINC00473 a | In vitro | SCC9 (Overexpression) | - | ↑ Cell viability, colony number, Bcl-2 ↓Bax, Apoptosis | [65] |
| LINC00473 a | In vitro | SCC25, CAL27 (shRNA-mediated knockdown and radiation) | - | ↑Apoptosis, Bax, ↓Cell viability, colony number, Bcl-2, β-catenin, c-Myc | [65] |
| Oral Cancer | |||||
| WDFY3-AS2 a | In vitro | CAL27, SCC9 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑E-cadherin ↓Cell proliferation, invasion, migration, vimentin, β-catenin, Myc, Slug | [72] |
| IGFL2-AS1 a | In vitro | CAL-27, SCC-15, SCC-9, SCC-4 (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | miR-1224-5p | ↑E-cadherin ↓Cell proliferation, invasion, migration, EMT, nuclear β-catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1, MMP-7 | [71] |
| HCG18 a | In vitro | HN30, SCC-4 (Overexpression) | - | ↑Cell proliferation, migration, invasion, Cyclin D1 | [62] |
| HCG18 a | In vitro | HN30, SCC-4 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↓Cell invasion, migration, AXIN2, c-Myc, survivin, Cyclin D1, β-catenin | [62] |
| HCG18 a | In vivo | Nude mice xenograft (Overexpression) | - | ↑Tumor weight, volume | [62] |
| SNHG17 a | In vitro | YD-38, SCC-9 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | miR-384 | ↑Apoptosis ↓Cell proliferation, viability, CTNNB1, ELF1, Wnt/β-catenin signaling | [78] |
| miR-626 b | In vitro | Ca9-22, HSC2 (miRNA inhibitor) | - | ↑RASSF4, E-cadherin ↓vimentin, N-cadherin, invasion, migration, FZD1, β-catenin | [110] |
| miR-626 b | In vitro | Ca9-22, HSC2 (Overexpression) | RASSF4 | ↑Invasion, migration, N-cadherin, β-catenin, FZD1 ↓E-cadherin | [110] |
| IGF2BP2-AS1 a | In vitro | CAL27, SCC-9 (knockdown) | - | ↑G1 phase arrest, apoptosis, Bax ↓Cell proliferation, colony formation, β-catenin, Cyclin D1, Bcl-2, MMP-2 | [111] |
| LINC00941 a | In vitro | HSC-3, OSC-19 (dCas9 tagged with KRAB-MeCP2) | - | ↓Cell proliferation, colony formation, cell number, CAPRIN2, β-catenin, p-LRP6, MYC, CCND1, SOX9 | [69] |
| LINC00941 a | In vivo | Nude mice (HSC-3 xenograft dCas9 tagged with KRAB-MeCP2) | - | ↓ Tumor formation, tumor weight | [69] |
| SNHG20 a | In vitro | SCC-9 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | miR-29a | ↑Apoptosis, miR-29a ↓Cell viability, invasion, migration, Wnt-3a, β-catenin | [82] |
| miR-29a b | In vitro | SCC-9 (Overexpression) | - | ↓Cell viability, invasion, migration, Wnt-3a, β-catenin | [82] |
| miR-29a b | In vitro | SCC-9 (miRNA inhibitor) | - | ↑SNHG20 | [82] |
| TIRY a | In vitro | Oral CAFs (Overexpression) | - | ↑Snail, Zeb1, α-SMA, β-catenin ↓miR-14 | [77] |
| TIRY a | In vitro | Tca8113 (CAF-conditioned media) (Overexpression) | - | ↑Invasion, metastasis, Snail, Wnt-3a ↓Phosphorylation of β-catenin | [77] |
| TIRY a | In vitro | Tca8113 (CAF-conditioned media) (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑miR-14 | [77] |
| miR-14 a | In vitro | Tca8113 (CAF-conditioned media) (Overexpression) | - | ↓Invasion, metastasis | [77] |
| HOTTIP a | In vitro | SCC25, UM1 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | miR-124-3p | ↑miR-124-3p, E-cadherin ↓Cell growth, invasion, migration, β-catenin, c-Myc | [84] |
| HOTTIP a | In vivo | Nude mice (sh-HOTTIP OTSCC xenografts) | - | ↑miR-124-3p, E-cadherin ↓Tumor weight, tumor volume, β-catenin, c-Myc, HMGA2 | [84] |
| AC104041.1 a | In vitro | SCC4 (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | miR-6817-3p | ↓Cell viability, migration, Wnt-2b, β-catenin, c-Myc, vimentin | [79] |
| AC104041.1 a | In vitro | CAL27 (Overexpression) | miR-6817-3p | ↑Cell viability, migration, Wnt-2b | [79] |
| AC104041.1 a | In vivo | BALB/c nude mice (SCC4 xenografts) (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↓Tumor volume | [79] |
| AC104041.1 a | In vivo | BALB/c nude mice (CAL27 xenografts) (Overexpression) | - | ↑Tumor volume | [79] |
| CCAT1 a | In vitro | KB, Cal-27 (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | miR-181a | ↑Apoptosis, Bax, miR-181a, Caspase-3 and -9 ↓Cell proliferation, colony formation, Bcl-2, Cyclin D1, CDK4, invasion, migration, p-GSK3β, β-catenin and c-Myc | [81] |
| CCAT1 a | In vivo | BALB/c mice with Cal-27 xenograft (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↓Tumor size, weight, p-GSK-3β, β-catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1, Ki-67 | [81] |
| PLAC2 a | In vitro | SCC-9 (Overexpression) | - | ↑Cell proliferation, Ki-67, invasion, migration, β-catenin, TCF-4, MMP-7 and -9, Cyclin D1 | [63] |
| PLAC2 a | In vitro | CAL-27 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↓Cell proliferation, Ki-67, Migration, Invasion, β-catenin, TCF-4, MMP-7 and -9, Cyclin D1 | [63] |
| PLAC2 a | In vivo | BALB/c nude mice (SCC-9 xenograft) (Overexpression) | - | ↑Tumor volume, metastasis, PLAC2, CBP, β-catenin | [63] |
| MINCR a | In vitro | SCC-25, TSCCA (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑Apoptosis, G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, Cleaved caspase-3 and -9, E-cadherin ↓Cell proliferation, migration, invasion, N-cadherin, β-catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 | [67] |
| AC007271.3 a | In vitro | SCC-9, SCC-15 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑Apoptosis ↓Cell proliferation, cell growth, Colony formation, invasion, migration, β-catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1, Bcl-2 | [68] |
| AC007271.3 a | In vitro | SCC-9, SCC-15 (Overexpression) | - | ↑β-catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1, Bcl-2 | [68] |
| AC007271.3 a | In vivo | SCC-9 nude mice xenograft (Overexpression) | - | ↑Keratinization, abnormal nuclear division, Ki-67, CD44, β-catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1, Bcl-2 | [68] |
| FTH1P3 a | In vitro | SCC-4, SCC-25 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↓Cell viability, invasion, β-catenin, p-AKT, p-GSK3β | [112] |
| miR-373-p b | In vitro | SCC-9, UM1 (Overexpression) | DKK1 | ↑N-cadherin, vimentin, Cell invasion, viability, β-catenin ↓E-cadherin, CK18, DKK1 | [113] |
| miR-373-3p b | In vitro | SCC-9, UM1 (miRNA inhibitor) | - | ↓N-cadherin, vimentin, invasion, cell viability, β-catenin | [113] |
| miR-218 b | In vitro | UM1cis, Cal-27cis (anti-miR) | PPP2R5A | ↑Cisplatin sensitivity, apoptosis, PPP2R5A ↓Cell viability, MRP1, ABCG2, p-gp, TopoIIβ, EZH2 | [114] |
| miR-218 b | In vitro | UM1cis (Overexpression) | PPP2R5A | ↑ β-catenin, GSK3β, MRP1, ABCG2, p-gp, TopoIIβ, EZH2, Cell viability, cell growth ↓PPP2R5A | [114] |
| MALAT1 a | In vitro | TSCC (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑E-cadherin, Bax, Apoptosis ↓Cell growth, invasion, migration, vimentin, β-catenin | [73] |
| MALAT1 a | In vitro | TSCC (Overexpression) | - | ↑Cell growth, invasion, migration, vimentin, β-catenin ↓E-cadherin, Bax, apoptosis | [73] |
| TUG1 a | In vitro | Tca8113, TSCCA (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑Apoptosis, Caspase-3 activity, Cleaved caspase-3 and -9, Bax ↓Cell proliferation, growth, colony formation, invasion, Bcl-2, β-catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 | [66] |
a: long non-coding RNA; b: micro RNA; ↑ Upregulation; ↓ Downregulation.

Table 2.
Wnt signaling modulating tumor-suppressive ncRNAs in HNC.
Table 2.
Wnt signaling modulating tumor-suppressive ncRNAs in HNC.
| ncRNA | Type of Study | Cell Line/Cancer Model | Target | Mechanism/Mode of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypopharyngeal Cancer | |||||
| miR-503 b | In vitro | FaDu (Overexpression) | - | ↓Cell invasion, WNT-3A, BCL11B, and CCND2, MMP-3, -7, and -9, FGF7, CTGF | [60] |
| miR-338-3p b | In vitro | FaDu (Overexpression) | ADAM17 | ↓Cell proliferation, ADAM17, cell migration, invasion, cyclin D1, MMP-2, nuclear β-catenin, p-pRb, Wnt/β-catenin | [92] |
| miR-338-3p b | In vitro | FaDu (Inhibitor) | - | ↑β-catenin, cyclin D1, p-pRb, MMP-2, sox-2, Nanog | [92] |
| Laryngeal Cancer | |||||
| miR-384 b | In vitro | TU212, TU686 | WISP1 | ↑Cell apoptosis, DNA fragmentation, Caspase-3 ↓Cell proliferation, WISP-1 | [91] |
| miR-384 b | In vitro | TU212, TU686 (Inhibitor) | - | ↓Caspase-3, DNA fragmentation | [91] |
| NEF a | In vitro | UM-SCC-17A (Overexpression) | - | ↑Cell apoptosis ↓Cell proliferation, β-catenin | [93] |
| Nasopharyngeal Cancer | |||||
| hsa_circ_0136839 c | In vitro | CNE2 (Overexpression) | - | ↓Cell proliferation, invasion, migration colony formation, G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, β-catenin | [56] |
| hsa_circ_0136839 c | In vitro | C666-1 (siRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑Cell proliferation, invasion, migration colony formation, β-catenin, c-Jun, LEF1, CD44, cyclin D1 | [56] |
| Oral Cancer | |||||
| miR-503 b | In vitro | SAS, OECM1 | - | ↓Cell invasion, WNT-3A, BCL11B, CCND2, MMP-3, 7, and 9, FGF7, CTGF | [60] |
| miR-638 b | In vitro | SCC-9 (Overexpression) | PLD1 | ↓Cell proliferation, invasion, migration, PLD1, β-catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 | [115] |
| miR-638 b | In vitro | SCC-9 (Inhibitor) | PLD1 | ↑PLD1, β-catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 | [115] |
| LINC00961 a | In vitro | SCC-1 (Overexpression) | - | ↑E-cadherin ↓Cell proliferation, invasion, migration, vimentin, N-cadherin, Snail, β-catenin | [90] |
| LINC00961 a | In vitro | SCC-1 (shRNA-mediated knockdown) | - | ↑Cell proliferation, Wnt/β-catenin signaling | [90] |
| miR-27b b | In vitro | Tca8113, SCC-4 (Overexpression) | FZD7 | ↓Cell proliferation, FZD7, Wnt, Cyclin D1, c-Myc | [88] |
| miR-9 b | In vitro | Tca8113, SCC-9 (Overexpression) | CXCR4 | ↑Cell apoptosis, G1/S cell cycle arrest ↓Cell proliferation, colony formation, cell invasion, CXCR4, β-catenin, Bcl-2, c-Myc | [86] |
| miR-9 b | In vitro | Nude mice xenograft (Overexpression) | CXCR4 | ↓Tumor growth, CXCR4, Ki-67 | [86] |
| miR-329b/miR-410 b | In vitro | OEC-M1, SCC-15 (Overexpression) | Wnt-7b | ↓Wnt-7b, TCF/LEF1transcriptional activity, cell proliferation, invasion, colony formation, β-catenin, p-GSK3β, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 | [89] |
| miR-329b/miR-410 b | In vitro | OC-3, SCC-4 (miR329-inhibitor/ miR410-inhibitor) | Wnt-7b | ↑Wnt-7b, TCF/LEF1transcriptional activity, β-catenin, c-Myc, Cyclin D1 | [89] |
| miR-329b/miR-410 b | In vivo | OEC-M1 xenograft (overexpression of miR329/miR410) | Wnt-7b | ↓Tumor weight, volume, Wnt-7b, β-catenin | [89] |
a: long non-coding RNA; b: micro RNA; c: circular RNA; ↑ Upregulation; ↓ Downregulation.
4.2. Interplay between ncRNAs and the WBC Pathway in the Modulating EMT, Invasion, and Migration
EMT is a biological process characterized by the transformation of epithelial cells into a more mobile mesenchymal phenotype, allowing them to invade and migrate to new tissues [116]. Importantly, EMT, invasion, and migration represent interconnected biological phenomena that collectively contribute to the progression of tumors from a benign to a more aggressive malignant state [117]. These sequential events are orchestrated through a complex network of signaling pathways, initiated by the downregulation of cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin, mediated by proteins such as Snail, Slug, Zeb 1/2, smad interacting protein 1 (SIP1), or Twist 1. Simultaneously, there is an upregulation of vimentin and N-cadherin expression, facilitating the necessary alterations in cellular properties for efficient tissue invasion and migration [117,118,119].
Numerous investigations have elucidated the pivotal role of ncRNAs in modulating Wnt signaling, which in turn influences the invasive phenotype, indicating their central function in directing the invasion and migration of HNSCC cells (Figure 2). For instance, Wang et al. (2020) delineated that the lncRNA GNAS-AS1 activated the Wnt signaling pathway by upregulating β-catenin. Additionally, the suppression of this lncRNA markedly decreased the metastatic capacity of NPC cells by attenuating matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) [107]. Another study documented that the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miRNA BART-22 enhanced EMT, invasion, and migration of NPC cells, by directly targeting motile sperm domain-containing protein 2 (MOSPD2). This miRNA exerts its effect by modulating the Wnt signaling cascade [105]. Zhao et al. (2020) found that miR-103 significantly suppressed the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP-3) while enhancing β-catenin and cyclin D1 expressions, which intensified the invasive and migratory propensities of NPC cells [106]. Another investigation by Liu et al. (2018) revealed that lncRNA ferritin heavy chain 1 pseudogene 3 (FTH1P3) increased migration and invasion in OSCC cells. Moreover, FTH1P3 silencing critically downregulated the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/WBC signaling cascade, as evidenced by reduced levels of β-catenin, phosphorylated Akt, and GSK3β [112]. Further studies have indicated that miR-574-5p enhanced invasiveness and migration in NPC cells by inhibiting the tumor suppressor gene forkhead box N3 (FOXN3), while miR-373-3p markedly aggravated EMT-induced metastasis by curbing DKK1, a negative regulator of Wnt signaling, in TSCC cells [108,113]. Additionally, miR-626 promoted EMT, invasion, and migration in OSCC cells through RASSF4 targeting and the consequent β-catenin signaling upregulation [110]. A notable finding by Chen et al. (2020) emphasized the lncRNA role of SNHG20 in amplifying OSCC cell migration and invasion by upregulating crucial WBC signaling elements β-catenin and Wnt-3a [82]. Concurrent studies have affirmed that lncRNAs like AC007271.3, MINCR, TUG1, IGF2BP2-AS1, and PLAC2, activated via H3K27 acetylation, escalate the invasion and migration in OSCC cells by modulating the canonical Wnt signaling pathway, thus advancing oral cancer progression [63,66,67,68,111]. Additionally, Lin et al. (2023) highlighted the pro-invasive effects of lncRNA WDFY3-AS2 by upregulating key proteins, including vimentin, slug, β-catenin, and c-Myc. Cao and Sun (2019) expounded on miR-200c’s crucial influence on augmenting NPC cell migration via direct DACH1 targeting [83]. Another investigation indicated that lncRNA MALAT1 promotes EMT and inhibits apoptosis in tongue cancer cells through the WBC signaling modulation [73].
Furthermore, another study demonstrated that the lncRNA TIRY activated the WBC signaling cascade within CAFs. This activation promoted EMT, invasion, and metastasis in OSCC cells by diminishing miR-14 levels through a sponging mechanism. At a mechanistic level, TIRY was observed to amplify the expression of molecular markers including Snail, Zeb1, α-SMA, Wnt-3a, and β-catenin [77]. Ji et al. (2019) reported the role of the nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) in augmenting EMT, migration, and invasion of NPC cells by inhibiting miR-34a-5p directly. Intriguingly, silencing NEAT1 led to an upregulation of miR-34a-5p and a concomitant downregulation of β-catenin, cyclin D1, c-Myc, N-cadherin, and vimentin in both NPC cell lines and the SCID mouse xenograft model [109]. Additionally, another study highlighted that silencing lncRNA HCG18 attenuated invasion and metastasis in NPC cells by downregulating Hedgehog and WBC signaling pathways, as well as by sponging miR-140 [80]. Another study by Xiong et al. (2020) emphasized that the lncRNA HOTTIP enhanced invasion and migration in tongue cancer cells by targeted repression of miR-124-3p. Notably, silencing HOTTIP resulted in the upregulation of miR-124-3p which, in turn, attenuated invasion, migration, and tumor proliferation by targeting HMGA2 through Wnt signaling modulation [84].
A myriad of investigations has elucidated the pivotal role of ncRNAs in hampering EMT, invasion, migration, and metastasis in HNSCC. For instance, the tumor suppressor miRNA, miR-503, was shown to curtail HNSCC cell invasion by downregulating WBC pathway constituents, including Wnt-3a and MMPs 3, 7, and 9. This miRNA also decreased the expression of invasion-related genes, including fibroblast growth factor 7 (FGF7) and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) [60]. Additionally, studies have confirmed that multiple miRNAs, such as miR-9, miR-638, miR-329, and miR-410, substantially reduced the invasive and migratory characteristics of OSCC cells by attenuating the WBC signaling cascade [86,89,115]. In another notable study, lncRNA LINC00961 was found to diminish invasion, migration, and EMT in TSCC cells, acting as a putative tumor suppressor in tongue cancer development [90]. This collective body of research emphasizes the integral role of ncRNAs in modulating the migration and invasion of cancer cells, making them essential focal points in oncological research.
4.3. Interplay between ncRNAs and the WBC Pathway in Modulating Chemoresistance and Radioresistance
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy constitute the cornerstones of therapeutic intervention for individuals afflicted with advanced or metastatic stages of HNSCC, as substantiated by pertinent research findings [120,121]. Cisplatin-based chemotherapy and concomitant radiotherapy or radio-chemotherapy are widely used against several HNSCC conditions, especially in unresectable tumors [121,122,123]. Nonetheless, in numerous instances, cancer cells develop resistance to these therapeutic modalities through a variety of mechanisms. One of these mechanisms involves the anomalous activation of the WBC signaling pathway, resulting in the upregulation of genes associated with chemoresistance. Notably, this includes genes involved in drug efflux pathways, such as ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) transporters, as well as genes implicated in epigenetic regulations, such as DNA methyltransferases [124,125]. Several ncRNAs have been substantiated as effective regulators of chemoresistance and radio-resistance in HNSCC cells by modulating WBC pathway. For instance, an investigation demonstrated that miR-218 directly targets protein phosphatase 2 regulatory subunit B’alpha (PPP2R5A), a tumor suppressor gene, influencing cancer progression and chemoresistance in oral cancer cells. The study further indicated that when miR-218 is downregulated, there is an inhibition of Wnt signaling, enhancing the sensitivity of oral cancer cells to cisplatin-based treatments. Additionally, the repression of miR-218 led to the decreased expression of several genes implicated in chemoresistance, such as ABCG2, multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1), and p-glycoprotein (p-gp) [114]. Another study showed that the upregulation of chemotherapy-induced lncRNA 1 (CILA1) significantly enhanced chemoresistance in TSCC cells accompanied by elevated invasion, metastasis, and EMT in vitro and in vivo. This study also confirmed that CILA1 exerted its functions by the upregulation of the WBC signaling pathway [126].
Additionally, a couple of studies have also demonstrated the modulation of radioresistance in HNSCC cells by lncRNAs via WBC signaling. For instance, the lncRNA LINC00473 enhanced the radioresistance of LC cells by activating WBC signaling. This study also demonstrated that the silencing of LINC00473 and X-ray treatment induced apoptosis and suppressed colony formation and the proliferation of LC cells [65]. In addition, another study demonstrated that the lncRNA DGCR5 promoted radioresistance in LC cells by sponging miR-506. Further, the silencing of DGCR5 enhanced radiosensitivity and downregulated Wnt signaling components, including β-catenin and Cyclin D1 [87]. Hence, a deeper investigation into the WBC signaling pathway elucidating the regulatory roles of ncRNAs within this pathway and comprehending the downstream implications of its activation is essential. Such insights are crucial for devising novel therapeutic strategies to enhance the efficacy of both chemotherapy and radiotherapy and more effectively target HNC.
5. Conclusions
HNC encompasses a spectrum of malignant conditions affecting the oral, nasal, nasopharyngeal, hypopharyngeal, and laryngeal regions. Deviations in the expression of proteins involved in various cellular activities and pathways constitute a significant factor in the advancement of HNSCC. The WBC signaling pathway exemplifies the complex cellular communication systems vital to both developmental and pathological contexts. While the WBC pathway is fundamental for cellular proliferation, morphogenesis, and homeostatic balance, its aberrations can lead to severe consequences. Genetic alterations within this pathway are associated with diverse cancers, including HNC. Over recent years, ncRNAs have gained prominence as potential therapeutic targets in numerous cancers, including HNC. Emerging research underscores the instrumental role of ncRNAs in HNC, modulating various signaling pathways, including WBC. Consequently, ncRNAs impact key oncogenic processes in HNC, such as cellular proliferation, differentiation, invasion, EMT, migration, and metastasis. Clinical trials are increasingly evaluating the utility of several ncRNAs as diagnostic and therapeutic indicators in oncology. For instance, one noteworthy study highlighted the potential of MALAT1 targeting miR-124 as a diagnostic biomarker for OSCC, as denoted in trial NCT05708209. The investigation encompassed 20 OSCC patients and 20 healthy controls, assessing MALAT1 and miR-124 levels in unstimulated saliva samples. Furthermore, ncRNAs critically influence the chemotherapeutic and radiotherapeutic resistance of HNSCC cells. Given the importance of ncRNAs in HNC, a thorough understanding of their specific roles is vital for the innovation of refined therapeutic strategies. This review describes the central role of ncRNAs in modulating cancer cell behavior, particularly through the WBC signaling mechanism. Nonetheless, further studies are essential to thoroughly discern the contributions of ncRNAs in HNC progression and to design groundbreaking therapeutic interventions for this malignancy.
Author Contributions
A.S.: Writing—original draft preparation, investigation, visualization, and figure and table preparation; B.B.: Writing, editing, and figure preparation; R.V.: Writing, editing, and figure preparation; M.S.A.: Writing and table preparation; M.A.: Writing, editing, and figure preparation; A.B.K. and G.S.: Contributed to the conceptualization, funding, overall supervision, and overall editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors disclose receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Ajaikumar B. Kunnumakkara’s Professional Development Fund (PDF), BSBE/ABK/01 from IIT Guwahati. The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University (KKU) for funding this research through the Research Group Program under the grant number R.G.P.2/431/44.
Acknowledgments
Anjana Sajeev acknowledges the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), the Ministry of Education (MOE), and the government of India for providing her with the fellowship. Figures were created with Biorender.com.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| α-SMA | Alpha smooth muscle actin |
| β-TrCP | Beta-transducin repeat-containing protein |
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| ADAM17 | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17 |
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| APC | Adenomatous polyposis coli |
| Bax | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
| BCL11B | B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11B |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 protein |
| CD44 | Cluster of differentiation 44 |
| CILA1 | Chemotherapy-induced long non-coding RNA 1 |
| CK1 | Casein kinase 1 |
| c-Myc | Cellular myelocytomatosis oncogene |
| CTGF | Connective tissue growth factor |
| CXCR4 | CXC chemokine receptor 4 |
| DACH1 | Dachshund family transcription factor 1 |
| DGCR5 | DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 5 |
| DKK1 | Dickkopf-1 |
| DKK3 | Dickkopf Wnt signaling pathway inhibitor 3 |
| ELF1 | E74 Like ETS Transcription Factor 1 |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 |
| FGF7 | Fibroblast growth factor 7 |
| FZD7 | Frizzled 7 |
| GSK3β | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta |
| HCG18 | HLA complex group 18 |
| HMGA2 | High mobility group A2 |
| HNC | Head and neck cancer |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| HPV | Human papilloma virus |
| LC | Laryngeal cancer |
| LEF1 | Lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1 |
| LRP | Lipoprotein receptor-related protein |
| LNEC | Laryngeal neuroendocrine carcinoma |
| LNM | Lymph node metastasis |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MOSPD2 | Motile sperm domain containing 2 |
| MRP1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 |
| ncRNA | Non-coding RNA |
| NUAK1 | NUAK family SNF1-like kinase 1 |
| p-gp | P-glycoprotein |
| PLAC2 | Placenta-specific protein 2 |
| PLD1 | Phospholipase D1 |
| PPP2R5A | Protein phosphatase 2 regulatory subunit B’alpha |
| RASSF4 | Ras association domain family member 4 |
| SETD7 | SET domain-containing 7 histone lysine methyl transferase |
| SLCO4A1 | AS1-solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 4A1 antisense RNA 1 |
| snoRNA | Small nucleolar RNA |
| SNHG1 | Small nucleolar RNA host gene 17 |
| SNHG3 | Small nucleolar RNA host gene 3 |
| TCF/LEF | T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor 1 |
| TCF4 | Transcription factor 4 |
| TIMP-3 | Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 |
| TopoII | topoisomerase IIβ |
| TSCC | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma |
| TUG1 | Taurine upregulated gene 1 |
| UCA1 | Urothelial Carcinoma Associated 1 |
| WBC | Wnt/β-catenin |
| WIF1 | Wnt inhibitory factor-1 |
| WISP1 | Wnt-induced secreted protein-1 |
| YAP/TAZ | Yes-associated protein 1/transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif |
References
- Leemans, C.R.; Braakhuis, B.J.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Roy, N.K.; Bordoloi, D.; Padmavathi, G.; Banik, K.; Khwairakpam, A.D.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Sukumar, P. Orai-1 and Orai-2 regulate oral cancer cell migration and colonisation by suppressing Akt/mTOR/NF-κB signalling. Life Sci. 2020, 261, 118372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monisha, J.; Roy, N.K.; Padmavathi, G.; Banik, K.; Bordoloi, D.; Khwairakpam, A.D.; Arfuso, F.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A. NGAL is downregulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma and leads to increased survival, proliferation, migration and chemoresistance. Cancers 2018, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.I.; Shin, D.M. Recent advances in head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, G.; Kreimer, A.R.; Viscidi, R.; Pawlita, M.; Fakhry, C.; Koch, W.M.; Westra, W.H.; Gillison, M.L. Case–control study of human papillomavirus and oropharyngeal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1944–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tergaonkar, V.; Krishna, S.; Androphy, E.J. Human papillomavirus type 16 E6-enhanced susceptibility of L929 cells to tumor necrosis factor α correlates with increased accumulation of reactive oxygen species. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 24819–24827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posner, M.R.; Hershock, D.M.; Blajman, C.R.; Mickiewicz, E.; Winquist, E.; Gorbounova, V.; Tjulandin, S.; Shin, D.M.; Cullen, K.; Ervin, T.J. Cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or with docetaxel in head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mody, M.D.; Rocco, J.W.; Yom, S.S.; Haddad, R.I.; Saba, N.F. Head and neck cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girisa, S.; Kumar, A.; Rana, V.; Parama, D.; Daimary, U.D.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Kumar, A.P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. From simple mouth cavities to complex oral mucosal disorders—Curcuminoids as a promising therapeutic approach. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsha, C.; Banik, K.; Ang, H.L.; Girisa, S.; Vikkurthi, R.; Parama, D.; Rana, V.; Shabnam, B.; Khatoon, E.; Kumar, A.P. Targeting AKT/mTOR in oral cancer: Mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monisha, J.; Padmavathi, G.; Roy, N.K.; Deka, A.; Bordoloi, D.; Anip, A.; B Kunnumakkara, A. NF-κB blockers gifted by mother nature: Prospectives in cancer cell chemosensitization. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 4173–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishor Roy, N.; Bordoloi, D.; Monisha, J.; Padmavathi, G.; Kotoky, J.; Golla, R.; B Kunnumakkara, A. Specific targeting of Akt kinase isoforms: Taking the precise path for prevention and treatment of cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattar, E.; Maung, K.Z.Y.; Chew, C.L.; Ghosh, A.; Mok, M.M.H.; Lee, P.; Zhang, J.; Chor, W.H.J.; Cildir, G.; Wang, C.Q. Rap1 regulates hematopoietic stem cell survival and affects oncogenesis and response to chemotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Wong, E.; Kua, N.; Ling Teo, H.; Tergaonkar, V.; Lane, D. Hexamethylene bisacetamide (HMBA) simultaneously targets akt and mapk pathway and represses NF-κB activity: Implications for cancer therapy. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3759–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Wong, E.; Bist, P.; Tergaonkar, V.; Lane, D. Nutlin-3 inhibits the NFκB pathway in a p53 dependent manner: Implications in lung cancer therapy. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, M.B.; Li, Y.; Tergaonkar, V. Current insights to regulation and role of telomerase in human diseases. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, C.Y.; Nusse, R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 781–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, B.T.; Tamai, K.; He, X. Wnt/β-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deldar Abad Paskeh, M.; Mirzaei, S.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Sethi, G. Wnt/β-Catenin signaling as a driver of hepatocellular carcinoma progression: An emphasis on molecular pathways. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 1415–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, I.S.; Goel, A.; Warrier, S.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Garg, M. The multidimensional role of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human malignancies. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 199–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Wnt/beta-catenin signalling: Function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niehrs, C. The complex world of WNT receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xie, R.; Shu, B.; Landay, A.L.; Wei, C.; Reiser, J.; Spagnoli, A.; Torquati, A.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A.; et al. Wnt signaling in bone, kidney, intestine, and adipose tissue and interorgan interaction in aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1442, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clevers, H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 2006, 127, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perugorria, M.J.; Olaizola, P.; Labiano, I.; Esparza-Baquer, A.; Marzioni, M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Bujanda, L.; Banales, J.M. Wnt-beta-catenin signalling in liver development, health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skronska-Wasek, W.; Mutze, K.; Baarsma, H.A.; Bracke, K.R.; Alsafadi, H.N.; Lehmann, M.; Costa, R.; Stornaiuolo, M.; Novellino, E.; Brusselle, G.G.; et al. Reduced Frizzled Receptor 4 Expression Prevents WNT/beta-Catenin-driven Alveolar Lung Repair in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salyakina, D.; Tsinoremas, N.F. Non-coding RNAs profiling in head and neck cancers. NPJ Genomic Med. 2016, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, T.; Barker, D.; Birney, E.; Cameron, G.; Chen, Y.; Clark, L.; Cox, T.; Cuff, J.; Curwen, V.; Down, T. The Ensembl genome database project. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Mostafavi, E.; Aref, A.R.; Sethi, G.; Wang, L.; Tergaonkar, V. Non-coding RNA-based regulation of inflammation. Semin. Immunol. 2022, 59, 101606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panni, S.; Lovering, R.C.; Porras, P.; Orchard, S. Non-coding RNA regulatory networks. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2020, 1863, 194417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardiello, F.; Falco, M.; Tortoriello, G.; Riccardi, F.; Pellini, R.; Iorio, B.; Russo, G.; Longo, G.; Coppola, C.; Takeuchi, T.; et al. Poorly Differentiated Neuroendocrine Larynx Carcinoma: Clinical Features and miRNAs Signature-A New Goal for Early Diagnosis and Therapy? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Ricciardiello, F.; Lombardi, A.; Biganzoli, E.; Fornili, M.; De Bortoli, D.; Mesolella, M.; Cossu, A.M.; Scrima, M.; et al. Definition of miRNA Signatures of Nodal Metastasis in LCa: miR-449a Targets Notch Genes and Suppresses Cell Migration and Invasion. Mol. Ther.—Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R. Wingless a new mutant in Drosophila melanogaster. Drosoph. Inf. Serv. 1973, 50, 134. [Google Scholar]
- Nusse, R.; Varmus, H.E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell 1982, 31, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinzler, K.W.; Nilbert, M.C.; Su, L.K.; Vogelstein, B.; Bryan, T.M.; Levy, D.B.; Smith, K.J.; Preisinger, A.C.; Hedge, P.; McKechnie, D.; et al. Identification of FAP locus genes from chromosome 5q21. Science 1991, 253, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zheng, S.; Jin, S.H.; Zhang, S.Z. Somatic mutations of APC gene in carcinomas from hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 834–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.P.; Pandith, A.A.; Hussain, M.U.; Yousuf, A.; Khan, M.S.; Wani, K.A.; Mudassar, S. Novelty of Axin 2 and lack of Axin 1 gene mutation in colorectal cancer: A study in Kashmiri population. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 355, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guezguez, B.; Almakadi, M.; Benoit, Y.D.; Shapovalova, Z.; Rahmig, S.; Fiebig-Comyn, A.; Casado, F.L.; Tanasijevic, B.; Bresolin, S.; Masetti, R.; et al. GSK3 Deficiencies in Hematopoietic Stem Cells Initiate Pre-neoplastic State that Is Predictive of Clinical Outcomes of Human Acute Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voeller, H.J.; Truica, C.I.; Gelmann, E.P. β-Catenin mutations in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 2520–2523. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Virshup, D.M. Wnt Signaling and Drug Resistance in Cancer. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 97, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Spranger, S.; Fuchs, E.; Lopez-Soto, A. WNT Signaling in Cancer Immunosurveillance. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 44–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsengimana, J.; Laye, J.; Filia, A.; O’Shea, S.; Muralidhar, S.; Pozniak, J.; Droop, A.; Chan, M.; Walker, C.; Parkinson, L.; et al. beta-Catenin-mediated immune evasion pathway frequently operates in primary cutaneous melanomas. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2048–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akasu, M.; Shimada, S.; Kabashima, A.; Akiyama, Y.; Shimokawa, M.; Akahoshi, K.; Kudo, A.; Yamaoka, S.; Tanabe, M.; Tanaka, S. Intrinsic activation of beta-catenin signaling by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated exon skipping contributes to immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Rindtorff, N.; Boutros, M. Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, N.; Morris, L.G.; Lee, W.; Chan, T.A. Unraveling the molecular genetics of head and neck cancer through genome-wide approaches. Genes Dis. 2014, 1, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zeng, Q.; Yu, G.; Li, S.; Wang, C.Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling inhibits death receptor-mediated apoptosis and promotes invasive growth of HNSCC. Cell. Signal. 2006, 18, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, S.; Yonekawa, A.; Harada, C.; Hamada, M.; Katagiri, W.; Nakazawa, M.; Yura, Y. Involvement of the Wnt-beta-catenin pathway in invasion and migration of oral squamous carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmi, A.A.; Tola, R.; Rashid, K.; Ali, A.H.; Dowlah, T.; Malik, U.A.; Zia, S.; Saleem, M.; Anjali, F.; Irfan, M. Clinicopathological Parameters Predicting Nodal Metastasis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cureus 2023, 15, e40744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lim, Y.C. Wnt/beta-catenin/Slug pathway contributes to tumor invasion and lymph node metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2021, 38, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, W.; Chen, Q.; Chen, M. Non-Coding RNAs and their Integrated Networks. J. Integr. Bioinform. 2019, 16, 20190027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, A.A. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer-Advances and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, K.K.; Kumar, A.; Banik, K.; Verma, E.; Khatoon, E.; Harsha, C.; Sethi, G.; Gupta, S.C.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Long noncoding RNAs in triple-negative breast cancer: A new frontier in the regulation of tumorigenesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 7938–7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahariya, S.; Paddibhatla, I.; Kumar, S.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Pallepati, A.; Gutti, R.K. Long non-coding RNA: Classification, biogenesis and functions in blood cells. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Cai, Y.; Guo, L.; Huang, W.; Yan, J.; Lai, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Peng, L. hsa_circ_0136839 regulates the malignant phenotypes of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 245, 154433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisignano, G.; Michael, D.C.; Visal, T.H.; Pirlog, R.; Ladomery, M.; Calin, G.A. Going circular: History, present, and future of circRNAs in cancer. Oncogene 2023, 42, 2783–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayashi, M.; Yoshida, M.; Tsunematsu, T.; Ogawa, I.; Sasahira, T.; Kuniyasu, H.; Imoto, I.; Abiko, Y.; Xu, D.; Fukunaga, S.; et al. microRNA-203 suppresses invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition induction via targeting NUAK1 in head and neck cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8223–8239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishabh, K.; Khadilkar, S.; Kumar, A.; Kalra, I.; Kumar, A.P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. MicroRNAs as modulators of oral tumorigenesis—A focused review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.J.; Fan, K.H.; You, G.R.; Huang, S.F.; Kang, C.J.; Huang, Y.F.; Huang, Y.C.; Chang, J.T.; Cheng, A.J. Tumor Suppressor miRNA-503 Inhibits Cell Invasion in Head and Neck Cancer through the Wnt Signaling Pathway via the WNT3A/MMP Molecular Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Bu, P. Non-coding RNA in cancer. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Ying, K. Long non-coding RNA human leucocyte antigen complex group-18 HCG18 (HCG18) promoted cell proliferation and migration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through cyclin D1-WNT pathway. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 9425–9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Qi, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, R. lncRNA PLAC2 activated by H3K27 acetylation promotes cell proliferation and invasion via the activation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Huang, L.; Lu, Y.G.; Zheng, D.L. Roles of the Wnt Signaling Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 590912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.B.; Ji, X.J.; Zhang, M.; Gao, L.Y. Upregulation of lncRNA LINC00473 promotes radioresistance of HNSCC cells through activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7305–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Yang, C.; Shang, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, J. LncRNA, TUG1 regulates the oral squamous cell carcinoma progression possibly via interacting with Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Gene 2017, 608, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Q.; Jin, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, F. LncRNA MINCR activates Wnt/beta-catenin signals to promote cell proliferation and migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.R.; Zheng, Z.N.; Chen, Y.C.; Wu, Q.Q.; Huang, G.Z.; Li, F.; Zeng, W.S.; Lv, X.Z. LncRNA AC007271.3 promotes cell proliferation, invasion, migration and inhibits cell apoptosis of OSCC via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Wu, S.; Zou, C.; Wei, H. LINC00941 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression via activating CAPRIN2 and canonical WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 10512–10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Mao, D.; He, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. SLCO4A1-AS1 regulates laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cell phenotypes via the Wnt pathway. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, S.; Tan, L.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. IGFL2-AS1 facilitates tongue squamous cell carcinoma progression via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Ding, J.M.; Zheng, X.Z.; Chen, J.G. Immunity-related long noncoding RNA WDFY3-AS2 inhibited cell proliferation and metastasis through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Arch. Oral Biol. 2023, 147, 105625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Liang, L.; Ouyang, K.; Li, Z.; Yi, X. MALAT1 induces tongue cancer cells’ EMT and inhibits apoptosis through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2017, 46, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Yuan, K.; Chen, W. Effect of miR-25 on Proliferation of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells through Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9957161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. MicroRNA-215 promoted the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through targeting RB1 and activating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2020, 25, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Gong, C.; Yuan, K. LncRNA UCA1 promotes cell proliferation, invasion and migration of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Jin, N.; Bu, W.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Tong, J.; Li, D. Long non-coding RNA TIRY promotes tumor metastasis by enhancing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Qiao, T.; Yang, S.; Liu, L.; Zheng, M. SNHG17/miR-384/ELF1 axis promotes cell growth by transcriptional regulation of CTNNB1 to activate Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; et al. Antisense oligonucleotides targeting lncRNA AC104041.1 induces antitumor activity through Wnt2B/beta-catenin pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, T.T.; Ma, Y.H.; Jiang, Y.F. LncRNA HCG18 contributes to nasopharyngeal carcinoma development by modulating miR-140/CCND1 and Hedgehog signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 10387–10399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Ma, Z.H.; Wang, X. Long non-coding RNA CCAT1 is a prognostic biomarker for the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-181a-mediated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 2902–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.L.; Ding, S.Y.; Jinag, H. LncRNA SNHG20 enhances the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the miR-29a/DIXDC1/Wnt regulatory axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 5436–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Sun, J. MicroRNA-200c promotes tumor cell proliferation and migration by directly targeting dachshund family transcription factor 1 by the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Anticancer Drugs 2019, 30, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Tang, Y.; Tang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X. Downregulation of lncRNA HOTTIP Suppresses the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulation of HMGA2-Mediated Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 35, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Yao, D.F.; Xu, G.Z.; Zhou, Y.H. The knockdown of SNHG3 inhibits the progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by miR-340-5p/YAP1 axis and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Liu, K.; Wu, Y.; Fan, J.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Z. MicroRNA-9 inhibits the proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by suppressing expression of CXCR4 via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5017–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Shan, G. DGCR5 promotes cancer stem cell-like properties of radioresistant laryngeal carcinoma cells by sponging miR-506 via Wnt pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 18423–18431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, W.; Cao, G.; Dong, Z.; Xu, J.; Luo, T.; Zhang, S. MicroRNA-27b inhibits cell proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting FZD7 and Wnt signaling pathway. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017, 83, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiah, S.G.; Hsiao, J.R.; Chang, W.M.; Chen, Y.W.; Jin, Y.T.; Wong, T.Y.; Huang, J.S.; Tsai, S.T.; Hsu, Y.M.; Chou, S.T.; et al. Downregulated miR329 and miR410 promote the proliferation and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Wnt-7b. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7560–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shao, L.; Hu, Y. Long noncoding RNA LINC00961 inhibited cell proliferation and invasion through regulating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 12429–12435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Cao, H. MicroRNA-384 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis through directly targeting WISP1 in laryngeal cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 3018–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y. MiR-338-3p inhibits cell migration and invasion in human hypopharyngeal cancer via downregulation of ADAM17. Anticancer Drugs 2020, 31, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Fang, N.; Cui, Y.; Xiao, D.; Wang, X. Long non-coding RNA NEF inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells by inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4928–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Parama, D.; Daimari, E.; Girisa, S.; Banik, K.; Harsha, C.; Dutta, U.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Rationalizing the therapeutic potential of apigenin against cancer. Life Sci. 2021, 267, 118814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aswathy, M.; Banik, K.; Parama, D.; Sasikumar, P.; Harsha, C.; Joseph, A.G.; Sherin, D.R.; Thanathu, M.K.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Vasu, R.K. Exploring the cytotoxic effects of the extracts and bioactive triterpenoids from dillenia indica against oral squamous cell carcinoma: A scientific interpretation and validation of indigenous knowledge. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 834–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, B.; Jayram, H.; Nair, M.; Ajaikumar, K.; Padikkala, J. Free radical scavenging, antitumor and anticarcinogenic activity of gossypin. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 22, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banik, K.; Khatoon, E.; Harsha, C.; Rana, V.; Parama, D.; Thakur, K.K.; Bishayee, A.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Wogonin and its analogs for the prevention and treatment of cancer: A systematic review. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1854–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoloi, D.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. The potential of curcumin: A multitargeting agent in cancer cell chemosensitization. In Role of Nutraceuticals in Cancer Chemosensitization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Devi Khwairakpam, A.; Monisha, J.; Roy, N.K.; Bordoloi, D.; Padmavathi, G.; Banik, K.; Khatoon, E.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Vietnamese coriander inhibits cell proliferation, survival and migration via suppression of Akt/mTOR pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 31, 20190162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathi, G.; Rathnakaram, S.R.; Monisha, J.; Bordoloi, D.; Roy, N.K.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Potential of butein, a tetrahydroxychalcone to obliterate cancer. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeev, A.; Hegde, M.; Daimary, U.D.; Kumar, A.; Girisa, S.; Sethi, G.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Modulation of diverse oncogenic signaling pathways by oroxylin A: An important strategy for both cancer prevention and treatment. Phytomedicine 2022, 105, 154369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabnam, B.; Padmavathi, G.; Banik, K.; Girisa, S.; Monisha, J.; Sethi, G.; Fan, L.; Wang, L.; Mao, X.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Sorcin a potential molecular target for cancer therapy. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 11, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, J. Curcumin inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-9 cells proliferation by regulating miR-9 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 454, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Chen, Z.Z.; Xie, P.; Zhang, W.J.; Du, M.Y.; Liu, Y.T.; Zhu, H.Y.; Guo, Y.S. Isoliquiritigenin suppresses the proliferation and induced apoptosis via miR-32/LATS2/Wnt in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 856, 172352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Z.; Deng, J.; Xu, K.; Che, D.; Lin, J.; Jiang, P.; Gu, X.; Xu, B. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA BART22 serves as novel biomarkers and drives malignant transformation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y. MicroRNA-103 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma through targeting TIMP-3 and the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, E75–E82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.H.; Xie, H. Long non-coding RNA GNAS-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion via regulating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 3077–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, M.; Wan, Y.; Lei, L.; Ruan, H. miR-574-5p Targets FOXN3 to Regulate the Invasion of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells via Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820971659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Cui, F. The Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Targets miR-34a-5p and Drives Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Progression via Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.H.; Hu, X.D.; Yan, Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway participates in the effect of miR-626 on oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting RASSF4. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Lu, Z. Knockdown of lncRNA IGF2BP2-AS1 inhibits proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2022, 51, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gao, X.; Liu, C.L. Increased expression of lncRNA FTH1P3 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma cells migration and invasion by enhancing PI3K/Akt/GSK3b/ Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8306–8314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Liang, J.; Chen, G.; Li, W.; Tang, H.; Hou, J. miR-373-3p Targets DKK1 to Promote EMT-Induced Metastasis via the Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway in Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6010926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Z.; Hu, F.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Yu, Z.; Wang, T.T.; Liu, X.; Huang, H. MicroRNA-218 promotes cisplatin resistance in oral cancer via the PPP2R5A/Wnt signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2051–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.L.; Tang, H.Y.; Du, Y.; Tian, T.; Xiong, S.J. MiR-638 suppresses the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma through wnt/beta-catenin pathway by targeting phospholipase D1. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3278–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P. Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R.; Annese, T. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: A Historical Overview. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, A.; Perez-Moreno, M.A.; Rodrigo, I.; Locascio, A.; Blanco, M.J.; del Barrio, M.G.; Portillo, F.; Nieto, M.A. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takkunen, M.; Grenman, R.; Hukkanen, M.; Korhonen, M.; Garcia de Herreros, A.; Virtanen, I. Snail-dependent and -independent epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous carcinoma cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 54, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendenhall, W.M.; Hinerman, R.W.; Amdur, R.J.; Malyapa, R.S.; Lansford, C.D.; Werning, J.W.; Villaret, D.B. Postoperative radiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin. Med. Res. 2006, 4, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.; Ebadi, M.; Vo, K.; Novak, J.; Govindarajan, A.; Amini, A. An updated review on head and neck cancer treatment with radiation therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, R.; Rugman, F.; Dorman, E.; Stoney, P.; Wilson, J.; McCormick, M.; Veevers, A.; Stell, P. Cisplatinum and bleomycin for advanced or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A randomised factorial phase III controlled trial. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1985, 15, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argiris, A.; Li, Y.; Murphy, B.A.; Langer, C.J.; Forastiere, A.A. Outcome of elderly patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.F.; Zhang, D.J.; Zheng, Y.; Wen, L.J.; Yu, D.J.; Lu, Y.Q.; Zhao, Y. Abnormal Wnt signaling and overexpression of ABCG2 contributes to drug efflux properties of side population cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 4352–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickstrom, M.; Dyberg, C.; Milosevic, J.; Einvik, C.; Calero, R.; Sveinbjornsson, B.; Sanden, E.; Darabi, A.; Siesjo, P.; Kool, M.; et al. Wnt/beta-catenin pathway regulates MGMT gene expression in cancer and inhibition of Wnt signalling prevents chemoresistance. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Sun, L.; Xie, S.; Zhang, S.; Fan, S.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Pan, G.; Wang, W.; Weng, B.; et al. Chemotherapy-Induced Long Non-coding RNA 1 Promotes Metastasis and Chemo-Resistance of TSCC via the Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1494–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).