Performance of a Pharmaceutical Single-Use Stirred Tank Operating at Different Filling Volumes: Mixing Time, Fluid Dynamics and Power Consumption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Rig
2.2. Stereo-PIV Measurements
2.3. PLIF Measurements
2.4. ERT Measurements
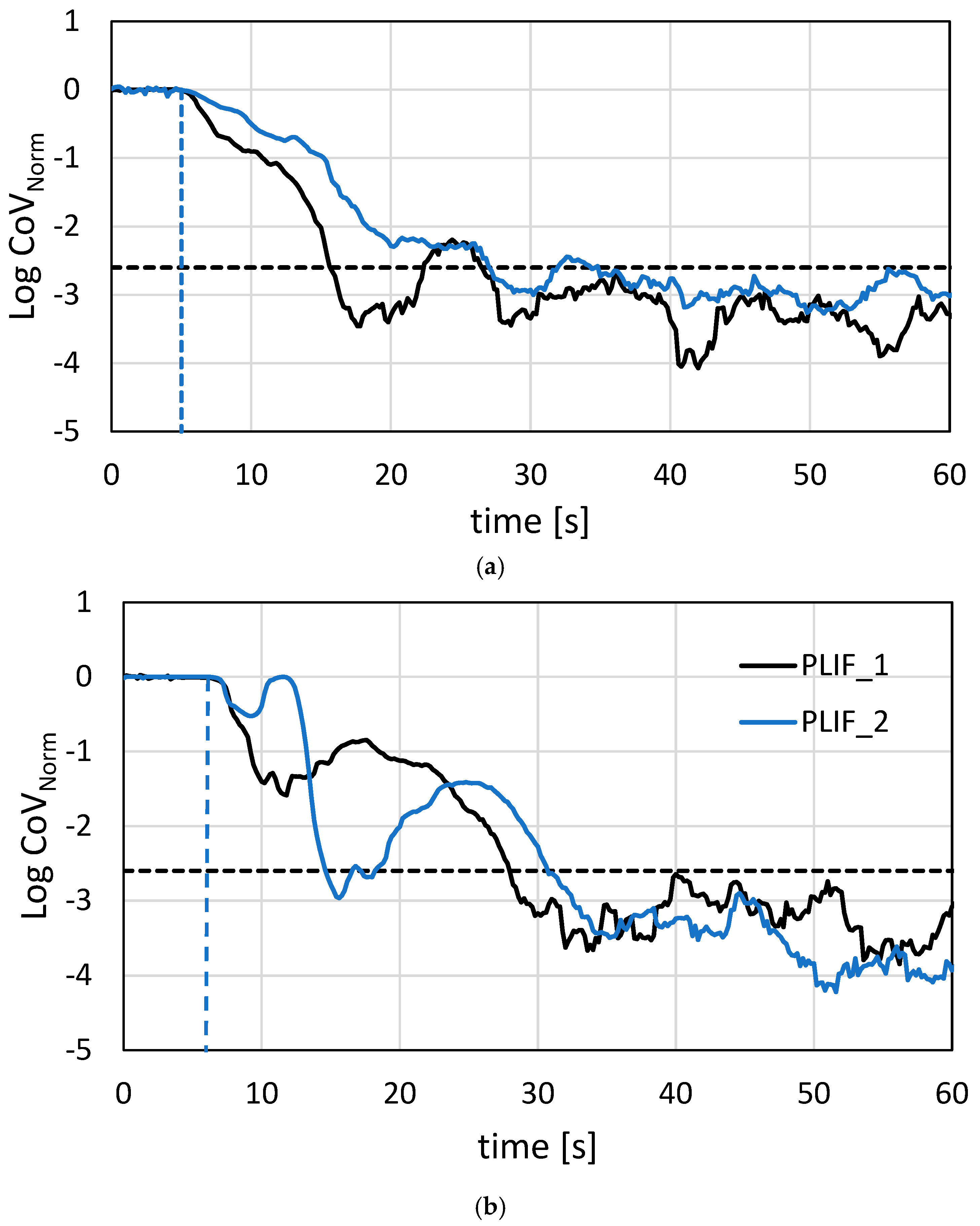
2.5. Repeatability of the PLIF Measurement
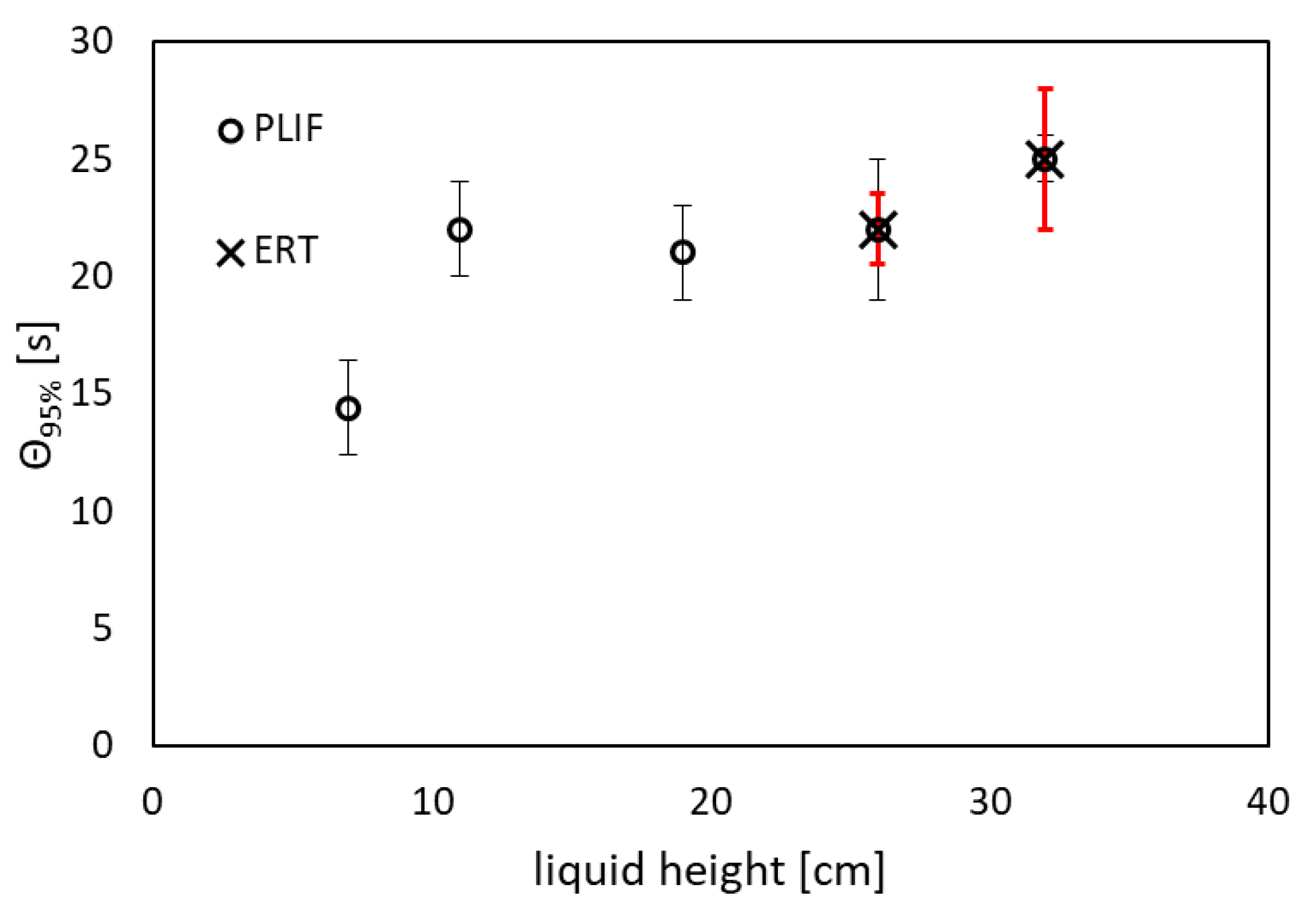
2.6. Congruency Between PLIF and ERT Measurements
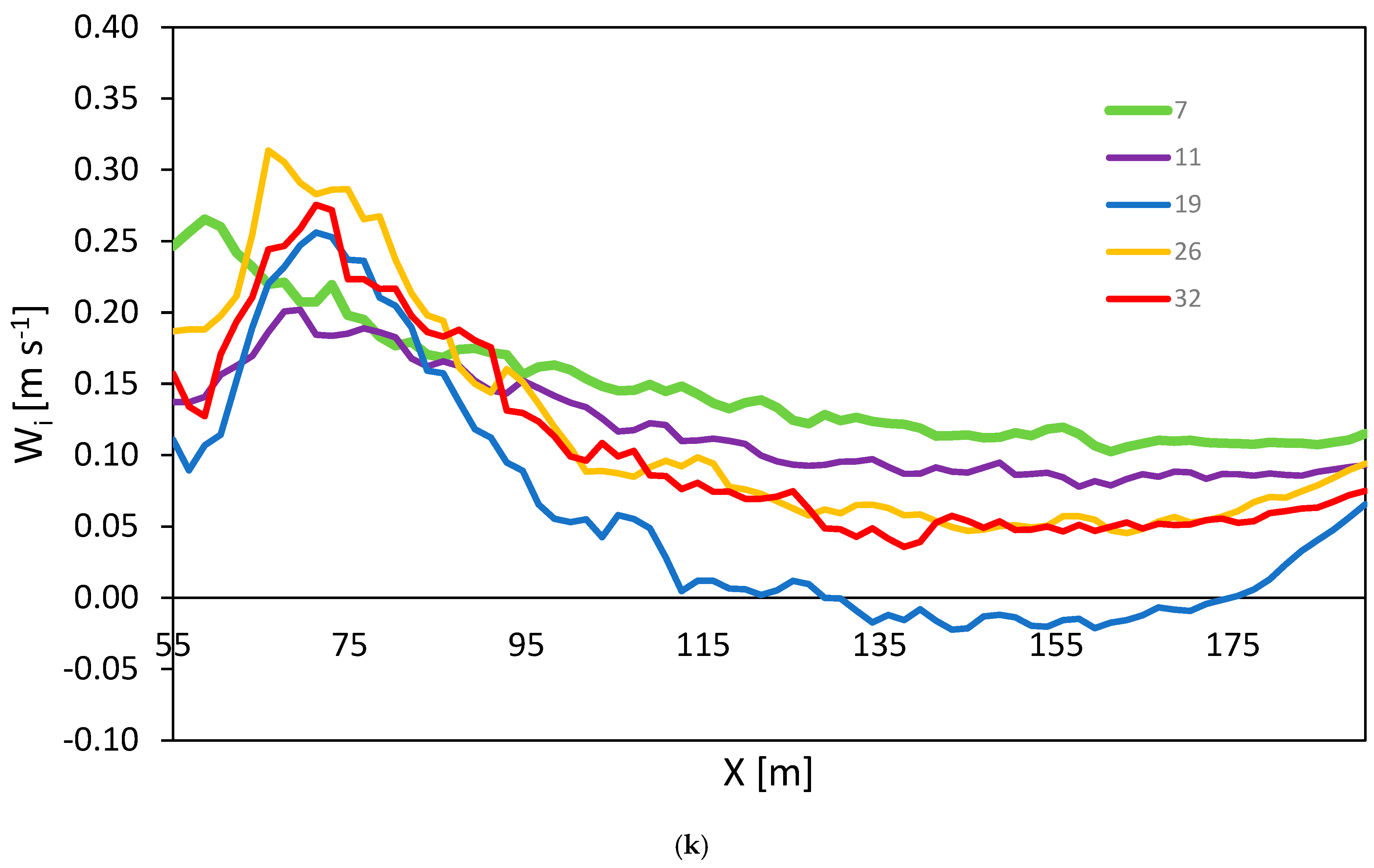
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDFs | cumulative density functions |
| CND | average non-dimensional conductivity |
| CoV | Coefficient of Variance |
| CoVnorm | Normalized Coefficient of Variance |
| D | impeller diameter [m] |
| DAS | data acquisition system |
| ERT | Electro Resistance Tomography |
| f | function |
| H | Height of [cm] |
| MSBP | Modified Sensitivity Back Projection |
| N | impeller speed [rpm] |
| Np | number of pixels/non-dimensional conductivity values per plane |
| P | Power [W] |
| PI | Pixel intensity |
| PIV | Particle Image Velocimetry |
| PLIF | Planar Laser-Induced Fluorescence |
| Po | power number |
| R6G | rhodamine 6 G |
| RMS | root mean square |
| rpm | round per minute |
| SUBs | Single-use bioreactors |
| T | Tank diameter [cm] |
| t | time [s] |
| U | radial velocity [m/s] |
| V | Volume [m3] |
| V | axial velocity [m/s] |
| W | tangential velocity [m/s] |
| θ95 | mixing time [s] |
| χi | Normalized function |
References
- Bernemann, V.; Fitschen, J.; Leupold, M.; Scheibenbogen, K.-H.; Maly, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Wucherpfennig, T.; Schlüter, M. Characterization Data for the Establishment of Scale-Up and Process Transfer Strategies between Stainless Steel and Single-Use Bioreactors. Fluids 2024, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberini, F.; Albano, A.; Singh, P.; Christodoulou, C.; Montante, G.; Maluta, F.; Paglianti, A. Fluid dynamics and power consumptions in a single use stirred tank adopted in the pharmaceutical industry. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 204, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemart, R.; Vandersluis, M.; Zhao, M.; Sukhija, K.; Sidhu, N.; Stout, J. A Single-use Strategy to Enable Manufacturing of Affordable Biologics. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algorri, M.; Abernathy, M.J.; Cauchon, N.S.; Christian, T.R.; Lamm, C.F.; Moore, C.M.V. Re-Envisioning Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Increasing Agility for Global Patient Access. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busciglio, A.; Montante, G.; Paglianti, A. Flow field and homogenization time assessment in continuously-fed stirred tanks. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 102, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Serrano, I.; Komuczki, D.P.; Dürauer, A. A modelling approach for volumetric power input in the microscale and its utilization for the scale-up of solid-liquid mixing systems. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2023, 184, 109303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govara, S.; Hosseinalipour, S.M.; Soleimani, M. Design, experimental optimization, and flow analysis of a novel bioreactor for dynamic mammalian cell culture at laboratory scale using Box-Behnken design. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 211, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schembri, L.; Caputo, G.; Ciofalo, M.; Grisafi, F.; Lima, S.; Scargiali, F. CFD simulations of the transition between non-aerated and aerated conditions in uncovered unbaffled stirred tanks. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 302, 120824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ducci, A.; Micheletti, M. Mixing Time in Intermediate-Sized Orbitally Shaken Reactors with Small Orbital Diameters. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, G.; Anderlei, T.; Micheletti, M.; Yianneskis, M.; Ducci, A. On the measurement and scaling of mixing time in orbitally shaken bioreactors. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 82, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbridge, J.N.; Barrett, T.A.; Ducci, A.; Micheletti, M. Power, mixing and flow dynamics of the novel AllegroTM stirred tank reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 271, 118545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasova, G.G.; Ducci, A.; Micheletti, M. Fluid dynamics and mixing in a novel intermittently rotating bioreactor for CAR-T cell therapy: Spin-down from incomplete spin-up. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 205, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatopoulos, K.; Alberini, F.; Batchelor, H.; Simmons, M.J.H. Use of PLIF to assess the mixing performance of small volume USP 2 apparatus in shear thinning media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 145, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megue Kamkeng, L.; Loubière, C.; Dufaud, O.; Marchal, P.; Le Creurer, B.; Olmos, E. Anaerobic digester scale-down study: Particle Image Velocimetry and Computational Fluid Dynamics scaling criteria validation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 298, 120299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, G.; Albano, A.; Simmons, M.J.H.; Stitt, H.E.; Brunazzi, E.; Alberini, F. Assessing Blending of Non-Newtonian Fluids in Static Mixers by Planar Laser-Induced Fluorescence and Electrical Resistance Tomography. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberini, F.; Simmons, M.J.H.; Ingram, A.; Stitt, E.H. Use of an areal distribution of mixing intensity to describe blending of non-newtonian fluids in a kenics KM static mixer using PLIF. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, A.; Alberini, F.; Maluta, F.; Moucha, T.; Montante, G.; Paglianti, A. Liquid mixing time and gas distribution in aerated multiple-impeller stirred tanks. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 184, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglianti, A.; Carletti, C.; Busciglio, A.; Montante, G. Solid distribution and mixing time in stirred tanks: The case of floating particles. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 95, 1789–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.L.; Atiemo-Obeng, V.A.; Kresta, S.M. (Eds.) Handbook of Industrial Mixing; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.1002/0471451452 (accessed on 24 September 2024).
- Armenante, P.M.; Luo, C.; Chou, C.C.; Fort, I.; Medek, J. Velocity profiles in a closed, unbaffled vessel: Comparison between experimental LDV data and numerical CFD predictions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 3483–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, S. Mixing Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons Halstead Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1975; Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=1185590 (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Mahmud, T.; Haque, J.N.; Roberts, K.J.; Rhodes, D.; Wilkinson, D. Measurements and modelling of free-surface turbulent flows induced by a magnetic stirrer in an unbaffled stirred tank reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 4197–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamo, R.; Micale, G.; Grisafi, F.; Brucato, A.; Ciofalo, M. Large-eddy simulation of turbulent flow in an unbaffled stirred tank driven by a Rushton turbine. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 2303–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, A.; Nienow, A.W.; Simmons, M.J.H. Use of angle resolved PIV to estimate local specific energy dissipation rates for up- and down-pumping pitched blade agitators in a stirred tank. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šrom, O.; Šoóš, M.; Kuschel, M.; Wucherpfennig, T.; Fitschen, J.; Schlüter, M. Study of hydrodynamic stress in cell culture bioreactors via lattice-Boltzmann CFD simulations supported by micro-probe shear stress method. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 208, 109337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilts, F.; Labisch, J.J.; Orbay, S.; Harsy, Y.M.J.; Steger, M.; Pagallies, F.; Amann, R.; Pflanz, K.; Wolff, M.W. Stability studies for the identification of critical process parameters for a pharmaceutical production of the Orf virus. Vaccine 2023, 41, 4731–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilander, J.; Svensson, F.J.E.; Rasmuson, A. Flow instabilities, energy levels, and structure in stirred tanks. AIChE J. 2006, 52, 4039–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Stephenson, A.; Jimenez, J.; Jewell, D.; Gillis, P. Modeling flow and residence time distribution in an industrial-scale reactor with a plunging jet inlet and optional agitation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2008, 86, 1462–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Santos, T.; Gutkowski, A.N.; Mendoza, V.; Szasz, R.Z.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Castro, F.; Perez, J.R. Swirl Influence on Mixing and Reactive Flows. In Proceedings of the ASME 2016 Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting Collocated with the ASME 2016 Heat Transfer Summer Conference and the ASME 2016 14th International Conference on Nanochannels, Microchannels, and Minichannels, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 July 2016; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforaki, L.; Montante, G.; Lee, K.C.; Yianneskis, M. On the origin, frequency and magnitude of macro-instabilities of the flows in stirred vessels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 2937–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforaki, L.; Yu, J.; Baldi, S.; Genenger, B.; Lee, K.C.; Durst, F.; Yianneskis, M. On the variation of precessional flow instabilities with operational parameters in stirred vessels. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 102, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| V(L) | H (cm) | R6G (mg) | mL |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.92 | 7 | 0.54 | 2.2 |
| 17.16 | 11 | 0.85 | 3.4 |
| 29.64 | 19 | 1.48 | 5.9 |
| 40.57 | 26 | 2.02 | 8.0 |
| 49.93 | 32 | 2.49 | 10.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alberini, F.; Albano, A.; Singh, P.; Montante, G.; Maluta, F.; Di Pasquale, N.; Paglianti, A. Performance of a Pharmaceutical Single-Use Stirred Tank Operating at Different Filling Volumes: Mixing Time, Fluid Dynamics and Power Consumption. Fluids 2025, 10, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10030064
Alberini F, Albano A, Singh P, Montante G, Maluta F, Di Pasquale N, Paglianti A. Performance of a Pharmaceutical Single-Use Stirred Tank Operating at Different Filling Volumes: Mixing Time, Fluid Dynamics and Power Consumption. Fluids. 2025; 10(3):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10030064
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlberini, Federico, Andrea Albano, Pushpinder Singh, Giuseppina Montante, Francesco Maluta, Nicodemo Di Pasquale, and Alessandro Paglianti. 2025. "Performance of a Pharmaceutical Single-Use Stirred Tank Operating at Different Filling Volumes: Mixing Time, Fluid Dynamics and Power Consumption" Fluids 10, no. 3: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10030064
APA StyleAlberini, F., Albano, A., Singh, P., Montante, G., Maluta, F., Di Pasquale, N., & Paglianti, A. (2025). Performance of a Pharmaceutical Single-Use Stirred Tank Operating at Different Filling Volumes: Mixing Time, Fluid Dynamics and Power Consumption. Fluids, 10(3), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10030064






